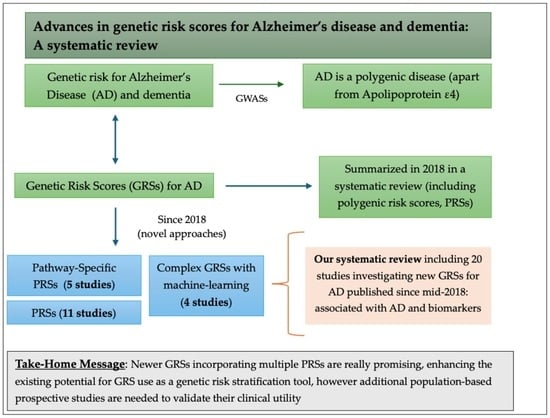
Advances in Genetic Risk Scores for Alzheimer’s Disease and Dementia: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Systematic Review Search Strategy
2.2. Screening and Eligibility Strategy
2.3. Risk of Bias Assessment
3. Results
3.1. PRSs
3.1.1. Studies Investigating Cognitive Outcomes
3.1.2. Studies Investigating Biomarkers as Outcome
3.2. P-PRSs
3.3. Complex GRSs
4. Discussion
4.1. GRSs in the Context of PRSs
4.2. P-PRS for AD-Related Pathways
4.3. Other Complex GRSs
4.4. Limitations and Strengths of Our Study
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raz, L.; Knoefel, J.; Bhaskar, K. The neuropathology and cerebrovascular mechanisms of dementia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2016, 36, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corey-Bloom, J. The ABC of Alzheimer’s disease: Cognitive changes and their management in Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias. Int. Psychogeriatr. 2002, 14 (Suppl. 1), 51–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C. Etiology of Alzheimer’s Disease. Discov. Med. 2023, 35, 757–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, R.A. Risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease. Folia Neuropathol. 2019, 57, 87–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S.J.; Renton, A.E.; Fulton-Howard, B.; Podlesny-Drabiniok, A.; Marcora, E.; Goate, A.M. The complex genetic architecture of Alzheimer’s disease: Novel insights and future directions. EBioMedicine 2023, 90, 104511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belloy, M.E.; Napolioni, V.; Greicius, M.D. A Quarter Century of APOE and Alzheimer’s Disease: Progress to Date and the Path Forward. Neuron 2019, 101, 820–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Battista, A.M.; Heinsinger, N.M.; Rebeck, G.W. Alzheimer’s Disease Genetic Risk Factor APOE-ε4 Also Affects Normal Brain Function. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2016, 13, 1200–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, J.C.; Ibrahim-Verbaas, C.A.; Harold, D.; Naj, A.C.; Sims, R.; Bellenguez, C.; DeStafano, A.L.; Bis, J.C.; Beecham, G.W.; Grenier-Boley, B.; et al. Meta-analysis of 74,046 individuals identifies 11 new susceptibility loci for Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1452–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunkle, B.W.; Grenier-Boley, B.; Sims, R.; Bis, J.C.; Damotte, V.; Naj, A.C.; Boland, A.; Vronskaya, M.; van der Lee, S.J.; Amlie-Wolf, A.; et al. Genetic meta-analysis of diagnosed Alzheimer’s disease identifies new risk loci and implicates Aβ, tau, immunity and lipid processing. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 414–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, I.E.; Savage, J.E.; Watanabe, K.; Bryois, J.; Williams, D.M.; Steinberg, S.; Sealock, J.; Karlsson, I.K.; Hägg, S.; Athanasiu, L.; et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis identifies new loci and functional pathways influencing Alzheimer’s disease risk. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruchaga, C.; Del-Aguila, J.L.; Saef, B.; Black, K.; Fernandez, M.V.; Budde, J.; Ibanez, L.; Deming, Y.; Kapoor, M.; Tosto, G.; et al. Polygenic risk score of sporadic late-onset Alzheimer’s disease reveals a shared architecture with the familial and early-onset forms. Alzheimers Dement. 2018, 14, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.W.; Mak, T.S.; O’Reilly, P.F. Tutorial: A guide to performing polygenic risk score analyses. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 2759–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escott-Price, V.; Sims, R.; Bannister, C.; Harold, D.; Vronskaya, M.; Majounie, E.; Badarinarayan, N.; Perades, G.; Consortia, I.; Morgan, K.; et al. Common polygenic variation enhances risk prediction for Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 2015, 138, 3673–3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, T.; Sabuncu, M.R.; Smoller, J.W.; Sperling, R.A.; Mormino, E.C. Dissociable influences of APOE epsilon4 and polygenic risk of AD dementia on amyloid and cognition. Neurology 2018, 90, e1605–e1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleegers, K.; Bettens, K.; De Roeck, A.; Van Cauwenberghe, C.; Cuyvers, E.; Verheijen, J.; Struyfs, H.; Van Dongen, J.; Vermeulen, S.; Engelborghs, S.; et al. A 22-single nucleotide polymorphism Alzheimer’s disease risk score correlates with family history, onset age, and cerebrospinal fluid Abeta42. Alzheimers Dement. 2015, 11, 1452–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desikan, R.S.; Fan, C.C.; Wang, Y.; Schork, A.J.; Cabral, H.J.; Cupples, L.A.; Thompson, W.K.; Besser, L.; Kukull, W.A.; Holland, D.; et al. Genetic assessment of age-associated Alzheimer disease risk: Development and validation of a polygenic hazard score. PLoS Med. 2017, 14, e1002258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukadam, N.; Giannakopoulou, O.; Bass, N.; Kuchenbaecker, K.; McQuillin, A. Genetic risk scores and dementia risk across different ethnic groups in UK Biobank. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0277378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igo, R.P., Jr.; Kinzy, T.G.; Cooke Bailey, J.N. Genetic Risk Scores. Curr. Protoc. Hum. Genet. 2019, 104, e95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, H.; Möllers, T.; Perna, L.; Brenner, H. The genetic risk of Alzheimer’s disease beyond APOE ε4: Systematic review of Alzheimer’s genetic risk scores. Transl. Psychiatry 2018, 8, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Τesi, N.; van der Lee, S.J.; Hulsman, M.; Jansen, I.E.; Stringa, N.; van Schoor, N.M.; Scheltens, P.; van der Flier, W.M.; Huisman, M.; Reinders, M.J.T.; et al. Immune response and endocytosis pathways are associated with the resilience against Alzheimer’s disease. Transl. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Vasiljevic, E.; Deming, Y.K.; Jonaitis, E.M.; Koscik, R.L.; Van Hulle, C.A.; Lu, Q.; Carboni, M.; Kollmorgen, G.; Wild, N.; et al. Effect of Pathway-specific Polygenic Risk Scores for Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) on Rate of Change in Cognitive Function and AD-related Biomarkers among Asymptomatic Individuals. Alzheimers Dis. 2023, 94, 1587–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, K.; Fu, W.; Liu, C.L.; Ho, P.C.; Wang, H.; Lee, W.P.; Chou, S.Y.; Wang, L.S.; Tzeng, J.Y. The prediction of Alzheimer’s disease through multi-trait genetic modeling. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1168638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Aoust, T.; Clocchiatti-Tuozzo, S.; Rivier, C.A.; Mishra, A.; Hachiya, T.; Grenier-Boley, B.; Soumaré, A.; Duperron, M.G.; Le Grand, Q.; Bouteloup, V.; et al. Polygenic score integrating neurodegenerative and vascular risk informs dementia risk stratification. Alzheimers Dement. 2025, 21, e70014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Int. J. Surg. 2021, 88, 105906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Non-Randomised Studies in Meta-Analyses. Available online: http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.htm (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Sohani, Z.N.; Meyre, D.; de Souza, R.J.; Joseph, P.G.; Gandhi, M.; Dennis, B.B.; Norman, G.; Anand, S.S. Assessing the quality of published genetic association studies in meta-analyses: The quality of genetic studies (Q-Genie) tool. BMC Genet. 2015, 16, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tin, A.; Bressler, J.; Simino, J.; Sullivan, K.J.; Mei, H.; Windham, B.G.; Griswold, M.; Gottesman, R.F.; Boerwinkle, E.; Fornage, M.; et al. Genetic Risk, Midlife Life’s Simple 7, and Incident Dementia in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. Neurology 2022, 99, e154–e163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peloso, G.M.; Beiser, A.S.; Satizabal, C.L.; Xanthakis, V.; Vasan, R.S.; Pase, M.P.; Destefano, A.L.; Seshadri, S. Cardiovascular health, genetic risk, and risk of dementia in the Framingham Heart Study. Neurology 2020, 95, e1341–e1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Yuan, S.; Lu, D.; Ling, Y.; Huang, X.; Lyu, J.; Xu, A. Dietary inflammatory index, genetic susceptibility and risk of incident dementia: A prospective cohort study from UK biobank. J. Neurol. 2024, 271, 1286–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamalaki, E.; Charisis, S.; Mourtzi, N.; Hatzimanolis, A.; Ntanasi, E.; Kosmidis, M.H.; Constantinides, V.C.; Pantes, G.; Kolovou, D.; Dardiotis, E.; et al. Genetic risk for Alzheimer’s disease and adherence to the Mediterranean diet: Results from the HELIAD study. Nutr. Neurosci. 2024, 27, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Xie, S.; Cui, J.; Li, Y.; Li, T.; Wang, Y.; Jia, J. Polygenic Risk Score Reveals Genetic Heterogeneity of Alzheimer’s Disease between the Chinese and European Populations. J. Prev. Alzheimers Dis. 2024, 11, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S.J.; McFall, G.P.; Dixon, R.A.; Cherbuin, N.; Eramudugolla, R.; Anstey, K.J. Alzheimer’s Environmental and Genetic Risk Scores are Differentially Associated with General Cognitive Ability and Dementia Severity. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2019, 33, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenowitz, W.D.; Fornage, M.; Launer, L.J.; Habes, M.; Davatzikos, C.; Yaffe, K. Alzheimer’s Disease Genetic Risk, Cognition, and Brain Aging in Midlife. Ann. Neurol. 2023, 93, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanan, V.K.; Gebre, R.K.; Graff-Radford, J.; Hofrenning, E.; Algeciras-Schimnich, A.; Figdore, D.J.; Lowe, V.J.; Mielke, M.M.; Knopman, D.S.; Ross, O.A.; et al. Genetic risk scores enhance the diagnostic value of plasma biomarkers of brain amyloidosis. Brain 2023, 146, 4508–4519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadmaan, G.; Dalmasso, M.C.; Ramirez, A.; Hiltunen, M.; Kemppainen, N.; Lehtisalo, J.; Mangialasche, F.; Ngandu, T.; Rinne, J.; Soininen, H.; et al. Alzheimer’s disease genetic risk score and neuroimaging in the FINGER lifestyle trial. Alzheimers Dement. 2024, 20, 4345–4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buto, P.T.; Wang, J.; La Joie, R.; Zimmerman, S.C.; Glymour, M.M.; Ackley, S.F.; Hoffmann, T.J.; Yaffe, K.; Zeki Al Hazzouri, A.; Brenowitz, W.D. Genetic risk score for Alzheimer’s disease predicts brain volume differences in mid and late life in UK biobank participants. Alzheimers Dement. 2024, 20, 1978–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Lee, S.J.; Wolters, F.J.; Ikram, M.K.; Hofman, A.; Ikram, M.A.; Amin, N.; van Duijn, C.M. The effect of APOE and other common genetic variants on the onset of Alzheimer’s disease and dementia: A community- based cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wightman, D.P.; Jansen, I.E.; Savage, J.E.; Shadrin, A.A.; Bahrami, S.; Holland, D.; Rongve, A.; Børte, S.; Winsvold, B.S.; Drange, O.K.; et al. A genome-wide association study with 1,126,563 individuals identifies new risk loci for Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 1276–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Li, F.; Wei, C.; Zhu, M.; Qu, Q.; Qin, W.; Tang, Y.; Shen, L.; Wang, Y.; Shen, L.; et al. Prediction of Alzheimer’s disease using multi-variants from a Chinese genome-wide association study. Brain 2021, 144, 924–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rojas, I.; Moreno-Grau, S.; Tesi, N.; Grenier-Boley, B.; Andrade, V.; Jansen, I.E.; Pedersen, N.L.; Stringa, N.; Zettergren, A.; Hernández, I.; et al. Common variants in Alzheimer’s disease and risk stra tification by polygenic risk scores. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellenguez, C.; Küçükali, F.; Jansen, I.E.; Kleineidam, L.; Moreno-Grau, S.; Amin, N.; Naj, A.C.; Campos-Martin, R.; Grenier-Boley, B.; Andrade, V.; et al. New insights into the genetic etiology of Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 412–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schork, N.J.; Elman, J.A. Pathway-specific polygenic risk scores correlate with clinical status and Alzheimer’s-related biomarkers. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2023, 95, 915–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, K.; Liu, Y.; Liu, B.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. A Pathway-Specific Polygenic Risk Score Is Associated with Tau Pathology and Cognitive Decline. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2022, 85, 1745–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caspers, S.; Röckner, M.E.; Jockwitz, C.; Bittner, N.; Teumer, A.; Herms, S.; Hoffmann, P.; Nöthen, M.M.; Moebus, S.; Amunts, K.; et al. Pathway-Specific Genetic Risk for Alzheimer’s Disease Differentiates Regional Patterns of Cortical Atrophy in Older Adults. Cereb. Cortex 2020, 30, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabuncu, M.R.; Buckner, R.L.; Smoller, J.W.; Lee, P.H.; Fischl, B.; Sperling, R.A. The association between a polygenic Alzheimer score and cortical thickness in clinically normal subjects. Cereb. Cortex 2012, 22, 2653–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deming, Y.; Vasiljevic, E.; Morrow, A.; Miao, J.; Van Hulle, C.; Jonaitis, E.; Ma, Y.; Whitenack, V.; Kollmorgen, G.; Wild, N.; et al. Neuropathology-based APOE genetic risk score better quantifies Alzheimer’s risk. Alzheimers Dement. 2023, 19, 3406–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Hu, R.; Zhang, G.; Zhe, Y.; Hu, B.; He, J.; Wang, Z.; Qi, X. A Weighted Genetic Risk Score Based on Four APOE-Independent Alzheimer’s Disease Risk Loci May Supplement APOE E4 for Better Disease Prediction. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 69, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiman, E.M.; Arboleda-Velasquez, J.F.; Quiroz, Y.T.; Huentelman, M.J.; Beach, T.G.; Caselli, R.J.; Chen, Y.; Su, Y.; Myers, A.J.; Hardy, J.; et al. Exceptionally low likelihood of Alzheimer’s dementia in APOE2 homozygotes from a 5,000-person neuropathological study. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenowitz, W.D.; Zimmerman, S.C.; Filshtein, T.J.; Yaffe, K.; Walter, S.; Hoffmann, T.J.; Jorgenson, E.; Whitmer, R.A.; Glymour, M.M. Extension of Mendelian Randomization to Identify Earliest Manifestations of Alzheimer Disease: Association of Genetic Risk Score for Alzheimer Disease with Lower Body Mass Index by Age 50 Years. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2021, 190, 2163–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, Y.; Ackley, S.F.; Glymour, M.M.; Yaffe, K.; Brenowitz, W.D. Genetic Risk of Alzheimer’s Disease and Sleep Duration in Non-Demented Elders. Ann. Neurol. 2021, 89, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, C.R., Jr.; Andrews, J.S.; Beach, T.G.; Buracchio, T.; Dunn, B.; Graf, A.; Hansson, O.; Ho, C.; Jagust, W.; McDade, E.; et al. Revised criteria for diagnosis and staging of Alzheimer’s disease: Alzheimer’s Association Workgroup. Alzheimers Dement. 2024, 20, 5143–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Study | Population Characteristics | GWASs 1 | SNPs 2 | Result for GRS 3 by outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mukadam et al., 2022 [17] | N = 364.879 From UK Biobank | Lambert et al. [8] | 21 SNPs (p < 5 × 10−8) | GRS related to increased dementia risk (OR 4: 1.21 for each SD 5 increase) |
| Tin et al., 2022 [27] | Ν = 11.561 8.823 European Americans (EA) 2.738 African Americans (AA) | Kunkle et al. [9] | 44 SNPs for EA 9 SNPs for AA | GRS associated with higher dementia risk (EA, HR 6: 1.44 for each SD increase; AA, HR: 1.26 for each SD increase) |
| Peloso et al., 2020 [28] | N = 1.211 From Framingham Heart Study Over 60 years old | Van der Lee et al. [37] | 23 SNPs | High GRS (>80th percentile) associated with a 2.6-fold-higher dementia risk compared to the lowest quantile (<20th) |
| Peng et al., 2023 [29] | N = 207.301 From UK Biobank 39–72 years old | Jansen et al. [10] | 29 SNPs | Higher GRS with higher dietary inflammatory indexes were related to a higher AD 7 risk (HR: 1.757) |
| Mamalaki et al., 2023 [30] | N = 537 From HELIAD study Over 65 years old | Wightman et al. [38] | 38 SNPs (p < 0.05) | GRS associated with increased AD risk (HR: 1.928 for each SD increase) |
| Li et al., 2024 [31] | N = 3020 From China Over 60 years old | Chinese GWAS [39] | 20 SNPs (p < 5 × 10−8) | High GRS related to increased late-onset AD risk (OR: 3.15) |
| Andrews et al., 2019 [32] | N = 1061 From Australia Community-dwelling, >60 years | Lambert et al. [8] | 23 SNPs 2 for APOE | GRS cross-sectionally associated with episodic memory (−0.10) and cognitive variability (−0.08) |
| Brenowitz et al., 2023 [33] | N = 1252 From San Francisco Middle-aged | Kunkle et al. [9] | 25 SNPs | GRS related cross-sectionally to worse Montreal Cognitive Assessment (−0.14 SD), but not composite cognitive score |
| Study | Population Characteristics | GWASs 1 | SNPs 2 | Result for GRS 3 by outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li et al., 2024 [31] | N = 3020 From China, over 60 years old | Chinese GWAS [39] | 20 SNPs (p < 5 × 10−8) | GRS related to CSF 4 P-Tau181 and inversely related to CSF Aβ42, CSF Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio |
| Ramanan et al., 2023 [34] | N = 962 From Mayo Clinic Study of Aging | De Rojas et al. [40] | 21 SNPs (p < 5 × 10−8) | GRS related to greater amyloid PET 5 levels and plasma P-Tau181 |
| Saadman et al., 2024 [35] | N = 1260 From Finland | Bellenguez et al. [41] | 83 SNPs | GRS not related to PET amyloid deposition or MRI 6 volumes |
| Buto et al., 2023 [36] | N = 47.502 From UK Biobank | Kunkle et al. [9] | 26 SNPs (2 for APOE 7) | GRS associated with age-related reduction in specific MRI regions |
| Study | Population Characteristics | GWASs 1 | p-PRS 2 | Cognitive Outcome | Biomarker Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tesi et al., 2020 [20] | N = 1779 From the Longitudinal Aging Study Amsterdam | Many GWAS 29 SNPs 3 | (1) B-amyloid metabolism (2) Immune response (3) Cholesterol dysfunction (4) Endocytosis (5) Angiogenesis | All p-PRSs were related to increased AD 4 risk | |
| Xu et al., 2023 [21] | N = 1175 From the Wisconsin Registry for Alzheimer’s Prevention | Kunkle et al. [9] 23 SNPs | (1) AβPP metabolism (2) Immune response (3) Cholesterol metabolism (4) Endocytosis (5) Tau pathology (6) Axonal development | P-PRS related to preclinical cognitive changes in
| P-PRSs related to age-dependent changes in
|
| Schork et al., 2023 [42] | N = 1411 From the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) European ancestry | Kunkle et al. [9] 351.203 SNPs | (1) Amyloid processing (2) Inflammatory response (3) Protein localization (4) Cholesterol transport (5) Immune signaling (6) Endocytosis (7) Humoral immune response (8) Receptor metabolic process (9) Response to misfolded protein (10) Phototransduction (11) Regulation of cell junction (12) Regulation of protein tyrosine (13) Mitophagy | 8 p-PRSs related to baseline AD diagnosis | P-PRSs related to the following biomarkers:
|
| Sun et al., 2021 [43] | N = 567 From the ADNI | Kunkle et al. [9] 60 SNPs | (1) Tau-protein binding and kinase activity | P-PRS related to memory impairment | P-PRS related to
|
| Caspers et al., 2020 [44] | N = 537 From 1000BRAINS Older adults from Bochum | Kunkle et al. [9] and Sabuncu et al. [45] 20 SNPs p < 5 × 10−8 | (1) AβPP metabolism (2) Immune response (3) Cholesterol metabolism (4) Endocytosis (5) MAPT metabolism (6) Axon development | Two p-PRSs (cholesterol and AβPP metabolism) related to regional cortical atrophy |
| Study | Population Characteristics | Genetic Study | SNPs 1 | Result for GRS 2 by Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deming et al., 2023 [46] | N = 1045 From the Wisconsin Registry for AD 3 Prevention and Research | Reiman et al. [48] | APOE 4-npscore | The APOE-npscore explained more variance of CSF 5 Aβ42/40, CSF P-Tau181, and P-Tau181/Aβ42 than APOE ε4 carrier status or ε4 allele count |
| Zhang et al., 2019 [47] | N = 1259 From Inner Mongolia (China) | Many GWAS 7 and the NHGRI catalog | Weighted (wGRS) with 7 SNPs (3 for APOE) | The wGRS was related to increased AD risk The AUC 8 for wGRS was significantly greater than the AUC for simple-count GRS |
| Clark et al., 2023 [22] | N = 5869 From the National Alzheimer’s Coordinating Center (NACC) | Many GWASs for 25 traits * related to AD | Meta-GRS | The meta-GRS was related to a 57% increase in the AD risk for each SD 9 increase (HR 10 = 1.577) |
| D’ Aoust et al., 2025 [23] | N = 3702 From French cities Community-dwelling, ≥65 | Many GWASs for 27 traits ** related to dementia | I-PRS Dem | The iPRS-DEM was related to increased dementia risk in the elderly (HR= 1.15), a result validated in two cohorts |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sampatakakis, S.N.; Mourtzi, N.; Hatzimanolis, A.; Scarmeas, N. Advances in Genetic Risk Scores for Alzheimer’s Disease and Dementia: A Systematic Review. Neurol. Int. 2025, 17, 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint17070099
Sampatakakis SN, Mourtzi N, Hatzimanolis A, Scarmeas N. Advances in Genetic Risk Scores for Alzheimer’s Disease and Dementia: A Systematic Review. Neurology International. 2025; 17(7):99. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint17070099
Chicago/Turabian StyleSampatakakis, Stefanos N., Niki Mourtzi, Alex Hatzimanolis, and Nikolaos Scarmeas. 2025. "Advances in Genetic Risk Scores for Alzheimer’s Disease and Dementia: A Systematic Review" Neurology International 17, no. 7: 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint17070099
APA StyleSampatakakis, S. N., Mourtzi, N., Hatzimanolis, A., & Scarmeas, N. (2025). Advances in Genetic Risk Scores for Alzheimer’s Disease and Dementia: A Systematic Review. Neurology International, 17(7), 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint17070099