From Farmworkers to Urban Residents: Mapping Multi-Class Pesticide Exposure Gradients in Morocco via Urinary Biomonitoring
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
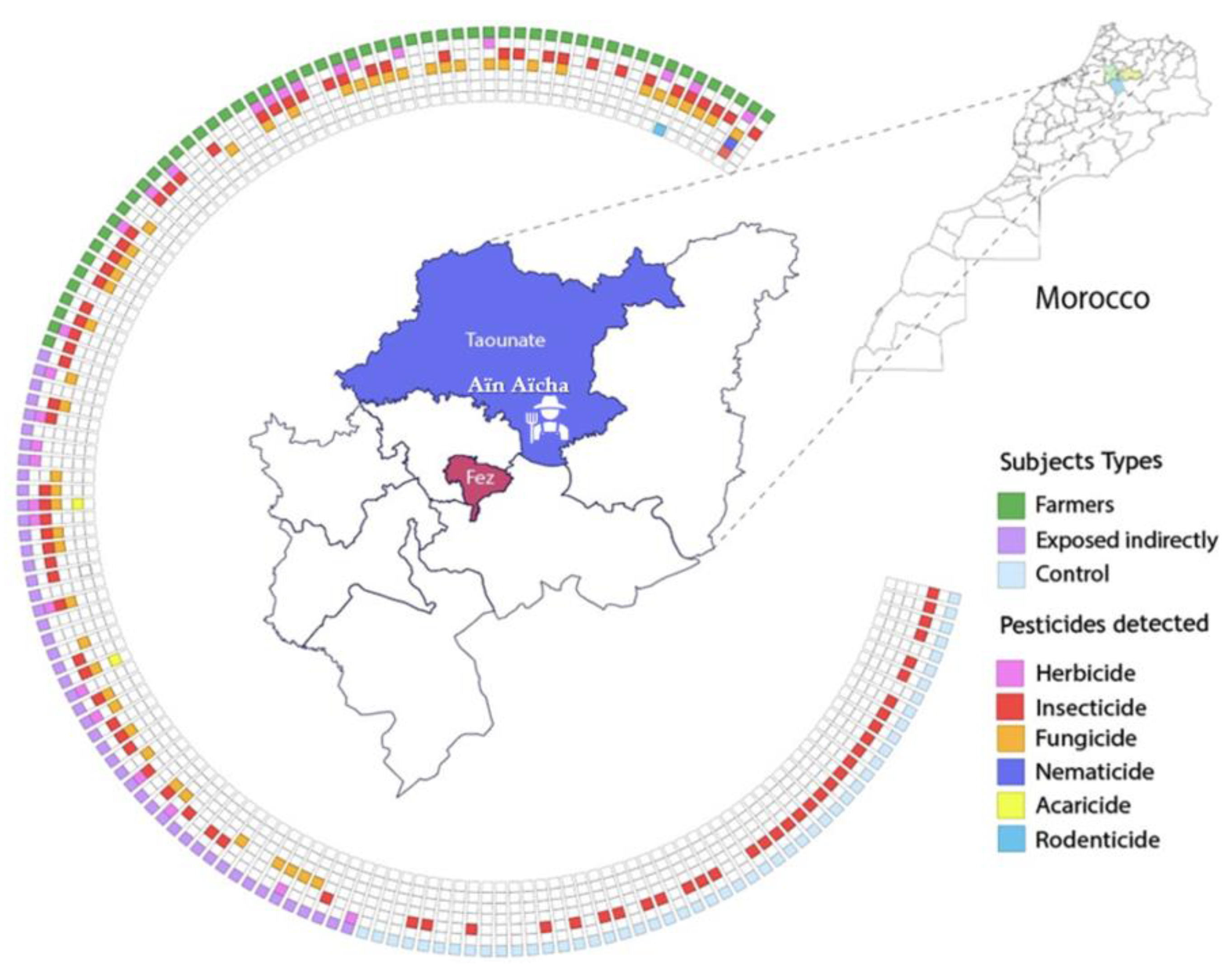
2.2. Study Area and Sampling Design
2.3. Pesticides Preparation and Extraction
2.3.1. General Pesticide Screening
2.3.2. Pyrethroid Metabolites Biomonitoring
2.3.3. Organophosphate Metabolite Biomonitoring
2.4. Instrumental Analysis
2.4.1. General Pesticide Screening
2.4.2. Pyrethroid Metabolites
2.4.3. Organophosphate Metabolite
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Survey Data
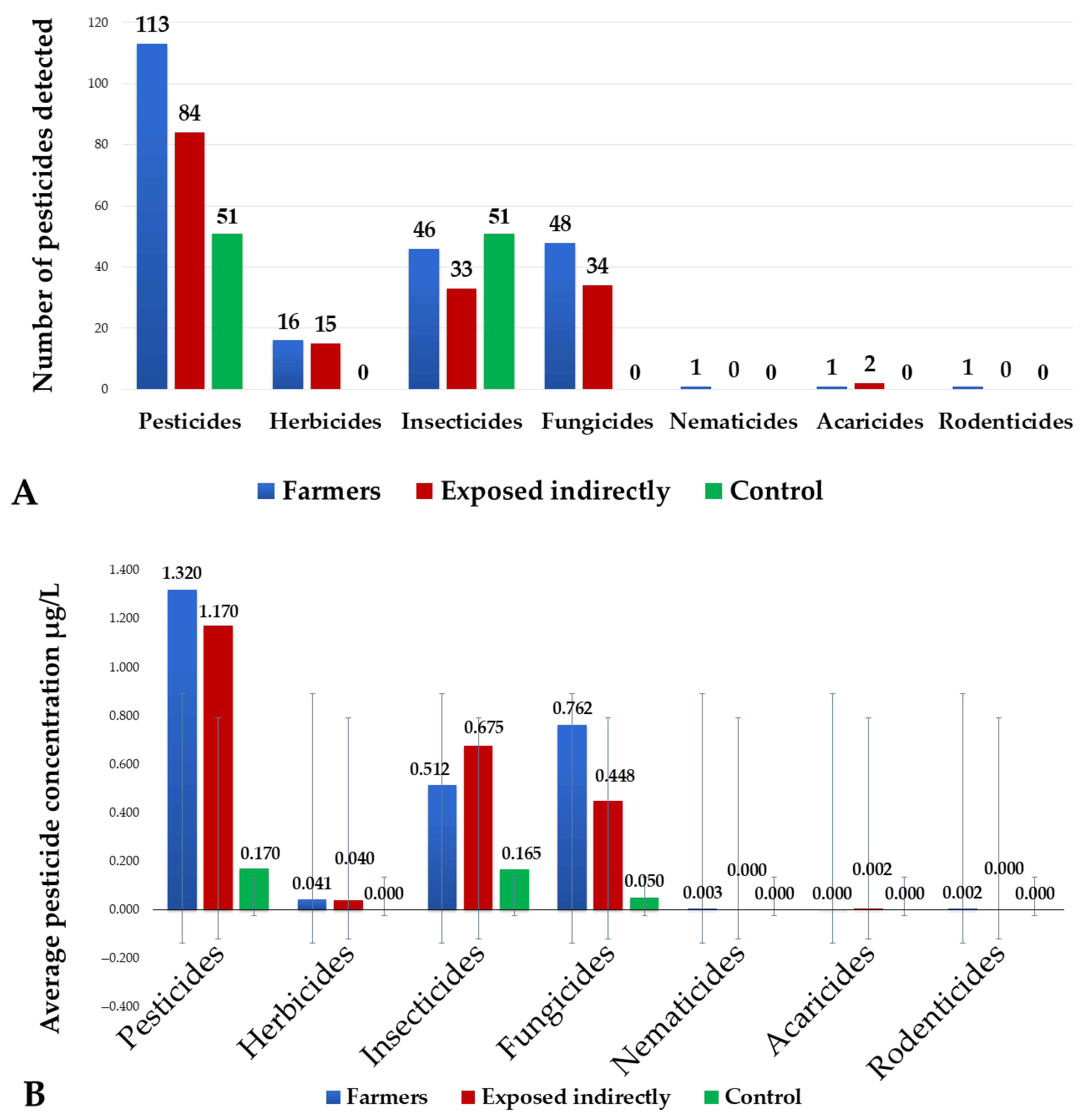
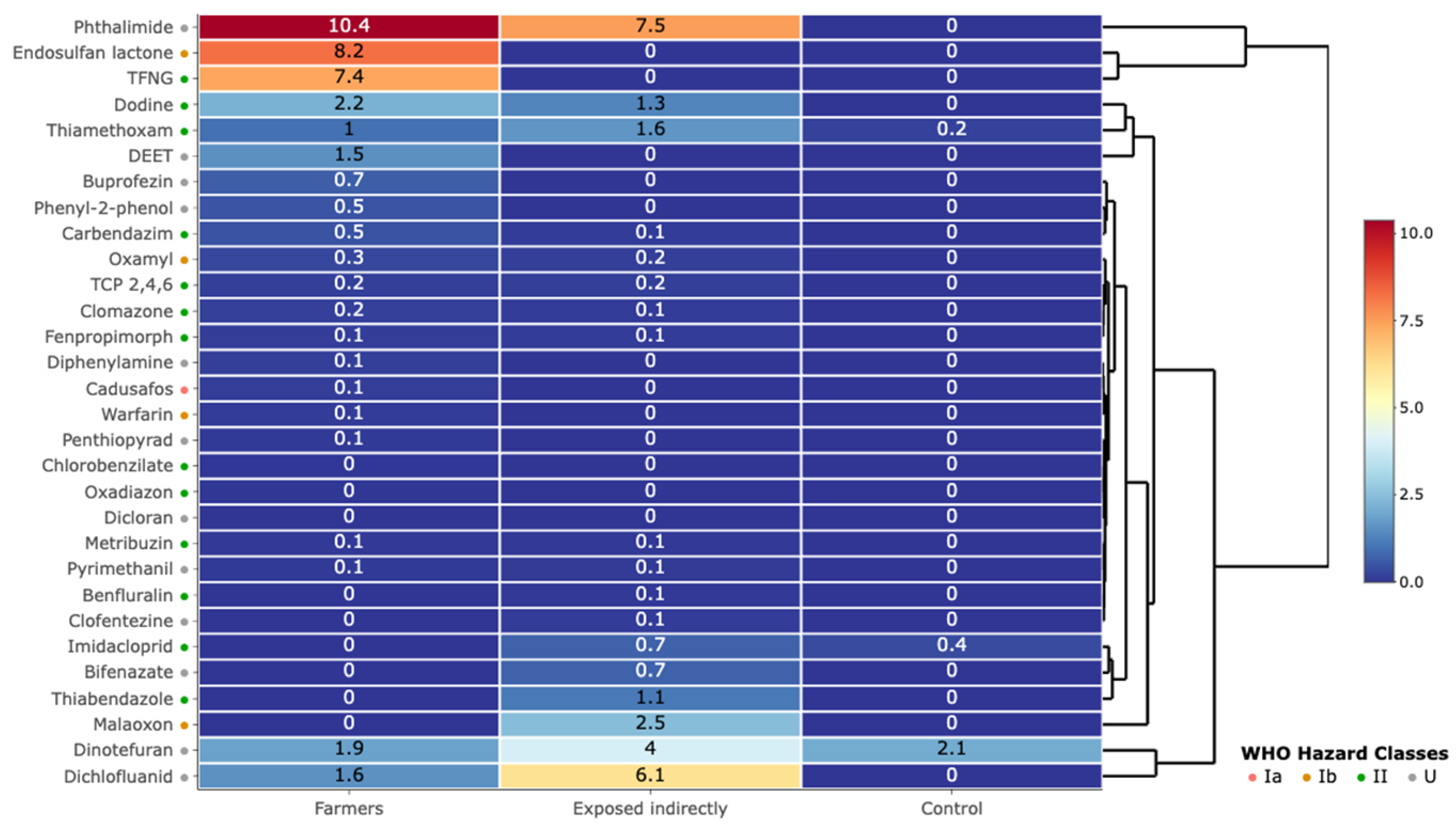
3.2. Pesticide Contamination in Urine Samples
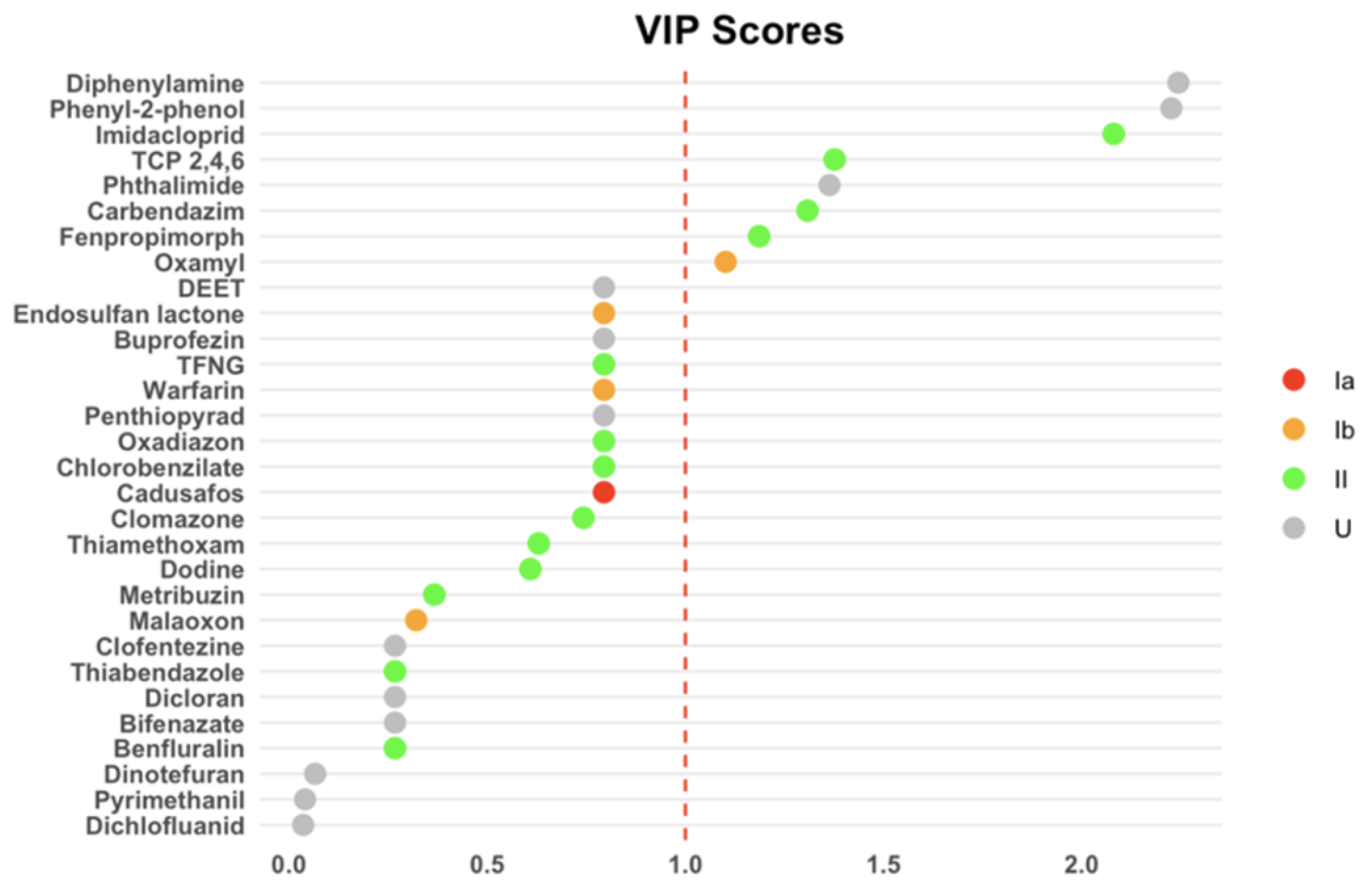
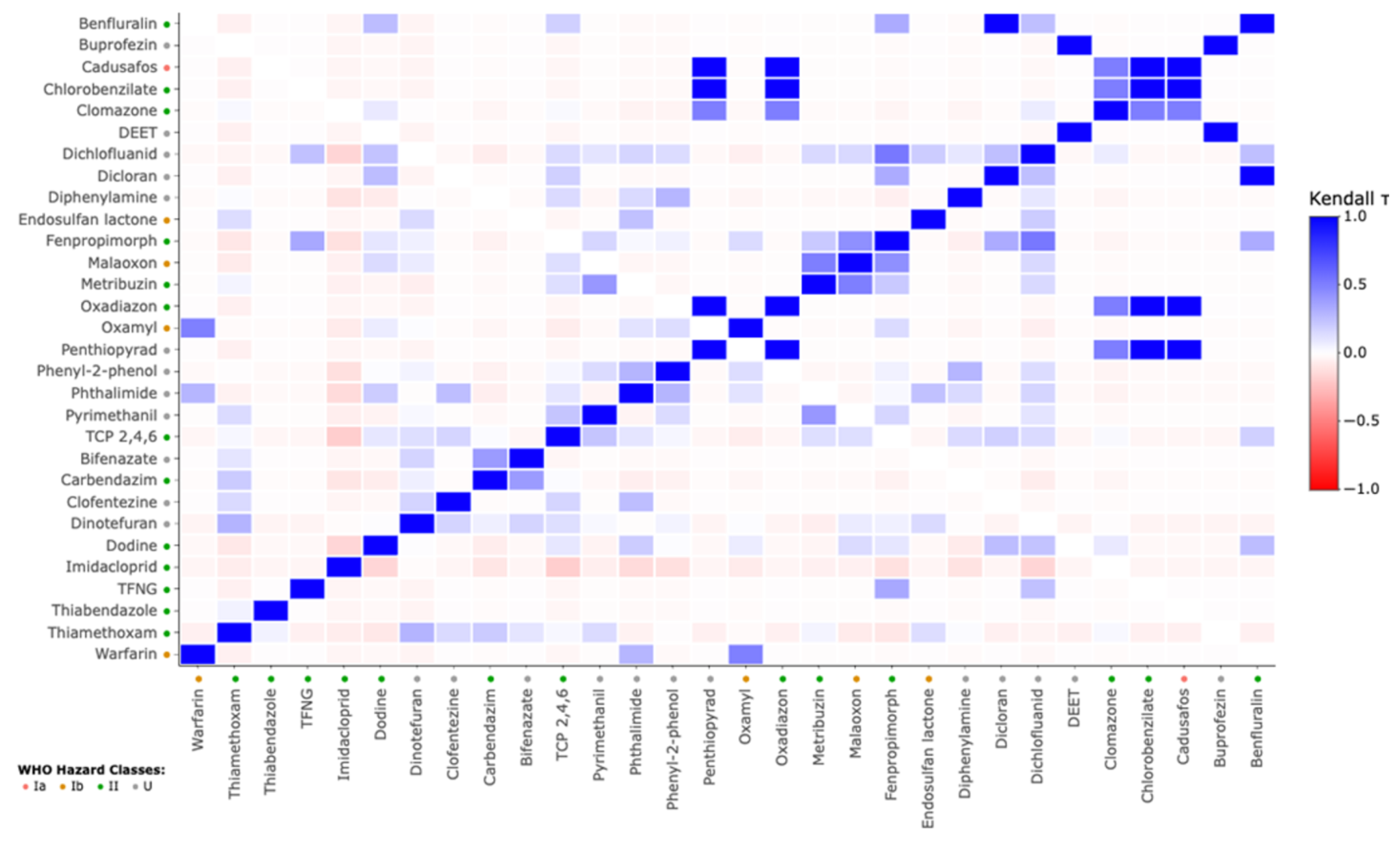
3.3. Correlation of Urinary Pesticide Concentrations with Sociodemographic Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LC-MS/MS | Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry |
| IS | Internal standard |
| MRM | Multiple reaction monitoring |
| LOD | Limit of detection |
| PLS-DA | Partial least squares-discriminant analysis |
| PPE | Personal protective equipment |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| EDCs | Endocrine disruptors |
References
- Filipoiu, D.C.; Bungau, S.G.; Endres, L.; Negru, P.A.; Bungau, A.F.; Pasca, B.; Radu, A.F.; Tarce, A.G.; Bogdan, M.A.; Behl, T.; et al. Characterization of the Toxicological Impact of Heavy Metals on Human Health in Conjunction with Modern Analytical Methods. Toxics 2022, 10, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolopoulou-Stamati, P.; Maipas, S.; Kotampasi, C.; Stamatis, P.; Hens, L. Chemical Pesticides and Human Health: The Urgent Need for a New Concept in Agriculture. Front. Public Health 2016, 4, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Li, M.; Achal, V. A Comprehensive Review on Environmental and Human Health Impacts of Chemical Pesticide Usage. Emerg. Contam. 2025, 11, 100410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekhar, C.; Khosya, R.; Thakur, K.; Mahajan, D.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, S.; Sharma, A.K.A. Systematic Review of Pesticide Exposure, Associated Risks, and Long-Term Human Health Impacts. Toxicol. Rep. 2024, 13, 101840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, M.F.; Ahmad, F.A.; Alsayegh, A.A.; Zeyaullah, M.; AlShahrani, A.M.; Muzammil, K.; Saati, A.A.; Wahab, S.; Elbendary, E.Y.; Kambal, N.; et al. Pesticides Impacts on Human Health and the Environment with Their Mechanisms of Action and Possible Countermeasures. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Khadda, Z.; Fagroud, M.; El Karmoudi, Y.; Ezrari, S.; Berni, I.; De Broe, M.; Behl, T.; Bungau, S.G.; Sqalli Houssaini, T. Farmers’ Knowledge, Attitudes, and Perceptions Regarding Carcinogenic Pesticides in Fez Meknes Region (Morocco). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahouq, M.; Bahouq, H.; Soulaymani, A. Bibliographic Review of Phytopharmacovigilance Actions and Measures on Plant Protection Products in Morocco. E3S Web Conf. 2021, 319, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quindroit, P.; Crépet, A.; Brochot, C. Estimating human exposure to pyrethroids’ mixtures from biomonitoring data using physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling. Environ. Res. 2021, 192, 110281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin-Chan, M.; Navarro-Yepes, J.; Quintanilla-Vega, B. Environmental Pollutants as Risk Factors for Neurodegenerative Disorders: Alzheimer and Parkinson Diseases. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ben Khadda, Z.; Fagroud, M.; El Karmoudi, Y.; Ezrari, S.; Elhanafi, L.; Radu, A.F.; Bungau, S.G.; Houssaini, T.S. Association between Pesticide Exposure and End-Stage Renal Disease: A Case-Control Study from Morocco Based on the STROBE Guidelines. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 288, 117360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marx-Stoelting, P.; Niemann, L.; Ritz, V.; Ulbrich, B.; Gall, A.; Hirsch-Ernst, K.I.; Pfeil, R.; Solecki, R. Assessment of Three Approaches for Regulatory Decision Making on Pesticides with Endocrine Disrupting Properties. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 70, 590–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewence, A.; Brescia, S.; Johnson, I.; Rumsby, P.C. An Approach to the Identification and Regulation of Endocrine Disrupting Pesticides. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 78, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ben Khadda, Z.; Bungau, S.G.; El Balkhi, S.; Ezrari, S.; Radu, A.-F.; Houssaini, T.S.; Achour, S. Urinary Biomonitoring of Exposure to Glyphosate and Its Metabolite Amino-Methyl Phosphonic Acid among Farmers and Non-Farmers in Morocco. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2025, 113, 104620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palma-Gudiel, H.; Fañanás, L. Prenatal Exposures and Behavioral Epigenetics in Human Infants and Children. In Developmental Human Behavioral Epigenetics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, L.; Kang, Q.; Tian, Y. Pesticide Residues: Bridging the Gap between Environmental Exposure and Chronic Disease through Omics. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 287, 117335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopf, N.B.; Rousselle, C.; Poddalgoda, D.; Lamkarkach, F.; Bessems, J.; Schmid, K.; Jones, K.; Takaki, K.; Casteleyn, L.; Jeddi, M.Z.A. Harmonized Occupational Biomonitoring Approach. Environ. Int. 2024, 191, 108990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manno, M. Biological Monitoring for Environmental Health Risk Assessment. In Environmental Geochemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 101–119. [Google Scholar]
- Santonen, T.; Aitio, A.; Fowler, B.A.; Nordberg, M. Biological Monitoring and Biomarkers. In Handbook on the Toxicology of Metals; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 155–171. [Google Scholar]
- Guimarães, M.T.; Cunha, M.G.; Carvalho, D.P.; Ribeiro, T.S.; Martins, L.C.; Braga, A.L.F.; Pereira, L.A.A. Influence of Environmental Contamination on Pregnancy Outcomes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 14950–14959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Ciaula, A.; Gentilini, P.; Diella, G.; Lopuzzo, M.; Ridolfi, R. Biomonitoring of Metals in Children Living in an Urban Area and Close to Waste Incinerators. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balderrama-Carmona, A.P.; Valenzuela-Rincón, M.; Zamora-Álvarez, L.A.; Adan-Bante, N.P.; Leyva-Soto, L.A.; Silva-Beltrán, N.P.; Morán-Palacio, E.F. Herbicide Biomonitoring in Agricultural Workers in Valle Del Mayo, Sonora Mexico. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 28480–28489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogidi, O.I.; Onwuagba, C.G.; Richard-Nwachukwu, N. Biomonitoring Tools, Techniques and Approaches for Environmental Assessments. In Biomonitoring of Pollutants in the Global South; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 243–273. [Google Scholar]
- Zarrouk, E.; El Balkhi, S.; Saint-Marcoux, F. Critical Evaluation of High-Resolution and Low-Resolution Mass Spectrometry for Biomonitoring of Human Enviromental Exposure to Pesticides. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2024, 2, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijssen, R.; Lommen, A.; van den Top, H.; van Dam, R.; Meuleman-Bot, C.; Tienstra, M.; Zomer, P.; Sunarto, S.; van Tricht, F.; Blokland, M. Assessment of Exposure to Pesticides: Residues in 24 h Duplicate Diets versus Their Metabolites in 24 h Urine Using Suspect Screening and Target Analysis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2024, 416, 635–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippi, I.; Fernández, P.; Grimalt, J.O.; Butinof, M.; Amé, M.V.; Muñoz, S.E. Glyphosate and AMPA in Saliva and Other Traditional Human Matrices. New Findings for Less Invasive Biomonitoring to the Exposure to Pesticides. Environ. Adv. 2024, 15, 100474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, C.; Jeung, E.-B. Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals and Disease Endpoints. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenichel, P.; Brucker-Davis, F.; Chevalier, N. Perturbateurs Endocriniens–Reproduction et Cancers Hormono-Dépendants. Presse Med. 2016, 45, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaglova, N.V.; Yaglov, V. V Endocrine Disruptors Are a Novel Direction of Endocrinologic Scientific Investigation. Ann. Russ. Acad. Med. Sci. 2012, 67, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Calaf, G.M.; Ponce-Cusi, R.; Aguayo, F.; Muñoz, J.P.; Bleak, T.C. Endocrine Disruptors from the Environment Affecting Breast Cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asteria, C.; Morpurgo, P.S.; Cerutti, N.; Hall, J.M. Endocrine Disruptors in Obesity. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1526898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arab, A.; Mostafalou, S. Neurotoxicity of Pesticides in the Context of CNS Chronic Diseases. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2022, 32, 2718–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, A.C.F.; Kamikawachi, R.C.; de Figueiredo Eufrasio Pauly, G.; Campos, B.G.; Castro, Í.B.; de Souza Abessa, D.M. Adverse Effects of Dichlofluanid on Neotropical Marine Organisms. Discov. Ocean. 2025, 2, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jestin-Guyon, N.; Raherison-Semjen, C. Pesticide Exposure and Chronic Respiratory Diseases. Rev. Mal. Respir. 2024, 41, 343–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, T.; Ikenaka, Y.; Nomiyama, K.; Honda, M.; Suzuki, N.; Hoshi, N.; Tabuchi, Y. An Adverse Outcome Pathway-Based Approach to Assess the Neurotoxicity by Combined Exposure to Current-Use Pesticides. Toxicology 2023, 500, 153687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jornod, F.; Rugard, M.; Tamisier, L.; Coumoul, X.; Andersen, H.R.; Barouki, R.; Audouze, K. AOP4EUpest: Mapping of Pesticides in Adverse Outcome Pathways Using a Text Mining Tool. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 4379–4381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Lucas, G.; Vela, N.; El Aatik, A.; Navarro, S. Environmental Risk of Groundwater Pollution by Pesticide Leaching through the Soil Profile. In Pesticides-Use and Misuse and Their Impact in the Environment; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; ISBN 1838800476. [Google Scholar]
- Bucheli, T.D.; Barmettler, E.; Bartolomé, N.; Hilber, I.; Hornak, K.; Meuli, R.G.; Reininger, V.; Riedo, J.; Rösch, A.; Sutter, P. Pesticides in Agricultural Soils: Major Findings from Various Monitoring Campaigns in Switzerland. Chimia 2023, 77, 750–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tampieri, F.; Durighello, A.; Biondo, O.; Gąsior, M.; Knyś, A.; Marotta, E.; Paradisi, C. Kinetics and Products of Air Plasma Induced Oxidation in Water of Imidacloprid and Thiamethoxam Treated Individually and in Mixture. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2019, 39, 545–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurwadkar, S.; Evans, A.; DeWinne, D.; White, P.; Mitchell, F. Modeling Photodegradation Kinetics of Three Systemic Neonicotinoids—Dinotefuran, Imidacloprid, and Thiamethoxam—In Aqueous and Soil Environment. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 1718–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheets, L.P.; Li, A.A.; Minnema, D.J.; Collier, R.H.; Creek, M.R.; Peffer, R.C. A Critical Review of Neonicotinoid Insecticides for Developmental Neurotoxicity. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2016, 46, 153–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sass, J.B.; Donley, N.; Freese, W. Neonicotinoid Pesticides: Evidence of Developmental Neurotoxicity from Regulatory Rodent Studies. Front. Toxicol. 2024, 6, 1438890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, W.; Jones, K.; Fuhrimann, S.; Naim, Z.; Sidek, B.; Sams, C.; Harding, A.; Povey, A.; Atuhaire, A.; Basinas, I.; et al. Factors Influencing Occupational Exposure to Pyrethroids and Glyphosate: An Analysis of Urinary Biomarkers in Malaysia, Uganda and the United Kingdom. Environ. Res. 2024, 242, 117651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed, M.F.; Shaheen, M.; Ahmad, I.; Zakir, A.; Nadeem, M.; Chishti, A.A.; Shahid, M.; Bakhsh, K.; Damalas, C.A. Pesticide Exposure in the Local Community of Vehari District in Pakistan: An Assessment of Knowledge and Residues in Human Blood. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 587, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouwer, M.; Kromhout, H.; Vermeulen, R.; Duyzer, J.; Kramer, H.; Hazeu, G.; De Snoo, G.; Huss, A. Assessment of Residential Environmental Exposure to Pesticides from Agricultural Fields in the Netherlands. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2018, 28, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faure, E.; Béranger, R.; Fervers, B.; Schüz, J.; Blain, J. A GIS-Based Method to Define Geographical Determinants of Environmental Exposure to Agricultural Pesticides in France. Rev. D’épidémiologie Santé Publique 2018, 66, S333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, A.; Koch, H.M.; Bury, D.; Koslitz, S.; Kolossa-Gehring, M.; Conrad, A.; Murawski, A.; McGrath, J.A.; Leahy, M.; Brüning, T. A Human Biomonitoring Study Assessing Glyphosate and Aminomethylphosphonic Acid (AMPA) Exposures among Farm and Non-Farm Families. Toxics 2022, 10, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugeng, A.J. From Field to Home: Assessing Air Infiltration and Soil Track-In Transport Pathways of Agricultural Pesticides into Farmworkers’ Home and Identifying Risk Factors for Increased in-Home Pesticide Levels; The University of Arizona: Tucson, AZ, USA, 2016; ISBN 1339748061. [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira, W.V.; da Silva, J.L.; Braga, E.P.P.; Kupski, L.; Garda-Buffon, J. The Do Pesticides and Mycotoxins in Water Pose an Exposure Risk to Humans? Agua Y Territ. Landsc. 2025, 25, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.; Gai, L.; Harkes, P.; Tan, G.; Ritsema, C.J.; Alcon, F.; Contreras, J.; Abrantes, N.; Campos, I.; Baldi, I. Pesticide Residues with Hazard Classifications Relevant to Non-Target Species Including Humans Are Omnipresent in the Environment and Farmer Residences. Environ. Int. 2023, 181, 108280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajput, S.; Sharma, R.; Kumari, A.; Kaur, R.; Sharma, G.; Arora, S.; Kaur, R. Pesticide Residues in Various Environmental and Biological Matrices: Distribution, Extraction, and Analytical Procedures. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022, 24, 6032–6052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudi, M.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; Lyu, J.; Yang, L.; Tong, S.; Yu, Q.J.; Ruan, H.D.; Atabila, A. Exposure Routes and Health Risks Associated with Pesticide Application. Toxics 2022, 10, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrigou, A.; Laurent, C.; Berthet, A.; Colosio, C.; Jas, N.; Daubas-Letourneux, V.; Jackson Filho, J.-M.; Jouzel, J.-N.; Samuel, O.; Baldi, I. Critical Review of the Role of PPE in the Prevention of Risks Related to Agricultural Pesticide Use. Saf. Sci. 2020, 123, 104527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbeek, J.H.; Rajamaki, B.; Ijaz, S.; Sauni, R.; Toomey, E.; Blackwood, B.; Tikka, C.; Ruotsalainen, J.H.; Balci, F.S.K. Personal Protective Equipment for Preventing Highly Infectious Diseases Due to Exposure to Contaminated Body Fluids in Healthcare Staff. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 4, CD011621. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sapbamrer, R.; Thammachai, A. Factors Affecting Use of Personal Protective Equipment and Pesticide Safety Practices: A Systematic Review. Environ. Res. 2020, 185, 109444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romano, M.E.; Buckley, J.P.; Li, X.; Herbstman, J.B.; Kannan, K.; Lee, S.; Schantz, S.L.; Trasande, L.; Karagas, M.R.; Perera, F. Changes in Urinary Concentrations of Contemporary and Emerging Chemicals in Commerce during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the Environmental Influences on Child Health Outcomes (ECHO) Program. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0317358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, M.; Chauncey, A.; Ogle-Mustafa, C.; Chichester, M. Determinants of the Use of Personal Protective Equipment: A Literature Review. J. Educ. Soc. Behav. Sci. 2023, 36, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trubetskov, A.D.; Makhonko, M.N.; Shkrobova, N.V.; Shelekhova, T. V Problems of Using Personal Protective Equipment in Modern Conditions. Russ. J. Occup. Health Ind. Ecol. 2023, 63, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu*, M.; Griffin, L. A Pilot Study of Healthcare Workers’ Experience With Personal Protective Equipment. In Proceedings of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society Annual Meeting, Atlanta, GA, USA, 10–14 October 2022; SAGE Publications: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2022; Volume 66, pp. 898–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Zhang, S.; Chen, X.; Wang, T.; Yi, X.; Yeerkenbieke, G.; Shi, S.; Lu, X. Evaluation of the Risk of Human Exposure to Thiamethoxam by Extrapolation from a Toxicokinetic Experiment in Rats and Literature Data. Environ. Int. 2023, 173, 107823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Phung, D.; Dong, F.; Xu, J.; Liu, X.; Wu, X.; Liu, Q.; He, M.; Pan, X.; Li, R.; et al. Urinary Monitoring of Neonicotinoid Imidacloprid Exposure to Pesticide Applicators. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 669, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA); Álvarez, F.; Arena, M.; Auteri, D.; Leite, S.B.; Binaglia, M.; Castoldi, A.F.; Chiusolo, A.; Cioca, A.; Colagiorgi, A.; et al. Peer Review of the Pesticide Risk Assessment of the Active Substance Folpet. EFSA J. 2023, 21, e08139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Feature | Overall | Farmers | Exposed Indirectly | Control | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cohort | 154 | 56 | 48 | 50 | |
| Age (years) | 0.232 a | ||||
| Mean ± SD | 47.45 ± 14.48 | 53.53 ± 13.88 | 49.83 ± 14.38 | 38.36 ± 10.39 | |
| Median | 47.00 | 53.00 | 50.50 | 34.50 | |
| Range | [22–87] | [29–80] | [22–87] | [26–70] | |
| Interquartile range | 23.50 | 21.00 | 21.50 | 14.75 | |
| Gender | <0.001 b | ||||
| Man | 73 (47.4%) | 56 (100%) | 6 (12.5%) | 11 (22%) | |
| Female | 81 (52.6%) | 0 (0%) | 42 (87.5%) | 39 (78%) | |
| Education | <0.001 c | ||||
| None | 60 (38.96%) | 29 (51.7%) | 31 (64.6%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Primary school | 40 (25.97%) | 25 (44.6%) | 15 (31.25%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Secondary school | 18 (11.68%) | 2 (3.7%) | 2 (4.15%) | 14 (28%) | |
| University | 36 (23.39%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 36 (72%) | |
| Living on farm | <0.001 b | ||||
| Yes | 98 (63.64%) | 56 (100%) | 42 (87.5%) | 0 (0%) | |
| No | 56 (36.36%) | 0 (0%) | 6 (12.5%) | 50 (100%) | |
| Drinking water source | <0.001 b | ||||
| Tap | 64 (41.56%) | 7 (12.5%) | 3 (6.25%) | 50 (100%) | |
| Wells and rivers | 90 (58.44) | 49 (87.5%) | 45 (93.75%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Origin of the food consumed | <0.001 b | ||||
| Market | 86 (55.9) | 14 (25) | 22 (45.8) | 50 (100) | |
| Farm | 68 (44.1) | 42 (75) | 26 (54.2) | 0 (0) | |
| Pesticide use | 0.005 b | ||||
| Yes | 80 (51.94%) | 56 (100%) | 24 (50%) | 0 (0%) | |
| No | 74 (48.06%) | 0 (0%) | 24 (50%) | 50 (100%) | |
| Use of PPE | <0.001 b | ||||
| Yes | 13 (8.5) | 13 (23.2) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | |
| No | 141 (91.5) | 43 (76.8) | 48 (100) | 50 (100) |
| Pesticide | >LOD | Maximum Concentration | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Substance | Type | Hazardous Class | Farmers | Exposed Indirectly | C | Farmers | Exposed Indirectly | C |
| Benfluralin | Herbicide | II | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0 |
| Buprofezin | Insecticide | U | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.66 | 0 | 0 |
| Cadusafos | Nematicide | Ia | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.14 | 0 | 0 |
| Chlorobenzilate | Acaricide | II | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.02 | 0 | 0 |
| Clomazone | Herbicide | II | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0.18 | 0.11 | 0 |
| DEET | Insecticide | U | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1.54 | 0 | 0 |
| Dichlofluanid | Fungicide | U | 10 | 7 | 0 | 7.10 | 22.13 | 0 |
| Dicloran | Fungicide | U | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.09 | 0 |
| Diphenylamine | Fungicide | U | 8 | 0 | 0 | 0.23 | 0 | 0 |
| Endosulfan Lactone | Insecticide | Ib | 1 | 0 | 0 | 8.24 | 0 | 0 |
| Fenpropimorph | Fungicide | II | 5 | 4 | 0 | 0.18 | 0.16 | 0 |
| Malaoxon | Insecticide | Ib | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0.00 | 3.9 | 0 |
| Metribuzin | Herbicide | II | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0.05 | 0.052 | 0 |
| Oxadiazon | Herbicide | II | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.02 | 0 | 0 |
| Oxamyl | Insecticide | Ib | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0.50 | 0.15 | 0 |
| Penthiopyrad | Fungicide | U | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.06 | 0 | 0 |
| Phenyl 2, phenol | Fungicide | U | 10 | 0 | 0 | 1.21 | 0 | 0 |
| Phthalimide | Fungicide | U | 9 | 4 | 0 | 30.90 | 20.40 | 0 |
| Pyrimethanil | Fungicide | U | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0.06 | 0.10 | 0 |
| Trichlorophenol 2,4,6 | Herbicide | II | 12 | 12 | 0 | 0.29 | 0.34 | 0 |
| Bifenazate | Acaricide | U | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.73 | 0 |
| Carbendazim | Fungicide | II | 4 | 2 | 0 | 0.92 | 0.15 | 0 |
| Clofentezine | Acaricide | U | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.11 | 0 |
| Dinotefuran | Insecticide | U | 16 | 13 | 9 | 4.82 | 18.62 | 4.44 |
| Dodine | Fungicide | II | 1 | 15 | 0 | 2.20 | 2.97 | 0 |
| Imidacloprid | Insecticide | II | 0 | 2 | 28 | 0.00 | 1.29 | 2.05 |
| Tetrachlorvinphos | Insecticide | II | 1 | 0 | 0 | 7.36 | 0 | 0 |
| Thiabendazole | Fungicide | II | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0.00 | 1.14 | 0 |
| Thiamethoxam | Insecticide | II | 24 | 15 | 14 | 9.26 | 9.31 | 0.34 |
| Warfarin | Rodenticide | Ib | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.11 | 0 | 0 |
| Var | Herbicide (μg/L) | Insecticide (μg/L) | Fungicide (μg/L) | Acaricide (μg/L) | Nematicide (μg/L) | Rodenticide (μg/L) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | Est Coeff. | p | M | Est Coeff. | p | M | Est Coeff. | p | M | Est Coeff. | p | M | Est Coeff. | p | M | Est Coeff. | p | |
| Age | - | 0.001 (−0.001–0.001) | 0.645 | - | −0.008 (−0.022–0.007) | 0.297 | - | −0.088 (−0.031–0.012) | 0.390 | - | −0.101 (-) | 0.313 | - | −0.076 (-) | 0.443 | - | −0.151 (-) | 0.150 |
| Gender | −0.007 (−0.032–0.017) | 0.562 | −0.125 (−0.542–0.293) | 0.556 | −0.439 (−1.048–0.171) | 0.157 | 0.029 (−0.003–0.004) | 0.765 | 0.009 (−0.004–0.004) | 0.926 | −0.099 (−0.005–0.002) | 0.337 | ||||||
| Man | 0.034 | - | 0.444 | - | 0.675 | - | 0.000 | - | 0.001 | - | 0.001 | - | ||||||
| Female | 0.021 | 0.457 | 0.183 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | ||||||||||||
| Education | −0.014 (−0.031–0.004) | 0.134 | −0.255 (−0.558–0.047) | 0.097 | −0.353 (−0.794–0.089) | 0.117 | −0.419 (−0.006–−0.001) | 0.014 | −0.042 (−0.003–0.003) | 00.805 | −0.223 (−0.004–0.001) | 0.209 | ||||||
| None | 0.044 | - | 0.637 | - | 0.821 | - | 0.001 | - | 0.000 | - | 0.001 | - | ||||||
| Primary school | 0.035 | 0.510 | 0.324 | 0.000 | 0.003 | 0.000 | ||||||||||||
| Secondary school | 0.007 | 0.271 | 0.078 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | ||||||||||||
| University | 0.000 | 0.161 | 0 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | ||||||||||||
| Living on farm | - | −0.018 (−0.062–0.026) | 0.419 | - | 0.085 (−0.564–0.938) | 0.623 | - | −0.133 (−1.229–0.962) | 0.810 | - | 0.566 (0.004–0.017) | 0.001 | - | −0.214 (−0.013–0.003) | 0.208 | - | 0.083 (−0.005–0.008) | 0.639 |
| Yes | 0.040 | - | 0.530 | - | 0.654 | - | 0.000 | - | 0.001 | - | 0.001 | - | ||||||
| No | 0.004 | 0.313 | 0.000 | 0.002 | 0.000 | 0.000 | ||||||||||||
| Drinking water | - | −0.009 (−0.046–0.028) | 0.644 | - | 0.247 (−0.093–1.168) | 0.094 | - | −0.298 (−1.219–0.623) | 0.524 | - | 0.110 (−0.003–0.007) | 0.445 | - | −0.369 (−0.015–−0.002) | 0.011 | - | −0.072 (−0.007–0.004) | 0.634 |
| Tap | 0.008 | - | 0.186 | - | 0.782 | - | 0.000 | - | 0.002 | - | 0.000 | - | ||||||
| Wells and rivers | 0.039 | 0.621 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.001 | ||||||||||||
| Origin of the food consumed | - | 0.009 (−0.017–0.034) | 0.494 | - | 0.066 (−0.291–0.571) | 0.521 | - | −0.048 (−0.677–0.582) | 0.881 | - | −0.195 (−0.007–0.000) | 0.054 | - | −0.075 (−0.006–0.003) | 0.452 | - | −0.064 (−0.005–0.003) | 0.543 |
| Farm | 0.036 | - | 0.500 | - | 0.670 | - | 0.002 | - | 0.002 | - | 0.001 | - | ||||||
| Market | 0.020 | 0.413 | 0.215 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | ||||||||||||
| Pesticide use | - | −0.039 (−0.039–0.029) | 0.777 | - | 0.521 (−0.085–1.080) | 0.093 | - | −0.096 (−0.946–0.754) | 0.824 | - | 0.029 (−0.004–0.005) | 0.833 | - | −0.054 (−0.007–0.005) | 0.005 | - | −0.038 (−0.006–0.004) | 0.792 |
| Yes | 0.040 | - | 0.456 | - | 0.692 | - | 0.000 | - | 0.001 | - | 0.001 | - | ||||||
| No | 0.013 | 0.840 | 0.118 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | ||||||||||||
| Use of PPE | - | 0.204 (0.008–0.086) | 0.019 | - | 0.000 (−0.664–0.662) | 0.998 | - | 0.748 (−0.220–1.715) | 0.129 | - | −0.044 (−0.007–0.004) | 0.612 | - | −0.231 (−0.016–0.002) | 0.008 | - | 0.074 (−0.003–0.008) | 0.415 |
| Yes | 0.007 | - | 0.392 | - | 0.256 | - | 0.010 | - | 0.106 | - | 0.000 | - | ||||||
| No | 0.002 | 0.457 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | ||||||||||||
| R2 | 0.127 | - | 0.089 | 0.079 | 0.119 | 0.122 | 0.034 | |||||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ben Khadda, Z.; Radu, A.-F.; El Balkhi, S.; Mustapha, F.; El Karmoudi, Y.; Bungau, G.; Marquet, P.; Sqalli Houssaini, T.; Achour, S. From Farmworkers to Urban Residents: Mapping Multi-Class Pesticide Exposure Gradients in Morocco via Urinary Biomonitoring. J. Xenobiot. 2025, 15, 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox15040120
Ben Khadda Z, Radu A-F, El Balkhi S, Mustapha F, El Karmoudi Y, Bungau G, Marquet P, Sqalli Houssaini T, Achour S. From Farmworkers to Urban Residents: Mapping Multi-Class Pesticide Exposure Gradients in Morocco via Urinary Biomonitoring. Journal of Xenobiotics. 2025; 15(4):120. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox15040120
Chicago/Turabian StyleBen Khadda, Zineb, Andrei-Flavius Radu, Souleiman El Balkhi, Fagroud Mustapha, Yahya El Karmoudi, Gabriela Bungau, Pierre Marquet, Tarik Sqalli Houssaini, and Sanae Achour. 2025. "From Farmworkers to Urban Residents: Mapping Multi-Class Pesticide Exposure Gradients in Morocco via Urinary Biomonitoring" Journal of Xenobiotics 15, no. 4: 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox15040120
APA StyleBen Khadda, Z., Radu, A.-F., El Balkhi, S., Mustapha, F., El Karmoudi, Y., Bungau, G., Marquet, P., Sqalli Houssaini, T., & Achour, S. (2025). From Farmworkers to Urban Residents: Mapping Multi-Class Pesticide Exposure Gradients in Morocco via Urinary Biomonitoring. Journal of Xenobiotics, 15(4), 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox15040120






