Abstract
Paraquat (PQ) is one of the most used herbicide globally; applied around trees in orchards and between crop rows to control broad-leaved and grassy weeds. Its oxidation results in the formation of superoxides which causes damage to cellular components. In this study, we determined the antioxidant effect vitamin C has on hemograms [hemoglobin (Hb), packed cell volume (PCV) and total white blood cells count] of rats under these toxic insults. The animals grouped (A-D), comprising subgroups without vitamin C (A1, B1, C1, D1) and subgroups on vitamin C (A2, B2, C2, D2), received different sub-lethal doses of PQ administered intraperitoneally monthly to the animals over a period of three months. The Hb values obtained were significantly reduced (P≤0.05) at month 1 and (P≤0.001) at months 2 and 3. These changes became more pronounced with increased dose and time. Vitamin C treated subgroups (B2, C2 and D2) had better Hb values than those without it (B1, C1 and D1) but the values were still significantly low when compared to the control subgroups (A1 and A2). This same trend was observed in the PCV results obtained. The Control subgroups showed that vitamin C treated subgroup (A2) had a more improved hemogram values than subgroup on water only (A1), but they were all higher than that of the test subgroups. These PQ induced anaemia were ameliorated by the subsequent administration of vitamin C, and continuous treatment with vitamin C restored the health status of the animals so treated.
Introduction
Paraquat (PQ), a controversial herbicide, is one of the most used total contact herbicide globally; it is applied around trees in orchards and between crop rows to control broad-leaved and grassy weeds.[1] Because PQ has a redox potential of –446 mV, any reducing agent with sufficient energy can donate an electron to the bipyridylium divalent cation (PQ2+), to form a free radical (PQ+), which its oxidation results in the formation of the original PQ2+ and a transfer of the released electron to oxygen which subsequently leads to the formation of toxic superoxides called Reacti e Oxygen Species which when in excess escapes the electron transport chain and causes damage to cellular components.[2]
The hemograms [hemoglobin (Hb), packed cell volume (PCV) and total white blood cells count (T-WBC)] are hematological parame-ters used in accessing blood functionality in health and diseased state.[3] Few of its primary functions are to detect anaemia, polycy- taemia, leucocytosis, leucocytopenia, etc. They also contribute in assessing transporta- tion, distribution, regulation and protection of body fluids.[3]
Toxic substances, such as PQ, through the formation of oxygen free radicals (ROS) results in the destruction of cellular compo- nents leading to hemolysis (destruction of red blood cells),[4] production failure (by attacking stem cells),[5] transportation failure (by chelat- ing iron, other metals and proteins involved in cellular functions),[6] regulatory and protective failure (by affecting leucocytes and platelet production).[6]
Vitamin C, a potent water soluble vitamin, has been shown to function as an antioxidant. It has affinity for many free radicals,[7] thereby minimizing the damage caused by oxidative stress. Vitamin C directly scavenges ROS with and without enzyme catalysts and can indirect- ly scavenge them by recycling other antioxi- dants (e.g. tocopherol) to the reduced form.[8,9] By reacting with activated oxygen more readi- ly than any other aqueous components ascor- bate protects critical macromolecules from oxidative damage.[8] In cells, vitamin C is main- tained in its reduced form by reacting with glu- tathione, which can be catalyzed by protein disulphide isomerase and glutaredoxins.[10,11] In addition to its direct antioxidant effects, vita- min C is also a substrate for the antioxidant enzyme ascorbate peroxidase, a function that is particularly important in stress resistance in plants.[12,13]
Because of this potent functionality of vita- min C, this study was geared towards assess- ing the acceptability of vitamin C as an adjunct in treatment and management of Paraquat tox- icity cases.
Materials and Methods
Materials
Rats
A total of 96 male Albino rats (Rattus nor egicus), weighing between 180-220g [average body weight (BW) 0.2±0.02 kg], were used for the study. Prior to experimentation, all the animals were allowed two weeks to accli- matize to their environment during which period they all had free access to tap water and were fed with pelletized finisher feed (ad libi- tum), all with negligible vitamin C content.
Paraquat
The paraquat used was purchased as a liter volume of 20% w/v solution with the trade name Dizmazone (Dizengoff W.A. Ltd, Lagos, Nigeria) properly sealed in an opaque plastic container. It was kept at room temperature and during use proper caution was taken to avoid fire, spillage or poisoning.
Vitamin C
Pure vitamin C (1000 mg) caplets from Mason Natural® Trade name of Mason Vitamins, Inc. (Miami Lakes, FL, USA), were used for the research.
Methods
Two mL of different sub-lethal doses of the toxicant (PQ) was intraperitoneally (ip) administered to the animals, under anaesthet- ics,[14] in different dosed subgroups – A1, A2 (0.0 g/kg); B1, B2 (0.02 g/kg); C1, C2 (0.04 g/kg) and D1, D2 (0.06 g/kg) – on biweekly basis for 3 months [subgroups A1 and A2 was given 2 mL of 0.9 N normal saline (ip) in conformity with international standard in checking injection sites reaction]. The subgrouped animals were designated into: i) for non-vitamin C treat- ment; and ii) for vitamin C treatment, as indi- cated in Table 1.

Table 1.
Treatment chart for the subgroups.
Subsequently, vitamin C solution (200 mg/L) was prepared in place of water and were provided to the animals in drinking water bot- tles with glass sipper tubes for rats in sub- groups 2 (A2, B2, C2 and D2), while ordinary drinking water with negligible vitamin c con- tent was provided to the animals in subgroups 1 (A1, B1, C1 and D1) all through the study peri-od (Table 1). The water and vitamin C bottles were refilled at least trice daily irrespective of the volume of water or vitamin c remaining in the in-use bottles. It will be note worthy to state that at month 3, the food and water con- sumption by the rats were affected by PQ intoxication, mainly the subgroups dosed 0.06g/kg BW without vitamin C treatment (D1).
On monthly intervals, 4 animals per sub- group were selected, anaesthetized with gaseous isoflurane anaesthetic machine, the induction chamber was prefilled with 4% isoflurane and oxygen (0.6 L/min). The rats were placed in the induction chamber and observed for signs of lateral recumbence, steady breathing and no attempt to right itself when the induction chamber is slightly tilted, only then is it anaesthetized enough for trans- fer to the mask on the rodent breathing circuit. Open the lid of the induction chamber and quickly check for absence of the pedal reflex.[15 If present, 3 mL of blood sample were collected using 23G needle attached to 5 mL syringe and the blood samples collected were decanted into Ethylenediaminetetracetic acid containers using cardiac puncture procedures.[14] After mixing, the samples were ready for the hema- tological estimations of Hb, PCV and T-WBC using cyanmethemoglobin method, microhe- matocrit method and improved Neubaur count-ing chamber method, respectively.[5]
Animal care
We do affirm that in carrying out this research that The Nigerian Institutional and National Guide for the care and use of laborato- ry animals were followed.
Data computation
The Excel (2007) window’s package and two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) statisti- cal methods were used for the result analysis, with levels of significance measured at P<0.05 and 0.001 respectively.
Results
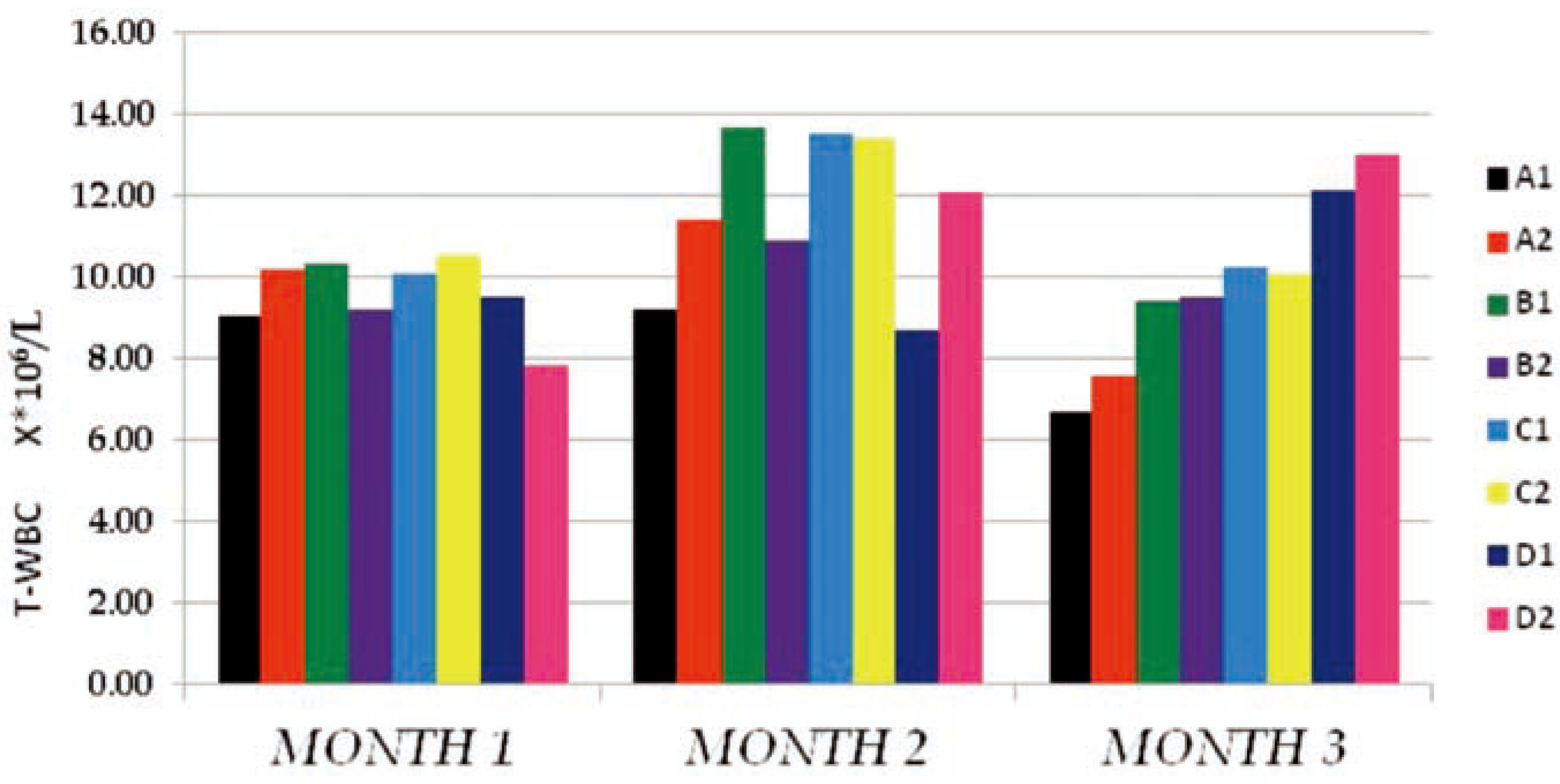
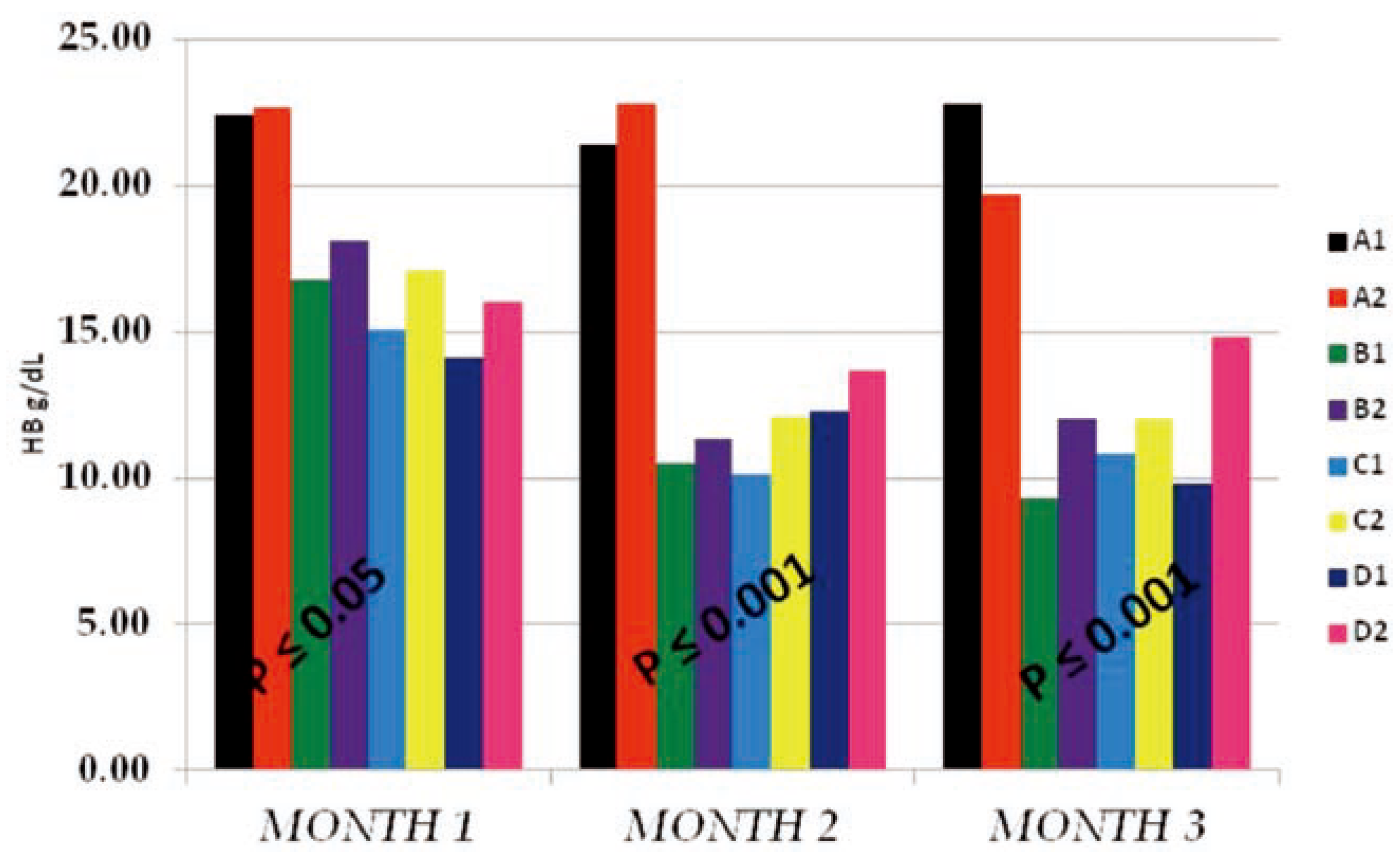
The T-WBC counts of the individual sub- groups for the 3 months study were presented in Figure 1 above. The results obtained indicat- ed that, from months 1–2, there existed no observable effect by either PQ or vitamin C on T-WBC values. The control and tests subgroups values were similar, with negligible dose and time effects on either the subgroups on PQ alone (B1, C1 and D1) or the subgroups which in addition to PQ insult received vitamin C (A2, B2, C2 and D2). It is either that PQ toxicity does not trigger immune response or that the dose and duration of toxicity was not enough for such effect to be noticeable. Another reason could be that the route of administration of PQ (ip) hinders humoral or passive immune response. At month 3, a somewhat increased difference existed between the control sub- groups and the test subgroups which were dose dependent at P≤0.05, but the within sub- groups comparison indicated no difference between the PQ only treated subgroups (B1, C1 and D1) and the subgroups which in addition to PQ insult received vitamin C (A2, B2, C2 and D2). This supported the summation that fur- ther studies with longer dose and time effect needs to be carried out to completely deter- mine what will happen on the T-WBC studied. The Hb mean values obtained (Figure 2) shows that PQ toxicity actively reduced the Hb levels of the test subgroups (B1, B2, C1, C2, D1 and D2) when compared to the control sub- groups (A1 and A2) at P≤0.05 (month 1) and P≤0.001 (months 2 and 3). The reduction was found to be more on the subgroups that received PQ (ip) only (B1, C1 and D1) than the subgroups which in-addition to PQ insult received vitamin C (B2, C2 and D2). We noticed that the effect was both dose and time depend- ent and also that there were an existing interac- tion between the dose effect and the time of exposure. The within subgroups comparison showed that the subgroups which in-addition to PQ insult received vitamin C (B2, C2 and D2) had a higher Hb values than the subgroups that received PQ (ip) only (B1, C1 and D1), indicat- ing that vitamin c improved their Hb level even with the dose and time of exposure effects.
Figure 1.
The total white blood cells count (T-WBC106/L) mean values of the different subgroups for the 3 months study period.
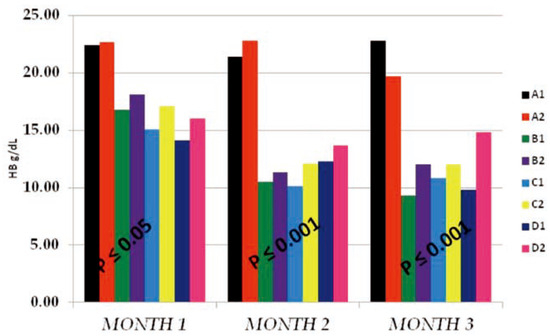
Figure 2.
The hemoglobin (HB g/dL) mean values of the different subgroups for the 3 months study period.
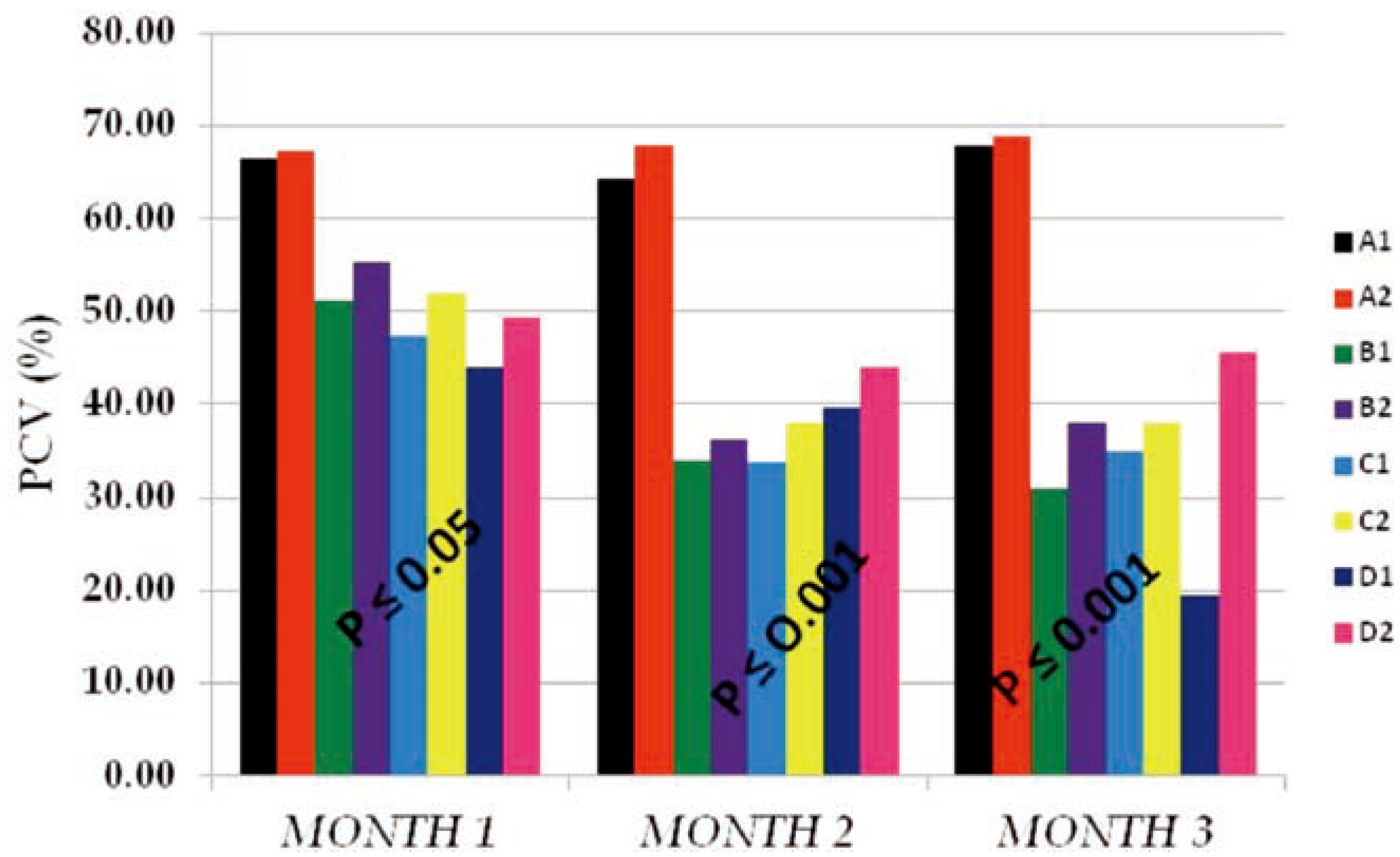
The PCV mean values obtained in Figure 3 also followed the same pattern with that of Hb in Figure 2. Reduction in the volume of the red cells of test subgroups (B1, B2, C1, C2, D1 and D2) from months 1 to 3 as compared to that of the control subgroups (A1 and A2) within the same period of time signifies that PQ toxicity actively affected the red cells number and func- tionality through hemolysis, membrane enzyme disruption, etc. Also we observed that these effects were less in vitamin c treated subgroups than the subgroups on PQ insult only indicating that vitamin C has a life saving effect on cells that were placed under toxic insult. The data obtained also showed that there was an interaction between dose of PQ given and the time of exposure. The higher the dose given and the time of exposure the more the PCV mean values were reduced.
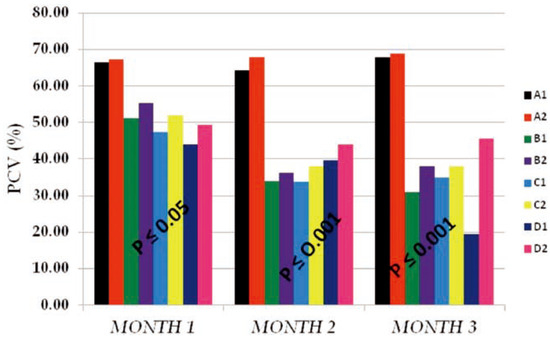
Figure 3.
The packed cell volume (PCV %) mean values of the different subgroups for 3 months study period.
Discussion
PQ is a well known herbicide that has been extensively used for the defoliation of weeds in farmland, recreational, public and industrial sites.1 Its toxicity effect is initiated by its abili- ty to form ROS causing disruption of cell mem- brane functionality and possibly cell death.16 Vitamin c has been shown to scavenge these ROS with or without enzyme catalysis thereby restoring cell functionality.9,8
In this study, we investigated the ameliora- tive effect of vitamin C on PQ toxicity using hematological cells that are easily affected by PQ toxicity. We hypothesized that T-WBC and red blood cells when subjected to toxic insult in i o will respond easily, and that subsequent and continuous administration of vitamin C will arrest these ROS and restore cell function- ality in the affected animals. To investigate this, we choose, PCV, Hb and T-WBC parame- ters, reason being that they are easily affected by hemolysis, inflammation, enzyme deactiva- tion, etc occasioned by toxic insult, and also they respond quickly to the repairing and restoring effect of vitamin c on cell membrane, cytosol and endoplasmic enzyme activities.
The results of the mean T-WBC counts (Figure 1) indicated that there were no observ- able changes in the values obtained from months 1-2 in both the dose and time of expo- sure effects in the subgroups treated. These was corroborated by the results from other studies where the changes observed in T-WBC of animals under PQ insult treated with vari- ous antioxidant were not significantly differ- ent from that of the control animals used.[17,18] At month 3, there seemed to be a noticeable increase in the T-WBC mean values of the test subgroups when compared to the control, but the within subgroup comparison showed no difference between the vitamin c treated sub- groups and those on PQ only. This made us suggest that the dose and time of exposure may not have been enough to conclusively determine the immune cell toxicity effect.
Hb mean values of the test subgroups (Figure 2) were significantly lower than the control subgroups at P≤0.05 (month 1) and P≤0.001 (months 2 and 3), respectively. These test subgroups reduction in Hb mean values was found to be both dose and time of expo- sure dependent, with the subgroups on vita- min c having much better Hb values than that of the test subgroups on PQ treatment only. Also the vitamin c treated control subgroup (A2) has a better improved Hb than the nega- tive control (A1). This interaction between the dose given and the time of exposure effects where supported by the findings that vitamin c confers some level of Protection: Prevention, Interception and Repair, thereby stopping hemolysis and destruction of red cells.[17,18,19,20] Also the work on Dapsone treatment indicated that vitamin C alongside vitamin E has a protective effect on the erythrocyte against haemolysis caused by dapsone in patient with dermatitis herpetiformis.[21]
Similarly, the PCV mean values (Figure 3) obtained followed the same pattern with that of the Hb. The reduction in volume were as a result of hemolysis, lipid peroxidation, super- oxide formation and elevated nutrient cataly- sis occasioned by the toxic insult,2 these effects were dose and time dependent,22 occur- ring at the expense of cellular reducing equiv- alent, such as nicotinamide adenine dinu- cleotide phosphate-oxidase, and having conse- quences in other metabolic processes.[22,23,24] These processes led to the phenotypic observa- tions like loss of weight, inability to feed, hair loss, redness of the eyes and high incidence of labored breathe among test subgroups at high- er doses (0.04 and 0.06 g PQ/kg body weight), especially on the subgroups on PQ dose only. This same subgroups recorded high incidence of death among test animals.
Finally, the dosage, time of exposure and their interaction effects observed on the Hb and PCV mean values obtained from test sub- groups on PQ only and those that received vita- min c during PQ insult indicates that truly vita- min c has the capability to reduce or limit toxic insult occasioned by PQ or any other xenobi- otics. Therefore we suggest that vitamin C treatment should be incorporated into the first-line regimen on cases of toxicity reported in emergency health facilities.
Conclusions
This study has demonstrated the life saving effects of antioxidant (vitamin C) on the chronic toxic insults of PQ administered intraperitoneally to rats.
Exposure of rats to PQ induced massive anaemia and mild leucocytosis that were dose and time dependent, but the subsequent admin-istration of the antioxidant (vitamin C) amelio- rated these effects and normalized the hemograms depending on the dose and dura- tion of the treatment. It is evident that vitamin C continuous administration during toxic insult should be one of the first-line treatments given to patients, and that it should be extended even after patient’s recovery to completely repair the cells and tissues that were damaged.
Author Contributions
BNO, as the lead author, was involved in the research proper, analyzing the samples and making sure that all went well with the study; CUO, carried out the statistical analysis and assisted in proof reading of the materials before publication; VI, performed the serious statistical areas that needed in-depth analysis and designed the graphical representation of the data for visual understanding.
Conflicts of Interest
Conflict of interests: the authors declare no potential conflict of interests.
References
- IPCS-INCHEM International programme on chemical safety. Environmental Health Criteria 39. Paraquat and diquat; 1984. Available online: http://www.inchem.org/ documents/ehc/ehc/ehc39.htm.
- Punchard, N.A.; Kelly, F.J.; (Eds), *!!! REPLACE !!!*. Free radicals: A practical approach. IRL Press: Oxford, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Bain, B.J. Blood cells: A practical guide, 2nd ed.; Blackwell Science: Malden, MA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Dacie, J.V.; Lewis, S.M. Practical haematology, 8th ed.; Churchill Livingstone: Edinburgh, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Cheesbrough, M. Haematological tests: District laboratory practice in tropical countries. Part 2; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000; pp. 267–387. [Google Scholar]
- Evantt, B.L.; Gibbs, W.N.; Lewis, S.M.; McArthur, J.R. Fundamental diagnostic haematologyanaemia. World Health Organization & US Department of Health & Human Services, CDC 2nd edition. WHO, 1211, 27; WHO Publications: Geneva, Switzerland, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Foyer, C. Ascorbic acid. In antioxidants in higher plants; Alscher, R.G., Hess, J.L., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1993; pp. 31–58. [Google Scholar]
- Asada, K. Ascorbate peroxidase – hydrogen peroxide – scavenging enzyme in plants. Physiol Plant 1992, 85, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loewus, F.A. Ascorbic acid and its metabol- ic products. In The biochem- istry of plants; Preiss, J., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1988; pp. 85–107. [Google Scholar]
- Meister, A. Glutathione – ascorbic acid antioxidant system in animals. J Biol Chem 1994, 269, 9397–9400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, W.; Xu, D.; Yang, Y.; Rocque, P. Mammalian thioltransferase (glutaredox- in) and protein disulphide isomerase have dehydroascorbate reductase activity. J Biol Chem 1990, 265, 15361–15364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shigeoka, S.; Ishikawa, T.; Tamoi, M.; Miyagawa, Y.; Takeda, T.; Yabuta, Y.; et al. Regulation and function of ascorbate per- oxidase isoenzymes. J Exp Bot 2002, 53, 1305–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carr, A.; Frei, B. Does vitamin c act as a pro- oxidant under physiological conditions? Faseb J 1999, 13, 1007–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Animal Care and Ethics Committee. Blood collection in rodents and rabbits. Newcastle: ACEC, University of Newcastle; 1999. Available online: http://www.newcas- tle.edu. au/research/animal/revision/acec 29.pdf (accessed on June 2007).
- Diel, K.H.; Hull, R.; Morton, D.; Pfister, R.; Rabemampianina, Y.; Smith, D.; et al. A good practice guide to the administration of substances and removal of blood including routes and volumes. J Appl Toxicol 2001, 21, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sies, H. Strategies of antioxidant defense. Eur J Biochem 1993, 215, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buettner, G.R. The pecking order of free radicals and antioxidants, lipid peroxida- tion, alphatocopherol and ascorbate. Arch Biochem Biophys 1993, 300, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyer, R.E. The role of ascorbate in antioxi- dant protection of biomembranes: Interac- tion with vitamin E and coenzyme Q. J Bioenerg Biomembr 1994, 26, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wefers, H.; Sies, H. The protection by ascor- bate and glutathione against microsomal lipid peroxidation is dependent on vitamin E. Eur J Biochem 1988, 174, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, M.I.; Srivastava, U.S. Vitamin-E metabolism and its application. Nutr Res 1996, 16, 1767–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prussick, R.; Ali, M.A.; Rosenthal, D.; Guyatt, G. The protective effect of vitamin E on the hemolysis associated with dapsone treat- ment in patients with dermatitis herpeti- formis. Arch Dermatol 1992, 128, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachur, N.R.; Gordon, S.L.; Gee, M.V. A general mechanism for microsomal activation of quinine anticancer agents to free radicals. Cancer Res 1978, 38, 1745–1750. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kappus, H.; Sies, H. Toxic drug effects associ- ated with oxygen metabolism, redox cycling and lipid peroxidation. Experiential 1981, 37, 1233–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thor, H.; Smith, M.T.; Hartzell, P.; Bellomo, G.; Jewell, S.A.; Orrenius, S. The metabolism of menadione (2–metyl–1, 4–naphtoquino- ne) by isolated hepatocytes. J Biol Chem 1982, 257, 12419–12425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2013 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).