Ibrutinib in Refractory or Relapsing Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
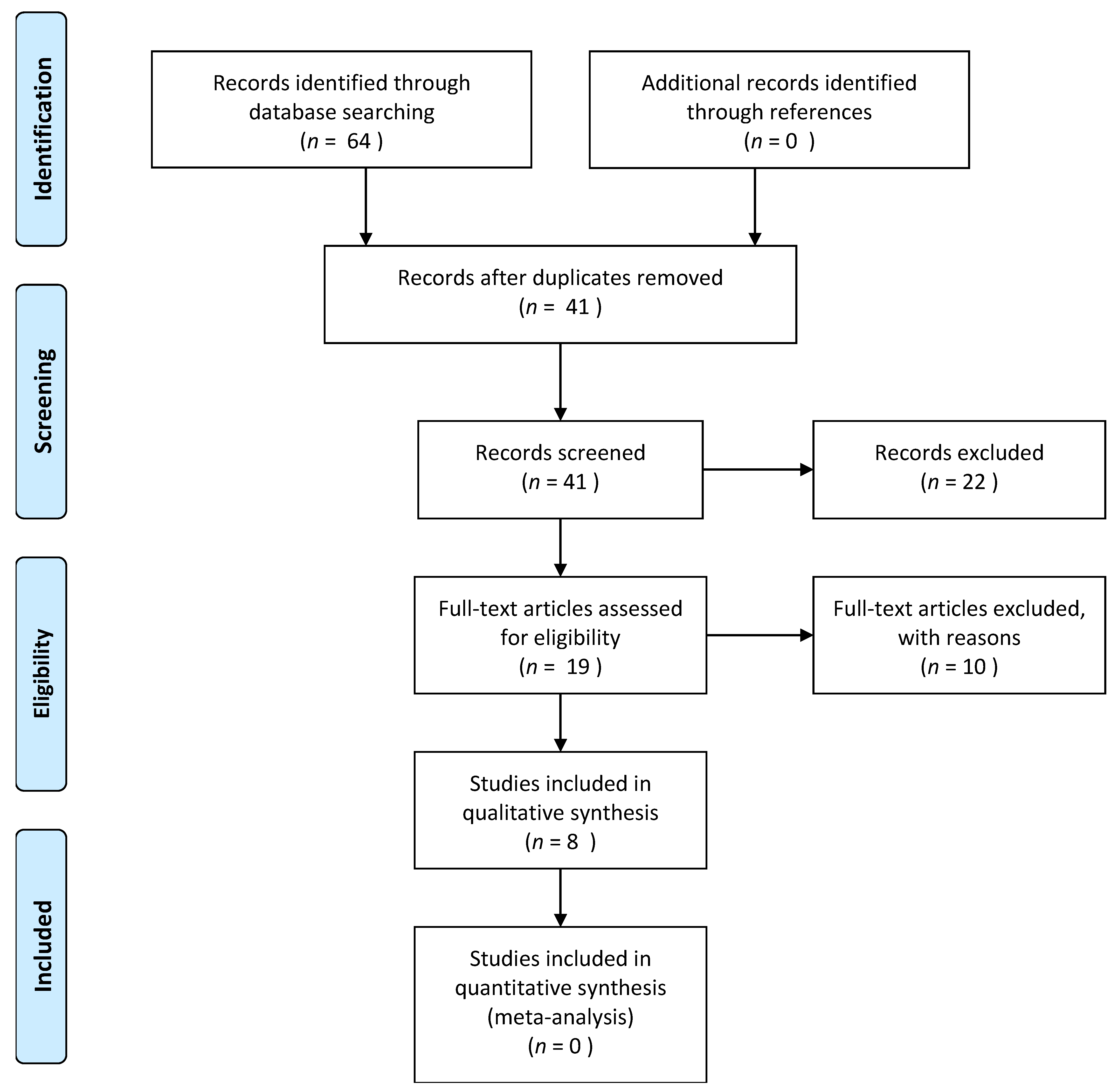
2. Materials and Methods
- Study type(s): clinical trials, prospective, or retrospective studies published in the English language were considered eligible for this study;
- Study participant(s): patients of any age with R/R PCNSL, irrespective of subtypes, treated with ibrutinib monotherapy or combination therapy;
- Study outcome(s): reporting either efficacy or safety endpoints, including the Overall Response (ORR), Complete Response (CR), Partial Response (PR), Progression-Free Survival (PFS), Overall Survival (OS), and adverse events.
- Case reports and case series with ≤ 2 cases;
- Review articles;
- Studies that were published in a language other than English;
- Research that did not report the outcomes of interest listed above.
3. Results
3.1. Monotherapy
3.2. Combination Therapy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grommes, C.; DeAngelis, L.M. Primary CNS Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2410–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camilleri-Broët, S.; Crinière, E.; Broët, P.; Delwail, V.; Mokhtari, K.; Moreau, A.; Kujas, M.; Raphaël, M.; Iraqi, W.; Sautès-Fridman, C.; et al. A uniform activated B-cell-like immunophenotype might explain the poor prognosis of primary central nervous system lymphomas: Analysis of 83 cases. Blood 2006, 107, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilleri-Broët, S.; Martin, A.; Moreau, A.; Angonin, R.; Hénin, D.; Gontier, M.F.; Rousselet, M.C.; Caulet-Maugendre, S.; Cuillière, P.; Lefrancq, T.; et al. Primary central nervous system lymphomas in 72 immunocompetent patients: Pathologic findings and clinical correlations. Groupe Ouest Est d’étude des Leucénies et Autres Maladies du Sang (GOELAMS). Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1998, 110, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, M. The vanishing role of whole brain radiotherapy for primary central nervous system lymphoma. Neuro Oncol. 2014, 16, 1035–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mead, G.M.; Bleehen, N.M.; Gregor, A.; Bullimore, J.; Shirley, D.; Rampling, R.P.; Trevor, J.; Glaser, M.G.; Lantos, P.; Ironside, J.W.; et al. A medical research council randomized trial in patients with primary cerebral non-Hodgkin lymphoma: Cerebral radiotherapy with and without cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone chemotherapy. Cancer 2000, 89, 1359–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreri, A.J.M.; Holdhoff, M.; Nayak, L.; Rubenstein, J.L. Evolving Treatments for Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. B 2019, 39, 454–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löw, S.; Han, C.H.; Batchelor, T.T. Primary central nervous system lymphoma. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2018, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, A.; Boisselier, B.; Labreche, K.; Marie, Y.; Polivka, M.; Jouvet, A.; Adam, C.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Miquel, C.; Eimer, S.; et al. Mutational analysis of primary central nervous system lymphoma. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 5065–5075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
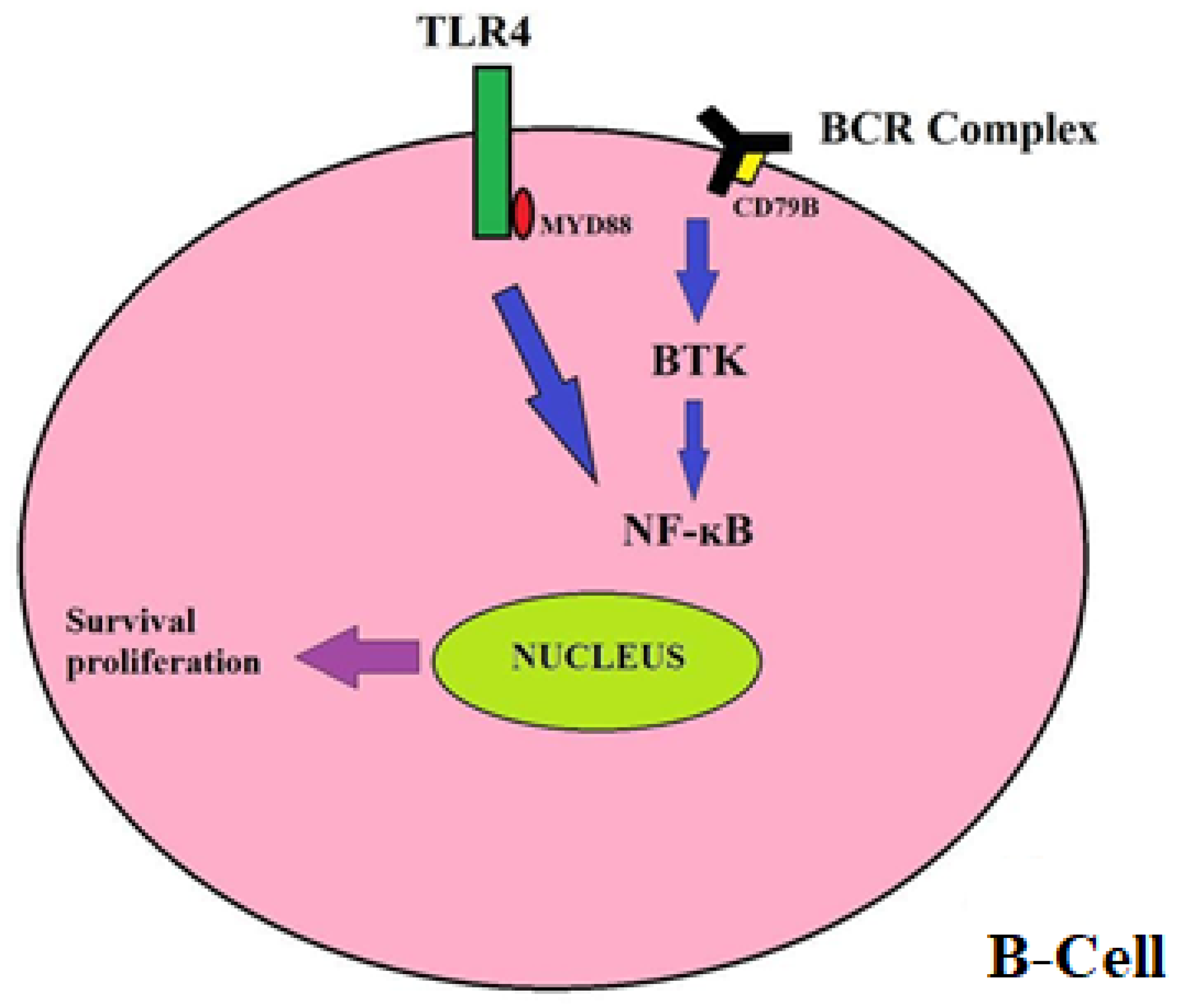
- Lionakis, M.S.; Dunleavy, K.; Roschewski, M.; Widemann, B.C.; Butman, J.A.; Schmitz, R.; Yang, Y.; Cole, D.E.; Melani, C.; Higham, C.S.; et al. Inhibition of B Cell Receptor Signaling by Ibrutinib in Primary CNS Lymphoma. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 833–843.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.E.; Ngo, V.N.; Lenz, G.; Tolar, P.; Young, R.M.; Romesser, P.B.; Kohlhammer, H.; Lamy, L.; Zhao, H.; Yang, Y.; et al. Chronic active B-cell-receptor signalling in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Nature 2010, 463, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groen, R.A.L.; Schrader, A.M.R.; Kersten, M.J.; Pals, S.T.; Vermaat, J.S.P.V. MYD88 in the driver’s seat of B-cell lymphomagenesis: From molecular mechanisms to clinical implications. Haematologica 2019, 104, 2337–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, J.T.; Peters, K.B. Ibrutinib in primary central nervous system diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. CNS Oncol. 2020, 9, CNS51. [Google Scholar]
- Dubovsky, J.A.; Beckwith, K.A.; Natarajan, G.; Woyach, J.A.; Jaglowski, S.; Zhong, Y.; Hessler, J.D.; Liu, T.-M.; Chang, B.Y.; Larkin, K.M.; et al. Ibrutinib is an irreversible molecular inhibitor of ITK driving a Th1-selective pressure in T lymphocytes. Blood 2013, 122, 2539–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: Explanation and elaboration. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2009, 62, e1–e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grommes, C.; Pastore, A.; Palaskas, N.; Tang, S.S.; Campos, C.; Schartz, D.; Codega, P.; Nichol, D.; Clark, O.; Hsieh, W.-Y.; et al. Ibrutinib unmasks critical role of bruton tyrosine kinase in primary CNS lymphoma. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 1018–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grommes, C.; Tang, S.S.; Wolfe, J.; Kaley, T.J.; Daras, M.; Pentsova, E.I.; Piotrowski, A.F.; Stone, J.; Lin, A.; Nolan, C.P.; et al. Phase 1b trial of an ibrutinib-based combination therapy in recurrent/refractory CNS lymphoma. Blood 2019, 133, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamoun, K.; Choquet, S.; Boyle, E.; Houillier, C.; Larrieu-Ciron, D.; Al Jijakli, A.; Delrieu, V.; Delwail, V.; Morschhauser, F.; Hoang-Xuan, K.; et al. Ibrutinib monotherapy in relapsed/refractory CNS lymphoma: A retrospective case series. Neurology 2017, 88, 101–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauer, E.M.; Waterhouse, M.; Braig, M.; Mutter, J.; Bleul, S.; Duque-Afonso, J.; Duyster, J.; Marks, R.; Reinacher, P.C.; Prinz, M.; et al. Ibrutinib in patients with relapsed/refractory central nervous system lymphoma: A retrospective single-centre analysis. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 190, e110-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, K.L.; Manos, K.; Casey, J.; Crawford, J.; Ho, S.-J.; Issa, S.; Grigg, A.; Wood, P.; Gandhi, M.K.; Hawkes, E.A.; et al. Outcomes for Patients with Primary or Secondary Central System Lymphoma Treated with Ibrutinib: A Multicentre Retrospective Analysis. Blood 2019, 134, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soussain, C.; Choquet, S.; Blonski, M.; Leclercq, D.; Houillier, C.; Rezai, K.; Houillier, C.; Rezai, K.; Bijou, F.; Houot, R.; et al. Ibrutinib monotherapy for relapse or refractory primary CNS lymphoma and primary vitreoretinal lymphoma: Final analysis of the phase II ‘proof-of-concept’ iLOC study by the Lymphoma study association (LYSA) and the French oculo-cerebral lymphoma (LOC) net. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 117, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Chen, F.; Li, Y.; Jiang, X.; Liu, S.; Guo, H.; Huang, L.; Wei, X.; Liang, Z.; Li, W.; et al. Characteristics and Outcomes of Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma: A Retrospective Study of 91 Cases in a Chinese Population. World Neurosurg. 2019, 123, e15–e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paydas, S. Management of adverse effects/toxicity of ibrutinib. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2019, 136, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fürstenau, M.; Simon, F.; Cornely, O.A.; Hicketier, T.; Eichhorst, B.; Hallek, M.; Mellinghoff, S.C. Invasive Aspergillosis in Patients Treated with Ibrutinib. HemaSphere 2020, 4, e309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mato, A.R.; Nabhan, C.; Thompson, M.C.; Lamanna, N.; Brander, D.M.; Hill, B.; Howlett, C.; Skarbnik, A.; Cheson, B.D.; Clive, Z.; et al. Toxicities and outcomes of 616 ibrutinib-treated patients in the United States: A real-world analysis. Haematologica 2018, 103, 874–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comino-Mendez, I.; Turner, N. Predicting Relapse with Circulating Tumor DNA Analysis in Lung Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 1368–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Sandhu, S.; Lee, R.J.; Li, J.; Callahan, J.; Ftouni, S.; Dhomen, N.; Middlehurst, P.; Wallace, A.; Raleigh, J.; et al. Prediction and monitoring of relapse in stage III melanoma using circulating tumor DNA. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, S.; Park, B.H. Circulating Tumor DNA as a Marker for Disease Relapse in Early-Stage Breast Cancer—Bad Blood. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 1479–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arthurs, B.; Wunderle, K.; Hsu, M.; Kim, S. Invasive aspergillosis related to ibrutinib therapy for chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Respir. Med. Case Rep. 2017, 21, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, A.N.R.; Bittner, Z.; Liu, X.; Dang, T.-M.; Radsak, M.P.; Brunner, C. Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase: An Emerging Key Player in Innate Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Jung, J.; Victor, E.; Arceo, J.; Gokhale, S.; Xie, P. Clinical Trials of the BTK Inhibitors Ibrutinib and Acalabrutinib in Human Diseases Beyond B Cell Malignancies. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 737943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bercusson, A.; Colley, T.; Shah, A.; Warris, A.; Armstrong-James, D. Ibrutinib blocks Btk-dependent NF-ĸB and NFAT responses in human macrophages during Aspergillus fumigatus phagocytosis. Blood 2018, 132, 1985–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, S.; Shah, A.; Mazon Moya, M.; Marzola, V.; Jensen, B.; Reed, A.; Birrell, M.A.; Saijo, S.; Mostowy, S.; Shaunak, S.; et al. Phagocytosis-dependent activation of a TLR9-BTK-calcineurin-NFAT pathway co-ordinates innate immunity to Aspergillus fumigatus. EMBO Mol. Med. 2015, 7, 240–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaff, L.R.; Grommes, C. Update on Novel Therapeutics for Primary CNS Lymphoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 5372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narita, Y.; Nagane, M.; Mishima, K.; Terui, Y.; Arakawa, Y.; Yonezawa, H.; Asai, K.; Fukuhara, N.; Sugiyama, K.; Shinojima, N.; et al. Phase I/II study of tirabrutinib, a second-generation Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in relapsed/refractory primary central nervous system lymphoma. Neuro Oncol. 2021, 23, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Study | Origin | Design | R/R Cases (n) | Median Age | Previous Treatment | Mono/Combined | Ibrutinib Dose | Median Follow-Up |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chamoun 2016 | France and Belgium | Retrospective study | 14 | 68 y (range 48–79) | High-dose methotrexate-based chemotherapy. The median number of previous therapies was 3 (range 2–9). | Monotherapy Four patients received steroids for cerebral edema | 560 mg once daily 1 patient received a 420 mg dose | N/A |
| Lionakis 2017 | USA | Phase I clinical trial | 13 | 66 (range 49–87) | Median of 2 (range 1–6) prior treatments | Monotherapy window followed by DA-TEDDi-R combination therapy | 560–840 mg | N/A |
| Grommes 2017 | USA | Phase I clinical trial | 13 | 69 (60–80) | All received high-dose methotrexate-based chemotherapy. Two received radiation. Median 2 (1–8) before treatment | Monotherapy | 560 and 840 mg | 479 days (range, 354–739) |
| Grommes 2019 | USA | Phase I clinical trial | 9 | 62 y (range, 23–74) | High-dose methotrexate-based chemotherapy with a heterogeneous combination of rituximab, an alkylating agent, radiation therapy, and stem cell therapy | Ibrutinib-based combination therapy followed by ibrutinib monotherapy maintenance 2: HD-MTX plus ibrutinib 7: RTX-HD-MTX plus ibrutinib | 560 to 840 mg | 19.7 months (range, 12.7–27.1) |
| Mao 2018 | China | Retrospective Study | 3 | N/A | High-dose methotrexate-based chemotherapy | Combined therapy | 560 mg once daily | N/A |
| Soussain 2019 | France | Phase II clinical trial | 52 | 70 y (range, 52–81 y). | High-dose methotrexate-based chemotherapy | Monotherapy Steroids in initial four weeks for cerebral edema | 560 mg once daily | 25.7 months |
| Lewis 2019 | Australia | Retrospective Study | 8 | 65 y | High-dose methotrexate-based chemotherapy with radiotherapy, rituximab, and other chemotherapy. Median 1 (0–3) before treatment | Monotherapy in some patients and combined therapy (radiation plus chemotherapy) in the rest. | Daily dose was 560 mg (range 420–840 mg); | 14 months |
| Lauer 2020 | Germany | Retrospective Study | 5 | 63 y (range: 53–82) | All patients were heavily pretreated (median of two prior treatment regimens), with 100% of patients receiving high-dose cytarabine and/or HD-MTX. Some received high-dose chemotherapy and autologous stem cell transplantation. | Monotherapy in some patients and combined therapy (radiation plus chemotherapy) in the rest. | 560 mg once daily | 427 days (range: 75–711) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nepal, G.; Khurana, M.; Bucheli, D.H.; Bhandari, S.; Joshi, U.; Bhagat, R.; Rehrig, J.H.; Pudasainee, P.; Shing, Y.K.; Ortiz, J.F.; et al. Ibrutinib in Refractory or Relapsing Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma: A Systematic Review. Neurol. Int. 2022, 14, 99-108. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint14010009
Nepal G, Khurana M, Bucheli DH, Bhandari S, Joshi U, Bhagat R, Rehrig JH, Pudasainee P, Shing YK, Ortiz JF, et al. Ibrutinib in Refractory or Relapsing Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma: A Systematic Review. Neurology International. 2022; 14(1):99-108. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint14010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleNepal, Gaurav, Mahika Khurana, Domenica Herrera Bucheli, Siddhartha Bhandari, Utsav Joshi, Riwaj Bhagat, Jessica Holly Rehrig, Prasun Pudasainee, Yow Ka Shing, Juan Fernando Ortiz, and et al. 2022. "Ibrutinib in Refractory or Relapsing Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma: A Systematic Review" Neurology International 14, no. 1: 99-108. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint14010009
APA StyleNepal, G., Khurana, M., Bucheli, D. H., Bhandari, S., Joshi, U., Bhagat, R., Rehrig, J. H., Pudasainee, P., Shing, Y. K., Ortiz, J. F., Ojha, R., Gajurel, B. P., Quinonez, J., Ruxmohan, S., Albert, T., Licata, S., & Stien, J. (2022). Ibrutinib in Refractory or Relapsing Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma: A Systematic Review. Neurology International, 14(1), 99-108. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint14010009






