Novel Gene-Informed Regional Brain Targets for Clinical Screening for Major Depression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Curation of Gene Lists
2.2. Development of the ATLANTE Pipeline
2.3. MD Gene-Region Network Graph Generation, Analysis, and Community Clustering
2.4. Cluster-Informed Gene Ontology Analysis
2.5. Statistical, Visualisation and Data Management Tools
3. Results
3.1. Creation and Validation of the ATLANTE Pipeline
3.2. MD-Associated Genes Are Enriched in Discrete Brain Regions
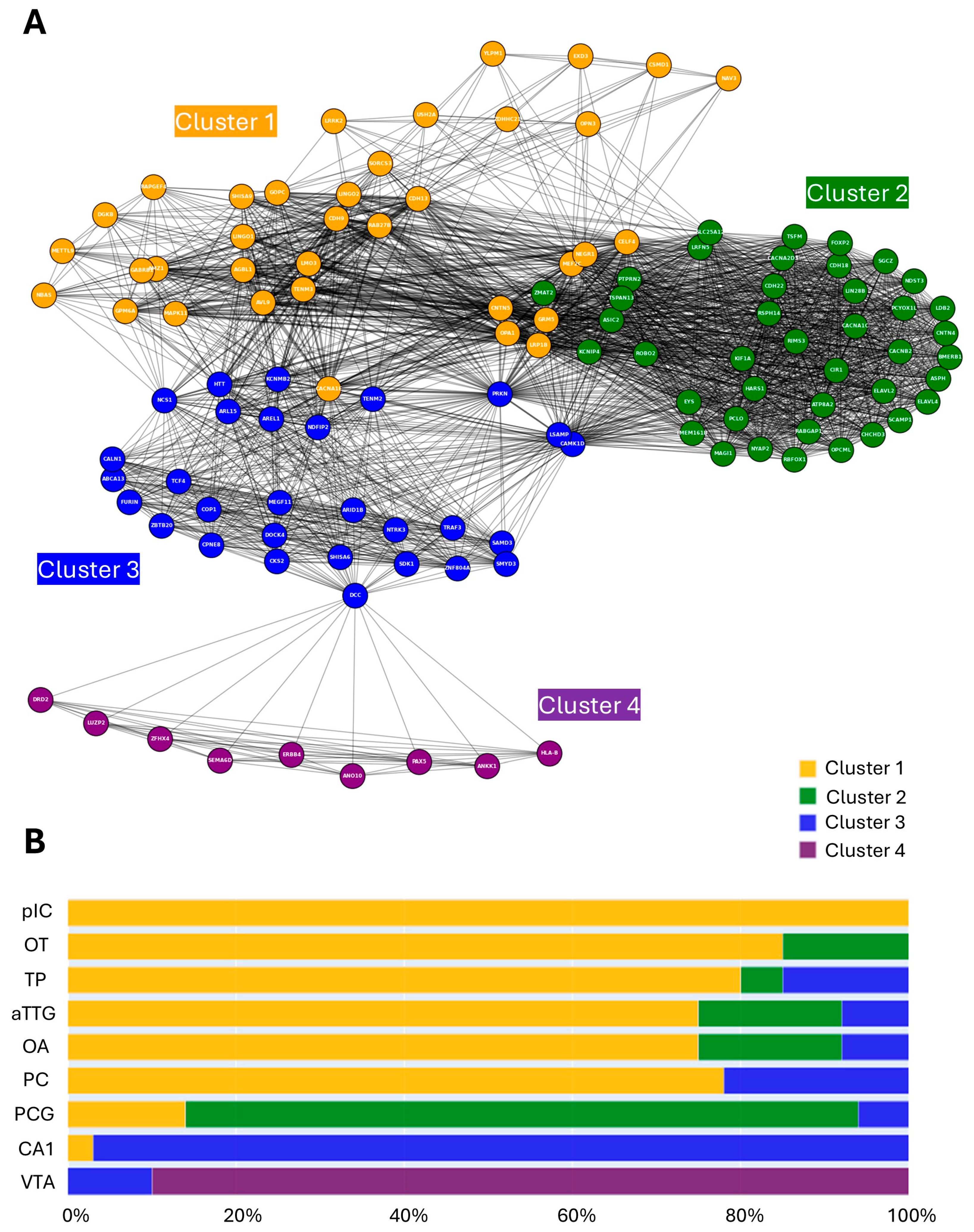
3.3. Brain Regions Exhibit Both Shared and Non-Overlapping MD-Associated Gene Architecture
3.4. Hub Genes Identified via Nodal Analysis
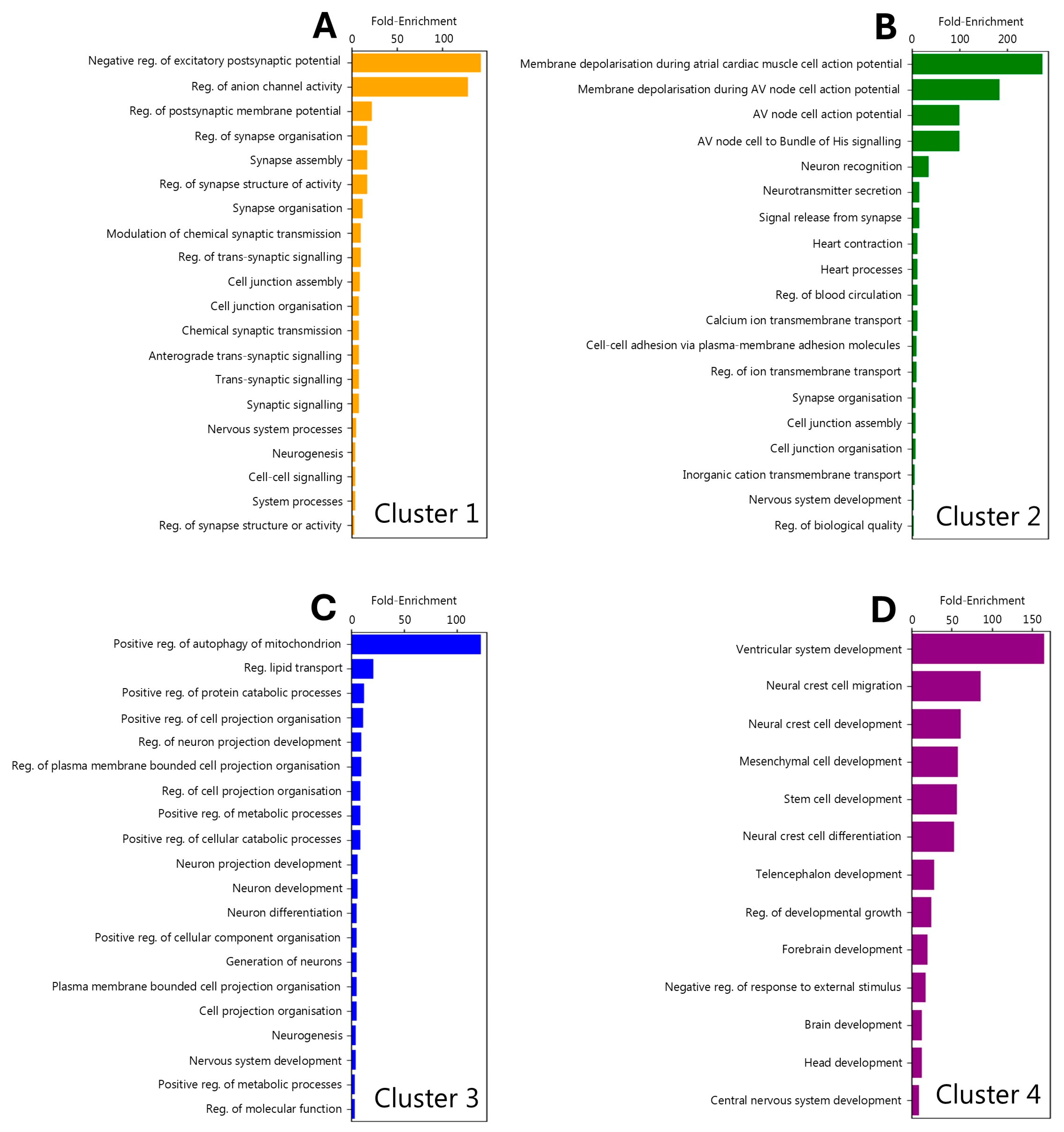
3.5. Regional Localisation of Gene Ontology Signatures
4. Discussion
4.1. Summary of Results
4.2. Major Depression Genes Associate with Dopaminergic Signalling, Olfaction, and Parkinson’s Disease
4.3. Cortical Regions Amenable to Clinical Screening and the Potential for MD Subtype Segregation
4.4. Gene Ontology-by-Cluster Indiciates the Presence of Molecularly Distinct Pathologies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| aPCL | Anterior paracentral lobule |
| aTTG | Anterior transverse temporal gyrus |
| CA1 | Cornu ammonis 1 region of the hippocampus |
| CAMK1D | Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase 1D |
| CC | Cerebellar cortex |
| CM | Centromedial thalamic nucleus |
| CNTN5 | Contactin 5 |
| DAT | Dopamine transporter |
| DCC | Deleted in colorectal cancer |
| DMH | Dorsomedial nucleus |
| DSM | Diagnostic and Statistical Manual |
| FNL | Flocculonodular lobe |
| GRM5 | Metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 |
| GWAS | Genome-wide association study |
| Hb | Habenula |
| LGN | Lateral geniculate nucleus |
| LHA | Lateral hypothalamic nucleus |
| LT | Lateral thalamic nuclei |
| MB | Mammillary body |
| MD | Medial dorsal thalamic nucleus |
| MD | Major Depression |
| MDD | Major Depressive Disorder |
| MGN | Medial geniculate body |
| MPO | Medial periolivary nucleus |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| nTPM | Normalised transcripts per million |
| OA | Olfactory area |
| OT | Olfactory tubercle |
| PCG | Postcentral gyrus |
| PD | Parkinson’s Disease |
| PG | Perirhinal gyrus |
| PHQ | Personal Health Questionnaire |
| pIC | Posterior insular cortex |
| POA | Preoptic area |
| PRKN | Parkin |
| PRT | Pretectal area |
| PUL | Pulvinar |
| PVN | Paraventricular nucleus |
| Rh | Nucleus rhomboideus |
| SDS | Self-Rating Depression Scale |
| SSD | Sub-Syndromal Depression |
| STN | Subthalamic nucleus |
| TP | Temporal pole |
| Ve | Vermis |
| VPL | Ventral posterolateral thalamic nucleus |
| VPM | Ventral posteromedial thalamic nucleus |
| VT | Ventral thalamic nuclei |
| VTA | Ventral tegmental area |
Appendix A
| Ensembl ID | Gene Symbol | Source Study | Enriched |
|---|---|---|---|
| ENSG00000179869 | ABCA13 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000139567 | ACVRL1 | [29] | NO |
| ENSG00000273540 | AGBL1 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000161618 | ALDH16A1 | [30] | NO |
| ENSG00000111275 | ALDH2 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000120697 | ALG5 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000174945 | AMZ1 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000170209 | ANKK1 | [22] | YES |
| ENSG00000160746 | ANO10 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000120318 | ARAP3 | [30] | NO |
| ENSG00000119682 | AREL1 | [22,29] | YES |
| ENSG00000075884 | ARHGAP15 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000049618 | ARID1B | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000185305 | ARL15 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000108684 | ASIC2 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000198363 | ASPH | [30] | YES |
| ENSG00000148219 | ASTN2 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000132932 | ATP8A2 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000158321 | AUTS2 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000105778 | AVL9 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000182272 | B4GALNT4 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000138688 | BLTP1 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000166780 | BMERB1 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000171634 | BPTF | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000169925 | BRD3 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000151067 | CACNA1C | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000198216 | CACNA1E | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000157445 | CACNA2D3 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000165995 | CACNB2 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000081803 | CADPS2 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000183166 | CALN1 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000183049 | CAMK1D | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000166960 | CCDC178 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000177352 | CCDC71 | [22] | NO |
| ENSG00000101017 | CD40 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000140945 | CDH13 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000145526 | CDH18 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000149654 | CDH22 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000113100 | CDH9 | [22,32] | YES |
| ENSG00000101489 | CELF4 | [22,29] | YES |
| ENSG00000106554 | CHCHD3 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000124177 | CHD6 | [22] | NO |
| ENSG00000101204 | CHRNA4 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000138433 | CIR1 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000123975 | CKS2 | [30,32] | YES |
| ENSG00000080802 | CNOT4 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000144619 | CNTN4 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000149972 | CNTN5 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000155052 | CNTNAP5 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000143207 | COP1 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000139117 | CPNE8 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000124207 | CSE1L | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000183117 | CSMD1 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000183230 | CTNNA3 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000198561 | CTNND1 | [22] | NO |
| ENSG00000077063 | CTTNBP2 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000172817 | CYP7B1 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000139990 | DCAF5 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000187323 | DCC | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000136267 | DGKB | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000102780 | DGKH | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000150672 | DLG2 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000119689 | DLST | [22,32] | NO |
| ENSG00000105877 | DNAH11 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000128590 | DNAJB9 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000128512 | DOCK4 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000149295 | DRD2 | [22] | YES |
| ENSG00000107105 | ELAVL2 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000162374 | ELAVL4 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000164035 | EMCN | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000183798 | EMILIN3 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000100393 | EP300 | [22] | NO |
| ENSG00000178568 | ERBB4 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000091831 | ESR1 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000196482 | ESRRG | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000006468 | ETV1 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000139083 | ETV6 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000187609 | EXD3 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000188107 | EYS | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000149485 | FADS1 | [29,32] | NO |
| ENSG00000134824 | FADS2 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000113391 | FAM172A | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000115392 | FANCL | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000145982 | FARS2 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000134452 | FBH1 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000119616 | FCF1 | [29] | NO |
| ENSG00000114861 | FOXP1 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000285708 | FOXP2 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000128573 | FRAT2 | [22] | NO |
| ENSG00000181274 | FTO | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000140718 | FURIN | [30,32] | YES |
| ENSG00000140564 | FUT11 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000196968 | GABRB1 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000163288 | GALNT13 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000144278 | GIGYF2 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000204120 | GNAO1 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000087258 | GOLGA1 | [22] | NO |
| ENSG00000136935 | GOPC | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000047932 | GPC5 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000179399 | GPC6 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000183098 | GPM6A | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000150625 | GPR27 | [30] | NO |
| ENSG00000170837 | GPX1 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000233276 | GRM5 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000168959 | GRM8 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000179603 | GTF2IRD1 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000006704 | HARS1 | [22] | YES |
| ENSG00000170445 | HARS2 | [22] | NO |
| ENSG00000112855 | HLA-B | [22] | YES |
| ENSG00000234745 | HOGA1 | [30] | NO |
| ENSG00000241935 | HTT | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000197386 | IRF4 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000137265 | KCNIP4 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000185774 | KCNMB2 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000197584 | KDELR2 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000275163 | KIF1A | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000136240 | KIRREL3 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000130294 | KLC1 | [22,30,32] | NO |
| ENSG00000149571 | KLHDC8B | [29] | NO |
| ENSG00000126214 | LAMB2 | [29] | NO |
| ENSG00000185909 | LDB2 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000172037 | LIN28B | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000169744 | LINGO1 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000187772 | LINGO2 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000169783 | LMO3 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000174482 | LRFN5 | [22] | YES |
| ENSG00000048540 | LRMDA | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000165379 | LRP1B | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000148655 | LRRK2 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000168702 | LSAMP | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000188906 | LUZP2 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000185565 | MACROD2 | [30] | NO |
| ENSG00000187398 | MAD1L1 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000172264 | MAGI1 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000002822 | MAML3 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000151276 | MAPK11 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000196782 | MARCHF1 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000185386 | MARK3 | [22] | NO |
| ENSG00000145416 | MEF2C | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000075413 | MEGF11 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000081189 | METTL16 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000157890 | METTL9 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000127804 | MGST1 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000197006 | MKRN1 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000008394 | MLEC | [22] | NO |
| ENSG00000133606 | MPHOSPH9 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000110917 | MT1X | [30] | NO |
| ENSG00000051825 | MYBPC3 | [22] | NO |
| ENSG00000187193 | MYT1 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000134571 | NAA11 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000196132 | NAV1 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000156269 | NAV3 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000134369 | NBAS | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000067798 | NCS1 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000151779 | NDFIP2 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000107130 | NDST3 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000102471 | NDUFAF3 | [22] | NO |
| ENSG00000164100 | NEGR1 | [22,30] | YES |
| ENSG00000178057 | NFIA | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000172260 | NKAIN2 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000162599 | NOS1 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000188580 | NPAS3 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000089250 | NPM1 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000151322 | NRDC | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000181163 | NRXN1 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000078618 | NTM | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000179915 | NTRK3 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000182667 | NXPH1 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000140538 | NYAP2 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000122584 | OPA1 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000144460 | OPCML | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000198836 | OPN3 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000183715 | OSBP2 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000054277 | PACRG | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000203668 | PAX5 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000184792 | PBRM1 | [22] | NO |
| ENSG00000112530 | PCDH9 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000196092 | PCDHA1 | [22] | NO |
| ENSG00000163939 | PCDHA2 | [22] | NO |
| ENSG00000184226 | PCDHA3 | [22] | NO |
| ENSG00000204970 | PCLO | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000204969 | PCYOX1L | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000255408 | PDE4B | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000186472 | PFDN1 | [22] | NO |
| ENSG00000145882 | PLCL2 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000184588 | PMFBP1 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000113068 | PPP3CC | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000154822 | PRKN | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000118557 | PRMT6 | [30] | NO |
| ENSG00000120910 | PSEN2 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000185345 | PTCH1 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000198890 | PTPRD | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000143801 | PTPRG | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000288674 | PTPRN2 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000185920 | RAB27B | [22,32] | YES |
| ENSG00000153707 | RABGAP1 | [22,32] | YES |
| ENSG00000144724 | RANGAP1 | [22] | NO |
| ENSG00000155093 | RAPGEF4 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000041353 | RBFOX1 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000011454 | RERE | [22,32] | NO |
| ENSG00000188394 | RFTN2 | [22] | NO |
| ENSG00000100401 | RIMS3 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000091428 | ROBO2 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000078328 | RSPH14 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000142599 | RSRC1 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000162944 | SAMD3 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000117016 | SAMD5 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000185008 | SCAMP1 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000100218 | SDK1 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000174891 | SEMA6D | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000164483 | SETBP1 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000203727 | SFMBT2 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000085365 | SGCD | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000146555 | SGCZ | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000137872 | SHANK2 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000152217 | SHISA6 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000198879 | SHISA9 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000170624 | SLC25A12 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000185053 | SLC39A13 | [22] | NO |
| ENSG00000162105 | SLC4A9 | [22] | NO |
| ENSG00000188803 | SLC7A5 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000237515 | SMYD3 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000115840 | SNX29 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000165915 | SORCS3 | [22,29,32] | YES |
| ENSG00000113073 | SOX5 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000103257 | SOX6 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000185420 | SP4 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000048471 | SPPL3 | [22,29,32] | NO |
| ENSG00000156395 | ST8SIA1 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000134532 | STK24 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000110693 | SUFU | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000105866 | TANK | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000157837 | TBCA | [22] | NO |
| ENSG00000111728 | TCF4 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000102572 | TENM2 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000107882 | TENM3 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000136560 | THAP5 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000171530 | THRA | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000196628 | THSD7B | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000145934 | TMEM106B | [22,32] | NO |
| ENSG00000218336 | TMEM161B | [22] | YES |
| ENSG00000177683 | TMEM258 | [29] | NO |
| ENSG00000126351 | TRAF3 | [29] | YES |
| ENSG00000144229 | TSFM | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000106460 | TSPAN13 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000164180 | UBE3B | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000134825 | USH2A | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000131323 | XRCC3 | [22] | NO |
| ENSG00000123297 | YLPM1 | [29] | YES |
| ENSG00000106537 | ZBTB20 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000151148 | ZC3H7B | [22] | NO |
| ENSG00000042781 | ZCCHC2 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000126215 | ZDHHC21 | [22] | YES |
| ENSG00000119596 | ZDHHC5 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000181722 | ZFHX3 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000100403 | ZFHX4 | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000141664 | ZFYVE21 | [22] | NO |
| ENSG00000175893 | ZHX3 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000156599 | ZMAT2 | [22] | YES |
| ENSG00000140836 | ZMIZ1 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000091656 | ZMYM4 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000100711 | ZMYND8 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000174306 | ZNF197 | [22] | NO |
| ENSG00000146007 | ZNF423 | [32] | NO |
| ENSG00000108175 | ZNF445 | [22,32] | NO |
| ENSG00000146463 | ZNF638 | [22] | NO |
| ENSG00000101040 | ZNF804A | [32] | YES |
| ENSG00000186448 | ZNHIT1 | [30] | NO |
References
- APA. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Rush, A.J.; Carmody, T.J.; Ibrahim, H.M.; Trivedi, M.H.; Biggs, M.M.; Shores-Wilson, K.; Crismon, M.L.; Toprac, M.G.; Kashner, T.M. Comparison of self-report and clinician ratings on two inventories of depressive symptomatology. Psychiatr. Serv. 2006, 57, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrman, H.; Kieling, C.; McGorry, P.; Horton, R.; Sargent, J.; Patel, V. Reducing the global burden of depression: A Lancet-World Psychiatric Association Commission. Lancet 2019, 393, e42–e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hare, D.L.; Toukhsati, S.R.; Johansson, P.; Jaarsma, T. Depression and cardiovascular disease: A clinical review. Eur. Heart J. 2013, 35, 1365–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartorius, N. Depression and diabetes. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 20, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deschênes, S.S.; Burns, R.J.; Schmitz, N. Associations between depression, chronic physical health conditions, and disability in a community sample: A focus on the persistence of depression. J. Affect. Disord. 2015, 179, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baune, B.T.; Miller, R.; McAfoose, J.; Johnson, M.; Quirk, F.; Mitchell, D. The role of cognitive impairment in general functioning in major depression. Psychiatry Res. 2010, 176, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschfeld, R.M.; Montgomery, S.A.; Keller, M.B.; Kasper, S.; Schatzberg, A.F.; Möller, H.J.; Healy, D.; Baldwin, D.; Humble, M.; Versiani, M.; et al. Social functioning in depression: A review. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2000, 61, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunnarsson, A.B.; Hedberg, A.K.; Håkansson, C.; Hedin, K.; Wagman, P. Occupational performance problems in people with depression and anxiety. Scand. J. Occup. Ther. 2023, 30, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, L. Quality of life in depression and anxiety. Int. Rev. Psychiatry 2002, 14, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohls, J.K.; König, H.H.; Quirke, E.; Hajek, A. Anxiety, Depression and Quality of Life-A Systematic Review of Evidence from Longitudinal Observational Studies. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organisation. Depressive Disorder (Depression). Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/depression (accessed on 10 May 2025).
- Beck, A.; Ward, C.; Mendelson, M.; Mock, J.; Erbaugh, J. An inventory for measuring depression. Arch. General. Psychiatry 1961, 4, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroenke, K.; Spitzer, R.; Williams, J. The PHQ-9: Validity of a brief depression severity measure. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2001, 16, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zung, W. From art to science: The diagnosis and treatment of depression. Arch. General. Psychiatry 1973, 29, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judd, L.; Paulus, M.; Wells, K.; Rapaport, M. Socioeconomic burden of subsyndromal depressive symptoms and major depression in a sample of the general population. Am. J. Psychiatry 1996, 163, 1411–1417. [Google Scholar]
- Lyness, J.; Kim, J.; Tang, W.; Tu, X.; Conwell, Y.; King, D.; Caine, E. The clinical significance of subsyndromal depression in older primary care patients. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2007, 15, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendler, K.S.; Ohlsson, H.; Lichtenstein, P.; Sundquist, J.; Sundquist, K. The Genetic Epidemiology of Treated Major Depression in Sweden. Am. J. Psychiatry 2018, 175, 1137–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, P.F.; Neale, M.C.; Kendler, K.S. Genetic epidemiology of major depression: Review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Psychiatry 2000, 157, 1552–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kendall, K.M.; Van Assche, E.; Andlauer, T.F.M.; Choi, K.W.; Luykx, J.J.; Schulte, E.C.; Lu, Y. The genetic basis of major depression. Psychol. Med. 2021, 51, 2217–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripke, S.; Wray, N.R.; Lewis, C.M.; Hamilton, S.P.; Weissman, M.M.; Breen, G.; Byrne, E.M.; Blackwood, D.H.; Boomsma, D.I.; Cichon, S.; et al. A mega-analysis of genome-wide association studies for major depressive disorder. Mol. Psychiatry 2013, 18, 497–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Navoly, G.; Giannakopoulou, O.; Levey, D.F.; Koller, D.; Pathak, G.A.; Koen, N.; Lin, K.; Adams, M.J.; Rentería, M.E.; et al. Multi-ancestry genome-wide association study of major depression aids locus discovery, fine mapping, gene prioritization and causal inference. Nat. Genet. 2024, 56, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wray, N.R.; Ripke, S.; Mattheisen, M.; Trzaskowski, M.; Byrne, E.M.; Abdellaoui, A.; Adams, M.J.; Agerbo, E.; Air, T.M.; Andlauer, T.M.F.; et al. Genome-wide association analyses identify 44 risk variants and refine the genetic architecture of major depression. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 668–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyde, C.L.; Nagle, M.W.; Tian, C.; Chen, X.; Paciga, S.A.; Wendland, J.R.; Tung, J.Y.; Hinds, D.A.; Perlis, R.H.; Winslow, A.R. Identification of 15 genetic loci associated with risk of major depression in individuals of European descent. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1031–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, D.M.; Adams, M.J.; Shirali, M.; Clarke, T.-K.; Marioni, R.E.; Davies, G.; Coleman, J.R.I.; Alloza, C.; Shen, X.; Barbu, M.C.; et al. Genome-wide association study of depression phenotypes in UK Biobank identifies variants in excitatory synaptic pathways. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, D.M.; Adams, M.J.; Clarke, T.K.; Hafferty, J.D.; Gibson, J.; Shirali, M.; Coleman, J.R.I.; Hagenaars, S.P.; Ward, J.; Wigmore, E.M.; et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis of depression identifies 102 independent variants and highlights the importance of the prefrontal brain regions. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, B.L.; Campos, A.I.; Whiteman, D.C.; Olsen, C.M.; Gordon, S.D.; Walker, A.J.; Dean, O.M.; Berk, M.; Hickie, I.B.; Medland, S.E.; et al. The Australian Genetics of Depression Study: New Risk Loci and Dissecting Heterogeneity Between Subtypes. Biol. Psychiatry 2022, 92, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, N.; Bigdeli, T.B.; Kretzschmar, W.; Li, Y.; Liang, J.; Song, L.; Hu, J.; Li, Q.; Jin, W.; Hu, Z.; et al. Sparse whole-genome sequencing identifies two loci for major depressive disorder. Nature 2015, 523, 588–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, D.F.; Stein, M.B.; Wendt, F.R.; Pathak, G.A.; Zhou, H.; Aslan, M.; Quaden, R.; Harrington, K.M.; Nuñez, Y.Z.; Overstreet, C.; et al. Bi-ancestral depression GWAS in the Million Veteran Program and meta-analysis in >1.2 million individuals highlight new therapeutic directions. Nat. Neurosci. 2021, 24, 954–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Als, T.D.; Kurki, M.I.; Grove, J.; Voloudakis, G.; Therrien, K.; Tasanko, E.; Nielsen, T.T.; Naamanka, J.; Veerapen, K.; Levey, D.F.; et al. Depression pathophysiology, risk prediction of recurrence and comorbid psychiatric disorders using genome-wide analyses. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 1832–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APA. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th ed.; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, M.J.; Streit, F.; Meng, X.; Awasthi, S.; Adey, B.N.; Choi, K.W.; Chundru, V.K.; Coleman, J.R.I.; Ferwerda, B.; Foo, J.C.; et al. Trans-ancestry genome-wide study of depression identifies 697 associations implicating cell types and pharmacotherapies. Cell 2025, 188, 640–652.e649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hormozdiari, F.; van de Bunt, M.; Segrè, A.V.; Li, X.; Joo, J.W.J.; Bilow, M.; Sul, J.H.; Sankararaman, S.; Pasaniuc, B.; Eskin, E. Colocalization of GWAS and eQTL Signals Detects Target Genes. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 99, 1245–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Candille, S.I.; Choi, Y.; Xie, D.; Jiang, L.; Li-Pook-Than, J.; Tang, H.; Snyder, M. Variation and genetic control of protein abundance in humans. Nature 2013, 499, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sey, N.Y.A.; Hu, B.; Mah, W.; Fauni, H.; McAfee, J.C.; Rajarajan, P.; Brennand, K.J.; Akbarian, S.; Won, H. A computational tool (H-MAGMA) for improved prediction of brain-disorder risk genes by incorporating brain chromatin interaction profiles. Nat. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, L.; Zhou, H.; Xu, X.; Zuo, Z. Brain structural and functional changes in patients with major depressive disorder: A literature review. PeerJ 2019, 7, e8170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.F.; Peng, W.; Sweeney, J.A.; Jia, Z.Y.; Gong, Q.Y. Brain structure alterations in depression: Psychoradiological evidence. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2018, 24, 994–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Macleod, I.; Su, A.I. BioGPS and MyGene.info: Organizing online, gene-centric information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D561–D565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, A.I.; Cooke, M.P.; Ching, K.A.; Hakak, Y.; Walker, J.R.; Wiltshire, T.; Orth, A.P.; Vega, R.G.; Sapinoso, L.M.; Moqrich, A.; et al. Large-scale analysis of the human and mouse transcriptomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 4465–4470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, A.I.; Wiltshire, T.; Batalov, S.; Lapp, H.; Ching, K.A.; Block, D.; Zhang, J.; Soden, R.; Hayakawa, M.; Kreiman, G.; et al. A gene atlas of the mouse and human protein-encoding transcriptomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 6062–6067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.; Tammimies, K.; Pellecchia, G.; Alipanahi, B.; Hu, P.; Wang, Z.; Pinto, D.; Lau, L.; Nalpathamkalam, T.; Marshall, C.R.; et al. Brain-expressed exons under purifying selection are enriched for de novo mutations in autism spectrum disorder. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 742–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richiardi, J.; Altmann, A.; Milazzo, A.C.; Chang, C.; Chakravarty, M.M.; Banaschewski, T.; Barker, G.J.; Bokde, A.L.; Bromberg, U.; Büchel, C.; et al. BRAIN NETWORKS. Correlated gene expression supports synchronous activity in brain networks. Science 2015, 348, 1241–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlén, M.; Fagerberg, L.; Hallström, B.M.; Lindskog, C.; Oksvold, P.; Mardinoglu, A.; Sivertsson, Å.; Kampf, C.; Sjöstedt, E.; Asplund, A.; et al. Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science 2015, 347, 1260419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondel, V.D.; Guillaume, J.-L.; Lambiotte, R.; Lefebvre, E. Fast unfolding of communities in large networks. J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2008, 2008, P10008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.X.; Jung, D.; Yao, R. ShinyGO: A graphical gene-set enrichment tool for animals and plants. Bioinformatics 2019, 36, 2628–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kluyver, T.; Ragan-Kelley, B.; Perez, F.; Granger, B.; Bussonnier, M.; Frederic, J.; Kelley, K.; Hamrick, J.; Grout, J.; Corlay, S.; et al. Jupyter Notebooks—A Publishing Format for Reproducible Computational Workflows; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- McKinney, W. Data Structures for Statistical Computing in Python. In Proceedings of the 9th Python in Science Conference, Austin, TX, USA, 28 June–3 July 2010; pp. 56–61. [Google Scholar]
- Hunter, J.D. Matplotlib: A 2D Graphics Environment. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2007, 9, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagberg, A.; Swart, P.J.; Schult, D.A. Exploring Network Structure, Dynamics, and Function Using NetworkX; Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL): Los Alamos, NM, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Serretti, A. Anhedonia: Current and future treatments. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. Rep. 2025, 4, e70088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Haenen, H.A.; Bossuyt, A. Dopamine D2 receptors in depression measured with single photon emission computed tomography. Biol. Psychiatry 1994, 35, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pare, C.M.B.; Yeung, D.P.H.; Price, K.; Stacey, R.S. 5-Hydroxytryptamine, noradrenaline, and dopamine in brainstem, hypothalamus, and caudate nucleus of controls and of patients committing suicide by coal-gas poisoning. Lancet 1969, 294, 133–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarchiapone, M.; Carli, V.; Camardese, G.; Cuomo, C.; Di Giuda, D.; Calcagni, M.L.; Focacci, C.; De Risio, S. Dopamine transporter binding in depressed patients with anhedonia. Psychiatry Res. 2006, 147, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, L.S.; Mehta, M.; Ahn, C.; Corniquel, M.; Verma, G.; Delman, B.; Hof, P.R.; Jacob, Y.; Balchandani, P.; Murrough, J.W. Ventral tegmental area integrity measured with high-resolution 7-Tesla MRI relates to motivation across depression and anxiety diagnoses. Neuroimage 2022, 264, 119704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayegh, F.J.P.; Mouledous, L.; Macri, C.; Pi Macedo, J.; Lejards, C.; Rampon, C.; Verret, L.; Dahan, L. Ventral tegmental area dopamine projections to the hippocampus trigger long-term potentiation and contextual learning. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikemoto, S. Dopamine reward circuitry: Two projection systems from the ventral midbrain to the nucleus accumbens-olfactory tubercle complex. Brain Res. Rev. 2007, 56, 27–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haber, S.N.; Knutson, B. The Reward Circuit: Linking Primate Anatomy and Human Imaging. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010, 35, 4–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taalman, H.; Wallace, C.; Milev, R. Olfactory Functioning and Depression: A Systematic Review. Front. Psychiatry 2017, 8, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atanasova, B.; El-Hage, W.; Chabanet, C.; Gaillard, P.; Belzung, C.; Camus, V. Olfactory anhedonia and negative olfactory alliesthesia in depressed patients. Psychiatry Res. 2010, 176, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohli, P.; Soler, Z.M.; Nguyen, S.A.; Muus, J.S.; Schlosser, R.J. The Association Between Olfaction and Depression: A Systematic Review. Chem. Senses 2016, 41, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliyan, Y.; Wroblewski, K.E.; McClintock, M.K.; Pinto, J.M. Olfactory Dysfunction Predicts the Development of Depression in Older US Adults. Chem. Senses 2021, 46, bjaa075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haehner, A.; Masala, C.; Walter, S.; Reichmann, H.; Hummel, T. Incidence of Parkinson’s disease in a large patient cohort with idiopathic smell and taste loss. J. Neurol. 2019, 266, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jennings, D.; Siderowf, A.; Stern, M.; Seibyl, J.; Eberly, S.; Oakes, D.; Marek, K.; for the PARS Investigators. Conversion to Parkinson Disease in the PARS Hyposmic and Dopamine Transporter–Deficit Prodromal Cohort. JAMA Neurol. 2017, 74, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doty, R.L.; Deems, D.A.; Stellar, S. Olfactory dysfunction in parkinsonism: A general deficit unrelated to neurologic signs, disease stage, or disease duration. Neurology 1988, 38, 1237–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fullard, M.E.; Morley, J.F.; Duda, J.E. Olfactory Dysfunction as an Early Biomarker in Parkinson’s Disease. Neurosci. Bull. 2017, 33, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponsen, M.M.; Stoffers, D.; Booij, J.; van Eck-Smit, B.L.; Wolters, E.; Berendse, H.W. Idiopathic hyposmia as a preclinical sign of Parkinson’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 2004, 56, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reijnders, J.S.A.M.; Ehrt, U.; Weber, W.E.J.; Aarsland, D.; Leentjens, A.F.G. A systematic review of prevalence studies of depression in Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2008, 23, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, H.; Nordström, A.; Nordström, P. Depression and subsequent risk of Parkinson disease. Neurology 2015, 84, 2422–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, C.; Westenberger, A. Genetics of Parkinson’s disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a008888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Tang, M.X.; Mejia-Santana, H.; Rosado, L.; Louis, E.D.; Caccappolo, E.; Comella, C.; Colcher, A.; Siderowf, A.; Jennings, D.; et al. The relation between depression and parkin genotype: The CORE-PD study. Park. Relat. Disord. 2011, 17, 740–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belujon, P.; Grace, A.A. Dopamine System Dysregulation in Major Depressive Disorders. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017, 20, 1036–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.D.; Yi, L.X.; Wang, D.Q.; Lim, T.M.; Tan, E.K. Role of dopamine in the pathophysiology of Parkinson’s disease. Transl. Neurodegener. 2023, 12, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slavich, G.M.; Irwin, M.R. From stress to inflammation and major depressive disorder: A social signal transduction theory of depression. Psychol. Bull. 2014, 140, 774–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlajinac, H.; Sipetic, S.; Marinkovic, J.; Ratkov, I.; Maksimovic, J.; Dzoljic, E.; Kostic, V. The Stressful Life Events and Parkinson’s Disease: A Case–Control Study. Stress Health 2013, 29, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiguro, M.; Baba, H.; Maeshima, H.; Shimano, T.; Inoue, M.; Ichikawa, T.; Yasuda, S.; Shukuzawa, H.; Suzuki, T.; Arai, H. Increased Serum Levels of α-Synuclein in Patients With Major Depressive Disorder. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2019, 27, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubelzu, M.; Morera-Herreras, T.; Irastorza, G.; Gómez-Esteban, J.C.; Murueta-Goyena, A. Plasma and serum alpha-synuclein as a biomarker in Parkinson’s disease: A meta-analysis. Park. Relat. Disord. 2022, 99, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciubuc-Batcu, M.T.; Stapelberg, N.J.C.; Headrick, J.P.; Renshaw, G.M.C. A mitochondrial nexus in major depressive disorder: Integration with the psycho-immune-neuroendocrine network. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Mol. Basis Dis. 2024, 1870, 166920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henrich, M.T.; Oertel, W.H.; Surmeier, D.J.; Geibl, F.F. Mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease—A key disease hallmark with therapeutic potential. Mol. Neurodegener. 2023, 18, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Li, J.; Wang, J. Altered neural activities during emotion regulation in depression: A meta-analysis. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2024, 49, E334–E344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Zhang, H. Functional connectivity density of postcentral gyrus predicts rumination and major depressive disorders in males. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2025, 347, 111939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Peng, W.; Sun, H.; Kuang, W.; Li, W.; Jia, Z.; Gong, Q. High-field magnetic resonance imaging of structural alterations in first-episode, drug-naive patients with major depressive disorder. Transl. Psychiatry 2016, 6, e942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnellbächer, G.J.; Rajkumar, R.; Veselinović, T.; Ramkiran, S.; Hagen, J.; Shah, N.J.; Neuner, I. Structural alterations of the insula in depression patients—A 7-Tesla-MRI study. Neuroimage Clin. 2022, 36, 103249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Fan, D.; Liu, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, C. Insula network connectivity mediates the association between childhood maltreatment and depressive symptoms in major depressive disorder patients. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, I.D.; Sharpley, C.F.; Bitsika, V.; Vessey, K.A.; Jesulola, E.; Agnew, L.L. Functional Network Connectivity for Components of Depression-Related Psychological Fragility. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; She, S.; Qiu, Y.; Li, Z.; Wu, X.; Hu, H.; Zheng, W.; Huang, R.; Wu, H. Multi-modal MRI measures reveal sensory abnormalities in major depressive disorder patients: A surface-based study. NeuroImage Clin. 2023, 39, 103468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Sasabayashi, D.; Yücel, M.; Whittle, S.; Lorenzetti, V.; Walterfang, M.; Suzuki, M.; Pantelis, C.; Malhi, G.S.; Allen, N.B. Different Frequency of Heschl’s Gyrus Duplication Patterns in Neuropsychiatric Disorders: An MRI Study in Bipolar and Major Depressive Disorders. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 917270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrier, C.; Wong, P.; Penhune, V.; Zatorre, R.; Parrish, T.; Abrams, D.; Kraus, N. Relating structure to function: Heschl’s gyrus and acoustic processing. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalighinejad, B.; Patel, P.; Herrero, J.L.; Bickel, S.; Mehta, A.D.; Mesgarani, N. Functional characterization of human Heschl’s gyrus in response to natural speech. Neuroimage 2021, 235, 118003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turker, S.; Reiterer, S.M.; Seither-Preisler, A.; Schneider, P. “When Music Speaks”: Auditory Cortex Morphology as a Neuroanatomical Marker of Language Aptitude and Musicality. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurlburt, R.T.; Alderson-Day, B.; Kühn, S.; Fernyhough, C. Exploring the Ecological Validity of Thinking on Demand: Neural Correlates of Elicited vs. Spontaneously Occurring Inner Speech. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.L.; Shi, X.N.; Zhao, J.L.; Jia, Q.; Xu, W.; Dun, W.W.; Zhao, Y.Y. Negative rumination in depression subtypes with melancholic features and anxious distress. Front. Psychol. 2025, 16, 1515500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, R.J. EEG measures of cerebral asymmetry: Conceptual and methodological issues. Int. J. Neurosci. 1988, 39, 71–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, J.; Davidson, R. Left Frontal Hypoactivation in Depression. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 1991, 100, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesulola, E.; Sharpley, C.; Bitsika, V.; Agnew, L.; Wilson, P. Frontal Alpha Asymmetry as a pathway to behavioural withdrawal in depression: Research findings and issues. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 292, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpley, C.; Bitsika, V. Joining the dots: Neurobiological links in a Functional analysis of depression. Behav. Brain Funct. 2010, 6, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferster, C.B. A Functional Analysis of Depression. Am. Psychol. 1973, 28, 857–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zug, R. Developmental disorders caused by haploinsufficiency of transcriptional regulators: A perspective based on cell fate determination. Biol. Open 2022, 11, bio058896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagenauer, M.H.; Sannah, Y.; Hebda-Bauer, E.K.; Rhoads, C.; O’Connor, A.M.; Flandreau, E.; Watson, S.J., Jr.; Akil, H. Resource: A curated database of brain-related functional gene sets (Brain.GMT). MethodsX 2024, 13, 102788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Odierna, G.L.; Sharpley, C.F.; Bitsika, V.; Evans, I.D.; Vessey, K.A. Novel Gene-Informed Regional Brain Targets for Clinical Screening for Major Depression. Neurol. Int. 2025, 17, 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint17060096
Odierna GL, Sharpley CF, Bitsika V, Evans ID, Vessey KA. Novel Gene-Informed Regional Brain Targets for Clinical Screening for Major Depression. Neurology International. 2025; 17(6):96. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint17060096
Chicago/Turabian StyleOdierna, G. Lorenzo, Christopher F. Sharpley, Vicki Bitsika, Ian D. Evans, and Kirstan A. Vessey. 2025. "Novel Gene-Informed Regional Brain Targets for Clinical Screening for Major Depression" Neurology International 17, no. 6: 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint17060096
APA StyleOdierna, G. L., Sharpley, C. F., Bitsika, V., Evans, I. D., & Vessey, K. A. (2025). Novel Gene-Informed Regional Brain Targets for Clinical Screening for Major Depression. Neurology International, 17(6), 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint17060096






