Abstract
Mononchida members are predatory nematodes with the potential to reduce the number of plant-parasitic nematodes in the soil. During a survey on Mononchida in Iran, several populations of Mylonchulus were recovered from various localities. A population of M. hawaiiensis was studied using 18S rDNA. The phylogenetic analysis using Bayesian inference placed the sequenced M. hawiinesis (OP210758) together with other M. hawaiiensis from Japan (AB361438-AB361442) with a 1.00 posterior probability support. In addition, morphological differences between six Mylonchulus (Nematoda; order: Mononchida; Family: Mylonchulidae) populations were investigated in Iran using discriminant analyses (DA), PERMANOVA, and principal coordinate analysis (PCoA). The purpose was to evaluate the efficacy of PCoA and DA in separating the Mylonchulus species, namely M. sigmaturus, M. paitensis, M. lacustris, M. brachyuris, M. kermaninesis, and M. hawaiiensis. To achieve this, 16 morphometric measurements (body length, a, b, c, c′, V, G1, G2, buccal cavity length, buccal cavity width, dorsal tooth apex, dorsal tooth length, neck length, amphid from anterior end, rectum, and tail length) were made on 160 specimens. The analysis of variance showed that all features were significantly different among the species, except a, b, and the amphid position from the anterior end and tail length. The stepwise discriminant analysis revealed that body length, tail length, neck length, and c′ value were the four most discriminating variables useful to distinguish clearly the six species of Mylonchulus. The variables with strong discriminatory power correctly classified 98.87% of individuals from Iran’s sample of known Mylonchulus species. The results provide a morphometric basis for effectively distinguishing Mylonchulus species.
1. Introduction
The threat group of invertebrates in 1861 by Diesing was considered in Nematoda [1]. In Nematoda, the order Mononchida [2,3] comprises predators found in various habitats, including terrestrial to aquatic [4]. These groups of nematodes play an essential role in the dynamics of the fauna of the soil [5]. Mononchida members play a crucial role in decreasing the plant-parasitic nematodes; however, this predatory behaviour is mainly investigated in the controlled environment [6]. In contrast, Clarkus papillatus is being studied for controlling Meloidogyne in the sugar beet field [7]. Besides, Mononchids have no food preference and feed on a variety of soil microorganisms, including nematodes [4]. Additionally, the predatory nematodes have a potential for mass rearing on the medium [6]. Conversely, diversity in the prey has been observed for the various genera of Mononchida [4]. Therefore, their precise identification helps to find out a suitable predator to combat the plant-parasitic nematodes in future research. The genus Mylonchulus [8] (Nematoda; order: Mononchida; family: Mylonchulidae), is a broadly distributed taxon with six species being reported from Iran [5,6,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17]. Morphology, morphometrics, and molecular characters are the primary distinguishing tool for predator nematodes [4,5]. However, in some species of the Mylonchulus, the morphology and morphometrics overlap [4], so species identification becomes problematic. Multivariate analysis of morphometric characteristics has been used to differentiate species of the animals, such as fish [18], or different populations belonging to the same species using discriminant analysis for nematodes [19,20]. However, the usefulness of multivariate analysis to distinguish the Mylonchulus species has not yet been investigated. Therefore, the present study aimed (1) to study the molecular characteristics of M. hawaiiensis using 18S rDNA, and (2) to discriminate the species of Mylonchulus using discriminant analysis (DA) and principal coordinate analysis (PCoA).
2. Material and Method
2.1. Nematode Isolation, Processing, and Identification
Soil samples were collected from various localities in Iran (Figure 1 and Table 1). Nematode extraction was achieved using the modified tray method [21]. Extracted nematodes were fixed with a hot 4% formaldehyde solution, preserved in an anhydrous glycerine utilizing the procedure described by De Grisse [22], and mounted on microscopic glass slides. The nematodes were then identified using Ahmad and Jairajpuri [4], up to species level.
Figure 1.
Localities of the sampling (red star) for Mylonchulus species in Iran.

Table 1.
Geographic locations and coordination of the species studied.
2.2. DNA Extraction, PCR, and Phylogenetic Analysis
DNA isolation was completed based on the Chelex method [23]. Two individuals of the species were hand-picked with a fine tip needle and transferred to a 1.5 mL Eppendorf tube containing 20 μL nuclease-free water. The nematodes in the tube were crushed with the tip of a fine sterilised needle and vortexed. Thirty microliters of 5% Chelex® 50 and five µL of proteinase K were added to the tube and mixed. The tube with the crushed nematode was set at 56 °C for 2 hours, then 95 °C for 10 min to deactivate the proteinase K, and spun for 2 min at 16000 rpm [24]. The supernatant was extracted from the tube and stored at −20 °C. Afterward, the forward and reverse primers, 988F (5′-CTCAAAGATTAAGCCATGC-3′) and 1912R (5′-TTTACGGTCAGAACTAGGG-3′) [25], were used in the PCR reactions for partial amplification of the 18S rDNA region. PCR was conducted with eight μL of the DNA template, 12.5 μL of 2X PCR Master Mix green (NEB, Hitchin, UK), one μL of each primer (10 pmol μL−1), and ddH2O for a final volume of 25 μL. The amplification was processed using a bio-rad thermocycler (Hercules, CA, USA), with the following program: initial denaturation for 3 min at 94 °C; 37 cycles of denaturation for 45 s at 94 °C; 54 °C annealing temperature; extension from 45 s to 1 min at 72 °C; and finally an extension step of 6 min at 72 °C followed by a temperature on hold at 4 °C. After DNA amplification, four μL of PCR product was loaded on a 1.5% agarose gel in TBE buffer (40 mM Tris, 40 mM boric acid, and one mM EDTA) for assessment of the DNA bands. The band was dyed with SafeView classic (abm life science, Vancouver, Pretoria, Canada) and photographed on a UV transilluminator. The PCR product was kept at −20 °C. Finally, Inqaba Biotech company (Pretoria, South Africa) purified and sequenced the PCR product. The ribosomal DNA sequences were analyzed and edited with BioEdit [26] and aligned using CLUSTAL W [27]. A phylogenetic tree was produced using the Bayesian inference method as implemented in the program MrBayes 3.1.2 [28]. Analysis using the GTR+G+I model was started with a random starting tree and ran with the Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) for 106 generations for 18S rDNA. The tree was checked with the TreeView software [29]. In addition, as outgroups, based on 18S rDNA, Bathyodontus mirus [30,31] (AY284744; FJ969116) was used for the phylogenetic analysis as an outgroup. The original partial 18S rDNA sequence of M. hawaiiensis was deposited in GenBank under the accession number OP210758.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
The samples were collected from various localities in Iran (Figure 1 and Table 1). A PERMANOVA was performed with the morphometrics obtained from fixed specimens from 16 traits in Primer v7 (Auckland, New Zealand)/PERMANOVA+ [32]. First, a pretreatment was conducted to standardize the data using the Log10 as used for morphometric data provided by Nattero et al. [33] of the 16 traits analyzed to transform the variables of different measurement units to the same scale. A matrix of Euclidean distances was then constructed, and the PERMANOVA was performed. The statistical significance of the analysis was tested with 999 permutations based on a type III sum of squares. The general patterns of morphological variation of the studied populations in each management category were analyzed using a Principal Coordinates Analysis as implemented in Primer v7/PERMANOVA+ [32]. Therefore, the same pretreatment and Euclidian distance considered in the PERMANOVA design were used. Totally, 160 individuals were analyzed for this study. The morphometric data were extracted from the fixed specimens. Twenty-six specimens of each species, excluding M. sigmaturus of which thirty specimens were analyzed. Sixteen morphometric characters, viz. body length (L), “a” (body length/greatest body diameter), “b” (body length/distance from anterior to pharyngeal-intestinal valve), c (body length/tail length), “c′” (tail length/tail diameter at anus), V (% distance of vulva from anterior/body length), G1 (% anterior genital branch length/body length), G2 (% posterior genital branch length/body length), buccal cavity length, buccal cavity width, dorsal tooth length, dorsal tooth apex (% dorsal tooth apex form the anterior end of buccal cavity/buccal cavity length), amphids opening to anterior end, neck length, rectum, and tail length were used for analysis. The morphometrics were obtained from the fixed nematode specimens. Data on the morphometric measurements of the species were analyzed using XLSTAT [34]. Using a stepwise model, the same characters were used for discriminant analysis (DA). Before the examination, the measures were standardized for study with XLSTAT software [34]. The morphometric data were standardized by Log10. Additionally, the hierarchical cluster was studied using the spearman correlation coefficient using XLSTAT.
3. Results
3.1. Molecular Analysis
The phylogenetic tree indicated Mylonchulus as a monophyletic group with a 1.00 posterior probability support (Figure 2). The Bayesian tree placed the Iranian population of M. hawaiiensis together with the other molecularly identified as M. hawaiiensis with 1.00 posterior probability. However, another population of the same species (JQ742964) from Iran was placed differently in the phylogenetic tree under the Mylonchulus group (Figure 2).
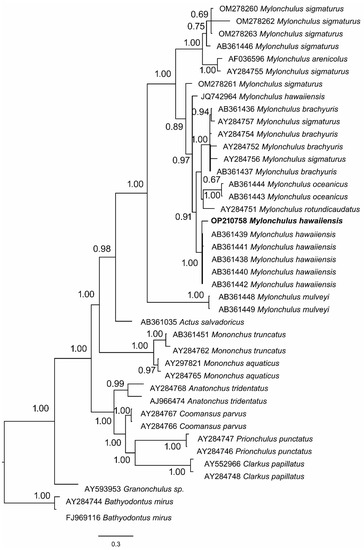
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic tree using Bayesian inference, including the newly sequenced M. hawaiiensis based on 18S rDNA.
Pairwise Maximum Composite Likelihood distance for the 18S rDNA region of M. hawaiiensis disclosed that the genetic distances ranged from 0.000 to 0.002. Iranian population (OP210758) has the same genetic distance (0.001) with the Japanese (AB361438-AB361442), and the Iranian population (JQ742964) (Table 2). Despite the molecularly identified population as M. hawaiiensis placed separately; however, the genetic distance showed no differences among the populations.

Table 2.
Genetic pairwise distance of different populations of Mylonchulus hawaiiensis.
3.2. Morphometric Characteristics
The species identified morphologically (Figure 3) resembles the information provided for the species of Mylonchulus by Ahmad and Jairajpuri [4]. However, the result indicated that a, b, and amphidial position to anterior end and tail length had no significant effect (p > 0.05) on the morphology of the Mylonchulus species (Figure 3 and Table 3). Based on F and Wilks’ Lambda, the main discriminant variables in the present study were: c, dorsal tooth apex, G2%, dorsal tooth length, and neck (Table 3).
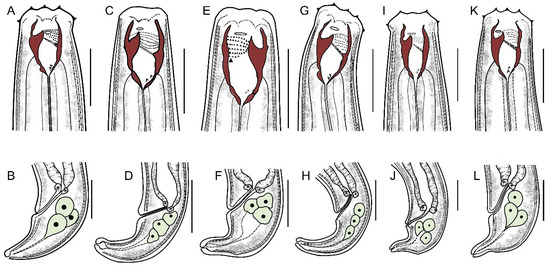
Figure 3.
Line illustrations of six Mylonchulus species. (A,B) Mylonchulus brachyuris (Bütschli, 1873) Cobb, 1917. (C,D) Mylonchulus hawaiiensis (Cassidy, 1931) Goodey, 1951. (E,F) Mylonchulus kermaniensis Shokoohi, Mehrabi-Nasab, Mirzaei, and Peneva, 2013. (G,H) Mylonchulus lacustris (Cobb in Cobb, 1915) Andrássy, 1958. (I,J) Mylonchulus paitensis Yeates, 1992. (K,L) Mylonchulus sigmaturus (Cobb, 1917) Altherr, 1953. (Up-row: Anterior end. Down-row: posterior end. Scale bar: 25 µm).

Table 3.
Discriminant functions for the morphometric variables of six Mylonchulus species from Iran.
Table 3.
Discriminant functions for the morphometric variables of six Mylonchulus species from Iran.
| Wilks’ Lambda | F | Sig. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Body Length | 0.434 | 5.749 | 0.002 |
| a | 0.598 | 2.961 | 0.034 |
| b | 0.752 | 1.45 | 0.246 |
| c | 0.208 | 16.787 | 0.000 |
| c′ | 0.441 | 5.573 | 0.002 |
| V | 0.353 | 8.08 | 0.000 |
| G1% | 0.561 | 3.448 | 0.019 |
| G2% | 0.289 | 10.841 | 0.000 |
| Neck | 0.343 | 8.434 | 0.000 |
| Buccal cavity length | 0.558 | 3.479 | 0.018 |
| Buccal cavity width | 0.392 | 6.818 | 0.001 |
| Dorsal tooth apex | 0.268 | 12.041 | 0.000 |
| Amphidial position to ant. end | 0.68 | 2.074 | 0.107 |
| Dorsal tooth length | 0.32 | 9.36 | 0.000 |
| Rectum | 0.614 | 2.77 | 0.044 |
| Tail length | 0.776 | 1.27 | 0.312 |
The highest values in the ratio of the Mylonchulus species were found in M. paitensis (a = 30.0 ± 0.8), M. hawaiiensis (b = 24.0 ± 1.5), M. kermaniensis (c = 33.1 ± 1.6), M. lacustris (c′ = 1.9 ± 0.03), and M. paitensis (V = 64.4 ± 0.4). Regarding the G1%, M. paitensis (18.0 ± 1.0), and G2%, M. kermaniensis (20.8 ± 0.2) showed the highest value (Table 4).

Table 4.
Descriptive statistics of morphometrics for six Mylonchulus species from Iran (Mean ± Standard Error). Characters with similar letters have no significant differences.
Table 4.
Descriptive statistics of morphometrics for six Mylonchulus species from Iran (Mean ± Standard Error). Characters with similar letters have no significant differences.
| Genus | M. paitensis | M. brachyuris | M. sigmaturus | M. lacustris | M. kermaniensis | M. hawaiiensis | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body length | 1164.5 ± 74.1 a | 1198.6 ± 50.9 a | 1263.1 ± 24.1 ac | 979.6 ± 25.8 b | 1357.2 ± 31.6 c | 1195.8 ± 62.9 a | 0.000 |
| a | 30.0 ± 0.8 ac | 28.2 ± 1.7 abc | 31.9 ± 1.9 c | 26.0 ± 1.3 ab | 29.0 ± 1.6 ac | 24.0 ± 1.5 b | 0.17 |
| b | 3.4 ± 0.1 a | 3.5 ± 0.1 ab | 3.5 ± 0.2 ab | 3.4 ± 0.1 ab | 3.6 ± 0.1 ab | 3.7 ± 0.1 b | 0.222 |
| c | 29.7 ± 0.6 a | 30.8 ± 0.7 ac | 31.8 ± 0.7 ac | 21.5 ± 0.3 b | 33.1 ± 1.6 c | 23.5 ± 1.2 b | 0.000 |
| c′ | 1.4 ± 0.02 a | 1.4 ± 0.08 a | 1.5 ± 0.08 ac | 1.9 ± 0.03 b | 1.5 ± 0.07 a | 1.7 ± 0.09 c | 0.000 |
| V | 64.4 ± 0.4 a | 61.8 ± 0.6 a | 63.4 ± 0.2 a | 58.5 ± 1.2 b | 63.5 ± 0.7 a | 55.3 ± 1.8 c | 0.000 |
| G1% | 18.0 ± 1.0 a | 16.0 ± 0.9 a | 16.7 ± 1.0 a | 11.4 ± 0.6 b | 16.8 ± 0.9 a | 16.3 ± 1.4 a | 0.002 |
| G2% | 16.9 ± 1.2 a | 14.3 ± 1.5 a | 15.8 ± 1.1 a | 9.4 ± 0.2 b | 20.8 ± 0.2 c | 17.1 ± 1.4 a | 0.000 |
| Neck | 348.1 ± 24.3 ac | 341.8 ± 8.1 c | 362.5 ± 3.9 ac | 283.9 ± 3.4 b | 378.5 ± 7.3 a | 289.8 ± 12.1 b | 0.000 |
| Buccal cavity length | 24.8 ± 0.6 ac | 23.4 ± 0.3 c | 25.3 ± 0.2 ac | 24.9 ± 0.3 ac | 25.8 ± 0.4 ab | 27.3 ± 1.1 b | 0.009 |
| Buccal cavity width | 13.9 ± 0.6 ac | 12.7 ± 0.5 ce | 13.3 ± 0.8 ace | 11.5 ± 0.2 e | 16.3 ± 0.5 b | 14.8 ± 0.9 ab | 0.000 |
| Dorsal tooth apex | 3.6 ± 0.7 a | 4.0 ± 0.1 a | 4.5 ± 0.2 ab | 5.6 ± 0.2 bd | 7.0 ± 0.3 c | 6.4 ± 0.3 dc | 0.000 |
| Amphidial position to ant. end | 10.1 ± 1.3 a | 9.5 ± 0.3 a | 12.8 ± 0.6 b | 9.8 ± 0.2 a | 10.4 ± 0.3 a | 10.5 ± 0.4 a | 0.082 |
| Dorsal tooth length | 8.1 ± 0.3 ac | 7.7 ± 0.3 a | 8.1 ± 0.1 ac | 7.6 ± 0.1 a | 8.5 ± 0.2 c | 6.3 ± 0.3 b | 0.000 |
| Rectum | 22.5 ± 1.5 ac | 23.6 ± 0.7 c | 22.0 ± 0.3 abc | 20.2 ± 0.7 ab | 20.0 ± 0.3 b | 20.3 ± 1.1 ab | 0.024 |
| Tail | 39.7 ± 2.9 a | 39.1 ± 2.2 a | 40.0 ± 0.7 ab | 45.6 ± 0.9 b | 42.2 ± 1.8 ab | 43.3 ± 1.7 ab | 0.131 |
The morphometrical differences between the six Mylonchulus species are shown in Figure 4 and Figure 5. In Figure 4, the hierarchical cluster plot shows the similarity of the different Mylonchulus species. The similarity distances obtained from the morphometric measurements are graphically represented, a first cluster grouped M. lacustris, a second cluster made up of M. hawaiiensis, a third cluster that includes M. kermaniensis, and the fourth group made up M. paitensis, M. sigmaturus, and M. brachyuris. The fourth group showed overlapped morphometrics, and morphometrical variation was observed (Figure 4).
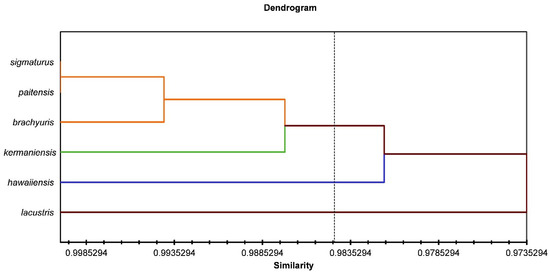
Figure 4.
Hierarchical cluster analysis for six species of Mylonchulus.
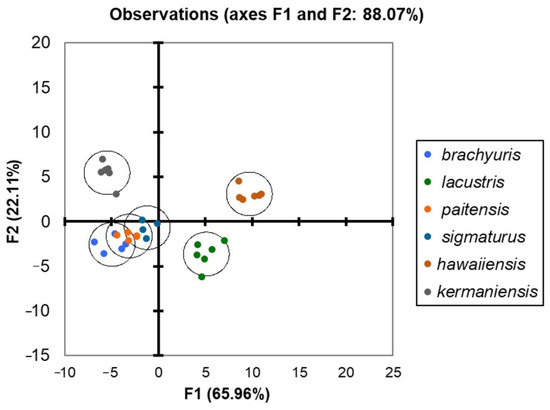
Figure 5.
Discriminant analysis plot for six species of Mylonchulus.
The different and distinctive morphometrical models for each species are reflected in Figure 5, which reveals a precise spatial distribution of each Mylonchulus species, with an overlap of M. paitensis, M. brachyuris, and M. sigmaturus. The DA plot (Figure 5) clearly separated M. hawaiiensis, M. lacustris, and M. kermaniensis.
Moreover, the PERMANOVA evidenced that 90.5% of the variation was presented among the populations (p < 0.001) (Figure 6 and Table 5). Likewise, the PCoA showed a broad variation similar to that identified by the DA and PERMANOVA test among M. paitensis, M. sigmaturus, and M. brachyuris. In PCoA (Figure 6), four groups of species were distinguished. The groups include (1) M. hawaiiensis, (2) M. kermaniensis, (3) M. lacustris, and (4) M. paitensis, M. sigmaturus, and M. brachyuris. Pairwise distance between the populations of Mylonchulus (Table 6), showed the same result obtained by the PCoA result displayed in Figure 6. The pairwise distance showed a high similarity of M. paitensis with M. sigmaturus (r = 0.28), and M. brachyuris (r = 0.33). In contrast, M. hawaiiensis showed highest distance compared with M. lacustris (r = 1.81), and M. kermaniensis (r = 0.77) (Table 6).
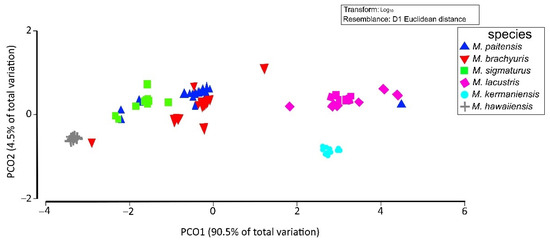
Figure 6.
Principal coordinates analysis (PCoA) ordination indicates the relationships among populations for six species of Mylonchulus.

Table 5.
Permutational analysis of variance (PERMANOVA) for sixteen morphological traits in different populations of Mylonchulus.

Table 6.
Pairwise distance between the populations of Mylonchulus using Primer 7 software.
4. Discussion
The present results indicate that 18S rDNA sequence data are a valuable marker for the phylogenetic analysis within Mylonchulus species. This agrees with the previous result obtained [5,11,35]. Tree topology using Bayesian inference shows that M. hawaiiensis stand separately, which contrasts with the result obtained by Olia et al. [35]. However, the genetic distance revealed no significant differences among the populations from Iran and Japan. Therefore, the variation that exists may be due to the geographic location. Shokoohi et al. [11] and Koohkan et al. [5] indicated that the populations of Mylonchulus make a monophyletic group. The present study obtained the same result.
Overall, the environment and geographic location are key factors in nematodes’ morphological variation [36]. They have indicated forest soil to be a more favorable condition for soil nematode dynamics. Besides, the genetic diversity showed to be affected by the geographic location of the nematode species [37]. Therefore, some environmental conditions and expression of genetic differences could be responsible for changes in the morphology of various nematode species. Predator nematodes of the order Mononchida are present in diverse habitats, from cultivated to natural lands [4]. The result indicated that three species, including M. sigmaturus, M. paitensis, and M. brachyuris overlap the morphometrics. They have a similar range for body length (1000–1392 µm for M. sigmaturus; 980–1400 µm for M. paitensis; and 1100–1580 µm for M. brachyuris), and tail length (31–48 µm for M. sigmaturus; 31–49 µm for M. paitensis; and 39–56 µm for M. brachyuris) [9,10]. However, they have different tail morphology which is similar to M. sigmaturus and M. brachyuris with the terminal spinneret. Tail in M. sigmaturus and M. paitensis are conoid, bent ventrally, with short and set off digitate portion. Whereas M. brachyuris is conical without a set off digitate part and spinneret open sub-terminally.
The results allowed for morphometric differentiation in six Mylonchulus species using sixteen features. The species analyzed could be discriminated by the morphometric models generated, demonstrating that discriminant analysis supported differentiating the species. Moreover, these morphological variables could be used to increase the consistency of specimens’ classification in each species. Stock and Kaya [38] indicated that PCA and discriminant analysis are helpful tools to differentiate the Heterorhabditis species, and they have shown reliable morphometrics to identify the EPN species. Rubtsova et al. [39] showed the efficiency of discriminant analysis and hierarchical analysis in distinguishing the Longidorus species. Moreover, Stock and Nadler [40] analyzed the Panagrellus, which differentiated the species sufficiently using Discriminant analysis. In addition, PCA has been successfully used to separate the Panagrellus species [40]. The same results were obtained in the recent work. PERMANOVA and PCoA already been used to study Mexican plants such as Agave maximiliana [41] and marine nematodes such as Paracanthonchus gynodiporata [42]. A morphological variation has been observed using non-metric Dimensional Scale for P. gynodiporata along the coastline of Brazil [42]. The same result was obtained in the present study, in which morphological variation exists among the populations of Mylonchulus.
In the present study, canonical plots of females derived from the results obtained by the discriminant analysis, hierarchical clustering, and principal component analysis showed a high degree of clustering among the analyzed species of Mylonchulus. The morphometric characters chosen played a vital role in the discrimination process. This suggests that the morphometric features selected should be used to identify Mylonchulus species. Therefore, we consider that morphological features, e.g., the body length, buccal cavity length and width, tooth length, G1, and G2%, neck, and tail length, should be considered together with morphometric characters for the identification based on the females for this group of nematodes. Overall, the biology of the animals needs morphometrics [43] which affect the development, evolution, relationship, and adaptation. In some cases, such as Prionchlus punctatus and Mononchus aquaticus, their life cycle takes 45 and 15 days at 25 °C, respectively [44,45]. Besides, the morphometrics of the above-mentioned species are different, which affects their life cycle. In another study, Cohn and Mordechai [46] observed that a high population of M. sigmaturus is significantly correlated with a low population density of Tylenchulus semipenetrans. Conversely, the availability of the citrus nematode as prey affects the morphometrics of M. sigmaturus. However, due to the lack of information on the biology of mononchids in Iran, discussing the relationship between biology and morphometrics is complicated.
5. Conclusions
This research aimed to analyze morphometric differentiation among six Mylonchulus species of Mylonchulus from Iran and prove the effectiveness of the multivariate analysis. The six species analyzed could be discriminated by the generated morphometric model, therefore showing that discriminant analysis helped differentiate species. The discriminant analysis approach showed significant differences between species and sameness within each species. However, the discriminant analysis showed overlap between M. sigmaturus and M. paitensis, which indicates that these two species should be reconsidered for their identification based on morphometrics. Additionally, the result suggests a synonymous potential between those two species. Although, the morphometric and molecular characters used in the present study are still reliable for distinguishing M. kermaniensis, M. lacustris, and M. hawaiiensis. However, more molecular markers in combination with the information derived from morphological features will help study the variability of the species.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.S.; methodology, E.S. and N.M.; software, E.S.; validation, E.S. and N.M.; formal analysis, E.S.; investigation, E.S.; resources, E.S. and N.M.; data curation, E.S.; writing—original draft preparation, E.S.; writing—review and editing, E.S. and N.M.; visualization, E.S.; supervision, E.S.; project administration, E.S.; funding acquisition, E.S. and N.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding, and The APC was funded by the University of Limpopo.
Data Availability Statement
The morphometric data were generated based on the permanent slides of the authors. All data used for the statistical analysis were presented as figures and tables in the paper.
Acknowledgments
We thank Hadi Panahi for his great assistance in sampling nematodes. The authors acknowledge the University of Limpopo for APC. We also thank Amini for her comments on the statistical analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chitwood, B.G. The English word “Nema” revised. Sys. Biol. 1957, 4, 1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jairajpuri, M.S. Studies on Mononchida of India. I. The genera Hadronchus, Iotonchus and Miconchus and a revised classification of Mononchida, new order. Nematologica 1969, 15, 557–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassidy, G.H. Some mononchs of Hawaii. Hawaiian Plant. Rec. 1931, 35, 305–339. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, W.; Jairajpuri, M.S. Mononchida: The predaceous nematodes. In Nematology Monographs and Perspectives; Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2010; Volume 7, 298p. [Google Scholar]
- Koohkan, M.; Shokoohi, E.; Mullin, P. Phylogenetic relationships of three families of the suborder Mononchina Kirjanova & Krall, 1969 inferred from 18S rDNA. Nematology 2015, 17, 1113–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koohkan, M.; Shokoohi, E. Mass Production and Prey Species of Mylonchulus sigmaturus (Nematoda: Mylonchulidae) in the Laboratory. Acta. Zool. Bulgarica. 2014, 66, 555–558. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, Z.; Kim, Y.H. A review on the role of predatory soil nematodes in the biological control of plant parasitic nematodes. App. Soil Ecol. 2007, 35, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobb, M.V. Some freshwater nematodes of the Douglas Lake Region of Michigan, USA. Trans. Am. Micros. Soc. 1915, 34, 21–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahmand, S.; Eskandari, A.; Orselli, L.; Karegar, A. Some known species of the genera Mononchus Bastian, 1865 and Mylonchulus (Cobb, 1916) Altherr, 1953 (Nematoda: Mononchina) from Semnan province, Iran. Nematol. Mediter. 2009, 37, 145–154. [Google Scholar]
- Koohkan, M.; Shokoohi, E.; Abolafia, J. Study of some mononchids (Mononchida) from Iran with a compendium of the genus Anatonchus. Trop. Zool. 2014, 27, 88–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokoohi, E.; Mehrabi-Nasab, A.; Mirzaei, M.; Peneva, V. Study of mononchids from Iran, with description of Mylonchulus kermaniensis sp. n. (Nematoda: Mononchida). Zootaxa 2013, 3599, 519–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodey, T. Soil and Freshwater Nematodes; Methuen: London, UK, 1951; p. 390. [Google Scholar]
- Yeates, G.W. Nematodes from New Caledonia. 1. Introduction and Mononchoidea. Fundam. Appl. Nematol. 1992, 15, 101–126. [Google Scholar]
- Andrássy, I. Über das System der Mononchiden (Mononchidae Chitwood, 1937; Nematoda). Ann. Hist. Nat. Musei Natl. Hung. 1958, 50, 151–171. [Google Scholar]
- Cobb, N.A. The Mononchs. A genus of free-living predatory nematodes. Soil Sci. 1917, 3, 431–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altherr, E. Nématodes du sol du Jura vaudois et français. I. Bull. Soc. Vaud. Sci. Nat. 1953, 65, 429–460. [Google Scholar]
- Bütschli, O. Beitrage zur Kenntnis der freilebenden Nematoden. Nova Acta Acad. Caesareae Leipold-Carol. Nat. Curios 1873, 36, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Martinez, A.; De-Pablos-Heredero, C.; González, M.; Rodriguez, J.; Barba, C.; García, A. Usefulness of discriminant analysis in the morphometric differentiation of six native freshwater species from Ecuador. Animals 2021, 11, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyaku, S.T.; Kantety, R.V.; Lawrence, K.S.; van Santen, E.; Sharma, G.C. Canonical discriminant analysis of Rotylenchulus reniformis in Alabama. Nematropica 2013, 43, 171–181. [Google Scholar]
- Królaczyk, K.; Zaborski, D.; Dzierzba, E.; Kavetska, K.M. Redescription of Quasiamidostomum Fulicae (Rudolphi, 1819) Lomakin, 1991 (Nematoda: Amidostomatidae), a parasite of Fulica Atra (Gruiformes). J. Vet. Res. 2020, 64, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokoohi, E. Observation on Hemicriconemoides brachyurus (Loos, 1949) Chitwood & Birchfield, 1957 associated with grass in South Africa. Helminthologia 2022, 59, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Grisse, A.T. Contribution to the Morphology and the Systematics of the Criconematidae (Taylor, 1936) Thorne, 1949; Faculty of Agricultural Sciences: Gent, Belgium, 1969; p. 35. [Google Scholar]
- Straube, D.; Juen, A. Storage and shipping of tissue samples for DNA analyses: A case study on earthworms. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2013, 57, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokoohi, E. Morphological and molecular characterisation of Boleodorus volutus Lima & Siddiqi, 1963 from South Africa with the first SEM observations of the species. Russian J. Nematol. 2021, 29, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carta, L.K.; Li, S. Improved 18S small subunit rDNA primers for problematic nematode amplification. J. Nematol. 2018, 50, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nuc. Acids Sym. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibson, T.J. CLUSTAL W: Improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucl. Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Huelsenbeck, J. MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1572–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, R.D. TreeView: An application to display phylogenetic trees on personal computers. Comput. Appl. Biosci. 1996, 12, 357–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrássy, I. Eine interessante Nematodenfauna der Gerste. Nematologische Notizen. Acta Zool. Acad. Sci. Hung. 1956, 2, 307–317. [Google Scholar]
- Hopper, B.E.; Cairns, E.J. Taxonomic Keys to Plant, Soil and Aquatic Nematodes; Alabama Polytechnic Institute: Auburn, AL, USA, 1959; p. 176. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, K.R.; Gorley, R.N. PRIMER v7, 2015; Massey University Press: Auckland, New Zealand, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Nattero, J.; Piccinali, R.V.; Macedo Lopes, C.; Hernández, M.L.; Abrahan, L.; Lobbia, P.A.; Rodríguez, C.S.; de la Fuente, L.C. Morphometric variability among the species of the Sordida subcomplex (Hemiptera: Reduviidae: Triatominae): Evidence for differentiation across the distribution range of Triatoma sordida. Paras. Vec. 2017, 10, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addinsoft. XLSTAT, Analyse de données et Statistique avec MS Excel; Addinsoft: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Olia, M.; Ahmad, W.; Araki, M.; Minaka, N. Molecular characterization of some species of Mylonchulus (Nematoda: Mononchida) from Japan and comments on the status of Paramylonchulus and Pakmylonchulus. Nematology 2009, 11, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisa, R.U.; Tantray, A.Y.; Kouser, N.; Allie, K.A.; Wani, S.M.; Alamri, S.A.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Wijaya, L.; Shah, A.A. Influence of ecological and edaphic factors on biodiversity of soil nematodes. Saudi. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 3049–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, J.; Simões, M.J.; Gomes, P.; Barroso, C.; Pinho, D.; Conceição, L.; Fonseca, L.; Abrantes, I.; Pinheiro, M.; Conceição, E. Assessment of the Geographic Origins of Pinewood Nematode Isolates via Single Nucleotide Polymorphism in Effector Genes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, S.P.; Kaya, H.K. A multivariate analysis of morphometric characters of Heterorhabditis species (Nemata: Heterorhabditidae) and the role of morphometrics in the taxonomy of species of the genus. J. Parasitol. 1996, 82, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubtsova, T.V.; Chizhov, V.N.; Subbotin, S.A. Longidorus artemisiae sp. n. (Nematoda: Longidoridae) from roots of Artemisia sp., Rostov region, Russia. Russ. J. Nematol. 1999, 7, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Stock, S.P.; Nadler, S.A. Morphological and molecular characterisation of Panagrellus spp. (Cephalobina: Panagrolaimidae): Taxonomic status and phylogenetic relationships. Nematology 2006, 8, 921–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-Toledo, D.; Vargas-Ponce, O.; Ascencio-Ramírez, S.; Valadez-Sandoval, L.M.; Pérez-Alquicira, J.; Morales-Saavedra, J.; Huerta-Galván, O.F. Morphological and genetic variation in monocultures, forestry systems and wild populations of Agave maximiliana of western Mexico: Implications for its conservation. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apolônio Silva de Oliveira, D.; Decraemer, W.; Moens, T.; dos Santos, G.A.P.; Derycke, S. Low genetic but high morphological variation over more than 1000 km coastline refutes omnipresence of cryptic diversity in marine nematodes. BMC Evol. Biol. 2017, 17, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oxnard, C.; O’Higgins, P. Biology clearly needs morphometrics. Does morphometrics need biology? Biol. Theory 2009, 4, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maertens, D. Observations on life cycle of Prionchulus punctatus (Cobb, 1917) and culture conditions. Biol. Jb. Dodonaea 1975, 43, 197–218. [Google Scholar]
- Grootaert, P.; Maertens, D. Cultivation and life cycle of Mononchus aquaticus. Nematologica 1976, 22, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohn, E.; Mordechai, E. Biological control of citrus nematode. Phytoparasitica 1973, 1, Abstract. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).