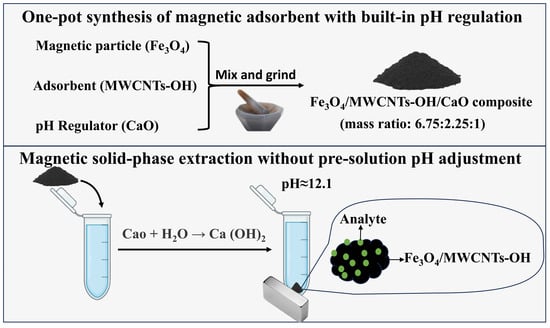
Rapid and Simplified Determination of Amphetamine-Type Stimulants Using One-Pot Synthesized Magnetic Adsorbents with Built-In pH Regulation Coupled with Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Solution Preparation
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. Material Preparation
2.5. Extraction Procedure
2.6. LC-MS/MS Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Experimental Design
3.2. Optimization of Extraction Conditions
3.2.1. Mass of CaO in the Composite
3.2.2. Mass of Fe3O4 and MWCNT-OH in the Composite
3.2.3. Type of Desorption Solvent
3.2.4. Acid Concentration in Desorption Solvent
3.2.5. Volume of Desorption Solvent
3.3. Performance Evaluation
3.4. Method Validation
3.5. Sample Analysis
3.6. Method Comparison
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATS | Amphetamine-type stimulants |
| A | 1-phenylpropan-2-amine |
| MA | N-methyl-1-phenylpropan-2-amine |
| GC-MS | Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry |
| LC-MS/MS | Liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry |
| LLE | Liquid–liquid extraction |
| LPME | Liquid-phase microextraction |
| DLLME | Dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction |
| MSPE | Magnetic solid-phase extraction |
| PMMA | 1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-N-methylpropan-2-amine |
| MDMA | 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine |
| 2F-A | 1-(2-fluorophenyl)propan-2-amine |
| 4Cl-A | 1-(4-chlorophenyl)propan-2-amine |
| 4F-A | 1-(4-fluorophenyl)propan-2-amine |
| MDA | 3,4-methylenedioxyamphetamine |
| FA | Formic acid |
| MeOH | Methanol |
| ACN | Acetonitrile |
| EtOH | Ethanol |
| ESI | Electrospray ionization |
| MRM | Multiple reaction monitoring |
References
- Rasmussen, N. Chapter Two—Amphetamine-Type Stimulants: The Early History of Their Medical and Non-Medical Uses. In International Review of Neurobiology; Taba, P., Lees, A., Sikk, K., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; Volume 120, pp. 9–25. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, D.-N.; Shi, J.-J.; Hao, W.; Wu, N.; Li, J. Advances and challenges in pharmacotherapeutics for amphetamine-type stimulants addiction. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 780, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, A.F.B.; de Melo Vieira, A.; Santos, J.M. Trends and challenges in analytical chemistry for multi-analysis of illicit drugs employing wastewater-based epidemiology. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2023, 415, 3749–3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cumming, C.; Armstrong, G.; Borschmann, R.; Foulds, J.A.; Newton-Howes, G.; McKetin, R.; Vallesi, S.; Preen, D.; Young, J. Amphetamine-type stimulant use and self-harm: Protocol for a systematic review of observational studies. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e057029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bano, H.; Suleman, S.; Anzar, N.; Parvez, S.; Narang, J. A review on advancement of biosensors for the detection of amphetamine drug. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2024, 104, 9330–9358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, R.; Altamimi, M.J.; Hachem, M. State-of-the-Art Analytical Approaches for Illicit Drug Profiling in Forensic Investigations. Molecules 2022, 27, 6602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourani, N.; Taghvimi, A.; Bavili-Tabrizi, A.; Javadzadeh, Y.; Dastmalchi, S. Microextraction Techniques for Sample Preparation of Amphetamines in Urine: A Comprehensive Review. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2024, 54, 1304–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragan, A.-M.; Parrilla, M.; Feier, B.; Oprean, R.; Cristea, C.; De Wael, K. Analytical techniques for the detection of amphetamine-type substances in different matrices: A comprehensive review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 145, 116447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanu, A.B. Recent developments in sample preparation techniques combined with high-performance liquid chromatography: A critical review. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1654, 462444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wu, X.; Luan, T.; Jiang, R.; Ouyang, G. Sample preparation and instrumental methods for illicit drugs in environmental and biological samples: A review. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1640, 461961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanferla, D.T.P.; Sano Lini, R.; Marchioni, C.; Mossini, S.A.G. Drugs of abuse: A narrative review of recent trends in biological sample preparation and chromatographic techniques. Forensic Chem. 2022, 30, 100442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalavi, S.; Asadi, S.; Nojavan, S.; Fakhari, A.R. Recent Advances in Microextraction Procedures for Determination of Amphetamines in Biological Samples. Bioanalysis 2019, 11, 437–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Q.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Zhou, L.; Wan, H.; Yin, Q.; Chen, D. Facile Synthesis of Aptamer-Functionalized Polydopamine-Coated Magnetic Graphene Oxide Nanocomposites for Highly Efficient Purification of His-Tagged Proteins. J. Sep. Sci. 2024, 47, e202400471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Öztürk Er, E.; Dalgıç Bozyiğit, G.; Büyükpınar, Ç.; Bakırdere, S. Magnetic Nanoparticles Based Solid Phase Extraction Methods for the Determination of Trace Elements. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2022, 52, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, L.; Jiang, X.; Wu, N.; Li, J.; Di, B.; Yan, F. Synthesis of a novel polydopamine and C18 dual-functionalized magnetic core-shell mesoporous nanocomposite for enrichment and analysis of widely abused illegal drugs in urine samples on site and in the laboratory. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 212, 114656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cao, S.; Tian, J.; You, J.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Z. A magnetic solid phase extraction based on DES/ZIF-MGO coupled with UPLC-MS/MS for the simultaneous detection and consumption evaluation of four illicit drugs. Microchem. J. 2024, 200, 110448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Dong, T.; Jiang, X.; Li, J.; Di, B.; Yan, F. Preparation of polydopamine-functionalized mesoporous silica-coated core/shell magnetic nanocomposite for efficiently extracting five amphetamine-type stimulants from wastewater followed by UPLC-MS/MS determination. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 426, 128082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elboraie, M.Z.; Elbashir, A.A.; Eid, E.E.M.; Aboul-Enein, H.Y. Dispersive solid-phase extraction for simultaneous determination of four amphetamines drugs in urine using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2022, 19, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, N.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Yan, S.; Ma, L.; Xu, X.; Chen, D. One-pot derivatization/magnetic solid-phase extraction coupled with liquid chromatography-fluorescence detection for the rapid determination of sulfonamide residues in honey. Food Chem. X 2024, 21, 101090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, N.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Yan, S.; Xu, X.; Chen, D. One-pot derivatization/magnetic solid-phase extraction combined with high-performance liquid chromatography-fluorescence detection for rapid analysis of biogenic amines in alcoholic beverages. Food Chem. 2024, 460, 140754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Deng, B.; Chen, J.; Feng, R.; Wang, S.; Li, S.; Chen, D.; Hua, L. One-pot synthesis of magnetic adsorbent with integrated pH regulation for convenient and rapid determination of antidepressant in biofluids. Microchem. J. 2025, 209, 112834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.-y.; Qin, M.; Wu, G.-p.; Zhou, Y.-t.; Zhu, J.-x.; Peng, H. Quantitative determination of amphetamine-type stimulants in sewage and urine by hybrid monolithic column solid-phase microextraction coupled with UPLC-QTRAP MS/MS. Talanta 2024, 269, 125437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Xia, X.; Xu, X.; Yang, Y.; Chen, D. Magnetic phytic acid-modified kapok fiber biochar as a novel sorbent for magnetic solid-phase extraction of antidepressants in biofluids. Anal. Chim. Acta 2024, 1296, 342295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirok, B.W.J.; Gargano, A.F.G.; Schoenmakers, P.J. Optimizing separations in online comprehensive two-dimensional liquid chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 68–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.-C.; Wang, X.-Y.; Wang, G.-B.; Zhang, H.-J.; Yang, P.; Wei, J.-C.; Yang, Y.-L.; Yuan, D.-D.; Chen, D. An eco-friendly kapok fiber-supported liquid microextraction using natural deep eutectic solvent as extractant for convenient biological samples preparations: A proof-of-concept study. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2024, 42, 101814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Xiang, Y.; Chen, L.; Xiang, P.; Li, Y. Magnetic solid-phase extraction based on polydopamine-coated magnetic nanoparticles for rapid and sensitive analysis of eleven illicit drugs and metabolites in wastewater with the aid of UHPLC-MS/MS. J. Chromatogr. A 2024, 1718, 464703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulia, S.; Primaharinastiti, R.; Purwanto, D.A. Development and Validation GC/MS Method for Methamphetamine Analysis in Urine by Miniaturization QuEChERS. Sci. Technol. Indones. 2023, 8, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Guo, C.; Zhang, H.; Deng, Y.; Tan, X.; Gao, Y.; Xu, J. Determination of Illicit Drugs in Sediments Using a Modified QuEChERS Method Coupled with UPLC-MS/MS. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2025, 53, 100540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Wei, X.; Shen, X.; Zhu, W.; Yi, S.; Huang, C. Synthesis of molecularly-imprinted polymers towards a group of amphetamine-type stimulants by reflux precipitation polymerization with a pseudo template. J. Chromatogr. A 2023, 1688, 463738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
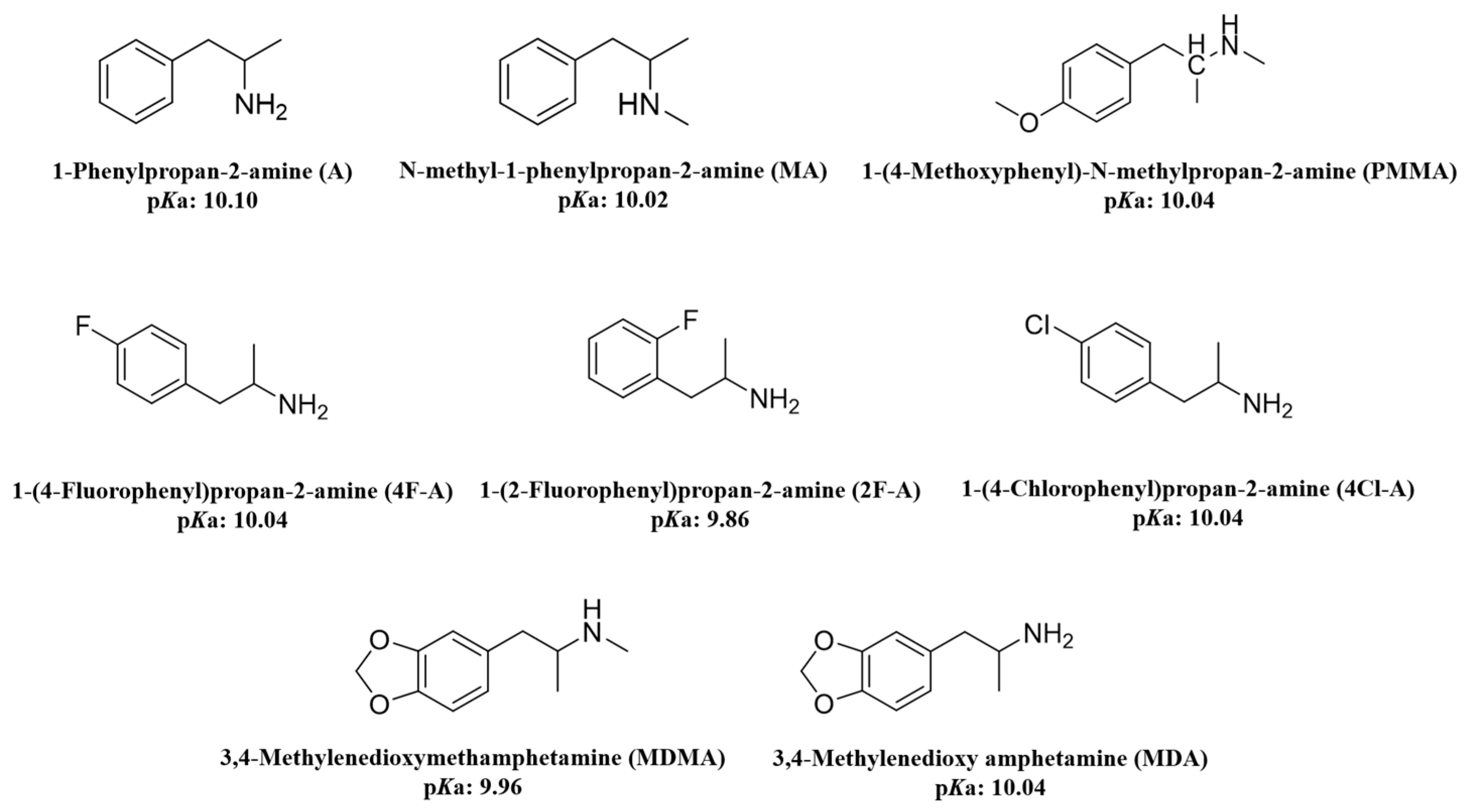



| Analyte | Retention Time (min) | Parent Ion (m/z) | Product Ion (m/z) | Collision Energy (eV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 1.98 | 136.1 | 91.1 * | 20 |
| 119.1 | 13 | |||
| A-d5 | 1.96 | 141.2 | 124.1 * | 14 |
| 93.1 | 21 | |||
| 2F-A | 2.27 | 154.2 | 109.1 * | 26 |
| 83.1 | 42 | |||
| MA | 2.42 | 150.1 | 91.1 * | 30 |
| 119.1 | 13 | |||
| 4F-A | 2.53 | 154.2 | 109.1 * | 12 |
| 83.0 | 40 | |||
| MDA | 2.54 | 180.1 | 105.1 * | 14 |
| 163.0 | 22 | |||
| MDMA | 3.07 | 194.2 | 163.1 * | 14 |
| 105.1 | 25 | |||
| MDMA-d5 | 3.02 | 199.1 | 165.1 * | 5 |
| 107.1 | 16 | |||
| PMMA | 3.64 | 180.1 | 121.1 * | 21 |
| 149.2 | 13 | |||
| 4Cl-A | 4.80 | 170.1 | 125.0 * | 20 |
| 153.1 | 11 |
| Matrix Effect | A | 2F-A | MA | 4F-A | MDA | MDMA | PMMA | 4Cl-A |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Absolute matrix effect | 66.1% | 65.3% | 56.8% | 67.2% | 73.4% | 73.1% | 73.2% | 65.6% |
| IS-normalized matrix effect | 104% | 103.3% | 88.5% | 105.2% | 104.1% | 104.2% | 103.4% | 102.1% |
| Analyte | Linear Range (ng/mL) | Linear Equation | R2 | LOD (ng/mL) | LOQ (ng/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0.1–40 | Y = 11.978x − 0.879 | 0.9998 | 0.020 | 0.067 |
| 2F-A | 0.1–40 | Y = 23.590x − 1.470 | 0.9948 | 0.020 | 0.067 |
| MA | 0.2–20 | Y = 18.551x − 1.999 | 0.9825 | 0.050 | 0.167 |
| 4F-A | 0.1–40 | Y = 12.404x − 0.555 | 0.9932 | 0.030 | 0.100 |
| MDA | 0.2–20 | Y = 0.365x + 0.039 | 0.9827 | 0.060 | 0.200 |
| MDMA | 0.1–40 | Y = 1.675x − 0.024 | 0.9998 | 0.020 | 0.067 |
| PMMA | 0.1–40 | Y = 1.901x − 0.044 | 0.9997 | 0.020 | 0.067 |
| 4Cl-A | 0.2–40 | Y = 0.471x + 0.013 | 0.9963 | 0.060 | 0.200 |
| Analyte | Added (ng/mL) | Intra-Day | Inter-Day (n = 3) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recovery (%) | RSDs (%) | Recovery (%) | RSDs (%) | ||
| A | 0.2 | 101.7 | 6.2 | 96.3 | 8 |
| 4 | 100.7 | 6 | 98.1 | 5.5 | |
| 20 | 104.1 | 7.3 | 107.9 | 10 | |
| 2F-A | 0.2 | 92.8 | 2.7 | 99.3 | 5.7 |
| 4 | 98 | 4.1 | 102.7 | 4.6 | |
| 20 | 96.4 | 6.5 | 102.1 | 7.7 | |
| MA | 0.2 | 99.3 | 5 | 100 | 4.7 |
| 4 | 100.5 | 2.4 | 102.8 | 3.9 | |
| 20 | 98.5 | 7.5 | 105.9 | 11.5 | |
| 4F-A | 0.2 | 98.3 | 3.9 | 93.4 | 5.9 |
| 4 | 102.3 | 4.6 | 99.1 | 6.9 | |
| 20 | 98 | 6 | 93 | 7.5 | |
| MDA | 0.2 | 104.8 | 2.4 | 102.6 | 4.6 |
| 4 | 103.7 | 3.7 | 100.8 | 4 | |
| 20 | 100.8 | 5 | 103.4 | 8.3 | |
| MDMA | 0.2 | 97.2 | 2.2 | 101 | 5.6 |
| 4 | 101.4 | 1.1 | 101.4 | 3.5 | |
| 20 | 95.8 | 5.4 | 101.4 | 7.5 | |
| PMMA | 0.2 | 97.5 | 2.2 | 102.1 | 8.8 |
| 4 | 103.6 | 3.5 | 106.2 | 8.5 | |
| 20 | 99.3 | 5 | 104.6 | 10.8 | |
| 4Cl-A | 0.2 | 102 | 3.9 | 96.6 | 10.4 |
| 4 | 104.4 | 4.8 | 109 | 8.3 | |
| 20 | 102.6 | 4.2 | 107 | 11.6 | |
| Spiking Level (ng/mL) | Detected Level (ng/mL) (Mean ± SD) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 2F-A | MA | 4F-A | MDA | MDMA | PMMA | 4Cl-A | |
| 0.8 | 0.78 ± 0.03 | 0.77 ± 0.04 | 0.74 ± 0.01 | 0.85 ± 0.06 | 0.82 ± 0.03 | 0.75 ± 0.06 | 0.74 ± 0.08 | 0.82 ± 0.03 |
| 8 | 8.13 ± 0.02 | 8.53 ± 0.07 | 8.29 ± 0.04 | 8.44 ± 0.05 | 7.43 ± 0.07 | 7.64 ± 0.04 | 7.64 ± 0.05 | 7.85 ± 0.02 |
| Sample | Sample Preparation Method | Detection Technique | LOD (ng/mL) | Ref. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Magnetic Adsorbent | Pre-Adjustment of Sample pH | Post Processing After Elution | Processing Time | ||||
| Wastewater | MSPE | Fe3O4@nSiO2@mSiO2@PDA (complex synthesis) | Yes | Yes | >18 min | LC-MS/MS | 0.001–0.005 | [17] |
| Urine samples | MSPE | Fe3O4@nSiO2@mSiO2@PDA-C18 (complex synthesis) | Yes | Yes | >18 min | LC-MS/MS | 0.01–0.1 | [15] |
| Wastewater | MSPE | DES/ZIF-MGO (complex synthesis) | Yes | Yes | >40 min | LC-MS/MS | 0.02–1.55 | [16] |
| Wastewater | MSPE | Fe3O4@PDA (complex synthesis) | Yes | No | >15 min | LC-MS/MS | 0.002–0.005 | [26] |
| Urine samples | QuEChERS | / | Yes | Yes | >15 min | GC-MS | 360 | [27] |
| Sediments | QuEChERS | / | No | Yes | >12 h | LC-MS/MS | 0.0077–0.0299 (ng/g) | [28] |
| Urine and Wastewater | SPE | MIP | No | No | >40 min | LC-MS/MS | 0.05–0.29 | [29] |
| Water | MSPE with built-in pH regulation | Fe3O4/MWCNTs-OH (simple one-pot grinding) | No | No | ~5 min | LC-MS/MS | 0.02–0.06 | Present work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Zeng, X.; Jia, R.; Liu, Y.; Li, D.; Chen, D. Rapid and Simplified Determination of Amphetamine-Type Stimulants Using One-Pot Synthesized Magnetic Adsorbents with Built-In pH Regulation Coupled with Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Xenobiot. 2025, 15, 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox15040102
Shan Y, Chen Y, Li J, Zeng X, Jia R, Liu Y, Li D, Chen D. Rapid and Simplified Determination of Amphetamine-Type Stimulants Using One-Pot Synthesized Magnetic Adsorbents with Built-In pH Regulation Coupled with Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Journal of Xenobiotics. 2025; 15(4):102. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox15040102
Chicago/Turabian StyleShan, Yabing, Ying Chen, Jiayi Li, Xianbin Zeng, Rui Jia, Yuwei Liu, Dongmei Li, and Di Chen. 2025. "Rapid and Simplified Determination of Amphetamine-Type Stimulants Using One-Pot Synthesized Magnetic Adsorbents with Built-In pH Regulation Coupled with Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry" Journal of Xenobiotics 15, no. 4: 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox15040102
APA StyleShan, Y., Chen, Y., Li, J., Zeng, X., Jia, R., Liu, Y., Li, D., & Chen, D. (2025). Rapid and Simplified Determination of Amphetamine-Type Stimulants Using One-Pot Synthesized Magnetic Adsorbents with Built-In pH Regulation Coupled with Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Journal of Xenobiotics, 15(4), 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox15040102