The Role of Interferon Regulatory Factors in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
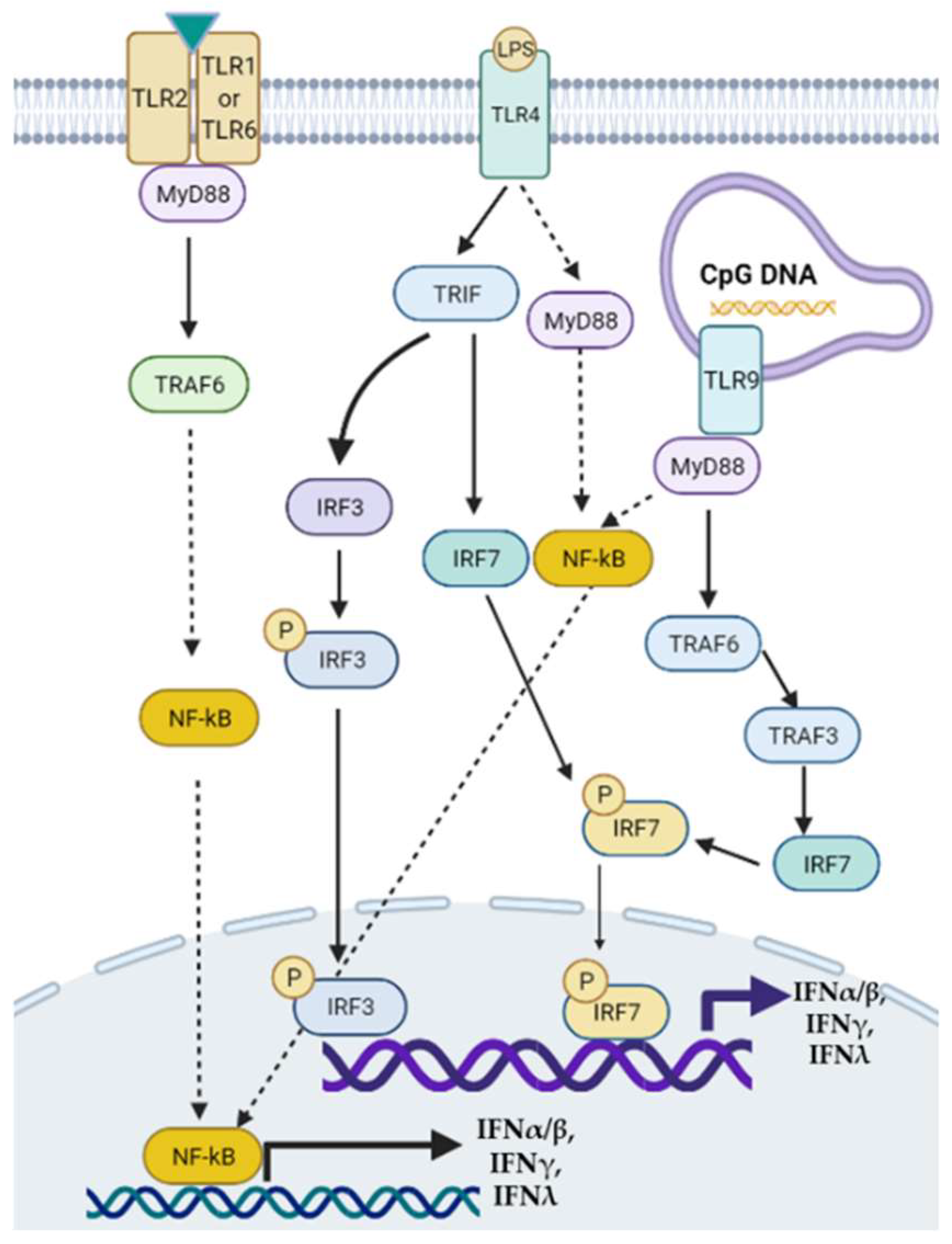
2. Interferons in NAFLD and NASH
3. Roles of IRFs in NAFLD and NASH
3.1. IRF1
3.2. IRF2
3.3. IRF3
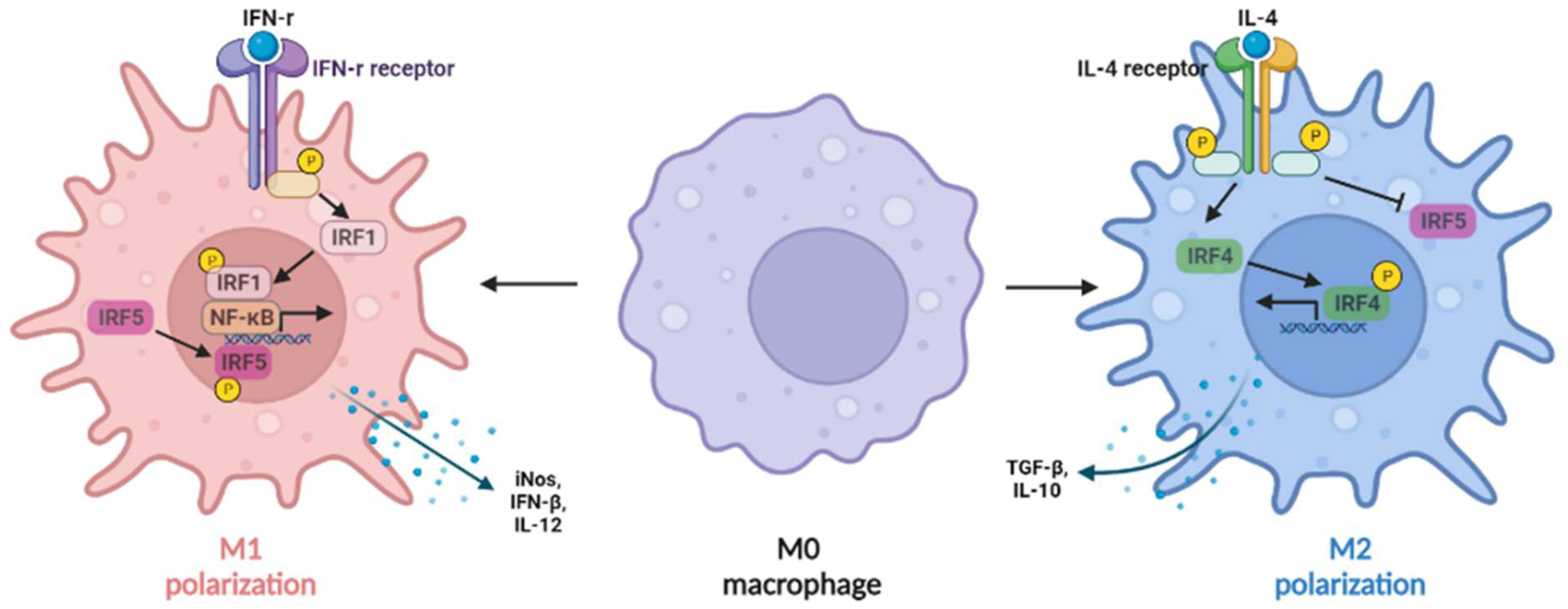
3.4. IRF4
3.5. IRF5
3.6. IRF6
3.7. IRF7
3.8. IRF8
3.9. IRF9
4. IRFs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
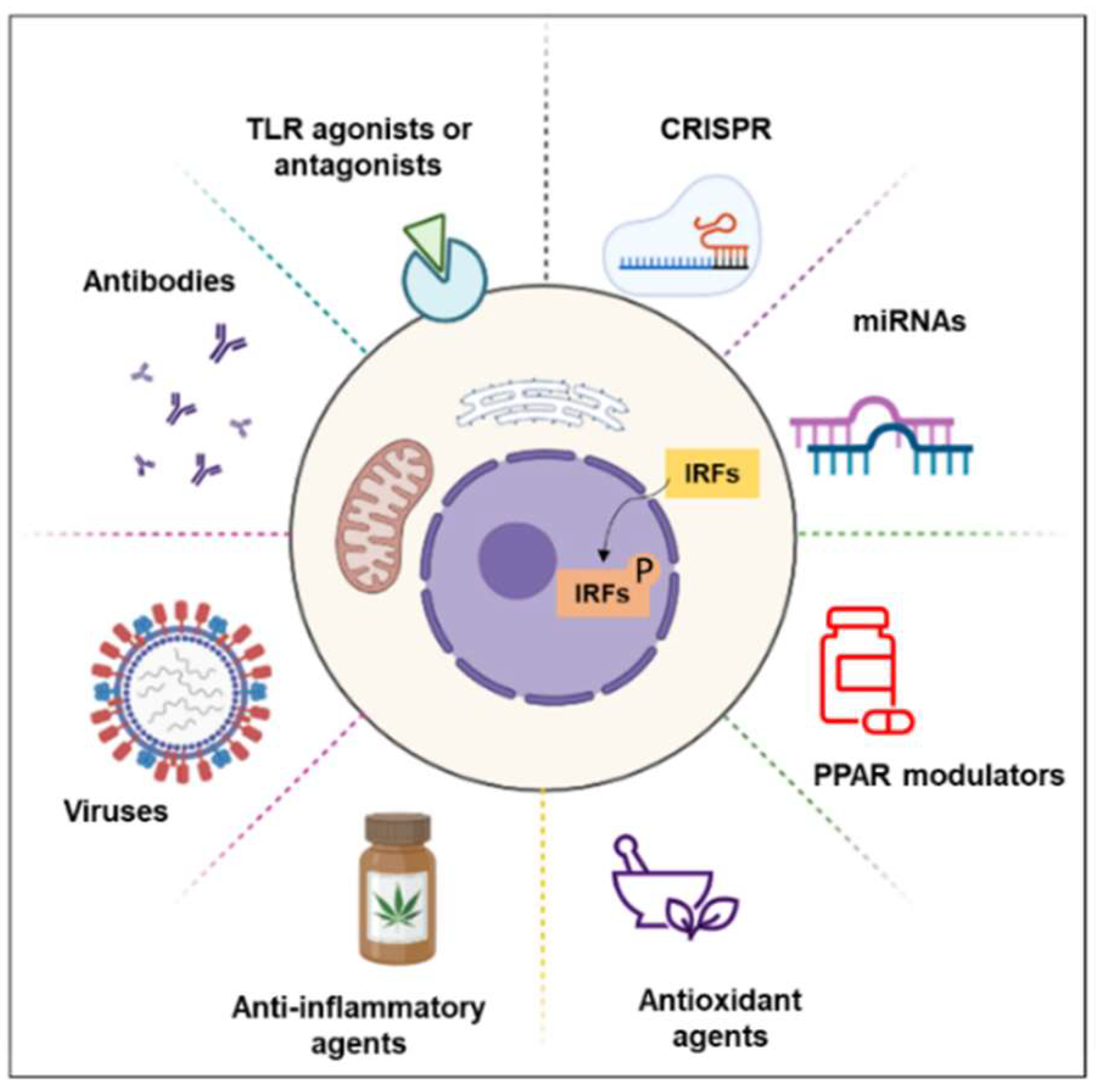
5. Treatment
5.1. miRNAs
5.2. PPAR Modulators
5.3. Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Agents
5.4. TLR Agonists or Antagonists
5.5. Others
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Estes, C.; Razavi, H.; Loomba, R.; Younossi, Z.; Sanyal, A.J. Modeling the epidemic of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease demonstrates an exponential increase in burden of disease. Hepatology 2018, 67, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Q.; Martin, R.C.; Shi, X.; Pandit, H.; Yu, Y.; Liu, X.; Guo, W.; Tan, M.; Bai, O.; Meng, X.; et al. Lack of FGF21 promotes NASH-HCC transition via hepatocyte-TLR4-IL-17A signaling. Theranostics 2020, 10, 9923–9936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hindson, J. Molecular landscape of NASH-HCC. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Yang, M. The Emerging Factors and Treatment Options for NAFLD-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cholankeril, G.; Patel, R.; Khurana, S.; Satapathy, S.K. Hepatocellular carcinoma in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: Current knowledge and implications for management. World J. Hepatol. 2017, 9, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, T.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Sullivan, S.; Nadeau, K.J.; Green, M.; Roncal, C.; Nakagawa, T.; Kuwabara, M.; Sato, Y.; Kang, D.H.; et al. Fructose and sugar: A major mediator of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 1063–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alwahsh, S.M.; Gebhardt, R. Dietary fructose as a risk factor for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 1545–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwahsh, S.M.; Xu, M.; Seyhan, H.A.; Ahmad, S.; Mihm, S.; Ramadori, G.; Schultze, F.C. Diet high in fructose leads to an overexpression of lipocalin-2 in rat fatty liver. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 1807–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yang, M. Current Options and Future Directions for NAFLD and NASH Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pafili, K.; Roden, M. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) from pathogenesis to treatment concepts in humans. Mol. Metab. 2021, 50, 101122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Kimchi, E.T.; Staveley-O’Carroll, K.F.; Li, G. Astaxanthin Prevents Diet-Induced NASH Progression by Shaping Intrahepatic Immunity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ipsen, D.H.; Lykkesfeldt, J.; Tveden-Nyborg, P. Molecular mechanisms of hepatic lipid accumulation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 3313–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.Y.; Takahara, T.; Kawai, K.; Fujino, M.; Sugiyama, T.; Tsuneyama, K.; Tsukada, K.; Nakae, S.; Zhong, L.; Li, X.K. IFN-γ deficiency attenuates hepatic inflammation and fibrosis in a steatohepatitis model induced by a methionine- and choline-deficient high-fat diet. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2013, 305, G891–G899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, W.M.; Ryu, T.; Lee, J.H.; Shim, Y.R.; Kim, M.H.; Kim, H.H.; Kim, Y.E.; Yang, K.; Kim, K.; Choi, S.E.; et al. Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 in Natural Killer Cells Attenuates Liver Fibrosis by Exerting Cytotoxicity to Activated Stellate Cells. Hepatology 2021, 74, 2170–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Chen, Q.; Yi, J.; Lan, X.; Lu, K.; Du, X.; Guo, Z.; Guo, Y.; Geng, M.; Li, D.; et al. IFN-γ contributes to the hepatic inflammation in HFD-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis by STAT1β/TLR2 signaling pathway. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 134, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, H.; Xue, B.; Deng, R.; Huang, X.; Xu, Y.; Chen, S.; Tian, R.; Wang, X.; Xun, Z.; et al. IRF1 Promotes the Innate Immune Response to Viral Infection by Enhancing the Activation of IRF3. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e01231-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zan, J.; Xu, R.; Tang, X.; Lu, M.; Xie, S.; Cai, J.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, J. RNA helicase DDX5 suppresses IFN-I antiviral innate immune response by interacting with PP2A-Cβ to deactivate IRF3. Exp. Cell Res. 2020, 396, 112332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taneja, V.; Kalra, P.; Goel, M.; Khilnani, G.C.; Saini, V.; Prasad, G.; Gupta, U.D.; Krishna Prasad, H. Impact and prognosis of the expression of IFN-α among tuberculosis patients. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0235488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonczyk, A.; Krist, B.; Sajek, M.; Michalska, A.; Piaszyk-Borychowska, A.; Plens-Galaska, M.; Wesoly, J.; Bluyssen, H.A.R. Direct Inhibition of IRF-Dependent Transcriptional Regulatory Mechanisms Associated With Disease. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, M.; Fujita, T.; Kimura, Y.; Maruyama, M.; Harada, H.; Sudo, Y.; Miyata, T.; Taniguchi, T. Regulated expression of a gene encoding a nuclear factor, IRF-1, that specifically binds to IFN-beta gene regulatory elements. Cell 1988, 54, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanai, H.; Negishi, H.; Taniguchi, T. The IRF family of transcription factors: Inception, impact and implications in oncogenesis. Oncoimmunology 2012, 1, 1376–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eguchi, J.; Yan, Q.W.; Schones, D.E.; Kamal, M.; Hsu, C.H.; Zhang, M.Q.; Crawford, G.E.; Rosen, E.D. Interferon regulatory factors are transcriptional regulators of adipogenesis. Cell Metab. 2008, 7, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvestre, M.F.; Kieswich, J.; Yaqoob, M.M.; Holness, M.J.; Sugden, M.C.; Caton, P.W. A key role for interferon regulatory factors in mediating early-life metabolic defects in male offspring of maternal protein restricted rats. Horm. Metab. Res. 2014, 46, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Eguchi, J.; Kong, X.; Tenta, M.; Wang, X.; Kang, S.; Rosen, E.D. Interferon regulatory factor 4 regulates obesity-induced inflammation through regulation of adipose tissue macrophage polarization. Diabetes 2013, 62, 3394–3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Wen, X.; Gao, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhong, C.; Nie, J.; Liang, H. IRF-4 deficiency reduces inflammation and kidney fibrosis after folic acid-induced acute kidney injury. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 100, 108142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Yang, K.; Xiao, T.; Xiong, J.; Wang, K.; Liu, C.; He, T.; Yu, Y.; et al. IRF-1 promotes renal fibrosis by downregulation of Klotho. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 4415–4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabié, A.; Mai, L.T.; Dagenais-Lussier, X.; Hammami, A.; van Grevenynghe, J.; Stäger, S. IRF-5 Promotes Cell Death in CD4 T Cells during Chronic Infection. Cell Rep. 2018, 24, 1163–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gapud, E.J.; Trejo-Zambrano, M.I.; Gomez-Banuelos, E.; Tiniakou, E.; Antiochos, B.; Granville, D.J.; Andrade, F.; Casciola-Rosen, L.; Rosen, A. Granzyme B Induces IRF-3 Phosphorylation through a Perforin-Independent Proteolysis-Dependent Signaling Cascade without Inducing Cell Death. J. Immunol. 2021, 206, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Li, Y.; Misumi, I.; González-López, O.; Hensley, L.; Cullen, J.M.; McGivern, D.R.; Matsuda, M.; Suzuki, R.; Sen, G.C.; et al. IRF3-mediated pathogenicity in a murine model of human hepatitis A. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhuang, Z.J.; Bian, D.X.; Ma, X.J.; Xun, Y.H.; Yang, W.J.; Luo, Y.; Liu, Y.L.; Jia, L.; Wang, Y.; et al. Toll-like receptor-4 signalling in the progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease induced by high-fat and high-fructose diet in mice. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2014, 41, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, S.; Meissner, E.G.; Funk, E.; Poonia, S.; Shokeen, V.; Thakur, A.; Poonia, B.; Sarin, S.K.; Trehanpati, N.; Kottilil, S. Elevated hepatic lipid and interferon stimulated gene expression in HCV GT3 patients relative to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatol. Int. 2016, 10, 937–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klune, J.R.; Dhupar, R.; Kimura, S.; Ueki, S.; Cardinal, J.; Nakao, A.; Nace, G.; Evankovich, J.; Murase, N.; Tsung, A.; et al. Interferon regulatory factor-2 is protective against hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2012, 303, G666–G673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghazarian, M.; Revelo, X.S.; Nøhr, M.K.; Luck, H.; Zeng, K.; Lei, H.; Tsai, S.; Schroer, S.A.; Park, Y.J.; Chng, M.H.Y.; et al. Type I Interferon Responses Drive Intrahepatic T cells to Promote Metabolic Syndrome. Sci. Immunol. 2017, 2, eaai7616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, Y.S.; Kim, J.W.; Park, S.; Shon, C.; Kim, S.; Eo, S.K.; Kwon, J.K.; Lim, C.W.; Kim, B. Toll-Like Receptor-7 Signaling Promotes Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis by Inhibiting Regulatory T Cells in Mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2018, 188, 2574–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quiroga, A.D.; Comanzo, C.G.; Heit Barbini, F.J.; Lucci, A.; Vera, M.C.; Lorenzetti, F.; Ferretti, A.C.; Ceballos, M.P.; Alvarez, M.L.; Carrillo, M.C. IFN-α-2b treatment protects against diet-induced obesity and alleviates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2019, 379, 114650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sin, W.-X.; Yeong, J.P.-S.; Lim, T.J.F.; Su, I.H.; Connolly, J.E.; Chin, K.-C. IRF-7 Mediates Type I IFN Responses in Endotoxin-Challenged Mice. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhagen, F.; McFarland, A.P.; Rodriguez, L.G.; Tewary, P.; Jarret, A.; Savan, R.; Klinman, D.M. IRF-5 and NF-κB p50 co-regulate IFN-β and IL-6 expression in TLR9-stimulated human plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2013, 43, 1896–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, K.M.; Fabre, T.; Sciurba, J.C.; Gieseck, R.L., 3rd; Borthwick, L.A.; Vannella, K.M.; Acciani, T.H.; de Queiroz Prado, R.; Thompson, R.W.; White, S.; et al. Type 2 immunity is protective in metabolic disease but exacerbates NAFLD collaboratively with TGF-β. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imanishi, T.; Unno, M.; Kobayashi, W.; Yoneda, N.; Akira, S.; Saito, T. mTORC1 Signaling Controls TLR2-Mediated T-Cell Activation by Inducing TIRAP Expression. Cell Rep. 2020, 32, 107911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Pandey, S.P.; Barnes, B.J.; Turner, J.R.; Abraham, C. T Cell-Intrinsic IRF5 Regulates T Cell Signaling, Migration, and Differentiation and Promotes Intestinal Inflammation. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarantino, G.; Costantini, S.; Citro, V.; Conforti, P.; Capone, F.; Sorice, A.; Capone, D. Interferon-alpha 2 but not Interferon-gamma serum levels are associated with intramuscular fat in obese patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, Y.; Sugiyama, M.; Murata, K.; Yoshio, S.; Kurosaki, M.; Hashimoto, S.; Yatsuhashi, H.; Nomura, H.; Kang, J.H.; Takeda, T.; et al. Association of serum IFN-λ3 with inflammatory and fibrosis markers in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 50, 894–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petta, S.; Valenti, L.; Tuttolomondo, A.; Dongiovanni, P.; Pipitone, R.M.; Cammà, C.; Cabibi, D.; Di Marco, V.; Fracanzani, A.L.; Badiali, S.; et al. Interferon lambda 4 rs368234815 TT>δG variant is associated with liver damage in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2017, 66, 1885–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelka, K.; Latz, E. IRF5, IRF8, and IRF7 in human pDCs-the good, the bad, and the insignificant? Eur. J. Immunol. 2013, 43, 1693–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesev, E.V.; LeDesma, R.A.; Ploss, A. Decoding type I and III interferon signalling during viral infection. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 914–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalska, A.; Blaszczyk, K.; Wesoly, J.; Bluyssen, H.A.R. A Positive Feedback Amplifier Circuit That Regulates Interferon (IFN)-Stimulated Gene Expression and Controls Type I and Type II IFN Responses. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irving, A.T.; Zhang, Q.; Kong, P.S.; Luko, K.; Rozario, P.; Wen, M.; Zhu, F.; Zhou, P.; Ng, J.H.J.; Sobota, R.M.; et al. Interferon Regulatory Factors IRF1 and IRF7 Directly Regulate Gene Expression in Bats in Response to Viral Infection. Cell Rep. 2020, 33, 108345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jefferies, C.A. Regulating IRFs in IFN Driven Disease. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negishi, H.; Taniguchi, T.; Yanai, H. The Interferon (IFN) Class of Cytokines and the IFN Regulatory Factor (IRF) Transcription Factor Family. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2018, 10, a028423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Cao, S.; Herman, L.M.; Ma, X. Differential regulation of interleukin (IL)-12 p35 and p40 gene expression and interferon (IFN)-gamma-primed IL-12 production by IFN regulatory factor 1. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 198, 1265–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yang, M.; Ericsson, A.C. Function of Macrophages in Disease: Current Understanding on Molecular Mechanisms. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 620510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidman, J.S.; Troutman, T.D.; Sakai, M.; Gola, A.; Spann, N.J.; Bennett, H.; Bruni, C.M.; Ouyang, Z.; Li, R.Z.; Sun, X.; et al. Niche-Specific Reprogramming of Epigenetic Landscapes Drives Myeloid Cell Diversity in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Immunity 2020, 52, 1057–1074.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Banerjee, S.; Guo, S.; Xie, N.; Liu, G. IFN Regulatory Factor 2 Inhibits Expression of Glycolytic Genes and Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Proinflammatory Responses in Macrophages. J. Immunol. 2018, 200, 3218–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Ji, Y.X.; Zhang, P.; Cheng, L.; Chen, Y.; Chen, J.; Su, Y.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, T.; et al. Hepatic IRF2BP2 Mitigates Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Directly Repressing the Transcription of ATF3. Hepatology 2020, 71, 1592–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.A.; Zhang, R.; She, Z.G.; Zhang, X.F.; Jiang, D.S.; Wang, T.; Gao, L.; Deng, W.; Zhang, S.M.; Zhu, L.H.; et al. Interferon regulatory factor 3 constrains IKKβ/NF-κB signaling to alleviate hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance. Hepatology 2014, 59, 870–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzler, J.; Ganjam, G.K.; Pretz, D.; Oelkrug, R.; Koch, C.E.; Legler, K.; Stöhr, S.; Culmsee, C.; Williams, L.M.; Tups, A. Central inhibition of IKKβ/NF-κB signaling attenuates high-fat diet-induced obesity and glucose intolerance. Diabetes 2015, 64, 2015–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, R.; Zhou, C. Recent Advances in Understanding the Role of IKKβ in Cardiometabolic Diseases. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 752337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglass, J.D.; Dorfman, M.D.; Fasnacht, R.; Shaffer, L.D.; Thaler, J.P. Astrocyte IKKβ/NF-κB signaling is required for diet-induced obesity and hypothalamic inflammation. Mol. Metab. 2017, 6, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Zhuge, F.; Nagashimada, M.; Ota, T. Novel Action of Carotenoids on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Macrophage Polarization and Liver Homeostasis. Nutrients 2016, 8, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.C.; Smith, A.M.; Everts, B.; Colonna, M.; Pearce, E.L.; Schilling, J.D.; Pearce, E.J. Metabolic Reprogramming Mediated by the mTORC2-IRF4 Signaling Axis Is Essential for Macrophage Alternative Activation. Immunity 2016, 45, 817–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasanthakumar, A.; Moro, K.; Xin, A.; Liao, Y.; Gloury, R.; Kawamoto, S.; Fagarasan, S.; Mielke, L.A.; Afshar-Sterle, S.; Masters, S.L.; et al. The transcriptional regulators IRF4, BATF and IL-33 orchestrate development and maintenance of adipose tissue-resident regulatory T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabrizi, M.; Marchetti, V.; Mavilio, M.; Marino, A.; Casagrande, V.; Cavalera, M.; Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Mezza, T.; Sorice, G.P.; Fiorentino, L.; et al. IL-21 is a major negative regulator of IRF4-dependent lipolysis affecting Tregs in adipose tissue and systemic insulin sensitivity. Diabetes 2014, 63, 2086–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sindhu, S.; Kochumon, S.; Thomas, R.; Bennakhi, A.; Al-Mulla, F.; Ahmad, R. Enhanced Adipose Expression of Interferon Regulatory Factor (IRF)-5 Associates with the Signatures of Metabolic Inflammation in Diabetic Obese Patients. Cells 2020, 9, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzaid, F.; Lagadec, F.; Albuquerque, M.; Ballaire, R.; Orliaguet, L.; Hainault, I.; Blugeon, C.; Lemoine, S.; Lehuen, A.; Saliba, D.G.; et al. IRF5 governs liver macrophage activation that promotes hepatic fibrosis in mice and humans. JCI Insight 2016, 1, e88689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krausgruber, T.; Blazek, K.; Smallie, T.; Alzabin, S.; Lockstone, H.; Sahgal, N.; Hussell, T.; Feldmann, M.; Udalova, I.A. IRF5 promotes inflammatory macrophage polarization and TH1-TH17 responses. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmas, E.; Toubal, A.; Alzaid, F.; Blazek, K.; Eames, H.L.; Lebozec, K.; Pini, M.; Hainault, I.; Montastier, E.; Denis, R.G.; et al. Irf5 deficiency in macrophages promotes beneficial adipose tissue expansion and insulin sensitivity during obesity. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Han, C.J.; Zhang, J.Z.; He, W.Z.; Zhao, G.J.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, L.; Deng, K.Q.; Liu, Y.; Fan, H.F.; et al. Hepatic Interferon Regulatory Factor 6 Alleviates Liver Steatosis and Metabolic Disorder by Transcriptionally Suppressing Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor γ in Mice. Hepatology 2019, 69, 2471–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.A.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, S.; Deng, S.; Jiang, D.; Zhong, J.; Yang, L.; Wang, T.; Hong, S.; Guo, S.; et al. Interferon regulatory factor 7 deficiency prevents diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 305, E485–E495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Sato, S.; Ishii, K.J.; Coban, C.; Hemmi, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Terai, K.; Matsuda, M.; Inoue, J.; Uematsu, S.; et al. Interferon-alpha induction through Toll-like receptors involves a direct interaction of IRF7 with MyD88 and TRAF6. Nat. Immunol. 2004, 5, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, S.; Salem, D.; Gros, P. Role of IRF8 in immune cells functions, protection against infections, and susceptibility to inflammatory diseases. Hum. Genet. 2020, 139, 707–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langlais, D.; Barreiro, L.B.; Gros, P. The macrophage IRF8/IRF1 regulome is required for protection against infections and is associated with chronic inflammation. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 585–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berghout, J.; Langlais, D.; Radovanovic, I.; Tam, M.; MacMicking, J.D.; Stevenson, M.M.; Gros, P. Irf8-regulated genomic responses drive pathological inflammation during cerebral malaria. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiau, C.E.; Kaufman, Z.; Meireles, A.M.; Talbot, W.S. Differential requirement for irf8 in formation of embryonic and adult macrophages in zebrafish. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Yan, C.; Gong, Z. Interaction of hepatic stellate cells with neutrophils and macrophages in the liver following oncogenic kras activation in transgenic zebrafish. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhu, J.; Smith, S.; Foldi, J.; Zhao, B.; Chung, A.Y.; Outtz, H.; Kitajewski, J.; Shi, C.; Weber, S.; et al. Notch-RBP-J signaling regulates the transcription factor IRF8 to promote inflammatory macrophage polarization. Nat. Immunol. 2012, 13, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.A.; Zhang, R.; Jiang, D.; Deng, W.; Zhang, S.; Deng, S.; Zhong, J.; Wang, T.; Zhu, L.H.; Yang, L.; et al. Interferon regulatory factor 9 protects against hepatic insulin resistance and steatosis in male mice. Hepatology 2013, 58, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Ding, W.; Cao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Ni, S.; Shi, T.; Fu, W. Interferonregulatoryfactor-8(IRF-8) regulates the expression of matrix metalloproteinase-13 (MMP-13) in chondrocytes. Cell Stress Chaperones 2018, 23, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.J.; Liang, L.; Li, J.; Wu, H.; Dong, L.; Liu, T.T.; Shen, X.Z. IRF-2 Inhibits Gastric Cancer Invasion and Migration by Down-Regulating MMP-1. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 65, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Zheng, L.; Du, Q.; Yazdani, H.; Dong, K.; Guo, Y.; Geller, D.A. Interferon regulatory factor 1(IRF-1) activates anti-tumor immunity via CXCL10/CXCR3 axis in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Cancer Lett. 2021, 506, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Zheng, L.; Du, Q.; Yan, B.; Geller, D.A. Interferon regulatory factor 1 (IRF-1) and IRF-2 regulate PD-L1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2020, 69, 1891–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokota, S.; Yoshida, O.; Dou, L.; Spadaro, A.V.; Isse, K.; Ross, M.A.; Stolz, D.B.; Kimura, S.; Du, Q.; Demetris, A.J.; et al. IRF-1 promotes liver transplant ischemia/reperfusion injury via hepatocyte IL-15/IL-15Rα production. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 6045–6056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klune, J.R.; Bartels, C.; Luo, J.; Yokota, S.; Du, Q.; Geller, D.A. IL-23 mediates murine liver transplantation ischemia-reperfusion injury via IFN-γ/IRF-1 pathway. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2018, 315, G991–G1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, M.M.; Xu, Y.Y.; Chen, L.; Li, X.Y.; Qin, J.; Shen, Y. TLR3 expression correlates with apoptosis, proliferation and angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma and predicts prognosis. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoneda, K.; Sugimoto, K.; Shiraki, K.; Tanaka, J.; Beppu, T.; Fuke, H.; Yamamoto, N.; Masuya, M.; Horie, R.; Uchida, K.; et al. Dual topology of functional Toll-like receptor 3 expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma: Differential signaling mechanisms of TLR3-induced NF-kappaB activation and apoptosis. Int. J. Oncol. 2008, 33, 929–936. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Xie, H.; Li, X.; Feng, Y.; Xie, S.; Qu, J.; Xie, A.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Yang, J.; et al. Interferon Regulatory Factor 4 Regulates the Development of Polymorphonuclear Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells Through the Transcription of c-Myc in Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 627072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevik, O.; Li, D.; Baljinnyam, E.; Manvar, D.; Pimenta, E.M.; Waris, G.; Barnes, B.J.; Kaushik-Basu, N. Interferon regulatory factor 5 (IRF5) suppresses hepatitis C virus (HCV) replication and HCV-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 21676–21689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Li, Y.; Shi, G.; Du, S.; Wang, X.; Ye, W.; Zhang, Z.; Chu, Y.; Ma, S.; Wang, D.; et al. Hepatic interferon regulatory factor 8 expression suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma progression and enhances the response to anti-programmed cell death protein-1 therapy. Hepatology 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalec, K.; Wright, G.E.B.; Drögemöller, B.I.; Aminkeng, F.; Bhavsar, A.P.; Kingwell, E.; Yoshida, E.M.; Traboulsee, A.; Marrie, R.A.; Kremenchutzky, M.; et al. Common variation near IRF6 is associated with IFN-β-induced liver injury in multiple sclerosis. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1081–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.K.; Khedr, A.; Bader El Din, N.G.; Khairy, A.; El Awady, M.K. Increased incidence of cytomegalovirus coinfection in HCV-infected patients with late liver fibrosis is associated with dysregulation of JAK-STAT pathway. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goya, T.; Imoto, K.; Tashiro, S.; Aoyagi, T.; Takahashi, M.; Kurokawa, M.; Suzuki, H.; Tanaka, M.; Kato, M.; Kohjima, M.; et al. The Efficacy of Tofogliflozin on Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterol. Insights 2022, 13, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, A.; Shastri, Y.; Al Otaibi, M.; Buchel, E.; Saleh, H.; Ahmad, R.; Ahmed, H.; Al Idris, F.; Ahmed, S.; Guda, M.; et al. Expert Opinion on the Management of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) in the Middle East with a Focus on the Use of Silymarin. Gastroenterol. Insights 2021, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vulf, M.; Shunkina, D.; Komar, A.; Bograya, M.; Zatolokin, P.; Kirienkova, E.; Gazatova, N.; Kozlov, I.; Litvinova, L. Analysis of miRNAs Profiles in Serum of Patients With Steatosis and Steatohepatitis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 736677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Liang, Z.; Du, Q.; Yang, M.; Geller, D.A. MicroRNA-23a downregulates the expression of interferon regulatory factor-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, P.Q.; Zhang, J.H.; Du, Q.; Dong, K.; Luo, J.; Heres, C.; Geller, D.A. Analysis of the relationship between microRNA-31 and interferon regulatory factor-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Du, Q.; Cui, X.; Wan, P.; Kaltenmeier, C.; Luo, J.; Yan, B.; Yan, Y.; Geller, D.A. MicroRNA-301a (miR-301a) is induced in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and down- regulates the expression of interferon regulatory factor-1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 524, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ma, C.; Tang, X.; Tang, Q.; Lou, L.; Yu, Y.; Zheng, F.; Wu, J.; Yang, X.B.; Wang, W.; et al. The Reciprocal Interaction Between LncRNA CCAT1 and miR-375-3p Contribute to the Downregulation of IRF5 Gene Expression by Solasonine in HepG2 Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Xu, S.J.; Xie, S.J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.H.; Zhang, W.Q.; Zheng, M.N.; Zhou, H.; Qu, L.H. MicroRNA-122 supports robust innate immunity in hepatocytes by targeting the RTKs/STAT3 signaling pathway. eLife 2019, 8, 41159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Zhang, H.; Hao, Y.; Xu, F.; Yang, J.; Zhang, R.; Lu, G.; Zheng, Z.; Cui, M.; Qi, C.F.; et al. Reprogramming macrophage orientation by microRNA 146b targeting transcription factor IRF5. EBioMedicine 2016, 14, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varley, C.L.; Bacon, E.J.; Holder, J.C.; Southgate, J. FOXA1 and IRF-1 intermediary transcriptional regulators of PPARgamma-induced urothelial cytodifferentiation. Cell Death Differ. 2009, 16, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Zhu, X.; McLntee, F.L.; Xiao, H.; Zhang, J.; Fu, M.; Chen, Y.E. Interferon regulatory factor-1 mediates PPARgamma-induced apoptosis in vascular smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2004, 24, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xu, J.; Rosenthal, S.; Zhang, L.-J.; McCubbin, R.; Meshgin, N.; Shang, L.; Koyama, Y.; Ma, H.-Y.; Sharma, S.; et al. Identification of Lineage-Specific Transcription Factors That Prevent Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells and Promote Fibrosis Resolution. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1728–1744.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merecz-Sadowska, A.; Sitarek, P.; Śliwiński, T.; Zajdel, R. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Extracts and Pure Compounds Derived from Plants via Modulation of Signaling Pathways, Especially PI3K/AKT in Macrophages. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nizamutdinova, I.T.; Kim, Y.M.; Chung, J.I.; Shin, S.C.; Jeong, Y.K.; Seo, H.G.; Lee, J.H.; Chang, K.C.; Kim, H.J. Anthocyanins from black soybean seed coats preferentially inhibit TNF-alpha-mediated induction of VCAM-1 over ICAM-1 through the regulation of GATAs and IRF-1. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 7324–7330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jantaratnotai, N.; Utaisincharoen, P.; Sanvarinda, P.; Thampithak, A.; Sanvarinda, Y. Phytoestrogens mediated anti-inflammatory effect through suppression of IRF-1 and pSTAT1 expressions in lipopolysaccharide-activated microglia. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2013, 17, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yang, M.; Ericsson, A.C. The Potential Gut Microbiota-Mediated Treatment Options for Liver Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 524205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, A.T.; Tzvetkov, E.; Pereira, A.; Wu, Y.; Kasar, S.; Przetak, M.M.; Vlach, J.; Niewold, T.B.; Jensen, M.A.; Okitsu, S.L. TLR7 and TLR8 Differentially Activate the IRF and NF-κB Pathways in Specific Cell Types to Promote Inflammation. Immunohorizons 2020, 4, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatelia, K.; Singh, K.; Singh, R. TLRs: Linking inflammation and breast cancer. Cell. Signal. 2014, 26, 2350–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, H.D.; Lee, E.; Shin, J.; Park, B.; Lee, S. STRAP positively regulates TLR3-triggered signaling pathway. Cell. Immunol. 2017, 318, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiles, B.; Wang, Y.; Stahl, A.; Bassilian, S.; Lee, W.P.; Kim, Y.J.; Sherwin, R.; Devaskar, S.; Lesche, R.; Magnuson, M.A.; et al. Liver-specific deletion of negative regulator Pten results in fatty liver and insulin hypersensitivity [corrected]. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 2082–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, J.; Xu, S.; Okada, T.; Liu, Y.; Zuo, G.; Tang, J.; Zhang, J.H.; Shi, H. T0901317, an Agonist of Liver X Receptors, Attenuates Neuronal Apoptosis in Early Brain Injury after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Rats via Liver X Receptors/Interferon Regulatory Factor/P53 Upregulated Modulator of Apoptosis/Dynamin-1-Like Protein Pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2021, 2021, 8849131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| IRFs | Model | Expression * | Function | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IRF1 | NASH rat | Increased | IFN-γ in rat NASH liver upregulated IRF1 expression, resulting in liver inflammation progression. | [15] |
| IRF2 | M1-like macrophages | Decreased | Knockdown of IRF2 accelerated lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced activation of macrophages by regulating hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF-1α)-dependent glycolysis. | [53] |
| IRF3 | NAFLD mice | Decreased | IRF3 deficiency dramatically promoted diet-induced hepatic steatosis, and insulin resistance, whereas overexpression of IRF3 induced hemostasis of glucose and lipid balance metabolism, via regulating nuclear factor-kappa B kinase subunit beta (IKKβ)/nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) signaling pathway. | [55] |
| IRF4 | M2-like macrophages | Increased | IRF4 is involved in M2-like macrophage polarization induced by IL-4 or mediated by the mTORC2 signaling pathway. | [59,60] |
| IRF5 | Mice with liver fibrosis | Increased | Mice with IRF5 knockdown in myeloid cells were protected from metabolic stress or toxin-induced liver fibrosis, compared with wild-type controls. | [64] |
| IRF6 | NAFLD mice | Decreased | Cellular mechanism study showed that knockout IRF6 specifically in hepatocytes accelerated liver steatosis, while overexpression of IRF6 in hepatocytes ameliorated liver steatosis. | [67] |
| IRF7 | Obese mice | Increased | IRF7 deficiency reduced body weight, insulin resistance, hepatic macrophage infiltration, inflammation, and steatosis in mice on a high-fat diet (HFD). | [68] |
| IRF8 | Zebrafish with liver fibrosis | Increased | Knocking down IRF8 in zebrafish caused a reduction in macrophage numbers and the number and activation of hepatic stellate cells. | [73,74] |
| IRF9 | Obese mice | Decreased | IRF9 knockout increased insulin resistance, hepatic steatosis, inflammation in mice on HFD. | [76] |
| IRFs | Disease | Expression | Function | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IRF1 | HCC | Upregulated | IRF1 was upregulated in mouse and human HCC cells treated with IFN-γ to upregulate PD-L1 expression. | [80] |
| IRF2 | HCC | Upregulated | IRF2 was positively associated with IRF1 and PD-L1 expression in HCC. | [80] |
| IRF3 | HCC | Decreased | The expression of IRF3 in HCC tissues was positively correlated with TLR3 expression. | [83] |
| IRF4 | HCC | Upregulated | IRF4 mediated differentiation of polymorphonuclear myeloid-derived suppressor cells (PMN-MDSCs) in human HCC tumor tissues. | [85] |
| IRF5 | HCC | Decreased | IRF5 can inhibit hepatitis C virus (HCV)-induced HCC by suppressing HCV replication. | [86] |
| IRF6 | Liver injury in patients with multiple sclerosis | Mutation | The rs2205986 variant near IRF6 was associated with IFN-β-induced liver injury in patients with multiple sclerosis. | [88] |
| IRF7 | Viral infection-induced liver fibrosis | Decreased | IRF7 was downregulated in patients with cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection and late fibrosis, compared with that in CMV-negative patients. | [89] |
| IRF8 | HCC | Decreased | Overexpression of IRF8 can significantly improve antitumor effects by increasing an-ti-PD-1 therapy and regulating the infiltration of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) and T-cell function in the HCC tumor microenvironment. | [87] |
| IRF9 | Hepatitis C virus genotype 3 infection | Increased | Hepatitis C virus genotype 3 infection was associated with increased expression of interferon-stimulated genes including IRF9. | [31] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, C.; Liu, S.; Yang, M. The Role of Interferon Regulatory Factors in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Gastroenterol. Insights 2022, 13, 148-161. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent13020016
Zhang C, Liu S, Yang M. The Role of Interferon Regulatory Factors in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology Insights. 2022; 13(2):148-161. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent13020016
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Chunye, Shuai Liu, and Ming Yang. 2022. "The Role of Interferon Regulatory Factors in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis" Gastroenterology Insights 13, no. 2: 148-161. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent13020016
APA StyleZhang, C., Liu, S., & Yang, M. (2022). The Role of Interferon Regulatory Factors in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology Insights, 13(2), 148-161. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent13020016






