Hyperkinetic Movement Disorder in KARS1-Related Disease: An Illustrative Video-Recorded Case and Narrative Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Case Description
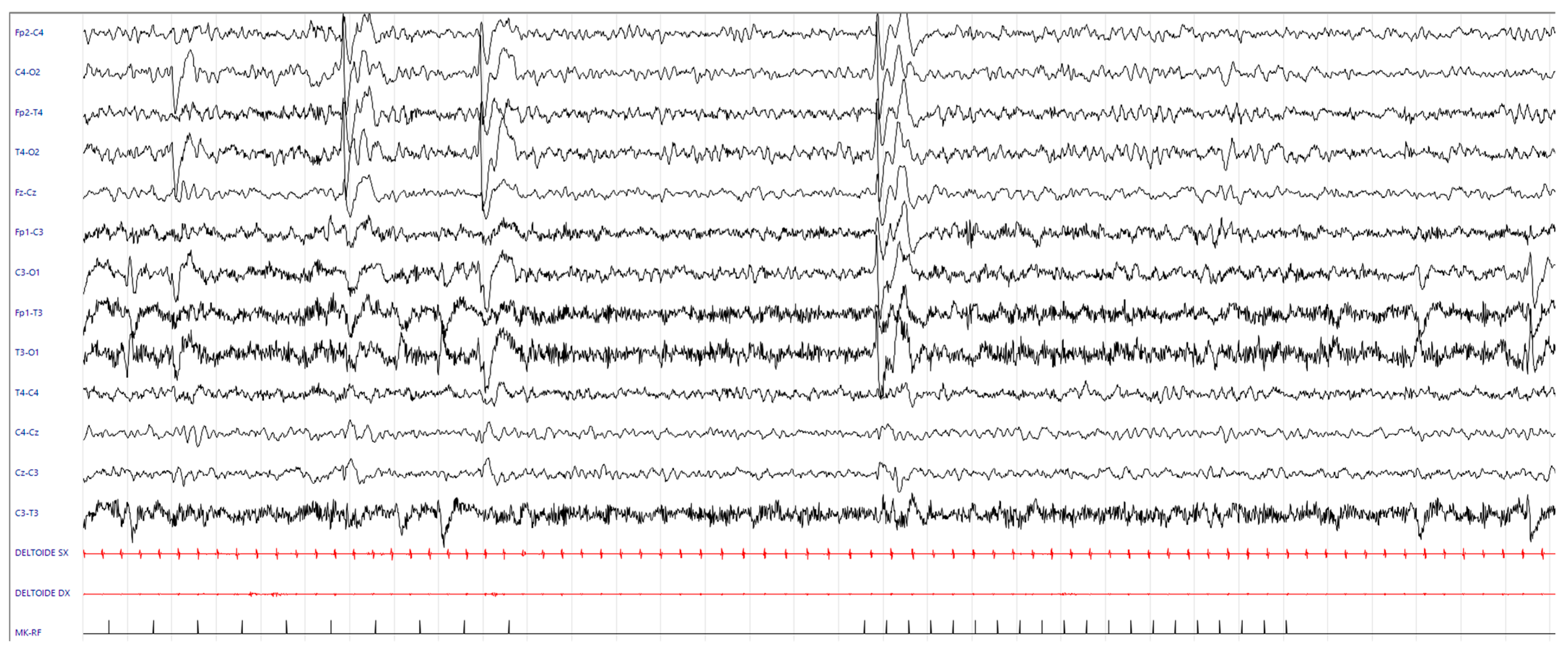
3.1. Medical History
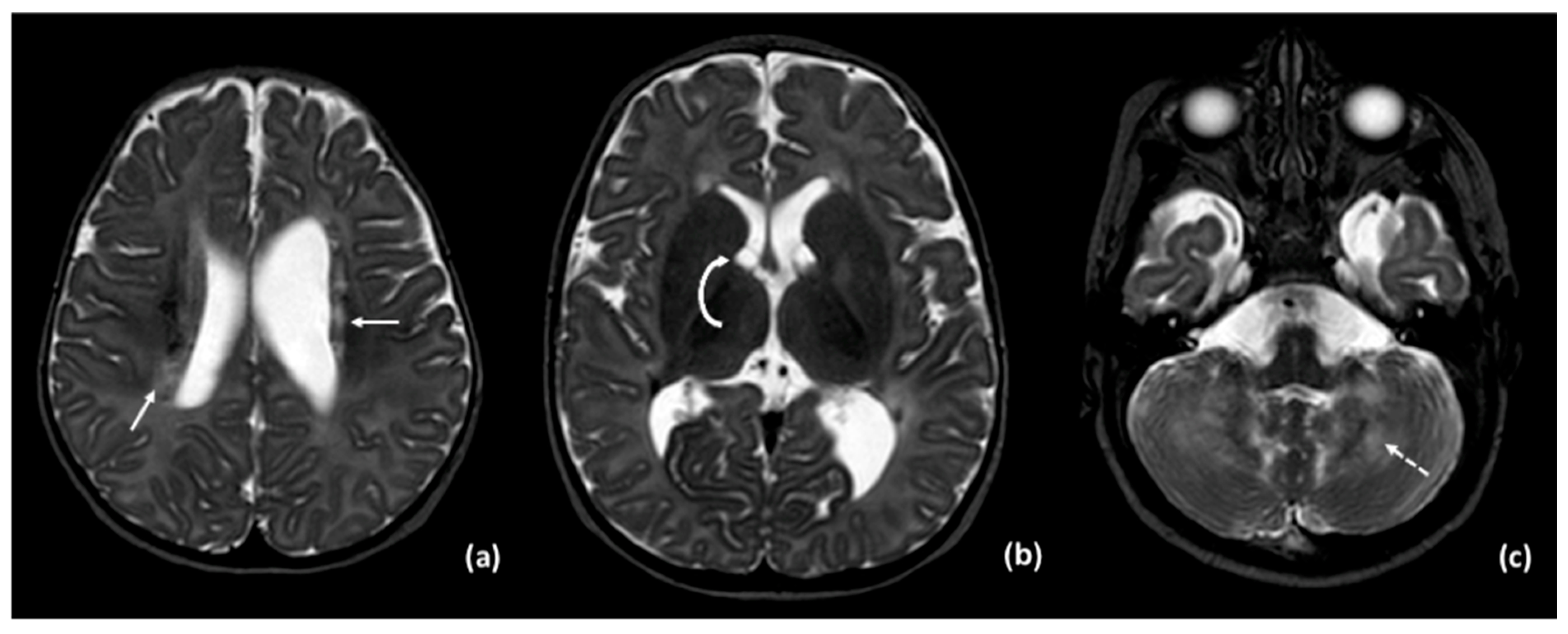
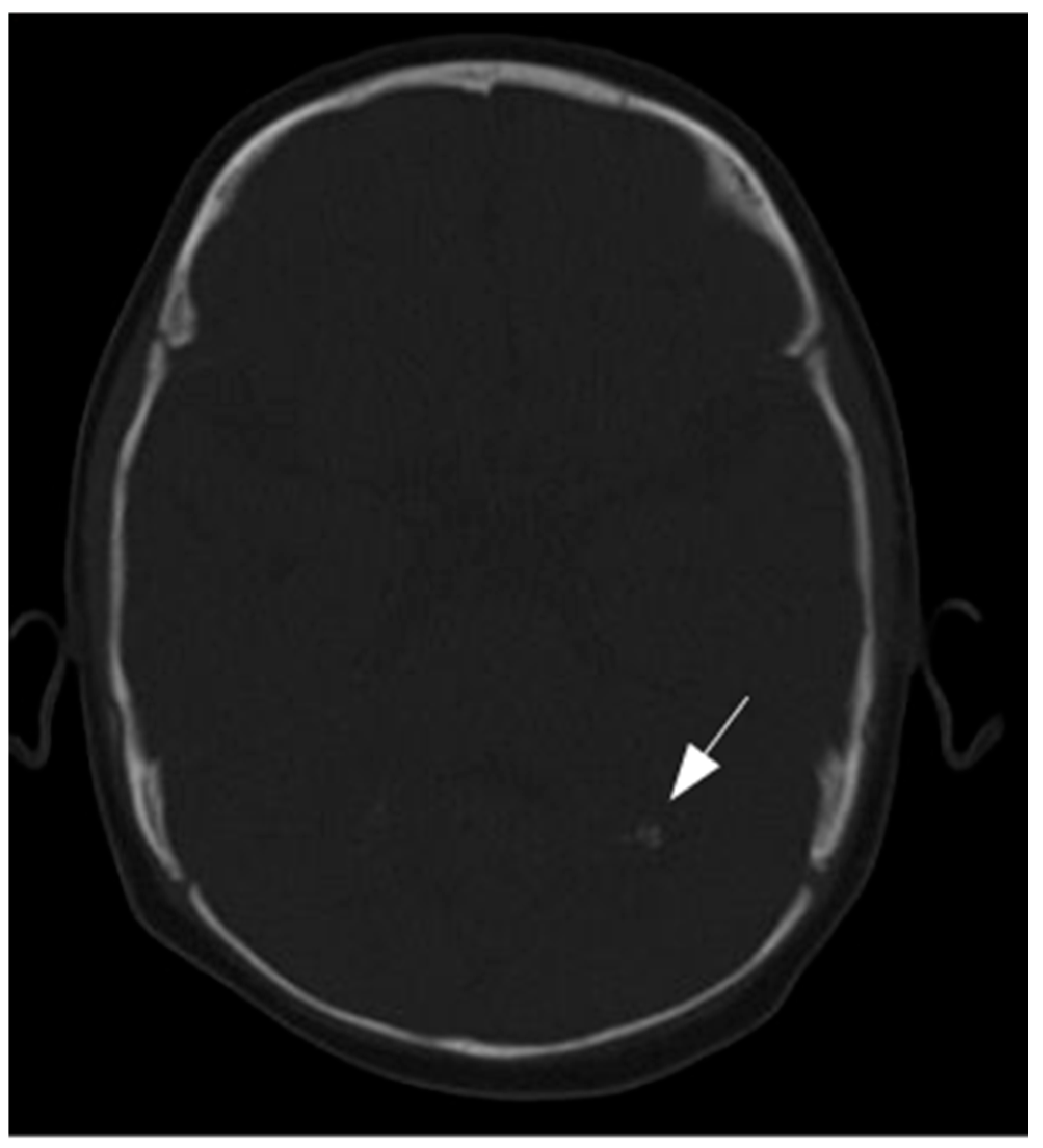
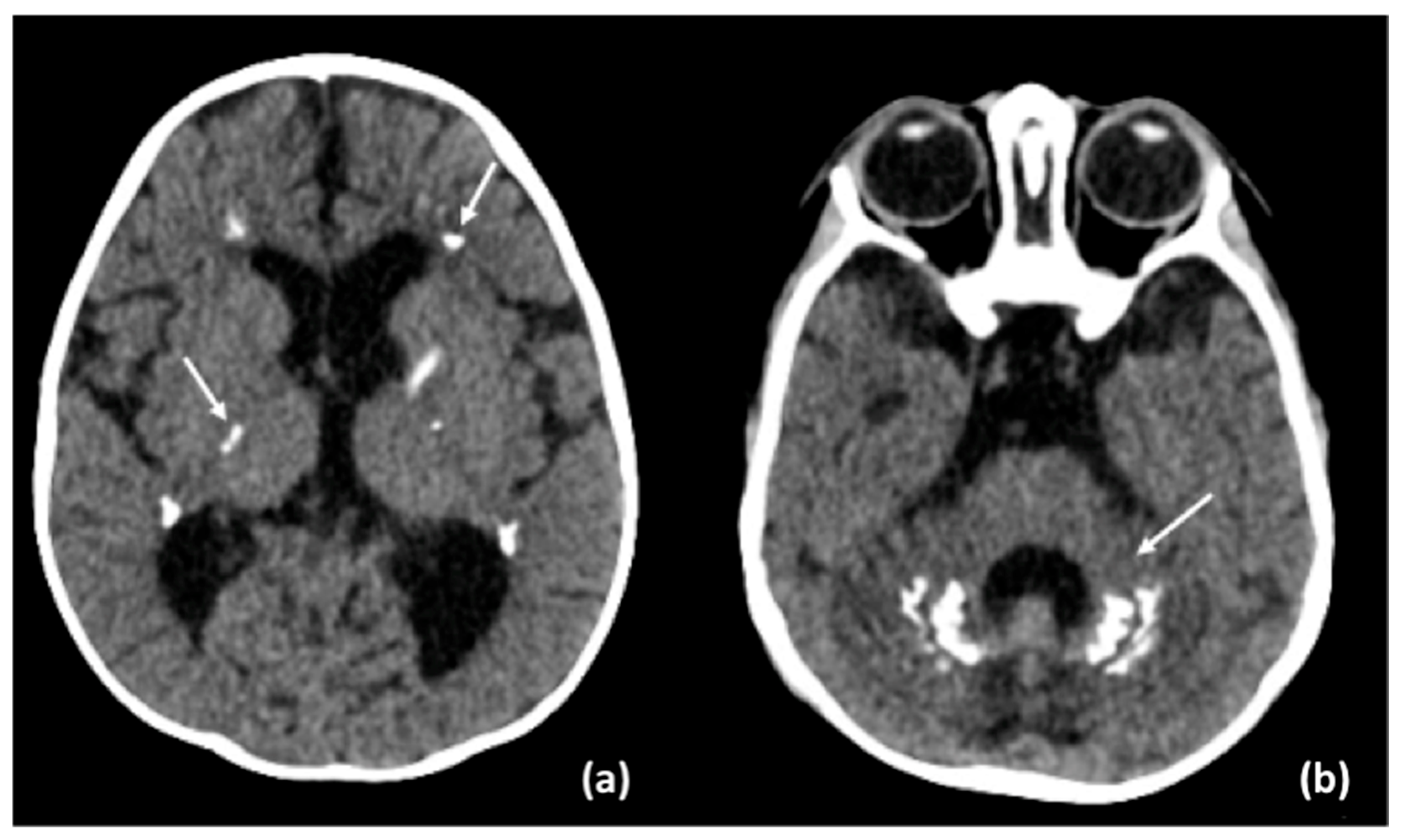
3.2. Results of Imaging Data
3.3. Results of Laboratory Tests
3.4. Differential Diagnosis
3.5. Genetic Tests and Final Diagnosis
3.6. Possibile Precision Medicine Treatment
3.7. Follow-Up
4. Narrative Literature Review
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Binsabbar, N.; Tabassum, S. Undiscovered Phenotype of KARS1 Related Mitochondrial Leukoencephalopathy. JBCGenetics 2023, 6, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peluso, F.; Palazzo, V.; Indolfi, G.; Mari, F.; Pasqualetti, R.; Procopio, E.; Nesti, C.; Guerrini, R.; Santorelli, F.; Giglio, S. Leopard-like retinopathy and severe early-onset portal hypertension expand the phenotype of KARS1-related syndrome: A case report. BMC Med. Genom. 2021, 14, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saettini, F.; Guerra, F.; Fazio, G.; Bugarin, C.; McMillan, H.J.; Ohtake, A.; Ardissone, A.; Itoh, M.; Giglio, S.; Cappuccio, G.; et al. Antibody Deficiency in Patients with Biallelic KARS1 Mutations. J. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 43, 2115–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, M.; Dai, H.; Horike, S.; Gonzalez, J.; Kitami, Y.; Meguro-Horike, M.; Kuki, I.; Shimakawa, S.; Yoshinaga, H.; Ota, Y.; et al. Biallelic KARS pathogenic variants cause an early-onset progressive leukodystrophy. Brain 2019, 142, 560–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Song, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Lu, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, M.; Xi, J.; Luo, S.; et al. Loss-of-function mutations in Lysyl-tRNA synthetase cause various leukoencephalopathy phenotypes. Neurol. Genet. 2019, 5, e565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.-J.; Vona, B.; Barbalho, P.G.; Kaiyrzhanov, R.; Maroofian, R.; Petree, C.; Severino, M.; Stanley, V.; Varshney, P.; Bahena, P.; et al. Biallelic variants in KARS1 are associated with neurodevelopmental disorders and hearing loss recapitulated by the knockout zebrafish. Genet. Med. 2021, 23, 1933–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappuccio, G.; Ceccatelli Berti, C.; Baruffini, E.; Sullivan, J.; Shashi, V.; Jewett, T.; Stamper, T.; Maitz, S.; Canonico, F.; Revah-Politi, A.; et al. Bi-allelic KARS1 pathogenic variants affecting functions of cytosolic and mitochondrial isoforms are associated with a progressive and multisystem disease. Hum. Mutat. 2021, 42, 745–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrigni, D.; Diodato, D.; Di Nottia, M.; Torraco, A.; Bellacchio, E.; Rizza, T.; Tozzi, G.; Verardo, M.; Piemonte, F.; Tasca, G.; et al. Novel mutations in KARS cause hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and combined mitochondrial respiratory chain defect. Clin. Genet. 2017, 91, 918–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohda, M.; Tokuzawa, Y.; Kishita, Y.; Nyuzuki, H.; Moriyama, Y.; Mizuno, Y.; Hirata, T.; Yatsuka, Y.; Yamashita-Sugahara, Y.; Nakachi, Y.; et al. A Comprehensive Genomic Analysis Reveals the Genetic Landscape of Mitochondrial Respiratory Chain Complex Deficiencies. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1005679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardissone, A.; Tonduti, D.; Legati, A.; Lamantea, E.; Barone, R.; Dorboz, I.; Boespflug-Tanguy, O.; Nebbia, G.; Maggioni, M.; Garavaglia, B.; et al. KARS-related diseases: Progressive leukoencephalopathy with brainstem and spinal cord calcifications as new phenotype and a review of literature. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2018, 13, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, H.M.; Sakaguchi, R.; Liu, C.; Igarashi, T.; Pehlivan, D.; Chu, K.; Iyer, R.; Cruz, P.; Cherukuri, P.F.; Hansen, N.F.; et al. Compound Heterozygosity for Loss-of-Function Lysyl-tRNA Synthetase Mutations in a Patient with Peripheral Neuropathy. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2010, 87, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.-L.; He, L.-X.; Yu, L.-J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.-J.; Wang, E.-D.; Yang, T. Mutations in KARS cause early-onset hearing loss and leukoencephalopathy: Potential pathogenic mechanism. Hum. Mutat. 2017, 38, 1740–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, S.A.; Schene, I.F.; Kok, G.; Jansen, J.M.; Nikkels, P.G.J.; Van Gassen, K.L.I.; Terheggen-Lagro, S.W.J.; Van Der Crabben, S.N.; Hoeks, S.E.; Niers, L.E.M.; et al. Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase deficiencies in search of common themes. Genet. Med. 2019, 21, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejma, T.A.; Beidler, W.S.; VanSickle, E.A.; Prokop, J.W.; Brown, W.T.; Scheurer-Monaghan, A.; Rossetti, L.Z. Expansion of the phenotypic spectrum of KARS1-related disorders to include arthrogryposis multiplex congenita and summary of experiences with lysine supplementation. Am. J. Med. Genet. Pt. A 2024, 194, e63811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzzenente, B.; Assouline, Z.; Barcia, G.; Rio, M.; Boddaert, N.; Munnich, A.; Rötig, A.; Metodiev, M.D. Inhibition of mitochondrial translation in fibroblasts from a patient expressing the KARS p.(Pro228Leu) variant and presenting with sensorineural deafness, developmental delay, and lactic acidosis. Hum. Mutat. 2018, 39, 2047–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orcesi, S.; La Piana, R.; Uggetti, C.; Tonduti, D.; Pichiecchio, A.; Pasin, M.; Viselner, G.; Comi, G.P.; Del Bo, R.; Ronchi, D.; et al. Spinal Cord Calcification in an Early-Onset Progressive Leukoencephalopathy. J. Child. Neurol. 2011, 26, 876–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan, H.J.; Humphreys, P.; Smith, A.; Schwartzentruber, J.; Chakraborty, P.; Bulman, D.E.; Beaulieu, C.L.; FORGE Canada Consortium; Majewski, J.; Boycott, K.M.; et al. Congenital Visual Impairment and Progressive Microcephaly Due to Lysyl–Transfer Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) Synthetase (KARS) Mutations: The Expanding Phenotype of Aminoacyl–Transfer RNA Synthetase Mutations in Human Disease. J. Child. Neurol. 2015, 30, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, A.; Rojas, J.; Aivasovsky, I.; Vergara, S.; Castellanos, M.; Prieto, C.; Celis, L. Progressive Early-Onset Leukodystrophy Related to Biallelic Variants in the KARS Gene: The First Case Described in Latin America. Genes 2020, 11, 1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Knaap, M.S.; Van Der Voorn, P.; Barkhof, F.; Van Coster, R.; Krägeloh-Mann, I.; Feigenbaum, A.; Blaser, S.; Vles, J.S.H.; Rieckmann, P.; Pouwels, P.J.W. A new leukoencephalopathy with brainstem and spinal cord involvement and high lactate. Ann. Neurol. 2003, 53, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basit, S.; Lee, K.; Habib, R.; Chen, L.; Umm-e-Kalsoom; Santos-Cortez, R.L.P.; Azeem, Z.; Andrade, P.; Ansar, M.; Ahmad, W.; et al. DFNB89, a novel autosomal recessive nonsyndromic hearing impairment locus on chromosome 16q21-q23.2. Hum. Genet. 2011, 129, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Santos-Cortez, R.L.P.; Lee, K.; Azeem, Z.; Antonellis, P.J.; Pollock, L.M.; Khan, S.; Irfanullah; Andrade-Elizondo, P.B.; Chiu, I.; Adams, M.D.; et al. Mutations in KARS, Encoding Lysyl-tRNA Synthetase, Cause Autosomal-Recessive Nonsyndromic Hearing Impairment DFNB89. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 93, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanger, T.D.; Chen, D.; Fehlings, D.L.; Hallett, M.; Lang, A.E.; Mink, J.W.; Singer, H.S.; Alter, K.; Ben-Pazi, H.; Butler, E.E.; et al. Definition and classification of hyperkinetic movements in childhood. Mov. Disord. 2010, 25, 1538–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauly, M.; Korenke, G.; Diaw, S.; Grözinger, A.; Cazurro-Gutiérrez, A.; Pérez-Dueñas, B.; González, V.; Macaya, A.; Serrano Antón, A.; Peterlin, B.; et al. The Expanding Phenotypical Spectrum of WARS2-Related Disorder: Four Novel Cases with a Common Recurrent Variant. Genes 2023, 14, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skorvanek, M.; Rektorova, I.; Mandemakers, W.; Wagner, M.; Steinfeld, R.; Orec, L.; Han, V.; Pavelekova, P.; Lackova, A.; Kulcsarova, K.; et al. WARS2 mutations cause dopa-responsive early-onset parkinsonism and progressive myoclonus ataxia. Park. Relat. Disord. 2022, 94, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coughlin, C.R.; Scharer, G.H.; Friederich, M.W.; Yu, H.-C.; Geiger, E.A.; Creadon-Swindell, G.; Collins, A.E.; Vanlander, A.V.; Coster, R.V.; Powell, C.A.; et al. Mutations in the mitochondrial cysteinyl-tRNA synthase gene, CARS2, lead to a severe epileptic encephalopathy and complex movement disorder. J. Med. Genet. 2015, 52, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Valles-Ibáñez, G.; Hildebrand, M.S.; Bahlo, M.; King, C.; Coleman, M.; Green, T.E.; Goldsmith, J.; Davis, S.; Gill, D.; Mandelstam, S.; et al. Infantile-onset myoclonic developmental and epileptic encephalopathy: A new RARS2 phenotype. Epilepsia Open 2022, 7, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, S.; Butala, A.; Mahida, S.; Richter, J.; Mu, W.; Poretti, A.; Vernon, H.; VanGerpen, J.; Atwal, P.S.; Middlebrooks, E.H.; et al. Expansion of the clinical spectrum associated with AARS2-related disorders. Am. J. Med. Genet. Pt. A 2019, 179, 1556–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, M.-Y.; Chang, Y.-Y.; Yeh, T.-H.; Lin, T.-K.; Lu, C.-S. Leukoencephalopathy with brainstem and spinal cord involvement and lactate elevation (LBSL) with a novel DARS2 mutation and isolated progressive spastic paraparesis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 372, 229–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Balushi, A.; Matviychuk, D.; Jobling, R.; Salomons, G.S.; Blaser, S.; Mercimek-Andrews, S. Phenotypes and genotypes of mitochondrial aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase deficiencies from a single neurometabolic clinic. JIMD Rep. 2020, 51, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ticci, C.; Orsucci, D.; Ardissone, A.; Bello, L.; Bertini, E.; Bonato, I.; Bruno, C.; Carelli, V.; Diodato, D.; Doccini, S.; et al. Movement Disorders in Children with a Mitochondrial Disease: A Cross-Sectional Survey from the Nationwide Italian Collaborative Network of Mitochondrial Diseases. JCM 2021, 10, 2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.; Abel, S.; McClure, M.; Foster, J.; Walke, M.; Jayakar, P.; Bademci, G.; Tekin, M. Novel Causative Variants in DYRK1A, KARS, and KAT6A Associated with Intellectual Disability and Additional Phenotypic Features. J. Pediatr. Genet. 2017, 6, 077–083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheidecker, S.; Bär, S.; Stoetzel, C.; Geoffroy, V.; Lannes, B.; Rinaldi, B.; Fischer, F.; Becker, H.D.; Pelletier, V.; Pagan, C.; et al. Mutations in KARS cause a severe neurological and neurosensory disease with optic neuropathy. Hum. Mutat. 2019, 40, 1826–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieber, D.S.; Calvo, S.E.; Shanahan, K.; Slate, N.G.; Liu, S.; Hershman, S.G.; Gold, N.B.; Chapman, B.A.; Thorburn, D.R.; Berry, G.T.; et al. Targeted exome sequencing of suspected mitochondrial disorders. Neurology 2013, 80, 1762–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferasin, V.; Raicich, A.; Ancora, C.; Bonemazzi, I.; Di Paola, A.; D’Errico, I.; Nosadini, M.; Ancona, C.; Pelizza, M.F.; Cassina, M.; et al. Hyperkinetic Movement Disorder in KARS1-Related Disease: An Illustrative Video-Recorded Case and Narrative Literature Review. Neurol. Int. 2025, 17, 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint17090143
Ferasin V, Raicich A, Ancora C, Bonemazzi I, Di Paola A, D’Errico I, Nosadini M, Ancona C, Pelizza MF, Cassina M, et al. Hyperkinetic Movement Disorder in KARS1-Related Disease: An Illustrative Video-Recorded Case and Narrative Literature Review. Neurology International. 2025; 17(9):143. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint17090143
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerasin, Veronica, Arianna Raicich, Caterina Ancora, Ilaria Bonemazzi, Alessandro Di Paola, Ignazio D’Errico, Margherita Nosadini, Claudio Ancona, Maria Federica Pelizza, Matteo Cassina, and et al. 2025. "Hyperkinetic Movement Disorder in KARS1-Related Disease: An Illustrative Video-Recorded Case and Narrative Literature Review" Neurology International 17, no. 9: 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint17090143
APA StyleFerasin, V., Raicich, A., Ancora, C., Bonemazzi, I., Di Paola, A., D’Errico, I., Nosadini, M., Ancona, C., Pelizza, M. F., Cassina, M., & Toldo, I. (2025). Hyperkinetic Movement Disorder in KARS1-Related Disease: An Illustrative Video-Recorded Case and Narrative Literature Review. Neurology International, 17(9), 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint17090143






