Do Isopropylammonium Glyphosate and LiCl Impact the Spore Diversity and Functions of Aquatic Fungi Involved in Plant Litter Decomposition in Streams?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Leaf Processing, Study Area, and Field Procedures
2.2. Microcosm Assays
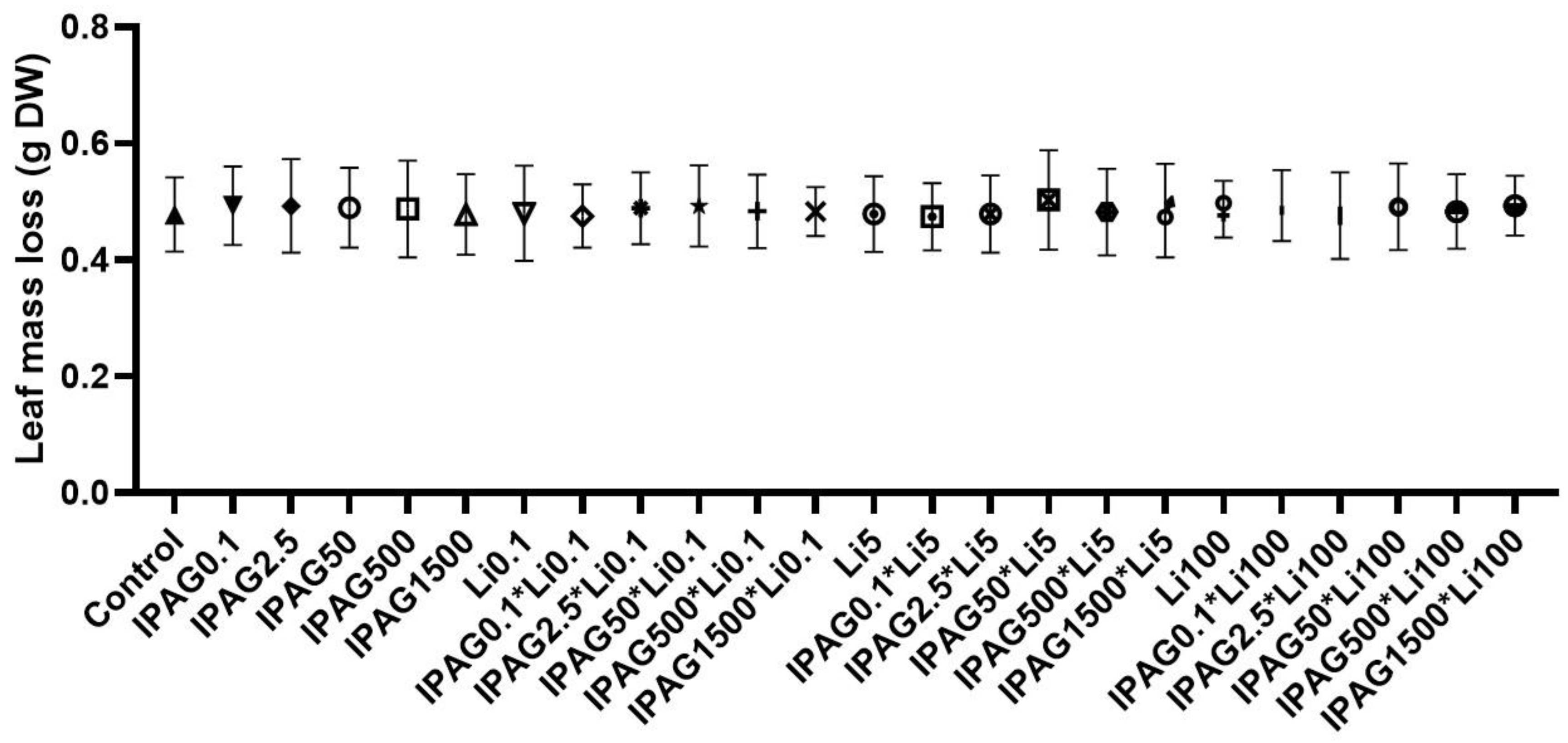
2.3. Leaf Mass Loss
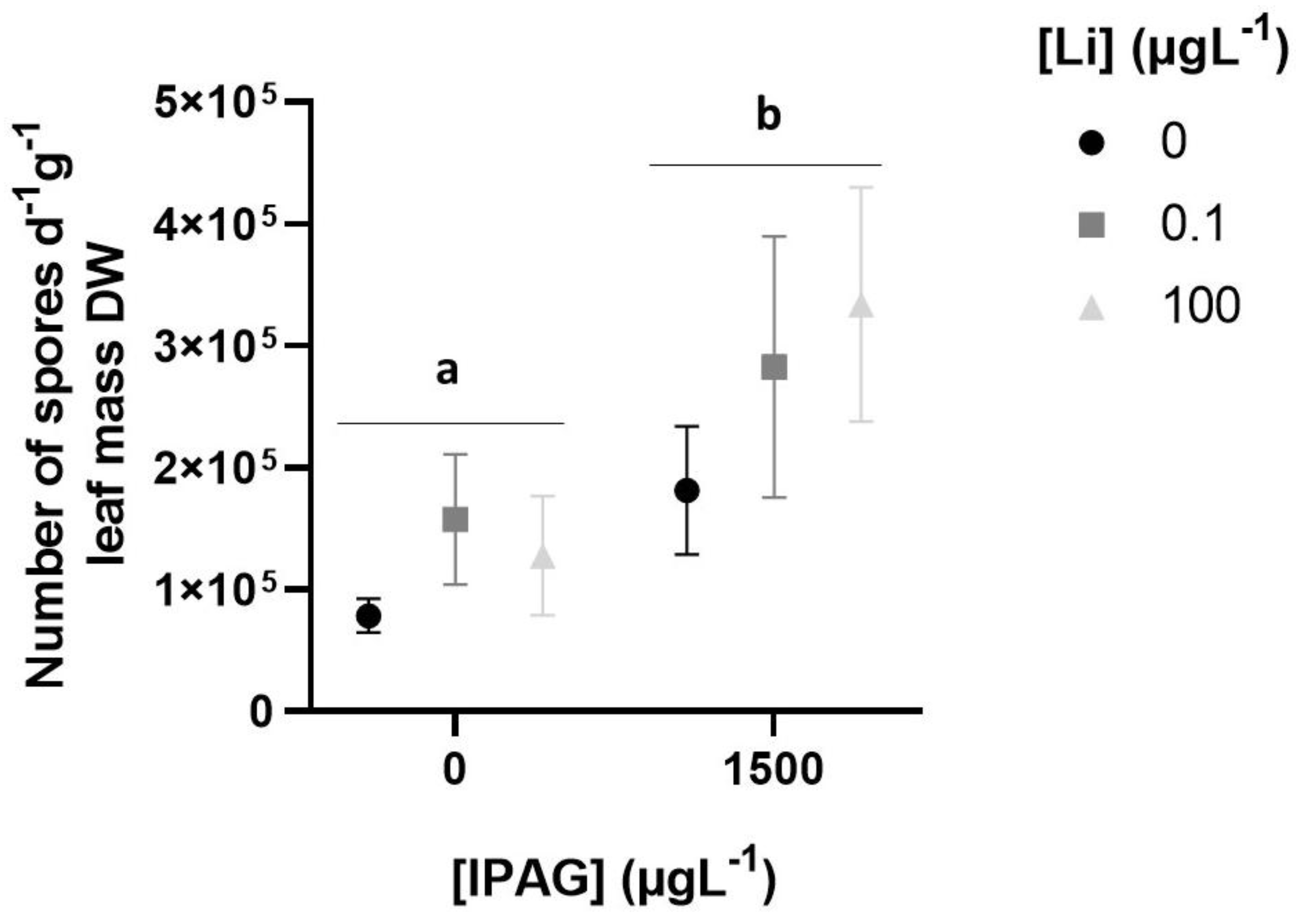
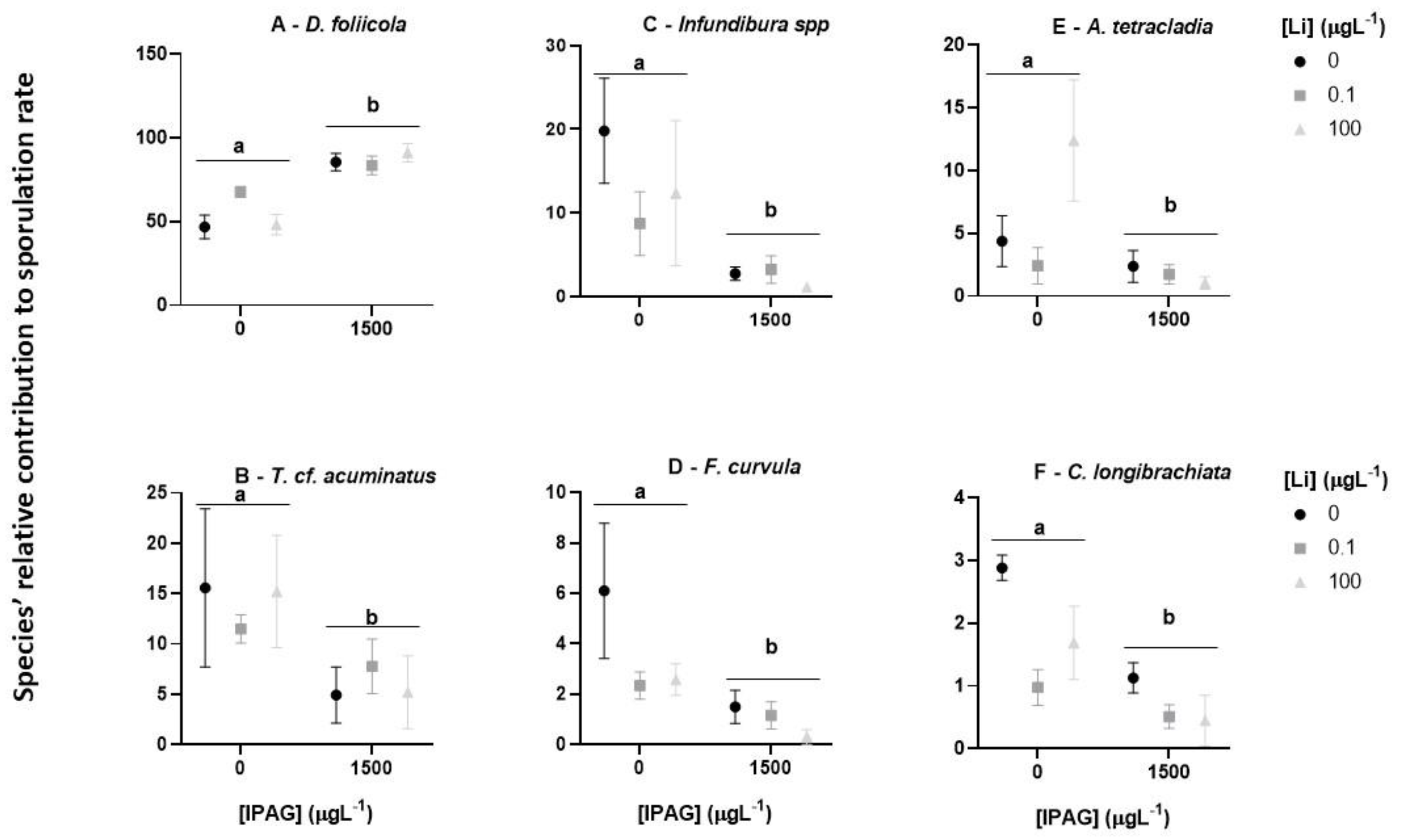
2.4. Total Fungal Sporulation and Fungal Diversity
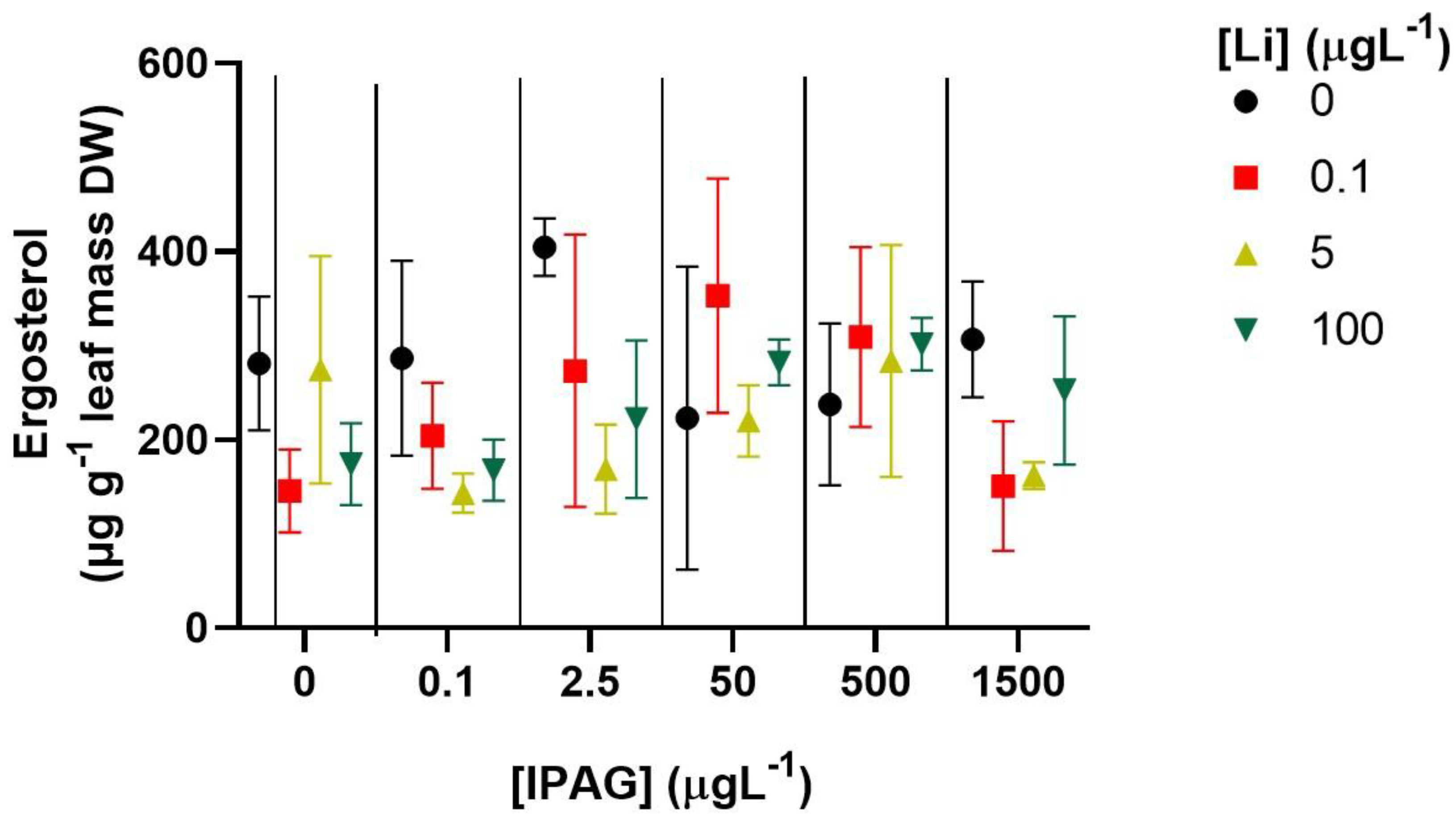
2.5. Fungal Biomass
2.6. Data Treatment
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Isopropylammonium Glyphosate and LiCl Alone and in Combination on Microbial Decomposition of Plant Litter and Total Sporulation and Spore Diversity of Aquatic Fungi
3.2. Effects of Isopropylammonium Glyphosate and LiCl Alone or in Combination on Fungal Biomass
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dudgeon, D. Multiple threats imperil freshwater biodiversity in the Anthropocene. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, R942–R995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deeksha; Shukla, A.K. Ecosystem Services: A Systematic Literature Review and Future Dimension in Freshwater Ecosystems. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiner, V.C.; Feckler, A.; Fernández, D.; Frisch, K.; Muñoz, K.; Szöcs, E.; Zubrod, J.P.; Bundschuh, M.; Rasmussen, J.; Kefford, B.; et al. Similar recovery time of microbial functions from fungicide stress across biogeographical regions. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Lin, X.; Li, L.; Lin, S. Differential growth responses of marine phytoplankton to herbicide glyphosate. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascoal, C.; Cássio, F.; Marcotegui, A.; Sanz, B.; Gomes, P. Role of fungi, bacteria and invertebrates in leaf litter breakdown in a polluted river. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2005, 24, 784–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabulo, J.; Pradhan, A.; Pascoal, C.; Cássio, F. Can microplastics from personal care products affect stream microbial decomposers in the presence of silver nanoparticles? Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 832, 155038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, E.B.; Knelman, J.E.; Schindlbacher, A.; Sicilliano, S.; Breulmann, M.; Yannarell, A.; Beman, J.M.; Abell, G.; Philippot, L.; Prosser, J.; et al. Microbes as engines of ecosystem function: When does community structure enhance predictions of ecosystem processes? Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentão, A.R.; Pascoal, C.; Castro, B.B.; Cássio, F. Fungistatic effect of agrochemical and pharmaceutical fungicides on non-target aquatic decomposers does not translate into decreased fungi- or invertebrate-mediated decomposition. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 712, 135676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, A.; Bach, M.; Frede, H.G. Pollution of surface waters with pesticides in Germany: Modeling non-point source inputs. Agriculture. Ecosyst. Environ. 2000, 80, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, R. Field studies on exposure, effects, and risk mitigation of aquatic nonpoint-source insecticide pollution—A review. J. Environ. Qual. 2004, 33, 419–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, J.J.; Wiberg-Larsen, P.; Baattrup-Pedersen, A.; Monverg, R.J.; Kronvang, B. Impacts of pesticides and natural stressors on leaf litter decomposition in agricultural streams. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 416, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helander, M.; Pauna, A.; Saikkonen, K.; Saloniemi, I. Glyphosate residues in soil affect crop plant germination and growth. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leino, L.; Tall, T.; Helander, M.; Saloniemi, I.; Saikkonen, K.; Ruuskanen, S.; Puigbò, P. Classification of the glyphosate target enzyme (5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase) for assessing sensitivity of organisms to the herbicide. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 408, 124556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peruzzo, P.J.; Porta, A.A.; Ronco, A.E. Levels of glyphosate in surface waters, sediments and soils associated with direct sowing soybean cultivation in north pampasic region of Argentina. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 156, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giesy, J.P.; Dobson, S.; Solomon, K.R. Ecotoxicological risk assessment for roundup herbicide. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2000; Volume 167, pp. 35–120. [Google Scholar]
- Guilherme, S.; Santos, G.M.A.; Pacheco, M. European eel (Angilla anguilla) genotoxic and pro-oxidant responses following short-term exposure to Roundup—A glyphosate-based herbicide. Mutagenesis 2010, 25, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glozier, N.E.; Struger, J.; Cessna, A.J.; Gledhill, M.; Rondeau, M.; Ernst, W.R.; Sekela, M.A.; Cagampan, S.J.; Sverko, E.; Murphy, C.; et al. Occurrence of glyphosate and acidic herbicides in select urban rivers and streams in Canada. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2012, 19, 821–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harayashiki, C.A.Y.; Varela, A.S., Jr.; de Souza Machado, A.A.; da Costa Cabrera, L.; Primel, E.G.; Bianchini, A.; Corcini, C.D. Toxic effects of the herbicide Roundup in the guppy Poecilia vivipara acclimated to fresh water. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 142–143, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrauzer, G.N. Lithium: Occurrence, Dietary Intakes, Nutritional Essentiality. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2002, 21, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanveer, M.; Hasanuzzama, M.; Wang, L. Lithium in environment and potential targets to reduce lithium toxicity in plants. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2019, 38, 1574–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, V.M.; Ribeiro, J.S.; Coelho, E.L.D.; Freitas, M.B.J.G. Recycling of spent lithium-ion batteries as a sustainable solution to obtain raw materials for different applications. J. Energy Chem. 2023, 79, 118–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, B.; Ughal, M.N.; Tanveer, M.; Gupta, D.; Abbas, G. Is lithium biologically an important or toxic element to living organisms? An overview. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, E.E.; Gerretsen, P.; Pollock, B.; Graff-Guerrero, A. Psychiatry benefits of lithium in water supplies may be due to protection from the neurotoxicity of lead exposure. Med. Hypotheses 2018, 115, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavanagh, L.; Keohane, J.; Cleary, J.; Cabellos, G.G.; Lloyd, A. Lithium in the natural waters of the South East of Ireland. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Gao, L.; Zhang, Z.; Tao, S.; Pang, Q.; Li, A.; Deng, H.; Yu, H. Lithium promotes the production of reactive oxygen species via GSK-3b/TSC2/TOR signaling in the gill of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Chemosphere 2018, 195, 854–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewuzie, U.; Nnorom, I.C.; Eze, S.O. Lithium in drinking water sources in rural and urban communities in Southeastern Nigeria. Chemosphere 2020, 245, 125593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobolev, O.I.; Gutyj, B.V.; Darmohray, L.M.; Sobolievа, S.V.; Ivanina, V.V.; Kuzmenko, O.A.; Karkach, P.M.; Fesenko, V.F.; Bilkevych, V.V.; Mashkin, Y.O.; et al. Lithium in the natural environment and its migration in the trophic. Ukr. J. Ecol. 2019, 9, 195–203. [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa, H.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Pereira, E.; Freitas, R. Lithium: A review on concentrations and impacts in marine and coastal systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muturi, E.J.; Donthu, R.K.; Fields, C.J.; Moise, I.K.; Kim, C.-H. Effects of pesticides on microbial communities in container aquatic habitats. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessner, M.O. Ergosterol as a measure of fungal biomass. In Methods in Study Litter Decomposition: A Practical Guide; Graça, M.A.S., Barlocher, F., Gessner, M.O., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 189–195. [Google Scholar]
- Feckler, A.; Bundschuh, M. Decoupled structure and function of leaf-associated microorganisms under anthropogenic pressure: Potential hurdles for environmental monitoring. Freshw. Sci. 2020, 39, 652–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, I.; Pascoal, C.; Cássio, F. Intraspecific traits change effects on ecosystem functioning under metal stress. Oecologia 2011, 166, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, S.; Cássio, F.; Pascoal, C.; Barlocher, F. Taxa-area relationship of aquatic fungi on deciduous leaves. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obojska, A.; Lejczak, B.; Kubrak, M. Degradation of phosphonates by Streptomycetes isolates. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1999, 9, 872e876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ternan, N.G.; Mc Grath, J.W.; McMullan, G.; Quin, J.P. Review: Organophosphonates: Occurrence, synthesis and biodegradation by microorganisms. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1998, 14, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bier, R.L.; Bernhardt, E.S.; Boot, C.M.; Graham, E.B.; Hall, E.K.; Lennon, J.T.; Nemergut, D.R.; Osborne, B.B.; Ruíz-González, C.; Schimel, J.P.; et al. Linking microbial community structure ad microbial processes: An empirical and conceptual overview. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2015, 91, fiv113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascoal, C.; Cássio, F.; Marvanová, L. Anthropogenic stress may affect aquatic hyphomycetes diversity more than leaf decomposition in a low-order stream. Arch. Hydrobiol. 2005, 162, 481–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodrigues, J.; Gerós, H.; Côrte-Real, M.; Cássio, F. Do Isopropylammonium Glyphosate and LiCl Impact the Spore Diversity and Functions of Aquatic Fungi Involved in Plant Litter Decomposition in Streams? J. Xenobiot. 2025, 15, 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox15030065
Rodrigues J, Gerós H, Côrte-Real M, Cássio F. Do Isopropylammonium Glyphosate and LiCl Impact the Spore Diversity and Functions of Aquatic Fungi Involved in Plant Litter Decomposition in Streams? Journal of Xenobiotics. 2025; 15(3):65. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox15030065
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodrigues, Jorge, Hernâni Gerós, Manuela Côrte-Real, and Fernanda Cássio. 2025. "Do Isopropylammonium Glyphosate and LiCl Impact the Spore Diversity and Functions of Aquatic Fungi Involved in Plant Litter Decomposition in Streams?" Journal of Xenobiotics 15, no. 3: 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox15030065
APA StyleRodrigues, J., Gerós, H., Côrte-Real, M., & Cássio, F. (2025). Do Isopropylammonium Glyphosate and LiCl Impact the Spore Diversity and Functions of Aquatic Fungi Involved in Plant Litter Decomposition in Streams? Journal of Xenobiotics, 15(3), 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox15030065







