Manifestation of Congenital CMV-Related Hearing Loss in Cohort Followed at Ear, Nose, and Throat Clinic
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Assessment Variables and Follow-Up Periods
2.3. Audiometric Function Tests
2.3.1. Auditory Brainstem Responses (ABRs)
2.3.2. Conditioned Orientation Reflex Responses (CORs)
2.3.3. Pure Tone Audiometries (PTAs) Including Play Audiometries
2.4. Definitions
2.4.1. Hearing Loss Laterality
2.4.2. Hearing Loss Severity
2.4.3. Hearing Loss Progression
2.4.4. Symptomatic cCMV Infection and cCMV Infection with Isolated Hearing Loss
2.4.5. Congenital Hearing Loss and Later Onset Hearing Loss
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
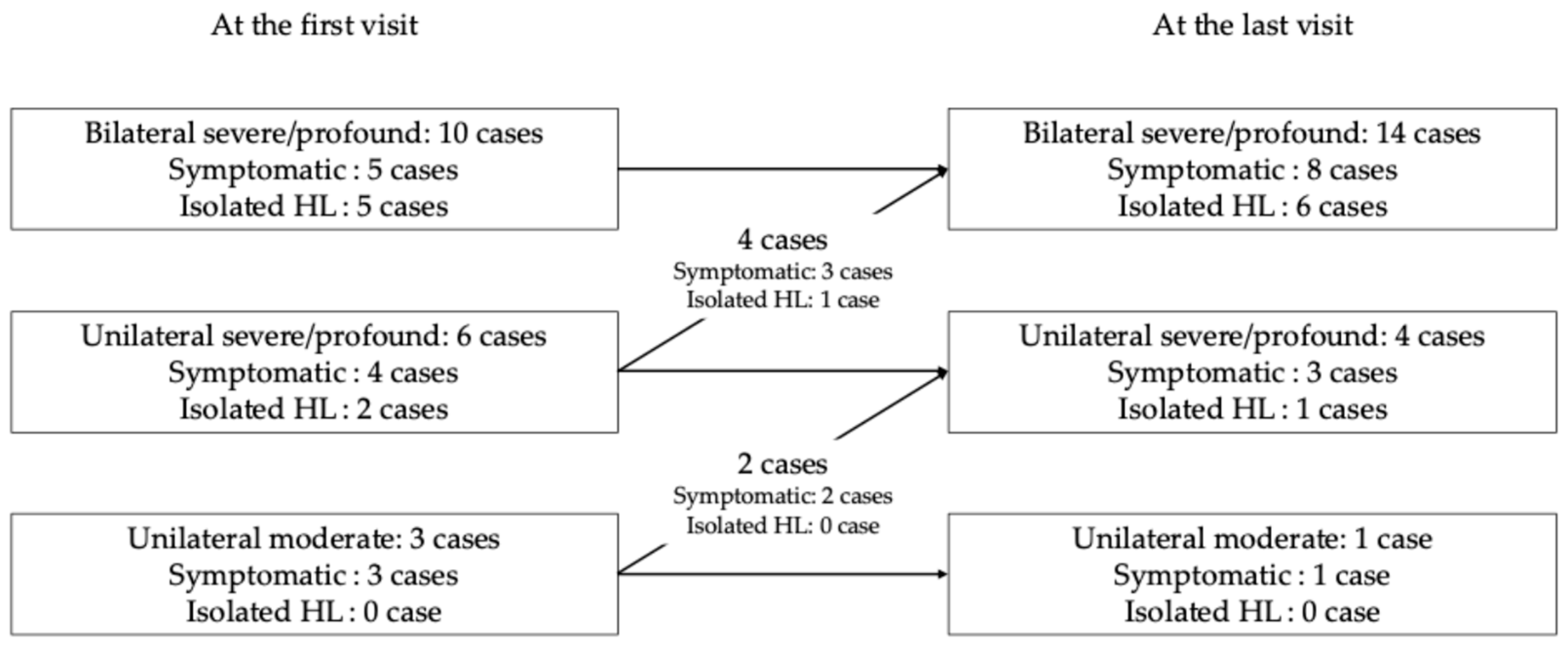
3.1. Hearing Loss at the First Visit Among Patients with Congenital Hearing Loss
3.2. Hearing Loss at the Last Visit
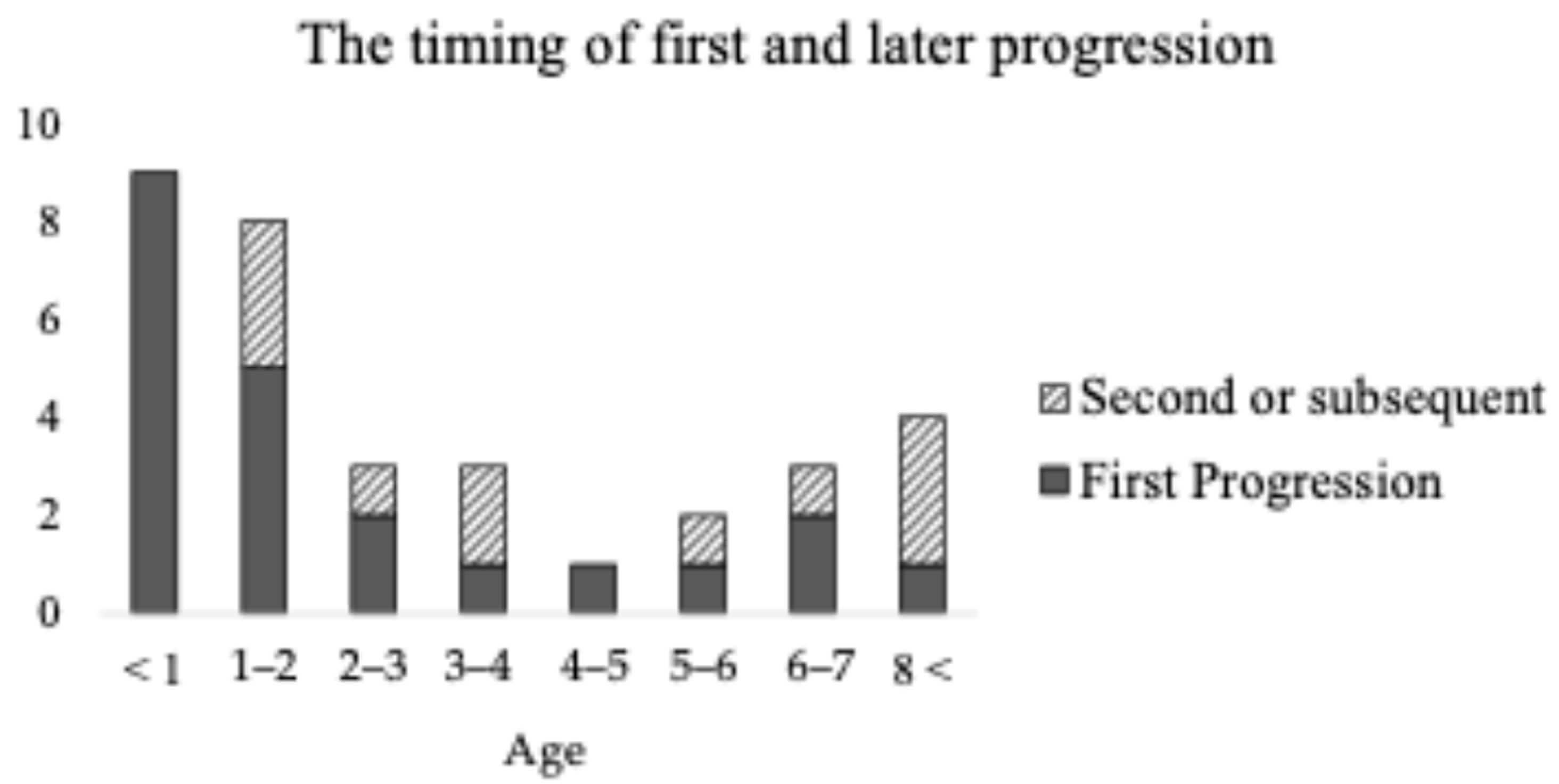
3.3. Progression Timing
3.4. Intellectual Disability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CMV | Cytomegalovirus |
| ID | Intellectual Disability |
References
- Adachi, N.; Ito, K.; Sakata, H.; Yamasoba, T. Etiology and one-year follow-up results of hearing loss identified by screening of newborn hearing in Japan. Otolaryngol. Head. Neck Surg. 2010, 143, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, C.C.; Nance, W.E. Newborn Hearing Screening—A Silent Revolution. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 2151–2164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Foulon, I.; Naessens, A.; Foulon, W.; Casteels, A.; Gordts, F. A 10-year prospective study of sensorineural hearing loss in children with congenital cytomegalovirus infection. J. Pediatr. 2008, 153, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, K.B.; Dable, A.J.; Boppana, S.B.; Pass, R.F. Newborn hearing screening: Will children with hearing loss caused by congenital cytomegalovirus infection be missed? J. Pediatr. 1999, 135, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, K.B.; McCollister, F.P.; Dahle, A.J.; Boppana, S.; Britt, W.J.; Pass, R.F. Progressive and fluctuating sensorineural hearing loss in children with asymptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus infection. J. Pediatr. 1997, 130, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahle, A.J.; Fowler, K.B.; Wright, J.D.; Boppana, S.B.; Britt, W.J.P.R. Longitudinal investigation of hearing disorders in children with congenital cytomegalovirus. J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 2000, 11, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carraro, M.; Almishaal, A.; Hillas, E.; Firpo, M.; Park, A.; Harrison, R.V. Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Infection Causes Degeneration of Cochlear Vasculature and Hearing Loss in a Mouse Model. JARO—J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2017, 18, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Shi, K.; Nielson, C.; Graham, E.M.; Price, M.S.; Haller, T.J.; Carraro, M.; Firpo, M.A.; Park, A.H.; Harrison, R.V. Hearing loss caused by CMV infection is correlated with reduced endocochlear potentials caused by strial damage in murine models. Hear. Res. 2022, 417, 108454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shi, X.; Qiao, Y.; Xu, K.; Zeng, L.; Wang, C.; Xu, Z.; Niu, H. Observation of permeability of blood-labyrinth barrier during cytomegalovirus-induced hearing loss. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2014, 78, 995–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Zhang, S.; Yang, J. Coexistence of IL-6 -572C/G and ICAM-1 K469E polymorphisms among patients with sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2018, 245, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, R.D.; Yoo, Y.G.; Golemac, M.; Pugel, E.P.; Jonjic, S.; Britt, W.J. Murine CMV-Induced Hearing Loss Is Associated with Inner Ear Inflammation and Loss of Spiral Ganglia Neurons. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, W.; Wang, C.; Shi, X.; Qiu, S.; Zhang, S.; Xu, B.; Chen, M.; Jiang, W.; Dong, H.; Qiao, Y. MCMV triggers ROS/NLRP3-associated inflammasome activation in the inner ear of mice and cultured spiral ganglion neurons, contributing to sensorineural hearing loss. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 3448–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiura, S.; Yoshikawa, T.; Nishiyama, Y.; Morishita, Y.; Sato, E.; Hattori, T.; Nakashima, T. Detection of human cytomegalovirus DNA in perilymph of patients with sensorineural hearing loss using real-time PCR. J. Med. Virol. 2003, 69, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corazzi, V.; Fordington, S.; Brown, T.H.; Donnelly, N.; Bewick, J.; Ehsani, D.; Pelucchi, S.; Bianchini, C.; Ciorba, A.; Borsetto, D. Late-onset, progressive sensorineural hearing loss in the paediatric population: A systematic review. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2024, 281, 3397–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanzieri, T.M.; Chung, W.; Flores, M.; Blum, P.; Caviness, A.C.; Bialek, S.R.; Grosse, S.D.; Miller, J.A.; Demmler-Harrison, G.; Congenital Cytomegalovirus Longitudinal Study Group. Hearing loss in children with asymptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus infection. Pediatrics 2017, 139, e20162610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goderis, J.; De Leenheer, E.; Smets, K.; Van Hoecke, H.; Keymeulen, A.; Dhooge, I. Hearing loss and congenital CMV infection: A systematic review. Pediatrics 2014, 134, 972–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrecillas, V.; Allen, C.M.; Greene, T.; Park, A.; Chung, W.; Lanzieri, T.M.; Demmler-Harrison, G. Should You Follow the Better-Hearing Ear for Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection and Isolated Sensorineural Hearing Loss? Otolaryngol—Head Neck Surg. 2020, 162, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldè, M.; Caputo, E.; Di Berardino, F.; Ambrosetti, U.; Barozzi, S.; Piatti, G.; Zanetti, D.; Pignataro, L.; Cantarella, G. Hearing outcomes in children with congenital cytomegalovirus infection: From management controversies to lack of parents’ knowledge. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2023, 164, 111420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapasak, B.; Cronkite, D.A.; Hustedt-Mai, A.R.; Morlet, T.M.; Parkes, W.J.; Maul, T.M.; Pritchett, C.V. Hearing outcomes in children with Congenital Cytomegalovirus: A multi-center, single-enterprise experience. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2022, 163, 111376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stagno, S. Cytomegalovirus. In Infectious Diseases of the Fetus and Newborn Infant, 4th ed.; Remington, J.S., Klein, J.O., Eds.; W.B. Saunders Co.: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1995; pp. 312–353. [Google Scholar]
- Kabani, N.; Ross, S.A. Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 221, S9–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimberlin, D.W.; Jester, P.M.; Sánchez, P.J.; Ahmed, A.; Arav-Boger, R.; Michaels, M.G.; Ashouri, N.; Englund, J.A.; Estrada, B.; Jacobs, R.F.; et al. Valganciclovir for symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 933–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Rosal, T.; Baquero-Artigao, F.; Blázquez, D.; Noguera-Julian, A.; Moreno-Pérez, D.; Reyes, A.; Vilas, J. Treatment of symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus infection beyond the neonatal period. J. Clin. Virol. 2012, 55, 72–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimberlin, D.W.; Lin, C.-Y.; Sánchez, P.J.; Demmler, G.J.; Dankner, W.; Shelton, M.; Jacobs, R.F.; Vaudry, W.; Pass, R.F.; Kiell, J.M.; et al. Effect of ganciclovir therapy on hearing in symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus disease involving the central nervous system: A randomized, controlled trial. J. Pediatr. 2003, 143, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goderis, J.; Keymeulen, A.; Smets, K.; Van Hoecke, H.; De Leenheer, E.; Boudewyns, A.; Desloovere, C.; Kuhweide, R.; Muylle, M.; Royackers, L.; et al. Hearing in Children with Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection: Results of a Longitudinal Study. J. Pediatr. 2016, 172, 110–115.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No. | Age at First Visit | Onset | Symptomatic | ID | Treatment Age | Treatment Duration | Sex | Hearing at Last Visit | Progression |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5 mos. | Congenital | Symptomatic | Yes | 1 mo. | 6 mos. | F | Unilateral profound and unilateral moderate | Yes |
| 2 | 2 mos. | Later onset | Symptomatic | Yes | 3 wks. | 6 mos. | F | Unilateral severe | Yes |
| 3 | 17 y.o. | Unknown | Symptomatic | Yes | 6 yrs. | 6 mos. | M | Bilateral profound | Yes |
| 4 | 2 mos. | Congenital | Isolated HL | No | 1 mo. | 6 mos. | M | Unilateral profound | No |
| 5 | 6 mos. | Congenital | Symptomatic | Yes | 3 wks. | 6 mos. | F | Unilateral profound | No |
| 6 | 4 mos. | Congenital | Symptomatic | Yes | 1 mo. | 6 mos. | M | Unilateral profound | Yes |
| 7 | 1 mo. | Later onset | Symptomatic | No | 3 mos. | 6 mos. | M | Unilateral moderate | Yes |
| 8 | 1 yr. 3 mos. | Congenital | Symptomatic | Yes | 1 wk. | 6 mos. | M | Unilateral moderate | Yes |
| 9 | 5 mos. | Congenital | Symptomatic | Yes | 3 wks. | 6 mos. | F | Bilateral profound | Yes |
| 10 | 2 yrs. 3 mos. | Congenital | Symptomatic | Yes | 3 wks. | 1 mo. | M | Bilateral profound | Yes |
| 11 | 4 yrs. 0 mo. | Congenital | Isolated HL | No | 1 mo. | 6 wks | F | Bilateral severe | Yes |
| Bilateral Severe/Profound (n, %) | Other Bilateral (n, %) | Unilateral (n, %) | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Congenital | 14 (74) | 1 (5) | 4 (21) | 19 |
| Symptomatic | 8 (67) | 1 (8) | 3 (25) | 12 |
| Isolated HL | 6 (86) | 0 (0) | 1 (14) | 7 |
| Later onset | 8 (62) | 1 (8) | 4 (31) | 13 |
| Symptomatic | 2 (40) | 1 (20) | 2 (40) | 5 |
| Isolated HL | 6 (75) | 0 (0) | 2 (25) | 8 |
| Unknown onset | 3 (75) | 0 (0) | 1 (25) | 4 |
| Symptomatic | 2 (100) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 |
| Isolated HL | 1 (50) | 0 (0) | 1 (50) | 2 |
| Total | 25 (69) | 2 (6) | 9 (25) | 36 |
| Symptomatic | 12 (63) | 2 (11) | 5 (26) | 19 |
| Isolated HL | 13 (76) | 0 (0) | 4 (24) | 17 |
| With ID (n, %) | Without ID (n, %) | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Congenital hearing loss | 11 (79) | 3 (21) | 14 |
| Later onset hearing loss | 8 (44) | 10 (56) | 18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koyama, H.; Kashio, A.; Kamogashira, T.; Sakata, A.; Urata, S.; Mori, A.; Kondo, K. Manifestation of Congenital CMV-Related Hearing Loss in Cohort Followed at Ear, Nose, and Throat Clinic. Audiol. Res. 2025, 15, 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15050139
Koyama H, Kashio A, Kamogashira T, Sakata A, Urata S, Mori A, Kondo K. Manifestation of Congenital CMV-Related Hearing Loss in Cohort Followed at Ear, Nose, and Throat Clinic. Audiology Research. 2025; 15(5):139. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15050139
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoyama, Hajime, Akinori Kashio, Teru Kamogashira, Aki Sakata, Shinji Urata, Anjin Mori, and Kenji Kondo. 2025. "Manifestation of Congenital CMV-Related Hearing Loss in Cohort Followed at Ear, Nose, and Throat Clinic" Audiology Research 15, no. 5: 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15050139
APA StyleKoyama, H., Kashio, A., Kamogashira, T., Sakata, A., Urata, S., Mori, A., & Kondo, K. (2025). Manifestation of Congenital CMV-Related Hearing Loss in Cohort Followed at Ear, Nose, and Throat Clinic. Audiology Research, 15(5), 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15050139






