A Case of Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension Complicated with both Infratentorial and Supratentorial Cortical Superficial Siderosis: Novel Imaging Findings on Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Magnetic Resonance Imaging Offering Clues to Pathophysiology
Abstract
1. Introduction
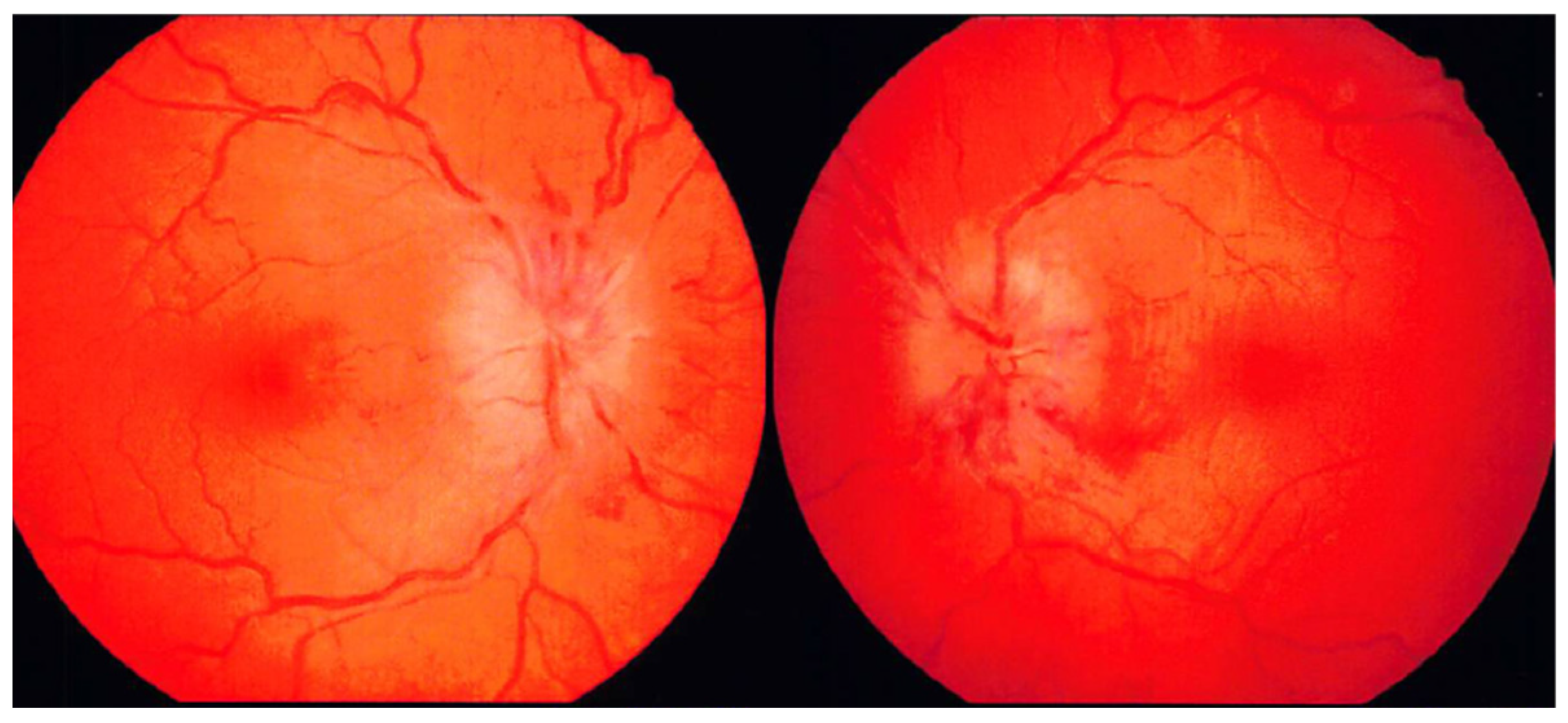
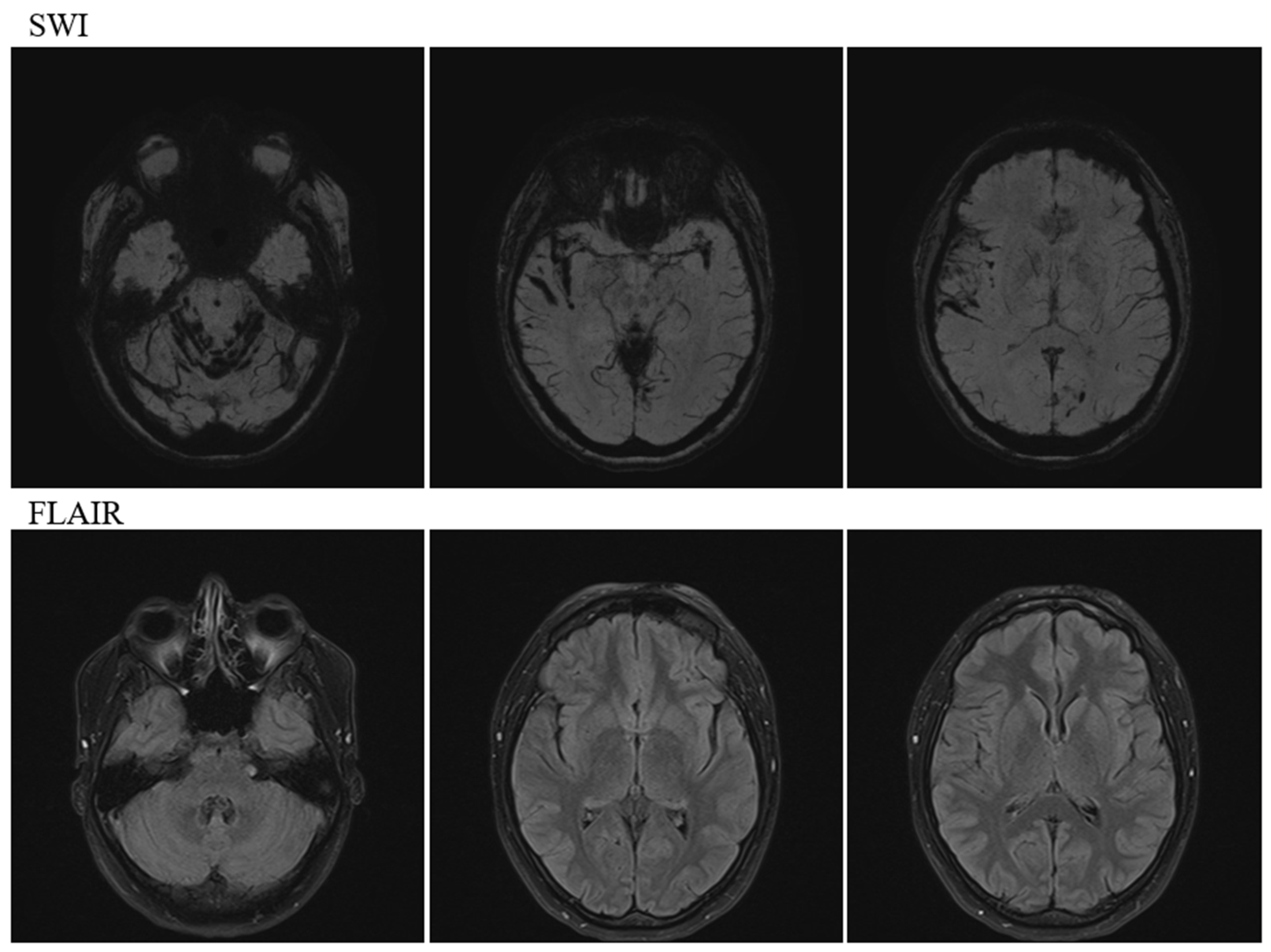
2. Case Description
3. Discussion
3.1. Causal Relationship between IIH and SS
3.2. Was SS Asymptomatic in This Case?
3.3. Did SS Affect the Clinical Course of IIH?
3.4. CSF Circulation in IIH with SS
3.5. Limitations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, M.T.M.; Bhatti, M.T.; Danesh-Meyer, H.V. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension: Pathophysiology, diagnosis and management. Rev. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2022, 95, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markey, K.A.; Mollan, S.P.; Jensen, R.H.; Sinclair, A.J. Understanding idiopathic intracranial hypertension: Mechanisms, management, and future directions. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wall, M.; George, D. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension. A prospective study of 50 patients. Brain 1991, 114 Pt 1A, 155–180. [Google Scholar]
- Kesler, A.; Stolovic, N.; Bluednikov, Y.; Shohat, T. The incidence of idiopathic intracranial hypertension in Israel from 2005 to 2007, results of a nationwide survey. Eur. J. Neurol. 2014, 21, 1055–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durcan, F.J.; Corbett, J.J.; Wall, M. The incidence of pseudotumor cerebri. Population studies in Iowa and Louisiana. Arch. Neurol. 1988, 45, 875–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radhakrishnan, K.; Ahlskog, J.E.; Cross, S.A.; Kurland, L.T.; O’Fallon, W.M. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerebri). Descriptive epidemiology in Rochester, Minn, 1976 to 1990. Arch. Neurol. 1993, 50, 78–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramaniam, S.; Fletcher, W.A. Obesity and weight loss in idiopathic intracranial hypertension: A narrative review. J. Neuroophthalmol. 2017, 37, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, M.; Turtzo, C.; Llinas, R.H. Superficial siderosis: A case report and review of the literature. Nat. Clin. Pract. Neurol. 2007, 3, 54–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, D.; Chatterjee, F.; Farmer, S.F.; Rudge, P.; McCarron, M.O.; Cowley, P.; Werring, D.J. Infratentorial superficial siderosis: Classification, diagnostic criteria, and rational investigation pathway. Ann. Neurol. 2017, 81, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N. Beyond superficial siderosis: Introducing “duropathies”. Neurology 2012, 78, 1992–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Miller, G.M.; Piepgras, D.G.; Mokri, B. A unifying hypothesis for a patient with superficial siderosis, low-pressure headache, intraspinal cyst, back pain, and prominent vascularity. J. Neurosurg. 2010, 113, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokri, B. Spontaneous intracranial hypotension. Continuum 2015, 21, 1086–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schievink, W.I.; Maya, M.; Moser, F.; Nuño, M. Long-term risks of persistent ventral spinal CSF leaks in SIH: Superficial siderosis and bibrachial amyotrophy. Neurology 2021, 97, e1964–e1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosmorsky, G.S. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension: Pseudotumor cerebri. Headache 2014, 54, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, S.; Hiratsuka, S.; Otani, T.; Ii, S.; Wada, S.; Oshima, M.; Nozaki, K.; Watanabe, Y. Usefulness of intravoxel incoherent motion MRI for visualizing slow cerebrospinal fluid motion. Fluids Barriers CNS 2023, 20, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidauer, S.; Neuhaus, E.; Hattingen, E. Cerebral superficial siderosis: Etiology, neuroradiological features and clinical findings. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2023, 33, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Harskamp, N.J.; Rudge, P.; Cipolotti, L. Cognitive and social impairments in patients with superficial siderosis. Brain 2005, 128 Pt 5, 1082–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uttner, I.; Tumani, H.; von Arnim, C.; Brettschneider, J. Cognitive impairment in superficial siderosis of the central nervous system: A case report. Cerebellum 2009, 8, 61–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, N.E.; Sheffield, S.; Hope, J.K. Superficial siderosis of the central nervous system: A late complication of cerebellar tumors. Neurology 1999, 52, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fearnley, J.M.; Stevens, J.M.; Rudge, P. Superficial siderosis of the central nervous system. Brain 1995, 118 Pt 4, 1051–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürk, K.; Skalej, M.; Dichgans, J. High prevalence of CSF-containing cysts in superficial hemosiderosis of the central nervous system. J. Neurol. 2001, 248, 1005–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Cohen-Gadol, A.A.; Wright, R.A.; Miller, G.M.; Piepgras, D.G.; Ahlskog, J.E. Superficial siderosis. Neurology 2006, 66, 1144–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savoiardo, M.; Maccagnano, E.; Pareyson, D.; Grisoli, M. Superficial siderosis. Neurology 2007, 68, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koeppen, A.H.; Michael, S.C.; Li, D.; Chen, Z.; Cusack, M.J.; Gibson, W.M.; Petrocine, S.V.; Qian, J. The pathology of superficial siderosis of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol. 2008, 116, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulioti, G.; Gray, L.; Amrhein, T.J. Popping the balloon: Abrupt onset of a spinal CSF leak and spontaneous intracranial hypotension in idiopathic intracranial hypertension, a case report. Headache 2022, 62, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.H.; Chen, H.C.; Tung, H.; Wu, Y.Y.; Chen, H.M.; Pan, K.J.; Cheng, D.C.; Chen, J.H.; Chen, C.C.C.; Chai, J.W.; et al. Noninvasive assessment of intracranial elastance and pressure in spontaneous intracranial hypotension by MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2018, 48, 1255–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffith, B.; Capobres, T.; Patel, S.C.; Marin, H.; Katramados, A.; Poisson, L.M. CSF pressure change in relation to opening pressure and CSF volume removed. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 39, 1185–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, S.K. Rebound intracranial hypertension. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2024, 28, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

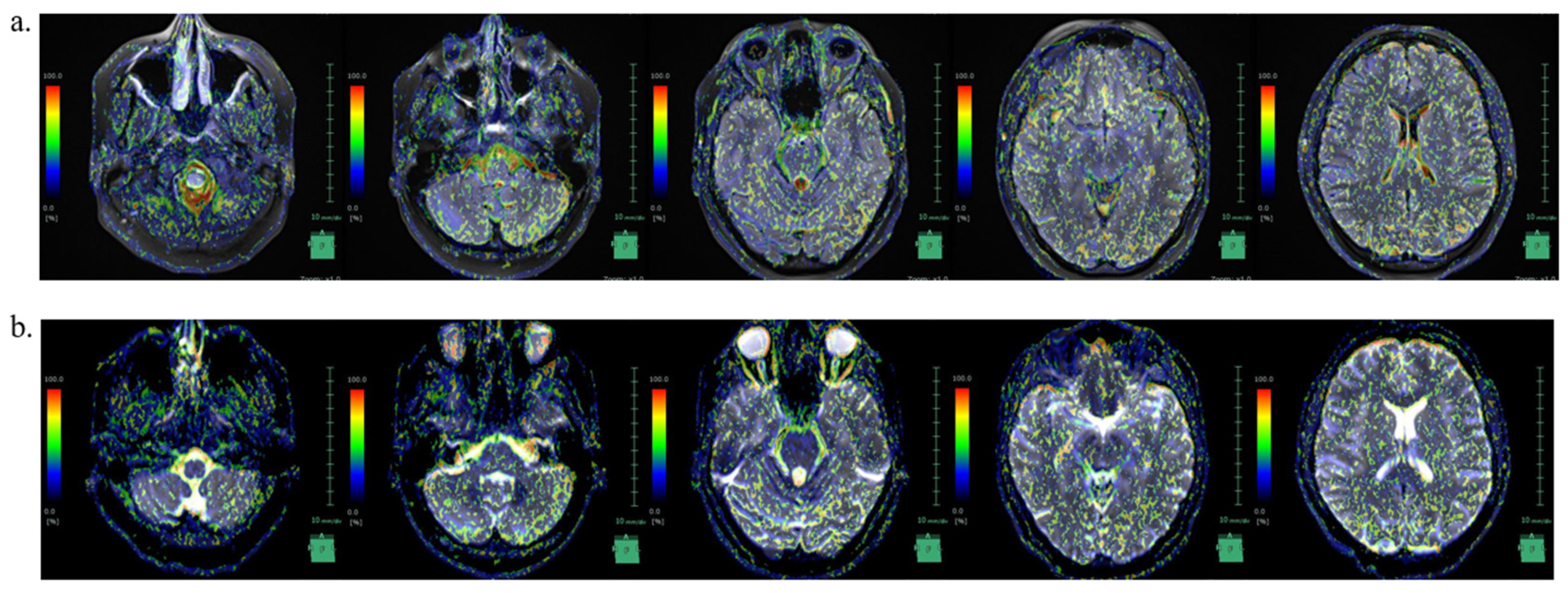
| IICP State | Decreased ICP State | |
|---|---|---|
| Foramen magnum | 70.6 | 86.9 |
| Right foramen of Luschka | 44.3 | 89.1 |
| Left foramen of Luschka | 49.2 | 91.9 |
| Foramen of Magendie | 96.1 | 90.4 |
| Medullary cistern | 75.5 | 52.6 |
| Fourth ventricle | 87.4 | 77.3 |
| Right cerebellopontine angle | 11.7 | 97.7 |
| Left cerebellopontine angle | 96.8 | 59.7 |
| Right inferior horn of lateral ventricles | 11.5 | 10.1 |
| Left inferior horn of lateral ventricles | 4.1 | 6.8 |
| Interpeduncular cistern | 66.1 | 34.4 |
| Subarachnoid space of right temporal lobe | 94.8 | 13.1 |
| Subarachnoid space of left temporal lobe | 33.3 | 22.1 |
| Right sylvian fissure | 93.8 | 4.1 |
| Left sylvian fissure | 97.3 | 4.8 |
| Third ventricle | 80.8 | 57.5 |
| Right anterior horn of lateral ventricles | 98.6 | 9.6 |
| Left anterior horn of lateral ventricles | 1 | 98.9 |
| Right foramen of Monro | 58.3 | 3.5 |
| Left foramen of Monro | 96.2 | 1.3 |
| Right body of lateral ventricles | 89.9 | 47 |
| Left body of lateral ventricles | 99.2 | 0.9 |
| Subarachnoid space of right frontal lobe | 94.3 | 47 |
| Subarachnoid space of left frontal lobe | 98.7 | 98.2 |
| Right central sulcus | 86.7 | 90.8 |
| Left central sulcus | 94.4 | 53.6 |
| Subarachnoid space of right parietal lobe | 69 | 96.5 |
| Subarachnoid space of left parietal lobe | 83.5 | 96 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Watanabe, S.; Shibata, Y.; Ishikawa, E. A Case of Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension Complicated with both Infratentorial and Supratentorial Cortical Superficial Siderosis: Novel Imaging Findings on Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Magnetic Resonance Imaging Offering Clues to Pathophysiology. Neurol. Int. 2024, 16, 701-708. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16040053
Watanabe S, Shibata Y, Ishikawa E. A Case of Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension Complicated with both Infratentorial and Supratentorial Cortical Superficial Siderosis: Novel Imaging Findings on Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Magnetic Resonance Imaging Offering Clues to Pathophysiology. Neurology International. 2024; 16(4):701-708. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16040053
Chicago/Turabian StyleWatanabe, Shinya, Yasushi Shibata, and Eiichi Ishikawa. 2024. "A Case of Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension Complicated with both Infratentorial and Supratentorial Cortical Superficial Siderosis: Novel Imaging Findings on Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Magnetic Resonance Imaging Offering Clues to Pathophysiology" Neurology International 16, no. 4: 701-708. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16040053
APA StyleWatanabe, S., Shibata, Y., & Ishikawa, E. (2024). A Case of Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension Complicated with both Infratentorial and Supratentorial Cortical Superficial Siderosis: Novel Imaging Findings on Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Magnetic Resonance Imaging Offering Clues to Pathophysiology. Neurology International, 16(4), 701-708. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16040053






