Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia: Diagnostic Pitfalls in Prolonged Neonatal Jaundice
Abstract
1. Introduction
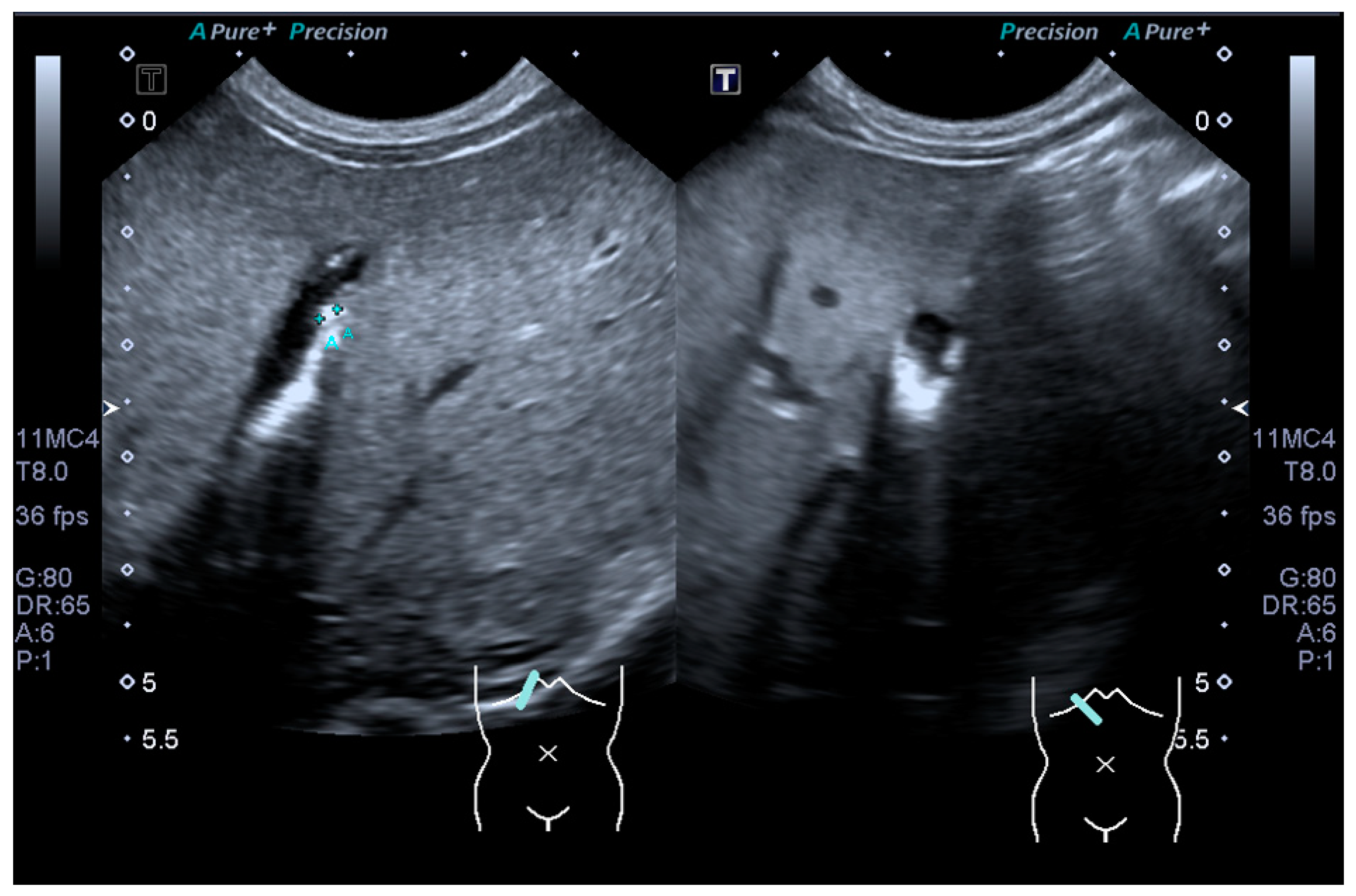
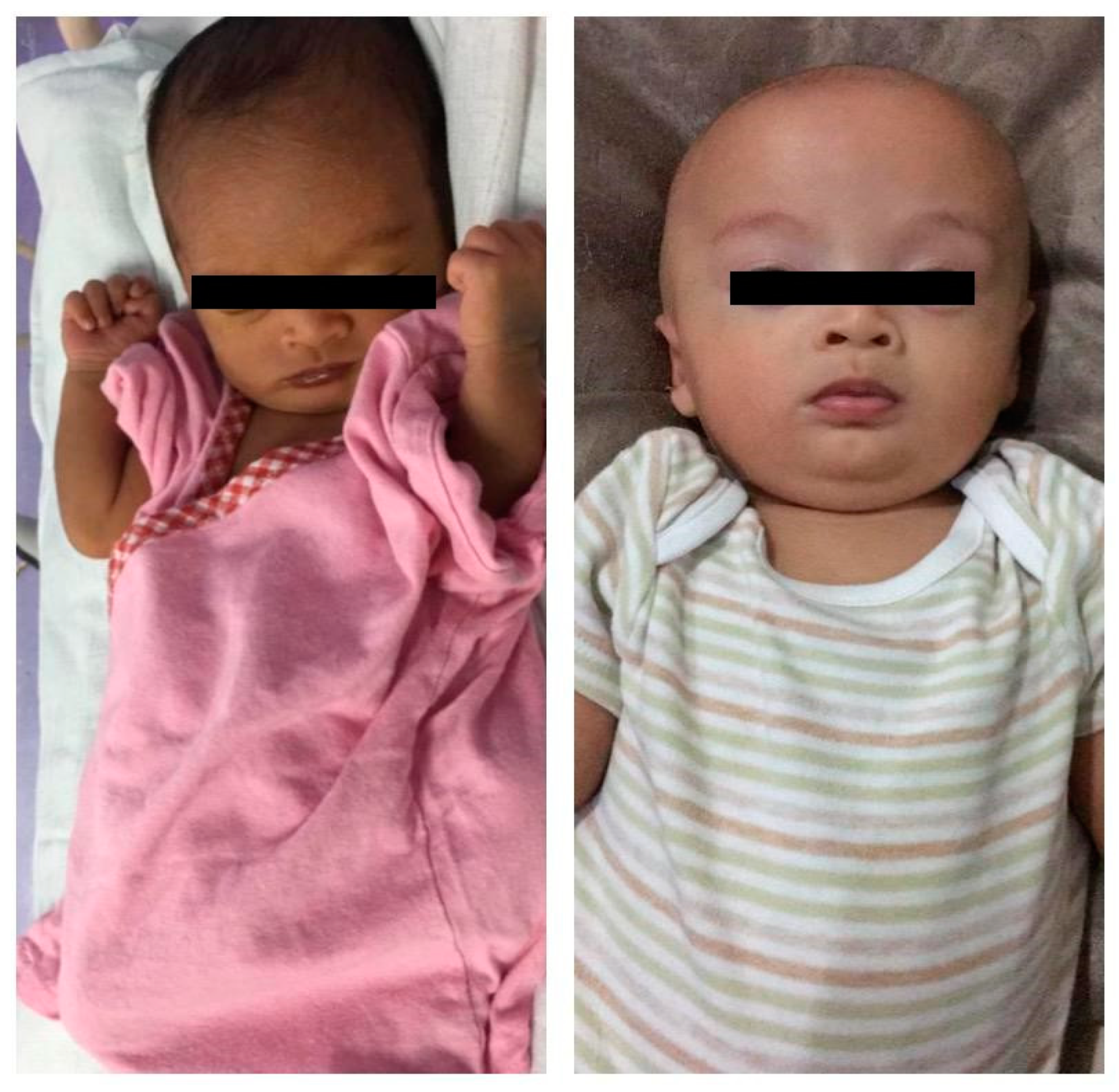
2. Case Report
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parsa, A.; New, M. Steroid 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency in Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 165, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignatelli, D.; Carvalho, B.L.; Palmeiro, A.; Barros, A.; Guerreiro, S.G.; Macut, D. The Complexities in Genotyping of Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia: 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Völkl, T.; Öhl, L.; Rauh, M.; Schöfl, C.; Doerr, H. Adrenarche and Puberty in Children with Classic Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia due to 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2011, 76, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, P.C.; Speiser, P.W. Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia due to 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency. Endocr. Rev. 2000, 21, 245–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keil, M.F.; Bosmans, C.; Van Ryzin, C.; Merke, D.P. Hypoglycemia during acute illness in children with classic congenital adrenal hyperplasia. J. Pediatr. Nurs. 2010, 25, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Speiser, P.W.; Arlt, W.; Auchus, R.J.; Baskin, L.S.; Conway, G.S.; Merke, D.P.; Meyer-Bahlburg, H.F.L.; Miller, W.L.; Murad, M.H.; Oberfield, S.E.; et al. Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Due to Steroid 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 4043–4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Maouche, D.; Arlt, W.; Merke, D.P. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Lancet 2017, 390, 2194–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phak, N.H.; Thomas, M.-I.H.-I. Paediatric Protocols for Malaysian Hospitals, 3rd ed.; Ministry of Health Malaysia: Selangor Darul Ehsan, Malaysia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Karnsakul, W.; Sawathiparnich, P.; Nimkarn, S.; Likitmaskul, S.; Santiprabhob, J.; Aanpreung, P. Anterior pituitary hormone effects on hepatic functions in infants with congenital hypopituitarism. Ann. Hepatol. 2007, 6, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodadad, A.; Modaresi, V.; Kiani, M.A.; Rabani, A.; Pakseresht, B. A case of lipoid congenital adrenal hyperplasia presenting with cholestasis. Iran. J. Pediatr. 2011, 21, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fawaz, R.; Baumann, U.; Ekong, U.; Fischler, B.; Hadzic, N.; Mack, C.L.; McLin, V.A.; Molleston, J.P.; Neimark, E.; Ng, V.L.; et al. Guideline for the Evaluation of Cholestatic Jaundice in Infants: Joint Recommendations of the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition and the European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2017, 64, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harpavat, S.; Finegold, M.J.; Karpen, S.J. Patients with biliary atresia have elevated direct/conjugated bilirubin levels shortly after birth. Pediatrics 2011, 128, e1428–e1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harpavat, S.; Garcia-Prats, J.A.; Shneider, B.L. Newborn Bilirubin Screening for Biliary Atresia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 605–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harpavat, S.; Ramraj, R.; Finegold, M.J.; Brandt, M.L.; Hertel, P.M.; Fallon, S.C.; Shepherd, R.W.; Shneider, B.L. Newborn Direct or Conjugated Bilirubin Measurements As a Potential Screen for Biliary Atresia. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2016, 62, 799–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.R.; Rosenthal, P.; Escobar, G.J.; Newman, T.B. Interpreting conjugated bilirubin levels in newborns. J. Pediatr. 2011, 158, 562–565.e561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, A.K.; Vora, P.V. Conjugated Hyperbilirubinemia in the Neonate and Young Infant. Pediatr. Emerg. Care 2018, 34, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merke, D.P.; Bornstein, S.R. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Lancet 2005, 365, 2125–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trakakis, E.; Basios, G.; Trompoukis, P.; Labos, G.; Grammatikakis, I.; Kassanos, D. An update to 21-hydroxylase deficient congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Gynecol. Endocrinol. Off. J. Int. Soc. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2010, 26, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thambiah, S.; Ahmad, Z.; Hambali, Z.; Osman, M.; Zain, M.; Zain, F.; Hong, J. Clinical presentation of congenital adrenal hyperplasia in selected multiethnic paediatric population. Malays. J. Med. Health Sci. 2015, 11, 77–83. [Google Scholar]
- Wijaya, M.; Huamei, M.; Jun, Z.; Du, M.; Li, Y.; Chen, Q.; Chen, H.; Song, G. Etiology of primary adrenal insufficiency in children: A 29-year single-center experience. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 32, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özyilmaz, B.; Aydin, M.; Gönül, O. Correlation of phenotype with the CYP21 gene mutation analysis of classic type congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency. J. Exp. Clin. Med. 2018, 35, 63–69. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, N.; Zafar, F.; Bangash, A.; Malik, A.; Mohammedi, K. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia with cholestatic jaundice. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2014, 64, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bauman, J.W., Jr.; Chang, B.S.; Hall, F.R. The effects of adrenalectomy and hypophysectomy on bile flow in the rat. Acta Endocrinol. 1966, 52, 404–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theiler-Schwetz, V.; Zaufel, A.; Schlager, H.; Obermayer-Pietsch, B.; Fickert, P.; Zollner, G. Bile acids and glucocorticoid metabolism in health and disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2019, 1865, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerick, K.M.; Whitington, P.F. Molecular basis of neonatal cholestasis. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2002, 49, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiehl, A.; Thaler, M.M.; Admirand, W.H. The effects of phenobarbital on bile salts and bilirubin in patients with intrahepatic and extrahepatic cholestasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1972, 286, 858–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
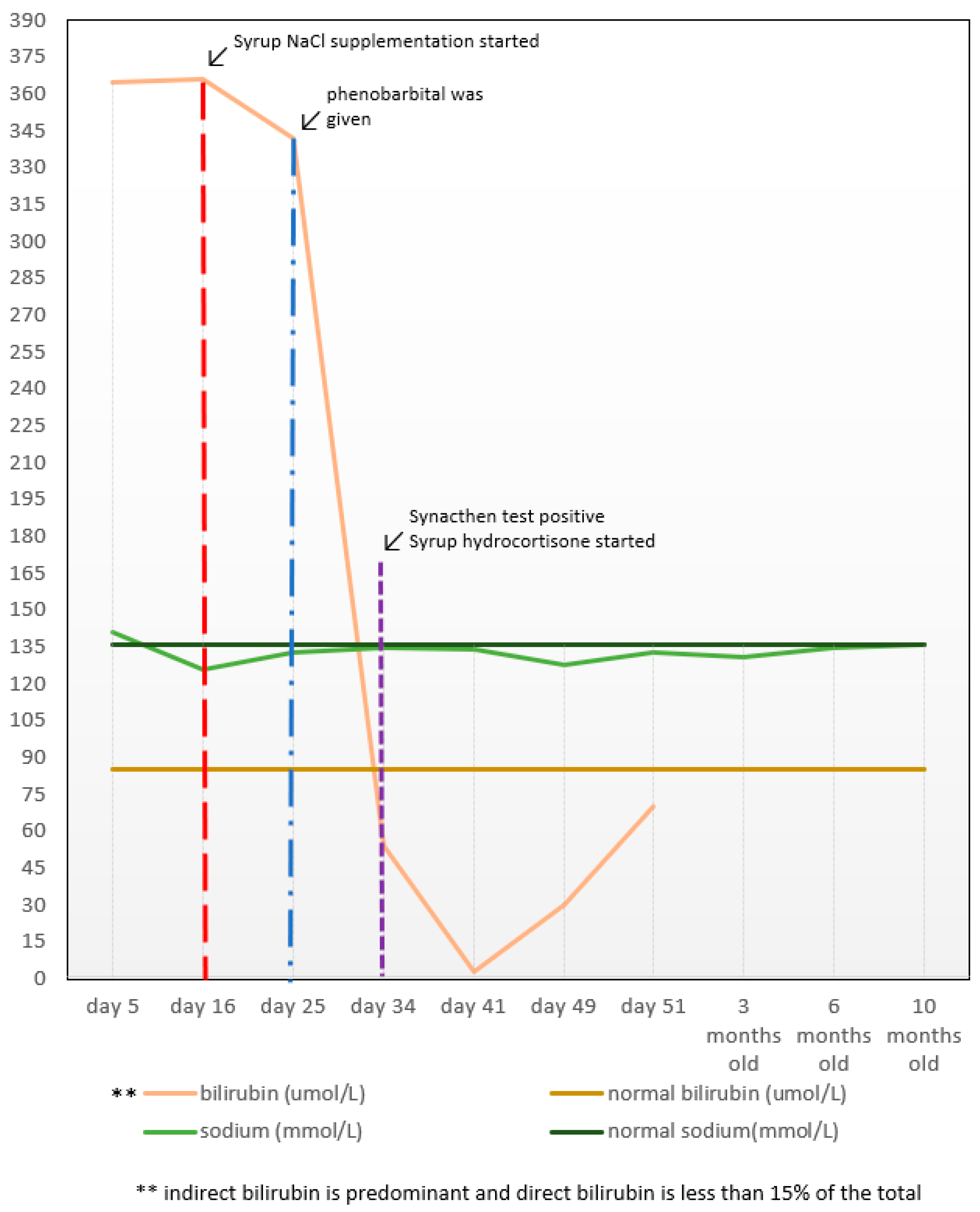
| Date | Age | Total Bilirubin (μmol/L) | Direct Bilirubin (μmol/L) | Sodium (mmol/L) | 17-OH P (nmol/L) | Cortisol (nmol/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 23 May 2019 | At birth | - | - | - | - | - |
| 28 May 2019 | Day 5 | 365 | 12.1 | 141 | - | - |
| 8 June 2019 | Day 16 | 366 | 11.1 | 126 | - | - |
| 17 June 2019 | Day 25 | 342 | 12.1 | 133 | - | - |
| 27 June 2019 | Day 34 | 54 | - | 135 | - | - |
| 4 July 2019 | Day 41 | 3.2 | - | 134 | - | - |
| 12 July 2019 | Day 49 | 30 | - | 128 | - | - |
| 16 July 2019 | Day 54 | 70 | - | 130 | - | - |
| 19 August 2019 | Day 69 | - | - | 133 | - | - |
| 6 September 2019 | 3-month-old | - | - | 131 | 241.1 (morning) >969.6 (30 min after) 916 (60 min after) | 61 (morning) 76 (30 min after) 96 (60 min after) |
| 20 December 2019 | 6-month-old | - | - | 135 | 135.8 | - |
| 15 April 2020 | 10-month-old | 7 | - | 136 | 46.7 | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rosli, N.A.; Mazapuspavina, M.Y.; Mohd Nor, N.S. Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia: Diagnostic Pitfalls in Prolonged Neonatal Jaundice. Clin. Pract. 2021, 11, 870-877. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract11040102
Rosli NA, Mazapuspavina MY, Mohd Nor NS. Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia: Diagnostic Pitfalls in Prolonged Neonatal Jaundice. Clinics and Practice. 2021; 11(4):870-877. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract11040102
Chicago/Turabian StyleRosli, Nur Athirah, Md Yasin Mazapuspavina, and Noor Shafina Mohd Nor. 2021. "Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia: Diagnostic Pitfalls in Prolonged Neonatal Jaundice" Clinics and Practice 11, no. 4: 870-877. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract11040102
APA StyleRosli, N. A., Mazapuspavina, M. Y., & Mohd Nor, N. S. (2021). Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia: Diagnostic Pitfalls in Prolonged Neonatal Jaundice. Clinics and Practice, 11(4), 870-877. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract11040102






