Erdheim–Chester Disease with Isolated CNS Involvement: A Systematic Review of the Literature
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cives, M.; Simone, V.; Rizzo, F.M.; Dicuonzo, F.; Cristallo Lacalamita, M.; Ingravallo, G.; Silvestris, F.; Dammacco, F. Erdheim-Chester disease: A systematic review. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2015, 95, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, R.A.; Hermann, R.C.; Parisi, J.E. Neurological manifestations of Erdheim-Chester disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1999, 66, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starkebaum, G.; Hendrie, P. Erdheim-Chester disease. Best Pr. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 34, 101510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, L.C.; O’Brien, K.J.; Ozkaya, N.; Lehky, T.; Meoded, A.; Gochuico, B.R.; Hannah-Shmouni, F.; Nath, A.; Toro, C.; Gahl, W.A.; et al. Neurological manifestations of Erdheim-Chester Disease. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2020, 7, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Z.; Kleinschmidt-DeMasters, B.K. CNS Erdheim–Chester Disease: A Challenge to Diagnose. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2017, 76, 986–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caparros-Lefebvre, D.; Pruvo, J.P.; Wallaert, B.; Petit, H. Neuroradiologic aspects of Chester-Erdheim disease. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1995, 16, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pineles, S.L.; Liu, G.T.; Acebes, X.; Arruga, J.; Nasta, S.; Glaser, R.; Pramick, M.; Fogt, F.; Le Roux, P.; Gausas, R.E. Presence of Erdheim-Chester Disease and Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis in the Same Patient: A Report of 2 Cases. J. Neuro Ophthalmol. 2011, 31, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, K.M.; Mandel, J.J.; Goodman, J.C.; Gopinath, S.; Patel, A.J. Intracranial Erdheim-Chester Disease Mimicking Parafalcine Meningioma: Report of Two Cases and Review of the Literature. World Neurosurg. 2018, 110, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marano, M.; Ms, A.T.; Motolese, F.; Quattrocchi, C.C.; Crescenzi, A.; Cirillo, G.; Di Lazzaro, V. Choreo-Athetosis and Ataxia as Leading Features in a Case of Erdheim-Chester Disease. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pr. 2020, 7, 215–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-Álvarez, M.; Macías-Casanova, R.; Fidalgo-Fernández, M.; González, J.P.M. Neurological Involvement in Erdheim-Chester Disease. J. Clin. Neurol. 2016, 12, 115–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calandra, C.R.; Bustos, A.; Falcon, F.; Arakaki, N. Erdheim-Chester disease: Atypical presentation of a rare disease. BMJ Case Rep. 2017, 11, bcr2017220827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradshaw, M.J.; Pawate, S.; Bloch, K.C.; Moots, P.; Reddy, N.M. Clinical Reasoning: A 52-year-old man with diplopia and ataxia. Neurology 2016, 87, e140–e143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, R.S.; Sannegowda, R.B.; Mathur, T. Erdheim-Chester disease with isolated craniocerebral involvement. BMJ Case Rep. 2013, 2013, bcr2012006823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todisco, A.; Cavaliere, C.; Vaglio, A.; Marano, M.; Bonometti, A.; Passoni, E.; Berti, E.; Cirillo, M.; Cirillo, G. Erdheim-Chester disease: A challenging diagnosis for an effective therapy. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2020, 194, 105841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, S.; Rafia, M.H.; Kadir, N.A.; Lip, A.C. Central nervous system Erdheim Chester disease presenting with raised intracranial pressure and cerebellar signs mimicking neurosarcoidosis with secondary cerebral venous thrombosis. Neurol. India 2014, 62, 446–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathis, S.; Godenèche, G.; Haroche, J.; Milin, S.; Julian, A.; Berthomet, A.; Baron, C.; Palazzo, P.; Neau, J.-P. Long-term outcome of basilar stenosis in Erdheim–Chester disease. Medicine 2016, 95, e4813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liotta, E.M.; Jhaveri, M.D.; Fox, J.C.; Venugopal, P.; Lewis, S.L. Erdheim-Chester Disease. Arch. Neurol. 2012, 69, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, H.; Wanibuchi, M.; Komatsu, K.; Akiyama, Y.; Mikami, T.; Sugita, S.; Hasegawa, T.; Kaya, M.; Takada, K.; Mikuni, N. Erdheim-Chester Disease Involving the Central Nervous System with the Unique Appearance of a Coated Vertebral Artery. NMC Case Rep. J. 2016, 3, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noh, S.M.; Kang, H.G. Embolic Infarction with Subdural Hemorrhage in Erdheim-Chester Disease. J. Clin. Neurol. 2020, 16, 349–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loureiro, B.M.C.; Altemani, A.M.; Reis, F. Erdheim-Chester disease with isolated neurological involvement. Radiol. Bras. 2018, 51, 206–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miron, G.; Karni, A.; Faust-Soher, A.; Giladi, N.; Alroy, H.; Gadoth, A. Erdheim-Chester disease presenting with chorea and mimicking IgG4-related disorder. Neurol. Clin. Pr. 2019, 9, 524–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conley, A.; Manjila, S.; Guan, H.; Guthikonda, M.; Kupsky, W.J.; Mittal, S. Non-Langerhans cell histiocytosis with isolated CNS involvement: An unusual variant of Erdheim-Chester disease. Neuropathology 2010, 30, 634–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moussouttas, M.; Roemer, S.; Dickson, D.W. Cerebral Microvascular Erdheim-Chester Disease: A Perivascular Hematopoietic Vasculopathy. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2021, 50, 746–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fargeot, G.; Stefanizzi, S.; Depuydt, S.; Klapczynski, F.; Ameri, A. Association between Ischemic Stroke and Erdheim–Chester Disease: A Case Report and Review of Literature. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2017, 26, e153–e155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, C.; Hall, C.A.; McCoubrie, P.; Renowden, S.A.; Cohen, N.; Scolding, N. Erdheim-Chester disease: 25-year history with early CNS involvement. BMJ Case Rep. 2016, 2016, bcr2016216747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, D.F.; Kung, S.; Sola, C.L.; Bostwick, M.J.; Swanson, J.W. Familial Hemiplegic Migraine, Neuropsychiatric Symptoms, and Erdheim-Chester Disease. Headache 2004, 44, 911–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, A.; Crahes, M.; Laquerrière, A.; Proust, F.; Derrey, S. Neurological form of Erdheim-Chester disease: Case report and review of the literature. Neurochirurgie 2014, 60, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, N.; Lavi, E.S. Clinical and Neuroimaging Manifestations of Erdheim–Chester Disease: A Review. J. Neuroimaging 2020, 31, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagnier, S.; Debruxelles, S.; Lepreux, S.; Sibon, I. Erdheim–Chester Disease: An Unusual Cause of Intracranial Vasculitis and Progressive Leukoencephalopathy. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2016, 25, e63–e65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, P.G.B.; Pereira, I.D.S.; Filho, V.B.L.; Dias, D.A.; Nóbrega, P.R.; Braga-Neto, P. Intracranial mass lesions and skin discoloration in the armpits as unusual clues to Erdheim-Chester disease: A case report. BMC Neurol. 2021, 21, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.D.; Aulino, J.P.; Jagasia, M.; Mawn, L.A. Erdheim-Chester Disease Mimicking Multiple Meningiomas Syndrome. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2004, 25, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jeon, I.; Choi, J.H. Isolated thoracic intramedullary Erdheim-Chester disease presenting with paraplegia: A case report and literature review. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumandaş, S.; Kurtsoy, A.; Canöz, O.; Patıroğlu, T.; Yikilmaz, A.; Per, H. Erdheim Chester disease: Cerebral involvement in childhood. Brain Dev. 2007, 29, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukazawa, T.; Tsukishima, E.; Sasaki, H.; Hamada, K.; Hamada, T.; Tashiro, K. Erdheim-Chester disease and slowly progressive cerebellar dysfunction. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1995, 58, 238–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohlega, S.; Alwatban, J.; Tulbah, A.; Bakheet, S.M.; Powe, J. Cerebral manifestation of Erdheim-Chester disease: Clinical and radiologic findings. Neurology 1997, 49, 1702–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evidente, V.G.H.; Adler, C.H.; Giannini, C.; Conley, C.R.; Parisi, J.E.; Fletcher, G.P. Erdheim-chester disease with extensive intraaxial brain stem lesions presenting as a progressive cerebellar syndrome. Mov. Disord. 1998, 13, 576–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pego-Reigosa, R.; Brañas-Fernández, F.; Martínez-Vázquez, F.; Rivas-Bande, M.J.; Sanjuanbenito, L.; García-Villanueva, M.; Cortés-Laíño, J.A. Erdheim-Chester Disease with Spinal Cord Manifestations. Eur. Neurol. 2000, 43, 242–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, A.; Perez, C.; Thejasvi Reddy, T.A.; Gupta, R.K. Erdheim-Chester Disease with Isolated CNS Involvement: A Case Report and Systematic Review of Literature (P15-9.003). Neurology 2022, 98 (Suppl. S18), 3455. [Google Scholar]
- Sung, Y.E.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, J.; Lee, K.Y. Erdheim-Chester Disease Involving Lymph Nodes and Liver Clinically Mimicking Lymphoma: A Case Report. J. Pathol. Transl. Med. 2018, 52, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegoraro, F.; Papo, M.; Maniscalco, V.; Charlotte, F.; Haroche, J.; Vaglio, A. Erdheim–Chester disease: A rapidly evolving disease model. Leukemia 2020, 34, 2840–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalli, G.; Guglielmi, B.; Berti, A.; Campochiaro, C.; Sabbadini, M.G.; Dagna, L. The multifaceted clinical presentations and manifestations of Erdheim–Chester disease: Comprehensive review of the literature and of 10 new cases. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 1691–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haroche, J.; Amoura, Z.; Dion, E.; Wechsler, B.; Costedoat-Chalumeau, N.; Cacoub, P.; Isnard, R.; Généreau, T.; Wechsler, J.; Weber, N.; et al. Cardiovascular Involvement, an Overlooked Feature of Erdheim-Chester Disease: Report of 6 new cases and a literature review. Medicine 2004, 83, 371–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estrada-Veras, J.I.; O’Brien, K.J.; Boyd, L.C.; Dave, R.H.; Durham, B.H.; Xi, L.; Malayeri, A.A.; Chen, M.Y.; Gardner, P.J.; Enriquez, J.R.A.; et al. The clinical spectrum of Erdheim-Chester disease: An observational cohort study. Blood Adv. 2017, 1, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnaud, L.L.; Hervier, B.; Néel, A.; Hamidou, M.A.; Kahn, J.E.; Wechsler, B.B.; Pérez-Pastor, G.G.; Blomberg, B.; Fuzibet, J.-G.J.-G.; Dubourguet, F.F.; et al. CNS involvement and treatment with interferon-α are independent prognostic factors in Erdheim-Chester disease: A multicenter survival analysis of 53 patients. Blood 2011, 117, 2778–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drier, A.; Haroche, J.; Savatovsky, J.; Godenèche, G.; Dormont, D.; Chiras, J.; Amoura, Z.; Bonneville, F. Cerebral, Facial, and Orbital Involvement in Erdheim-Chester Disease: CT and MR Imaging Findings. Radiology 2010, 255, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, A.; Hatzoglou, V.; Ulaner, G.; Rampal, R.; Hyman, D.M.; Abdel-Wahab, O.; Durham, B.H.; Dogan, A.; Ozkaya, N.; Yabe, M.; et al. Neurologic and oncologic features of Erdheim–Chester disease: A 30-patient series. Neuro Oncol. 2020, 22, 979–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lachenal, F.; Cotton, F.; Desmurs-Clavel, H.; Haroche, J.; Taillia, H.; Magy, N.; Hamidou, M.; Salvatierra, J.; Piette, J.-C.; Vital-Durand, D.; et al. Neurological manifestations and neuroradiological presentation of Erdheim-Chester disease: Report of 6 cases and systematic review of the literature. J. Neurol. 2006, 253, 1267–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nambirajan, A.; Sharma, M.C.; Garg, K.; Sriram, S.; Boorgula, M.T.; Suri, V. Large dural-based mass with bony hyperostosis in a 16-year-old male: IgG4-related disease mimicking lymphoplasmacyte-rich meningioma. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2019, 35, 1423–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haroche, J.; Cohen-Aubart, F.; Amoura, Z. Erdheim-Chester disease. Blood 2020, 135, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

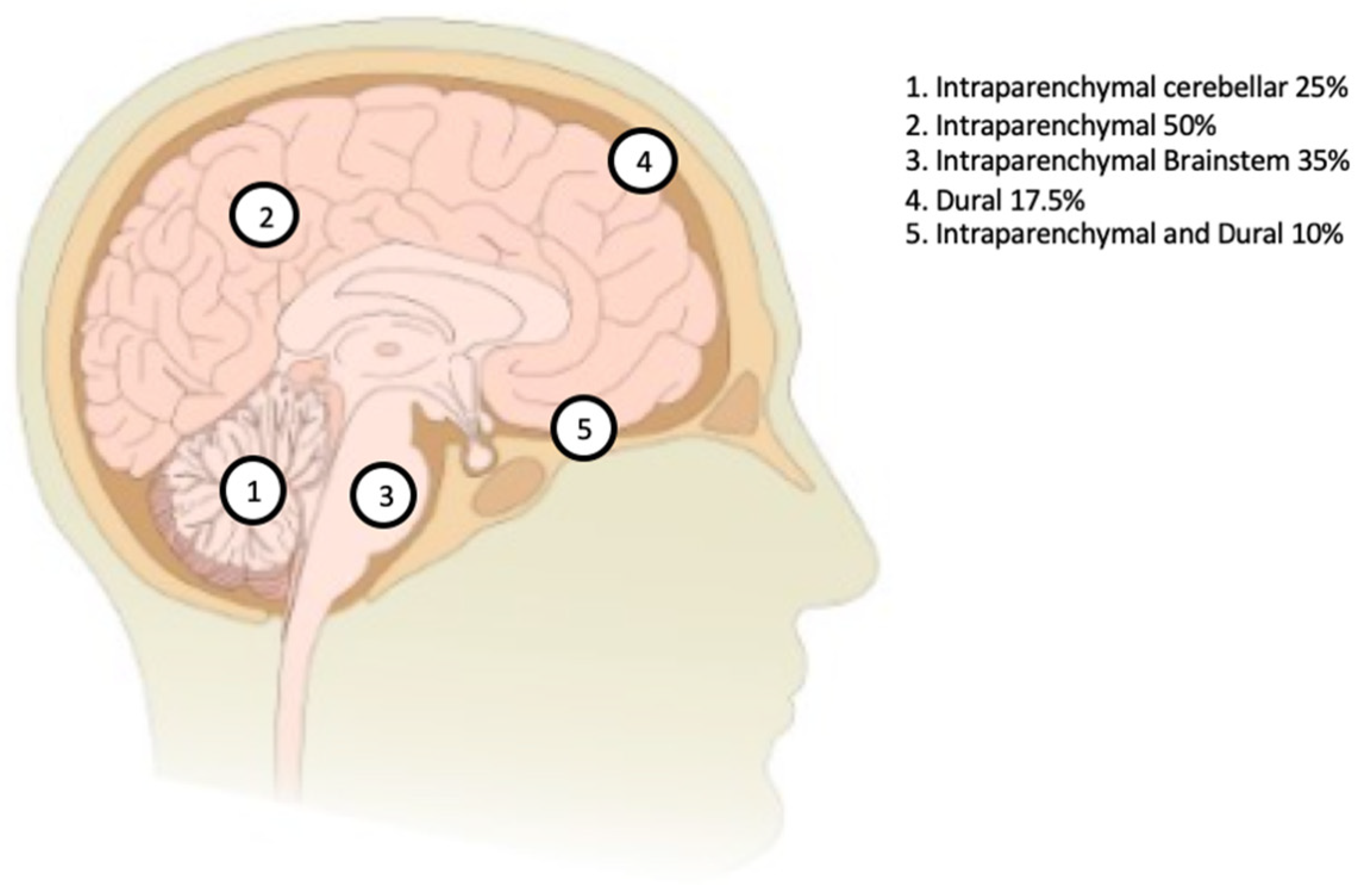
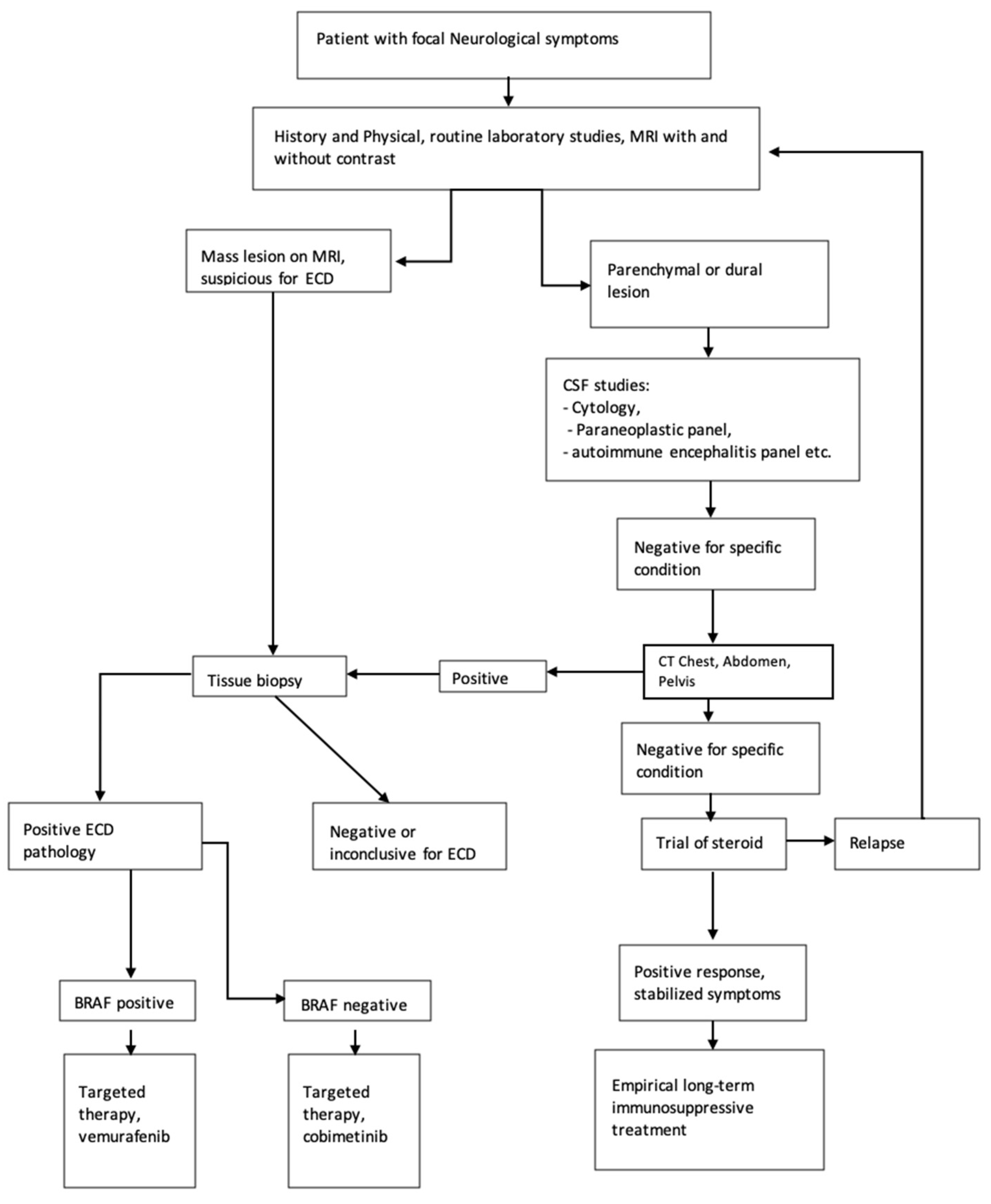
| Characteristic | No, Mean (+/− SD) | %, (Range) |
| Male | 19 | 47.5% |
| Female | 21 | 52.5% |
| Age and y at ECD diagnosis | 50.3 (+/− 15.09) | (10–75) |
| Follow-up duration in months | (1 to 144) | |
| Neurological presentation | Frequency (Case Count) | Frequency (%) |
| Cranial neuropathies | 21 | 52.5% |
| Ataxia | 20 | 50% |
| Headache | 12 | 30% |
| Limb weakness | 12 | 30% |
| Cognitive impairment | 10 | 25% |
| Vision loss/vision symptoms | 5 | 12.5% |
| Pyramidal | 8 | 20% |
| Dizziness | 4 | 10% |
| Asthenia | 3 | 7.5% |
| Seizure | 2 | 5% |
| Paresthesia/hypoesthesia | 6 | 15% |
| Syncope/loss of consciousness | 3 | 7.5% |
| Scanning speech | 5 | 12.5% |
| Aphasia | 1 | 2.5% |
| Presence of non-neurological symptoms | Frequency (case count) | Percentage |
| Bone symptoms | 20 | 50% |
| Hypopituitarism | 17 | 42.5% |
| Xanthelasma | 8 | 25% |
| Treatment | Number | Percentage * |
| Steroid | 15 | 37.5% |
| Interferon | 8 | 20% |
| Surgery or debulking | 7 | 17.5% |
| Vemurafenib | 5 | 12.5% |
| Chemotherapy | 3 | 7.5% |
| Radiation | 2 | 5% |
| Cobimetinib | 1 | 2.5% |
| Outcome * | Number | Percentage * |
| Improvement or stabilization of symptom | 20 | 50% |
| Progression | 13 | 32.5% |
| Death | 11 | 27.5% |
| Authors | Age | Gender | CNS Imaging Location | Management | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pan et al., 2017 no. 1 [5] | 47 | M | C, IP, BS, B | ND | M |
| Pan et al., 2017 no. 2 [5] | 67 | F | BS | V | I |
| Pan et al., 2017 no. 3 [5] | 46 | F | IP, D, B | Ch | P |
| Caparros- Lefebvra et al., 1995 no. 1 [6] | 74 | F | IP, D, B | ND | M |
| Caparros- Lefebvra et al., 1995 no. 2 [6] | 56 | F | IP, D, B | St | I |
| Pineles et al., 2011 no. 1 [7] | 26 | F | B | St, Ch, IFN | Stab |
| Pineles et al., 2011 no. 2 [7] | 32 | F | IP, B | IFN | I |
| Wagner et al., 2018 no. 1 [8] | 60 | M | D | S | I |
| Wagner et al., 2018 no. 2 [8] | 42 | F | D | S, IFN | P |
| Marano et al., 2020 [9] | 67 | M | C, BS, B | V | I |
| Alvarez- Alvarez et al., 2016 [10] | 74 | M | IP, D | St | I |
| Calandra et al., 2017 [11] | 42 | M | IP, B | St, IFN, S | I |
| Bradshaw et al., 2016 [12] | 52 | M | BS, B | St, V | I |
| Jain et al., 2013 [13] | 40 | M | IP, B | St | I |
| Todisco et al., 2020 [14] | 52 | M | C, BS, IP, D | V | I |
| Viswanathan et al., 2014 [15] | 50 | M | IP, D | IFN | I |
| Mathis et al., 2016 [16] | 59 | F | IFN | I | |
| Liotta et al., 2012 [17] | 41 | M | C, IP, B | IFN, St | I |
| Suzuki et al., 2016 [18] | 67 | M | IP, BS, B | S, St | P |
| Noh et al., 2020 [19] | 59 | F | C, IP | ND | ND |
| Loureiro et al., 2018 [20] | 25 | F | IP | ND | ND |
| Miron et al., 2019 [21] | 55 | M | C, IP, B | V | ND |
| Conley et al., 2010 [22] | 58 | F | IP | S | P |
| Moussouttas et al., 2021 [23] | 64 | M | IP | ND | P |
| Fargeot et al., 2017 [24] | 68 | F | IP, B | In | P |
| Rice et al., 2016 [25] | 46 | F | BS, B | St, PLEX | P |
| Black et al., 2004 [26] | 51 | M | IP, BS, B | ND | P |
| Perez et al., 2014 [27] | 28 | M | IP, BS, B | Ch | M |
| Garg et al., 2021 [28] | 44 | F | C, IP, BS, B | St | M |
| Sagnier et al., 2016 [29] | 64 | M | B | infliximab | M |
| Rodrigues et al., 2021 [30] | 42 | F | IP | St, IFN | Stab |
| Johnson et al., 2004 [31] | 34 | M | IP D, B | R | Stab |
| Jeon et al., 2021 [32] | 75 | F | BS, B | S | Stab |
| Kumandas et al., 2007 [33] | 10 | M | IP, D, B | St | ND |
| Fukazawa et al., 1995 [34] | 59 | F | C, B | ND | P |
| Bohlega et al., 1997 [35] | 37 | F | IP, BS, B | R | Stab |
| Evidente et al., 1998 [36] | 69 | M | C, BS, B | St | I |
| Wright et al., 1999 [2] | 42 | F | C, BS, B | St | I |
| Pego- Reigosa et al., 2000 [37] | 50 | F | D, B | St, S, R | ND |
| Haque et al., 2022 [38] | 38 | F | IP, D | IFN, S, C | Stab |
| Publication. | No. Patients/Article Type | CNS Symptoms (%) | Bone Symptoms (%) | Other Symptoms (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cives et al., 2015 [1] | 448, RCS | 55.6% (23.2% visual, 21.8% ataxia, 9.8% dysarthria, 7.1% para or hemiparesis) | 74.1% | 36.2% retroperitonea l10.7% cardiac 26.8% skin |
| Pegoraro et al., 2020 [40] | 360 | 39% | 89% | 65–75% with retroperitoneal 40–45% cardiac 25% diabetes insipidus 25–50% lung |
| Cavalli et al., 2013 [41] | 259 | 51% | * 50% | 30% retroperitoneal 25% diabetes insipidus 22% cardiac |
| Haroche et al., 2004 [42] | 72 | 35% | * 100% | 100% cardiovascular 35% diabetes insipidus 44% exophthalmos |
| Boyd et al., 2020 [4] | 62 | 94% (52% cognitive, 61% cranial neuropathy, 56% peripheral neuropathy, 46% cerebellar ataxia) | 22% proptosis | |
| Estrada- Veras et al., 2017 [43] | 60 | 92% (56% peripheral neuropathy, 48% cognitive, 40% cerebellar ataxia, 23% headache, 15% diplopia, 14% dysarthria) | 95%, (50% with bone pain) | 62% coated aorta 65% retroperitoneal 47% diabetes insipidus 30% restrictive lung pattern of breathing 25% xanthelasma |
| Arnaud et al., 2011 [44] | 53, RCS | 51% | 96% | 68% retroperitoneal 64% with cardiac involvement 28% with cutaneous involvement |
| Drier et al., 2010 [45] | 33, RCS | 45% (17% ataxia, 9% seizures, 9% panhypopituitarism) | 24% diabetes insipidus 21% exophthalmos | |
| Starkebaum, Hendrie, 2020 [3] | Research article | 50% | 95% (symptomatic in 50%) | 47% Diabetes insipidus |
| Publication | No. of Patients, Report Type | Brain MRI Findings |
|---|---|---|
| Bhatia et al., 2020 [46] | 30 patients; retrospective review involving patients who presented with neurological symptoms; single institute study | 60% with parenchymal lesions 33% with dural involvement |
| Lachenal et al., 2006 [47] | 6-patient case series with CNS involvement; a systematic review of 66 patients with CNS involvement | 44% with parenchymal lesions 37% with dural involvement 19% with parenchymal and dural lesions |
| Arnaud et al., 2011 [44] | 53 patients; prospective cohort | 43% with diencephalic involvement 17% with dural involvement |
| Drier et al., 2010 [45] | 33 patients; retrospective review | 47% with hypothalamic–pituitary axis involvement 23% with dural involvement |
| Boyd et al., 2020 [4] | 62 patients with ECD were prospectively enrolled in a natural history study | 50% with brain parenchymal lesions 6% meningeal involvement |
| Estrada- Veras et al., 2017 [43] | 60 patients; prospective cohort | 36% with parenchymal lesions 7% with meningeal involvement |
| Publication | Number of Cases, Report Type | Treatment | Prognosis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lachenal et al., 2006 [47] | 66, RCS | 73% steroids 43% chemotherapy or immunosuppressants 29% radiotherapy 18% underwent surgical treatment | 10% stabilized 42% progressed 48% died |
| Estrada- Veras et al., 2017 [43] | 60, RCS | 33% IV methylprednisolone 27% IFN alpha 12% anakinra | IFN alpha: 78% stabilized 17% progressed Anakinra: 57% stabilized 43% progressed Methylprednisolone data not available |
| Arnaud et al., 2011 [44] | 53, RCS | 57% steroids 87% interferon 42% chemotherapy or immunomodulatory therapy | 96% 1-year survival rate 68% 5-year survival rate |
| Bhatia et al., 2020 [46] | 30, RCS | 10% radiotherapy 24% conventional therapy—steroids, immunomodulatory therapy, IFN alpha, and chemotherapy 64% conventional therapy followed by targeted therapy, such as a BRAF inhibitor, MEK inhibitor, or combined BRAF/MEK inhibitors | With conventional therapy: 67% experienced progression 19% stabilized 14% experienced complete resolution With targeted therapy, 85% experienced partial or complete resolution of symptoms |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Haque, A.; Pérez, C.A.; Reddy, T.A.; Gupta, R.K. Erdheim–Chester Disease with Isolated CNS Involvement: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Neurol. Int. 2022, 14, 716-726. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint14030060
Haque A, Pérez CA, Reddy TA, Gupta RK. Erdheim–Chester Disease with Isolated CNS Involvement: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Neurology International. 2022; 14(3):716-726. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint14030060
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaque, Anam, Carlos A. Pérez, Thejasvi A. Reddy, and Rajesh K. Gupta. 2022. "Erdheim–Chester Disease with Isolated CNS Involvement: A Systematic Review of the Literature" Neurology International 14, no. 3: 716-726. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint14030060
APA StyleHaque, A., Pérez, C. A., Reddy, T. A., & Gupta, R. K. (2022). Erdheim–Chester Disease with Isolated CNS Involvement: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Neurology International, 14(3), 716-726. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint14030060






