Reuniting and Endolymphatic Duct Macrophages: Localization and Possible Roles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Image Analysis
2.3. Macrophage Populations
- The RD, ED and their associated vessels were segmented manually with ITK-SNAP from autofluorescence or vascular labeling signal stacks.
- ROI datasets were extracted with a custom FIJI (1.54p) script.
- Datasets were applied as mask to Iba1 signal image stacks, and ROIs were dilated to include surrounding macrophages.
- Macrophages were segmented from masked image stacks in a semi-automated way by thresholding the Iba1 signal and refining manually.
- Macrophage count was performed using the ImageJ (Version 1.54p) 3D Object counter.
- Tif stacks containing macrophage segmentations were loaded into MATLAB (Version R2021b) and binarized
- Macrophages were defined as objects using the bwlabeln function with 26 connectivity
- Macrophage volumes and convex hull volumes were measured with the regionprops3 function
- Small objects (<100 voxels) were removed with the function bwareaopen
- Large outliers deriving from segmentation artifacts were removed with rmoutlier
3. Results
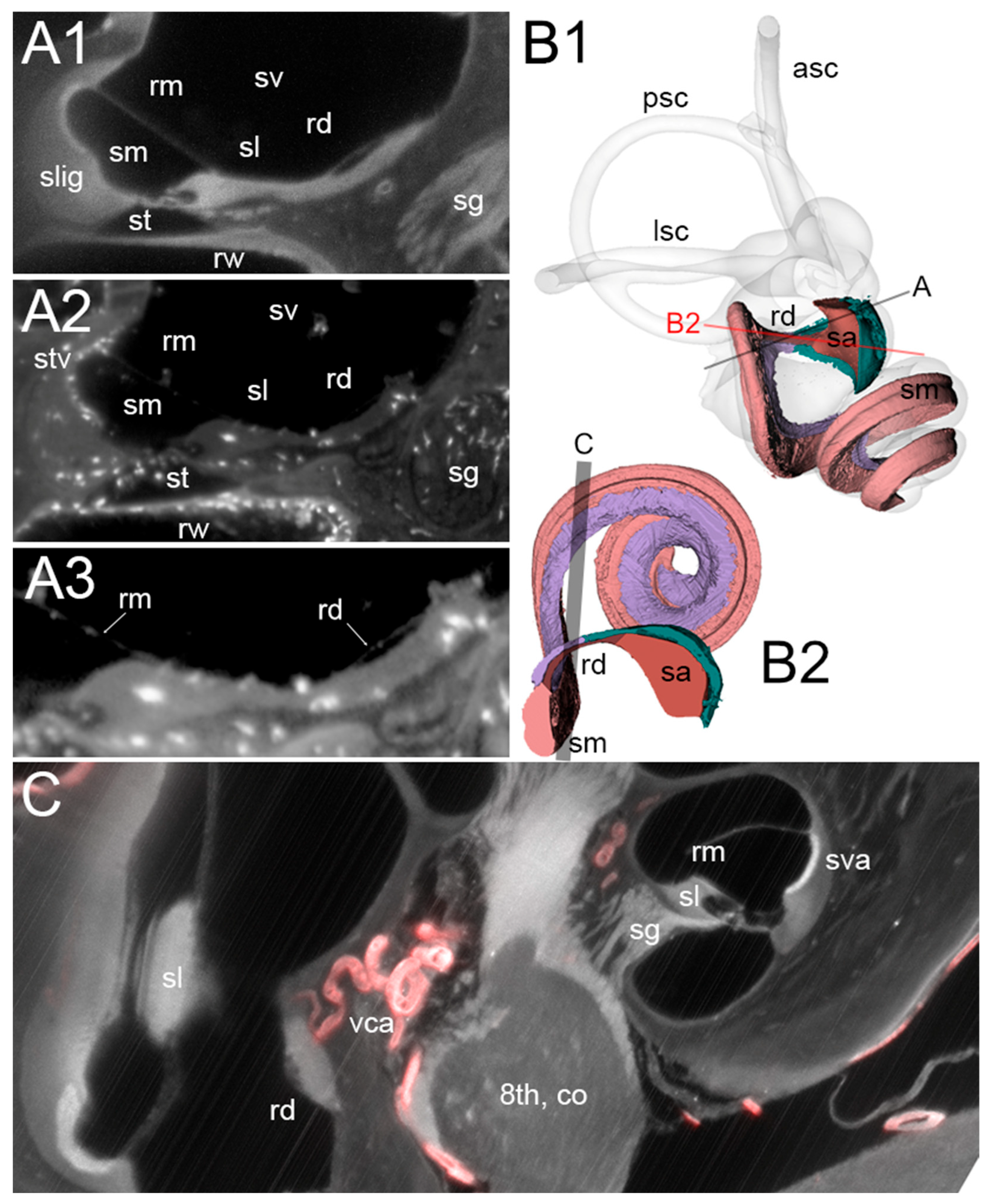
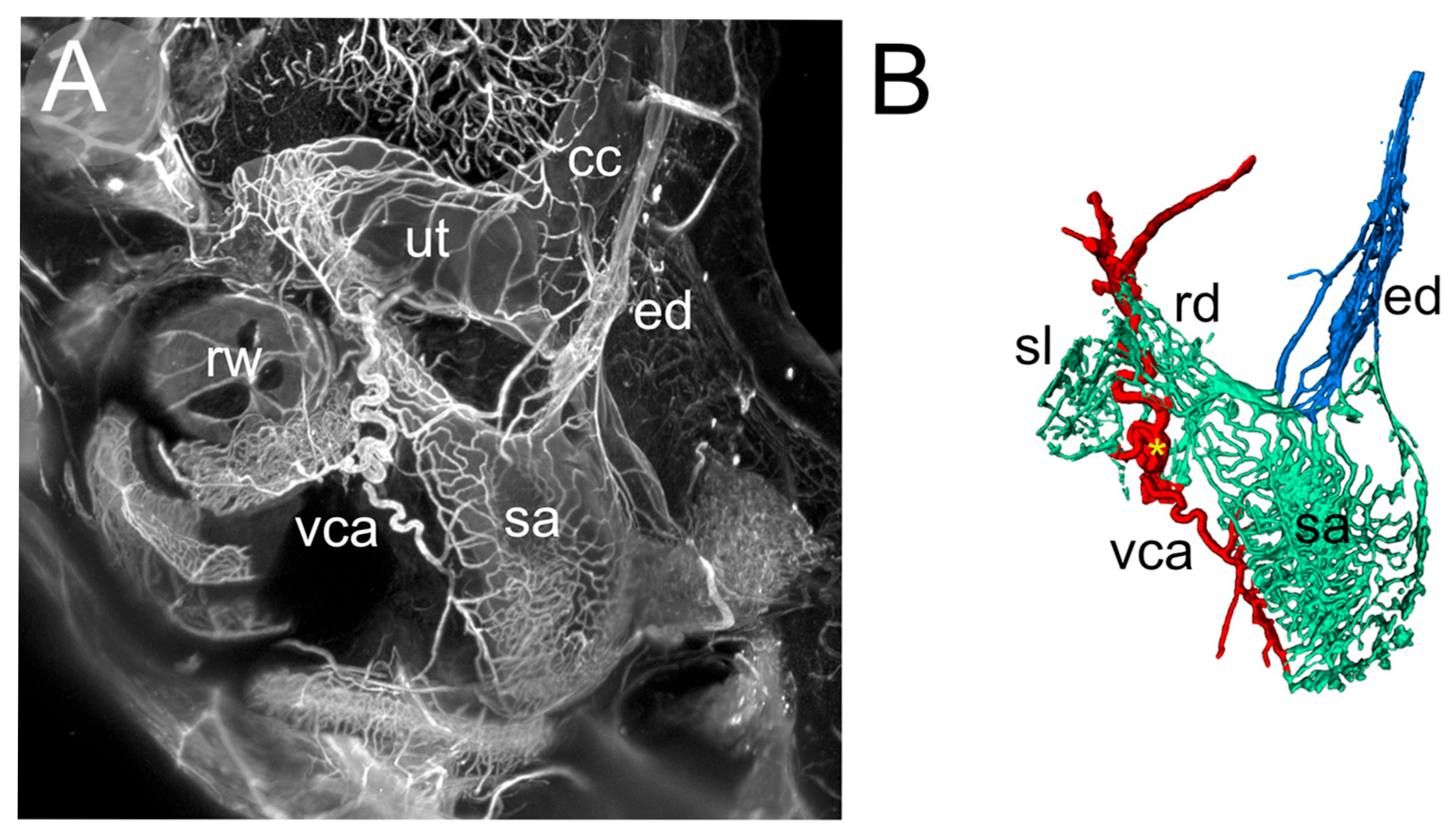
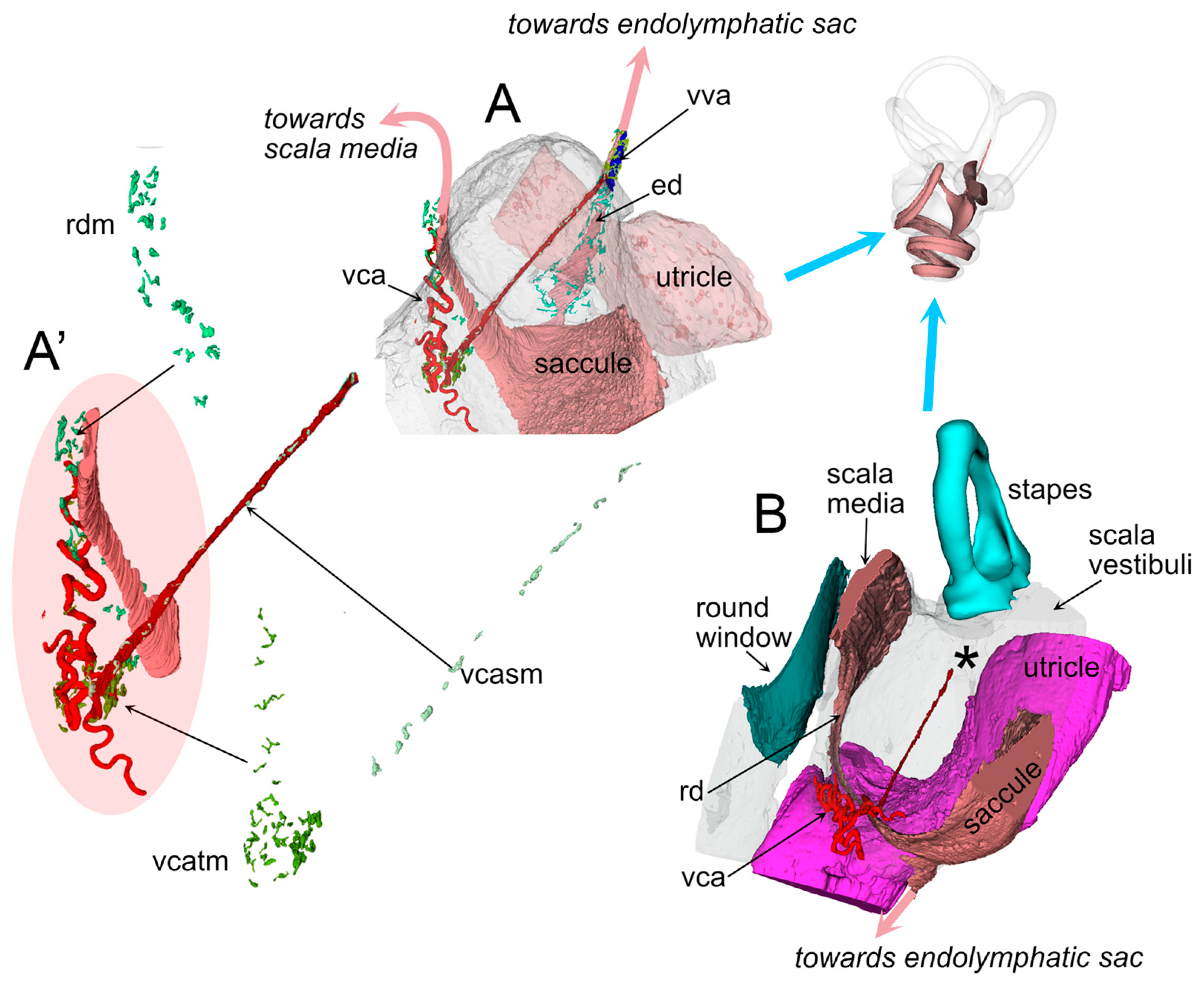
3.1. RD
3.2. ED
3.3. Macrophage Features
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BPPV | Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo |
| ColIV | Collagen IV |
| ED | Endolymphatic duct |
| MMP14 | Matrix metalloprotease 14 |
| RD | Reuniting duct |
| ROI | Region of interest |
| SMA | Smooth muscle actin |
| VCA | Vestibulocochlear artery |
References
- Konishi, S. The ductus reuniens and utriculo-endolymphatic valve in the presence of endolymphatic hydrops in guinea-pigs. J. Laryngol. Otol. 1977, 91, 1033–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, R.S.; Schuknecht, H.F.; Ota, C.Y.; Jones, D.D. Obliteration of the ductus reuniens. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 1980, 89, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamane, H.; Takayama, M.; Sunami, K.; Sakamoto, H.; Imoto, T.; Anniko, M. Blockage of reuniting duct in Meniere’s disease. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2010, 130, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamane, H.; Sunami, K.; Iguchi, H.; Sakamoto, H.; Imoto, T.; Rask-Andersen, H. Assessment of Meniere’s disease from a radiological aspect-saccular otoconia as a cause of Meniere’s disease? Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2012, 132, 1054–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornibrook, J.; Bird, P. A New Theory for Ménière’s Disease: Detached Saccular Otoconia. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2017, 156, 350–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornibrook, J. Saccular otoconia as a cause of Ménière’s disease: Hypothesis based on two theories. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2018, 132, 771–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornibrook, J.; Mudry, A.; Curthoys, I.; Smith, C.M. Ductus Reuniens and Its Possible Role in Menière’s Disease. Otol. Neurotol. 2021, 42, 1585–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Rajan, G.P.; Shaw, J.; Rohani, S.A.; Ladak, H.M.; Agrawal, S.; Rask-Andersen, H. A Synchrotron and Micro-CT Study of the Human Endolymphatic Duct System: Is Meniere’s Disease Caused by an Acute Endolymph Backflow? Front. Surg. 2021, 8, 662530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez De Linera-Alperi, M.; Dominguez, P.; Blanco-Pareja, M.; Menéndez Fernández-Miranda, P.; Manrique-Huarte, R.; Liaño, G.; Pérez-Fernández, N.; Suárez-Vega, V. Is endolymphatic hydrops, as detected in MRI, a truly cochleocentric finding? Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1477282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quick, M.E.; Bird, P.A. A review of Meniere’s disease-reflection of published MRI, ECochG and newer otoconial theory from Aotearoa New Zealand. J. R. Soc. N. Z. 2025, 55, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.M.; Curthoys, I.S.; Plontke, S.K.; Menzel, M.; Mukherjee, P.; Wong, C.; Laitman, J.T. Insights into Inner Ear Function and Disease Through Novel Visualization of the Ductus Reuniens, a Seminal Communication Between Hearing and Balance Mechanisms. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. JARO 2022, 23, 633–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamane, H.; Takayama, M.; Sunami, K.; Sakamoto, H.; Imoto, T.; Anniko, M. Visualization and assessment of saccular duct and endolymphatic sinus. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2011, 131, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Susaki, E.A. Unlocking the potential of large-scale 3D imaging with tissue clearing techniques. Microsc. Oxf. Engl. 2025, 74, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossellu, D.; Vivado, E.; Batti, L.; Gantar, I.; Pizzala, R.; Perin, P. Volumetric atlas of the rat inner ear from microCT and iDISCO+ cleared temporal bones. PeerJ 2025, 13, e19512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perin, P.; Voigt, F.F.; Bethge, P.; Helmchen, F.; Pizzala, R. iDISCO+ for the Study of Neuroimmune Architecture of the Rat Auditory Brainstem. Front. Neuroanat. 2019, 13, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perin, P.; Rossetti, R.; Ricci, C.; Cossellu, D.; Lazzarini, S.; Bethge, P.; Voigt, F.F.; Helmchen, F.; Batti, L.; Gantar, I.; et al. 3D Reconstruction of the Clarified Rat Hindbrain Choroid Plexus. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 692617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perin, P.; Cossellu, D.; Vivado, E.; Batti, L.; Gantar, I.; Voigt, F.F.; Pizzala, R. Temporal bone marrow of the rat and its connections to the inner ear. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1386654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frejo, L.; Lopez-Escamez, J.A. Cytokines and Inflammation in Meniere Disease. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2022, 15, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Escamez, J.A.; Perez-Carpena, P. Update on the pathophysiology, diagnosis and management of Ménière’s disease. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2024, 32, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frejo, L.; Cara, F.E.; Flook, M.; Robles-Bolivar, P.; Escalera-Balsera, A.; Montilla-Ibañez, M.A.; Dominguez-Duran, E.; Martinez-Martinez, M.; Perez-Carpena, P.; Lopez-Escamez, J.A. Allergy and autoinflammation drive persistent systemic inflammatory response in Meniere Disease: A longitudinal study. Clin. Immunol. 2025, 271, 110413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, V.G.; Xia, A.; Santa Maria, P.L. Immunological mechanisms in Meniere’s disease. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1639916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkerson, B.A.; Zebroski, H.L.; Finkbeiner, C.R.; Chitsazan, A.D.; Beach, K.E.; Sen, N.; Zhang, R.C.; Bermingham-McDonogh, O. Novel cell types and developmental lineages revealed by single-cell RNA-seq analysis of the mouse crista ampullaris. eLife 2021, 10, e60108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Malley, J.T.; Nadol, J.B.; McKenna, M.J. Anti CD163+, Iba1+, and CD68+ Cells in the Adult Human Inner Ear: Normal Distribution of an Unappreciated Class of Macrophages/Microglia and Implications for Inflammatory Otopathology in Humans. Otol. Neurotol. 2016, 37, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keithley, E.M. Inner ear immunity. Hear. Res. 2022, 419, 108518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hough, K.; Verschuur, C.A.; Cunningham, C.; Newman, T.A. Macrophages in the Cochlea; an Immunological Link between Risk Factors and Progressive Hearing Loss. Glia 2022, 70, 219–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, B.; Rask-Andersen, H. Osmotically induced macrophage activity in the endolymphatic sac. On the possible interaction between periaqueductal bone marrow cells and the endolymphatic sac. ORL 1992, 54, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Kurata, N.; Fukunaga, Y. Tissue-Resident Macrophages in the Stria Vascularis. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 818395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imoto, T.; Rask-Andersen, H.; Bagger-Sjöbäck, D. The role of the endolymphatic sac in statoconial formation and degradation. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 1983, 96, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renier, N.; Wu, Z.; Simon, D.J.; Yang, J.; Ariel, P.; Tessier-Lavigne, M. iDISCO: A simple, rapid method to immunolabel large tissue samples for volume imaging. Cell 2014, 159, 896–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barozzi, S.; Soi, D.; Intieri, E.; Giani, M.; Aldè, M.; Tonon, E.; Signorini, L.; Renieri, A.; Fallerini, C.; Perin, P.; et al. Vestibular and audiological findings in the Alport syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2020, 182, 2345–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voigt, F.F.; Kirschenbaum, D.; Platonova, E.; Pagès, S.; Campbell, R.A.A.; Kastli, R.; Schaettin, M.; Egolf, L.; van der Bourg, A.; Bethge, P.; et al. The mesoSPIM initiative: Open-source light-sheet microscopes for imaging cleared tissue. Nat Methods. 2019, 16, 1105–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yushkevich, P.A.; Gao, Y.; Gerig, G. ITK-SNAP: An interactive tool for semi-automatic segmentation of multi-modality biomedical images. In Proceedings of the 2016 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 August 2016; Volume 2016, pp. 3342–3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleiss, J.L. Measuring nominal scale agreement among many raters. Psychol. Bull. 1971, 76, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnitzerlein, M.; Greto, E.; Wegner, A.; Möller, A.; Aust, O.; Ben Brahim, O.; Blumenthal, D.B.; Zaburdaev, V.; Uderhardt, S. Cellular morphodynamics as quantifiers for functional states of resident tissue macrophages in vivo. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2025, 21, e1011859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulya, A.J. Anatomy of the Temporal Bone with Surgical Implications, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlmann, A.; von Düring, M. The endolymphatic duct and sac of the rat: A histological, ultrastructural, and immunocytochemical investigation. Cell Tissue Res. 1995, 282, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perin, P.; Marino, F.; Varela-Nieto, I.; Szczepek, A.J. Editorial: Neuroimmunology of the Inner Ear. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 635359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stothert, A.R.; Kaur, T. Innate Immunity to Spiral Ganglion Neuron Loss: A Neuroprotective Role of Fractalkine Signaling in Injured Cochlea. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 694292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manickam, V.; Gawande, D.Y.; Stothert, A.R.; Clayman, A.C.; Batalkina, L.; Warchol, M.E.; Ohlemiller, K.K.; Kaur, T. Macrophages Promote Repair of Inner Hair Cell Ribbon Synapses following Noise-Induced Cochlear Synaptopathy. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2023, 43, 2075–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Wang, K.; Qu, J.; Chen, D.; Chen, A.; You, Y.; Tang, J.; Zhang, H. Activated tissue-resident macrophages contribute to hair cell insults in noise-induced hearing loss in mice. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansson, B.; Rask-Andersen, H. Erythrocyte removal and blood clearance in the endolymphatic sac: An experimental and TEM study. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 1996, 116, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiot, A.; Felgner, M.J.; Brownell, D.; Rott, K.H.; Bogachuk, A.; Rosmus, D.-D.; Masuda, T.; Ching, A.; Atkinson, P.J.; Prinz, M.; et al. Single-cell, spatial, and fate-mapping analyses uncover niche dependent diversity of cochlear myeloid cells. bioRxiv 2024, preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, Y.; Ohsawa, K.; Kanazawa, H.; Kohsaka, S.; Imai, Y. Iba1 is an actin-cross-linking protein in macrophages/microglia. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 286, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, X.; Schart-Morén, N.; Li, H.; Ladak, H.M.; Agrawal, S.; Behr, R.; Rask-Andersen, H. Three-dimensional imaging of the human internal acoustic canal and arachnoid cistern: A synchrotron study with clinical implications. J. Anat. 2019, 234, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhong, A.; Wang, M.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, L. Mechanosensitive Piezo1 protein as a novel regulator in macrophages and macrophage-mediated inflammatory diseases. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1149336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Hang, L. Mechanical gated ion channel Piezo1: Function, and role in macrophage inflammatory response. Innate Immun. 2024, 30, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundberg, Y.W.; Zhao, X.; Yamoah, E.N. Assembly of the otoconia complex to the macular sensory epithelium of the vestibule. Brain Res. 2006, 1091, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, W.T.K.; Parnes, L.S.; Chole, R.A. Otoconia and otolithic membrane fragments within the posterior semicircular canal in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Laryngoscope 2017, 127, 709–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, D.J. Formation and fate of the otoconia: Scanning and transmission electron microscopy. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1973, 82, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickman, J.D.; Huss, D.; Lowe, M. Morphometry of otoconia in the utricle and saccule of developing Japanese quail. Hear. Res. 2004, 188, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lins, U.; Farina, M.; Kurc, M.; Riordan, G.; Thalmann, R.; Thalmann, I.; Kachar, B. The otoconia of the guinea pig utricle: Internal structure, surface exposure, and interactions with the filament matrix. J. Struct. Biol. 2000, 131, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucca, G.; Valli, S.; Valli, P.; Perin, P.; Mira, E. Why do benign paroxysmal positional vertigo episodes recover spontaneously? J. Vestib. Res. Equilib. Orientat. 1998, 8, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, H.; Hunt, M.A.; Kurtović, Z.; Sandor, K.; Kägy, P.B.; Fereydouni, N.; Julien, A.; Göritz, C.; Vazquez-Liebanas, E.; Mäe, M.A.; et al. CD163+ macrophages monitor enhanced permeability at the blood-dorsal root ganglion barrier. J. Exp. Med. 2024, 221, e20230675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Sample | Age (Days) | Sex | Signal | Voxel Size (µm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1a,b | 111 | F | Auto, Iba1 | 2 |
| R2 | 95 | F | Auto, Iba1 | 2 |
| R3 | 494 | M | Auto, SMA | 3.26 |
| R4 | 79 | M | ColIV | 4.08 |
| Solidity | Volume | Radius (um) | Number | Region |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 ± 0.2 | 5393 ± 3059 | 10.5 ± 2.0 | 301 | All |
| 0.4 ± 0.2 | 6066 ± 2885 | 11.0 ± 1.7 | 56 | Endolymphatic sinus |
| 0.7 ± 0.1 | 8266 ± 4385 | 12.2 ± 2.1 | 51 | ED |
| 0.5 ± 0.1 | 7267 ± 3785 | 11.7 ± 2.0 | 18 | RD |
| 0.5 ± 0.2 | 3748 ± 2162 | 9.3 ± 1.8 | 48 | VCA |
| 0.6 ± 0.2 | 8122 ± 4440 | 12.1 ± 2.2 | 63 | VVA |
| 0.7 ± 0.1 | 7404 ± 3218 | 11.9 ± 1.7 | 65 | Vestibular aqueduct |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vivado, E.; Cossellu, D.; Perin, P. Reuniting and Endolymphatic Duct Macrophages: Localization and Possible Roles. Audiol. Res. 2025, 15, 160. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15060160
Vivado E, Cossellu D, Perin P. Reuniting and Endolymphatic Duct Macrophages: Localization and Possible Roles. Audiology Research. 2025; 15(6):160. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15060160
Chicago/Turabian StyleVivado, Elisa, Daniele Cossellu, and Paola Perin. 2025. "Reuniting and Endolymphatic Duct Macrophages: Localization and Possible Roles" Audiology Research 15, no. 6: 160. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15060160
APA StyleVivado, E., Cossellu, D., & Perin, P. (2025). Reuniting and Endolymphatic Duct Macrophages: Localization and Possible Roles. Audiology Research, 15(6), 160. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15060160






