Anterior Hyperfunction Syndrome: Literature Review and Conceptual Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Selection Criteria
3. Results
3.1. Assessment and Diagnosis of AHS Risk Factors
3.2. Epidemiology
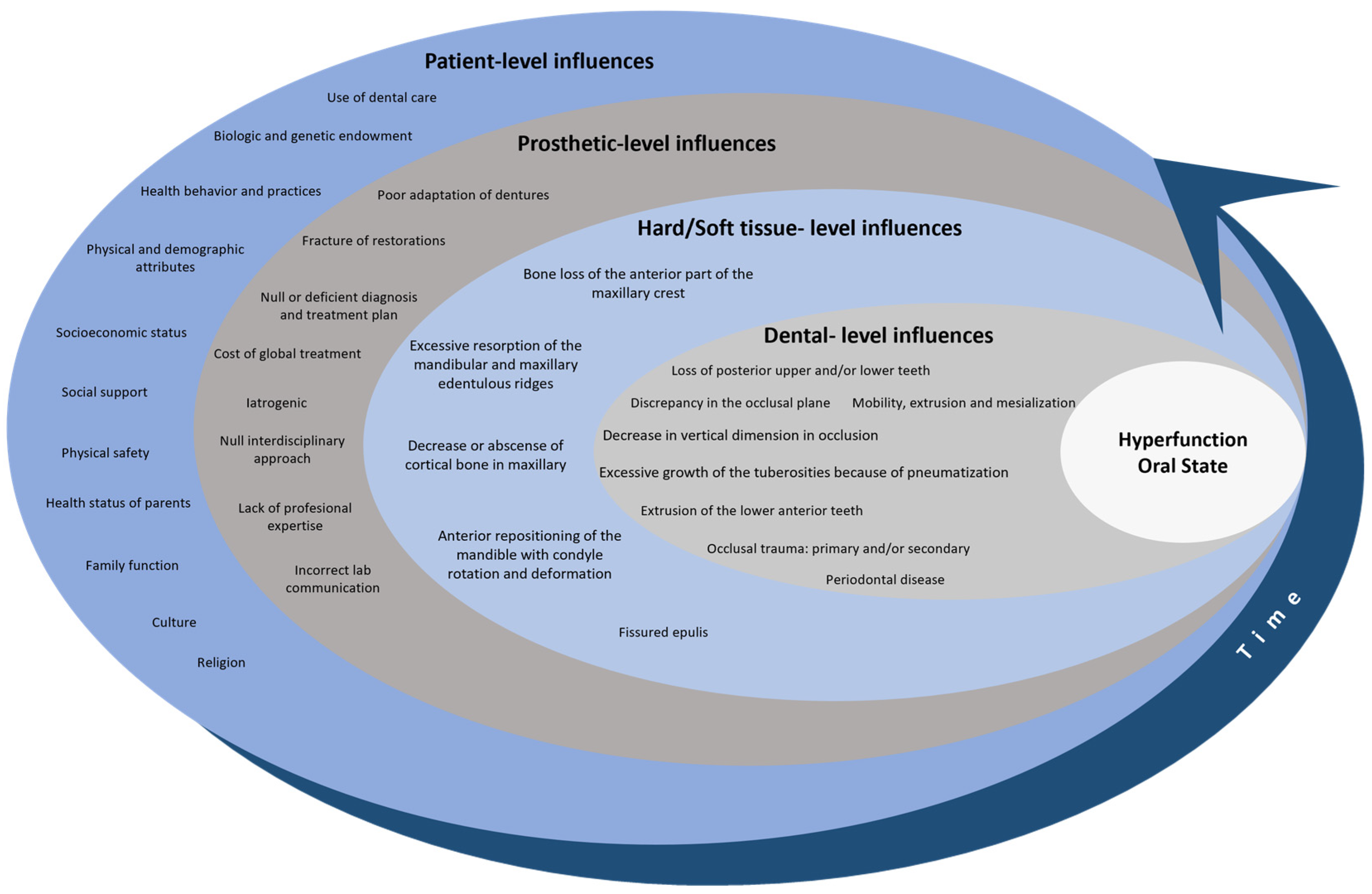
3.3. Hyperfunction Oral State: A Comprehensive Overview for a Conceptual Model
3.3.1. Patient-Level Influences
3.3.2. Prosthetic-Level Influences
3.3.3. Hard/Soft Tissue-Level Influences
3.3.4. Dental-Level Influences
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kelly, E. Changes Caused by a Mandibular Removable Partial Denture Opposing a Maxillary Complete Denture. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2003, 90, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunders, T.R.; Gillis, R.E.; Desjardins, R.P. The Maxillary Complete Denture Opposing the Mandibular Bilateral Distal-Extension Partial Denture: Treatment Considerations. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1979, 41, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolstunov, L. Combination Syndrome: Classification and Case Report. J. Oral Implant. 2007, 33, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driscoll, C.F.; Freilich, M.A.; Guckes, A.D.; Knoernschild, K.L.; Mcgarry, T.J.; Goldstein, G.; Goodacre, C.; Guckes, A.; Mor, S.; Rosenstiel, S.; et al. The Glossary of Prosthodontic Terms. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2017, 117, E1–E105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, Y.; Laufer, B.; Cardash, H.S. Modalities of Treatment for the Combination Syndrome. J. Prosthodont. 1995, 4, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolstunov, L. Management of Biomechanical Complication of Implant-Supported Restoration of a Patient with Combination Syndrome: A Case Report. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2009, 67, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauer, R.L.; Semidey, M.J. Diagnosis and Treatment of Temporomandibular Disorders. Am. Fam. Physician 2015, 91, 378–386. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, M.; Alani, A. Clinical Issues in Occlusion—Part II. Singap. Dent. J. 2015, 36, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tolstunov, L. Combination Syndrome Symptomatology and Treatment. Compend. Contin. Educ. Dent. 2011, 32, 62–66. [Google Scholar]
- Ogino, Y.; Kihara, M.; Yamada, J.; Toriya, K.; Koyano, K. Implant Treatments for Edentulous Maxilla with Anterior Hyperfunction. J. Oral Implant. 2015, 41, 731–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Singla, S. “Kelly’s Syndrome”—Prevention, Using Implant Supported Hybrid Denture: Clinical Considerations and Case Report with 5 Year Follow Up. IOSR J. Dent. Med. Sci. 2017, 16, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- de Kanter, R.J.A.M.; Battistuzzi, P.G.F.C.M.; Truin, G.-J. Temporomandibular Disorders: “Occlusion” Matters! Pain Res. Manag. 2018, 2018, 8746858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogino, Y.; Ayukawa, Y. Anterior Hyperfunction by Mandibular Anterior Teeth: A Narrative Review. Healthcare 2023, 11, 2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlsson, G.E. Responses of Jawbone to Pressure. Gerodontology 2004, 21, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buzayan, M.M.; Sivakumar, I.; Choudhary, S.; Tawfiq, O.; Mahdey, H.M.; Binti Mahmood, W.A.A. Prosthodontic Management of Combination Syndrome Case with Metal Reinforced Maxillary Complete Denture and Mandibular Teeth Supported Overdenture. Periodontics Prosthodont. 2018, 4, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, S.M. Combination Syndrome: A Treatment Approach. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1985, 54, 664–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, K.; Gongloff, R.K. Prevalence of the ‘Combination Syndrome’ among Denture Patients. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1989, 62, 642–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jameson, W.S. The Use of Linear Occlusion to Treat a Patient with Combination Syndrome: A Clinical Report. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2001, 85, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabianca, M. Combination Syndrome: Treatment with Dental Implants. Implant. Dent. 2003, 12, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Palmqvist, S.; Carlsson, G.E.; Wall, B. The Combination Syndrome: A Literature Review. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2003, 90, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madan, N.; Datta, K. Combination Syndrome. J. Indian Prosthodont. Soc. 2006, 6, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, M.C.G.; do Valle, A.L.; Ribeiro, M.C.M.; Pereira, J.R. Assessment of the Prevalence Index on Signs of Combination Syndrome in Patients Treated at Bauru School of Dentistry, University of Sao Paulo. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2007, 15, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Flanagan, D. Screwless Fixed Detachable Partial Overdenture Treatment for Atrophic Partial Edentulism of the Anterior Maxilla. J. Oral Implant. 2008, 34, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daher, T.; Dermendjian, S.; Morgano, S.M. Obtaining Maxillomandibular Records and Definitive Impressions in a Single Visit for a Completely Edentulous Patient with a History of Combination Syndrome. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2008, 99, 489–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murariu, M.C.; Preoteasa, E. The Anterior Hyperfunction Syndrom—Fem Simulation. Rom. J. Oral Rehabil. 2009, 1, 54–58. [Google Scholar]
- Gerritsen, A.E.; Allen, P.F.; Witter, D.J.; Bronkhorst, E.M.; Creugers, N.H. Tooth Loss and Oral Health-Related Quality of Life: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2010, 8, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jyoti, N.; Shah, N.; Karthik, M.M. Prosthodontic Rehabilitation of Patients with Combination Syndrome. Int. J. Dent. Clin. 2010, 2, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, S.; Kumar, G.; Kumar, M.; AD, M. Enigma of Combination Syndrome and Its Prosthodontics Way of Management: A Case Report. J. Int. Oral Health 2011, 3, 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Kilicarslan, M.A.; Akaltan, F.; Kasko, Y.; Kocabas, Z. Clinical Evaluation of Maxillary Edentulous Patients to Determine the Prevalence and Oral Risk Factors of Combination Syndrome. J. Dent. Sci. 2014, 9, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñarrocha, M.; Viña, J.A.; Carrillo, C.; Peñarrocha, D.; Peñarrocha, M. Rehabilitation of Reabsorbed Maxillae with Implants in Buttresses in Patients with Combination Syndrome. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2012, 70, e322–e330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.-W.; Liao, P.-B.; Chen, M.-S. Prosthodontic Treatment of a Patient with Combination Syndrome: A Clinical Case Report. J. Prosthodont. Implantol. 2012, 1, 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, T.O.; Ibrahim, R.O. Evaluation of Two Treatment Modalities for Patients with Combination Syndrome Suffering from Narrow Anterior Maxilla. Life Sci. J. 2013, 10, 2199–2210. [Google Scholar]
- de Resende, C.M.B.M.; Ribeiro, J.A.M.; Dias, K.d.C.; Carreiro, A.d.F.P.; do Rego, M.P.P.; de Queiroz, J.W.N.; Barbosa, G.A.S.; Oliveira, Â.G.R.d.C. Signs of Combination Syndrome and Removable Partial Denture Wearing. Rev. Odontol. UNESP 2014, 43, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlino, P.; Pettini, F.; Cantore, S.; Ballini, A.; Grassi, F.R.; Pepe, V. Surgical and Prosthetic Rehabilitation of Combination Syndrome. Case Rep. Dent. 2014, 2014, 186213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ucar Barroeta, A.; Berríos, M. El Síndrome de Combinación En Relación Con Rehabilitaciones Bucales Inadecuadas. MedULA Rev. Fac. Med. 2015, 24, 0798–3166. [Google Scholar]
- De Oliveira Pinto, A.F.; Gonçalves Júnior, N.O.; Teixeira Rodrigues, C.R. Hyperfunction Previous Syndrome: Case Report. Braz. J. Surg. Clin. Res. 2015, 12, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Narwal, A.; Chugh, A.; Rohtak, P.; Swami, R. Prosthodontic Management of a Patient with Combination Syndrome: A Clinical Case Report. Int. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 4, 509–513. [Google Scholar]
- Rajendran, S.; Baburajan, F. Combination Syndrome. Int. J. Prosthodont. Restor. Dent. 2012, 2, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy Juturu, R.K.; Mannava, P.; Preet Singh, H. Prevalence of Signs of Combination Syndrome: A Clinical Study. Saudi J. Oral Dent. Res. 2016, 1, 164–166. [Google Scholar]
- Korunoska-Stevkovska, V.; Guguvcevski, L.; Menceva, Z.; Gigovski, N.; Mijoska, A.N.; Nikolovska, J.; Bajraktarova-Valjakova, E. Prosthodontic Rehabilitation of Patient with Anterior Hyper Function Syndrome. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 5, 1000–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Singh, V.P.; Atri, B. Assessment of Signs of Combination Syndrome in Study Population: A clinical study. J. Adv. Med. Dent. Sci. Res. 2018, 6, 28–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Kumar, M.; Batra, R.; Sharma, C.; Mehta, S. Prosthodontic Management of Patient with Anterior Hyperfunction Syndrome: A Clinical Challenge. Dent. J. Adv. Stud. 2019, 6, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, A.; Qadeer, A.; Shakir, S. Frequency of Signs of Kelly’s Syndrome in Patients Presenting to the Prosthodontic Department of Khyber College of Dentistry. J. Khyber Coll. Dent. 2019, 9, 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- Bagga, R.; Robb, N.D.; Fenlon, M.R. An Investigation into the Prevalence of Combination Syndrome. J. Dent. 2019, 82, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penitente, P.; Freitas da Silva, E.; do Vale Souza, J.; de Freitas Jorge, C.; Bueno Carlini Bittencourt, A.; dos Santos, D.; Lamartine de Moraes Melo Neto, C.; Coelho Goiato, M. Combination Syndrome: A Literature Review of General Aspects and Treatments. J. Stomatol. 2022, 75, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merriam-Webster. Definition of Hyperfunction. In Merriam-Webster’s Collegiate Dictionary; Merriam-Webster: Springfield, IL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Oxford University Press. Definition of Hyperfunction. In Oxford English Dictionary; Editorial Team: Oxford, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher-Owens, S.A.; Gansky, S.A.; Platt, L.J.; Weintraub, J.A.; Soobader, M.-J.; Bramlett, M.D.; Newacheck, P.W. Influences on Children’s Oral Health: A Conceptual Model. Pediatrics 2007, 120, e510–e520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, A.I.; Tellez, M.; Pitts, N.B.; Ekstrand, K.R.; Ricketts, D.; Longbottom, C.; Eggertsson, H.; Deery, C.; Fisher, J.; Young, D.A.; et al. Caries Management Pathways Preserve Dental Tissues and Promote Oral Health. Community Dent. Oral Epidemiol. 2013, 41, e12–e40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reda, S.M.; Krois, J.; Reda, S.F.; Thomson, W.M.; Schwendicke, F. The Impact of Demographic, Health-Related and Social Factors on Dental Services Utilization: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Dent. 2018, 75, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, T.E. Factors Contributing to Dentists’ Extraction Decisions in Older Aduits. Spec. Care Dent. 1993, 13, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appukuttan, D. Strategies to Manage Patients with Dental Anxiety and Dental Phobia: Literature Review. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dent. 2016, 10, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nasser, L.; Lamster, I.B. Prevention and Management of Periodontal Diseases and Dental Caries in the Older Adults. Periodontol. 2000 2020, 84, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harish, P.; Joseph, S.A.; Sirajuddin, S.; Gundapaneni, V.; Chungkham, S.A. Iatrogenic Damage to the Periodontium Caused by Fixed Prosthodontic Treatment Procedures. Open Dent. J. 2015, 9, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brantley, C.F.; Bader, J.D.; Shugars, D.A.; Nesbit, S.P. Does The Cycle of Rerestoration Lead To Larger Restorations? JADA 1995, 126, 1407–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, N.Q.; Gonda, T.; Maeda, Y.; Ikebe, K. Average Rate of Ridge Resorption in Denture Treatment: A Systematic Review. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2021, 65, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugliese, F.; Zafeiriadis, A.A.; Hans, M.G. Growth of the Craniofacial Complex. In Pediatric Dentistry; Kotsanos, N., Sarnat, H., Park, K., Eds.; Textbooks in Contemporary Dentistry; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 155–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassani, M.Z. Aspects of Malpractice in Prosthodontics. J. Prosthodont. 2017, 26, 672–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markovics, D.; Szendi, R.; Vicko, K.; Rajnics, Z.; Marada, G.; Radnai, M. Incidence of Combination Syndrome Based on the Orthopantomograms Made between 2009 És 2014 at the Department of Prosthodontics, University of Pécs, Hungary. Fogorvosi Szle. 2016, 109, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

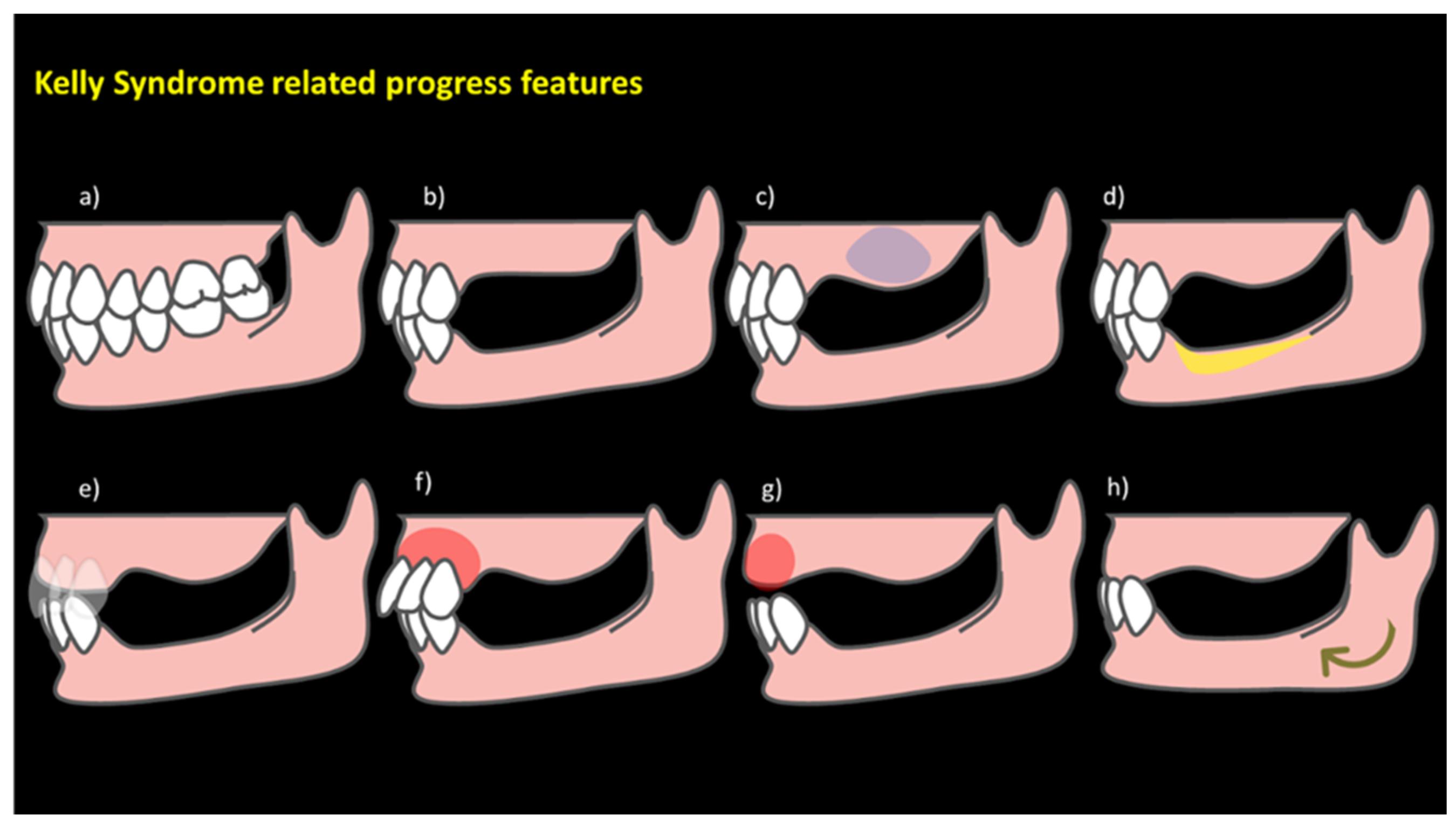
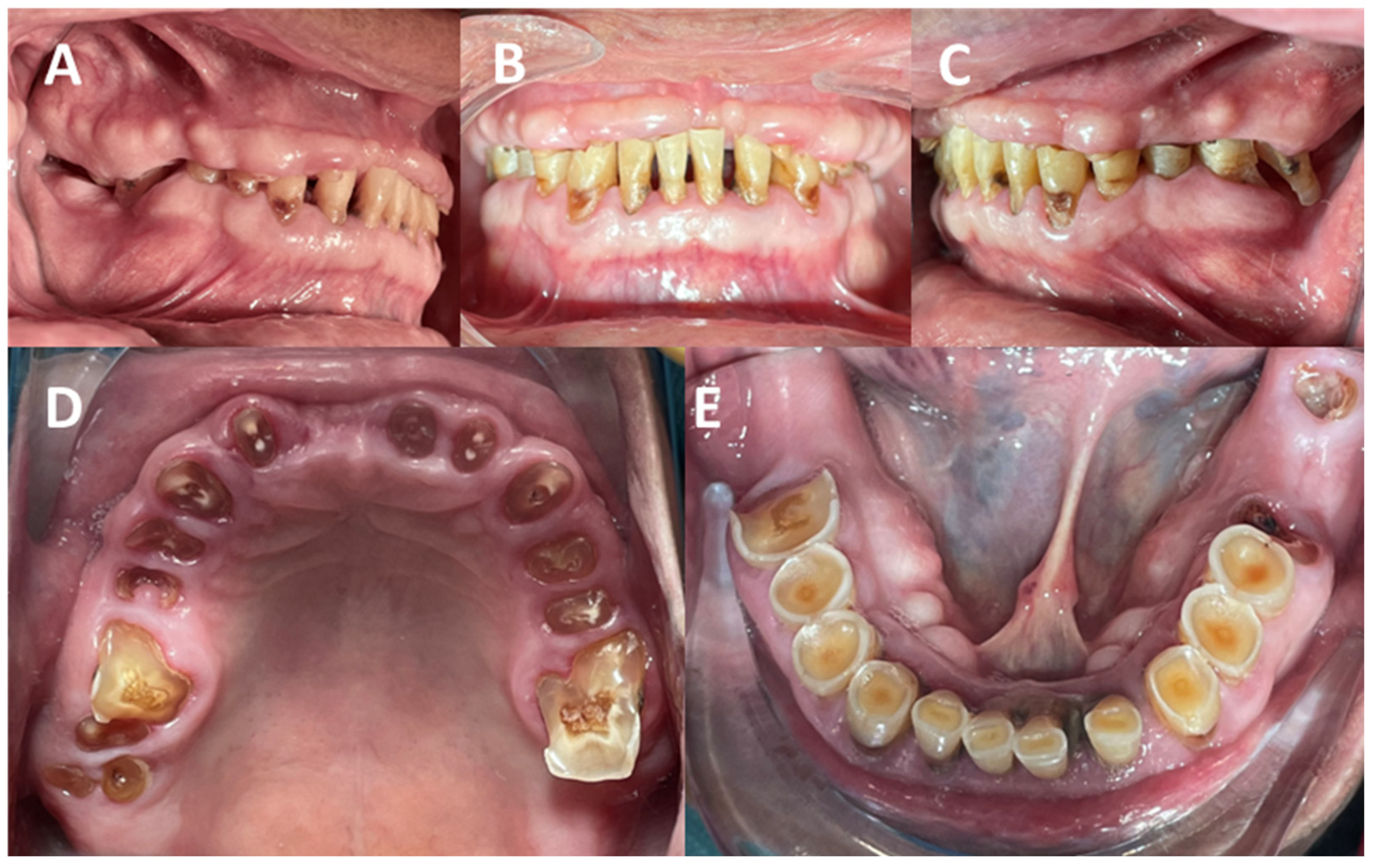
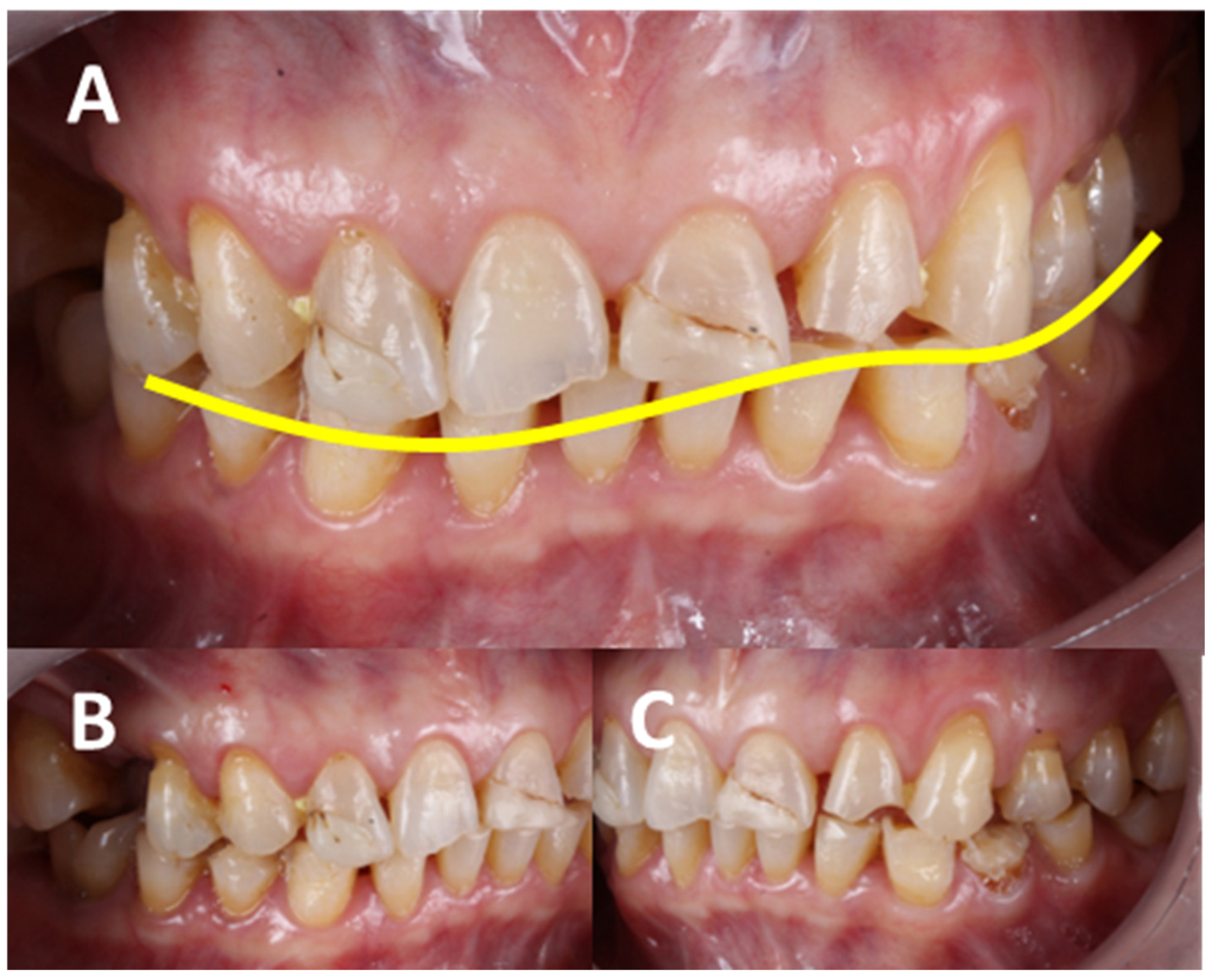


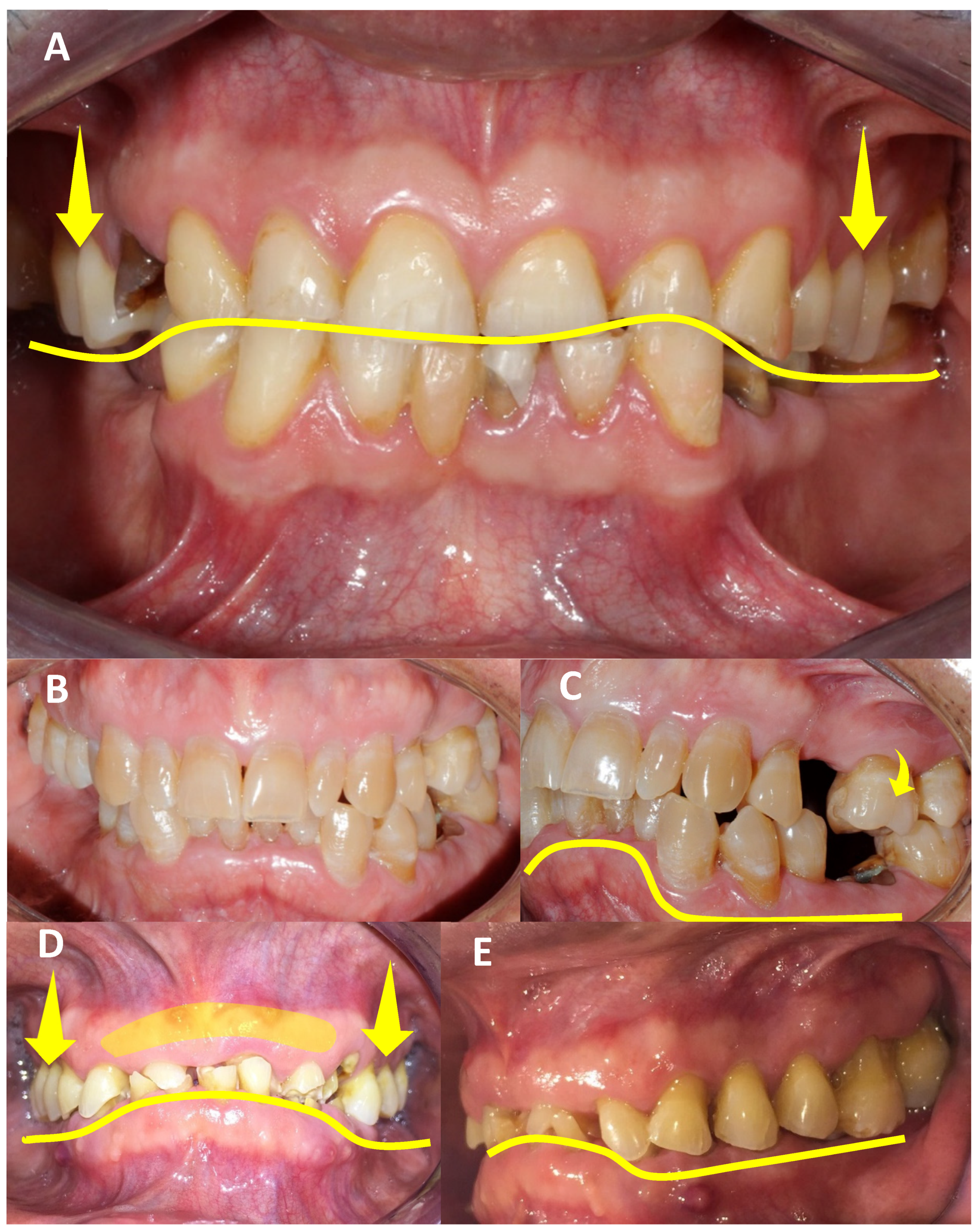
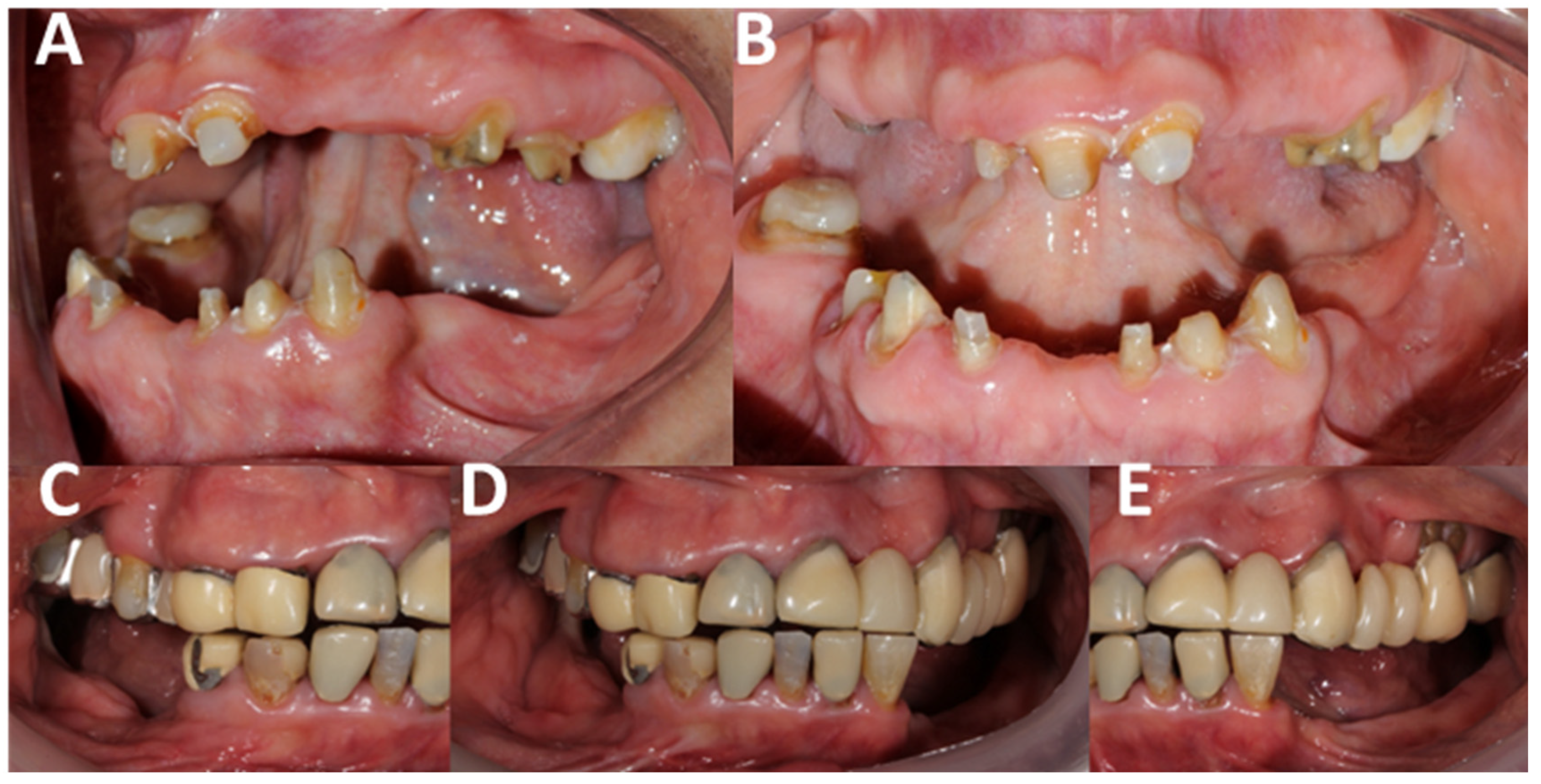
| Authors | AHS Risk Factors |
|---|---|
| Kelly, 1972 [1] | Bone loss of the anterior part of the maxillary crest; excessive growth of tuberosities; papillary hyperplasia in the hard palate; extrusion of the lower anterior teeth; excessive resorption of the mandibular edentulous ridges; excessive force; shearing forces; inadequate denture base coverage; underlying systemic causes |
| Saunders et al., 1979 [2] | Loss of vertical dimension in occlusion; discrepancy in the occlusal plane; anterior repositioning of the mandible; poor adaptation of prostheses; epulis fissuratum; periodontal disease; systemic disease; caries; oral hygiene |
| Schmitt et al., 1983 [16] | Occlusal stress |
| Shen et al., 1989 [17] | Periodontal disease |
| Langer et al., 1995 [5] | Poorly designed mandibular RPD |
| Jameson et al., 2001 [18] | Excessive anterior force |
| Cabianca et al., 2003 [19] | Posterior tooth loss; unstable occlusal plane |
| Palmqvist et al., 2003 [20] | Supraerupted maxillary molars; artificial denture teeth; |
| Carlsson et al., 2004 [14] | Anatomy; psychosocial aspects, mechanical devices; gender; age; facial morphology; duration of edentulousness; denture wearing habits; number of dentures worn; oral hygiene; parafunctions; occlusal loading; denture quality; nutrition; general health; medication; systemic; diseases; osteoporosis; corticosteroid treatment for asthma |
| Madan et al., 2006 [21] | Combination of complete maxillary dentures opposing class I mandibular RPD; retaining weak posterior teeth as abutments; conventional lower denture |
| Gonzalves et al., 2007 [22] | Lack of prosthesis adaptation |
| Tolstunov, 2007 [3] | Type of edentulism |
| Flanagan et al., 2008 [23] | Inappropriate treatment |
| Daher et al., 2008 [24] | Lack of professional expertise |
| Magureanu et al., 2009 [25] | Excessive pression in frontal region |
| Tolstunov, 2009; 2011 [6,9] | Abnormal traumatic occlusal forces |
| Gerritsen et al., 2010 [26] | Low quality of life |
| Jyoti et al., 2010 [27] | Null or deficient diagnosis and treatment plan |
| Rao et al., 2011 [28] | Deficient mandibular RPD |
| Kilicarslan et al., 2012 [29] | Edentulous maxilla |
| Peñarrocha et al., 2012 [30] | Marginal bone loss related to maxillary atrophy class |
| Feng et al., 2012 [31] | Edentulous maxilla opposed to natural mandibular anterior teeth; distal-extension RPD |
| Ibrahim et al., 2013 [32] | Low quality of bone in edentulous maxilla; deficient diagnosis; time |
| Resende et al., 2014 [33] | Mandibular RPD with inadequate technical quality; RPD absence |
| Carlino et al., 2014 [34] | Complete maxillary denture opposing complete denture attached to implants by bars or ball attachments; biomechanical stress to anterior maxilla of implants supported by prosthesis; lack of pre-prosthetic surgical intervention; no consideration of occlusion, vertical dimension, or occlusal plane; lack of follow-up |
| Barroeta et al., 2015 [35] | Deficient diagnosis; inadequate oral rehabilitation, lack of professional expertise; absence of lower RPD, inadequate lower RPD; lack of preventive treatment; decreased vertical dimension; maladaptation of the upper prosthesis; inverted prosthetic plane |
| Oliveira et al., 2015 [36] | Lack of diagnosis of the patient’s characteristics before treatment; combination of an upper tissue-supported prosthesis with lower RPD; inadequate occlusal schemes in prostheses; failure to eliminate the contact between the anterior teeth and the lower teeth |
| Narwal et al., 2015 [37] | Increasing pressure on the premaxillary alveolar ridge; loss of adequate posterior occlusal |
| Patel et al., 2015 [8] | Incorrect and inappropriate occlusal diagnosis for treatment planning |
| Rajendran et al., 2015 [38] | Lack of evaluation of dental history and the condition of the remaining mandibular anterior teeth; stress on the maxillary ridge, angle class III jaw relationships, parafunctional habits, and prolonged function with mandibular anterior teeth; degenerative changes in edentulous regions; inadequate treatment planning; failure to maintain oral tissue health; insufficient diagnosis, planning, and treatment implementation |
| Ogino et al., 2015 [10] | Patients failing to attend follow-up appointments; inadequate relationship between implant position and optimal artificial tooth positions; low quality and quantity of bone; absence of keratinized tissue; non-personalized treatments |
| Reddy et al., 2016 [39] | Lack of maxillary denture adaptation; need for replacement of maxillary denture; lack of mandibular denture adaptation; sex |
| Kumar et al., 2017 [11] | Inter-arch distance and relationship; lack of or null analysis of the anatomy of the maxilla using all tools available, including diagnostic models, X-ray images (radiographs, CBCT); incorrect impression technique; financial limitations for additional implants; lack of bone to support an adequate number of implants; loss of supporting structures for the lips and surrounding tissue; avoidance of bone grafting; no use of a tissue implant-supported hybrid denture as a less expensive and simpler option, within certain guidelines |
| Stevkovska et al., 2017 [40] | Lack of interdisciplinary therapy approach; delayed diagnosis; deficient treatment plan |
| Sharma et al., 2018 [41] | Lack of maxillary denture adaptation; not replacing the maxillary denture |
| Buzayan et al., 2018 [15] | Presence of a large torus palatinus and enlarged tuberosities; partially dentate mandibular arch with remaining anterior teeth; compromised sulcus depth: lack of pre-prosthetic surgical procedures; economic factors affecting treatment options; patient’s desires influencing the treatment plan; bone availability for dental implants; patient’s general health considerations; potential for progressive destructive changes in oral tissue without proper management |
| Verma et al., 2018 [42] | Reduced posterior occlusal contact; lack of use of implant-retained prostheses in the mandibular posterior area; extraction of upper posterior teeth; imbalanced occlusion |
| Akhtar et al., 2019 [43] | Inadequate surgical and prosthodontic treatment and lack of follow-up; tooth extrusion associated with RPD wearing; unsatisfactory lower dentures; non-simultaneous rehabilitation of residual arches; presence of preexisting signs before the provision of removable dentures; alveolar bone resorption as a natural phenomenon post-tooth loss; lack of scheduled follow-up sessions and proper guidance on denture care; poor preservation of posterior occlusion; inadequate treatment modalities, including poor-quality RPDs; failure to address papillary hyperplasia; lack of surgical procedures and proper impression techniques for flaccid tissue; poor fit, hygiene, and occlusion maintenance; insufficient use of implants to convert mandibular Kennedy Class 1 and 2 to Class 3, which could improve the masticatory efficiency, stability, and aesthetics; lack of implant-supported RPDs to reduce bone resorption |
| Bagga et al., 2019 [44] | Unsatisfactory dentures; periodontitis; maxillary complete dentures opposing mandibular anterior teeth |
| Penitente et al., 2022 [45] | Excessive bone resorption in the maxilla; occlusal architecture rearrangement; discrepancies between dental arches; divergent bone quality between maxilla and mandible; faster bone loss post-tooth extraction; greater bone loss with complete dentures; insufficient implant use; inadequate prosthetic and surgical planning; imbalanced occlusion; inadequate prosthesis material; insufficient posterior stabilization of the mandible |
| Ogino et al., 2023 [13] | Shift in mastication to anterior regions; excessive anterior occlusal function; occlusal trauma; lack of timely implant treatment; traumatic occlusion by preserved anterior teeth; excessive bone resorption in maxilla; lack of posterior occlusion; insufficient follow-up care; inadequate prosthetic treatment; loss of posterior occlusion support; improper implant placement; lack of cross-arch stabilization; inadequate bone quality and quantity; poor oral hygiene control; absence of keratinized tissue; inadequate prosthetic design; lack of individualized treatment approach |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aranda-Herrera, B.; Cruz, T.R.A.-d.l.; Jurado, C.A.; Garcia-Contreras, R. Anterior Hyperfunction Syndrome: Literature Review and Conceptual Model. Clin. Pract. 2024, 14, 1584-1600. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract14040128
Aranda-Herrera B, Cruz TRA-dl, Jurado CA, Garcia-Contreras R. Anterior Hyperfunction Syndrome: Literature Review and Conceptual Model. Clinics and Practice. 2024; 14(4):1584-1600. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract14040128
Chicago/Turabian StyleAranda-Herrera, Benjamin, Tania Rubi Agudo-de la Cruz, Carlos Alberto Jurado, and Rene Garcia-Contreras. 2024. "Anterior Hyperfunction Syndrome: Literature Review and Conceptual Model" Clinics and Practice 14, no. 4: 1584-1600. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract14040128
APA StyleAranda-Herrera, B., Cruz, T. R. A.-d. l., Jurado, C. A., & Garcia-Contreras, R. (2024). Anterior Hyperfunction Syndrome: Literature Review and Conceptual Model. Clinics and Practice, 14(4), 1584-1600. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract14040128










