A Retrospective Study of Lateral Antebrachial Cutaneous Nerve Neuropathy: Electrodiagnostic Findings and Etiologies in 49 Cases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
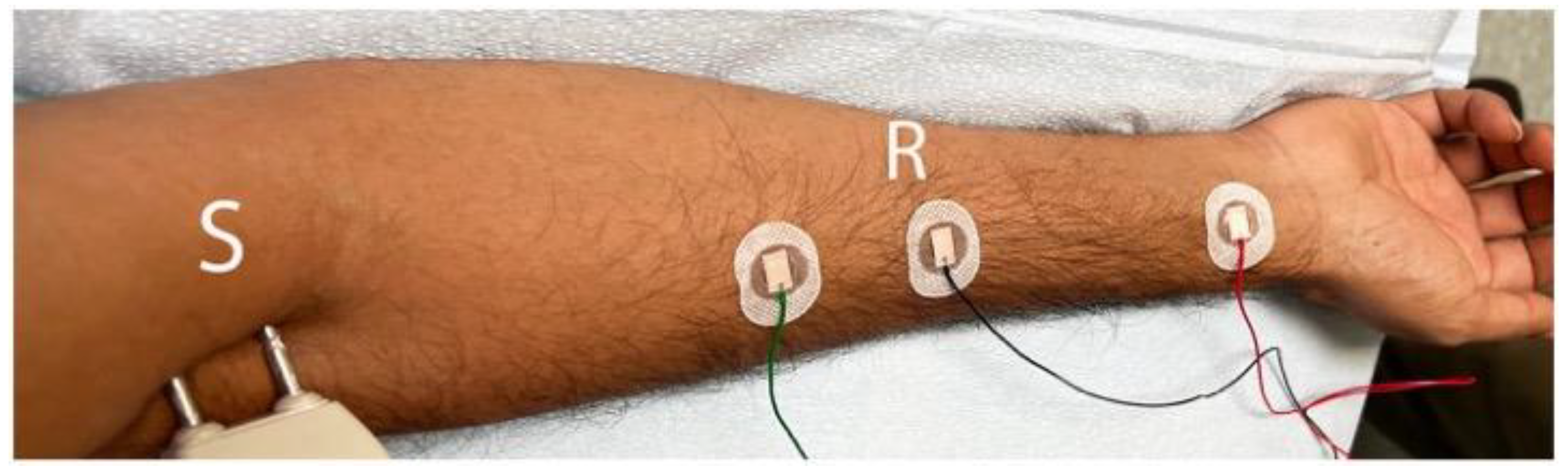
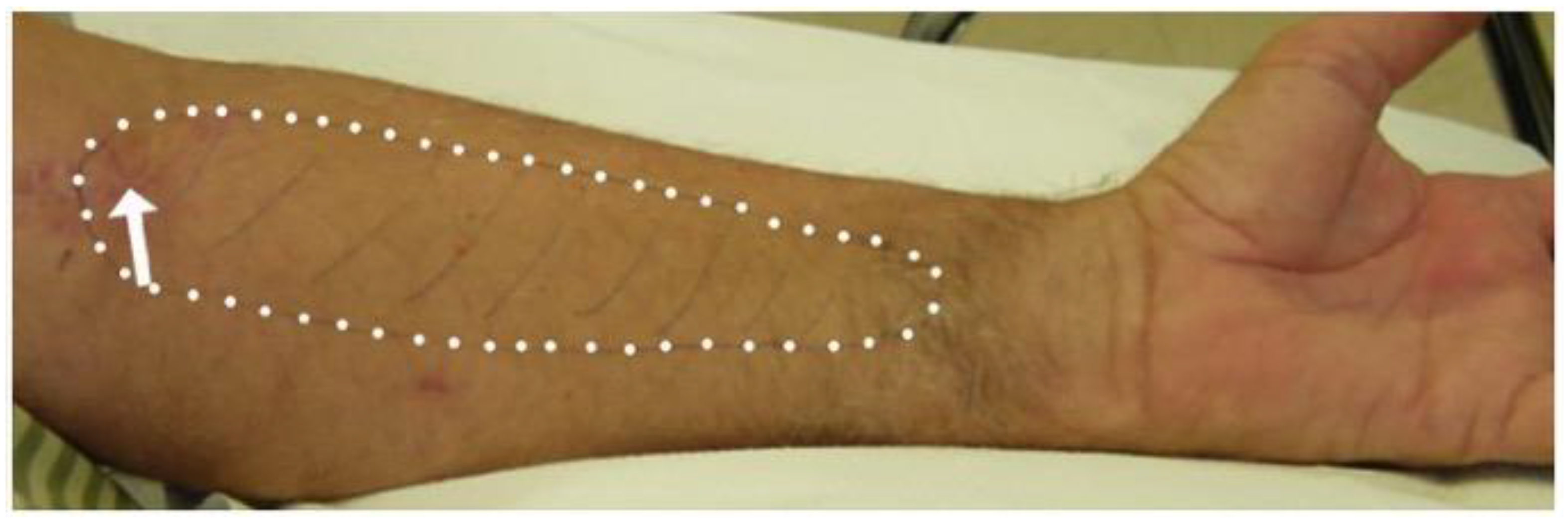
2.1. Electrodiagnostic Studies
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Institutional Review Board Approval of Research
3. Results
3.1. Demographics
3.2. Etiologies
3.3. Signs and Symptoms of LACN Neuropathy
3.4. Electrodiagnostic Studies
3.5. NCV SNAP Decreased Amplitude
3.6. NCV SNAP Increased Latency
3.7. Illustrative Cases
3.7.1. Patient 1
3.7.2. Patient 2
3.7.3. Patient 3
3.7.4. Patient 4
3.7.5. Patient 5
4. Discussion
4.1. Iatrogenic Injuries
4.2. Non-Iatrogenic Injuries
4.3. Large Series of LACN Neuropathy in the Literature
4.4. Electrodiagnostic Studies
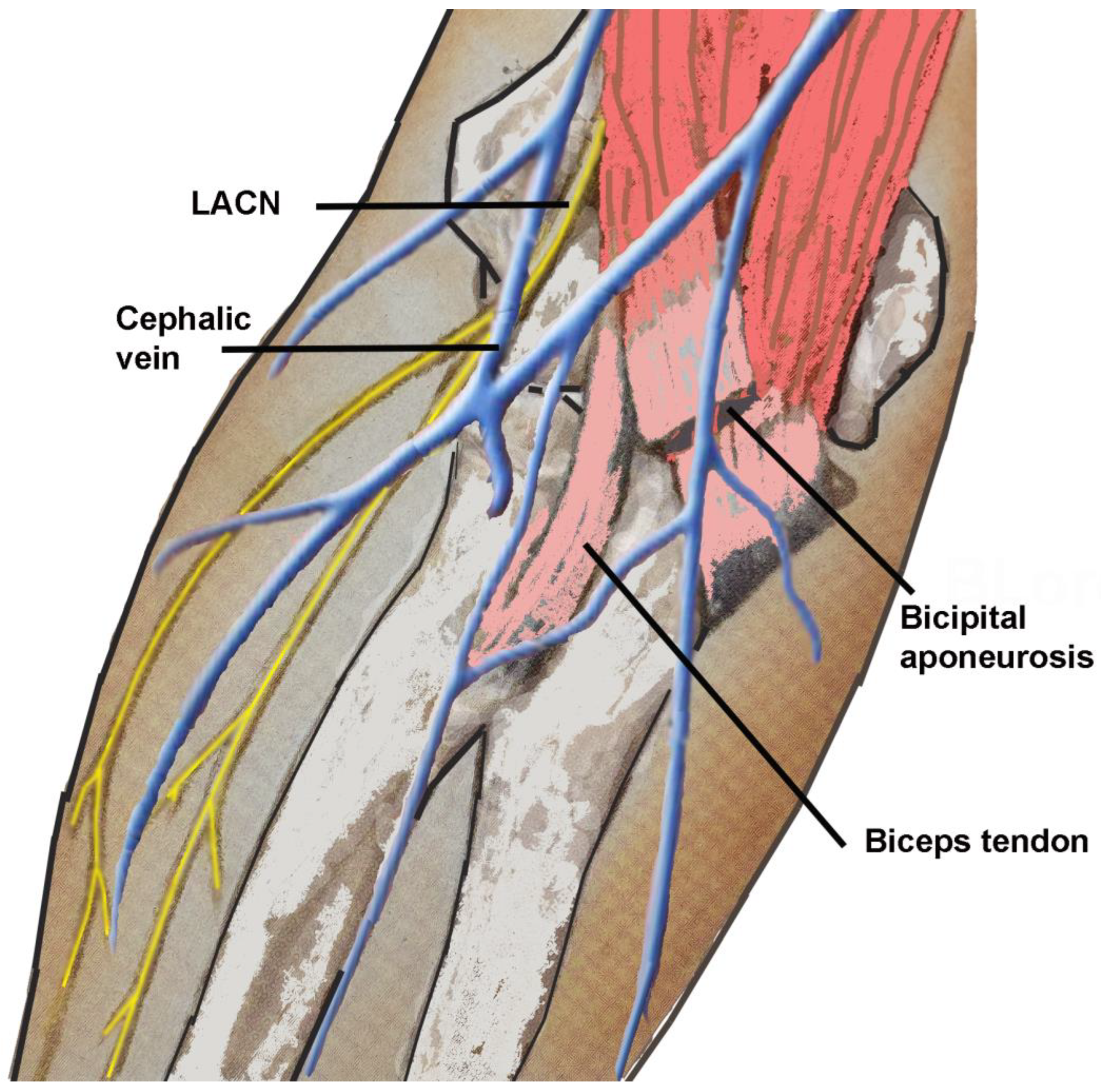
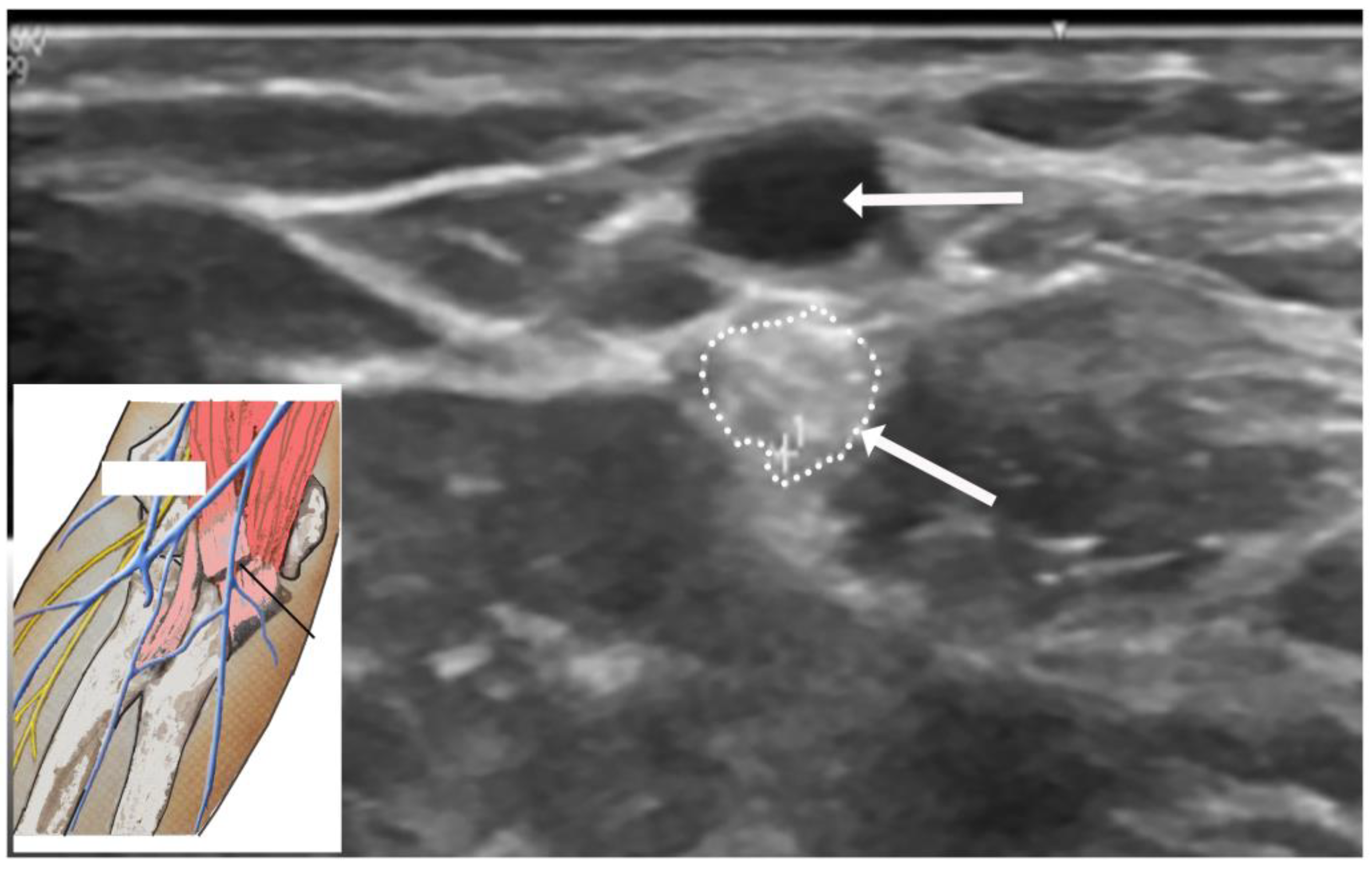
4.5. Ultrasound Studies
4.6. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davidson, J.J.; Bassett, F.H.; Nunley, J.A. Musculocutaneous nerve entrapment revisited. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 1998, 7, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsenthal, G.; Mondell, D.L.; Reischer, M.A.; Mack, R.H. Forearm pain secondary to compression syndrome of the lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1984, 65, 139–141. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khadanovich, A.; Benes, M.; Kaiser, R.; Herma, T.; Kachlik, D. Clinical anatomy of the lateral antebrachial cutaneous nerve: Is there any safe zone for interventional approach? Ann. Anat. 2024, 252, 152202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memon, A.B.; Mahmood, S.; Waseem, F.; Sherburn, F.; Nardone, A.; Ahmad, B.K. Lateral antebrachial cutaneous neuropathy: A review of 15 cases. Cureus 2022, 14, e25203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naam, N.H.; Massoud, H.A. Painful entrapment of the lateral antebrachial cutaneous nerve at the elbow. J. Hand Surg. Am. 2004, 29, 1148–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amarasooriya, M.; Bain, G.I.; Roper, T.; Bryant, K.; Iqbal, K.; Phadnis, J. Complications after distal biceps tendon repair: A systematic review. Am. J. Sports Med. 2020, 48, 3103–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, N.H.; Volpi, A.; Lynch, T.S.; Patel, R.M.; Cerynik, D.L.; Schickendantz, M.S.; Jones, M.H. Complications of distal biceps tendon repair: A meta-analysis of single-incision versus double-incision surgical technique. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2016, 4, 2325967116668137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, M.J.; DaCambra, M.P.; Hildebrand, K.A. Neurologic complications of distal biceps tendon repair with 1-incision endobutton fixation. Am. J. Orthop. 2014, 43, E159–E162. [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy, T.R.; Hudson, J.; Batech, M.; Acevedo, D.C.; Mirzayan, R. Surgical treatment of distal biceps tendon ruptures: An analysis of complications in 784 surgical repairs. Am. J. Sports Med. 2017, 45, 3020–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly, T.; Pasternak, I.; Meuli-Simmen, C.; Mauler, F. Iatrogenic rerouting of the lateral antebrachial cutaneous nerve during distal biceps tendon repair: A case report. JSES Open Access 2017, 1, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, J.A. Venipuncture-related lateral antebrachial cutaneous nerve injury: What to know? Braz. J. Anesthesiol. 2014, 64, 131–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayegani, S.M.; Azadi, A. Lateral antebrachial cutaneous nerve injury induced by phlebotomy. J. Brachial. Plex. Peripher. Nerve Inj. 2007, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sander, H.W.; Conigliari, M.F.; Masdeu, J.C. Antecubital phlebotomy complicated by lateral antebrachial cutaneous neuropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stitik, T.P.; Foye, P.M.; Nadler, S.F.; Brachman, G.O. Phlebotomy-related lateral antebrachial cutaneous nerve injury. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2001, 80, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, R.T.; Cohen, M.J. Lateral antebrachial cutaneous nerve injury as a complication of phlebotomy. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1985, 76, 299–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seoighe, D.M.; Baker, J.F.; Mulhall, K.J. Surgical trainees neuropraxia? An unusual case of compression of the lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2010, 96, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Judge, A.; Fecho, K. Lateral antebrachial cutaneous neuropathy as a result of positioning while under general anesthesia. Anesth. Analg. 2010, 110, 122–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.H. Lateral antebrachial cutaneous neuropathy after steroid injection at lateral epicondyle. J. Back Musculoskelet. Rehabil. 2015, 28, 419–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, D.M.; Nunley, J.A. Lateral antebrachial cutaneous neuroapthy. Oper. Tech. Sports Med. 2001, 9, 222–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassett, F.H.; Nunley, J.A. Compression of the musculocutaneous nerve at the elbow. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 1982, 64, 1050–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belzile, E.; Cloutier, D. Entrapment of the lateral antebrachial cutaneous nerve exiting through the forearm fascia. J. Hand Surg. Am. 2001, 26, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dailiana, Z.H.; Roulot, E.; Le, V.D. Surgical treatment of compression of the lateral antebrachial cutaneous nerve. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2000, 82, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillingham, B.L.; Mack, G.R. Compression of the lateral antebrachial cutaneous nerve by the biceps tendon. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 1996, 5, 330–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narasanagi, S.S. Compression of lateral cutaneous nerve of forearm. Neurol. India 1972, 20, 224–225. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- von Bergen, T.N.; Lourie, G.M. Etiology, diagnosis, and treatment of dynamic nerve compression syndromes of the elbow among high-level pitchers: A review of 7 cases. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2018, 6, 2325967118807131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberta, F.G.; Elattrache, N.S. Diagnosis and treatment of distal biceps and anterior elbow pain in throwing athletes. Sport. Med. Arthrosc. Rev. 2008, 16, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jablecki, C.K. Lateral antebrachial cutaneous neuropathy in a windsurfer. Muscle Nerve 1999, 22, 944–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannoulis, F.; Papoulidis, N.G.; Krexi, A.V. Lateral antebrachial nerve entrapment in compressive neuropathies of the upper extremity. In Compressive Neuropathies of the Upper Extremity: A Comprehensive Guide to Treatment, 1st ed.; Sotereanos, D.G., Papatheodorou, L.K., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 217–223. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, C.; Vishnubhakat, S. Compression of lateral antebrachial cutaneous nerve in waitresses. J. Clin. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2015, 16, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.R.; Bassini, L.; Magill, R. Compression neuropathy of the lateral antebracheal cutaneous nerve. Orthopedics 1991, 14, 173–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, B.R. Handbag paraesthesia. Lancet 1976, 2, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschbacher, R.; Koch, J.; Emsley, C.; Katz, B. Electrodiagnostic reference values for the lateral antebrachial cutaneous nerve: Standardization of a 10-cm distance. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2000, 81, 1563–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mwaturura, T.; Peters, M.J.; Glaris, Z.; Goetz, T.J. Safe drill trajectory for anatomic repair of distal biceps tendon through a single incision: A cadaveric study. J. Hand Surg. Am. 2023, 48, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, R.J.; Mahadevan, V.; Moss, A.L. Injury to the lateral cutaneous nerve of forearm after venous cannulation: A case report and literature review. Clin. Anat. 2012, 25, 659–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiavaras, M.M.; Jacobson, J.A.; Billone, L.; Lawton, J.M.; Lawton, J. Sonography of the lateral antebrachial cutaneous nerve with magnetic resonance imaging and anatomic correlation. J. Ultrasound Med. 2014, 33, 1475–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Metric | Number of Patients (n = 49) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (Mean) | 48.4 years (16–81 years) | 0.428 * | |
| Gender | Male Female | 31 (63.3%) 18 (36.7%) | 0.063 |
| Side of symptoms | Left Right | 21 (42.9%) 28 (57.1%) | 0.317 |
| Dominant hand | Right Left Ambidextrous | 43 (87.8%) 3 (6.1%) 3 (6.1%) | <0.001 |
| Symptomatic side corresponds to hand dominance | Yes No | 28 (57.1%) 21 (42.9%) | 0.317 |
| Symptom onset | Acute Gradual | 44 (89.8%) 5 (10.2%) | <0.001 |
| Etiology | Iatrogenic injury (direct or positional) | 30 (61.2%) | <0.001 |
| Biceps tendon repair | 11 (36.7%) | ||
| Phlebotomy | 5 (16.7%) | ||
| Rotator cuff repair | 4 (13.3%) | ||
| Elbow ** | 2 (6.7%) | ||
| During intense physical therapy | 2 (6.7%) | ||
| Dupuytren’s contracture | 1 (3.3%) | ||
| Trigger thumb | 1 (3.3%) | ||
| Shoulder (long head of biceps repair) | 1 (3.3%) | ||
| Repair fractured radius/ulna | 1 (3.3%) | ||
| Repair fractured humerus/nerve transfer | 1 (3.3%) | ||
| Granular cell tumor excision/removal of brachioradialis muscle | 1 (3.3%) | ||
| Non-iatrogenic injury | 15 (30.6%) | ||
| Laceration injury | 6 (40.0%) | ||
| Stretch injury *** | 5 (33.3%) | ||
| Fractured humerus | 1 (6.7%) | ||
| Fall (injury of long head of biceps tendon) | 1 (6.7%) | ||
| Workplace injury (biceps tendon tear) | 1 (6.7%) | ||
| Parsonage–Turner syndrome | 1 (6.7%) | ||
| Other | 4 (8.2%) | ||
| Compression by mass (lipoma; cystic lesion) | 2 (50.0%) | ||
| Idiopathic | 2 (50.0%) | ||
| Symptoms in distribution of LACN | Pain | 33 (67.3%) | 0.015 |
| Paresthesia | 27 (55.1%) | 0.190 | |
| Numbness | 23 (46.9%) | 0.553 | |
| Signs in distribution of LACN | Hypoesthesia | 45 (91.8%) | <0.001 |
| Dysesthesia | 7 (14.3%) | 0.052 | |
| NCV SNAP | Absent | 44 (89.8%) | <0.001 |
| Decreased amplitude | 5 (10.2%) | <0.001 | |
| Increased latency | 2 (4.1%) | <0.001 |
| Characteristics | Overall n = 49 | No n = 44 | Yes n = 5 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 50.0 [40.0, 56.0] | 50.0 [42.2, 56.2] | 48.0 [37.0, 52.0] | 0.779 |
| Female | 18 (36.7%) | 13 (29.5%) | 5 (100.0%) | 0.004 |
| Right Side | 28 (57.1%) | 25 (56.8%) | 3 (60.0%) | 1.000 |
| Dominant hand | 1.000 | |||
| Left | 3 (6.1%) | 3 (6.8%) | 0 (0.0%) | |
| Right Side | 43 (87.8%) | 38 (86.4%) | 5 (100.0%) | |
| Ambidextrous | 3 (6.1%) | 3 (6.8%) | 0 (0.0%) | |
| Symptomatic Side Corresponds Hand Dominance | 28 (57.1%) | 25 (56.8%) | 3 (60.0%) | 1.000 |
| Chronic Onset | 5 (10.2%) | 3 (6.8%) | 2 (40.0%) | 0.075 |
| Symptoms (Pain) | 33 (67.3%) | 30 (68.2%) | 3 (60.0%) | 1.000 |
| Symptoms (Paresthesia) | 28 (57.1%) | 23 (52.3%) | 5 (100.0%) | 0.062 |
| Symptoms (Numbness) | 23 (46.9%) | 22 (50.0%) | 1 (20.0%) | 0.353 |
| Signs (Hypoesthesia) | 45 (91.8%) | 41 (93.2%) | 4 (80.0%) | 0.359 |
| Signs (Dysesthesia) | 7 (14.3%) | 6 (13.6%) | 1 (20.0%) | 0.554 |
| Manner | 0.535 | |||
| Iatrogenic trauma | 30 (61.2%) | 27 (61.4%) | 3 (60.0%) | |
| Non-iatrogenic trauma | 9 (18.4%) | 9 (20.5%) | 0 (0.0%) | |
| Other | 10 (20.4%) | 8 (18.2%) | 2 (40.0%) |
| Characteristics | Overall n = 49 | No n = 47 | Yes n = 2 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 50.0 [40.0, 56.0] | 50.0 [41.5, 55.0] | 59.0 [48.0, 70.0] | 0.649 |
| Female | 18 (36.7%) | 16 (34.0%) | 2 (100.0%) | 0.130 |
| Right Side | 28 (57.1%) | 26 (55.3%) | 2 (100.0%) | 0.500 |
| Dominant hand | 1.000 | |||
| Left | 3 (6.1%) | 3 (6.4%) | 0 (0.0%) | |
| Right Side | 43 (87.8%) | 41 (87.2%) | 2 (100.0%) | |
| Ambidextrous | 3 (6.1%) | 3 (6.4%) | 0 (0.0%) | |
| Symptomatic Side Corresponds Hand Dominance | 28 (57.1%) | 26 (55.3%) | 2 (100.0%) | 0.500 |
| Chronic Onset | 5 (10.2%) | 3 (6.4%) | 2 (100.0%) | 0.009 |
| Symptoms (Pain) | 33 (67.3%) | 32 (68.1%) | 1 (50.0%) | 1.000 |
| Symptoms (Paresthesia) | 28 (57.1%) | 26 (55.3%) | 2 (100.0%) | 0.500 |
| Symptoms (Numbness) | 23 (46.9%) | 23 (48.9%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.491 |
| Signs (Hypoesthesia) | 45 (91.8%) | 44 (93.6%) | 1 (50.0%) | 0.158 |
| Signs (Dysesthesia) | 7 (14.3%) | 6 (12.8%) | 1 (50.0%) | 0.268 |
| Manner | 0.069 | |||
| Iatrogenic trauma | 30 (61.2%) | 30 (63.8%) | 0 (0.0%) | |
| Non-iatrogenic trauma | 9 (18.4%) | 9 (19.1%) | 0 (0.0%) | |
| Other | 10 (20.4%) | 8 (17.0%) | 2 (100.0%) |
| Study | Age (Mean) | Gender | Etiology | EDX Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Davidson et al. 1998 [1] (n = 15) | 18–59 years | M: 10 (66.7%) F: 5 (33.3%) | Not reported | Not reported |
| Naam et al. 2004 [5] (n = 23) | 38 years (19–64 years) | M: 15 (65.2%) F: 8 (34.8%) | 8: trauma to elbow 17: Workers’ compensation cases | All had positive nerve conduction study findings consistent with LACN dysfunction |
| Memon et al. 2022 [4] (n = 15) | 53 years (36–82 years) | M: 7 (46.7%) F: 8 (53.3%) | Iatrogenic injury: 10 (66.7%) (7 during orthopedic surgeries; 3 during antecubital fossa phlebotomy and intravenous placement) Non-iatrogenic injury: 4 (26.7%) (2 from repetitive forearm use, 1 from trauma, and 1 from a dog bite) Other: 1 (6.7%) (idiopathic) | 13: absent or reduced sensory amplitude 2: demyelinating pattern with prolonged sensory distal latencies Sensory responses absent in 7/13 patients with an axonal neuropathy pattern |
| Current study 2024 (n = 49) | 48.4 years (16–81 years) | M: 31 (63.3%) F: 18 (36.7%) | Iatrogenic injury: 30 (61.2%) (11 during biceps tendon repair, 5 during phlebotomy) Non-iatrogenic injury: 15 (30.6%) (6 due to laceration injury) Other: 4 (8.2%) (2 due to mass compression, 2 idiopathic) | SNAPs absent in 44 (89.8%) patients; SNAPs had a decreased amplitude in 5 (10.2%) patients and an increased latency in 2 (4.1%) patients |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iyer, V.G.; Shields, L.B.E.; Daniels, M.W.; Zhang, Y.P.; Shields, C.B. A Retrospective Study of Lateral Antebrachial Cutaneous Nerve Neuropathy: Electrodiagnostic Findings and Etiologies in 49 Cases. Neurol. Int. 2024, 16, 1143-1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16050086
Iyer VG, Shields LBE, Daniels MW, Zhang YP, Shields CB. A Retrospective Study of Lateral Antebrachial Cutaneous Nerve Neuropathy: Electrodiagnostic Findings and Etiologies in 49 Cases. Neurology International. 2024; 16(5):1143-1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16050086
Chicago/Turabian StyleIyer, Vasudeva G., Lisa B. E. Shields, Michael W. Daniels, Yi Ping Zhang, and Christopher B. Shields. 2024. "A Retrospective Study of Lateral Antebrachial Cutaneous Nerve Neuropathy: Electrodiagnostic Findings and Etiologies in 49 Cases" Neurology International 16, no. 5: 1143-1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16050086
APA StyleIyer, V. G., Shields, L. B. E., Daniels, M. W., Zhang, Y. P., & Shields, C. B. (2024). A Retrospective Study of Lateral Antebrachial Cutaneous Nerve Neuropathy: Electrodiagnostic Findings and Etiologies in 49 Cases. Neurology International, 16(5), 1143-1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16050086






