Abstract
African swine fever (ASF) is a highly contagious viral infection of domestic and wild pigs with high mortality. First reported in East Africa in the early 1900s, ASF was largely controlled in domestic pigs in many countries. However, in recent years ASF outbreaks have been reported in several countries in Europe and Asia. The occurrence of ASF in China, the largest pork producer in the world, in 2018 and in India, the country that surrounds and shares open borders with Nepal, has increased the risk of ASF transmission to Nepal. Lately, the pork industry has been growing in Nepal, overcoming traditional religious and cultural biases against it. However, the emergence of viral infections such as ASF could severely affect the industry’s growth and sustainability. Because there are no effective vaccines available to prevent ASF, the government should focus on preventing entry of the virus through strict quarantine measures at the borders, controls on illegal trade, and effective management practices, including biosecurity measures.
1. Introduction
African swine fever (ASF) is a devastating and economically important infectious disease of domestic and wild pigs with a high mortality rate. ASF is caused by the ASF virus (ASFV), a large double-stranded DNA virus of the Asfarviridae family. It is one of the diseases notifiable to the World Organization for Animal Health [1]. First described in East Africa in the early 1900s, ASFV subsequently spread to the European countries and the Caribbean but was largely controlled in domestic pigs by the end of 20th century [2]. The 21st century outbreaks of ASF in Georgia (2007), the Russian Federation (2007), China (2018), India (2020), and other European and Asian countries indicate its potential emergence as a major health threat to the global pig population [2,3].
Nepal is an agricultural country where the livestock sector alone contributes around 11.5% of gross domestic product (GDP) [4]. There are about 7.3 million cattle, 5.2 million buffalos, 0.8 million sheep, 11 million goats, and 1.4 million pigs in Nepal [4]. With reduced cultural bigotry toward pigs and pork consumption, and increased support and promotion of pig husbandry by the Government of Nepal, pig farming has been expanding in recent years [5]. In the past decade (from 2008/9 to 2018/19), the pig population and pork production in Nepal increased by 42.30% and 68.19%, respectively (Figure 1) [4,6]. Pork comprises 8% of total meat production in Nepal, and pork consumption is <1 kg per capita, out of a national average of approx. 11 kg of total meat consumed per capita [7].
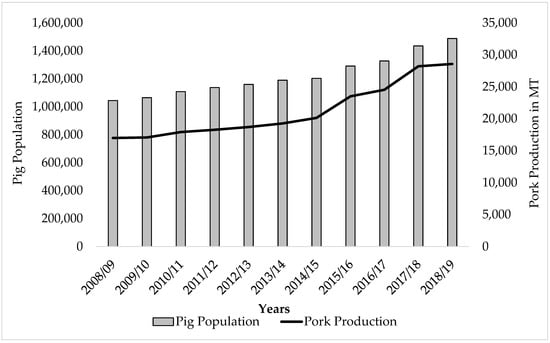
Figure 1.
Pig population and pork production from the year 2008/09 to 2018/19 in Nepal [4,6].
Pig farming is conducted in each of Nepal’s 77 districts. Jhapa district in the lowland plains (Terai) ranks first in pig population, with over 80,000 pigs, while Mustang in the trans-Himalayan climatic zone, with less than 100 pigs, ranks last (Figure 2) [7]. The pig population is higher in Provinces 1 and 5, where pig farming ethnic communities predominate (Figure 2) [7].
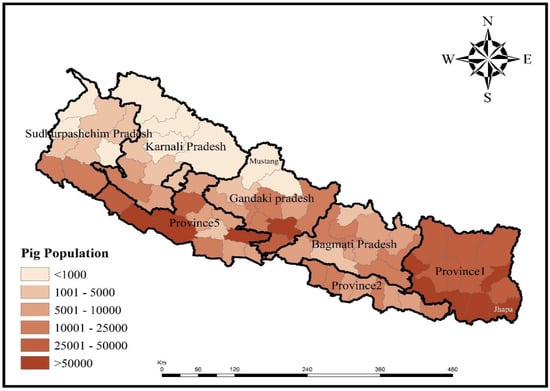
Figure 2.
Pig population in different districts of Nepal [7]. Map was created using ArcGIS version 10.8 (ESRI, West Redlands, CA, USA).
While pig farming is growing in Nepal, diseases such as ASF could jeopardize this industry, which already suffers from challenges in pig breeding, marketing, feed availability, and the management of other pig diseases. The recent outbreaks of ASF in Assam, India [3], which is around 670 km away from Nepal, and in China [8], the world’s largest pork producer and another country neighboring Nepal, are alarming signs and big threats to the Nepalese pig industry. In this scenario, this paper reviews the epidemiology of ASF globally and in Asian countries, with special emphasis on the challenges and future perspectives of ASF in Nepal.
2. African Swine Fever
African swine fever virus (ASFV) belongs to the Asfivirus genus in the Asfarviridae family and is the only known DNA arbovirus [2]. ASFV is an icosahedral, linear double-stranded DNA virus with a 170 to 190 kbp genome and an average diameter of 200 nm [9]. The virion has an outer envelope, capsid, inner envelope, core-shell, and nucleoid [9]. Genotyping of ASFV is based on the nucleotide sequence of a 478 bp variable region in the C-terminus of the viral p72 gene [2,10]. There are 24 genotypes of ASFV and 8 serotypes based on viral hemagglutinin CD2-like protein (CD2v) and C-type lectin [2].
Domestic pigs, wild suids, and soft ticks are the hosts of ASFV. Common warthogs (Phacochoerus africanus) are believed to be the original vertebrate host of ASFV and the most important reservoir host in Africa [11]. Virus transmission occurs through direct contact with an infected animal; indirect contact with contaminated objects; consumption of infected meat; and through the bites of tampans (Ornithodoros spp.) [12]. Transport of infected animals and contaminated products is one of the major reasons for the transmission and spread of the virus [13]. Airborne transmission over short distances has also been identified as a possible route [12,14]. The stable fly (Stomoxys calcitrans) can also act as a mechanical vector up to 48 h after ingesting the virus [15]. ASFV can be excreted in genital secretions but sexual transmission is not yet known [12].
The incubation period for ASF is 2–7 days, and it varies according to the route of infection [16]. The disease can be classified as peracute, acute, subacute, or chronic [17]. In the peracute form, most of the animals die without any clinical signs and minimal gross lesions, but hemorrhages will be evident during post mortem [17]. However, some animals may exhibit clinical signs such as fever (41–42 °C), rapid respiration, or hyperemia of the skin along with 100% morbidity and mortality [16]. Acute and subacute forms are commonly observed and are caused by highly and moderately virulent strains, respectively [16]. The signs associated with the acute form are elevated body temperature (40–42 °C), anorexia, apathy, inactivity, cyanosis in the extremities of legs, ears, and tail, vomiting, epistaxis, abortion, and death with 90–100% mortality within 7–10 days [13,14,17]. Diarrhea is associated with the acute form during secondary bacterial infection [16]. Early leucopenia, splenomegaly, and extensive necrosis and hemorrhage of lymphoid tissues are observed in the acute form [14]. The subacute disease is manifested with clinical signs similar to the acute cases but in a less severe form [17]. Fever and reduced feed intake are observed for 10–12 days [16]. Mortality can be anywhere between 30–70%, and the surviving animals can recover within 2–3 weeks [14]. Infection with a low virulent strain causes a chronic disease that does not show any specific clinical signs or vascular lesions, but lesions can be observed in bacterial coinfection [13]. It may persist for a longer duration and clinical signs such as pneumonia, stunting, emaciation, arthritis, and skin ulcers may be seen, with hemorrhages during post mortem along with fibrinous pericarditis and pleuritis [17]. Poor growth, oscillating fever, skin lesions, and soft painless swelling of joints are also associated with the chronic form [16].
3. Global Epidemiology of African Swine Fever
ASF was first reported from East Africa in 1921 [18]. It was also reported in southern, central, and West Africa during the early 1900s and is maintained in one of the three different transmission cycles: the sylvatic, tick-domestic pig, and domestic pig cycles [18]. Portugal had an outbreak of ASF in 1957, for the first time outside of Africa [13]. Several other outbreaks subsequently occurred in Western Europe in the 1970s and 1980s (Figure 3) [13]. ASF outbreaks in South and North America mainly occurred in the 1980s. To date, Papua New Guinea is the only Australian country to report its first outbreak of ASF, in 2020 [19,20].The spread of the ASF virus can be attributed to the growth in the pig population and production; presence of a reservoir non-symptomatic pig population; and globalization [13]. In the 21st century, ASF outbreaks have been reported from several European, African, and Asian and Pacific countries (Table 1) (Figure 3) [12,14,20].
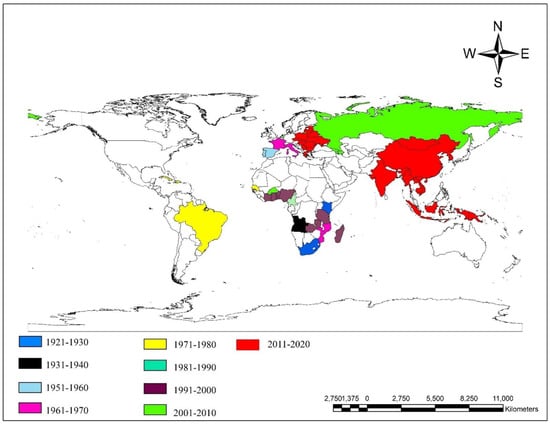
Figure 3.
Map of world showing ASF outbreaks from 1921 to 2020 [12,14,20]. Map was created using ArcGIS version 10.8 (ESRI, West Redlands, CA, USA).

Table 1.
Outbreaks of ASF in European, African, Asian, and Pacific countries in the 21st century [12,14,20].
ASF was first reported in India in January 2020. Subsequently, a total of 11 confirmed outbreaks (nine in Assam and two in Arunachal Pradesh) resulted in over 4100 ASF cases [21]. Over 3700 pigs died due to ASF, whereas around 14,000 pigs were culled in Assam alone [21]. Since the confirmation of the first outbreak in Liaoning Province on August 2018, China has reported 165 ASF outbreaks, with 1,193,000 pigs culled [22].
The current epidemiological data show that Europe accounts for the highest share of ASF outbreaks (66.87%), compared to Asia (32.72%) and Africa (0.41%) (Table 2) [20]. However, the majority of European outbreaks have been in wild boars, while those in Asia have been in domestic pigs. The loss of domestic pigs due to ASF has been very high (80%) in Asian countries compared to countries on other continents (Table 2). The persistence of ASF in wild boars and increasing outbreaks in domestic pigs have raise serious concerns for the global pig industry.

Table 2.
Cases of ASF reported from different continents from 2016 to 18 June 2020. (Losses include dead and culled animals) [20].
4. Factors Contributing to the Spread of ASF in Asia
Four of the top 10 pork producing countries in the world, namely China, Vietnam, the Philippines, and South Korea are in Asia; they produce 34,000, 2250, 1450, and 1350 thousand metric tons of pork, respectively [23]. Historically Asian countries have been less affected by ASF, probably due to the implementation of proper sanitary regulations and strict rules for the trade in animals and animal products [11]. Periodic outbreaks of other viral and prion diseases including BSE, influenza, and classical swine fever have further alerted Asian countries to strengthen their veterinary services and regulations [24].
In recent years, outbreaks of ASF have been reported from many Asian countries, including China, Laos, Vietnam, and India (Table 3) [25]. China is the key Asian country for the production and supply of pork to the global market. China also has international trade with various countries in Africa, where ASF is endemic and reemerging [11]. Therefore, outbreaks of ASF in China put all other Asian countries at high risk of ASFV transmission.

Table 3.
Outbreaks of ASF in Asian and Pacific regions. (2018–7 January 2021) [25].
The transport of live animals and pig products supports the spread of the virus at the regional level. Most Asian countries practice a system of free-range pig husbandry that causes endemic outbreaks of ASF. Illegal trade in pigs and pig products also favor the entry of ASFV and outbreaks of ASF in new areas [26]. Besides this, wild pigs may also serve as a reservoir of ASFV to Asian domestic pigs. Factors contributing to the spread of ASF in Asian countries, including the role of the soft tick Ornithodoros (Alectorobius) spp., wild boar, and the illegal trade, need further study [27].
5. Prevention and Control of ASF
There is no vaccine available for the effective control of the ASFV infection [13]. Once the disease is established in an area, it is extremely difficult to eradicate because ASFV can survive in meat and meat products, feeds, and various reservoirs including wild boars and ticks [17]. Culling a large number of pigs to prevent virus spread is one measure that has been successful. However, it faces ethical, environmental, and financial challenges [28]. Use of strict biosecurity measures remains the most effective method of ASF prevention. Limiting the access of people and vehicles into farms, requiring the use of separate clothing and boots inside farms, and the use of disinfectants and footbaths can reduce virus transmission [12]. The movement of pigs from infected areas must be restricted. Contact between wild boars and domesticated pigs should be prevented. Contaminated garbage from international airports and docks that are an important source of the virus should be incinerated instead of being fed to pigs [14]. Raising awareness among all the involved stakeholders, ensuring effective communication among them, launching user-friendly practical courses in biosecurity, and providing incentives such as compensation and insurance fees can be other effective aids to ASF preventive measures [29]. Contingency plans should be designed and made ready to implement when necessary, considering the geographical location, economy, epidemiological situation, and status of ASF in neighboring countries [14].
6. Risk of ASF in Nepal
ASF has created havoc in the pork industry worldwide. Even though ASF has been reported historically across Africa, America, Europe, and the Caribbean [30], its recent introduction was in 2007 in Caucasus, Georgia, followed by a rapid spread across Europe, Asia, and Africa [31]. Being a transboundary animal disease (TAD), the easy spread of the ASF virus through pigs and pork, contaminated feed, and equipment presents a great threat to pig-importing countries that lack proper surveillance and quarantine measures [32].
Nepal is a small landlocked country bordering China to the north and India on its other borders. The emergence of any new diseases in either of these neighboring countries presents a high risk of transmission to Nepal, owing to leaky borders, ineffective surveillance, and illegal imports of animals and animal products (Figure 4). Amid the introduction of ASF in surrounding countries, the government of Nepal imposed a ban on the import of pigs and pig products. However, illegal imports of these products are still an issue [33,34,35]. The pork industry has gained momentum in Nepal with a sustained growth trend in pork production and consumption through the past decade [4,6]. With the outbreaks of ASF in both neighboring countries, Nepal’s pork industry is now on the radar of this disease.
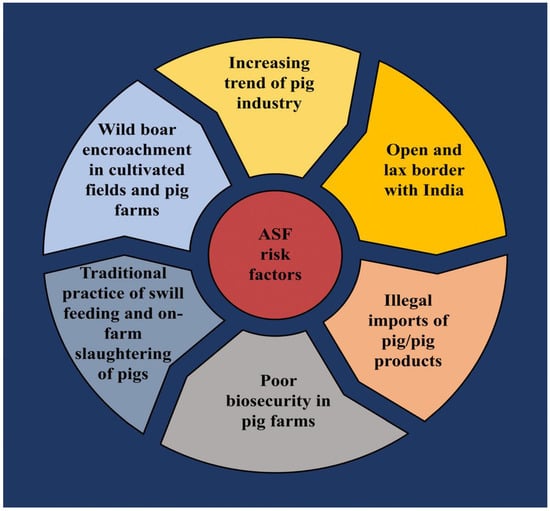
Figure 4.
Potential risk factors for ASF in Nepal.
Nepal has both conventional and modern pig farms, the majority of which are conventional with 1–2 pigs. Swill feeding is common in Nepal. Most of the pigs in the conventional system are raised on kitchen waste, grain by-products, and food industry by-products [36]. A large number of pigs are slaughtered on the farm itself as there are no registered pig slaughterhouses [37]. The practice of swill feeding along with slaughtering the animals on the farm are known as factors responsible for the spread of ASFV infection [38]. Most pig farms in the country have been built with locally available materials such as bamboo or wood laid upon mud rather than concrete [39,40]. In a majority of farms, there are no separate allocations for mating or farrowing, and the farms operate under poor sanitation measures [39]. The biosecurity measures at most of the farms are far from the basic standards. In addition, there is evidence of wild boar encroachment in agricultural fields and pig farms in different parts of the country [41,42]. The wild boars can be a potential source of infection for domestic pigs and even responsible for cross-country pathogen transmission, as the national parks and conservation areas in Nepal and India adjoin one another.
Between August 2018 and November 2019, China culled around 12 million pigs from 160 ASF outbreaks, losing billions of yuan [43]. A bilateral agreement between Nepal and China regarding the exchange of pigs and pig products can be risky if strict quarantine measures are not followed [44]. Nepal’s other neighbor, India, confirmed its first ASF cases in mid-May in Assam and Arunachal state, which have already culled around 15,000 pigs [45]. Besides China and India, there are several Asian countries such as South Korea, the Philippines, Vietnam, Cambodia, Hong Kong, and Vietnam that pose a constant menace to the Nepalese pork industry directly or indirectly through several international boundaries [46]. With the initial understanding of the infection in Arunachal Pradesh and Assam passing through Tibetan borders, the transmission in Laos and Myanmar, and a high number of deaths in China, the possibility of entry and existence of the virus in Nepal through the chain of international borders cannot be overlooked [46,47].
7. Challenges for ASF Control in Nepal
Nepal has not reported any cases of ASF as of 25 June 2020 [34], but the growth trend in pork imports through the past several years suggests an increased risk of virus entry into the country [48]. Apart from annual official imports of 8000–10,000 pig heads via India and 130 tons of pig products through China, Thailand, and Denmark, Nepal faces illegal imports of pigs through open borders coupled with ineffective quarantine measures [34,35]. Moreover, Nepal and India share transboundary wildlife habitats such as Chitwan National park and Valmiki Tiger reserve, Shuklaphanta National park, and Dudhwa Tiger Reserve, providing easy access for the movement of wild boars and increasing the transmission threat through sylvan routes [49]. Although the exact population of wild boar (Sus scrofa) is unknown, the number is likely to be increasing due to government protection of forest habitats [50]. A lack of programs for surveillance of ASFV in wild boars, lack of molecular diagnostic laboratories, very small budget allocations for wildlife research, porous borders, and a smaller pool of technical manpower are major challenges for ASF control in Nepal. The ability of the virus to resist harsh environmental conditions, paired with the traditional swill feeding system to raise pigs [40], could trigger havoc with impending severe losses in the Nepalese pork industry. Moreover, the lack of an effective vaccine against ASF, ineffective disease surveillance, and minimal awareness of the dynamics of disease transmission among traditional pig farmers may create complications in disease control once the virus is introduced [51].
8. Future Perspectives
Nepal’s government and related stakeholders may find it extremely difficult to control an epidemic of ASF after its introduction, judging from previous disease outbreak scenarios [52]. Amid fear of an ASF outbreak, the ban on the imports of pig products by the government [33] is certainly a good start, but as long as the illegal trade continues in the system [53], the imposed ban may not have any significance. Strict quarantine measures at the borders; strong coordination among national, federal, and local governments for disease surveillance and reporting; restriction of illegal transport of pigs and pig products; awareness of the transmission dynamics of the disease among traditional and modern pig farmers; and adoption of strict biosecurity measures by pig farms are essential to containing the potential hazard posed by the virus. The travel restrictions amidst the coronavirus pandemic may have reduced the transmission probability for the time being, but the entry of the virus through any of the borders is likely to have substantial effects on the pork industry in Nepal that may result in pig losses due to deaths or culling; decreased production; reduced exports of pig products; and lower income for a very long time [34].
9. Conclusions
Nepal has not reported any cases of ASF yet. However, ASFV has been circulating in China for a few years now and has recently been reported in various states of India. Outbreaks of ASF in two neighboring countries with which Nepal conducts trade in animals, feeds, and animal products raise concern over the potential for cross-country transmission of ASFV. Moreover, the risk is compounded as Nepal shares an open border with India, and illegal trading in animal and animal products through the open border is possible. In these circumstances, the Nepalese government needs to be more vigilant to prevent the entry of ASF in Nepal. Strict quarantine measures should be employed at the borders and the illegal trade in animals and animal products must be controlled. In addition, preparedness will be necessary for the early detection and management of ASF through epidemiological tracing and tracking; the culling of infected animals; disinfection of contaminated farms; and financial support to farmers to avert tremendous socioeconomic losses that may jeopardize the slowly but steadily growing pork industry in Nepal.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.S. and S.D.; methodology, D.S., S.B., S.P., U.P., S.J., and M.K.; validation, D.S., S.K., and S.D.; investigation, D.S., S.B., S.P., U.P., S.J., and M.K.; data curation, D.S. and U.P.; writing—original draft preparation, D.S., S.B., S.P., U.P., S.J., and M.K.; writing—review and editing, D.S., S.K., and S.D.; visualization, D.S.; supervision, S.K. and S.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data are available within the manuscript with relevant citations.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Blome, S.; Franzke, K.; Beer, M. African swine fever—A review of current knowledge. Virus Res. 2020, 287, 198099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudreault, N.N.; Madden, D.W.; Wilson, W.C.; Trujillo, J.D.; Richt, J.A. African Swine Fever Virus: An Emerging DNA Arbovirus. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, S.S.; Suresh, K.P.; Vashist, V.; Prajapati, A.; Pattnaik, B.; Roy, P. African swine fever: A permanent threat to Indian pigs. Vet. World 2020, 13, 2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, U.; Dahal, U.; Upadhyaya, N.; Chaudhari, S.; Dhakal, S. Livestock and poultry production in Nepal and current status of vaccine development. Vaccines 2020, 8, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, S.; Stephen, C.; Ale, A.; Joshi, D.D. Knowledge and practices of pig farmers regarding japanese encephalitis in kathmandu, nepal. Zoonoses Public Health 2012, 59, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MoALD. Krishi Dairy; Government of Nepal, Ministry of Agriculture and Livestock Development: Kathmandu, Nepal, 2020.
- MoALD. Statistical Information in Nepalese Agriculture 2018/2019; Government of Nepal, Ministry of Agriculture and Livestock Development: Kathmandu, Nepal, 2017.
- Ma, J.; Chen, H.; Gao, X.; Xiao, J.; Wang, H. African swine fever emerging in China: Distribution characteristics and high-risk areas. Prev. Vet. Med. 2020, 175, 104861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salas, M.L.; Andrés, G. African swine fever virus morphogenesis. Virus Res. 2013, 173, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achenbach, J.E.; Gallardo, C.; Nieto-Pelegrín, E.; Rivera-Arroyo, B.; Degefa-Negi, T.; Arias, M.; Jenberie, S.; Mulisa, D.D.; Gizaw, D.; Gelaye, E.; et al. Identification of a New Genotype of African Swine Fever Virus in Domestic Pigs from Ethiopia. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, 1393–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costard, S.; Mur, L.; Lubroth, J.; Sanchez-vizcaino, J.M.; Pfeiffer, D.U. Epidemiology of African swine fever virus. Virus Res. 2013, 173, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penrith, M.L.; Vosloo, W. Review of African swine fever: Transmission, spread and control. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 2009, 80, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanchez-Vizcaıno, J.M.; Mur, L.; Gomez-Villamandos, J.C.; Carrasco, L. An Update on the Epidemiology and Pathology of African Swine Fever. J. Comp. Path 2015, 152, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Vizcaíno, J.M.; Laddomada, A.; Arias, M.L. African Swine Fever Virus. In Diseases of Swine; Zimmerman, J.J., Karriker, L.A., Ramirez, A., Schwartz, K.J., Stevenson, G.W., Zhang, J., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 443–452. [Google Scholar]
- Mellor, P.S.; Kitching, R.P.; Wilkinson, P.J. Mechanical transmission of capripox virus and African swine fever virus by Stomoxys calcitrans. Res. Vet. Sci. 1987, 43, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mebus, C.A. African swine fever. Adv. Virus Res. 1988, 35, 251–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardley, R.C.; de Andrade, C.M.; Black, D.N.; de Castro Portugal, F.L.; Enjuanes, L.; Hess, W.R.; Mebus, C.; Ordas, A.; Rutili, D.; Sanchez Vizcaino, J.; et al. African swine fever virus. Arch. Virol. 1983, 76, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubisi, B.A.; Bastos, A.D.S.; Dwarka, R.M.; Vosloo, W. Molecular epidemiology of African swine fever in East Africa. Arch. Virol. 2005, 150, 2439–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penrith, M.L. Current status of African swine fever. CABI Agric. Biosci. 2020, 1, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OIE. Global Situation of African Swine Fever; World Organisation for Animal Health: Paris, France, 2020; Available online: http://www.gf-tads.org/ (accessed on 22 January 2021).
- OIE. African Swine Fever, India. Available online: https://www.oie.int/wahis_2/public/wahid.php/Reviewreport/Review?page_refer=MapFullEventReport&reportid=34283 (accessed on 22 January 2021).
- FAO. FAO ASF Situation Update—African Swine Fever (ASF)—FAO Emergency Prevention System for Animal Health (EMPRES-AH). Available online: http://www.fao.org/ag/againfo/programmes/en/empres/ASF/situation_update.html (accessed on 22 January 2021).
- Statista. Global Pork Production in 2020 by Country. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/273232/net-pork-production-worldwide-by-country/ (accessed on 29 January 2021).
- Ozawa, Y.; Makino, S.; Park, J.Y.; Chang, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; An, S.H. A review of recent unexpected animal disease events in Japan and Korea and the follow-up action taken. OIE Rev. Sci. Tech. 2006, 25, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OIE. Situational Updates of ASF in Asia and the Pacific. Available online: https://rr-asia.oie.int/en/projects/asf/situational-updates-of-asf/ (accessed on 22 January 2021).
- Shih, T.H.; Chou, C.C.; Morley, R.S. Monte Carlo simulation of animal-product violations incurred by air passengers at an international airport in Taiwan. Prev. Vet. Med. 2005, 68, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, J.; Alp, H.; Aksin, M.; Seitzer, U. Current status of ticks in Asia. Parasitol. Res. 2007, 101, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penrith, M.L. African swine fever. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2009, 76, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gortázar, C.; Ståhl, K.; Neimanis, A.S.; Rossi, S.; Segerstad, C.H.; Kuiken, T. African swine fever in wild boar in Europe: A notable challenge. Vet. Rec. 2015, 176, 199–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dei Giudici, S.; Franzoni, G.; Bonelli, P.; Bacciu, D.; Sanna, G.; Angioi, P.P.; Ledda, M.; Pilo, G.; Nicolussi, P.; Oggiano, A. Interaction of historical and modern Sardinian African swine fever viruses with porcine and wild-boar monocytes and monocyte-derived macrophages. Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karger, A.; Pérez-Núñez, D.; Urquiza, J.; Hinojar, P.; Alonso, C.; Freitas, F.B.; Revilla, Y.; Le Potier, M.F.; Montoya, M. An update on African swine fever virology. Viruses 2019, 11, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niederwerder, M.C.; Stoian, A.M.M.; Rowland, R.R.R.; Dritz, S.S.; Petrovan, V.; Constance, L.A.; Gebhardt, J.T.; Olcha, M.; Jones, C.K.; Woodworth, J.C.; et al. Infectious dose of African swine fever virus when consumed naturally in liquid or feed. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- THT. Import of Meat Products Banned Amid African Swine Fever Fears—The Himalayan Times—Nepal’s No.1 English Daily Newspaper|Nepal News, Latest Politics, Business, World, Sports, Entertainment, Travel, Life Style News. Available online: https://thehimalayantimes.com/kathmandu/import-of-meat-products-banned-amid-african-swine-fever-fears (accessed on 19 May 2021).
- Acharya, K.P.; Wilson, R.T. Pig production is at risk from African Swine Fever (ASF) in Nepal. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 2020, 2269–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, D.J.; Banjara, M.R.; Singh, V.K.; Joshi, A.B.; Gurung, C.K.; Das, M.L.; Matlashewski, G.; Olliaro, P.; Kroeger, A. Barriers of Visceral Leishmaniasis reporting and surveillance in Nepal: Comparison of governmental VL-program districts with non-program districts. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2019, 24, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gurung, T.B.; Gurung, T.B.; Shrestha, B.S.; Shrestha, N.P.; Bates, R.; Neupane, D.; Paudel, T.; Achhami, K. Pig and Pork Industry in Nepal. Proceedings of the 1st National Workshop on Pig and Pork Industry in Nepal, 10–11 December 2013, Kathmandu Nepal; Nepal Agricultural Research Council (NARC): Kathmandu, Nepal, 2014.
- RH. Consultants. National Livestock Welfare Survey A Situational Analysis of Livestock Sector in Nepal; Animal Nepal: Lalitpur, Nepal, 2018; Available online: https://www.animalnepal.org.np/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/National-Livestock-Welfare-Survey-Report-2-1.pdf (accessed on 22 January 2021).
- Bellini, S.; Casadei, G.; De Lorenzi, G.; Tamba, M. A review of risk factors of african swine fever incursion in pig farming within the European Union scenario. Pathogens 2021, 10, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nidup, K.; Joshi, D.D.; Gongora, J.; Moran, C. Farming and biodiversity of indigenous pigs in nepal. Biodiversity 2010, 11, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sah, R.P.; Jha, S.K.; Karki, S. Management System Including Health Care and Marketing of Pigs Adopted by Farmers in Dhankuta and Terhathum Districts. Nepal. Vet. J. 2018, 35, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimire, B. Wild Boars Wreak Havoc in Settlements Near Langtang National Park. Available online: https://kathmandupost.com/province-no-3/2021/01/21/wild-boars-wreak-havoc-in-settlements-near-langtang-national-park (accessed on 19 May 2021).
- Uprety, R. Mahottari District Sees Rise in Human-Wildlife Conflict and Poaching. Available online: https://kathmandupost.com/national/2019/04/29/mahottari-district-sees-rise-in-human-wildlife-conflict-and-poaching (accessed on 19 May 2021).
- Ding, Y.; Wang, Y. Big government: The fight against the African Swine Fever in China. J. Biosaf. Biosecur. 2020, 2, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RSS. Nepal looking forward to export pork meat to China. The Himalayan Times, 11 October 2019. Available online: https://thehimalayantimes.com/business/nepal-looking-forward-to-export-pork-meat-to-china(accessed on 22 January 2021).
- Bhattacharyya, R. India’s Northeast Hit by the African Swine Fever. The Diplomat. 22 May 2020. Available online: https://thediplomat.com/2020/05/indias-northeast-hit-by-the-african-swine-fever/ (accessed on 22 January 2021).
- Normile, D. African swine fever marches across much of Asia. Science 2019, 364, 617–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwala, T.; Gill, M. Explained: What is African Swine Fever reported in India for the first time? The Indian Express, 7 May 2020. Available online: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/african-swine-fever-in-india-6396736/(accessed on 22 January 2021).
- Knoema Nepal—Pig Meat Imports Quantity. Available online: https://knoema.com/atlas/Nepal/topics/Agriculture/Trade-Import-Quantity/Pig-meat-imports-quantity (accessed on 17 August 2020).
- Aggarwal, M. India-Nepal Agreement to Boost Transborder Conservation of Rhinos, Tigers. Available online: https://news.mongabay.com/2019/02/india-nepal-agreement-to-boost-transborder-conservation-of-rhinos-tigers/ (accessed on 17 August 2020).
- Pandey, P.; Shaner, P.J.L.; Sharma, H.P. The wild boar as a driver of human-wildlife conflict in the protected park lands of Nepal. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2016, 62, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teklue, T.; Sun, Y.; Abid, M.; Luo, Y.; Qiu, H.J. Current status and evolving approaches to African swine fever vaccine development. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, K.P.; Phuyal, S.; Acharya, N. PPR control program in Nepal: What next? VirusDisease 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panta, H.K. Supply Chain of Subsidized Chemical Fertilizers in Nepal. J. Inst. Agric. Anim. Sci. 2018, 35, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).