Idiopathic Normal-Pressure Hydrocephalus Revealed by Systemic Infection: Clinical Observations of Two Cases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Case Presentation
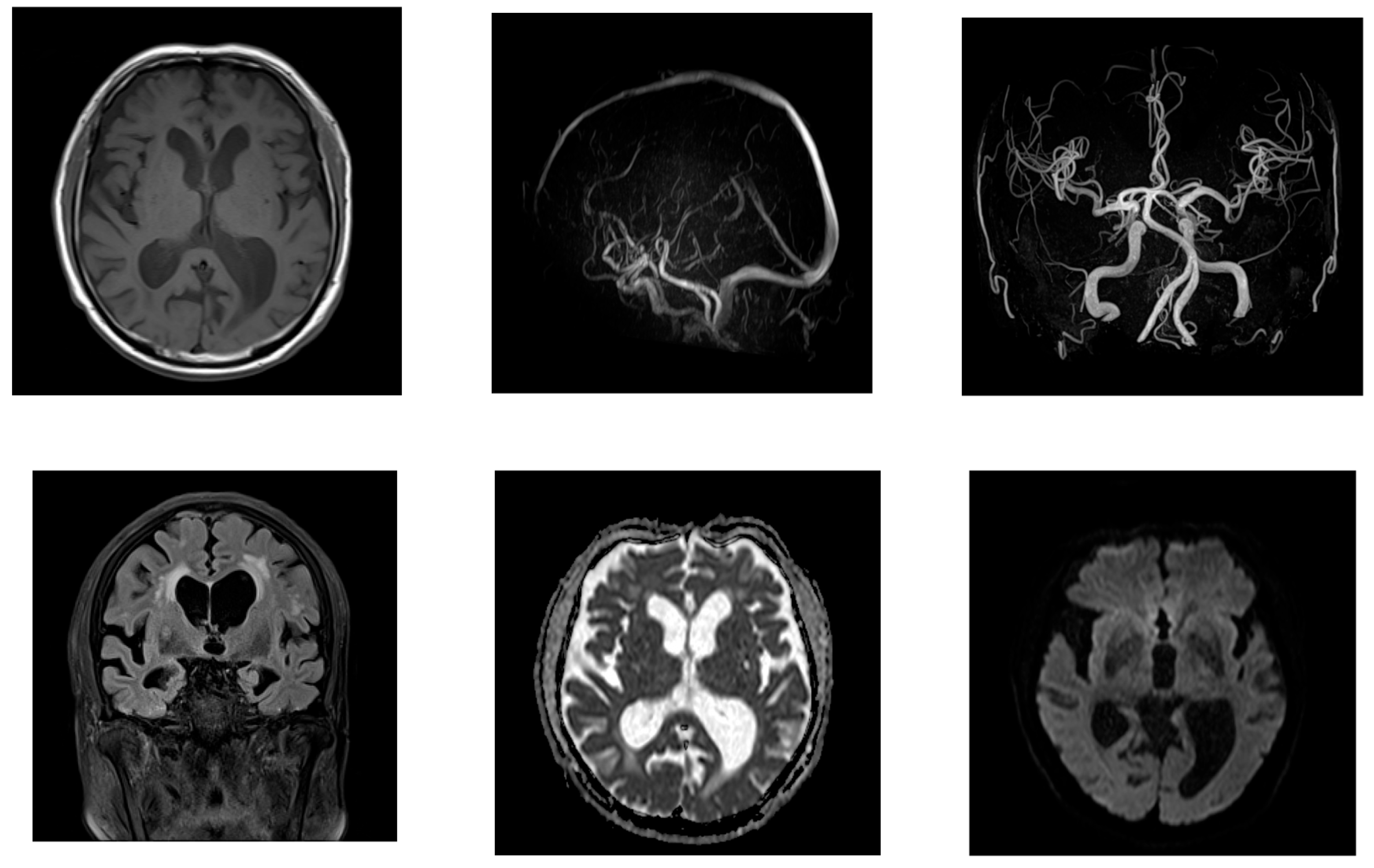
2.1. Case 1
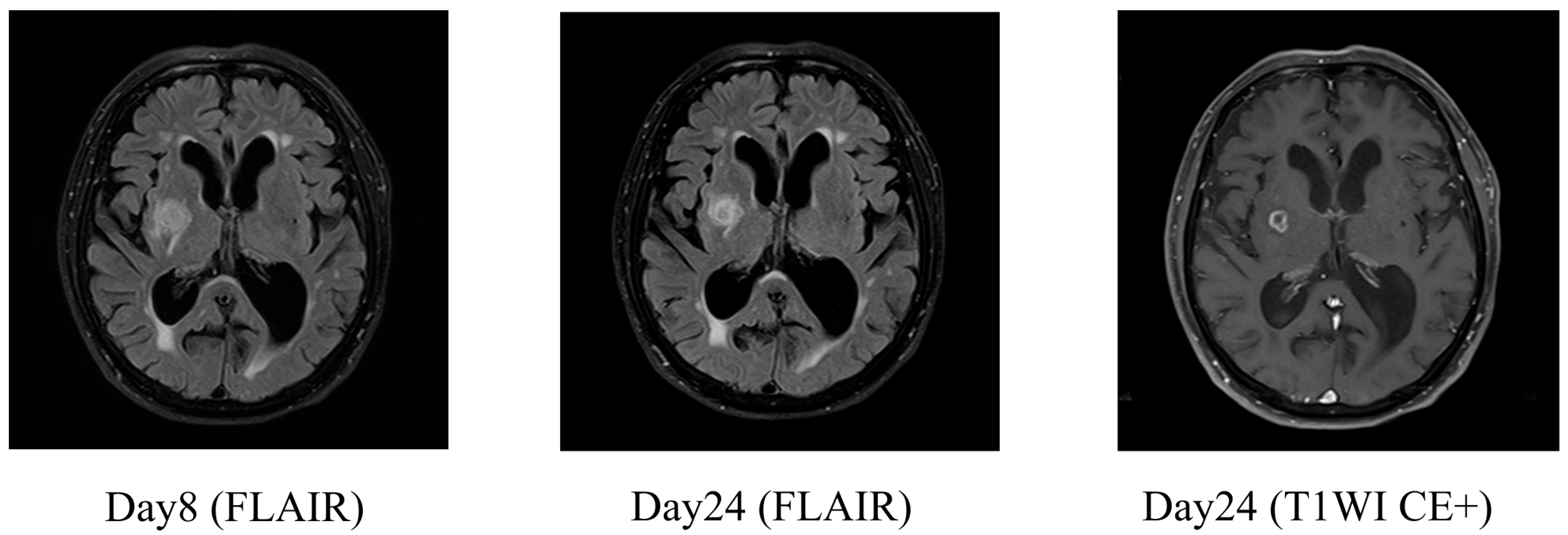
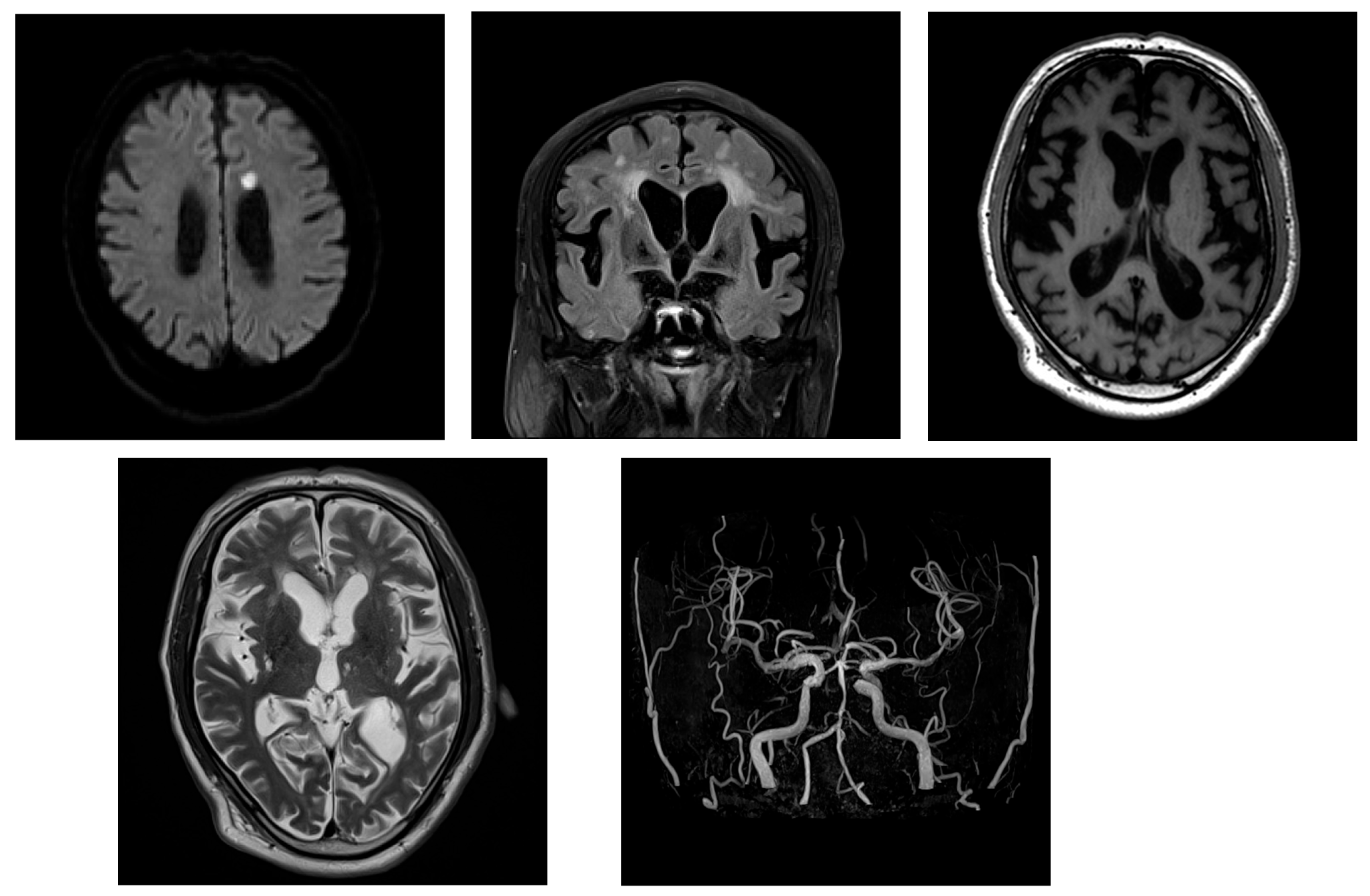
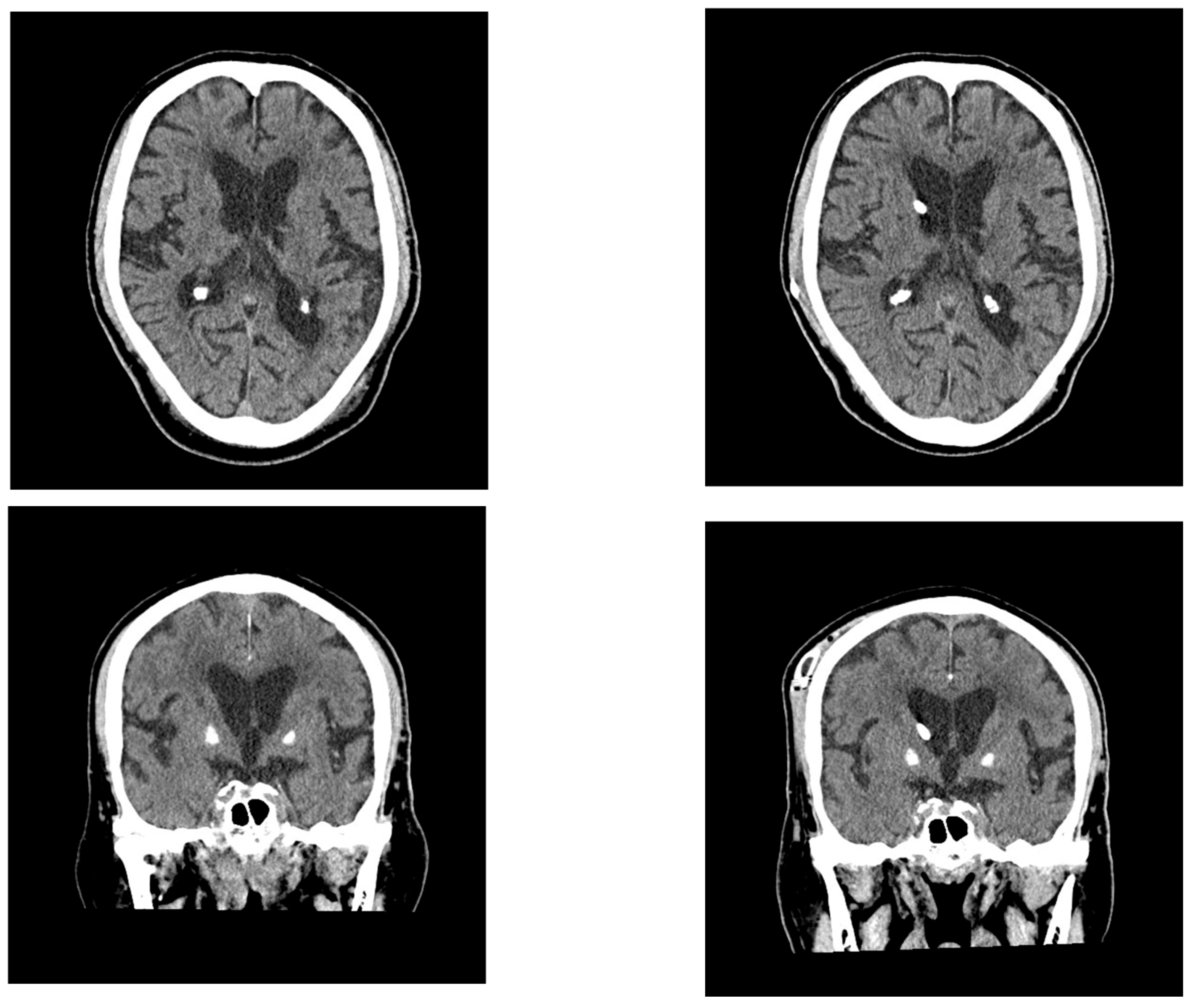
2.2. Case 2
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BBB | Blood–Brain Barrier |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal Fluid |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| DESH | Disproportionally Enlarged Subarachnoid Space Hydrocephalus |
| iNPH | Idiopathic Normal-Pressure Hydrocephalus |
| MMSE | Mini-Mental State Examination |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| SAE | Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy |
| VP | Ventriculoperitoneal |
References
- Nakajima, M.; Yamada, S.; Miyajima, M.; Ishii, K.; Kuriyama, N.; Kazui, H.; Kanemoto, H.; Suehiro, T.; Yoshiyama, K.; Kameda, M.; et al. Guidelines for Management of Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus (Third Edition): Endorsed by the Japanese Society of Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2021, 61, 63–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedergaard, M. Garbage truck of the brain. Science 2013, 340, 1529–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louveau, A.; Smirnov, I.; Keyes, T.J.; Eccles, J.D.; Rouhani, S.J.; Peske, J.D.; Derecki, N.C.; Castle, D.; Mandell, J.W.; Lee, K.S.; et al. Structural and functional features of central nervous system lymphatic vessels. Nature 2015, 523, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelhardt, B.; Vajkoczy, P.; Weller, R.O. The movers and shapers in immune privilege of the CNS. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Møllgård, K.; Beinlich, F.R.M.; Kusk, P.; Miyakoshi, L.M.; Delle, C.; Plá, V.; Hauglund, N.L.; Esmail, T.; Rasmussen, M.K.; Gomolka, R.S.; et al. A mesothelium divides the subarachnoid space into functional compartments. Science 2023, 379, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, M.; Uchino, T.; Yamada, S. Description of the latest neurofluid absorption mechanisms with reference to the linkage absorption mechanisms between extravascular fluid pathways and meningeal lymphatic vessels. Auton. Nerv. Syst. 2022, 59, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, B.C.; Karimy, J.K.; Kundishora, A.J.; Mestre, H.; Cerci, H.M.; Matouk, C.; Alper, S.L.; Lundgaard, I.; Nedergaard, M.; Kahle, K.T. Glymphatic System Impairment in Alzheimer’s Disease and Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus. Trends Mol. Med. 2020, 26, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Xiao, G. The Pathogenesis Based on the Glymphatic System, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus. Clin. Interv. Aging 2021, 16, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scollato, A.; Tenenbaum, R.; Bahl, G.; Celerini, M.; Salani, B.; Di Lorenzo, N. Changes in aqueductal CSF stroke volume and progression of symptoms in patients with unshunted idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2008, 29, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, W.A. An encephalographic ratio for estimating ventricular enlargement and cerebral atrophy. Arch. Neurol. Psychiatry 1942, 47, 931–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacobone, E.; Bailly-Salin, J.; Polito, A.; Friedman, D.; Stevens, R.D.; Sharshar, T. Sepsis-associated encephalopathy and its differential diagnosis. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 37 (Suppl. 10), S331–S336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gofton, T.E.; Young, G.B. Sepsis-associated encephalopathy. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2012, 8, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazeraud, A.; Pascal, Q.; Verdonk, F.; Heming, N. Sepsis-associated encephalopathy: A comprehensive review. Neurotherapeutics 2020, 17, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfister, D.; Siegemund, M.; Dell-Kuster, S.; Smielewski, P.; Rüegg, S.; Strebel, S.P.; Marsch, S.C.; Pargger, H.; Steiner, L.A. Cerebral perfusion in sepsis-associated delirium. Crit. Care 2008, 12, R63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Hematological Tests | ||
|---|---|---|
| WBC | 10.6 | ×109/L |
| Hb | 11.7 | g/dL |
| Plt | 96 | 109/L |
| Biochemical testing | ||
| ALB | 2.7 | g/dL |
| BUN | 51 | mg/dL |
| Cre | 1.66 | mg/dL |
| ALP | 227 | IU/L |
| AST | 59 | IU/L |
| ALT | 68 | IU/L |
| LDH | 1282 | IU/L |
| T-Bil | 0.9 | mg/dL |
| CRP | 19.19 | mg/dL |
| Glu | 234 | mg/dL |
| Na | 134 | mmol/L |
| K | 3.8 | mmol/L |
| Cl | 98 | mmol/L |
| Coagulation System Tests | ||
| D-dimar | 7.1 | μg/dL |
| Pre-Tap Test | Post-Tap Test ** | Post-Shunting | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TUG | time (s) | 44.2 | 29.3 | 21.27 |
| step (step) | 103 | 71 | - | |
| 10 m walking * | time (s) | - | - | 9.52 |
| step (step) | 19.5 | |||
| MMSE | 22/30 | 21/30 *** | 27/30 | |
| FAB | 10/18 | 11/18 | 16/18 |
| Hematological Tests | ||
|---|---|---|
| WBC | 12.4 | ×109/L |
| Hb | 17.0 | g/dL |
| Plt | 244 | 109/L |
| Biochemical testing | ||
| ALB | 3.8 | g/dL |
| BUN | 22 | mg/dL |
| Cre | 1.18 | mg/dL |
| ALP | 213 | IU/L |
| AST | 34 | IU/L |
| ALT | 33 | IU/L |
| LDH | 225 | IU/L |
| T-Bil | 1.3 | mg/dL |
| CRP | 9.11 | mg/dL |
| Glu | 174 | mg/dL |
| Na | 145 | mmol/L |
| K | 3.6 | mmol/L |
| Cl | 108 | mmol/L |
| Coagulation System Tests | ||
| D-dimar | — | μg/dL |
| Pre-Tap Test | Post-Tap Test ** | Post-Shunting | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TUG | time (s) | - | - | 18.74 |
| step (step) | ||||
| 10 m walking * | time (s) | 21.52 | 17.92 | 11.95 |
| step (step) | 27 | 24 | 21 | |
| MMSE | 11/30 | 16/30 | 15/30 | |
| FAB | 4/18 | 8/18 | 6/18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Watanabe, S.; Shibata, Y.; Baba, K.; Kuriyama, Y.; Ishikawa, E. Idiopathic Normal-Pressure Hydrocephalus Revealed by Systemic Infection: Clinical Observations of Two Cases. Neurol. Int. 2025, 17, 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint17060086
Watanabe S, Shibata Y, Baba K, Kuriyama Y, Ishikawa E. Idiopathic Normal-Pressure Hydrocephalus Revealed by Systemic Infection: Clinical Observations of Two Cases. Neurology International. 2025; 17(6):86. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint17060086
Chicago/Turabian StyleWatanabe, Shinya, Yasushi Shibata, Kosuke Baba, Yuhei Kuriyama, and Eiichi Ishikawa. 2025. "Idiopathic Normal-Pressure Hydrocephalus Revealed by Systemic Infection: Clinical Observations of Two Cases" Neurology International 17, no. 6: 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint17060086
APA StyleWatanabe, S., Shibata, Y., Baba, K., Kuriyama, Y., & Ishikawa, E. (2025). Idiopathic Normal-Pressure Hydrocephalus Revealed by Systemic Infection: Clinical Observations of Two Cases. Neurology International, 17(6), 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint17060086





