Machine Learning Versus Simple Clinical Models for Cochlear Implant Outcome Prediction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Patient Cohort
2.2. Predictor Variables
- -
- Age at onset of hearing loss (years);
- -
- Duration of hearing loss (months);
- -
- Age at implantation (years);
- -
- Preoperative four-frequency pure tone average (4FPTA: 0.5 kHz, 1 kHz, 2 kHz, 4 kHz) of the implanted ear;
- -
- Preoperative word recognition score at 65 dB with hearing aids (WRS65(HA)) of the implanted ear;
- -
- Preoperative maximum word recognition score (WRSmax) of the implanted ear;
- -
- CI experience (defined as the time span between the implantation date and the WRS65(CI), with a minimum rehabilitation period of 12 months).
2.3. Data Preparation
2.4. Models
2.5. Model Evaluation and Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
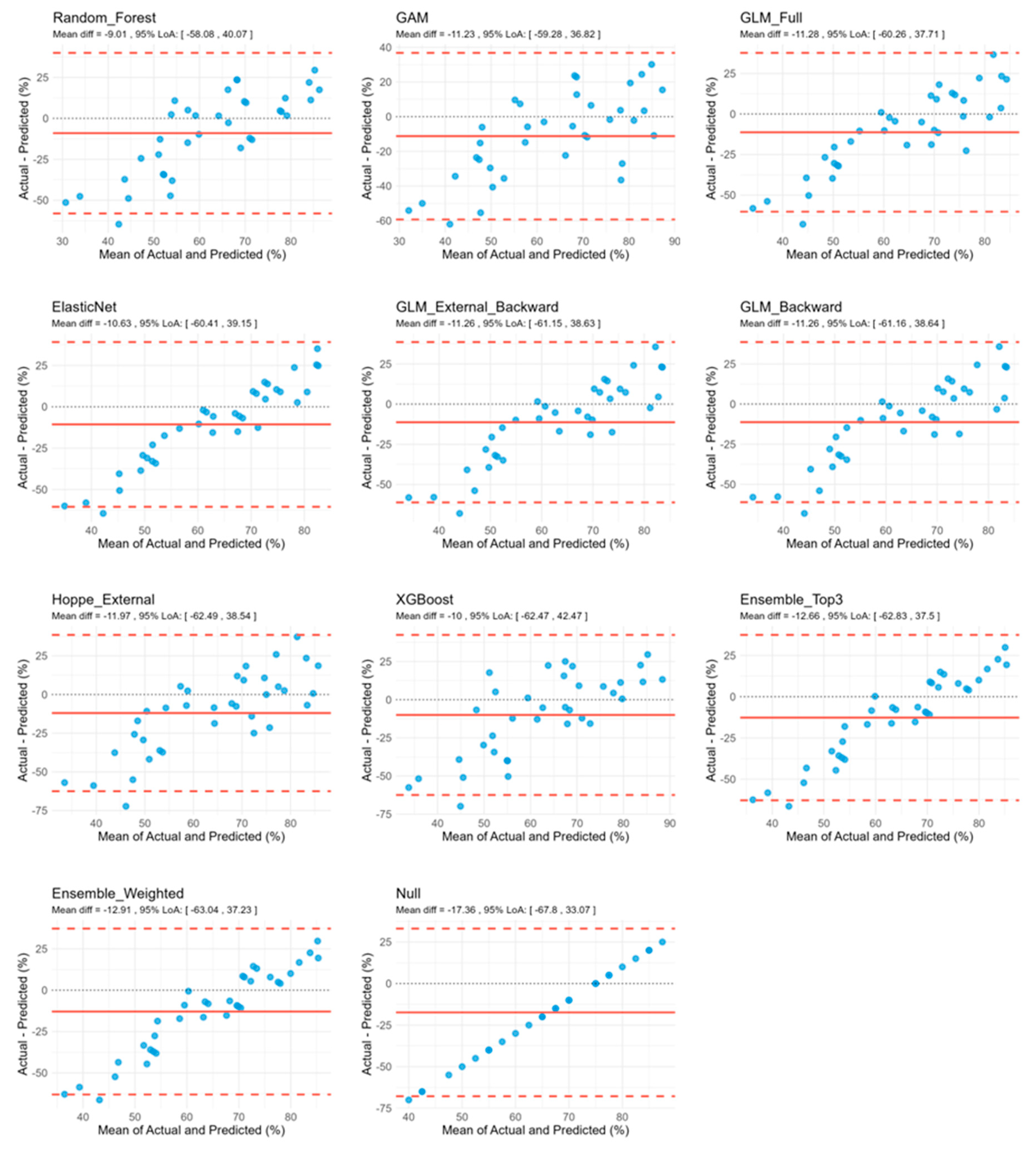
3.2. Model Performance Analysis
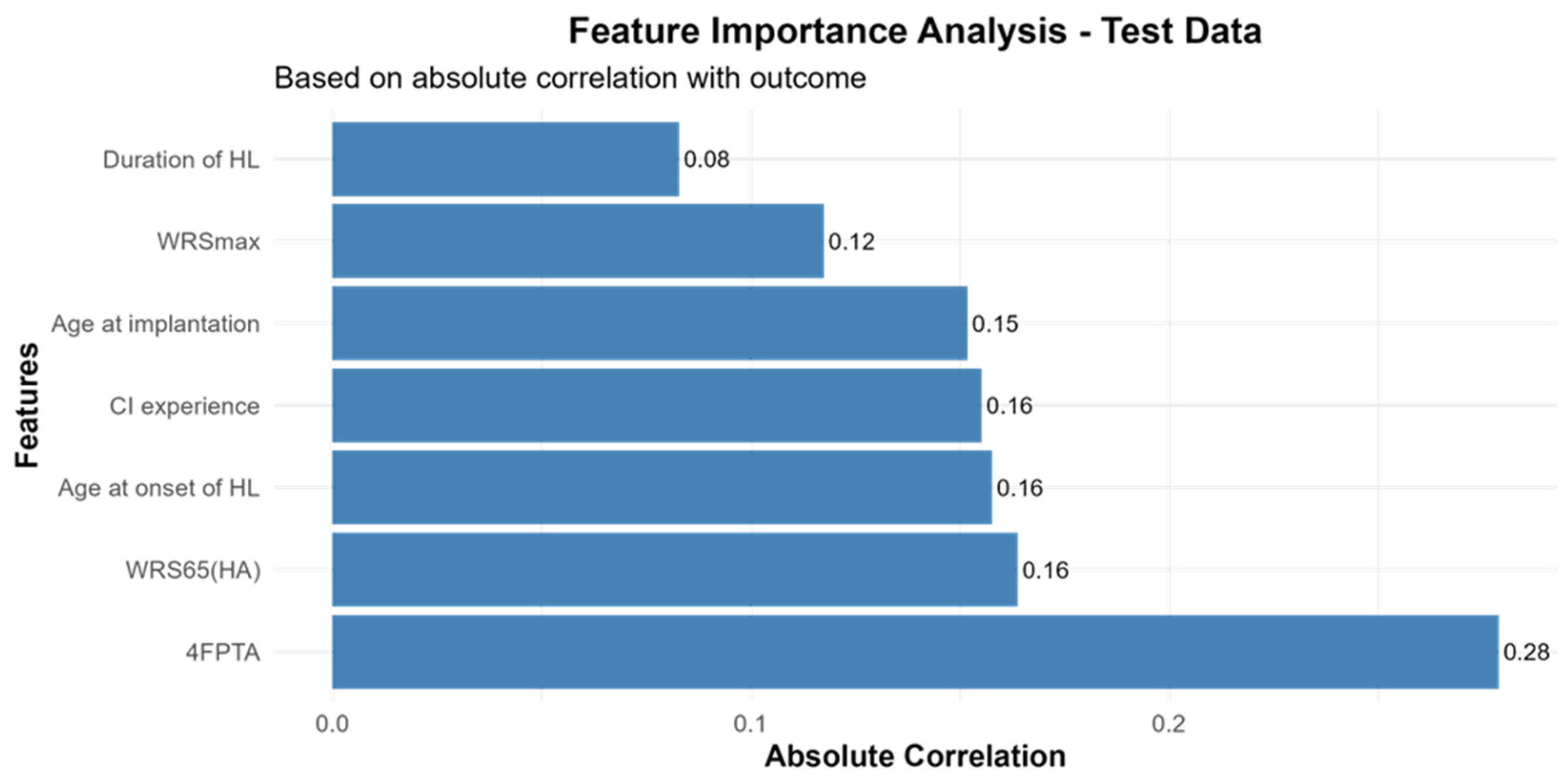
3.3. Feature Importance for CI-Outcome Predictions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- AWMF. S2k-Leitlinie Cochlea-Implantat Versorgung; AWMF-Register-Nr, 017/071; AWMF: Bradford, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kinney, S.E. Current Status of an Implantable Cochlear Pros thesis. Artif. Organs 1979, 3, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. World Report on Hearing; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- Blamey, P.; Artieres, F.; Baskent, D.; Bergeron, F.; Beynon, A.; Burke, E.; Dillier, N.; Dowell, R.; Fraysse, B.; Gallego, S.; et al. Factors affecting auditory performance of postlinguistically deaf adults using cochlear implants: An update with 2251 patients. Audiol. Neurootol. 2013, 18, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goudey, B.; Plant, K.; Kiral, I.; Jimeno-Yepes, A.; Swan, A.; Gambhir, M.; Buchner, A.; Kludt, E.; Eikelboom, R.H.; Sucher, C.; et al. A MultiCenter Analysis of Factors Associated with Hearing Outcome for 2,735 Adults with Cochlear Implants. Trends Hear. 2021, 25, 23312165211037525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazard, D.S.; Vincent, C.; Venail, F.; Van de Heyning, P.; Truy, E.; Sterkers, O.; Skarzynski, P.H.; Skarzynski, H.; Schauwers, K.; O’Leary, S.; et al. Pre-, per- and postoperative factors affecting performance of postlinguistically deaf adults using cochlear implants: A new conceptual model over time. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plant, K.; McDermott, H.; van Hoesel, R.; Dawson, P.; Cowan, R. Factors Predicting Postoperative Unilateral and Bilateral Speech Recognition in Adult Cochlear Implant Recipients with Acoustic Hearing. Ear Hear. 2016, 37, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roditi, R.E.; Poissant, S.F.; Bero, E.M.; Lee, D.J. A Predictive Model of Cochlear Implant Performance in Postlingually Deafened Adults. Otol. Neurotol. 2009, 30, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppe, U.; Hocke, T.; Hast, A.; Iro, H. Cochlear Implantation in Candidates With Moderate-to-Severe Hearing Loss and Poor Speech Perception. Laryngoscope 2021, 131, E940–E945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kang, W.S.; Park, H.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, J.W.; Kim, Y.; Seo, J.W.; Kwak, M.Y.; Kang, B.C.; Yang, C.J.; et al. Cochlear Implantation in Postlingually Deaf Adults is Time-sensitive Towards Positive Outcome: Prediction using Advanced Machine Learning Techniques. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 18004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowson, M.G.; Dixon, P.; Mahmood, R.; Lee, J.W.; Shipp, D.; Le, T.; Lin, V.; Chen, J.; Chan, T.C.Y. Predicting Postoperative Cochlear Implant Performance Using Supervised Machine Learning. Otol Neurotol. 2020, 41, e1013–e1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafieibavani, E.; Goudey, B.; Kiral, I.; Zhong, P.; Jimeno-Yepes, A.; Swan, A.; Gambhir, M.; Buechner, A.; Kludt, E.; Eikelboom, R.H.; et al. Predictive models for cochlear implant outcomes: Performance, generalizability, and the impact of cohort size. Trends Hear 2021, 25, 23312165211066174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziemba, O.C.; Merz, S.; Hocke, T. Evaluative audiometry after cochlear implant provision. HNO 2024, 72, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppe, U.; Hast, A.; Hornung, J.; Hocke, T. Evolving a Model for Cochlear Implant Outcome. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12 (Suppl. 1), 6215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heutink, F.; Verbist, B.M.; van der Woude, W.-J.; Meulman, T.J.; Briaire, J.J.; Frijns, J.H.M.; Vart, P.; Mylanus, E.A.M.; Huinck, W.J. Factors Influencing Speech Perception in Adults With a Cochlear Implant. Ear Hear. 2021, 42, 949–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoppe, U.; Hocke, T.; Hast, A.; Iro, H. Maximum monosyllabic score as a predictor for cochlear implant outcome. HNO 2019, 67, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thangavelu, K.; Nitzge, M.; Weiss, R.M.; Mueller-Mazzotta, J.; Stuck, B.A.; Reimann, K. Role of cochlear reserve in adults with cochlear implants following post-lingual hearing loss. Eur. Arch. OtoRhinoLaryngol. 2023, 280, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ollermann, R.; Böscke, R.; Neidhardt, J.; Radeloff, A. External Validation and Extension of a Cochlear Implant Performance Prediction Model: Analysis of the Oldenburg Cohort. Audiol. Res. 2025, 15, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. Generalized Additive Models. Stat. Sci. 1986, 1, 297–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Hastie, T. Regularization and variable selection via the elastic net. J. R. Statist. Soc. B 2005, 67, 301–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Bagging Predictors. Mach. Learn. 1996, 24, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, J. Greedy Function Approximation: A Gradient Boosting Machine. Ann. Stat. 2001, 29, 1189–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posit Team. RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R; Posit Software, PBC: Boston, MA, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Anthropic. Claude Sonnet 4.0 (Software). San Francisco, CA, USA. 2024. Available online: https://www.anthropic.com/claude/sonnet?utm_source=chatgpt.com (accessed on 20 October 2025).
- Shew, M.A.; Pavelchek, C.; Michelson, A.; Ortmann, A.; Lefler, S.; Walia, A.; Durakovic, N.; Phillips, A.; Rejepova, A.; Herzog, J.A.; et al. Machine Learning Feasibility in Cochlear Implant Speech Perception Outcomes-Moving Beyond Single Biomarkers for Cochlear Implant Performance Prediction. Ear Hear. 2025, 46, 1266–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demyanchuk, A.; Kludt, E.; Lenarz, T.; Buchner, A. A Machine Learning Model to Predict Postoperative Speech Recognition Outcomes in Cochlear Implant Recipients: Development, Validation, and Comparison with Expert Clinical Judgment. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.J.; Suh, M.W.; Park, M.K.; Koo, J.W.; Lee, J.H.; Oh, S.H. A Predictive Model for Cochlear Implant Outcome in Children with Cochlear Nerve Deficiency. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blamey, P.; Arndt, P.; Bergeron, F.; Bredberg, G.; Brimacombe, J.; Facer, G.; Larky, J.; Lindstrom, B.; Nedzelski, J.; Peterson, A.; et al. Factors affecting auditory performance of postlinguistically deaf adults using cochlear implants. Audiol. Neurootol. 1996, 1, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, F. A benchmarking crisis in biomedical machine learning. Nat. Med. 2025, 31, 1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | N | Median [Q1, Q3] | Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Duration of hearing loss (years) | 222 | 17 [9–28] | 1–80 |
| Age at implantation (years) | 236 | 63 [54–73] | 18–88 |
| CI experience (months) | 223 | 12 [12–24.25] | 10–140 |
| Preoperative 4FPTA of the implanted ear (dB HL) | 235 | 88.75 [80–96.25] | 63.75–112.5 |
| WRSmax (%) | 236 | 30 [15–50] | 5–100 |
| WRS65(HA) (%) | 236 | 15 [0–30] | 0–60 |
| WRS65(CI) (%) | 236 | 75 [55–80] | 5–100 |
| Model | RMSE | MAE | R2 | SD | Bias | Upper LoA | Lower LoA | Pb Slope | Pb Intercept | Correlation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Random_Forest | 26.28 | 20.62 | −0.073 | 25.04 | −9.01 | 40.07 | −58.08 | 0.094 | 61.25 | 0.248 |
| GAM | 26.66 | 21.20 | −0.104 | 24.52 | −11.23 | 36.82 | −59.28 | 0.177 | 58.66 | 0.327 |
| GLM_Full | 27.10 | 21.26 | −0.141 | 24.99 | −11.28 | 37.71 | −60.26 | 0.070 | 64.87 | 0.240 |
| ElasticNet | 27.20 | 21.23 | −0.150 | 25.40 | −10.63 | 39.15 | −60.41 | 0.027 | 66.73 | 0.161 |
| GLM_External_ Backward | 27.51 | 21.19 | −0.176 | 25.45 | −11.26 | 38.63 | −61.15 | 0.044 | 66.38 | 0.167 |
| GLM_Backward | 27.51 | 21.24 | −0.176 | 25.46 | −11.26 | 38.64 | −61.16 | 0.046 | 66.27 | 0.168 |
| Hoppe_External | 28.09 | 21.50 | −0.226 | 25.77 | −11.97 | 38.55 | −62.49 | 0.067 | 65.73 | 0.170 |
| XGBoost | 28.23 | 22.22 | −0.238 | 26.77 | −10.00 | 42.47 | −62.47 | 0.036 | 65.54 | 0.082 |
| Ensemble_Top3 | 28.23 | 21.97 | −0.238 | 25.59 | −12.66 | 37.50 | −62.83 | 0.020 | 69.17 | 0.115 |
| Ensemble_Weighted | 28.33 | 22.05 | −0.247 | 25.58 | −12.91 | 37.23 | −63.04 | 0.019 | 69.48 | 0.116 |
| Null | 30.74 | 23.75 | −0.468 | 25.73 | −17.36 | 33.07 | −67.80 | NaN | NaN | NA |
| Model | Mean RMSE Improvement [Lower CI, Upper CI] | p-Value | Mean MAE Improvement [Lower CI, Upper CI] | p-Value | Mean R2 Improvement [Lower CI, Upper CI] | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Random_Forest | 4.446 [1.395, 7.577] | 0.001 | 3.117 [−0.151, 6.416] | 0.031 | 0.406 [0.122, 0.711] | 0.001 |
| GAM | 4.063 [0.84, 7.199] | 0.01 | 2.554 [−0.892, 6.17] | 0.068 | 0.373 [0.084, 0.705] | 0.01 |
| GLM_Full | 3.617 [1.012, 5.927] | 0.003 | 2.454 [−0.39, 5.206] | 0.039 | 0.339 [0.091, 0.624] | 0.003 |
| ElasticNet | 3.51 [1.491, 5.342] | 0.001 | 2.486 [0.154, 4.831] | 0.02 | 0.331 [0.124, 0.583] | 0.001 |
| GLM_External_ Backward | 3.221 [0.955, 5.35] | 0.004 | 2.517 [0.022, 5.09] | 0.023 | 0.305 [0.085, 0.571] | 0.004 |
| GLM_Backward | 3.216 [0.872, 5.385] | 0.004 | 2.468 [−0.045, 5.074] | 0.032 | 0.304 [0.081, 0.575] | 0.004 |
| Hoppe_External | 2.658 [−0.219, 5.369] | 0.035 | 2.217 [−0.714, 5.078] | 0.06 | 0.253 [−0.018, 0.55] | 0.035 |
| XGBoost | 2.504 [−0.394, 5.315] | 0.047 | 1.498 [−1.954, 4.855] | 0.194 | 0.236 [−0.041, 0.51] | 0.047 |
| Ensemble_Top3 | 2.502 [0.941, 3.846] | 0 | 1.761 [−0.289, 3.705] | 0.043 | 0.239 [0.082, 0.42] | 0 |
| Ensemble_Weighted | 2.404 [0.94, 3.669] | 0 | 1.682 [−0.257, 3.532] | 0.041 | 0.23 [0.082, 0.403] | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ollermann, R.; Strodthoff, N.; Radeloff, A.; Böscke, R. Machine Learning Versus Simple Clinical Models for Cochlear Implant Outcome Prediction. Audiol. Res. 2025, 15, 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15060161
Ollermann R, Strodthoff N, Radeloff A, Böscke R. Machine Learning Versus Simple Clinical Models for Cochlear Implant Outcome Prediction. Audiology Research. 2025; 15(6):161. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15060161
Chicago/Turabian StyleOllermann, Rieke, Nils Strodthoff, Andreas Radeloff, and Robert Böscke. 2025. "Machine Learning Versus Simple Clinical Models for Cochlear Implant Outcome Prediction" Audiology Research 15, no. 6: 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15060161
APA StyleOllermann, R., Strodthoff, N., Radeloff, A., & Böscke, R. (2025). Machine Learning Versus Simple Clinical Models for Cochlear Implant Outcome Prediction. Audiology Research, 15(6), 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15060161





