Safety and Efficacy of Low-Dose Eptifibatide for Tandem Occlusions in Acute Ischemic Stroke
Abstract
1. Introduction
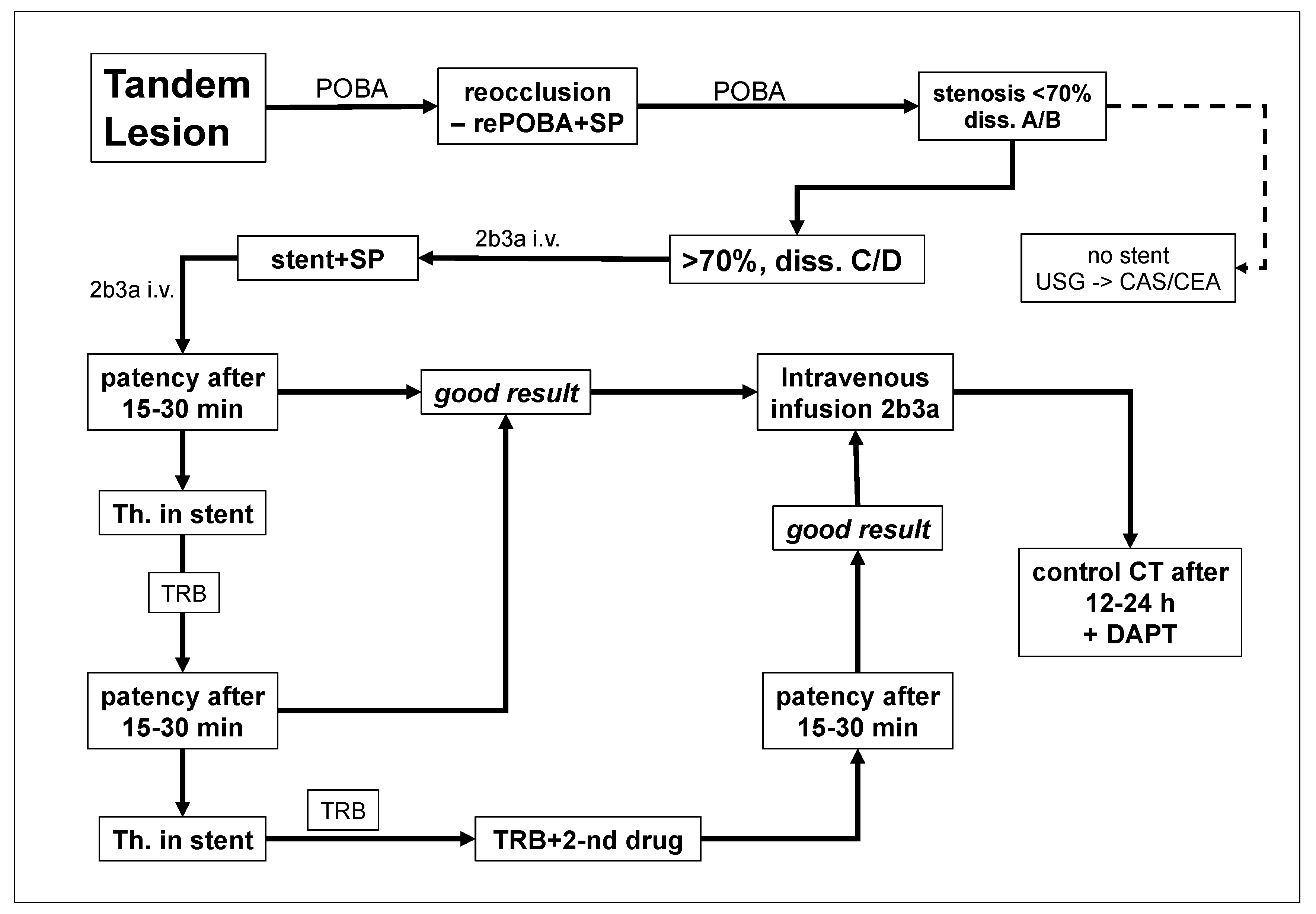
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Linfante, I.; Llinas, R.H.; Selim, M.; Chaves, C.; Kumar, S.; Parker, R.A.; Caplan, L.R.; Schlaug, G. Clinical and vascular outcome in internal carotid artery versus middle cerebral artery occlusions after intravenous tissue plasminogen activator. Stroke 2002, 33, 2066–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pechlaner, R.; Knoflach, M.; Matosevic, B.; Ruecker, M.; Schmidauer, C.; Kiechl, S.; Willeit, J. Recanalization of extracranial internal carotid artery occlusion after i.v. thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubiera, M.; Ribo, M.; Delgado-Mederos, R.; Santamarina, E.; Delgado, P.; Montaner, J.; Alvarez-Sabín, J.; Molina, C.A. Tandem internal carotid artery/middle cerebral artery occlusion: An independent predictor of poor outcome after systemic thrombolysis. Stroke 2006, 37, 2301–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkhemer, O.A.; Fransen, P.S.; Beumer, D.; Berg, L.A.V.D.; Lingsma, H.F.; Yoo, A.J.; Schonewille, W.J.; Vos, J.A.; Nederkoorn, P.J.; Wermer, M.J.H.; et al. A randomized trial of intraarterial treatment for acute ischemic stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, B.C.; Mitchell, P.J.; Kleinig, T.J.; Dewey, H.M.; Churilov, L.; Yassi, N.; Yan, B.; Dowling, R.J.; Parsons, M.W.; Oxley, T.J.; et al. Endovascular therapy for ischemic stroke with perfusion-imaging selection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1009–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, M.; Demchuk, A.M.; Menon, B.K.; Eesa, M.; Rempel, J.L.; Thornton, J.; Roy, D.; Jovin, T.G.; Willinsky, R.A.; Sapkota, B.L.; et al. Randomized assessment of rapid endovascular treatment of ischemic stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veunac, L.; Saliou, G.; Knebel, J.F.; Bartolini, B.; Puccinetlli, F.; Michel, P.; Haljdu, S.D. Revascularization of carotid artery occlusion using stenting versus non stenting in endovascular management of tandem occlusion stroke. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2022, 98, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovin, T.G.; Chamorro, A.; Cobo, E.; De Miquel, M.A.; Molina, C.A.; Rovira, A.; Román, L.S.; Serena, J.; Abilleira, S.; Ribo, M.; et al. Thrombectomy within 8 hours after symptom onset in ischemic stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2296–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, A.P.; Zaidat, O.O.; Liebeskind, D.S.; Yavagal, D.R.; Haussen, D.C.; Hellinger, F.R., Jr.; Jahan, R.; Jumaa, M.A.; Szeder, V.; Nogueira, R.G.; et al. Emergent management of tandem lesions in acute ischemic stroke: Analysis of the STRATIS registry. Stroke 2019, 50, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papanagiotou, P.; Haussen, D.C.; Turjman, F.; Labreuche, J.; Piotin, M.; Kastrup, A.; Steglich-Arnholm, H.; Holtmannspötter, M.; Taschner, C.; Eiden, S.; et al. (TITAN Investigators), Carotid stenting with antithrombotic agents and intracranial thrombectomy leads to the highest recanalization rate in patients with acute stroke with tandem lesions. ACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2018, 11, 1290–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallocha, M.; Chapot, R.; Nordmeyer, H.; Fiehler, J.; Weber, R.; Stracke, C.P. Treatment methods and early neurologic improvement after endovascular treatment of tandem occlusions in acute ischemic stroke. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gory, B.; Haussen, D.C.; Piotin, M.; Steglich-Arnholm, H.; Holtmannspötter, M.; Labreuche, J.; Kyheng, M.; Taschner, C.; Eiden, S.; Nogueira, R.G.; et al. Impact of intravenous thrombolysis and emergent carotid stenting on reperfusion and clinical outcomes in patients with acute stroke with tandem lesion treated with thrombectomy: A collaborative pooled analysis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2018, 25, 1115–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuberger, U.; Moteva, K.; Vollherbst, D.F.; Schönenberger, S.; Reiff, T.; Ringleb, P.A.; Bendszus, M.; Pfaff, J.A.R.; Möhlenbruch, M. Tandem occlusions in acute ischemic stroke: Impact of antithrombotic medication and complementary heparin on clinical outcome and stent patency. J. Neurointerv Surg. 2020, 12, 1088–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heck, D.; Brown, M. Carotid stenting and intracranial thrombectomy for treatment of acute stroke due to tandem occlusions with aggressive antiplatelet therapy may be associated with a high incidence of intracranial hemorrhage. J. Neurointerv Surg. 2015, 7, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, R.; Zinchenko, I.; Quenardelle, V.; Mihoc, D.; Manisor, M.; Richter, J.; Severac, F.; Simu, M.; Chibbaro, S.; Rouyer, O. Predictors and clinical impact of delayed stent thrombosis after thrombectomy for acute stroke with tandem lesions. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2019, 40, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, M.; Orlov, K.; Jensen, M.E.; Taylor, A.; Majoie, C.; Jayaraman, M.; Liu, J.; Milot, G.; Brouwer, P.; Yoshimura, S.; et al. A DELPHI consensus statement on antiplatelet management for intracranial stenting due to underlying atherosclerosis in the setting of mechanical thrombectomy. Neuroradiology 2021, 63, 627–632, Erratum in Neuroradiology 2021, 63, 1391–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poppe, A.Y.; Jacquin, G.; Roy, D.; Stapf, C.; Derex, L. Tandem carotid lesions in acute ischemic stroke: Mechanisms, therapeutic challenges, and future directions. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2020, 41, 1142–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, M.; Yoshimura, S.; Milot, G.; Fiehler, J.; Jayaraman, M.; Dorn, F.; Taylor, A.; Liu, J.; Albuquerque, F.; Jensen, M.; et al. Considerations for antiplatelet management of carotid stenting in the setting of mechanical thrombectomy: A Delphi consensus statement. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2020, 41, 2274–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osteraas, N.D.; Crowley, R.W.; Panos, N.; Dafer, R.M. Eptifibatide use following emergent carotid stenting in acute anterior circulation ischemic stroke with tandem occlusion. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2020, 29, 105021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasala, T.; Sattayaprasert, P.; Bhat, P.K.; Athappan, G.; Gandhi, S. Clinical and economic studies of eptifibatide in coronary stenting. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2014, 10, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jost, A.; Roels, C.; Brown, M.; Janjua, R.; Heck, D. Low-dose eptifibatide for tandem occlusion in stroke: Safety and carotid artery patency. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2021, 42, 738–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaoting, M.; Sun, X.; Cheng, H.; Burgin, W.S.; Luo, W.; Jia, W.; Liu, Y.; He, W.; Geng, X.; Zhu, L.; et al. Combined approach to eptifibatide and thrombectomy in acute ischemic stroke because of large vessel occlusion: A matched-control analysis. Stroke 2022, 53, 1580–1588. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, L.; Lin, J.; Deng, Y.; Li, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, W. Treatment of progressive ischemic stroke with low dose eptifibatide: A retrospective case control study. Exp. Ther. Med. 2023, 25, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, H. Efficacy outcomes and safety measures of intravenous tirofiban or eptifibatide for patients with acute ischemic stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2022, 53, 898–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marnat, G.; Mourand, I.; Eker, O.; Machi, P.; Arquizan, C.; Riquelme, C.; Ayrignac, X.; Bonafe, A.; Costalat, V. Endovascular management of tandem occlusion stroke related to internal carotid artery dissection using a distal to proximal approach: Insight from the RECOST Study. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2016, 37, 1281–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renu, A.; Blasco, J.; Laredo, C.; Llull, L.; Urra, X.; Obach, V.; López-Rueda, A.; Rudilosso, S.; Zarco, F.; González, E.; et al. Carotid stent occlusion after emergent stenting in acute ischemic stroke: Incidence, predictors and clinical relevance. Atherosclerosis 2020, 313, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waters, M.J.; Vargas, J.; Turk, A.; Chaudry, I.; Turner, R.D. Safety and efficacy of eptifibatide in acute ischemic stroke requiring extracranial carotid artery stenting. Interv. Neuroradiol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepp, D.; Berndt, M.; Mönch, S.; Ikenberg, B.; Wunderlich, S.; Maegerlein, C.; Zimmer, C.; Boeckh-Behrens, T.; Friedrich, B. Outcome and risk of hemorrhage in patients with tandem lesions after endovascular treatment: A propensity score-matched case-control study. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Patients Receiving Eptifibatide (n = 115) | Patients Not Receiving Eptifibatide (n = 33) | p Value (Fisher Exact Test) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years), mean (SD) | 65.0 (12.7) | 63.5 (14.1) | NS |
| Males/females—n (%) | 86/29 (75/25) | 28/5 (85/15) | NS |
| Medical history | |||
| hypertension—n (%) | 67 (58) | 18 (55) | NS |
| diabetes mellitus—n (%) | 42 (37) | 6 (18) | NS |
| coronary disease—n (%) | 30 (26) | 6 (18) | NS |
| history of myocardial infarction—n (%) | 19 (17) | 5 (15) | NS |
| NIHSS at admission—mean (SD) | 14 (5.3) | 16 (4.7) | NS |
| ASPECT at admission—mean (SD) | 8 (1.5) | 7 (1.4) | NS |
| Extracranial carotid lesion | |||
| Stenosis ≥ 80%—n (%) | 28 (24) | 9 (27) | NS |
| Occlusion—n (%) | 87 (76) | 24 (73) | NS |
| Intracranial occlusion location | |||
| Middle cerebral artery or anterior cerebral artery—n (%) | 78 (68) | 25 (76) | NS |
| Intracranial part of ICA—n (%) | 37 (32) | 8 (24) | NS |
| Intracranial thrombectomy technique | |||
| stent retriever—n (%) | 33 (29) | 13 (39) | NS |
| aspiration alone—n (%) | 82 (71) | 20 (61) | NS |
| Extracranial carotid procedure | |||
| Angioplasty alone | 4 | 33 | |
| Stenting | 111 | 0 | |
| Patients Receiving Eptifibatide (n = 115) | Patients Not Receiving Eptifibatide (n = 33) | Statistical Significance | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stent and/or ICA thrombosis | 6 (5.2%) | 5 (15.2%) | NS |
| Intracranial bleeding | 11 (9.5%) | 5 (15.2%) | NS |
| Intracranial bleeding or thrombosis | 16 (13.9%) | 9 (27.3%) | NS |
| 30-day mortality of any cause | 9 (7.8%) | 3 (9.1%) | NS |
| Mortality due to stroke | 4 (3.5%) | 2 (6.1%) | NS |
| Median duration of hospital stay duration (days) * | 9 (3–38) | 10 (4–57) | NS |
| Median score of the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale at baseline | 15 (2–23) | 16 (5–24) | NS |
| Median score of the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale at 30-day follow-up * | 3 (0–36) | 7 (0–21) | NS |
| Patients Receiving Eptifibatide (n = 115) | Patients Not Receiving Eptifibatide (n = 33) | |
|---|---|---|
| Patients without neurologic symptoms (NIHSS score: 0) | 26 (22.6%) | 3 (9.1%) |
| Patients with mild stroke symptoms (NIHSS score: 1–4) | 41 (35.7%) | 9 (27.3%) |
| Patients with moderate stroke symptoms (NIHSS score: 5–14) | 31 (27.0%) | 15 (45.5%) |
| Patients with severe stroke symptoms (NIHSS score: 15–24) | 7 (6.1%) | 3 (9.1%) |
| Patients with very severe stroke symptoms (NIHSS score: ≥25) | 1 (0.9%) | 0 |
| Death before 30-day follow-up | 9 (7.8%) | 3 (9.1%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Latacz, P.; Popiela, T.; Brzegowy, P.; Lasocha, B.; Kwiecień, K.; Simka, M. Safety and Efficacy of Low-Dose Eptifibatide for Tandem Occlusions in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Neurol. Int. 2024, 16, 253-262. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16010017
Latacz P, Popiela T, Brzegowy P, Lasocha B, Kwiecień K, Simka M. Safety and Efficacy of Low-Dose Eptifibatide for Tandem Occlusions in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Neurology International. 2024; 16(1):253-262. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16010017
Chicago/Turabian StyleLatacz, Paweł, Tadeusz Popiela, Paweł Brzegowy, Bartłomiej Lasocha, Krzysztof Kwiecień, and Marian Simka. 2024. "Safety and Efficacy of Low-Dose Eptifibatide for Tandem Occlusions in Acute Ischemic Stroke" Neurology International 16, no. 1: 253-262. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16010017
APA StyleLatacz, P., Popiela, T., Brzegowy, P., Lasocha, B., Kwiecień, K., & Simka, M. (2024). Safety and Efficacy of Low-Dose Eptifibatide for Tandem Occlusions in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Neurology International, 16(1), 253-262. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16010017








