Leukoaraiosis as a Predictor of Depression and Cognitive Impairment among Stroke Survivors: A Systematic Review
Abstract
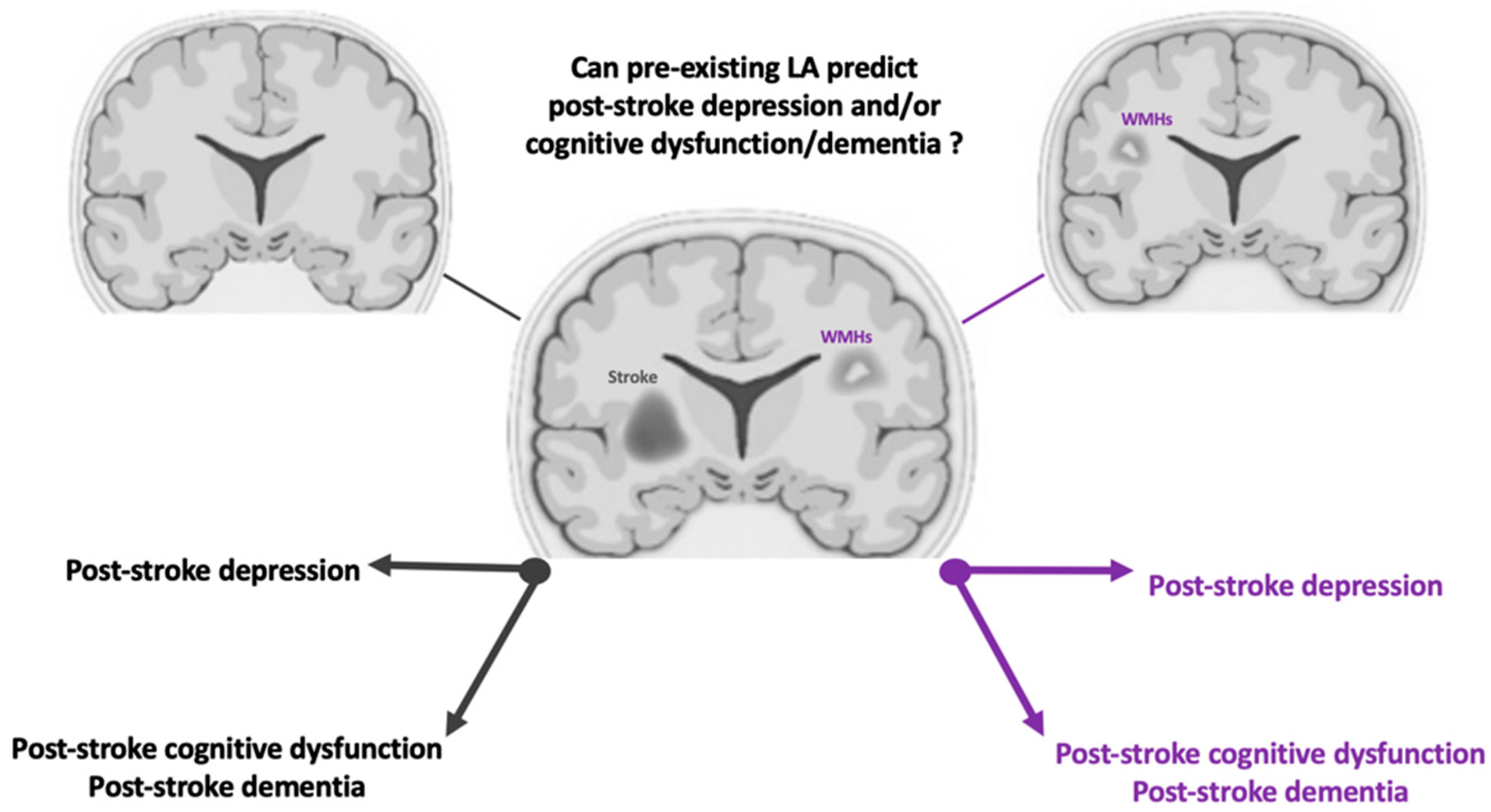
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Selection Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
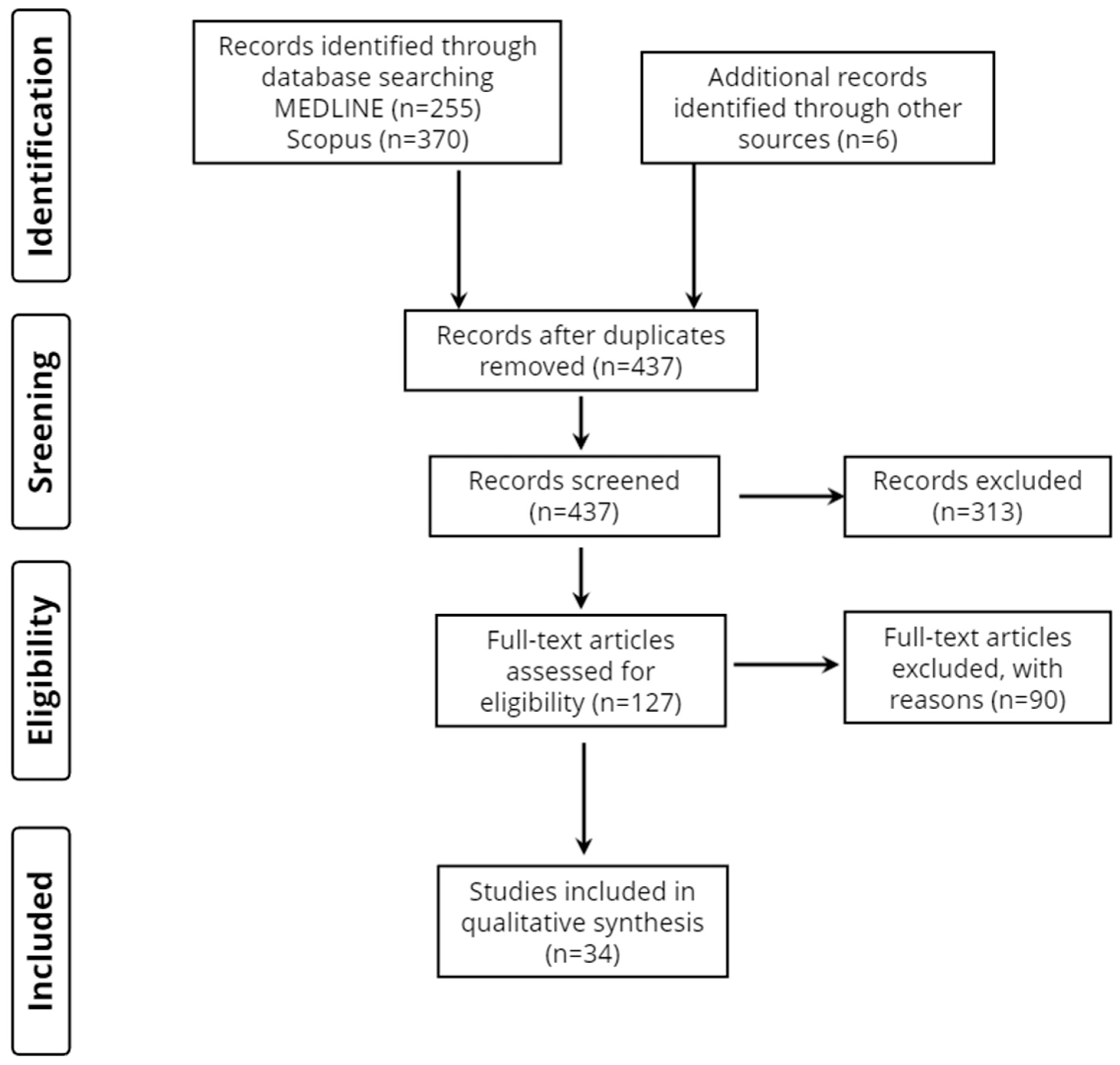
3.1. Database Searches and Quality Assessment of Included Studies
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Study Design
3.4. Stroke Patient Groups and Demographic Profiles
3.5. Reference Groups
3.6. Time of MRI Execution
4. Discussion
4.1. Depression and White Matter Hyperintensities
4.2. Cognitive Impairments and White Matter Hyperintensities
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACE | Addenbrooke’s Cognitive Examination |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| AIS | acute ischemic stroke |
| ARWMCS | Age-Related White Matter Change Scale |
| BMI | body mass index |
| cSVD | cerebral small vessel disease |
| CT | computed tomography |
| DES | executive dysfunction |
| DSM | Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders |
| DWI | Diffusion-weighted imaging |
| DWMHs | deep white matter hyperintensities |
| FLAIR | fluid-attenuated inversion recovery |
| GM | gray matter |
| HDS-R | Revised Hasegawa Dementia Rating Scale |
| ICH | intracerebral hemorrhage |
| LA | leukoaraiosis |
| MCI | mild cognitive impairment |
| MDD | major depression disorder |
| MADRS | Montgomery–Åsberg Depression Rating Scale |
| MMSE | Mini-Mental State Examination |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| NfL | neurofilament light chain |
| NIHSS | National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale |
| non-vaMCI | Non-vascular mild cognitive impairment |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses |
| PSD | post-stroke depression |
| PSDem | post-stroke dementia |
| PVS | periventricular space |
| SVD | small vessel disease |
| T2WI | T2-weighted imaging |
| TIA | transient ischemic attack |
| TSH | thyroid-stimulating hormone |
| VCI | vascular cognitive impairment |
| WM | white matter |
| WMHs | white matter hyperintensities |
| WMLs | white matter lesions |
References
- Benjamin, E.J.; Virani, S.S.; Callaway, C.W.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Chang, A.R.; Cheng, S.; Chiuve, S.E.; Cushman, M.; Delling, F.N.; Deo, R.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2018 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2018, 137, e67–e492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, G.A.; Mensah, G.A.; Johnson, C.O.; Addolorato, G.; Ammirati, E.; Baddour, L.M.; Barengo, N.C.; Beaton, A.Z.; Benjamin, E.J.; Benziger, C.P.; et al. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors, 1990–2019: Update From the GBD 2019 Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 2982–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grefkes, C.; Fink, G.R. Recovery from stroke: Current concepts and future perspectives. Neurol. Res. Pract. 2020, 2, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokkotis, C.; Giarmatzis, G.; Giannakou, E.; Moustakidis, S.; Tsatalas, T.; Tsiptsios, D.; Vadikolias, K.; Aggelousis, N. An Explainable Machine Learning Pipeline for Stroke Prediction on Imbalanced Data. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Yang, D.; Zeng, Y.; Wu, W. Risk Factors for Post-stroke Depression: A Meta-analysis. Front Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor-Rowan, M.; Momoh, O.; Ayerbe, L.; Evans, J.J.; Stott, D.J.; Quinn, T.J. Prevalence of pre-stroke depression and its association with post-stroke depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychol. Med. 2019, 49, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayerbe, L.; Ayis, S.; Wolfe, C.D.; Rudd, A.G. Natural history, predictors and outcomes of depression after stroke: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Psychiatry 2013, 202, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackett, M.L.; Pickles, K. Part I: Frequency of depression after stroke: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Int. J. Stroke 2014, 9, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, T.S.; Wium-Andersen, I.K.; Wium-Andersen, M.K.; Jorgensen, M.B.; Prescott, E.; Maartensson, S.; Kragh-Andersen, P.; Osler, M. Incidence of Depression After Stroke, and Associated Risk Factors and Mortality Outcomes, in a Large Cohort of Danish Patients. JAMA Psychiatry 2016, 73, 1032–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A.J.; Sheth, B.; Gill, J.; Yadegarfar, M.; Stubbs, B.; Yadegarfar, M.; Meader, N. Prevalence and predictors of post-stroke mood disorders: A meta-analysis and meta-regression of depression, anxiety and adjustment disorder. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry 2017, 47, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Mueller, C.; Li, Y.J.; Shen, W.D.; Stewart, R. Post stroke depression and risk of stroke recurrence and mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ageing Res. Rev. 2019, 50, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starkstein, S.E.; Hayhow, B.D. Treatment of Post-Stroke Depression. Curr. Treat. Options Neurol. 2019, 21, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano, S.; Domingo, J.; Rodriguez-Garcia, E.; Castro, M.D.; del Ser, T. Frequency of cognitive impairment without dementia in patients with stroke: A two-year follow-up study. Stroke 2007, 38, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blochl, M.; Meissner, S.; Nestler, S. Does depression after stroke negatively influence physical disability? A systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. J. Affect. Disord 2019, 247, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilari, K.; Needle, J.J.; Harrison, K.L. What are the important factors in health-related quality of life for people with aphasia? A systematic review. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2012, 93, S86–S95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoli, F.; Pompili, M.; Lillia, N.; Crocamo, C.; Salemi, G.; Clerici, M.; Carra, G. Rates and correlates of suicidal ideation among stroke survivors: A meta-analysis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg Psychiatry 2017, 88, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijajlovic, M.D.; Pavlovic, A.; Brainin, M.; Heiss, W.D.; Quinn, T.J.; Ihle-Hansen, H.B.; Hermann, D.M.; Assayag, E.B.; Richard, E.; Thiel, A.; et al. Post-stroke dementia—A comprehensive review. BMC Med. 2017, 15, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Kooten, F.; Koudstaal, P.J. Epidemiology of post-stroke dementia. Haemostasis 1998, 28, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seshadri, S.; Wolf, P.A. Lifetime risk of stroke and dementia: Current concepts, and estimates from the Framingham Study. Lancet Neurol. 2007, 6, 1106–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henon, H.; Pasquier, F.; Leys, D. Poststroke dementia. Cereb. Dis. 2006, 22, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, M. Leukoaraiosis. Pract. Neurol. 2008, 8, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Moon, G.J.; Bang, O.Y. Biomarkers for stroke. J. Stroke 2013, 15, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karatzetzou, S.; Tsiptsios, D.; Terzoudi, A.; Aggeloussis, N.; Vadikolias, K. Transcranial magnetic stimulation implementation on stroke prognosis. Neurol. Sci. 2022, 43, 873–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkantzios, A.; Tsiptsios, D.; Karatzetzou, S.; Kitmeridou, S.; Karapepera, V.; Giannakou, E.; Vlotinou, P.; Aggelousis, N.; Vadikolias, K. Stroke and Emerging Blood Biomarkers: A Clinical Prospective. Neurol. Int. 2022, 14, 784–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christidi, F.; Tsiptsios, D.; Fotiadou, A.; Kitmeridou, S.; Karatzetzou, S.; Tsamakis, K.; Sousanidou, A.; Psatha, E.A.; Karavasilis, E.; Seimenis, I.; et al. Diffusion Tensor Imaging as a Prognostic Tool for Recovery in Acute and Hyperacute Stroke. Neurol. Int. 2022, 14, 841–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazekas, F.; Barkhof, F.; Wahlund, L.O.; Pantoni, L.; Erkinjuntti, T.; Scheltens, P.; Schmidt, R. CT and MRI rating of white matter lesions. Cereb. Dis. 2002, 13, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christidi, F.; Tsiptsios, D.; Sousanidou, A.; Karamanidis, S.; Kitmeridou, S.; Karatzetzou, S.; Aitsidou, S.; Tsamakis, K.; Psatha, E.A.; Karavasilis, E.; et al. The Clinical Utility of Leukoaraiosis as a Prognostic Indicator in Ischemic Stroke Patients. Neurol. Int. 2022, 14, 952–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karatzetzou, S.; Tsiptsios, D.; Sousanidou, A.; Christidi, F.; Psatha, E.A.; Chatzaki, M.; Kitmeridou, S.; Giannakou, E.; Karavasilis, E.; Kokkotis, C.; et al. Elucidating the Role of Baseline Leukoaraiosis on Forecasting Clinical Outcome of Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients Undergoing Reperfusion Therapy. Neurol. Int. 2022, 14, 923–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuller, L.H.; Longstreth, W.T., Jr.; Arnold, A.M.; Bernick, C.; Bryan, R.N.; Beauchamp, N.J., Jr.; Cardiovascular Health Study Collaborative Research, G. White matter hyperintensity on cranial magnetic resonance imaging: A predictor of stroke. Stroke 2004, 35, 1821–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palumbo, V.; Boulanger, J.M.; Hill, M.D.; Inzitari, D.; Buchan, A.M.; Investigators, C. Leukoaraiosis and intracerebral hemorrhage after thrombolysis in acute stroke. Neurology 2007, 68, 1020–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groot, J.C.; De Leeuw, F.E.; Oudkerk, M.; Van Gijn, J.; Hofman, A.; Jolles, J.; Breteler, M.M. Periventricular cerebral white matter lesions predict rate of cognitive decline. Ann. Neurol. 2002, 52, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henon, H.; Vroylandt, P.; Durieu, I.; Pasquier, F.; Leys, D. Leukoaraiosis more than dementia is a predictor of stroke recurrence. Stroke 2003, 34, 2935–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, R.; Fazekas, F.; Kapeller, P.; Schmidt, H.; Hartung, H.P. MRI white matter hyperintensities: Three-year follow-up of the Austrian Stroke Prevention Study. Neurology 1999, 53, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Flier, W.M.; van Straaten, E.C.; Barkhof, F.; Verdelho, A.; Madureira, S.; Pantoni, L.; Inzitari, D.; Erkinjuntti, T.; Crisby, M.; Waldemar, G.; et al. Small vessel disease and general cognitive function in nondisabled elderly: The LADIS study. Stroke 2005, 36, 2116–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissela, B.; Lindsell, C.J.; Kleindorfer, D.; Alwell, K.; Moomaw, C.J.; Woo, D.; Flaherty, M.L.; Air, E.; Broderick, J.; Tsevat, J. Clinical prediction of functional outcome after ischemic stroke: The surprising importance of periventricular white matter disease and race. Stroke 2009, 40, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexopoulos, G.S.; Kiosses, D.N.; Klimstra, S.; Kalayam, B.; Bruce, M.L. Clinical presentation of the "depression-executive dysfunction syndrome" of late life. Am. J. Geriatr Psychiatry 2002, 10, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Firbank, M.J.; Teodorczuk, A.; van der Flier, W.M.; Gouw, A.A.; Wallin, A.; Erkinjuntti, T.; Inzitari, D.; Wahlund, L.O.; Pantoni, L.; Poggesi, A.; et al. Relationship between progression of brain white matter changes and late-life depression: 3-year results from the LADIS study. Br. J. Psychiatry 2012, 201, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debette, S.; Markus, H.S. The clinical importance of white matter hyperintensities on brain magnetic resonance imaging: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2010, 341, c3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloppenborg, R.P.; Nederkoorn, P.J.; Geerlings, M.I.; van den Berg, E. Presence and progression of white matter hyperintensities and cognition: A meta-analysis. Neurology 2014, 82, 2127–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inzitari, D.; Simoni, M.; Pracucci, G.; Poggesi, A.; Basile, A.M.; Chabriat, H.; Erkinjuntti, T.; Fazekas, F.; Ferro, J.M.; Hennerici, M.; et al. Risk of rapid global functional decline in elderly patients with severe cerebral age-related white matter changes: The LADIS study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2007, 167, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, L.; Hoo, Z.L.; Yan, T.Z.; Wardlaw, J.; Quinn, T.J. Prevalence of dementia in ischaemic or mixed stroke populations: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg Psychiatry 2022, 93, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wang, J.; Xia, Y.; Jiang, S.; Xu, P.; Tao, C.; Sun, W.; Liu, X. Thyroid Function Affects the Risk of Post-stroke Depression in Patients With Acute Lacunar Stroke. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 792843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaroonpipatkul, C.; Onwanna, J.; Tunvirachaisakul, C.; Jittapiromsak, N.; Rakvongthai, Y.; Chutinet, A.; Supasitthumrong, T.; Maes, M. Depressive symptoms due to stroke are strongly predicted by the volume and location of the cerebral infarction, white matter hyperintensities, hypertension, and age: A precision nomothetic psychiatry analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2022, 309, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Chen, L.; Ma, L.; Diao, S.; Qin, Y.; Fang, Q.; Li, T. A new nomogram including total cerebral small vessel disease burden for individualized prediction of early-onset depression in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 922530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douven, E.; Staals, J.; Freeze, W.M.; Schievink, S.H.; Hellebrekers, D.M.; Wolz, R.; Jansen, J.F.; van Oostenbrugge, R.J.; Verhey, F.R.; Aalten, P.; et al. Imaging markers associated with the development of post-stroke depression and apathy: Results of the Cognition and Affect after Stroke—A Prospective Evaluation of Risks study. Eur. Stroke J. 2020, 5, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, K.Y.; Kang, H.J.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, J.T.; Park, M.S.; Cho, K.H.; Kim, J.M. Associations of white matter hyperintensities with poststroke depression: A 1-year longitudinal study. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2019, 34, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnes-Vendrell, A.; Deus, J.; Molina-Seguin, J.; Pifarre, J.; Purroy, F. Depression and Apathy After Transient Ischemic Attack or Minor Stroke: Prevalence, Evolution and Predictors. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlovic, A.M.; Pekmezovic, T.; Zidverc Trajkovic, J.; Svabic Medjedovic, T.; Veselinovic, N.; Radojicic, A.; Mijajlovic, M.; Tomic, G.; Jovanovic, Z.; Norton, M.; et al. Baseline characteristic of patients presenting with lacunar stroke and cerebral small vessel disease may predict future development of depression. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2016, 31, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanislav, C.; Kropp, P.; Grittner, U.; Holzhausen, M.; Fazekas, F.; Jungehulsing, G.J.; Tatlisumak, T.; von Sarnowski, B.; Putaala, J.; Huber, R.; et al. Clinically relevant depressive symptoms in young stroke patients—Results of the sifap1 study. Neuroepidemiology 2015, 44, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruhwirth, V.; Enzinger, C.; Fandler-Hofler, S.; Kneihsl, M.; Eppinger, S.; Ropele, S.; Schmidt, R.; Gattringer, T.; Pinter, D. Baseline white matter hyperintensities affect the course of cognitive function after small vessel disease-related stroke: A prospective observational study. Eur. J. Neurol. 2021, 28, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasi, M.; Sugita, L.; Xiong, L.; Charidimou, A.; Boulouis, G.; Pongpitakmetha, T.; Singh, S.; Kourkoulis, C.; Schwab, K.; Greenberg, S.M.; et al. Association of Cerebral Small Vessel Disease and Cognitive Decline After Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Neurology 2021, 96, e182–e192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Li, Q.; Qin, L.; He, Y.; Luo, X.; Lan, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.M. Combination of Serum Neurofilament Light Chain Levels and MRI Markers to Predict Cognitive Function in Ischemic Stroke. Neurorehabil. Neural. Repair. 2021, 35, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, P.S.; Lee, K.P.; Lin, P.Y.; Su, H.C.; Yu, R.L.; Tsai, K.J.; Lin, S.H.; Chen, C.H. Factors Associated with Cognitive Outcomes After First-Ever Ischemic Stroke: The Impact of Small Vessel Disease Burden and Neurodegeneration. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2021, 83, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appleton, J.P.; Woodhouse, L.J.; Adami, A.; Becker, J.L.; Berge, E.; Cala, L.A.; Casado, A.M.; Caso, V.; Christensen, H.K.; Dineen, R.A.; et al. Imaging markers of small vessel disease and brain frailty, and outcomes in acute stroke. Neurology 2020, 94, e439–e452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suda, S.; Nishimura, T.; Ishiwata, A.; Muraga, K.; Aoki, J.; Kanamaru, T.; Suzuki, K.; Sakamoto, Y.; Katano, T.; Nishiyama, Y.; et al. Early Cognitive Impairment after Minor Stroke: Associated Factors and Functional Outcome. J. Stroke Cereb. Dis. 2020, 29, 104749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatawara, C.; Guevarra, A.; Ng, K.P.; Chander, R.; Kandiah, N. Interactions Between Acute Infarcts and Cerebrovascular Pathology Predict Poststroke Dementia. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2020, 34, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhi, N.; Geng, J.; Cao, W.; Yu, L.; Mi, J.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, Q.; Wen, W.; et al. Structural brain network measures are superior to vascular burden scores in predicting early cognitive impairment in post stroke patients with small vessel disease. Neuroimage Clin. 2019, 22, 101712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molad, J.; Hallevi, H.; Korczyn, A.D.; Kliper, E.; Auriel, E.; Bornstein, N.M.; Ben Assayag, E. Vascular and Neurodegenerative Markers for the Prediction of Post-Stroke Cognitive Impairment: Results from the TABASCO Study. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2019, 70, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Chen, Y.K.; Liu, Y.L.; Mok, V.C.T.; Ungvari, G.S.; Chu, W.C.W.; Seo, S.W.; Tang, W.K. Cerebral Small Vessel Disease Burden Is Associated With Accelerated Poststroke Cognitive Decline: A 1-Year Follow-Up Study. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry Neurol. 2019, 32, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamboni, G.; Griffanti, L.; Mazzucco, S.; Pendlebury, S.T.; Rothwell, P.M. Age-dependent association of white matter abnormality with cognition after TIA or minor stroke. Neurology 2019, 93, e272–e282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawe, R.L.; Findlater, S.E.; Kenzie, J.M.; Hill, M.D.; Scott, S.H.; Dukelow, S.P. Differential Impact of Acute Lesions Versus White Matter Hyperintensities on Stroke Recovery. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e009360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puy, L.; Barbay, M.; Roussel, M.; Canaple, S.; Lamy, C.; Arnoux, A.; Leclercq, C.; Mas, J.L.; Tasseel-Ponche, S.; Constans, J.M.; et al. Neuroimaging Determinants of Poststroke Cognitive Performance. Stroke 2018, 49, 2666–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatawara, C.; Ng, K.P.; Chander, R.; Kandiah, N. Associations between lesions and domain-specific cognitive decline in poststroke dementia. Neurology 2018, 91, e45–e54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Divya, K.P.; Menon, R.N.; Varma, R.P.; Sylaja, P.N.; Thomas, B.; Kesavadas, C.; Sunitha, J.; Lekha, V.S.; Deepak, S. Post-stroke cognitive impairment—A cross-sectional comparison study between mild cognitive impairment of vascular and non-vascular etiology. J. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 372, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, W.W.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Q.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.S.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, L.; Deng, Y.; Xu, Q. Deep microbleeds and periventricular white matter disintegrity are independent predictors of attention/executive dysfunction in non-dementia patients with small vessel disease. Int. Psychogeriatr. 2017, 29, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molad, J.; Kliper, E.; Korczyn, A.D.; Ben Assayag, E.; Ben Bashat, D.; Shenhar-Tsarfaty, S.; Aizenstein, O.; Shopin, L.; Bornstein, N.M.; Auriel, E. Only White Matter Hyperintensities Predicts Post-Stroke Cognitive Performances Among Cerebral Small Vessel Disease Markers: Results from the TABASCO Study. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2017, 56, 1293–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivakumar, L.; Riaz, P.; Kate, M.; Jeerakathil, T.; Beaulieu, C.; Buck, B.; Camicioli, R.; Butcher, K. White matter hyperintensity volume predicts persistent cognitive impairment in transient ischemic attack and minor stroke. Int. J. Stroke 2017, 12, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ren, W.; Shao, B.; Xu, H.; Cheng, J.; Wang, Q.; Gu, Y.; Zhu, B.; He, J. Leukoaraiosis is Associated with Worse Short-Term Functional and Cognitive Recovery after Minor Stroke. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2017, 57, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandzia, J.L.; Smith, E.E.; Horton, M.; Hanly, P.; Barber, P.A.; Godzwon, C.; Donaldson, E.; Asdaghi, N.; Patel, S.; Coutts, S.B. Imaging and Baseline Predictors of Cognitive Performance in Minor Ischemic Stroke and Patients With Transient Ischemic Attack at 90 Days. Stroke 2016, 47, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moulin, S.; Labreuche, J.; Bombois, S.; Rossi, C.; Boulouis, G.; Henon, H.; Duhamel, A.; Leys, D.; Cordonnier, C. Dementia risk after spontaneous intracerebral haemorrhage: A prospective cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedictus, M.R.; Hochart, A.; Rossi, C.; Boulouis, G.; Henon, H.; van der Flier, W.M.; Cordonnier, C. Prognostic Factors for Cognitive Decline After Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Stroke 2015, 46, 2773–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumral, E.; Gulluoglu, H.; Alakbarova, N.; Deveci, E.E.; Colak, A.Y.; Caginda, A.D.; Evyapan, D.; Orman, M. Cognitive Decline in Patients with Leukoaraiosis Within 5 Years after Initial Stroke. J. Stroke Cereb. Dis. 2015, 24, 2338–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, Y.; Deguchi, K.; Yamashita, T.; Morihara, R.; Matsuzono, K.; Kawahara, Y.; Sato, K.; Kono, S.; Hishikawa, N.; Ohta, Y.; et al. High Incidence of Dementia Conversion than Stroke Recurrence in Poststroke Patients of Late Elder Society. J. Stroke Cereb. Dis. 2015, 24, 1621–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douven, E.; Aalten, P.; Staals, J.; Schievink, S.H.J.; van Oostenbrugge, R.J.; Verhey, F.R.J.; Kohler, S. Co-occurrence of depressive symptoms and executive dysfunction after stroke: Associations with brain pathology and prognosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2018, 89, 859–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexopoulos, G.S.; Meyers, B.S.; Young, R.C.; Kalayam, B.; Kakuma, T.; Gabrielle, M.; Sirey, J.A.; Hull, J. Executive dysfunction and long-term outcomes of geriatric depression. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2000, 57, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.T.; Park, M.S.; Yoon, G.J.; Jung, H.J.; Choi, K.H.; Nam, T.S.; Lee, S.H.; Choi, S.M.; Kim, B.C.; Kim, M.K.; et al. White matter hyperintensity as a factor associated with delayed mood disorders in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Eur. Neurol. 2011, 66, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iosifescu, D.V.; Renshaw, P.F.; Dougherty, D.D.; Lyoo, I.K.; Lee, H.K.; Fraguas, R.; Cassano, P.; Nierenberg, A.A.; Fava, M. Major depressive disorder with anger attacks and subcortical MRI white matter hyperintensities. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 2007, 195, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharpe, M.; Hawton, K.; Seagroatt, V.; Bamford, J.; House, A.; Molyneux, A.; Sandercock, P.; Warlow, C. Depressive disorders in long-term survivors of stroke. Associations with demographic and social factors, functional status, and brain lesion volume. Br. J. Psychiatry 1994, 164, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotila, M.; Numminen, H.; Waltimo, O.; Kaste, M. Depression after stroke: Results of the FINNSTROKE Study. Stroke 1998, 29, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackett, M.L.; Anderson, C.S.; House, A.O. Management of depression after stroke: A systematic review of pharmacological therapies. Stroke 2005, 36, 1098–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.M.; Stewart, R.; Kim, S.W.; Shin, I.S.; Kim, J.T.; Park, M.S.; Park, S.W.; Kim, Y.H.; Cho, K.H.; Yoon, J.S. Associations of cytokine gene polymorphisms with post-stroke depression. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2012, 13, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ryck, A.; Fransen, E.; Brouns, R.; Geurden, M.; Peij, D.; Marien, P.; De Deyn, P.P.; Engelborghs, S. Poststroke depression and its multifactorial nature: Results from a prospective longitudinal study. J. Neurol. Sci. 2014, 347, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muresanu, D.F.; Popa-Wagner, A.; Stan, A.; Buga, A.M.; Popescu, B.O. The vascular component of Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Neurovasc. Res. 2014, 11, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forlani, C.; Morri, M.; Ferrari, B.; Dalmonte, E.; Menchetti, M.; De Ronchi, D.; Atti, A.R. Prevalence and gender differences in late-life depression: A population-based study. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry. 2014, 22, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutlubaev, M.A.; Hackett, M.L. Part II: Predictors of depression after stroke and impact of depression on stroke outcome: An updated systematic review of observational studies. Int. J. Stroke 2014, 9, 1026–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longstreth, W.T., Jr.; Arnold, A.M.; Beauchamp, N.J., Jr.; Manolio, T.A.; Lefkowitz, D.; Jungreis, C.; Hirsch, C.H.; O’Leary, D.H.; Furberg, C.D. Incidence, manifestations, and predictors of worsening white matter on serial cranial magnetic resonance imaging in the elderly: The Cardiovascular Health Study. Stroke 2005, 36, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, R.; Massaro, J.M.; Wolf, P.A.; Young, M.E.; Beiser, A.; Seshadri, S.; D’Agostino, R.B.; DeCarli, C. Association of white matter hyperintensity volume with decreased cognitive functioning: The Framingham Heart Study. Arch. Neurol. 2006, 63, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgakis, M.K.; Fang, R.; During, M.; Wollenweber, F.A.; Bode, F.J.; Stosser, S.; Kindlein, C.; Hermann, P.; Liman, T.G.; Nolte, C.H.; et al. Cerebral small vessel disease burden and cognitive and functional outcomes after stroke: A multicenter prospective cohort study. Alzheimers Dement. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantoni, L. Cerebral small vessel disease: From pathogenesis and clinical characteristics to therapeutic challenges. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazekas, F.; Kleinert, R.; Roob, G.; Kleinert, G.; Kapeller, P.; Schmidt, R.; Hartung, H.P. Histopathologic analysis of foci of signal loss on gradient-echo T2*-weighted MR images in patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: Evidence of microangiopathy-related microbleeds. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1999, 20, 637–642. [Google Scholar]
- Pendlebury, S.T.; Rothwell, P.M. Prevalence, incidence, and factors associated with pre-stroke and post-stroke dementia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2009, 8, 1006–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorelick, P.B.; Scuteri, A.; Black, S.E.; Decarli, C.; Greenberg, S.M.; Iadecola, C.; Launer, L.J.; Laurent, S.; Lopez, O.L.; Nyenhuis, D.; et al. Vascular contributions to cognitive impairment and dementia: A statement for healthcare professionals from the american heart association/american stroke association. Stroke 2011, 42, 2672–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbaz, A.; Vicente-Vytopilova, P.; Tavernier, B.; Sabia, S.; Dumurgier, J.; Mazoyer, B.; Singh-Manoux, A.; Tzourio, C. Motor function in the elderly: Evidence for the reserve hypothesis. Neurology 2013, 81, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kliper, E.; Ben Assayag, E.; Tarrasch, R.; Artzi, M.; Korczyn, A.D.; Shenhar-Tsarfaty, S.; Aizenstein, O.; Hallevi, H.; Mike, A.; Shopin, L.; et al. Cognitive state following stroke: The predominant role of preexisting white matter lesions. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, R.G.; Spalletta, G. Poststroke depression: A review. Can. J. Psychiatry 2010, 55, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivakumar, L.; Kate, M.; Jeerakathil, T.; Camicioli, R.; Buck, B.; Butcher, K. Serial montreal cognitive assessments demonstrate reversible cognitive impairment in patients with acute transient ischemic attack and minor stroke. Stroke 2014, 45, 1709–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortamais, M.; Artero, S.; Ritchie, K. Cerebral white matter hyperintensities in the prediction of cognitive decline and incident dementia. Int. Rev. Psychiatry 2013, 25, 686–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardlaw, J.M.; Smith, E.E.; Biessels, G.J.; Cordonnier, C.; Fazekas, F.; Frayne, R.; Lindley, R.I.; O’Brien, J.T.; Barkhof, F.; Benavente, O.R.; et al. Neuroimaging standards for research into small vessel disease and its contribution to ageing and neurodegeneration. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 822–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croall, I.D.; Lohner, V.; Moynihan, B.; Khan, U.; Hassan, A.; O’Brien, J.T.; Morris, R.G.; Tozer, D.J.; Cambridge, V.C.; Harkness, K.; et al. Using DTI to assess white matter microstructure in cerebral small vessel disease (SVD) in multicentre studies. Clin. Sci. 2017, 131, 1361–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordonnier, C.; Leys, D.; Dumont, F.; Deramecourt, V.; Bordet, R.; Pasquier, F.; Henon, H. What are the causes of pre-existing dementia in patients with intracerebral haemorrhages? Brain 2010, 133, 3281–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Database | Search Strategy |
|---|---|
| PubMed | (“leukoaraiosis” OR “white matter hyperintensities” OR “WMHs” OR “small vessel disease”) AND (“poststroke” OR “stroke outcome”) AND (“cognition” OR “dementia” OR “depression”) |
| Scopus | (“leukoaraiosis” OR “white matter hyperintensities” OR “WMHs” OR “small vessel disease”) AND (“poststroke” OR “stroke outcome”) AND (“cognition” OR “dementia” OR “depression”) |
| First Author (Year) | Type of Stroke, Study Design, Follow-Up Time, Participants (n) | Patients’ Demographics: Age (Years), Gender (M/F), Education (Years/Level), Marital/Occupational Status, Income, BMI | Time of MRI Acquisition/Leukoaraiosis or WHM Assessment | Clinical and/or Psychometric Scales | Main Results | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Guo (2022) [42] |
|
|
| NIHSS on admission and HAMD-24 and the Chinese version of the Lubben Social Network Scale one week post-stroke |
|
| 2. | Jaroonpipatkul (2022) [43] |
|
|
| NIHSS at baseline and at 3 months, mRS at baseline, and Montgomery–Åsberg Depression Rating Scale at 3 months |
|
| 3. | Zhou (2022) [44] |
|
|
| NIHSS and BI at baseline and MMSE and HAMD-17 at follow-up |
|
| 4. | Douven (2020) [45] |
|
|
| MINI and Apathy Evaluation Scale |
|
| 5. | Bae (2019) [46] |
|
|
| NIHSS, BI, MMSE, and MINI on admission and at 1 year follow-up |
|
| 6. | Carnes-Vendrell (2019) [47] |
|
|
| NIHSS, BI, and mRS at baseline and the Beck Depression Inventory and Montgomery–Åsberg Depression Rating Scale |
|
| 7. | Pavlovic (2016) [48] |
|
|
| mRS |
|
| 8. | Tanislav (2015) [49] |
|
|
| NIHSS at baseline and BDI |
|
| First Author (Year) | Type of Stroke, Study Design, Follow-Up Time, Participants (n) | Patients’ Demographics: Age (Years), Gender (M/F), Education (Years/Level), Marital/Occupational Status, Income, BMI | Time of MRI Acquisition/Leukoaraiosis or WHM Assessment | Clinical and/or Psychometric Scales | Main Results | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Georgakis (2022) [49] |
|
|
| NIHSS, mRS, GCS, MMSE, and MoCA at baseline and mRS, a global functional scale focused on motor recovery, BI, and the IADLs at follow-up |
|
| 2. | Fruhwirth (2021) [50] |
|
|
| NIHSS score and mRS |
|
| 3. | Pasi (2021) [51] |
|
|
| NIHSS and IQCODE at baseline |
|
| 4. | Peng (2021) [52] |
|
|
| NIHSS, mRS, and FIM cognitive sub-score |
|
| 5. | Sung (2021) [53] |
|
|
| NIHSS at baseline and MoCA, WAIS-III, WMS-III, Semantic Association of Verbal Fluency Test, and the WCST at 3 months and 1 year |
|
| 6. | Appleton (2020) [54] |
|
|
| NIHSS at baseline, mRS at day 90, t-MMSE, TICS-M, and verbal fluency (animal naming) |
|
| 7. | Suda (2020) [55] |
|
|
| NIHSS at admission, MoCA within 5 days of onset, mRS at discharge, and IQCODE pre-stroke |
|
| 8. | Yatawara (2020) [56] * |
|
|
| mRS, IQCODE, and MoCA |
|
| 9. | Du (2019) [57] |
|
|
| MMSE, MoCA, TMT A and B, Stroop Color and Word Test, ROCFT, Boston Naming Test, and HAM-D |
|
| 10. | Molad (2019) [58] |
|
|
| NIHSS, MoCA, and NeuroTrax computerized cognitive testing |
|
| 11. | Liang (2019) [59] |
|
|
| MMSE at 3, 9, and 15 months |
|
| 12. | Zamboni (2019) [60] |
|
|
| NIHSS at baseline and MoCA at 1, 3, 6, 12, 24, and 60 months |
|
| 13. | Hawe (2018) [61] |
|
|
| Chedoke–McMaster Stroke Assessment, Thumb Localizing Test, Behavioral Inattention Test, MoCA, and FIM |
|
| 14. | Puy (2018) [62] |
|
|
| NIHSS, mRS, MMSE, MoCA, and optimized GCS |
|
| 15. | Yatawara (2018) [63] * |
|
|
| IQCODE, PHQ-9, and mRS |
|
| 16. | Divya (2017) [64] |
|
|
| NIHSS, mRS, Malayalam version of Addenbrooke’s Cognitive Examination, WMS verbal and visual subsets, RAVLT, Delayed Matching to Sample Task 48, attention span, TMT A and B, WCST, HADS, and Scale for the Instrumental Activities of Daily Living |
|
| 17. | Cao (2017) [65] |
|
|
| NIHSS, HDRS, Trail-Making Test, Stroop Color and Word Test, category verbal fluency test, RAVLT, BNT, and ROCFT |
|
| 18. | Molad (2017) [66] |
|
|
| NIHSS and NeuroTraxTM computerized cognitive testing |
|
| 19. | Sivakumar (2017) [67] |
|
|
| NIHSS, MoCA, mRS, and GDS |
|
| 20. | Zhang (2017) [68] |
|
|
| NIHSS and MMSE at baseline and at 30 days |
|
| 21. | Mandzia (2016) [69] |
|
|
| mRS and CES-D |
|
| 22. | Moulin (2016) [70] ** |
|
|
| IQCODE, mRS, NIHSS, and MMSE |
|
| 23. | Benedictus (2015) [71] ** |
|
|
| IQCODE, mRS, MADRS, and MMSE |
|
| 24. | Kumral (2015) [72] |
|
|
| NIHSS at admission |
|
| 25. | Nakano (2015) [73] |
|
|
| MMSE, Revised Hasegawa Dementia Rating Scale, FAB, GDS, and apathy scale |
|
| First Author (Year) | Type of Stroke, Study Design, Follow-Up Time, Participants (n) | Patients’ Demographics: Age (Years), Gender (M/F), Education (Years/Level), Marital/Occupational Status, Income, BMI | Time of MRI Acquisition/Leukoaraiosis or WHM Assessment | Clinical and/or Psychometric Scales | Main Results | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Douven (2018) [74] |
|
|
| MMSE |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tziaka, E.; Christidi, F.; Tsiptsios, D.; Sousanidou, A.; Karatzetzou, S.; Tsiakiri, A.; Doskas, T.K.; Tsamakis, K.; Retzepis, N.; Konstantinidis, C.; et al. Leukoaraiosis as a Predictor of Depression and Cognitive Impairment among Stroke Survivors: A Systematic Review. Neurol. Int. 2023, 15, 238-272. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint15010016
Tziaka E, Christidi F, Tsiptsios D, Sousanidou A, Karatzetzou S, Tsiakiri A, Doskas TK, Tsamakis K, Retzepis N, Konstantinidis C, et al. Leukoaraiosis as a Predictor of Depression and Cognitive Impairment among Stroke Survivors: A Systematic Review. Neurology International. 2023; 15(1):238-272. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint15010016
Chicago/Turabian StyleTziaka, Eftychia, Foteini Christidi, Dimitrios Tsiptsios, Anastasia Sousanidou, Stella Karatzetzou, Anna Tsiakiri, Triantafyllos K. Doskas, Konstantinos Tsamakis, Nikolaos Retzepis, Christos Konstantinidis, and et al. 2023. "Leukoaraiosis as a Predictor of Depression and Cognitive Impairment among Stroke Survivors: A Systematic Review" Neurology International 15, no. 1: 238-272. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint15010016
APA StyleTziaka, E., Christidi, F., Tsiptsios, D., Sousanidou, A., Karatzetzou, S., Tsiakiri, A., Doskas, T. K., Tsamakis, K., Retzepis, N., Konstantinidis, C., Kokkotis, C., Serdari, A., Aggelousis, N., & Vadikolias, K. (2023). Leukoaraiosis as a Predictor of Depression and Cognitive Impairment among Stroke Survivors: A Systematic Review. Neurology International, 15(1), 238-272. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint15010016








