PLA Nanoplastics Accumulate but Do Not Cause Acute Toxicity to Marine Rotifers, Brine Shrimps, and Zebrafish Embryos
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Obtention and Characterisation of Test Materials
2.2. Test Organisms
2.3. Uptake and Localisation of Fluorescent PLA NPs in Zooplankton and Zebrafish Embryos
2.4. Acute Toxicity and Ingestion Tests in Zooplankton
| Mass Concentration (mg/L) | Number Concentration (Particles/L) |
|---|---|
| 100 | 1.22 × 1013 |
| 10 | 1.22 × 1012 |
| 1 | 1.22 × 1011 |
| 0.1 | 1.22 × 1010 |
| 0.01 | 1.22 × 109 |
2.5. Zebrafish Embryo Toxicity Test and Apoptosis Assay
2.6. Biochemical Biomarkers
2.6.1. Sample Preparation
2.6.2. Catalase (CAT) Activity
2.6.3. Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) Activity
2.6.4. Protein Concentration
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Secondary Characterisation of PLA NPs
3.2. Uptake and Localisation of Fluorescent PLA NPs
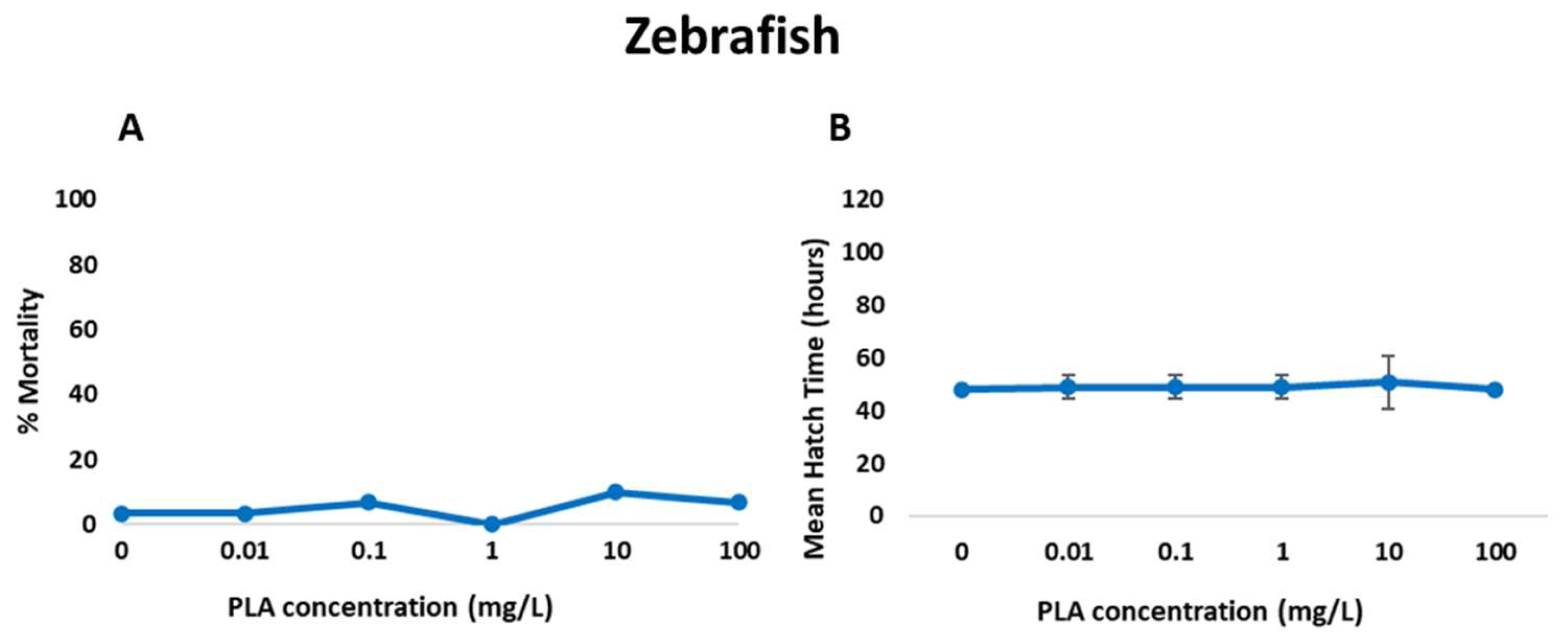
3.3. Acute Toxicity and Ingestion Impairment in Zooplankton
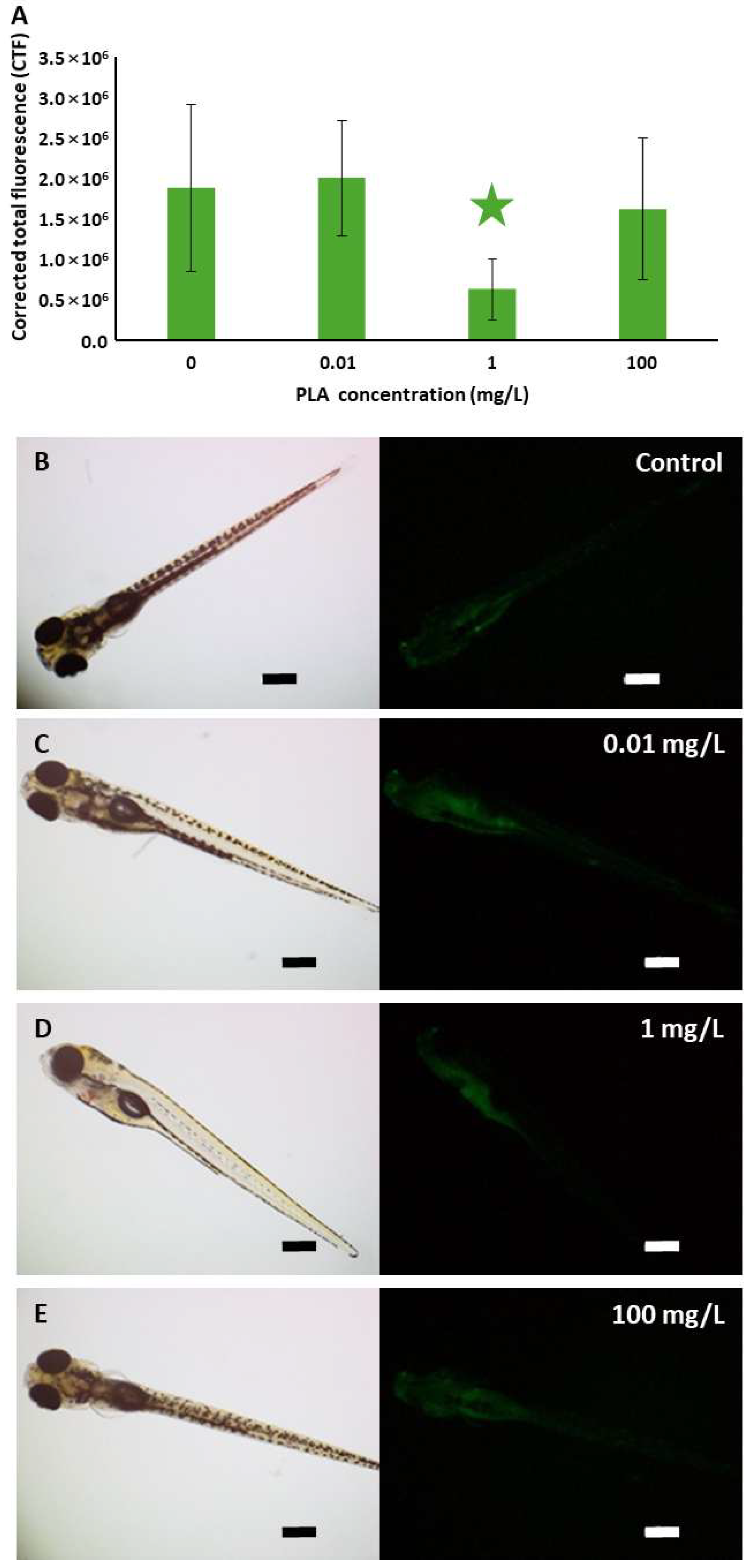
3.4. Zebrafish Embryo Toxicity and Cell Death
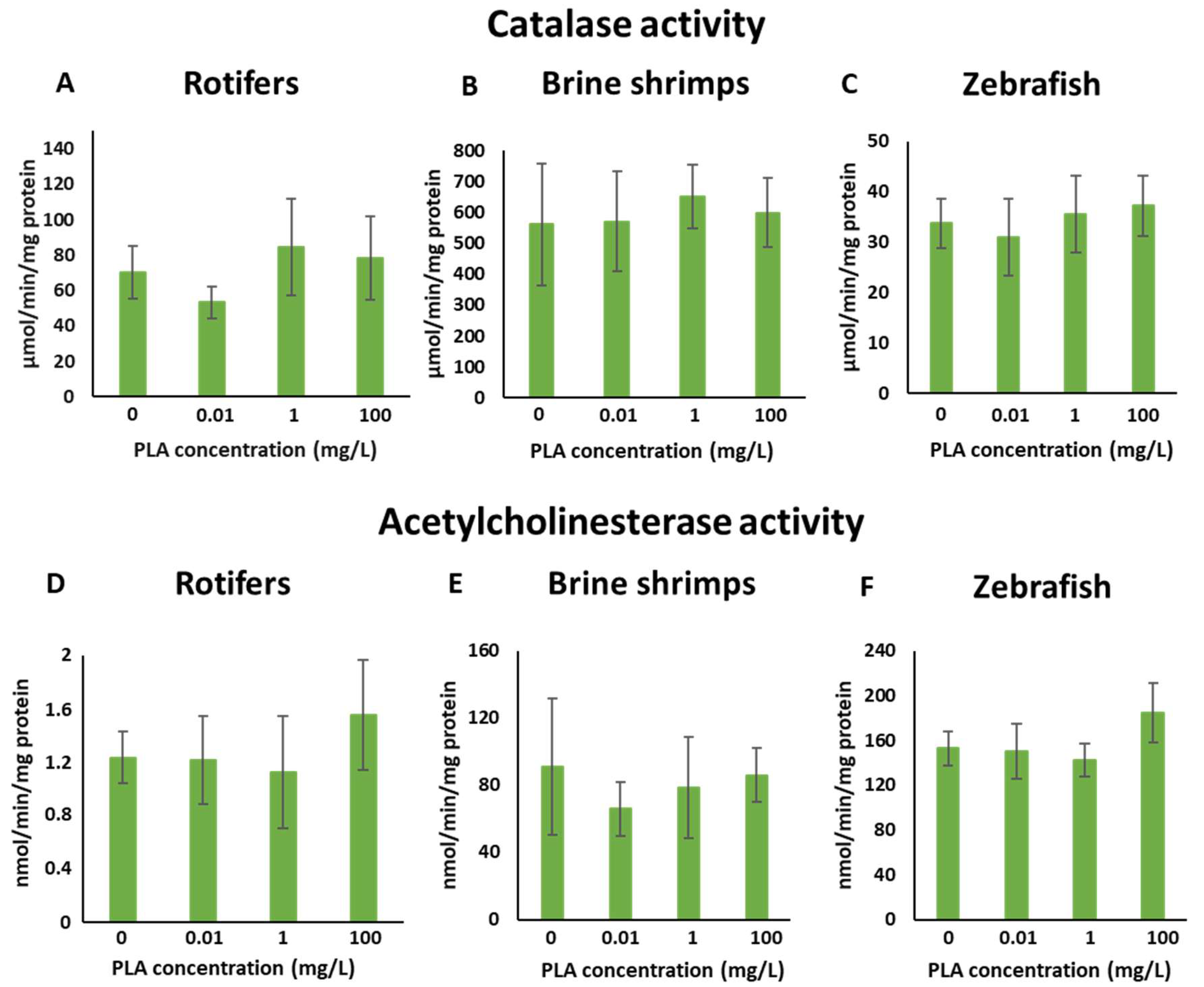
3.5. Biomarker Responses
4. Discussion
| Material | Species | References |
|---|---|---|
| Hydroxymethylfurfural | Daphnia magna | [64] |
| Polyhydroxyalkanoate microbeads | Nitokra lacustris pacifica | [65] |
| Polyhydroxyalkanoates | Streptomyces coelicolor | [9] |
| Polyhydroxybutyrate | Anabaena sp. Chlamydomonas reinhardtii Daphnia magna | [66] |
| Hydra viridissima | [67] | |
| Lates calcarifer | [68] | |
| Gammarus fossarum | [69] | |
| Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) Polyhydroxyalkanoate copolymer (PHBVV) | Artemia franciscana | [70] |
| Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) (PHBH) | Artemia salina | [71] |
| PHBV and PLA leachates | Aliivibrio fischeri Rhodomonas salina Paracentrotus lividus Mytilus galloprovincialis | [72] |
| Polybutylene succinate-polybutyrate adipate terephthalate (PBS-PBAT) leachate | Aliivibrio fischeri Oryzias latipes | [73] |
| Poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate, PBAT) | Danio rerio (embryo and juvenile) | [74] |
| PLA MPs | Daphnia magna | [75,76,77,78] |
| Diaphanosoma celebensis | [79] | |
| Artemia franciscana | [80,81] | |
| Vibrio fischeri Phaedactylum tricornutum Brachionus plicatilis Tigriopus fulvus Corophium insidiorium Gammarus aequicauda Artemia franciscana | [82] | |
| Tigriopus japonicus | [83] | |
| Paracentrotus lividus | [84,85,86] | |
| Mytilus galloprovincialis | [87] | |
| Mytilus edulis | [88,89] | |
| Perna viridis | [90] | |
| Danio rerio (larvae) | [91] | |
| Danio rerio (adults) | [92,93,94] | |
| Lates calcarifer | [95] | |
| Clarias gariepinus | [96] | |
| Perca fluviatilis | [97] | |
| Oryzias melastigma | [98] | |
| Oreochromis mossambicus | [99] | |
| Carassius auratus | [100] | |
| PLA NPs | Gammarus roeseli | [101] |
| Hydra viridissima | [102] | |
| Danio rerio (larvae) | [102,103] |
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ainali, N.M.; Kalaronis, D.; Evgenidou, E.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Bobori, D.C.; Kaloyianni, M.; Yang, X.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Lambropoulou, D.A. Do poly(lactic acid) microplastics instigate a threat? A perception for their dynamic towards environmental pollution and toxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 832, 155014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plastics Europe. Plastics—The Fast Facts 2024. 2024. Available online: https://plasticseurope.org/knowledge-hub/plastics-the-fast-facts-2024/ (accessed on 9 August 2025).
- Hartmann, N.B.; Hüffer, T.; Thompson, R.C.; Hassellöv, M.; Verschoor, A.; Daugaard, A.E.; Rist, S.; Karlsson, T.M.; Brennholt, N.; Cole, M.; et al. Are we speaking the same language? Recommendations for a definition and categorization framework for plastic debris. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zettler, E.R.; Mincer, T.J.; Amaral-Zettler, L.A. Life in the “Plastisphere”: Microbial communities on plastic marine debris. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 7137–7146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Chen, Z.; Wei, W.; Chen, J.; Ni, B.-J. Toxicity of micro/nanoplastics in the environment: Roles of plastisphere and eco-corona. Soil Environ. Health 2023, 1, 100002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Gómez, J.C.; Garrigós, M.; Garrigós, J. Plastic as a Vector of Dispersion for Marine Species With Invasive Potential A Review. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 9, 629756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochman, C.M.; Tahir, A.; Williams, S.L.; Baxa, D.V.; Lam, R.; Miller, J.T.; Teh, F.C.; Werorilangi, S.; Teh, S.J. Anthropogenic debris in seafood: Plastic debris and fibers from textiles in fish and bivalves sold for human consumption. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.; Love, D.C.; Rochman, C.M.; Neff, R.A. Microplastics in seafood and the implications for human health. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2018, 5, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Ahmad, S.; Ma, J.; Wang, D.; Tang, J. Comparative study on the toxic effects of secondary nanoplastics from biodegradable and conventional plastics on Streptomyces coelicolor M145. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 460, 132343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolte, T.M.; Hartmann, N.B.; Kleijn, J.M.; Garnæs, J.; van de Meent, D.; Jan Hendriks, A.; Baun, A. The toxicity of plastic nanoparticles to green algae as influenced by surface modification, medium hardness and cellular adsorption. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 183, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Feng, C.; Wu, Y.; Guo, X. Impacts of nanoplastics on bivalve: Fluorescence tracing of organ accumulation, oxidative stress and damage. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 392, 122418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, I.-C.; Shim, K.-Y.; Kim, K.; Jeong, C.-B. Maternal exposure to nanoplastic induces transgenerational toxicity in the offspring of rotifer Brachionus koreanus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 269, 109635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Liu, X.; Hou, Q.; Wang, Z. From natural environment to animal tissues: A review of microplastics(nanoplastics) translocation and hazards studies. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 855, 158686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Du, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Huang, Y.; Tian, J.; Jiang, Q.; Zhao, Y. Two genes related to reproductive development in the juvenile prawn, Macrobrachium nipponense: Molecular characterization and transcriptional response to nanoplastic exposure. Chemosphere 2021, 281, 130827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, J.A.; Kozal, J.S.; Jayasundara, N.; Massarsky, A.; Trevisan, R.; Geitner, N.; Wiesner, M.; Levin, E.D.; Di Giulio, R.T. Uptake, tissue distribution, and toxicity of polystyrene nanoparticles in developing zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 194, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, J.; Li, Y.; Gao, J.; Cao, R.; Shang, E.; Zhang, W. ROS-mediated photoaging pathways of nano- and micro-plastic particles under UV irradiation. Water Res. 2022, 216, 118320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Wei, X.; Hu, H.; Zhang, B.; Yang, D.; Du, H.; Zhu, R.; Sun, X.; Oh, Y.; Gu, N. Effects of oral administration of polystyrene nanoplastics on plasma glucose metabolism in mice. Chemosphere 2022, 288, 132607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.; Jiang, R.; Hu, S.; Xiao, X.; Wu, J.; Wei, S.; Xiong, Y.; Ouyang, G. Investigating the toxicities of different functionalized polystyrene nanoplastics on Daphnia magna. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 180, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, J.-H.; Seo, H.J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Lee, I.; Jeon, K.; Kim, B.; Lee, K. Polypropylene nanoplastic exposure leads to lung inflammation through p38-mediated NF-κB pathway due to mitochondrial damage. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2023, 20, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagner, M.; Boudry, G.; Courcot, L.; Vincent, D.; Dehaut, A.; Duflos, G.; Huvet, A.; Tallec, K.; Zambonino-Infante, J.L. Experimental evidence that polystyrene nanoplastics cross the intestinal barrier of European seabass. Environ. Int. 2022, 166, 107340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Tong, D.; Tian, D.; Yu, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhang, W.; Yu, Y.; Lu, L.; Zhang, X.; Pan, W.; et al. Exposure to Polystyrene Nanoplastics Led to Learning and Memory Deficits in Zebrafish by Inducing Oxidative Damage and Aggravating Brain Aging. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, 2301799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Bioplastics. What Are Bioplastics? 2024. Available online: https://www.european-bioplastics.org/bioplastics/ (accessed on 1 April 2024).
- Di Bartolo, A.; Infurna, G.; Dintcheva, N.T. A review of bioplastics and their adoption in the circular economy. Polymers 2021, 13, 1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naser, A.Z.; Deiab, I.; Darras, B.M. Poly (lactic acid)(PLA) and polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs), green alternatives to petroleum-based plastics: A review. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 17151–17196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Bioplastic. Bioplastics Market Development Update 2024. 2024. Available online: https://www.european-bioplastics.org/bioplastics-market-development-update-2024/ (accessed on 29 October 2025).
- Ali, S.S.; Abdelkarim, E.A.; Elsamahy, T.; Al-Tohamy, R.; Li, F.; Kornaros, M.; Zuorro, A.; Zhu, D.; Sun, J. Bioplastic production in terms of life cycle assessment: A state-of-the-art review. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2023, 15, 100254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuominen, J.; Kylmä, J.; Kapanen, A.; Venelampi, O.; Itävaara, M.; Seppälä, J. Biodegradation of lactic acid based polymers under controlled composting conditions and evaluation of the ecotoxicological impact. Biomacromolecules 2002, 3, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karava, V.; Siamidi, A.; Vlachou, M.; Christodoulou, E.; Zamboulis, A.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Kyritsis, A.; Klonos, P.A. Block copolymers based on poly(butylene adipate) and poly(l-lactic acid) for biomedical applications: Synthesis, structure and thermodynamical studies. Soft Matter 2021, 17, 2439–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perin, D.; Rigotti, D.; Fredi, G.; Papageorgiou, G.Z.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Dorigato, A. Innovative bio-based poly(lactic acid)/poly(alkylene furanoate)s fiber blends for sustainable textile applications. J. Polym. Environ. 2021, 29, 3948–3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredi, G.; Rigotti, D.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Dorigato, A. Tuning thermo-mechanical properties of poly(lactic acid) films through blending with bioderived poly(alkylene furanoate)s with different alkyl chain length for sustainable packaging. Polymer 2021, 218, 123527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysafi, I.; Ainali, N.M.; Bikiaris, D.N. Thermal degradation mechanism and decomposition kinetic studies of poly(lactic acid) and its copolymers with poly(hexylene succinate). Polymers 2021, 13, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzopoulou, Z.; Zamboulis, A.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Valera, M.A.; Mangas, A. Synthesis, properties, and enzymatic hydrolysis of poly (lactic acid)-co-poly (propylene adipate) block copolymers prepared by reactive extrusion. Polymers 2021, 13, 4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanusi, O.M.; Benelfellah, A.; Papadopoulos, L.; Terzopoulou, Z.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Hocine, N.A. Properties of poly(lactic acid)/montmorillonite/carbon nanotubes nanocomposites: Determination of percolation threshold. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 16887–16901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarani, E.; Črešnar, K.P.; Zemljič, L.F.; Chrissafis, K.; Papageorgiou, G.Z.; Lambropoulou, D.; Zamboulis, A.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Terzopoulou, Z. Cold crystallization kinetics and thermal degradation of PLA composites with metal oxide nanofillers. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Chen, F.; Li, Z.; Haider, M.R.; Wei, J.; Chen, G.; Wang, W.; Wang, J. Environmental risk assessment of microplastics and nanoplastics generated from biodegradable plastics in marine ecosystem. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 169, 117381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubeda, S.; Aznar, M.; Alfaro, P.; Nerín, C. Migration of oligomers from a food contact biopolymer based on polylactic acid (PLA) and polyester. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 3521–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahms, H.-U.; Hagiwara, A.; Lee, J.-S. Ecotoxicology, ecophysiology, and mechanistic studies with rotifers. Aquat. Toxicol. 2011, 101, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagiwara, A.; Suga, K.; Akazawa, A.; Kotani, T.; Sakakura, Y. Development of rotifer strains with useful traits for rearing fish larvae. Aquaculture 2007, 26, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, G.; Yoshinaga, T.; Yanagawa, Y.; Kinoshita, S.; Tsukamoto, K.; Watabe, S. Molecular characterization of Mn-superoxide dismutase and gene expression studies in dietary restricted Brachionus plicatilis rotifers. Hydrobiologia 2005, 546, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Zhu, S.; Li, J.; Hui, X.; Wang, G.-X. The developmental toxicity, bioaccumulation and distribution of oxidized single walled carbon nanotubes in Artemia salina. Toxicol. Res. 2018, 7, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulvasu, C.; Jennifer, S.M.; Prabhu, D.; Chandhirasekar, D. Toxicity effect of silver nanoparticles in brine shrimp Artemia. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 256919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ates, M.; Daniels, J.; Arslan, Z.; Farah, I.O.; Rivera, H.F. Comparative evaluation of impact of Zn and ZnO nanoparticles on brine shrimp (Artemia salina) larvae: Effects of particle size and solubility on toxicity. Environ. Sci. Process Impacts 2013, 15, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Gao, H.; Jin, S.; Li, R.; Na, G. The ecotoxicological effects of microplastics on aquatic food web, from primary producer to human: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 173, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batel, A.; Borchert, F.; Reinwald, H.; Erdinger, L.; Braunbeck, T. Microplastic accumulation patterns and transfer of benzo[a]pyrene to adult zebrafish (Danio rerio) gills and zebrafish embryos. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 918–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Álvarez, I.; Le Menach, K.; Devier, M.H.; Cajaraville, M.P.; Budzinski, H.; Orbea, A. Screening of the toxicity of polystyrene nano- and microplastics alone and in combination with benzo(a)pyrene in brine shrimp larvae and zebrafish embryos. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevisan, R.; Voy, C.; Chen, S.; Di Giulio, R.T. Nanoplastics decrease the toxicity of a complex PAH mixture but impair mitochondrial energy production in developing zebrafish. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 8405–8415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagat, J.; Zang, L.; Nishimura, N.; Shimada, Y. Zebrafish: An emerging model to study microplastic and nanoplastic toxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO-19820; Water Quality—Determination of the Acute Toxicity to the Marine Rotifer Brachionus Plicatilis. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- Snell, T.W. Rotifer Ingestion Test for Rapid Assessment of Toxicity. In Small-Scale Freshwater Toxicity Investigations: Toxicity Test Methods; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 323–335. [Google Scholar]
- Leusch, F.D.L.; Ziajahromi, S. Converting mg/L to Particles/L: Reconciling the Occurrence and Toxicity Literature on Microplastics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 11470–11472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OECD. 236: Fish Embryo Acute Toxicity (FET) Test. In OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals; Section 2; OECD: Paris, France, 2013; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Beckman, S. Using Acridine Orange to Measure Cell Death in Ethanol Treated Zebrafish Embryos. In Biotek Application Note; AN122717_23; Agilent Technologies: Santa Clara, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Johann, S.; Nüßer, L.; Goßen, M.; Hollert, H.; Seiler, T.B. Differences in biomarker and behavioral responses to native and chemically dispersed crude and refined fossil oils in zebrafish early life stages. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 136174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aebi, H. Catalase In Vitro. In Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1984; pp. 121–126. Volume 105. [Google Scholar]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.D.; Andres, V., Jr.; Featherstone, R.M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orbea, A.; González-Soto, N.; Lacave, J.M.; Barrio, I.; Cajaraville, M.P. Developmental and reproductive toxicity of PVP/PEI-coated silver nanoparticles to zebrafish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 199, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firth, D. Bias Reduction of Maximum Likelihood Estimates. Biometrika 1993, 80, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmidis, I. BRGLM: Bias Reduction in Binomial-Response Generalized Linear Models. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/brglm/brglm.pdf (accessed on 30 September 2025).
- Suman, A.; Mahapatra, A.; Gupta, P.; Ray, S.S.; Singh, R.K. Polystyrene microplastics modulated bdnf expression triggering neurotoxicity via apoptotic pathway in zebrafish embryos. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 271, 109699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Chankeshwara, S.V.; Thielbeer, F.; Jeong, J.; Donaldson, K.; Bradley, M.; Cho, W.-S. Surface charge determines the lung inflammogenicity: A study with polystyrene nanoparticles. Nanotoxicology 2016, 10, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Wang, X.; Ji, Z.; Sun, B.; Zhang, H.; Chang, C.H.; Lin, S.; Meng, H.; Liao, Y.-P.; Wang, M. Surface charge and cellular processing of covalently functionalized multiwall carbon nanotubes determine pulmonary toxicity. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 2352–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazi, M.-A.; Hamidi, M.; Mäkilä, E.M.; Zhang, H.; Almeida, P.V.; Kaasalainen, M.; Salonen, J.J.; Hirvonen, J.T.; Santos, H.A. The mechanisms of surface chemistry effects of mesoporous silicon nanoparticles on immunotoxicity and biocompatibility. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 7776–7789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, M.; Lynch, I.; Ejtehadi, M.R.; Monopoli, M.P.; Bombelli, F.B.; Laurent, S. Protein− nanoparticle interactions: Opportunities and challenges. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 5610–5637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swart, E.; de Boer, T.E.; Chen, G.; Vooijs, R.; van Gestel, C.A.; van Straalen, N.M.; Roelofs, D. Species-specific transcriptomic responses in Daphnia magna exposed to a bio-plastic production intermediate. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelia, T.S.M.; Sukri, S.N.F.; Nursabrina, A.; Jaapar, R.; Amin, M.; Bhubalan, K. Uptake and egestion of polyhydroxyalkanoate microbeads. J. Sustain. Sci. Manag. 2020, 15, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Pleiter, M.; Tamayo-Belda, M.; Pulido-Reyes, G.; Amariei, G.; Leganés, F.; Rosal, R.; Fernández-Piñas, F. Secondary nanoplastics released from a biodegradable microplastic severely impact freshwater environments. Environ. Sci. Nano 2019, 6, 1382–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.; Oliveira, M.; Almeida, M.; Lopes, I.; Venâncio, C. Short- and long-term toxicity of nano-sized polyhydroxybutyrate to the freshwater cnidarian Hydra viridissima. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 917, 170282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sai, S.; Mani, R.; Vijayakumar, P.; Ganesan, M.; Velu, K.; Ayyamperumal, R.; Rajagopal, R.; Chang, S.W.; Alfarhan, A.; Ravindran, B. Risk assessment of potential toxicity induced by bio and synthetic plastic microspheres in Lates calcarifer. Chemosphere 2022, 298, 134269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straub, S.; Hirsch, P.E.; Burkhardt-Holm, P. Biodegradable and petroleum-based microplastics do not differ in their ingestion and excretion but in their biological effects in a freshwater invertebrate Gammarus fossarum. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanadchangsaeng, N.; Pattanasupong, A. Evaluation of Biodegradabilities of Biosynthetic Polyhydroxyalkanoates in Thailand Seawater and Toxicity Assessment of Environmental Safety Levels. Polymers 2022, 14, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarretxe, J.; Alonso, L.; Aranburu, N.; Guerrica-Echevarría, G.; Orbea, A.; Iturrondobeitia, M. Sustainable PHBH–Alumina Nanowire Nanocomposites: Properties and Life Cycle Assessment. Polymers 2022, 14, 5033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laranjeiro, F.; Rotander, A.; López-Ibáñez, S.; Vilas, A.; Södergren Seilitz, F.; Clérandeau, C.; Sampalo, M.; Rial, D.; Bellas, J.; Cachot, J.; et al. Comparative assessment of the acute toxicity of commercial bio-based polymer leachates on marine plankton. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 946, 174403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dusacre, E.; Le Picard, C.; Hausard, V.; Rigolet, C.; Ekoja, F.; Jean, M.; Clérandeau, C.; Villette, S.; Lagarde, F.; Lecomte, S.; et al. Distinct toxicity profiles of conventional and biodegradable fishing nets’ leachates after artificial aging. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 489, 137609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, M.; Cai, K.; Zhang, J.; Tu, S.; Feng, J. Preparation of PBAT microplastics and their potential toxicity to zebrafish embryos and juveniles. Aquat. Toxicol. 2024, 275, 107065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, G.; Na, J.; Song, J.; Jung, J. Chronic toxicity of biodegradable microplastic (Polylactic acid) to Daphnia magna: A comparison with polyethylene terephthalate. Aquat. Toxicol. 2024, 266, 106790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savva, K.; Farré, M.; Barata, C. Sublethal effects of bio-plastic microparticles and their components on the behaviour of Daphnia magna. Environ. Res. 2023, 236, 116775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luangrath, A.; Na, J.; Kalimuthu, P.; Song, J.; Kim, C.; Jung, J. Ecotoxicity of polylactic acid microplastic fragments to Daphnia magna and the effect of ultraviolet weathering. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 271, 115974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, L.; Göttlich, S.; Oehlmann, J.; Wagner, M.; Völker, C. What are the drivers of microplastic toxicity? Comparing the toxicity of plastic chemicals and particles to Daphnia magna. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, W.; Jeong, H.; Tisn, M.L.; Favrelle-Huret, A.; Thielemans, W.; Zinck, P.; Souissi, S.; Lee, J.-S. The comparative toxicity of biobased, modified biobased, biodegradable, and petrochemical-based microplastics on the brackish water flea Diaphanosoma celebensis. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 944, 173747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoeythornkhajhornchai, P.; Kunjiek, T.; Chaipayang, S.; Phosri, S. Toxicity assessment of bioplastics on brine shrimp (Artemia franciscana) and cell lines. Emerg. Contam. 2023, 9, 100253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giannantonio, M.; Gambardella, C.; Miroglio, R.; Costa, E.; Sbrana, F.; Smerieri, M.; Carraro, G.; Utzeri, R.; Faimali, M.; Garaventa, F. Ecotoxicity of Polyvinylidene Difluoride (PVDF) and Polylactic Acid (PLA) microplastics in marine zooplankton. Toxics 2022, 10, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfra, L.; Albarano, L.; Rotini, A.; Biandolino, F.; Prato, E.; Carraturo, F.; Chiaretti, G.; Faraponova, O.; Salamone, M.; Sebbio, C.; et al. Can biodegradable plastics mitigate plastamination? Feedbacks from marine organisms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 487, 137179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, H.; Zhong, X.; Duan, Z.; Yi, X.; Cheng, F.; Xu, W.; Yang, X. Micro- and nanoplastics released from biodegradable and conventional plastics during degradation: Formation, aging factors, and toxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 833, 155275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quade, J.; López-Ibáñez, S.; Beiras, R. Mesocosm trials reveal the potential toxic risk of degrading bioplastics to marine life. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 179, 113673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe-Echeverría, T.; Beiras, R. Acute toxicity of bioplastic leachates to Paracentrotus lividus sea urchin larvae. Mar. Environ. Res. 2022, 176, 105605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viel, T.; Cocca, M.; Manfra, L.; Caramiello, D.; Libralato, G.; Zupo, V.; Costantini, M. Effects of biodegradable-based microplastics in Paracentrotus lividus Lmk embryos: Morphological and gene expression analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 334, 122129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capolupo, M.; Rafiq, A.; Coralli, I.; Alessandro, T.; Valbonesi, P.; Fabbri, D.; Fabbri, E. Bioplastic leachates characterization and impacts on early larval stages and adult mussel cellular, biochemical and physiological responses. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 319, 120951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, D.S.; Colgan, T.J.; Thompson, R.C.; Carolan, J.C. Exposure to microplastics reduces attachment strength and alters the haemolymph proteome of blue mussels (Mytilus edulis). Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, A.; Zalouk-Vergnoux, A.; Benali, S.; Mincheva, R.; Raquez, J.-M.; Bertrand, S.; Poirier, L. Are bio-based and biodegradable microplastics impacting for blue mussel (Mytilus edulis)? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 167, 112295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, P.W.S.; Falkenberg, L.J. Microplastics, both non-biodegradable and biodegradable, do not affect the whole organism functioning of a marine mussel. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 839, 156204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, J.P.J.; Estrela, F.N.; Rodrigues, A.S.d.L.; Guimarães, A.T.B.; Rocha, T.L.; Malafaia, G. Behavioral and biochemical consequences of Danio rerio larvae exposure to polylactic acid bioplastic. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 404, 124152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagas, T.Q.; Freitas, Í.N.; Montalvão, M.F.; Nobrega, R.H.; Machado, M.R.F.; Charlie-Silva, I.; Araújo APd, C.; Guimarães, A.T.B.; Alvarez TGd, S.; Malafaia, G. Multiple endpoints of polylactic acid biomicroplastic toxicity in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio). Chemosphere 2021, 277, 130279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Z.; Cheng, H.; Duan, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Gong, Z.; Zhang, H.; Sun, H.; Wang, L. Diet preference of zebrafish (Danio rerio) for bio-based polylactic acid microplastics and induced intestinal damage and microbiota dysbiosis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 429, 128332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, Y.; Li, X.; Zhuang, Z.; Li, J.; Luo, Q.; Chen, X. Enhanced reproductive toxicity of photodegraded polylactic acid microplastics in zebrafish. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 168742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Xu, P.; Zhou, W.; Xu, X.; Li, H.; He, W.; Yue, W.; Zhang, L.; Ding, D.; Suo, A. Impacts of conventional and biodegradable microplastics on juvenile Lates calcarifer: Bioaccumulation, antioxidant response, microbiome, and proteome alteration. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 179, 113744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, F.H.; Wong, C.; Choo, J.; Aun Sia, E.S.; Mujahid, A.; Müller, M. Increased transfer of trace metals and Vibrio sp. from biodegradable microplastics to catfish Clarias gariepinus. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 298, 118850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König Kardgar, A.; Ghosh, D.; Sturve, J.; Agarwal, S.; Carney Almroth, B. Chronic poly(l-lactide) (PLA)- microplastic ingestion affects social behavior of juvenile European perch (Perca fluviatilis). Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 881, 163425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Yin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Diao, X. Chronic exposure to low concentrations of microplastics causing gut tissue damage but non-significant changes in the microbiota of marine medaka larvae (Oryzias melastigma). Mar. Environ. Res. 2024, 195, 106381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, R.; Cheng, Z.; Peng, L.; Mehmood, T.; Gao, L.; Zhuo, S.; Wang, L.; Su, Y. Effects of biodegradable and conventional microplastics on the intestine, intestinal community composition, and metabolic levels in tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus). Aquat. Toxicol. 2023, 265, 106745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosrovyan, A.; Melkonyan, H.; Rshtuni, L.; Gabrielyan, B.; Kahru, A. Polylactic Acid-Based Microplastic Particles Induced Oxidative Damage in Brain and Gills of Goldfish Carassius auratus. Water 2023, 15, 2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Götz, A.; Beggel, S.; Geist, J. Dietary exposure to four sizes of spherical polystyrene, polylactide and silica nanoparticles does not affect mortality, behaviour, feeding and energy assimilation of Gammarus roeseli. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 238, 113581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamayo-Belda, M.; Venâncio, C.; Fernandez-Piñas, F.; Rosal, R.; Lopes, I.; Oliveira, M. Effects of petroleum-based and biopolymer-based nanoplastics on aquatic organisms: A case study with mechanically degraded pristine polymers. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 883, 163447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, J.; Zhang, S.; Xu, Y.; Wen, L.; Feng, X. Effects of microplastic exposure on the early developmental period and circadian rhythm of zebrafish (Danio rerio): A comparative study of polylactic acid and polyglycolic acid. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 258, 114994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergami, E.; Bocci, E.; Vannuccini, M.L.; Monopoli, M.; Salvati, A.; Dawson, K.A.; Corsi, I. Nano-sized polystyrene affects feeding, behavior and physiology of brine shrimp Artemia franciscana larvae. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 123, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snell, T.W.; Hicks, D.G. Assessing toxicity of nanoparticles using Brachionus manjavacas (Rotifera). Environ. Toxicol. 2011, 26, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Guo, H.; Wang, R.; Li, T.; Gu, L.; Sun, L. Accumulation and Distribution of Fluorescent Microplastics in the Early Life Stages of Zebrafish. Journal of visualized experiments. JoVE 2021, 173, e62117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, S.Y.; Bruce, T.F.; Bridges, W.C.; Klaine, S.J. Responses of Hyalella azteca to acute and chronic microplastic exposures. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 34, 2564–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuan, L.; Lin, L.; Shaoguo, R.; Junho, E.; Dong, W.; Samreen; Jun, W. Nanoplastics induce more severe multigenerational life-history trait changes and metabolic responses in marine rotifer Brachionus plicatilis: Comparison with microplastics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 449, 131070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, M.; Lindeque, P.; Fileman, E.; Halsband, C.; Goodhead, R.; Moger, J.; Galloway, T.S. Microplastic ingestion by zooplankton. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 6646–6655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schweizer, M.; Dieterich, A.; Corral Morillas, N.; Dewald, C.; Miksch, L.; Nelson, S.; Wick, A.; Triebskorn, R.; Köhler, H.-R. The importance of sediments in ecological quality assessment of stream headwaters: Embryotoxicity along the Nidda River and its tributaries in Central Hesse, Germany. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2018, 30, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xia, M.; Su, X.; Yuan, P.; Li, X.; Zhou, C.; Wan, Z.; Zou, W. Photolytic degradation elevated the toxicity of polylactic acid microplastics to developing zebrafish by triggering mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 413, 125321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travis, C.C. Use of Biomarkers in Assessing Health and Environmental Impacts of Chemical Pollutants; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 250. [Google Scholar]
- Forget, J.; Beliaeff, B.; Bocquene, G. Acetylcholinesterase activity in copepods (Tigriopus brevicornis) from the Vilaine River estuary, France, as a biomarker of neurotoxic contaminants. Aquat. Toxicol. 2003, 62, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaitonde, D.; Sarkar, A.; Kaisary, S.; Silva, C.D.; Dias, C.; Rao, D.P.; Ray, D.; Nagarajan, R.; De Sousa, S.N.; Sarker, S.; et al. Acetylcholinesterase activities in marine snail (Cronia contracta) as a biomarker of neurotoxic contaminants along the Goa coast, West coast of India. Ecotoxicology 2006, 15, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matozzo, V.; Tomei, A.; Marin, M.G. Acetylcholinesterase as a biomarker of exposure to neurotoxic compounds in the clam Tapes philippinarum from the Lagoon of Venice. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 50, 1686–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prüst, M.; Meijer, J.; Westerink, R.H. The plastic brain: Neurotoxicity of micro-and nanoplastics. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2020, 17, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, H.; Xia, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, T.; Xu, L.; Guo, Z.; Xu, H.; Xie, H.Q.; Zhao, B. Acetylcholinesterase is a potential biomarker for a broad spectrum of organic environmental pollutants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 8065–8074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tufi, S.; Leonards, P.; Lamoree, M.; de Boer, J.; Legler, J.; Legradi, J. Changes in neurotransmitter profiles during early zebrafish (Danio rerio) development and after pesticide exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 3222–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Tan, H.Y.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Z.J.; Lao, L.; Wong, C.W.; Feng, Y. The Role of oxidative stress and antioxidants in liver diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 26087–26124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cajaraville, M.P.; Hauser, L.; Carvalho, G.; Hylland, K.; Olabarrieta, I.; Lawrence, A.J.; Lowe, D.; Goksøyr, A. Genetic Damage and the Molecular/Cellular Response to Pollution. In Effects of Pollution in Fish; Lawrence, A.J., Hemingway, K.L., Eds.; Blackwell Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2003; pp. 14–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massarsky, A.; Trudeau, V.L.; Moon, T.W. Predicting the environmental impact of nanosilver. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 38, 861–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.; Im, J.; Choi, J. Integrating aggregate exposure pathway and adverse outcome pathway for micro/nanoplastics: A review on exposure, toxicokinetics, and toxicity studies. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 272, 116022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, P.; Xiang, C.; Li, X.; Chen, H.; Shi, X.; Li, X.; Huang, C.; Yu, Y.; Qi, J.; Li, A.J.; et al. Photoaged microplastics induce neurotoxicity via oxidative stress and abnormal neurotransmission in zebrafish larvae (Danio rerio). Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 881, 163480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
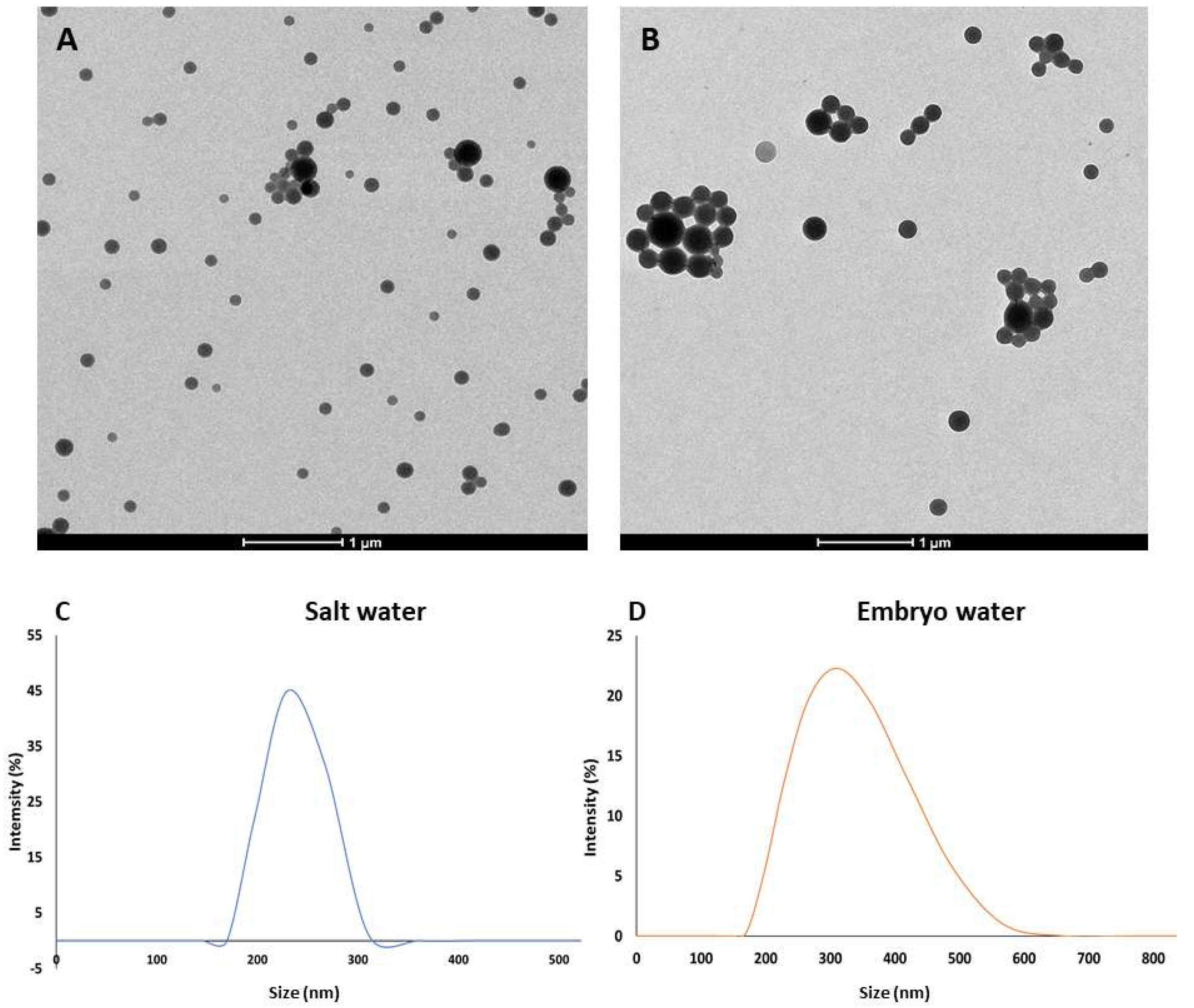
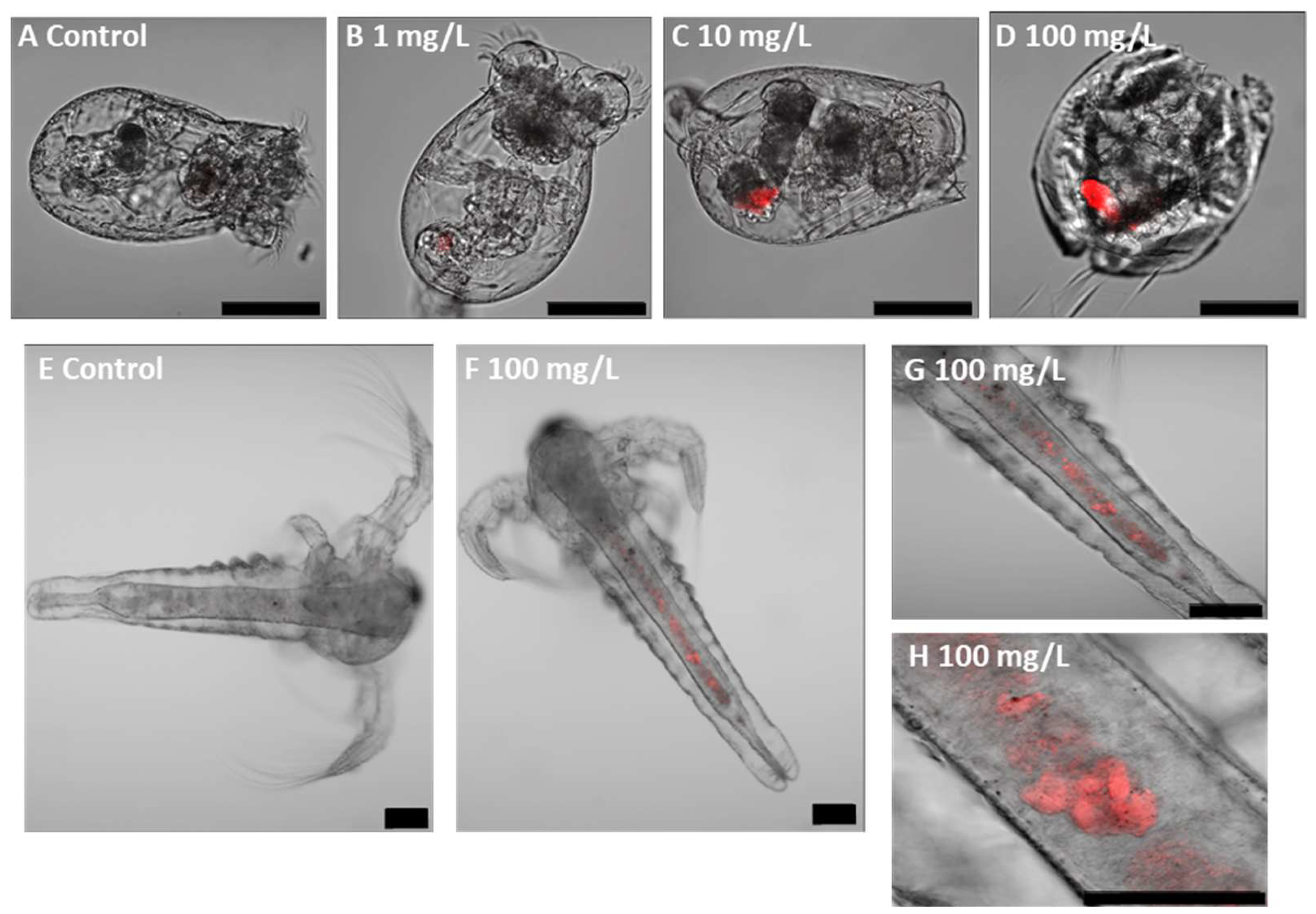



| PLA NP Concentration (mg/L) | Total Malformation Prevalence | Specific Malformations | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spinal Deformity | Yolk Sac Oedema | Pericardial Oedema | Curved Tail | ||
| 0 | 6.67 | N/O | 3.34 | 3.34 | 3.33 |
| 0.01 | 3.33 | N/O | N/O | N/O | 3.33 |
| 0.1 | 10 | 3.33 | 6.67 | 6.67 | N/O |
| 1 | 6.67 | 3.33 | 3.34 | 3.34 | N/O |
| 10 | 6.67 | 3.33 | N/O | N/O | 3.34 |
| 100 | 16.67 | 3.34 | N/O | N/O | 13.33 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mustapha, D.S.; Rodríguez-Díaz, O.; Cajaraville, M.P.; Orbea, A. PLA Nanoplastics Accumulate but Do Not Cause Acute Toxicity to Marine Rotifers, Brine Shrimps, and Zebrafish Embryos. J. Xenobiot. 2025, 15, 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox15060196
Mustapha DS, Rodríguez-Díaz O, Cajaraville MP, Orbea A. PLA Nanoplastics Accumulate but Do Not Cause Acute Toxicity to Marine Rotifers, Brine Shrimps, and Zebrafish Embryos. Journal of Xenobiotics. 2025; 15(6):196. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox15060196
Chicago/Turabian StyleMustapha, Doyinsola Suliat, Olga Rodríguez-Díaz, Miren P. Cajaraville, and Amaia Orbea. 2025. "PLA Nanoplastics Accumulate but Do Not Cause Acute Toxicity to Marine Rotifers, Brine Shrimps, and Zebrafish Embryos" Journal of Xenobiotics 15, no. 6: 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox15060196
APA StyleMustapha, D. S., Rodríguez-Díaz, O., Cajaraville, M. P., & Orbea, A. (2025). PLA Nanoplastics Accumulate but Do Not Cause Acute Toxicity to Marine Rotifers, Brine Shrimps, and Zebrafish Embryos. Journal of Xenobiotics, 15(6), 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox15060196







