Clinical Characteristics of Alcohol-Related Liver Disease in Albanian Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Liver Disease Classification
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Nutritional and Fibrosis Indices
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Socioeconomic Characteristics
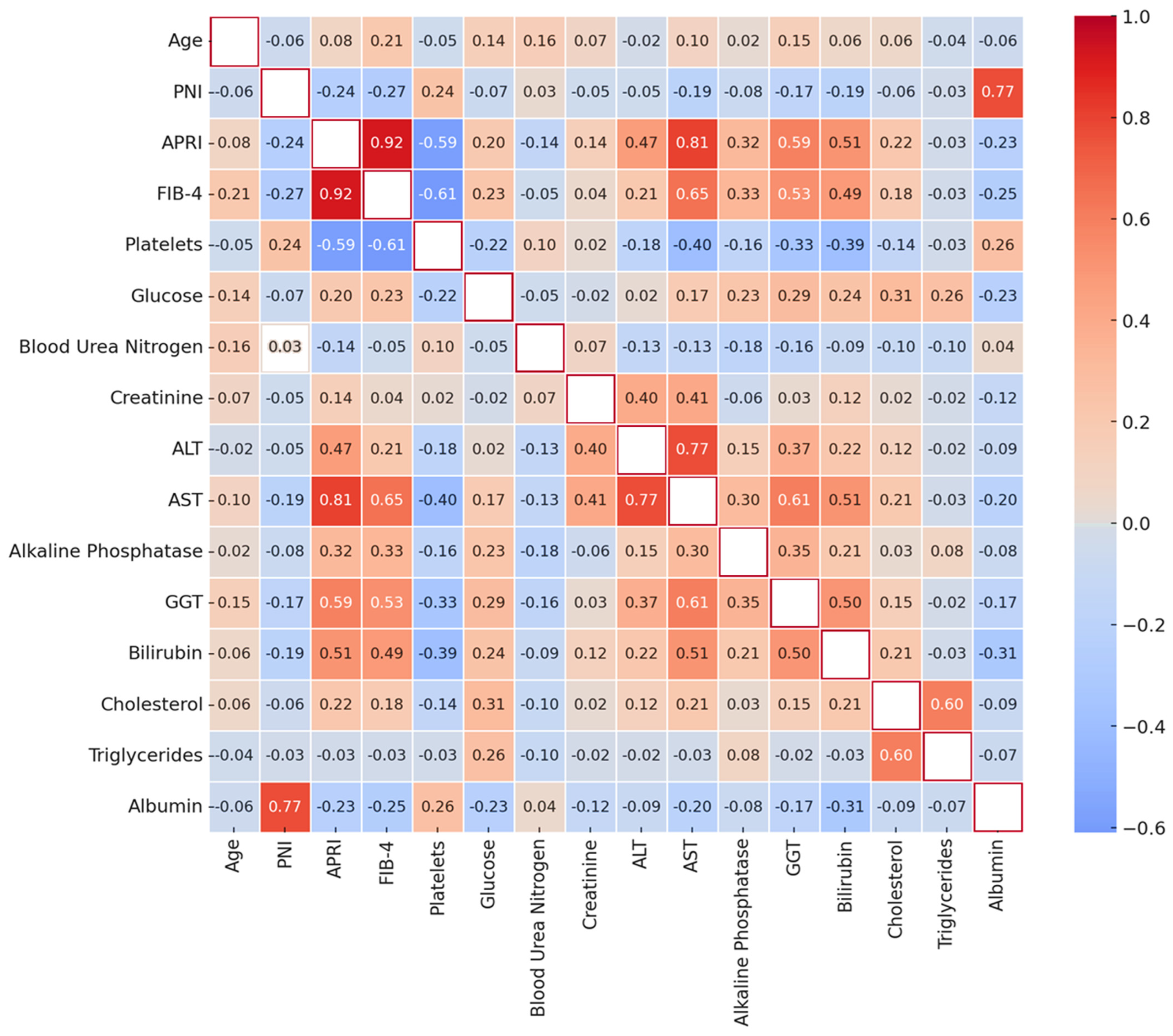
3.2. Correlations
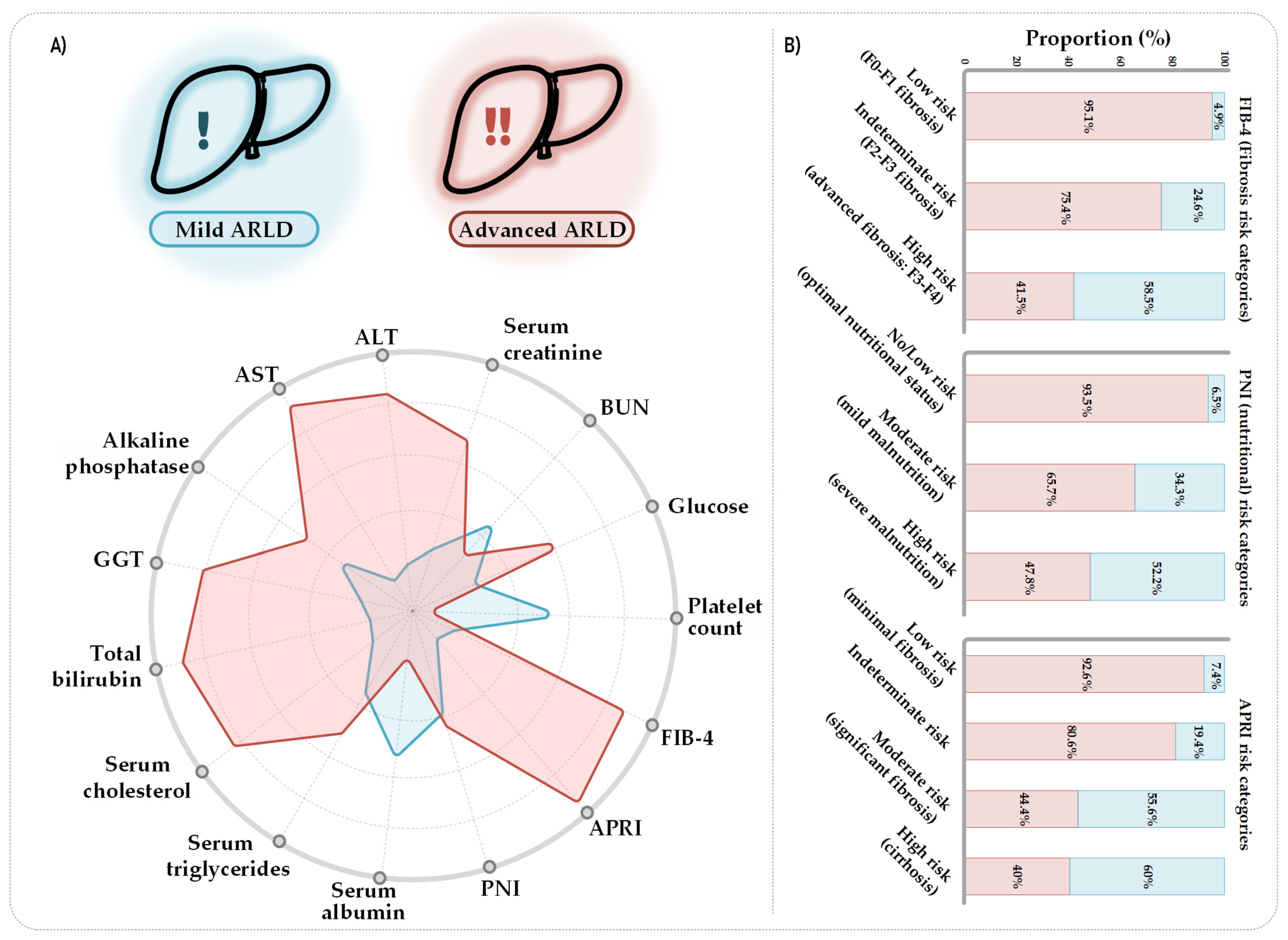
3.3. Clinical Profile and Fibrosis Risk
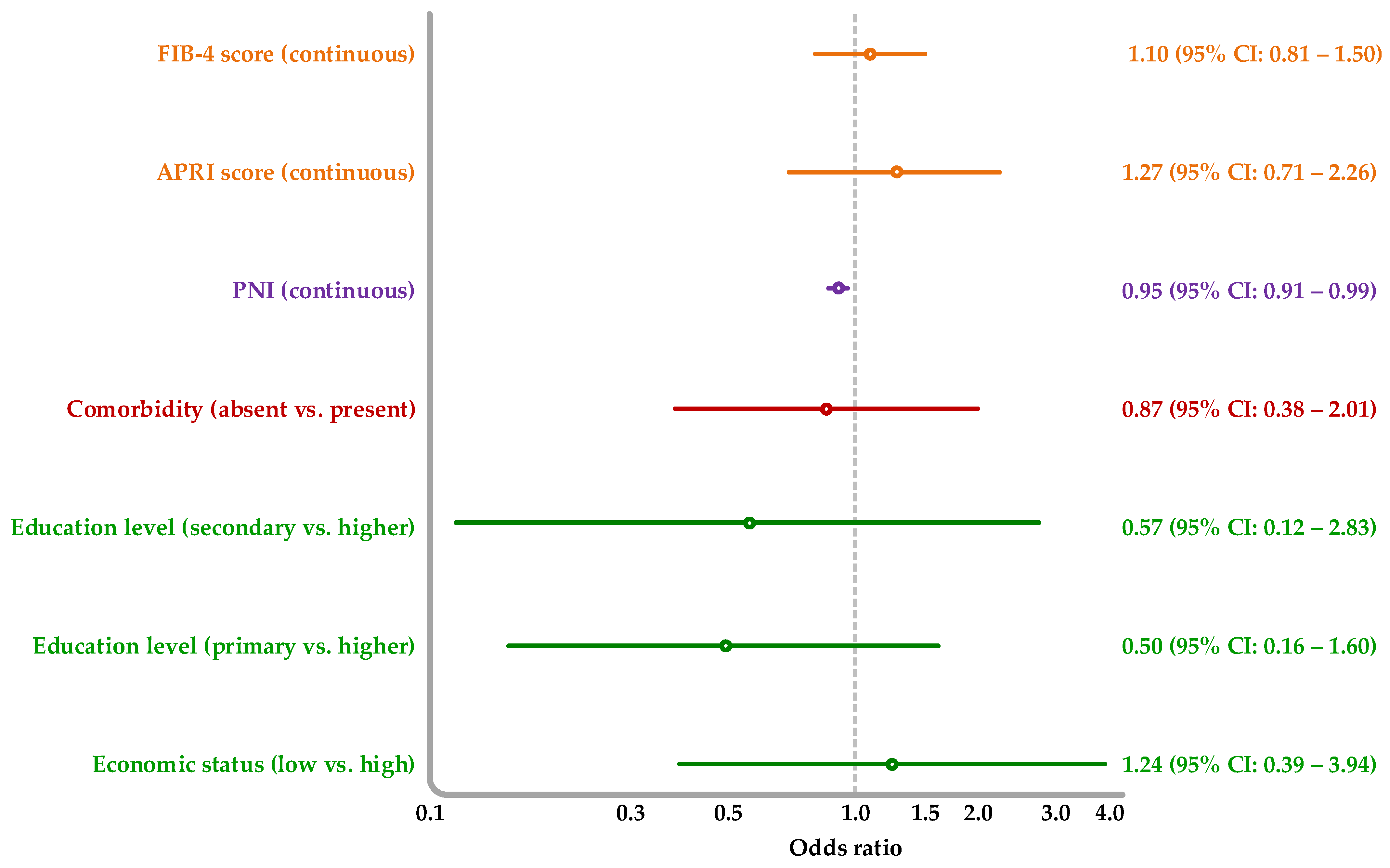
3.4. Association of Socioeconomic, Nutritional, and Liver Fibrosis Markers with Advanced Liver Disease
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ARLD | Alcohol-related liver disease |
| HBV | Hepatitis B virus |
| PNI | Prognostic Nutritional Index |
| APRI | AST-to-Platelet Ratio Index |
| FIB-4 | Fibrosis-4 Index |
| SES | Socioeconomic status |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| ALP | Alkaline phosphatase |
| GGT | γ-glutamyl transferase |
| BUN | Blood urea nitrogen |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| OR | Odds ratio |
References
- Niu, X.; Zhu, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Hao, Y.; Ma, L.; Li, Y.; Xing, H. Global prevalence, incidence, and outcomes of alcohol related liver diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Public Health 2023, 23, 859. [Google Scholar]
- Karlsen, T.H.; Sheron, N.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Carrieri, P.; Dusheiko, G.; Bugianesi, E.; Pryke, R.; Hutchinson, S.J.; Sangro, B.; Martin, N.K.; et al. The EASL–Lancet Liver Commission: Protecting the next generation of Europeans against liver disease complications and premature mortality. Lancet 2022, 399, 61–116. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kondili, L.A.; Cuko, L.; Chionne, P.; Candido, A.; Madonna, E.; Dentico, P.; Resuli, B.; Taliani, G.; Brunetto, M.R.; Rapicetta, M. Hepatitis B, C and Delta virus infections in Albanian patients with chronic liver disease: Evaluation of possible changes during the last 10 years. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 22, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resuli, B.; Prifti, S.; Kraja, B.; Nurka, T.; Basho, M.; Sadiku, E. Epidemiology of hepatitis B virus infection in Albania. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 849–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tresa, E.; Benmarhnia, T.; Clemens, T.; Burazeri, G.; Czabanowska, K. Europeanization process impacts the patterns of alcohol consumption in the Western Balkans. Eur. J. Public Health 2018, 28, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Albania: Substance Abuse Profile; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. Available online: https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/country-profiles/substances-abuse/alb.pdf (accessed on 12 April 2024).
- Hammer, J.H.; Parent, M.C.; Spiker, D.A. Global Status Report on Alcohol and Health 2018; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
- Shehi, A.; Nuro, A.; Marku, E.; Pecini, A. Study of methanol levels in some alcoholic beverages of Albania market. J. Int. Environ. Appl. Sci. 2013, 8, 354–358. [Google Scholar]
- Muhollari, T.; Szűcs, S.; Sajtos, Z.; McKee, M.; Baranyai, E.; Ádány, R.; Pál, L. Heavy metals in unrecorded Albanian rakia: A pilot study on a potential public health risk. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Pichard, A.; Mallet, V.; Nalpas, B.; Verkarre, V.; Nalpas, A.; Dhalluin-Venier, V.; Fontaine, H.; Pol, S. FIB-4: An inexpensive and accurate marker of fibrosis in HCV infection. comparison with liver biopsy and fibrotest. Hepatology 2007, 46, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wai, C.T.; Greenson, J.K.; Fontana, R.J.; Kalbfleisch, J.D.; Marrero, J.A.; Conjeevaram, H.S.; Lok, A.S.-F. A simple noninvasive index can predict both significant fibrosis and cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2003, 38, 518–526. [Google Scholar]
- Onodera, T.; Goseki, N.; Kosaki, G. Prognostic nutritional index in gastrointestinal surgery of malnourished cancer patients. Nihon Geka Gakkai Zasshi 1984, 85, 1001–1005. [Google Scholar]
- Sterling, R.K.; Lissen, E.; Clumeck, N.; Sola, R.; Correa, M.C.; Montaner, J.; Sulkowski, M.S.; Torriani, F.J.; Dieterich, D.T.; Thomas, D.L.; et al. Development of a simple noninvasive index to predict significant fibrosis in patients with HIV/HCV coinfection. Hepatology 2006, 43, 1317–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suan, M.A.M.; Chan, H.K.; Sem, X.; Shilton, S.; Hassan, M.R.A. Diagnostic performance of two non-invasive biomarkers used individually and in sequential combination for cirrhosis associated with hepatitis C virus infection. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EASL. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines on non-invasive tests for evaluation of liver disease severity and prognosis—2021 update. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 659–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. New Recommendations in the Updated WHO Guidelines for the Screening, Care and Treatment of Persons with Chronic Hepatitis C Infection: Policy Brief; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- Muhollari, T. Health Risks Associated with Consumption of Recorded and Unrecorded Spirits in Albania and Hungary. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Debrecen, Debrecen, Hungary, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Arndt, M.B.; Abate, Y.H.; Abbasi-Kangevari, M.; Abd ElHafeez, S.; Abdelmasseh, M.; Abd-Elsalam, S.; Abdulah, D.M.; Abdulkader, R.S.; Abidi, H.; Abiodun, O.; et al. Global, regional, and national progress towards the 2030 global nutrition targets and forecasts to 2050: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2024, 404, 2543–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tkachuk, B.; Congly, S.E. Quality standards on management of alcohol-related liver disease from the UK—Targets and tribulations. Hepatobiliary Surg. Nutr. 2024, 13, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, R.; Allison, M.; Anderson, S.; Aspinall, R.; Bardell, S.; Bains, V.; Buchanan, R.; Corless, L.; Davidson, I.; Dundas, P.; et al. Quality standards for the management of alcohol-related liver disease: Consensus recommendations from the British Association for the Study of the Liver and British Society of Gastroenterology ARLD special interest group. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2023, 10, e001221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi-Shirazi, L.; Veloso, M.P.; Frommlet, F.; Steindl-Munda, P.; Wrba, F.; Zehetmayer, S.; Marsik, C.; Ferenci, P. Differentiation of nonalcoholic from alcoholic steatohepatitis: Are routine laboratory markers useful? Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2008, 120, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, Y.; Ueno, T.; Sasaki, N.; Kuhara, K.; Yoshioka, S.; Tateishi, Y.; Nagata, E.; Kage, M.; Sata, M. Comparison of liver histology between patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and patients with alcoholic steatohepatitis in Japan. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2005, 29, 277s–281s. [Google Scholar]
- Kamran, U.; Towey, J.; Khanna, A.; Chauhan, A.; Rajoriya, N.; Holt, A. Nutrition in alcohol-related liver disease: Physiopathology and management. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 2916–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, R.E.; Conte, D.; Massironi, S. Diagnosis and treatment of nutritional deficiencies in alcoholic liver disease: Overview of available evidence and open issues. Dig. Liver Dis. 2015, 47, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorbi, D.; Boynton, J.; Lindor, K.D. The ratio of aspartate aminotransferase to alanine aminotransferase: Potential value in differentiating nonalcoholic steatohepatitis from alcoholic liver disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1999, 94, 1018–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D.K.; Rastogi, A.; Sakhuja, P.; Gondal, R.; Sarin, S.K. Comparison of clinical, biochemical and histological features of alcoholic steatohepatitis and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in Asian Indian patients. Indian J. Pathol. Microbiol. 2010, 53, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyblom, H.; Berggren, U.; Balldin, J.; Olsson, R. High AST/ALT ratio may indicate advanced alcoholic liver disease rather than heavy drinking. Alcohol Alcohol. 2004, 39, 336–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diehl, A.M.; Potter, J.; Boitnott, J.; Van Duyn, M.A.; Herlong, H.F.; Mezey, E. Relationship between pyridoxal 5′-phosphate deficiency and aminotransferase levels in alcoholic hepatitis. Gastroenterology 1984, 86, 632–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.A.; Kaplan, M.M. The SGOT/SGPT ratio—An indicator of alcoholic liver disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1979, 24, 835–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussavian, S.N.; Becker, R.C.; Piepmeyer, J.L.; Mezey, E.; Bozian, R.C. Serum gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase and chronic alcoholism. Influence of alcohol ingestion and liver disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1985, 30, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhari, S.; Waszkiewicz, N. Old and New Biomarkers of Alcohol Abuse: Narrative Review. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global Alcohol Action Plan 2022–2030; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024.
- Anton, R.F.; O’Malley, S.S.; Ciraulo, D.A.; Cisler, R.A.; Couper, D.; Donovan, D.M.; Gastfriend, D.R.; Hosking, J.D.; Johnson, B.A.; LoCastro, J.S.; et al. Combined pharmacotherapies and behavioral interventions for alcohol dependence: The COMBINE study: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2006, 295, 2003–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Department of Health and Human Services. Alcohol and Cancer Risk: A Report of the U.S. Surgeon General; HHS: Washington, DC, USA, 2025.
| Characteristic | All Patients (n = 200) | Mild Liver Disease (n = 157) | Advanced Liver Disease (n = 43) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | |||
| Male | 193 (96.5) [93.3–98.4] | 150 (95.5) [91.4–98.0] | 43 (100.0) [–] |
| Socioeconomic status | |||
| Middle SES | 166 (83.0) [77.3–87.7] | 134 (85.4) [79.2–90.2] | 32 (74.4) [60.1–85.6] |
| Low SES | 34 (17.0) [12.3–22.7] | 23 (14.6) [9.8–20.8] | 11 (25.6) [14.4–39.9] |
| Residence | |||
| Rural | 21 (10.5) [6.8–15.3] | 16 (10.2) [6.2–15.6] | 5 (11.6) [4.6–23.6] |
| Urban | 179 (89.5) [84.7–93.2] | 141 (89.8) [84.4–93.8] | 38 (88.4) [76.4–95.4] |
| Migration status | |||
| Not emigrated | 162 (81.0) [75.1–86.0] | 128 (81.5) [74.9–87.0] | 34 (79.1) [65.3–89.1] |
| Emigrated | 38 (19.0) [14.0–24.9] | 29 (18.5) [13.0–25.1] | 9 (20.9) [10.9–34.7] |
| Education level | |||
| Primary | 33 (16.5) [11.9–22.1] | 23 (14.6) [9.8–20.8] | 10 (23.3) [12.6–37.3] |
| Secondary | 142 (71.0) [64.4–77.0] | 114 (72.6) [65.3–79.1] | 28 (65.1) [50.3–78.0] |
| Tertiary | 25 (12.5) [8.5–17.6] | 20 (12.7) [8.2–18.6] | 5 (11.6) [4.6–23.6] |
| Marital status | |||
| Single | 64 (32.0) [26.0–38.9] | 53 (34.0) [26.9–41.6] | 11 (25.6) [14.4–39.9] |
| Married/in relationship | 114 (57.0) [50.3–64.0] | 86 (55.1) [47.3–62.8] | 28 (65.1) [50.3–78.0] |
| Separated | 17 (8.5) [5.3–13.0] | 13 (8.3) [4.8–13.4] | 4 (9.3) [3.2–20.6] |
| Widowed | 4 (2.0) [0.7–4.7] | 4 (2.6) [0.9–6.0] | 0 (0.0) [–] |
| Substance use disorder | |||
| Alcohol use disorder | 163 (81.5) [75.7–86.4] | 125 (79.6) [72.8–85.3] | 38 (88.4) [76.4–95.4] |
| Alcohol + other substance use | 37 (18.5) [13.6–24.3] | 32 (20.4) [14.7–27.2] | 5 (11.6) [4.6–23.6] |
| Comorbidities | |||
| None | 122 (61.0) [54.1–67.6] | 93 (59.2) [51.4–66.7] | 29 (67.4) [52.7–80.0] |
| ≥1 comorbidity | 78 (39.0) [32.4–45.9] | 64 (40.8) [33.3–48.6] | 14 (32.6) [20.0–47.3] |
| Characteristic | All Patients (n = 200) | Mild Liver Disease (n = 157) | Advanced Liver Disease (n = 43) | p-Value † |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 45 (44–49) | 44 (43–47) | 51 (48–56) | * |
| Alcohol Consumption 1 | ||||
| Duration (years) | 12 (12–15) | 10 (10–13) | 18 (15–20) | ** |
| Units per week | 24 (24–28) | 24 (24–28) | 24 (20–32) | |
| Volume (mL) | 600 (600–700) | 600 (600–700) | 600 (500–800) | |
| Smoking | ||||
| Pack-years | 30 (30–40) | 30 (30–40) | 30 (30–40) | |
| Duration (years) | 15 (15–20) | 15 (15–18) | 20 (20–25) | ** |
| Hematologic Markers | ||||
| White blood cell count (109/L) | 7.4 (7.0–7.8) | 7.8 (7.5–8.3) | 6.2 (5.7–7.3) | |
| Hematocrit (%) | 46 (46–47) | 47 (46–47) | 44 (41–46) | ** |
| Hemoglobin (g/L) | 150 (149–153) | 151 (150–154) | 139 (134–149) | ** |
| Platelet count (109/L) | 210 (193–220) | 220 (210–237) | 144 (130–183) | ** |
| Glucose Metabolism | ||||
| Blood glucose (mmol/L) | 4.8 (4.6–4.9) | 4.6 (4.5–4.9) | 5.5 (5.3–7.0) | ** |
| Renal Function | ||||
| Blood urea nitrogen (mmol/L) | 7.3 (7.0–7.9) | 7.5 (7.1–8.2) | 6.4 (6.1–8.3) | |
| Serum creatinine (µmol/L) | 67 (65–68) | 67 (66–69) | 66 (63–72) | |
| Liver Enzymes | ||||
| Alanine aminotransferase (U/L) | 36 (33–41) | 34 (29–40) | 48 (37–66) | * |
| Aspartate aminotransferase (U/L) | 39 (33–44) | 33 (29–39) | 83 (53–96) | ** |
| Alkaline phosphatase (U/L) | 66 (64–71) | 66 (62–71) | 66 (63–81) | |
| Gamma-glutamyl transferase (U/L) | 66 (54–78) | 49 (42–64) | 212 (125–341) | ** |
| Bilirubin and Lipids | ||||
| Total bilirubin (µmol/L) | 14 (12–15) | 13 (11–14) | 19 (16–27) | ** |
| Total cholesterol (mmol/L) | 5.0 (4.7–5.1) | 4.9 (4.7–5.1) | 5.2 (4.7–5.9) | |
| Triglycerides (mmol/L) | 1.3 (1.2–1.4) | 1.3 (1.2–1.5) | 1.4 (1.1–1.9) | |
| Protein and Coagulation Markers | ||||
| Total protein (g/L) | 70 (70–73) | 70 (70–74) | 70 (66–70) | |
| Serum albumin (g/L) | 40 (40–41) | 40 (40–41) | 32 (31–37) | ** |
| Nutritional and Fibrosis Indices | ||||
| PNI 2 | 50 (50–52) | 52 (51–53) | 44 (42–49) | ** |
| APRI 3 | 0.5 (0.5–0.7) | 0.4 (0.4–0.5) | 1.6 (1.0–2.6) | ** |
| FIB-4 Index 4 | 1.4 (1.3–1.8) | 1.2 (1.1–1.4) | 4.2 (2.5–6.5) | ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Osmanaj, D.; Kurti, F.; Shehu, K.; Themeli, Y.; Stroni, G.; Llanaj, E.; Babameto, A. Clinical Characteristics of Alcohol-Related Liver Disease in Albanian Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study. Gastroenterol. Insights 2025, 16, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent16020016
Osmanaj D, Kurti F, Shehu K, Themeli Y, Stroni G, Llanaj E, Babameto A. Clinical Characteristics of Alcohol-Related Liver Disease in Albanian Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study. Gastroenterology Insights. 2025; 16(2):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent16020016
Chicago/Turabian StyleOsmanaj, Dorina, Floreta Kurti, Klerida Shehu, Yllka Themeli, Gentian Stroni, Erand Llanaj, and Adriana Babameto. 2025. "Clinical Characteristics of Alcohol-Related Liver Disease in Albanian Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study" Gastroenterology Insights 16, no. 2: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent16020016
APA StyleOsmanaj, D., Kurti, F., Shehu, K., Themeli, Y., Stroni, G., Llanaj, E., & Babameto, A. (2025). Clinical Characteristics of Alcohol-Related Liver Disease in Albanian Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study. Gastroenterology Insights, 16(2), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent16020016







