Molecular Character of Mylonchulus hawaiiensis and Morphometric Differentiation of Six Mylonchulus (Nematoda; Order: Mononchida; Family: Mylonchulidae) Species Using Multivariate Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Method
2.1. Nematode Isolation, Processing, and Identification
2.2. DNA Extraction, PCR, and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Molecular Analysis
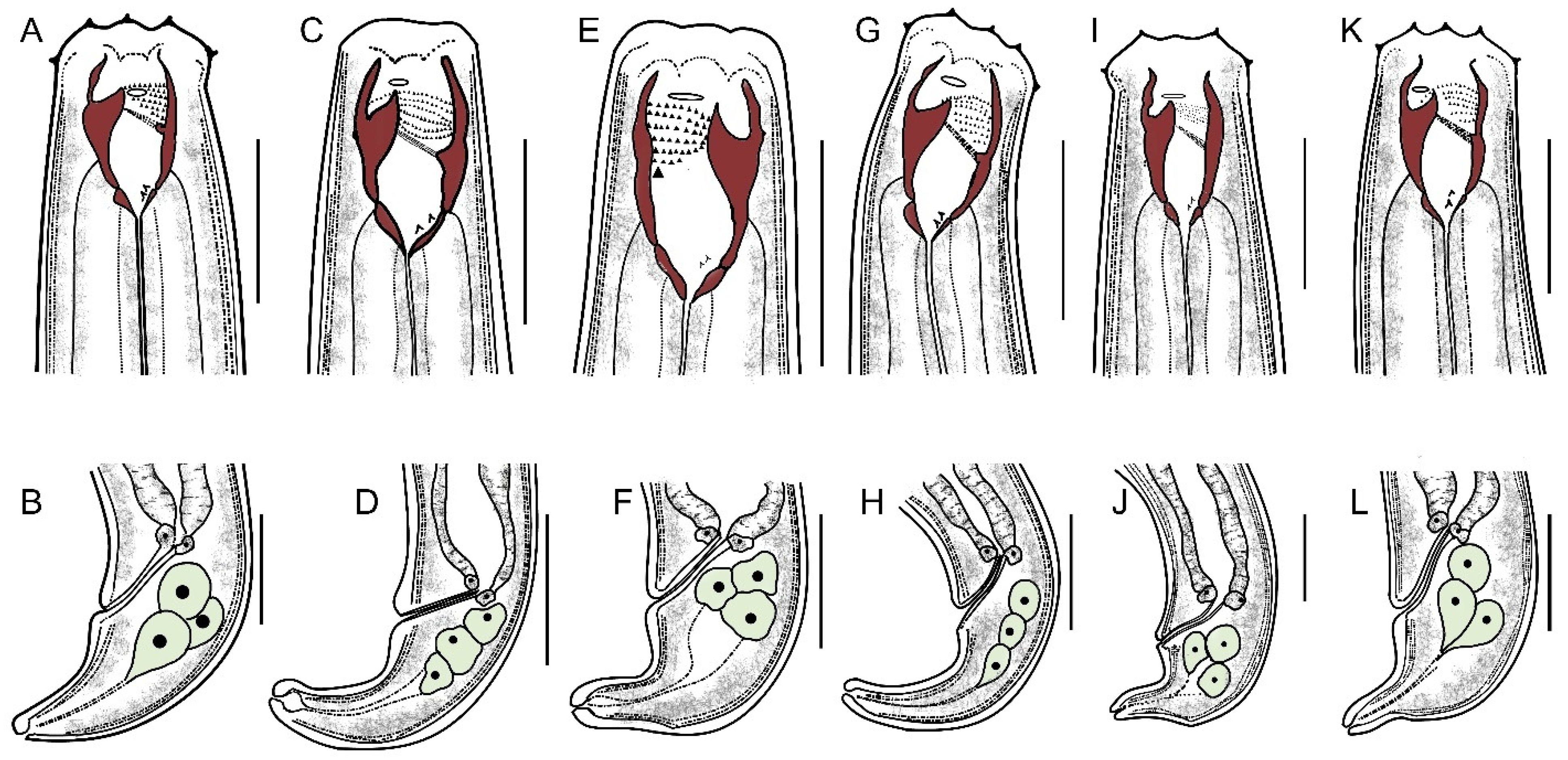
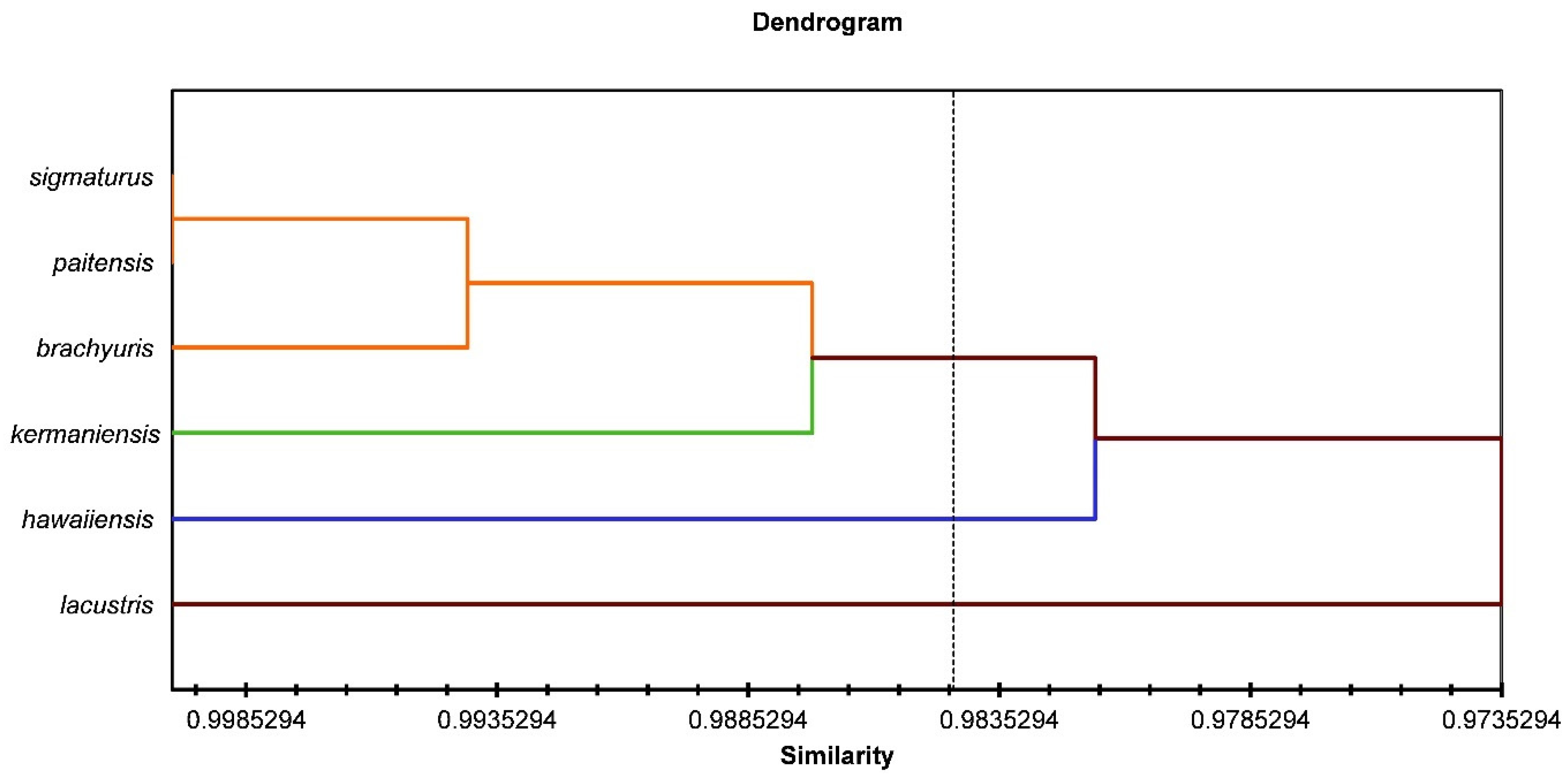
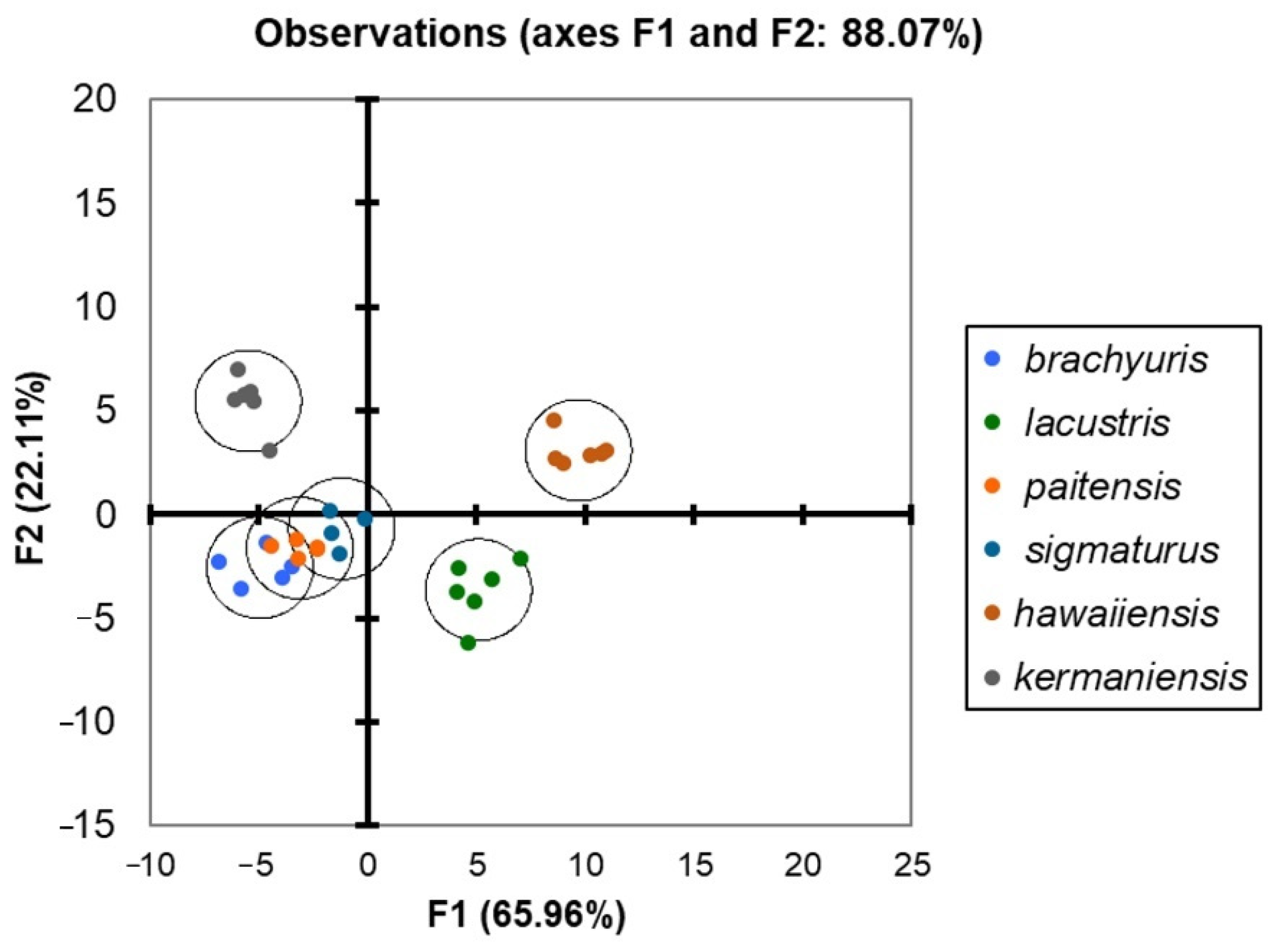
3.2. Morphometric Characteristics
| Wilks’ Lambda | F | Sig. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Body Length | 0.434 | 5.749 | 0.002 |
| a | 0.598 | 2.961 | 0.034 |
| b | 0.752 | 1.45 | 0.246 |
| c | 0.208 | 16.787 | 0.000 |
| c′ | 0.441 | 5.573 | 0.002 |
| V | 0.353 | 8.08 | 0.000 |
| G1% | 0.561 | 3.448 | 0.019 |
| G2% | 0.289 | 10.841 | 0.000 |
| Neck | 0.343 | 8.434 | 0.000 |
| Buccal cavity length | 0.558 | 3.479 | 0.018 |
| Buccal cavity width | 0.392 | 6.818 | 0.001 |
| Dorsal tooth apex | 0.268 | 12.041 | 0.000 |
| Amphidial position to ant. end | 0.68 | 2.074 | 0.107 |
| Dorsal tooth length | 0.32 | 9.36 | 0.000 |
| Rectum | 0.614 | 2.77 | 0.044 |
| Tail length | 0.776 | 1.27 | 0.312 |
| Genus | M. paitensis | M. brachyuris | M. sigmaturus | M. lacustris | M. kermaniensis | M. hawaiiensis | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body length | 1164.5 ± 74.1 a | 1198.6 ± 50.9 a | 1263.1 ± 24.1 ac | 979.6 ± 25.8 b | 1357.2 ± 31.6 c | 1195.8 ± 62.9 a | 0.000 |
| a | 30.0 ± 0.8 ac | 28.2 ± 1.7 abc | 31.9 ± 1.9 c | 26.0 ± 1.3 ab | 29.0 ± 1.6 ac | 24.0 ± 1.5 b | 0.17 |
| b | 3.4 ± 0.1 a | 3.5 ± 0.1 ab | 3.5 ± 0.2 ab | 3.4 ± 0.1 ab | 3.6 ± 0.1 ab | 3.7 ± 0.1 b | 0.222 |
| c | 29.7 ± 0.6 a | 30.8 ± 0.7 ac | 31.8 ± 0.7 ac | 21.5 ± 0.3 b | 33.1 ± 1.6 c | 23.5 ± 1.2 b | 0.000 |
| c′ | 1.4 ± 0.02 a | 1.4 ± 0.08 a | 1.5 ± 0.08 ac | 1.9 ± 0.03 b | 1.5 ± 0.07 a | 1.7 ± 0.09 c | 0.000 |
| V | 64.4 ± 0.4 a | 61.8 ± 0.6 a | 63.4 ± 0.2 a | 58.5 ± 1.2 b | 63.5 ± 0.7 a | 55.3 ± 1.8 c | 0.000 |
| G1% | 18.0 ± 1.0 a | 16.0 ± 0.9 a | 16.7 ± 1.0 a | 11.4 ± 0.6 b | 16.8 ± 0.9 a | 16.3 ± 1.4 a | 0.002 |
| G2% | 16.9 ± 1.2 a | 14.3 ± 1.5 a | 15.8 ± 1.1 a | 9.4 ± 0.2 b | 20.8 ± 0.2 c | 17.1 ± 1.4 a | 0.000 |
| Neck | 348.1 ± 24.3 ac | 341.8 ± 8.1 c | 362.5 ± 3.9 ac | 283.9 ± 3.4 b | 378.5 ± 7.3 a | 289.8 ± 12.1 b | 0.000 |
| Buccal cavity length | 24.8 ± 0.6 ac | 23.4 ± 0.3 c | 25.3 ± 0.2 ac | 24.9 ± 0.3 ac | 25.8 ± 0.4 ab | 27.3 ± 1.1 b | 0.009 |
| Buccal cavity width | 13.9 ± 0.6 ac | 12.7 ± 0.5 ce | 13.3 ± 0.8 ace | 11.5 ± 0.2 e | 16.3 ± 0.5 b | 14.8 ± 0.9 ab | 0.000 |
| Dorsal tooth apex | 3.6 ± 0.7 a | 4.0 ± 0.1 a | 4.5 ± 0.2 ab | 5.6 ± 0.2 bd | 7.0 ± 0.3 c | 6.4 ± 0.3 dc | 0.000 |
| Amphidial position to ant. end | 10.1 ± 1.3 a | 9.5 ± 0.3 a | 12.8 ± 0.6 b | 9.8 ± 0.2 a | 10.4 ± 0.3 a | 10.5 ± 0.4 a | 0.082 |
| Dorsal tooth length | 8.1 ± 0.3 ac | 7.7 ± 0.3 a | 8.1 ± 0.1 ac | 7.6 ± 0.1 a | 8.5 ± 0.2 c | 6.3 ± 0.3 b | 0.000 |
| Rectum | 22.5 ± 1.5 ac | 23.6 ± 0.7 c | 22.0 ± 0.3 abc | 20.2 ± 0.7 ab | 20.0 ± 0.3 b | 20.3 ± 1.1 ab | 0.024 |
| Tail | 39.7 ± 2.9 a | 39.1 ± 2.2 a | 40.0 ± 0.7 ab | 45.6 ± 0.9 b | 42.2 ± 1.8 ab | 43.3 ± 1.7 ab | 0.131 |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chitwood, B.G. The English word “Nema” revised. Sys. Biol. 1957, 4, 1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jairajpuri, M.S. Studies on Mononchida of India. I. The genera Hadronchus, Iotonchus and Miconchus and a revised classification of Mononchida, new order. Nematologica 1969, 15, 557–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassidy, G.H. Some mononchs of Hawaii. Hawaiian Plant. Rec. 1931, 35, 305–339. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, W.; Jairajpuri, M.S. Mononchida: The predaceous nematodes. In Nematology Monographs and Perspectives; Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2010; Volume 7, 298p. [Google Scholar]
- Koohkan, M.; Shokoohi, E.; Mullin, P. Phylogenetic relationships of three families of the suborder Mononchina Kirjanova & Krall, 1969 inferred from 18S rDNA. Nematology 2015, 17, 1113–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koohkan, M.; Shokoohi, E. Mass Production and Prey Species of Mylonchulus sigmaturus (Nematoda: Mylonchulidae) in the Laboratory. Acta. Zool. Bulgarica. 2014, 66, 555–558. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, Z.; Kim, Y.H. A review on the role of predatory soil nematodes in the biological control of plant parasitic nematodes. App. Soil Ecol. 2007, 35, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobb, M.V. Some freshwater nematodes of the Douglas Lake Region of Michigan, USA. Trans. Am. Micros. Soc. 1915, 34, 21–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahmand, S.; Eskandari, A.; Orselli, L.; Karegar, A. Some known species of the genera Mononchus Bastian, 1865 and Mylonchulus (Cobb, 1916) Altherr, 1953 (Nematoda: Mononchina) from Semnan province, Iran. Nematol. Mediter. 2009, 37, 145–154. [Google Scholar]
- Koohkan, M.; Shokoohi, E.; Abolafia, J. Study of some mononchids (Mononchida) from Iran with a compendium of the genus Anatonchus. Trop. Zool. 2014, 27, 88–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokoohi, E.; Mehrabi-Nasab, A.; Mirzaei, M.; Peneva, V. Study of mononchids from Iran, with description of Mylonchulus kermaniensis sp. n. (Nematoda: Mononchida). Zootaxa 2013, 3599, 519–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodey, T. Soil and Freshwater Nematodes; Methuen: London, UK, 1951; p. 390. [Google Scholar]
- Yeates, G.W. Nematodes from New Caledonia. 1. Introduction and Mononchoidea. Fundam. Appl. Nematol. 1992, 15, 101–126. [Google Scholar]
- Andrássy, I. Über das System der Mononchiden (Mononchidae Chitwood, 1937; Nematoda). Ann. Hist. Nat. Musei Natl. Hung. 1958, 50, 151–171. [Google Scholar]
- Cobb, N.A. The Mononchs. A genus of free-living predatory nematodes. Soil Sci. 1917, 3, 431–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altherr, E. Nématodes du sol du Jura vaudois et français. I. Bull. Soc. Vaud. Sci. Nat. 1953, 65, 429–460. [Google Scholar]
- Bütschli, O. Beitrage zur Kenntnis der freilebenden Nematoden. Nova Acta Acad. Caesareae Leipold-Carol. Nat. Curios 1873, 36, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Martinez, A.; De-Pablos-Heredero, C.; González, M.; Rodriguez, J.; Barba, C.; García, A. Usefulness of discriminant analysis in the morphometric differentiation of six native freshwater species from Ecuador. Animals 2021, 11, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyaku, S.T.; Kantety, R.V.; Lawrence, K.S.; van Santen, E.; Sharma, G.C. Canonical discriminant analysis of Rotylenchulus reniformis in Alabama. Nematropica 2013, 43, 171–181. [Google Scholar]
- Królaczyk, K.; Zaborski, D.; Dzierzba, E.; Kavetska, K.M. Redescription of Quasiamidostomum Fulicae (Rudolphi, 1819) Lomakin, 1991 (Nematoda: Amidostomatidae), a parasite of Fulica Atra (Gruiformes). J. Vet. Res. 2020, 64, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokoohi, E. Observation on Hemicriconemoides brachyurus (Loos, 1949) Chitwood & Birchfield, 1957 associated with grass in South Africa. Helminthologia 2022, 59, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Grisse, A.T. Contribution to the Morphology and the Systematics of the Criconematidae (Taylor, 1936) Thorne, 1949; Faculty of Agricultural Sciences: Gent, Belgium, 1969; p. 35. [Google Scholar]
- Straube, D.; Juen, A. Storage and shipping of tissue samples for DNA analyses: A case study on earthworms. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2013, 57, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokoohi, E. Morphological and molecular characterisation of Boleodorus volutus Lima & Siddiqi, 1963 from South Africa with the first SEM observations of the species. Russian J. Nematol. 2021, 29, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carta, L.K.; Li, S. Improved 18S small subunit rDNA primers for problematic nematode amplification. J. Nematol. 2018, 50, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nuc. Acids Sym. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibson, T.J. CLUSTAL W: Improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucl. Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Huelsenbeck, J. MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1572–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, R.D. TreeView: An application to display phylogenetic trees on personal computers. Comput. Appl. Biosci. 1996, 12, 357–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrássy, I. Eine interessante Nematodenfauna der Gerste. Nematologische Notizen. Acta Zool. Acad. Sci. Hung. 1956, 2, 307–317. [Google Scholar]
- Hopper, B.E.; Cairns, E.J. Taxonomic Keys to Plant, Soil and Aquatic Nematodes; Alabama Polytechnic Institute: Auburn, AL, USA, 1959; p. 176. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, K.R.; Gorley, R.N. PRIMER v7, 2015; Massey University Press: Auckland, New Zealand, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Nattero, J.; Piccinali, R.V.; Macedo Lopes, C.; Hernández, M.L.; Abrahan, L.; Lobbia, P.A.; Rodríguez, C.S.; de la Fuente, L.C. Morphometric variability among the species of the Sordida subcomplex (Hemiptera: Reduviidae: Triatominae): Evidence for differentiation across the distribution range of Triatoma sordida. Paras. Vec. 2017, 10, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addinsoft. XLSTAT, Analyse de données et Statistique avec MS Excel; Addinsoft: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Olia, M.; Ahmad, W.; Araki, M.; Minaka, N. Molecular characterization of some species of Mylonchulus (Nematoda: Mononchida) from Japan and comments on the status of Paramylonchulus and Pakmylonchulus. Nematology 2009, 11, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisa, R.U.; Tantray, A.Y.; Kouser, N.; Allie, K.A.; Wani, S.M.; Alamri, S.A.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Wijaya, L.; Shah, A.A. Influence of ecological and edaphic factors on biodiversity of soil nematodes. Saudi. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 3049–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, J.; Simões, M.J.; Gomes, P.; Barroso, C.; Pinho, D.; Conceição, L.; Fonseca, L.; Abrantes, I.; Pinheiro, M.; Conceição, E. Assessment of the Geographic Origins of Pinewood Nematode Isolates via Single Nucleotide Polymorphism in Effector Genes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, S.P.; Kaya, H.K. A multivariate analysis of morphometric characters of Heterorhabditis species (Nemata: Heterorhabditidae) and the role of morphometrics in the taxonomy of species of the genus. J. Parasitol. 1996, 82, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubtsova, T.V.; Chizhov, V.N.; Subbotin, S.A. Longidorus artemisiae sp. n. (Nematoda: Longidoridae) from roots of Artemisia sp., Rostov region, Russia. Russ. J. Nematol. 1999, 7, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Stock, S.P.; Nadler, S.A. Morphological and molecular characterisation of Panagrellus spp. (Cephalobina: Panagrolaimidae): Taxonomic status and phylogenetic relationships. Nematology 2006, 8, 921–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-Toledo, D.; Vargas-Ponce, O.; Ascencio-Ramírez, S.; Valadez-Sandoval, L.M.; Pérez-Alquicira, J.; Morales-Saavedra, J.; Huerta-Galván, O.F. Morphological and genetic variation in monocultures, forestry systems and wild populations of Agave maximiliana of western Mexico: Implications for its conservation. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apolônio Silva de Oliveira, D.; Decraemer, W.; Moens, T.; dos Santos, G.A.P.; Derycke, S. Low genetic but high morphological variation over more than 1000 km coastline refutes omnipresence of cryptic diversity in marine nematodes. BMC Evol. Biol. 2017, 17, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oxnard, C.; O’Higgins, P. Biology clearly needs morphometrics. Does morphometrics need biology? Biol. Theory 2009, 4, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maertens, D. Observations on life cycle of Prionchulus punctatus (Cobb, 1917) and culture conditions. Biol. Jb. Dodonaea 1975, 43, 197–218. [Google Scholar]
- Grootaert, P.; Maertens, D. Cultivation and life cycle of Mononchus aquaticus. Nematologica 1976, 22, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohn, E.; Mordechai, E. Biological control of citrus nematode. Phytoparasitica 1973, 1, Abstract. [Google Scholar]
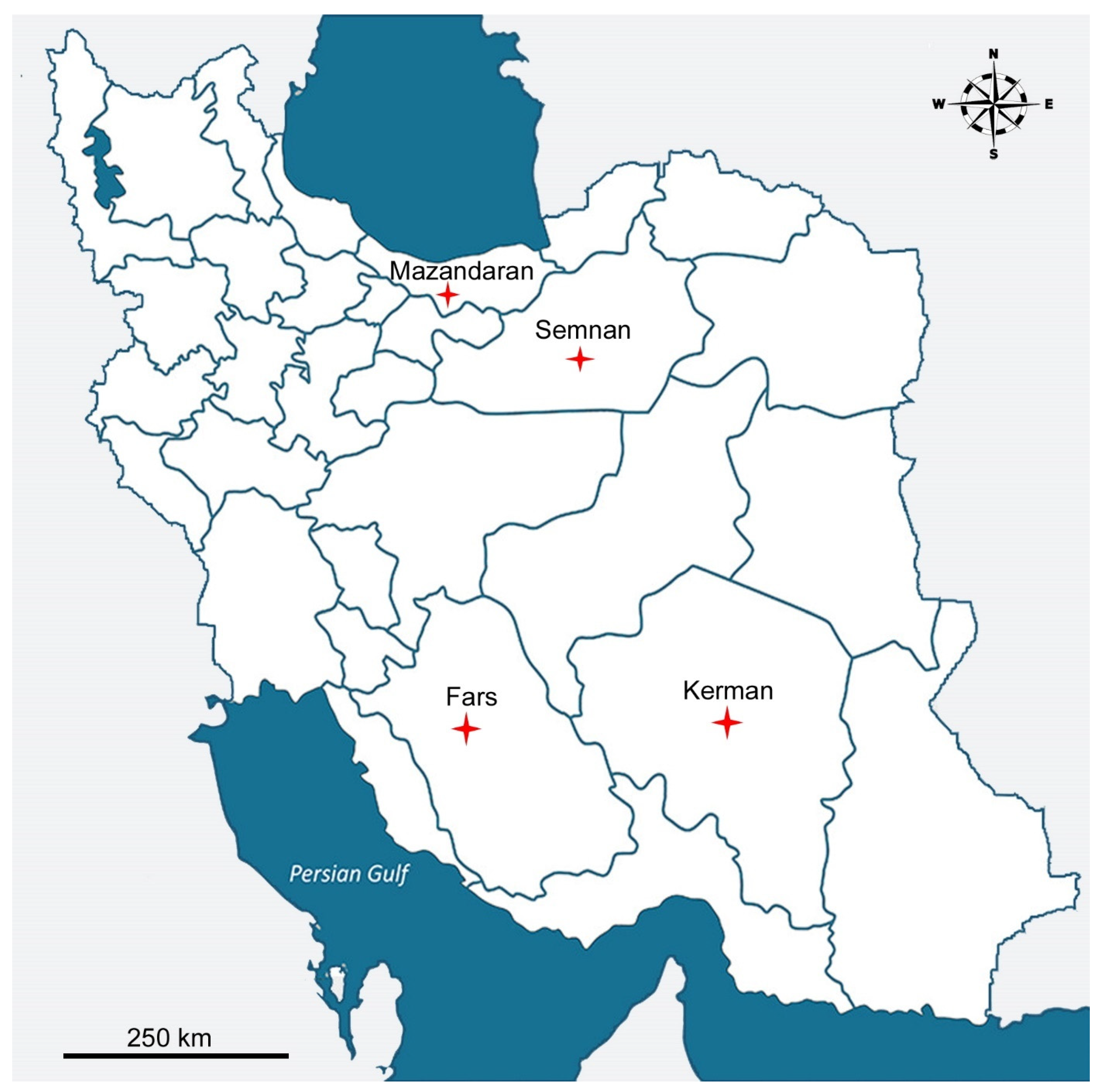


| Species | Province | Location | Host | GPS Coordinates |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. brachyuris | Kerman | Lalezar | walnut | N: 29°29′08.5″; E: 56°48′50.0″ |
| Mazandaran | Qaemshahr | forest soil | N: 36°23′56.75″; E: 52°49′33.97″ | |
| M. hawaiiensis | Kerman | Jiroft | soil | N: 28°58′36.77″; E: 57°38′3.80″ |
| M. kermaniensis | Kerman | Jiroft | soil | N: 28°58′36.77″; E: 57°38′3.80″ |
| M. lacustris | Kerman | Jiroft | citrus | N: 28°36′6.17″; E: 57°49′44.1″ |
| M. paitensis | Kerman | Andoohjerd | grassland | N: 30°14′12.10″; E: 57°45′10.9″ |
| Semnan | Damghan | walnut | N: 36°13′50.29″; E: 54°11′5.34″ | |
| Mazandaran | Qaemshahr | forest soil | N: 36°23′56.75″; E: 52°49′33.97″ | |
| M. sigmaturus | Kerman | Kerman | soil | N: 30°15′14.9″; E: 57°6′14.73″ |
| Fars | Shiraz | ash tree | N: 29°43′45.63″; E: 52°34′56.79″ |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accession Number | Locality | OP210758 | AB361439 | AB361441 | JQ742964 | AB361438 | AB361440 | AB361442 | |
| 1 | OP210758 | Iran | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | |
| 2 | AB361439 | Japan | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.003 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| 3 | AB361441 | Japan | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.003 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | |
| 4 | JQ742964 | Iran | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | |
| 5 | AB361438 | Japan | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| 6 | AB361440 | Japan | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| 7 | AB361442 | Japan | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Source | df | SS | MS | Pseudo-F | p (Perm) | Unique Perms |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| species | 5 | 895.46 | 179.09 | 397.34 | 0.001 | 998 |
| Variables | 154 | 69.412 | 0.45073 | |||
| Total | 159 | 964.88 |
| M. paitensis | M. brachyuris | M. sigmaturus | M. lacustris | M. kermaniensis | M. hawaiiensis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. paitensis | ||||||
| M. brachyuris | 0.33 | |||||
| M. sigmaturus | 0.28 | 0.38 | ||||
| M. lacustris | 0.93 | 0.76 | 0.89 | |||
| M. kermaniensis | 0.61 | 0.60 | 0.74 | 0.81 | ||
| M. hawaiiensis | 0.39 | 0.55 | 0.51 | 1.81 | 0.77 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shokoohi, E.; Moyo, N. Molecular Character of Mylonchulus hawaiiensis and Morphometric Differentiation of Six Mylonchulus (Nematoda; Order: Mononchida; Family: Mylonchulidae) Species Using Multivariate Analysis. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 13, 655-666. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres13030047
Shokoohi E, Moyo N. Molecular Character of Mylonchulus hawaiiensis and Morphometric Differentiation of Six Mylonchulus (Nematoda; Order: Mononchida; Family: Mylonchulidae) Species Using Multivariate Analysis. Microbiology Research. 2022; 13(3):655-666. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres13030047
Chicago/Turabian StyleShokoohi, Ebrahim, and Ngonidzashe Moyo. 2022. "Molecular Character of Mylonchulus hawaiiensis and Morphometric Differentiation of Six Mylonchulus (Nematoda; Order: Mononchida; Family: Mylonchulidae) Species Using Multivariate Analysis" Microbiology Research 13, no. 3: 655-666. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres13030047
APA StyleShokoohi, E., & Moyo, N. (2022). Molecular Character of Mylonchulus hawaiiensis and Morphometric Differentiation of Six Mylonchulus (Nematoda; Order: Mononchida; Family: Mylonchulidae) Species Using Multivariate Analysis. Microbiology Research, 13(3), 655-666. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres13030047







