Assessing the Nutritional Effect of Lupinus montanus on Zea mays HS-2 (Intercropping) and Identification of Nodular Bacteria through the Use of Rhizotrons
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Plant Material
2.3. Soil
2.4. Sources of Phosphorous
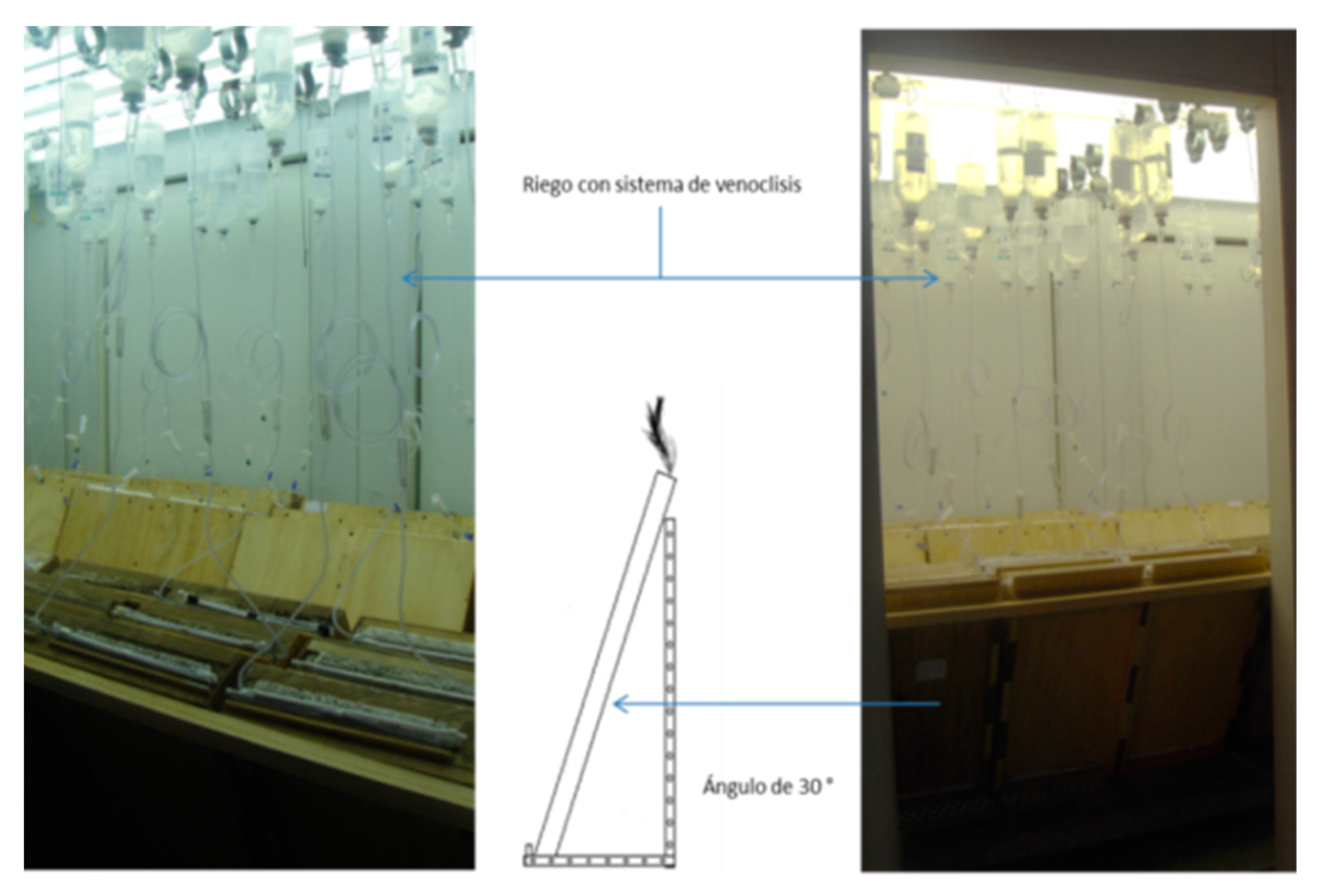
2.5. Glasshouse Experimentation
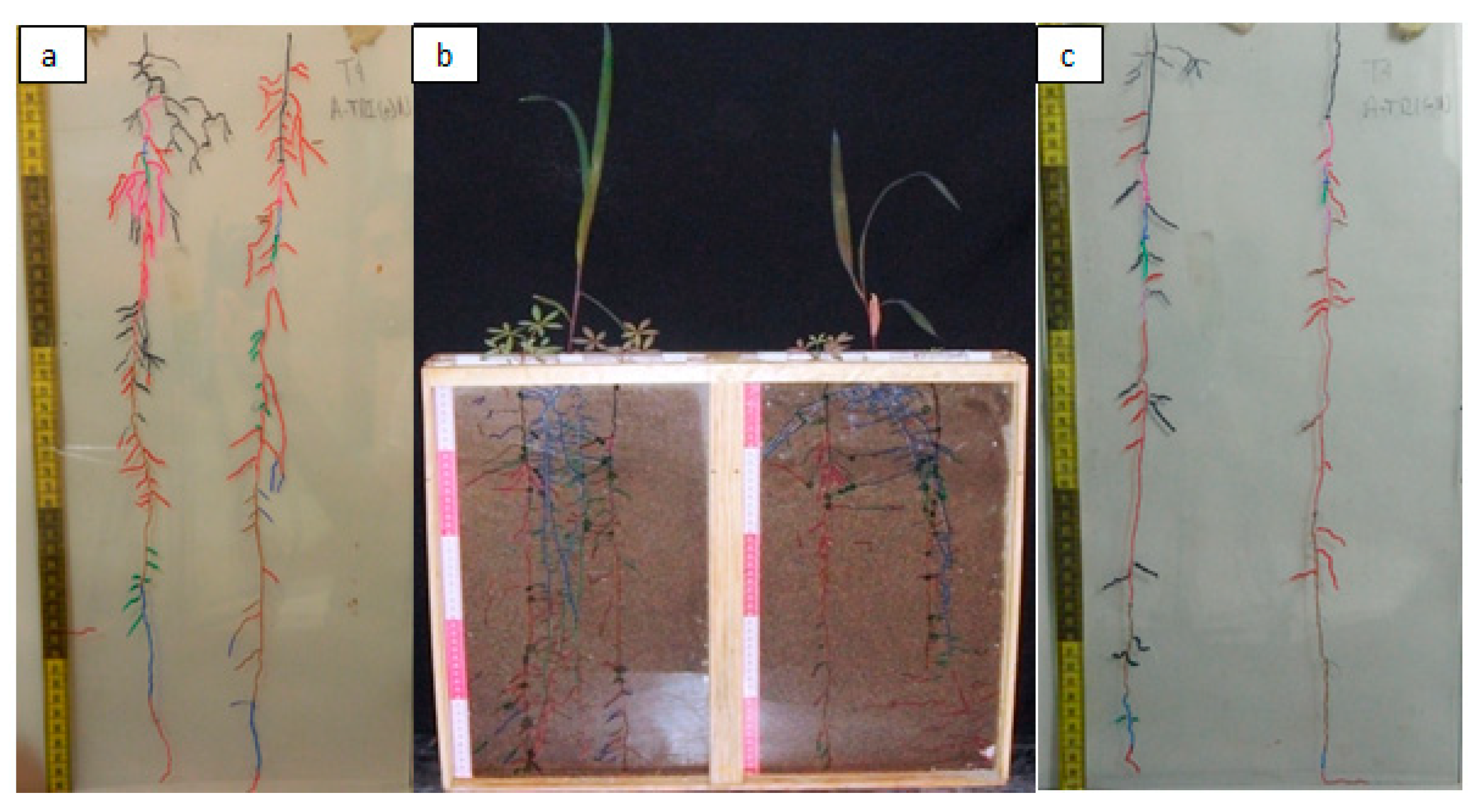
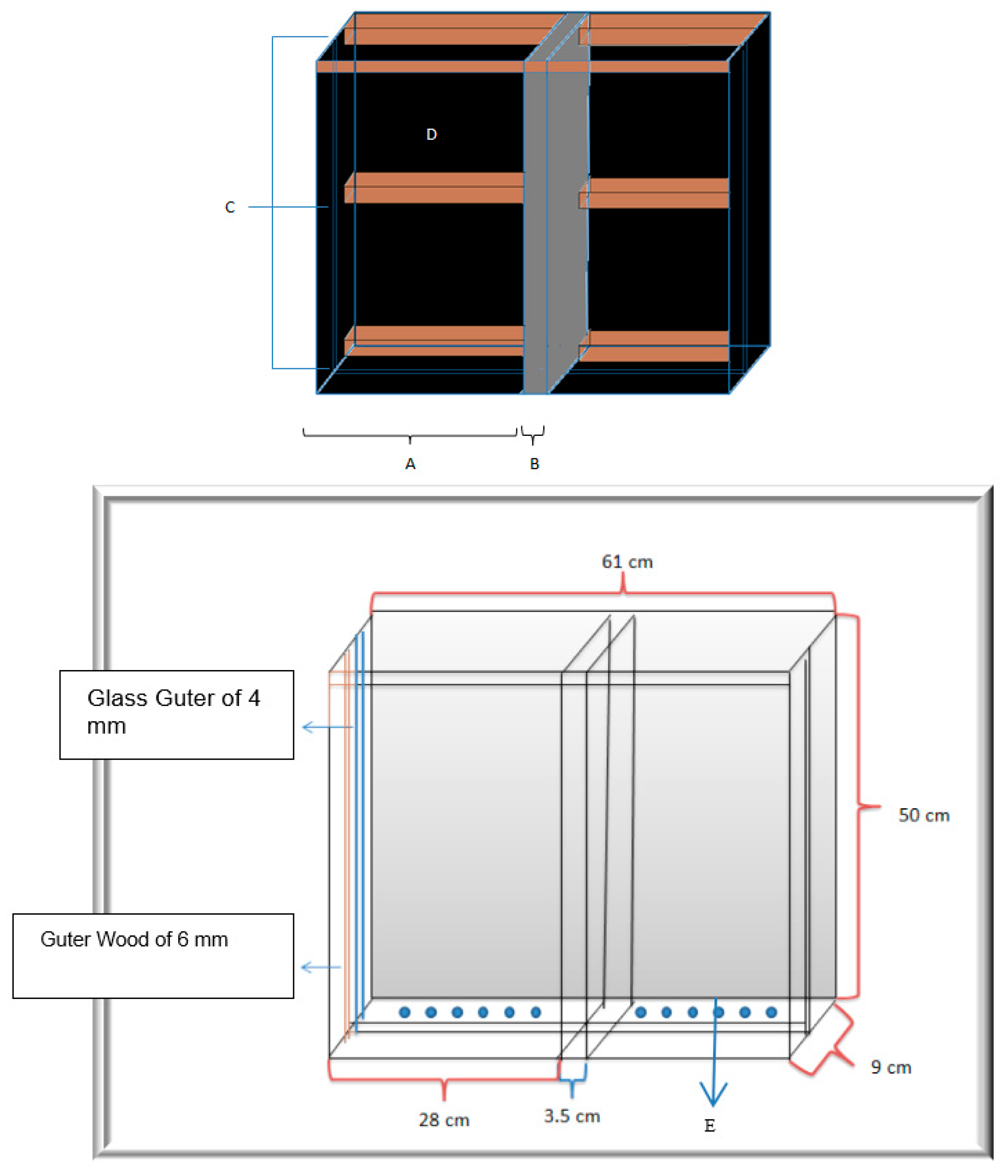
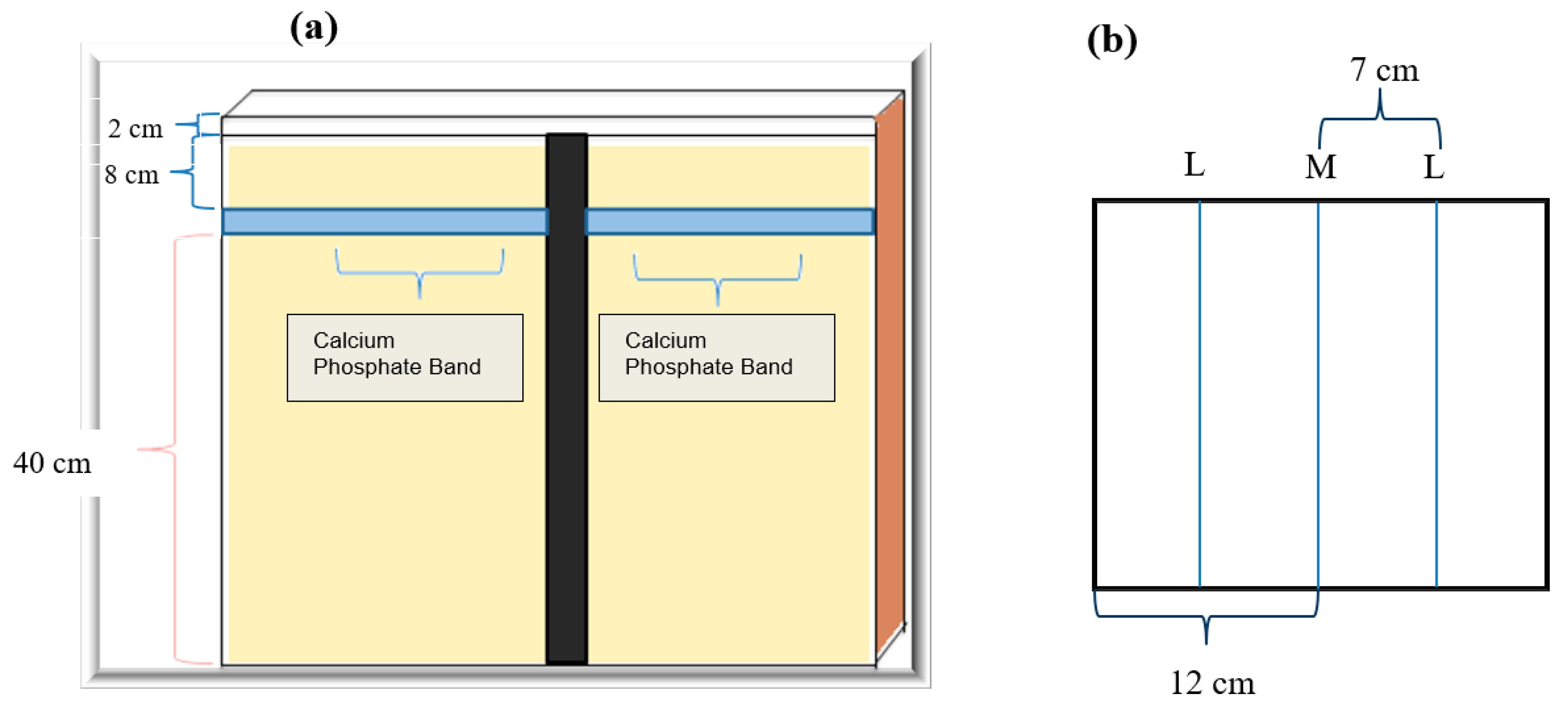
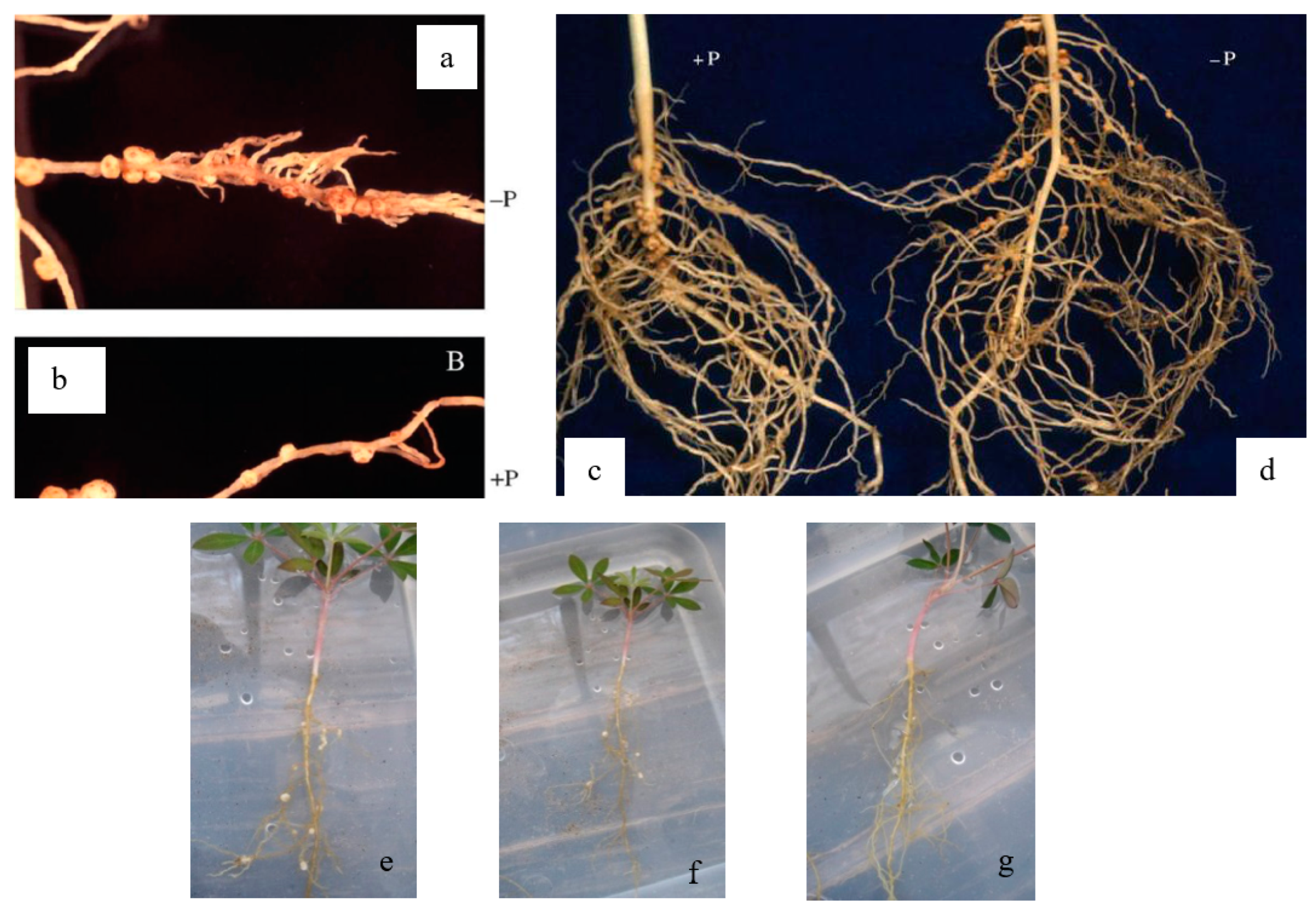
2.6. Rhizotron Design
2.7. Isolation of Atmospheric Nitrogen-Fixing Symbiotic Bacteria
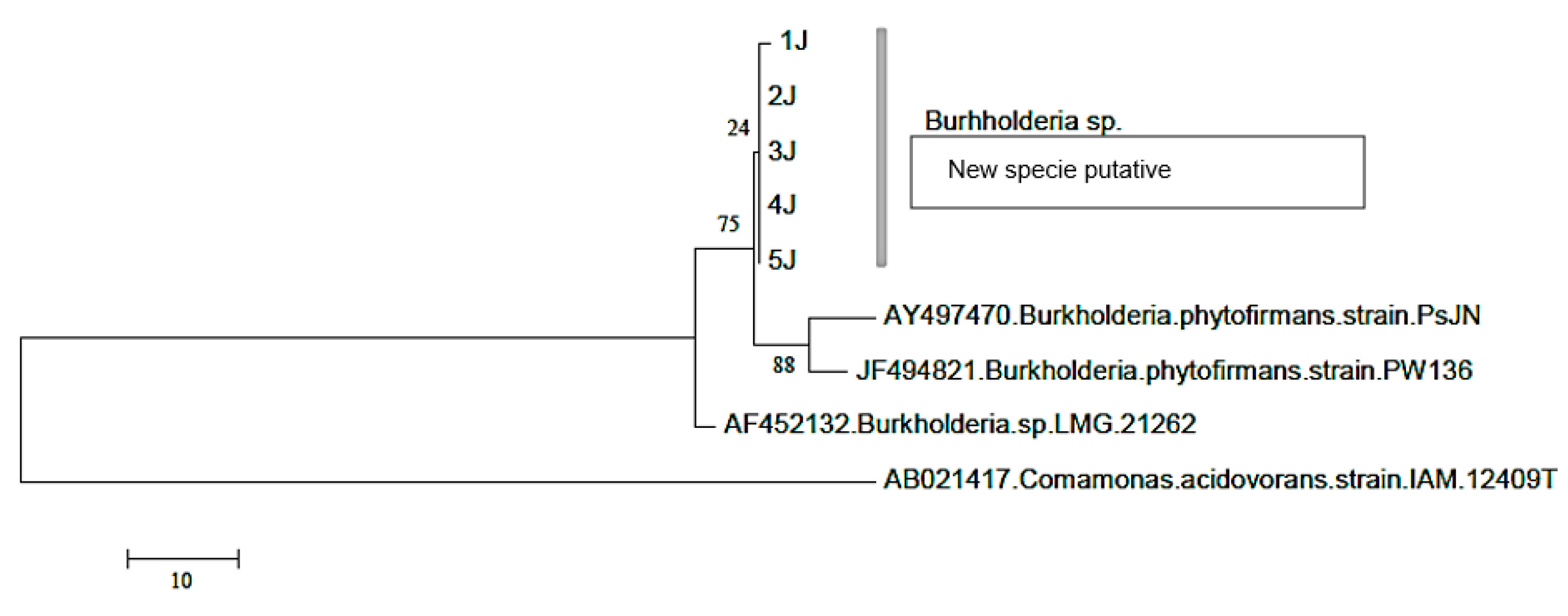
2.8. Identification of Nodular Bacteria
2.9. Construction of the Phylogenetic Tree
2.10. Development of the Experiment
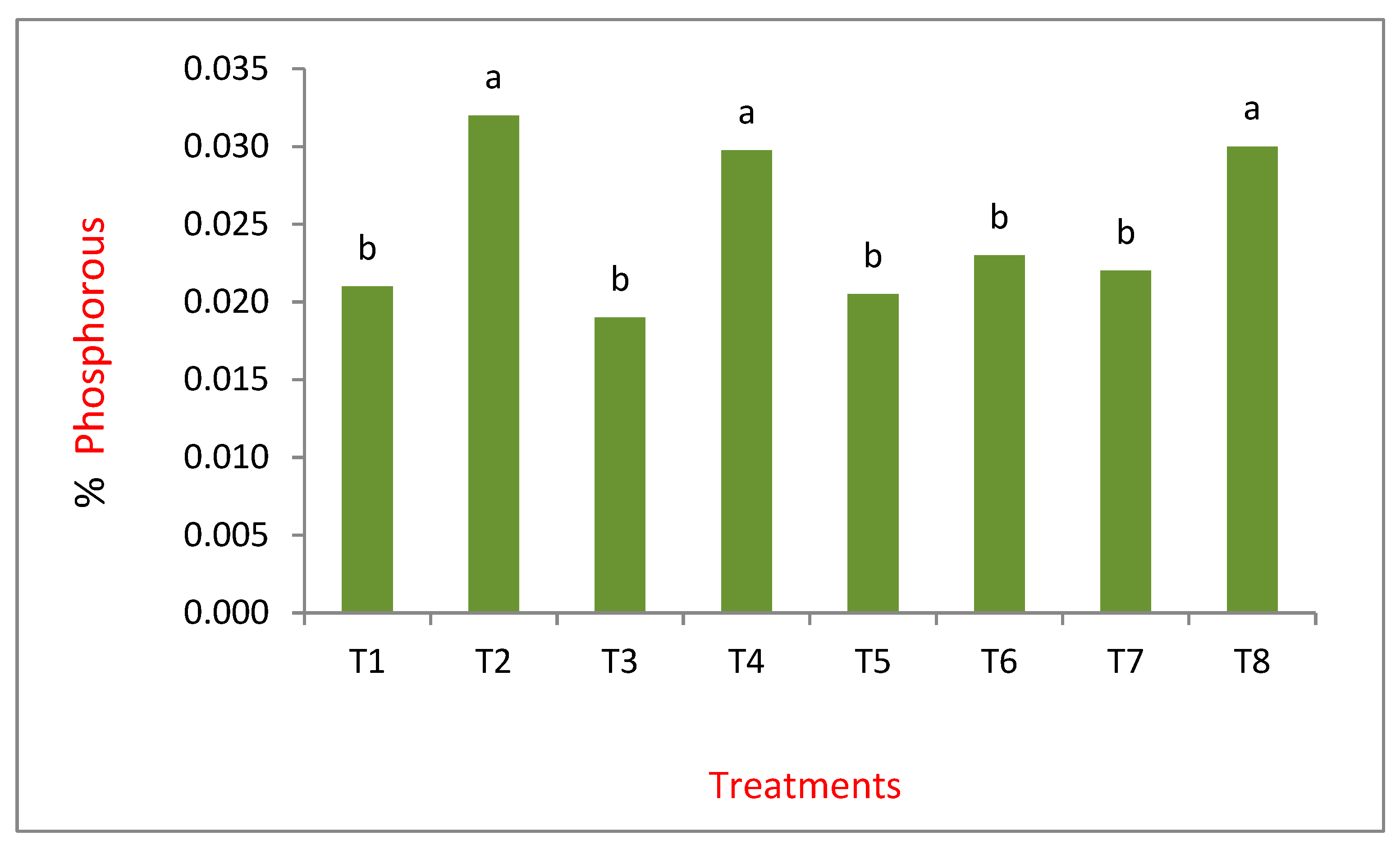
3. Results and Discussion
Nitrogen in Plant Tissue and the Maize Roots in Sandy Soil
4. Conclusions
- There is an opportunity for a new field of investigation in the nodulation and nitrogen fixation of Lupinus montanus since this research could evaluate nodulation with the Burkholderia bacteria.
- The use of Lupinus sp. is confirmed as an alternative in favor of more sustainable agricultural methods since it improves soil fertility in phosphorous-deficient soils. This could potentially contribute to the wealth of knowledge used to solve Mexico’s problem of food autonomy.
- As was observed during the experimental phase, the type and use of rhizotrons that were designed for the current study are only recommended for the evaluation of root systems in leguminous plants since crops with root systems like maize are more complicated and unreliable.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Significance Statements
References
- Fernández, M.T. Fósforo: Amigo o enemigo. In Sobre los Derivados de la Caña de Azúcar; ICIDCA: La Habana, Cuba, 2007; Volume 41, pp. 51–57. [Google Scholar]
- Schwerdtner, U.; Lacher, U.; Spohn, M. Lupin causes maize to increase organic acid exudation and phosphorus concentration in intercropping. J. Sustain. Agric. Environ. 2022, 1, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, J.C.; Anzola, A.J.; Contreras, T.A.; Salas, D.L.; Venegas, J.I.; Urban, M.O.; Beebe, E.S.; Rao, M.I. Influence of simultaneous intercropping of maize-bean with input of inorganic fertilizer on growth, development, and dry matter partitioning to yield components of two lines of common bean. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Bucio, J.; Cruz-Ramírez, A.; Herrera-Estrella, L. The role of nutrient availability in regulation root architecture. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2003, 6, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitter, A. Characterisitics and funtions of root systems. In Plant Roots: The Hidden Half, 3rd ed.; Waisel, Y., Eshel, A., Kafkafi, U., Eds.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 2–20. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, J.O.; Simpson, R.J.; Moore, A.D.; Chapman, D.F. Morphology and response of roots of pasture species to phosphorus and nitrogen nutrition. Plant Soil 2006, 286, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, J.P.; Brown, K.M. Topsoil foraging–an architectural adaptation of plants to low phosphorus availability. Plant Soil 2001, 237, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinkelaker, B.; Hengeler, C.; Marschner, H. Distribution and function of proteoid and other root clusters. Bot. Acta 1995, 108, 183–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, W.K.; Boundy, A. The acquisition of phosphorus by Lupinus albus L. IV. The effect of interplanting wheat and White lupin on the growth and mineral composition of the two especies. Plant Soil 1983, 70, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambers, H.; Shane, M.W.; Cramer, M.D.; Pearse, S.J.; Veneklaas, E.J. Root structure and functioning for efficient acquisition of phosphorus: Matching morphological and physiological traits. Ann. Bot. 2006, 98, 693–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinkelaker, B.; Römheld, V.; Marschner, H. Citric acid excretion and precipitation of calcium citrate in the rhizosphere of white of lupin (Lupinus albus L.). Plant Cell Environ. 1989, 12, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinsinger, P.; Gilkes, R.J. Root-Induced dissolution of phosphate rock in the rizhosphere of lupins grown in alkaline soil. Aust. J. Soil Res. 1995, 33, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Cruz Landero, N.; Espinosa-Hernández, V.; Guevara, E.; López-López, M.A.; Santos, A.T.; Ojeda-Trejo, E.; Alderete-Chavez, A. Lupinus versicolor response in soils contaminated heavy metals from a petroleum extraction field. J. Appl. Sci. 2010, 10, 694–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Eastwood, R.J.; Drummond, C.S.; Schifino-Wittmann, M.T.; Hughes, C.E. Diversity and evolutionary history of lupins-insights new phylogenies. “Lupins for Health and Wealth”. In Proceedings of the 12th International Lupin Conference, Fremantle, Australia, 14–18 September 2008; pp. 346–354. [Google Scholar]
- Bermúdez-Torres, K.; Robledo-Quintos, N.; Martínez-Herrera, J.; Tei, A.; Wink, M. Biodiversity of genus Lupinus in Mexico. Lupin, An Ancient Crop for the New Millenium. In Proceedings of the 9th International Lupin Conference, Canterbury, New Zealand, 20–24 June 1999; pp. 294–296. [Google Scholar]
- Bashir, M.K.; Mehmood, Y.; Hassan, S. Impact of agricultural credit on productivity of wheat crop: Evidence from Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan. Pak. J. Agric. Sci. 2010, 47, 405–409. [Google Scholar]
- Navas, P.B.; Marín, D. Comportamiento ecofisiológico de la asociación canavalia-maíz con y sin aplicación de nitrógeno y con diferentes arreglos cronológicos. Agron. Trop. 1995, 45, 609–635. [Google Scholar]
- Kisetu, N.E.; Baijukya, F.; Alois, N.P. Productivity of intercropping with maize and common bean over five cropping seasons on smallholder farms of Tanzania. Eur. J. Agron. 2020, 113, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebman, M. Sistemas de policultivos. In Agroecología: Bases Científicas para una Agricultura Sustentable; Altieri, M.A., Ed.; CLADES-Grupo Gestor Asociación Cubana de Agricultura Orgánica, ACAO: La Habana, Cuba, 1997; pp. 133–141. [Google Scholar]
- Mead, R.; Willey, R.W. The concept a land equivalent ratio and advantages in yields from intercropping. Exp. Agric. 1980, 16, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomwesigye, W.; Osiru, D.; Lemma, T.T.; Bedai, B.; Mwanjalolo, J.G.M. Effect of intercropping maize and beans on the maize yields in Isingiro Town Council, Isingiro District, South Western Uganda. Univers. J. Food Segurity 2022, 1, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandermeer, J. The Ecology of Intercropping; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1989; 273p. [Google Scholar]
- Benintenden, S. Calidad de Inoculantes comerciales para el cultivo de soja en la Argentina: Concentracion de rizobios y prescencia de contaminantes. Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 2010, 42, 129–132. [Google Scholar]
- Doyle, J.J.; Doyle, J.L. Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 1990, 12, 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G.; Gipson, T.J. CLUSTAL. W: Improving the sensitive of progressive multiple sequence aligment through sequence weighting, position specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Peterson, N.; Stecher, G.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGAS molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felseisten, J. Confidence limits on phylogenies: An approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 1985, 39, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremer, J.M. Total nitrogen. In Methods of Soil Análisis: Part 2; Black, C.A., Ed.; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1995; Volume 9, pp. 1149–1178. [Google Scholar]
- Sas, L.; Rengel, Z.; Tang, C. The effect of nitrogen nutrition on cluster root formation and proton extrusion by Lupinus albus. Ann. Bot. 2002, 89, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora, E.; Toro, M. Estimulación del crecimiento vegetal por Burkholderia cepacia, una cepa nativa de suelos ácidos de sabanas venezolanas. Agron. Trop. 2007, 57, 123–128. [Google Scholar]
- Weisskopf, L.S. Heller and L. Eberl. Burkholderia species are major inhabitans of White Lupin clusters roots. Appl. Enviromental Microbiol. 2011, 77, 7715–7720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.B. Interpretation of plan analysis for several agronomic crops. In Soil Testing and Plant Analysis, Part II, Plant Análisis; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1998; pp. 49–58. [Google Scholar]
- Akhtar, M.; Hernández, V.E.; Escobar, R.N.; Qazi, A.B.A.M. Asociación de Lupinus silvestris—Trigo y Disponibilidad de Fósforo en Calcisoles. Ph.D. Thesis, Colegio de Postgraduados, Montecillo, Mexico, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Marschner, H.; Romheld, V.; Kakmak, I. Root induced changes in nutrient availablity in the rizhosphere. J. Plant Nutr. 1987, 10, 175–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudyyanselage, D.S.; Dissanayaka, B.; Murayama, H.; Masuda, G.; Wasaki, J. Interspecific facilitation of P acquisition in intercropping of maize with white lupin in two contrasting soils as influenced by different rates and forms of P supply. Plant Soil 2015, 390, 223–236. [Google Scholar]
- Rodas, C.A.; Núñez, E.R.; Espinosa HV y Alcántar, G.G. Asociación Lupinus-maiz en la nutrición fosfatada en un andosol. Terra 2001, 19, 141–154. [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa, K.; Osaky, M.; Matzul, H.; Honma, M.; Tadano, T. Purification and propiertis of acid phosphatase secreted from lupin roots under phosphorus deficiency conditions. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1995, 4, 31–43. [Google Scholar]
- Paredes-Mendoza, M.; Espinosa-Victoria, D. Ácidos orgánicos producidos por rizobacterias que solubilizan fosfato: Revisión Crítica. Terra Latinoam. 2009, 28, 61–70. [Google Scholar]
- Egle, K.; Römer, W.; Keller, H. Exudation of low molecular weight organic acids by Lupinus albus L., Lupinus angustifolius L. and Lupinus luteus L. as affected by phosphorus supply. Agronomie 2003, 23, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearse, S.J.; Veneklaas, E.J.; Cawthray, G.; Bolland, M.D.A.; Lambers, H. Carboxylate composition of root exudates does not relate consistently to a crop species’ ability to use phosphorus from aluminium, iron or calcium phosphate sources. New Phytol. 2006, 173, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le-Roux, M.R.; Khan, S.; Valentine, A.J. Organic acid accumulation may inhibit N2 fixation in phosphorus stressed lupin nodules. J. Compil. New Phytologist 2007, 177, 956–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze, J.; Temple, G.; Temple, S.J.; Beschow, H.; Vance, C.P. Nitrogen fixation by White lupin under phosphorus deficiency. Ann. Bot. 2006, 98, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerke, J.; Romer, W.; Jungk, A. The excretion of citric and malic acid by proteoid roots of Lupinus albus effect on soil solution concentration of phosphate, Fe and Al in the proteoid rhizhosphere in samples of an oxisol and luvisol. Z Pflanz. Bodenk 1994, 157, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Attar, I.; Taha, K.; Oubohssaine, M.; Diouf, B.; Jenk, H.A.; Berraho, E.B.; Alami, I.T.; Aurag, J. Phytobenefitial bacterial inoculants for common bean growth and productivity in nitrogen and phosphorus deficient soils. Pak. J. Agric. Sci. 2022, 59, 157–163. [Google Scholar]
- Rubio, G.; Liao, H.; Yan, X.L.; Lynch, J. Topsoil foraging and its role in plant competitiveness for phosphorus in common bean. Crop Sci. 2003, 43, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisdale, S.L.; Nelson, W.L.; Beaton, J.D. Soil Fertility and Fertilizers, 4th ed.; MacMillan Publishing Company Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1985; 30p. [Google Scholar]

| Parameter | Technique | |
|---|---|---|
| pH (ratio 1:2) | 7.6 | Potentiometer in the saturation extract |
| Phosphorus (mg kg−1) | 2.6 | Olsen et al., 1965 |
| Total Nitrogen (%) | 0.01 | Micro-Kjeldahl |
| Phosphorus Source | Dose (gr) | Crop System | Steiner Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tribasic Calcium phosphate | 1 | M | A |
| Tribasic Calcium Phosphate | 1 | M/L | B |
| Tribasic Calcium Phosphate | 1 | M | A |
| Tribasic Calcium Phosphate | 1 | M/L | B |
| Dibasic Calcium Phosphate | 1 | M | A |
| Dibasic Calcium Phosphate | 1 | M/L | B |
| Dibasic Calcium Phosphate | 1 | M | A |
| Dibasic Calcium Phosphate | 1 | M/L | B |
| (+) | Inoculum | Lupinus montanus Number of Nodules | (−) | Inoculum | Lupinus montanus Number of Nodules Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plant 1 | Plant 2 | Plant 1 | Plant 2 | |||
| R1 | 15 | 21 | 36 | 14 | 12 | 26 |
| R2 | 15 | 18 | 33 | 12 | 15 | 37 |
| R3 | 27 | 19 | 46 | 15 | 8 | 23 |
| R4 | 22 | 15 | 37 | 16 | 9 | 25 |
| X = 38 a | X = 25.5 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Espinosa Gonzalez, J.; Espinosa Hernández, V.; Ojeda Trejo, E.; Delgadillo Martínez, J.; Molina Moreno, J.C.; Sánchez, F.L. Assessing the Nutritional Effect of Lupinus montanus on Zea mays HS-2 (Intercropping) and Identification of Nodular Bacteria through the Use of Rhizotrons. Int. J. Plant Biol. 2023, 14, 910-921. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijpb14040067
Espinosa Gonzalez J, Espinosa Hernández V, Ojeda Trejo E, Delgadillo Martínez J, Molina Moreno JC, Sánchez FL. Assessing the Nutritional Effect of Lupinus montanus on Zea mays HS-2 (Intercropping) and Identification of Nodular Bacteria through the Use of Rhizotrons. International Journal of Plant Biology. 2023; 14(4):910-921. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijpb14040067
Chicago/Turabian StyleEspinosa Gonzalez, Juan, Vicente Espinosa Hernández, Enrique Ojeda Trejo, Julián Delgadillo Martínez, Juan Celestino Molina Moreno, and Francisco Landeros Sánchez. 2023. "Assessing the Nutritional Effect of Lupinus montanus on Zea mays HS-2 (Intercropping) and Identification of Nodular Bacteria through the Use of Rhizotrons" International Journal of Plant Biology 14, no. 4: 910-921. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijpb14040067
APA StyleEspinosa Gonzalez, J., Espinosa Hernández, V., Ojeda Trejo, E., Delgadillo Martínez, J., Molina Moreno, J. C., & Sánchez, F. L. (2023). Assessing the Nutritional Effect of Lupinus montanus on Zea mays HS-2 (Intercropping) and Identification of Nodular Bacteria through the Use of Rhizotrons. International Journal of Plant Biology, 14(4), 910-921. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijpb14040067







