Fluorescein Angiography for Monitoring Neural Blood Flow in Chronic Nerve Compression Neuropathy: Experimental Animal Models and Preliminary Clinical Observations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Models
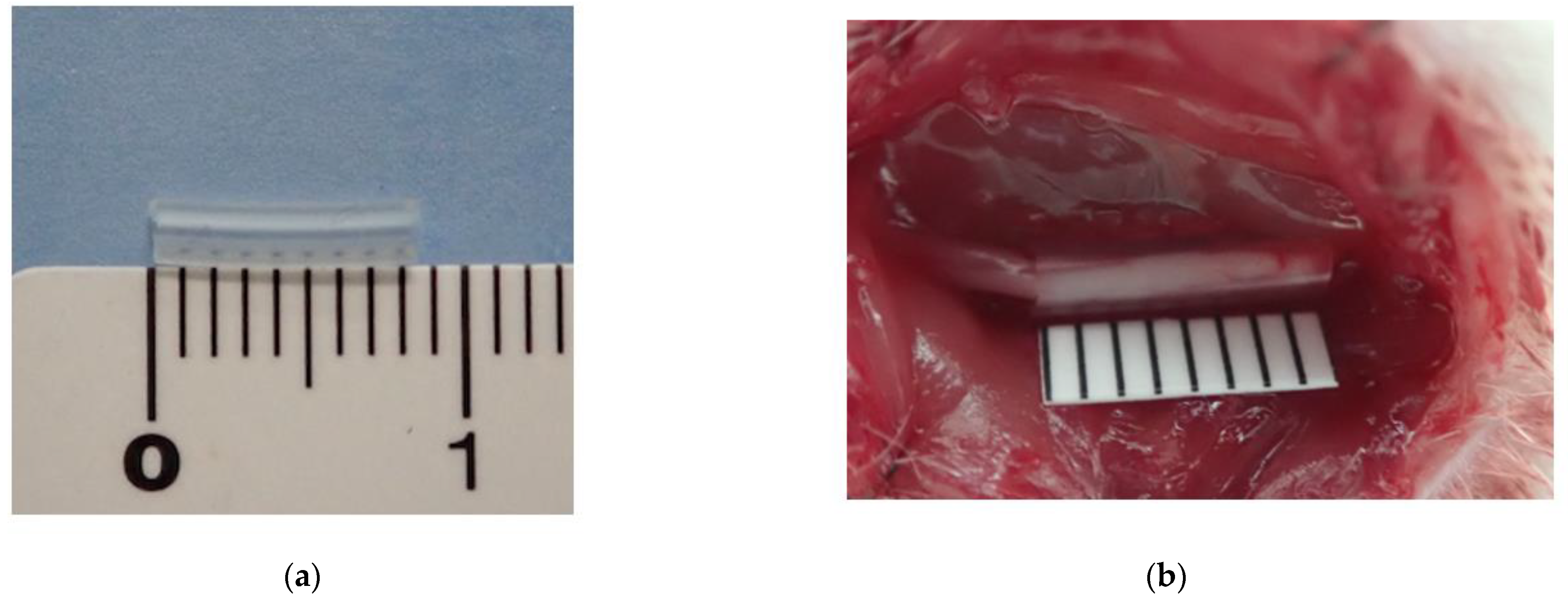
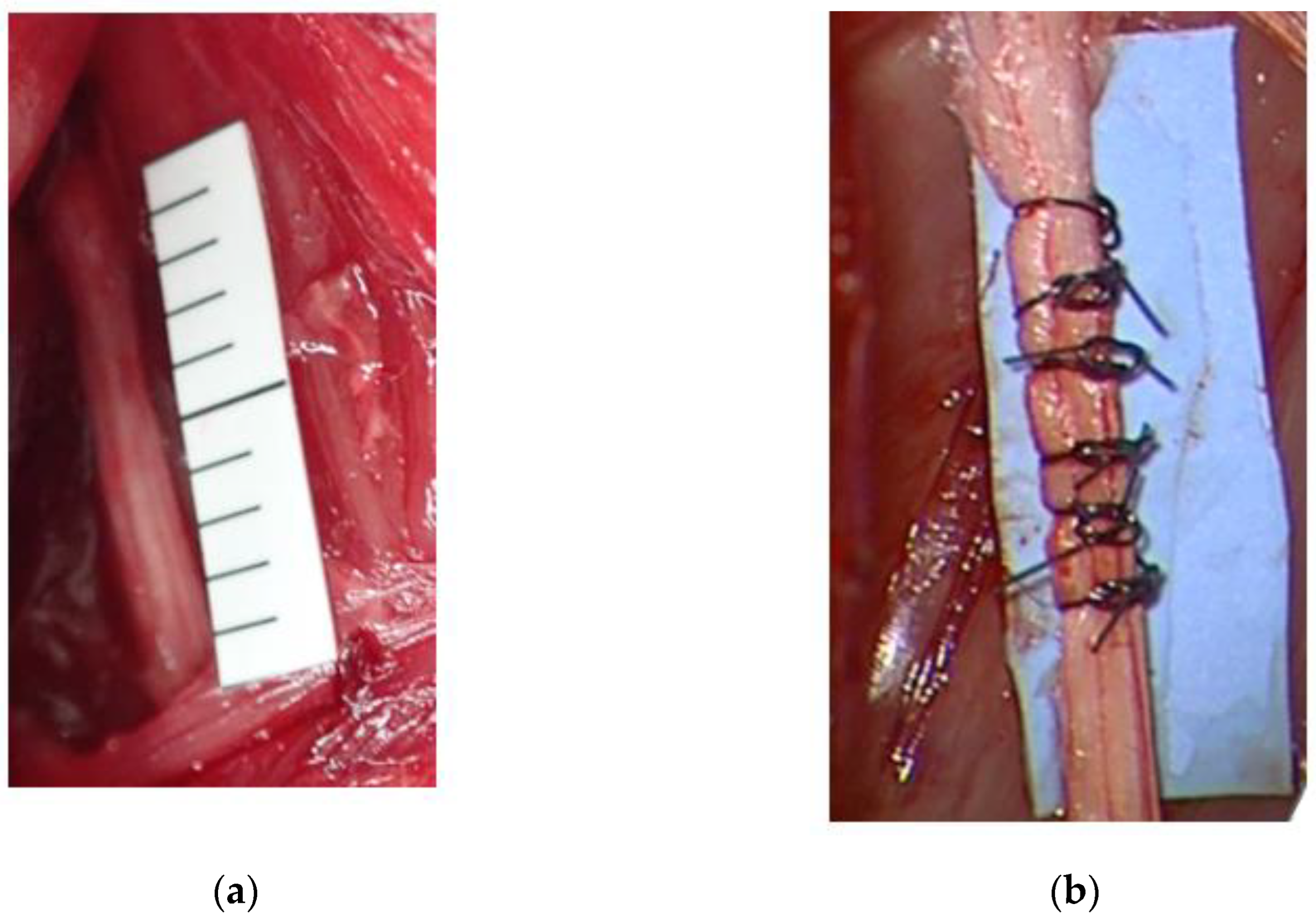
2.1.1. Rat CNC Model
2.1.2. Rabbit Severe Chronic Neuropathy Model
2.2. Clinical Study
2.2.1. Fluorescein Angiography (In Vivo and Clinical Study)
2.2.2. Electrodiagnostic Examination (In Vivo and Clinical Study)
2.2.3. Laser Doppler Flowmetry (In Vivo Study)
2.3. Histological Examination for the Rabbit Model
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Rat CNC Model
Blood Flow Evaluations
3.2. Rabbit Severe Chronic Neuropathy Model
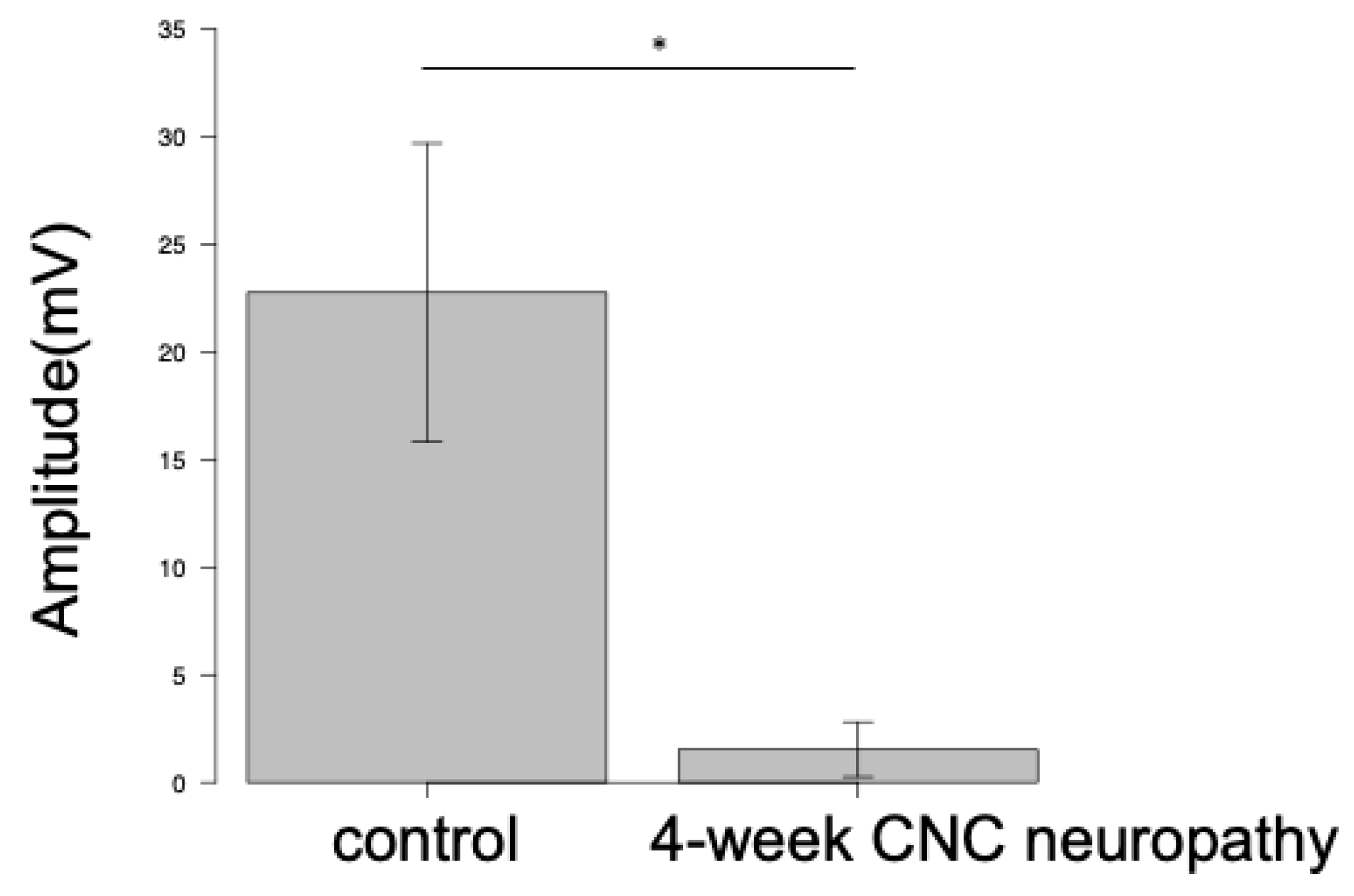
Electrodiagnostic Examination
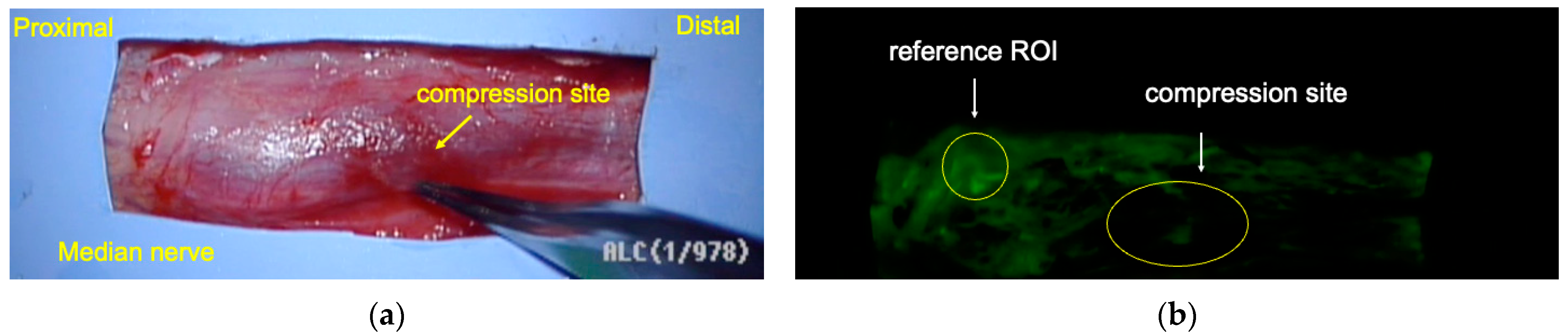
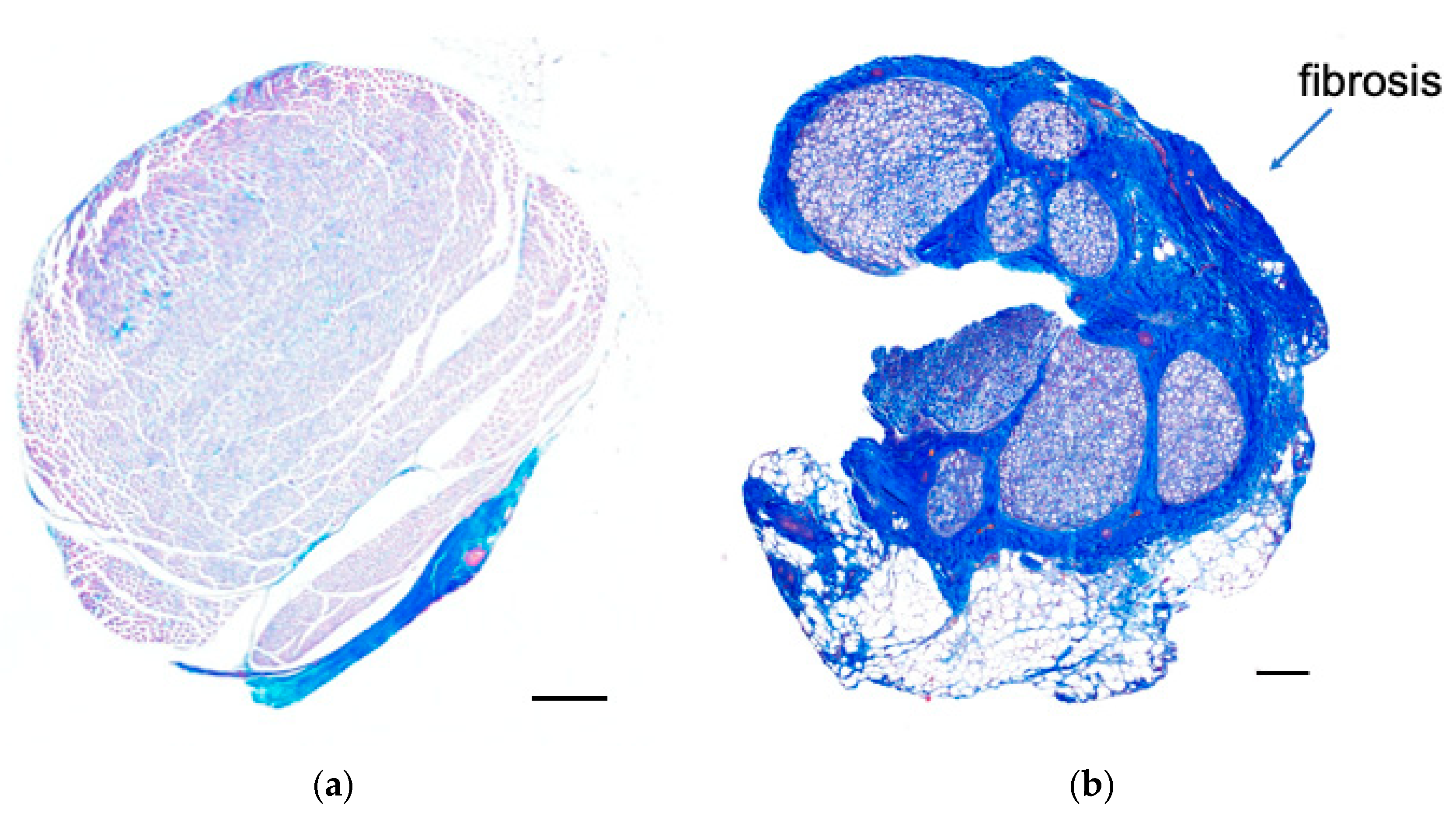
3.3. Histological Examination
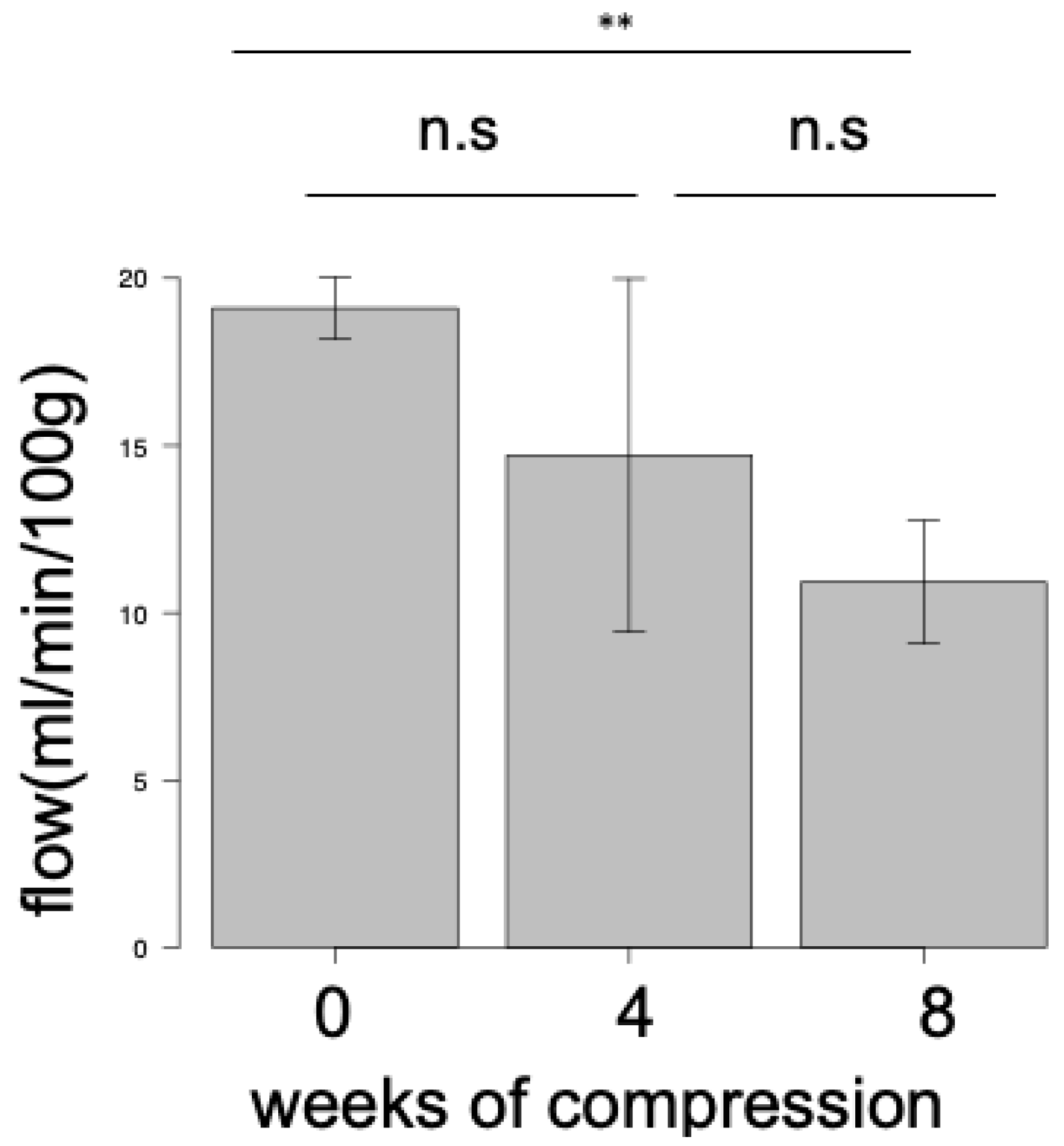
3.4. Blood Flow Evaluations
3.5. Clinical Study
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nordstrom, D.L.; DeStefano, F.; Vierkant, R.A.; Layde, P.M. Incidence of diagnosed carpal tunnel syndrome in a general population. Epidemiology 1998, 9, 342–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondelli, M.; Giannini, F.; Ballerini, M.; Ginanneschi, F.; Martorelli, E. Incidence of ulnar neuropathy at the elbow in the province of Siena (Italy). J. Neurol. Sci. 2005, 234, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarm, F.P.; Nagl, J.; Graf, K.; Reinges, M.H.; Uhl, E.; Krishnan, K.G.; Kolodziej, M.A. A prospective randomized study comparing retractor-endoscopic vs. open release of carpal tunnel and cubital tunnel syndromes. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2022, 222, 107437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pace, V.; Marzano, F.; Placella, G. Update on surgical procedures for carpal tunnel syndrome: What is the current evidence and practice? What are the future research directions? World J. Orthop. 2023, 14, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackinnon, S.E.; Lee Dellon, A.; Hudson, A.R.; Hunter, D.A. Histopathology of compression of the superficial radial nerve in the forearm. J. Hand Surg. Am. 1986, 11, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackinnon, S.E.; Dellon, A.L.; Hudson, A.R.; Hunter, D.A. Chronic Nerve Compression—An Experimental Model in the Rat. Ann. Plast. Surg. 1984, 13, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.; Hahn, P.; Choi, B.; Mozaffar, T.; Gupta, R. Early Surgical Decompression Restores Neurovascular Blood Flow and Ischemic Parameters in an in Vivo Animal Model of Nerve Compression Injury. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2014, 96, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wipperman, J.; Goerl, K. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Diagnosis and Management. Am. Fam. Physician 2016, 94, 993–999. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aboonq, M.S. Pathophysiology of carpal tunnel syndrome. Neurosciences 2015, 20, 4–9. [Google Scholar]
- Farias Zuniga, A.; Ghavanini, A.A.; Israelian, G.; Keir, P.J. Blood flow velocity but not tendon mechanics relates to nerve function in carpal tunnel syndrome patients. J. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 411, 116694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, E.; Shao, F.; Liebenberg, E.; Rempel, D.; Lotz, J.C. Carpal tunnel pressure alters median nerve function in a dose-dependent manner: A rabbit model for carpal tunnel syndrome. J. Orthop. Res. 2005, 23, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bland, J.D.P. A neurophysiological grading scale for carpal tunnel syndrome. Muscle Nerve 2000, 23, 1280–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Miedany, Y.; El Gaafary, M.; Youssef, S.; Ahmed, I.; Nasr, A. Ultrasound assessment of the median nerve: A biomarker that can help in setting a treat to target approach tailored for carpal tunnel syndrome patients. Springerplus 2015, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, K.D.; Roll, S.C.; Volz, K.R.; Freimer, M. Relationship Between Intraneural Vascular Flow Measured With Sonography and Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Diagnosis Based on Electrodiagnostic Testing. J. Ultrasound Med. 2012, 31, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joy, V.; Therimadasamy, A.K.; Chan, Y.C.; Wilder-Smith, E.P. Combined Doppler and B-mode sonography in carpal tunnel syndrome. J. Neurol. Sci. 2011, 308, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejaco, C.; Stradner, M.; Zauner, D.; Seel, W.; Simmet, N.E.; Klammer, A.; Heitzer, P.; Brickmann, K.; Gretler, J.; Fürst-Moazedi, F.C.; et al. Ultrasound for diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome: Comparison of different methods to determine median nerve volume and value of power Doppler sonography. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 1934–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiler, J.G.; Milek, M.A.; Carpenter, G.K.; Swiontkowski, M.F. Intraoperative assessment of median nerve blood flow during carpal tunnel release with laser Doppler flowmetry. J. Hand Surg. 1989, 14, 986–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hama, S.; Yokoi, T.; Okada, M.; Uemura, T.; Takamatsu, K.; Nakamura, H. Microvascular neural blood flow assessment for a chronic nerve compression neuropathy mouse model by fluorescein angiography. Neurol. Res. 2022, 44, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiterovich, K.A.; Maguire, M.G.; Murphy, R.P.; Schachat, A.P.; Bressler, N.M.; Bressler, S.B.; Fine, S.L. frequency of Adverse Systemic Reactions after fluorescein Angiography Results of a Prospective Study. Ophthalmology 1991, 98, 1139–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świątnicki, W.; Urbaniak, F.; Szymański, J.; Szymańska, A.; Komuński, P. Intra-operative fluorescein videoangiography-related nephrotoxicity in intracranial aneurysm surgery: Single center, observational cohort study. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2021, 203, 106597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, J.; Fromy, B.; Morel, G.; Roquelaure, Y.; Saumet, J.L.; Sigaudo-Roussel, D. Chronic sciatic nerve injury impairs the local cutaneous neurovascular interaction in rats. Pain 2012, 153, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Rowshan, K.; Chao, T.; Mozaffar, T.; Steward, O. Chronic nerve compression induces local demyelination and remyelination in a rat model of carpal tunnel syndrome. Exp. Neurol. 2004, 187, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.; Steward, O. Chronic nerve compression induces concurrent apoptosis and proliferation of Schwann cells. J. Comp. Neurol. 2003, 461, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, R.A.; Andary, M. Electrodiagnostic evaluation of carpal tunnel syndrome. Muscle Nerve 2011, 44, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, B.; Peljovich, A.E.; Afra, R.; Cho, M.S.; Gray, R.; Stephenson, J.; Gurman, A.; MacDermid, J.; Mlady, G.; Patel, A.T.; et al. The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guideline on. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2016, 98, 1750–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camitz, H. Surgical treatment of paralysis of opponens muscle of thumb. Acta Chir. Scand. 1929, 65, 77–81. [Google Scholar]
- Onode, E.; Uemura, T.; Takamatsu, K.; Yokoi, T.; Shintani, K.; Hama, S.; Miyashima, Y.; Okada, M.; Nakamura, H. Bioabsorbable nerve conduits three-dimensionally coated with human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neural stem/progenitor cells promote peripheral nerve regeneration in rats. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K.; Hisasue, S.I.; Ide, H.; Aoki, H.; Muto, S.; Yamaguchi, R.; Tsujimura, A.; Horie, S. The impact of increased bladder blood flow on storage symptoms after holmium laser enucleation of the prostate. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, W.W. Evaluation and management of peripheral nerve injury. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2008, 119, 1951–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDermid, J.C.; Doherty, T. Clinical and Electrodiagnostic Testing of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Narrative Review. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2004, 34, 565–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundborg, G. Intraneural microcirculation. Orthop. Clin. N. Am. 1988, 19, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfonso, C.; Jann, S.; Massa, R.; Torreggiani, A. Diagnosis, treatment and follow-up of the carpal tunnel syndrome: A review. Neurol. Sci. 2010, 31, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OʼBrien, J.P.; Mackinnon, S.E.; MacLean, A.R.; Hudson, A.R.; Dellon, A.L.; Hunter, D.A. A Model of Chronic Nerve Compression in the Rat. Ann. Plast. Surg. 1987, 19, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frerichs, K.U.; Feuerstein, G.Z. Laser-Doppler Flowmetry A Review of Its Application for Measuring Cerebral and Spinal Cord Blood Flow. Mol. Chem. Neuropathol. 1990, 12, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgos, J. Laser Doppler monitoring of cerebral blood flow. Neurol. Res. 1996, 18, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, W.F.; Tuma, R.; O’grady, T. Intraoperative measurement of spinal cord blood flow in syringomyelia. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2000, 102, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeykens, H.J.J.; De Moor, R.J.G. Laser doppler flowmetry. In Lasers in Endodontics: Scientific Background and Clinical Applications; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 171–190. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.C.; You, Y.K.; Lee, S.; Moon, D.H.; Lee, J.W. Evaluation of blood perfusion using laser doppler flowmetry during endoscopic lumbar sympathectomy in patients with plantar hyperhidrosis: A retrospective observational study. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rydevik, B.; Lundborg, G. Permeability of Intraneural Microvessels and Perineurium Following Acute, Graded Experimental Nerve Compression. Scand. J. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1977, 11, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, T. Biology of the blood-nerve barrier and its alteration in immune mediated neuropathies. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2013, 84, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerasuriya, A.; Mizisin, A.P. The Blood-Nerve Barrier: Structure and Functional Significance. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 686, 149–173. [Google Scholar]





| Characteristic (Total, n = 31) | Value |
|---|---|
| Age | |
| Years (mean ± SD) | 70.9 ± 11.3 |
| Sex | |
| Female | 19 (61.3%) |
| Male | 12 (38.7%) |
| Electrodiagnostic Examination | |
| Amplitude (mV) of APB CMAP, mean ± SD | 3.02 ± 4.3 |
| Amplitude (μV) of SNAP, mean ± SD | 1.21 ± 2.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saito, K.; Okada, M.; Yokoi, T.; Hama, S.; Nakamura, H. Fluorescein Angiography for Monitoring Neural Blood Flow in Chronic Nerve Compression Neuropathy: Experimental Animal Models and Preliminary Clinical Observations. Neurol. Int. 2024, 16, 976-991. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16050074
Saito K, Okada M, Yokoi T, Hama S, Nakamura H. Fluorescein Angiography for Monitoring Neural Blood Flow in Chronic Nerve Compression Neuropathy: Experimental Animal Models and Preliminary Clinical Observations. Neurology International. 2024; 16(5):976-991. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16050074
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaito, Kosuke, Mitsuhiro Okada, Takuya Yokoi, Shunpei Hama, and Hiroaki Nakamura. 2024. "Fluorescein Angiography for Monitoring Neural Blood Flow in Chronic Nerve Compression Neuropathy: Experimental Animal Models and Preliminary Clinical Observations" Neurology International 16, no. 5: 976-991. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16050074
APA StyleSaito, K., Okada, M., Yokoi, T., Hama, S., & Nakamura, H. (2024). Fluorescein Angiography for Monitoring Neural Blood Flow in Chronic Nerve Compression Neuropathy: Experimental Animal Models and Preliminary Clinical Observations. Neurology International, 16(5), 976-991. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16050074





