Brugada Syndrome and GPD1L: Definite Genotype-Phenotype Association?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Popa, I.P.; Serban, D.N.; Maranduca, M.A.; Serban, I.L.; Tamba, B.I.; Tudorancea, I. Brugada Syndrome: From Molecular Mechanisms and Genetics to Risk Stratification. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilde, A.A.; Semsarian, C.; Márquez, M.F.; Shamloo, A.S.; Ackerman, M.J.; Ashley, E.A.; Sternick, E.B.; Barajas-Martinez, H.; Behr, E.R.; Bezzina, C.R.; et al. European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA)/Heart Rhythm Society (HRS)/Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society (APHRS)/Latin American Heart Rhythm Society (LAHRS) Expert Consensus Statement on the State of Genetic Testing for Cardiac Diseases. Europace 2022, 24, 1307–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campuzano, O.; Sarquella-Brugada, G.; Fernandez-Falgueras, A.; Cesar, S.; Coll, M.; Mates, J.; Arbelo, E.; Perez-Serra, A.; del Olmo, B.; Jordá, P.; et al. Genetic interpretation and clinical translation of minor genes related to Brugada syndrome. Hum. Mutat. 2019, 40, 749–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdivia, C.R.; Ueda, K.; Ackerman, M.J.; Makielski, J.C. GPD1L links redox state to cardiac excitability by PKC-dependent phosphorylation of the sodium channel SCN5A. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2009, 297, H1446–H1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, R.; Barmada, M.M.; Nguyen, T.; Seibel, J.S.; Cavlovich, D.; Kornblit, C.A.; Angelilli, A.; Villanueva, F.; McNamara, D.M.; London, B. Clinical and molecular heterogeneity in the Brugada syndrome: A novel gene locus on chromosome 3. Circulation 2002, 105, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- London, B.; Michalec, M.; Mehdi, H.; Zhu, X.; Kerchner, L.; Sanyal, S.; Viswanathan, P.C.; Pfahnl, A.E.; Shang, L.L.; Madhusudanan, M.; et al. Mutation in glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 1 like gene (GPD1-L) decreases cardiac Na+ current and causes inherited arrhythmias. Circulation 2007, 116, 2260–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Yang, S.; Nykamp, K.; Garcia, J.; Lincoln, S.E.; Topper, S.E. Pathogenic variant burden in the ExAC database: An empirical approach to evaluating population data for clinical variant interpretation. Genome Med. 2017, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou Tayoun, A.N.; Pesaran, T.; DiStefano, M.T.; Oza, A.; Rehm, H.L.; Biesecker, L.G.; Harrison, S.M.; ClinGen Sequence Variant Interpretation Working Group. Recommendations for interpreting the loss of function PVS1 ACMG/AMP variant criterion. Hum. Mutat. 2018, 39, 1517–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesecker, L.G.; Byrne, A.B.; Harrison, S.M.; Pesaran, T.; Schäffer, A.A.; Shirts, B.H.; Tavtigian, S.V.; Rehm, H.L. ClinGen guidance for use of the PP1/BS4 co-segregation and PP4 phenotype specificity criteria for sequence variant pathogenicity classification. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2024, 111, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesecker, L.G.; Harrison, S.M.; ClinGen Sequence Variant Interpretation Working, G. The ACMG/AMP reputable source criteria for the interpretation of sequence variants. Genet. Med. 2018, 20, 1687–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pejaver, V.; Byrne, A.B.; Feng, B.J.; Pagel, K.A.; Mooney, S.D.; Karchin, R.; O’Donnell-Luria, A.; Harrison, S.M.; Tavtigian, S.V.; Greenblatt, M.S.; et al. Calibration of computational tools for missense variant pathogenicity classification and ClinGen recommendations for PP3/BP4 criteria. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2022, 109, 2163–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedley, P.L.; Jorgensen, P.; Schlamowitz, S.; Moolman-Smook, J.; Kanters, J.K.; Corfield, V.A.; Christiansen, M. The genetic basis of Brugada syndrome: A mutation update. Hum. Mutat. 2009, 30, 1256–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Norstrand, D.W.; Valdivia, C.R.; Tester, D.J.; Ueda, K.; London, B.; Makielski, J.C.; Ackerman, M.J. Molecular and functional characterization of novel glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 1 like gene (GPD1-L) mutations in sudden infant death syndrome. Circulation 2007, 116, 2253–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makiyama, T.; Akao, M.; Haruna, Y.; Tsuji, K.; Doi, T.; Ohno, S.; Nishio, Y.; Kita, T.; Horie, M. Mutation analysis of the glycerol-3 phosphate dehydrogenase-1 like (GPD1L) gene in Japanese patients with Brugada syndrome. Circ. J. 2008, 72, 1705–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paludan-Müller, C.; Ghouse, J.; Vad, O.B.; Herfelt, C.B.; Lundegaard, P.; Ahlberg, G.; Schmitt, N.; Svendsen, J.H.; Haunsø, S.; Bundgaard, H.; et al. Reappraisal of variants previously linked with sudden infant death syndrome: Results from three population-based cohorts. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 27, 1427–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.J.; Juang, J.J.; Lin, L.Y.; Liu, Y.B.; Ho, L.T.; Yu, C.C.; Huang, H.C.; Lin, T.T.; Liao, M.C.; Chen, J.J.; et al. Gender difference in clinical and genetic characteristics of Brugada syndrome: SADS-TW BrS registry. QJM Mon. J. Assoc. Physicians 2019, 112, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Yao, F.J.; Cheng, Y.J.; Ji, C.C.; Chen, X.M.; Wu, S.H. Early repolarization pattern associated with coronary artery disease and increased the risk of cardiac death in acute myocardium infarction. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2020, 25, e12768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Ji, C.C.; Cheng, Y.J.; Yao, H.; Chen, X.M.; Zheng, Z.H.; Wu, S. A novel mutation in GPD1-L associated with early repolarization syndrome via modulation of cardiomyocyte fast sodium currents. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 45, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Sanyal, S.; Gao, G.; Gurung, I.S.; Zhu, X.; Gaconnet, G.; Kerchner, L.J.; Shang, L.L.; Huang, C.L.-H.; Grace, A.; et al. Cardiac Na+ current regulation by pyridine nucleotides. Circ. Res. 2009, 105, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasdemir, C.; Payzin, S.; Kocabas, U.; Sahin, H.; Yildirim, N.; Alp, A.; Aydin, M.; Pfeiffer, R.; Burashnikov, E.; Wu, Y.; et al. High prevalence of concealed Brugada syndrome in patients with atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia. Heart Rhythm. 2015, 12, 1584–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahlin, E.; Gréen, A.; Gustavsson, P.; Liedén, A.; Nordenskjöld, M.; Papadogiannakis, N.; Pettersson, K.; Nilsson, D.; Jonasson, J.; Iwarsson, E. Identification of putative pathogenic single nucleotide variants (SNVs) in genes associated with heart disease in 290 cases of stillbirth. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Chen, Y.Q.; Fan, L.L.; Guo, S.; Li, J.J.; Jin, J.Y.; Xiang, R. Whole-exome sequencing identifies a novel mutation of GPD1L (R189X) associated with familial conduction disease and sudden death. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 1350–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschall, C.; Moscu-Gregor, A.; Klein, H.G. Variant panorama in 1,385 index patients and sensitivity of expanded next-generation sequencing panels in arrhythmogenic disorders. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2019, 9, S292–S298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Guo, Y.; Xia, H.; Xu, H.; Deng, H.; Yuan, L. Novel SCN5A and GPD1L Variants Identified in Two Unrelated Han-Chinese Patients With Clinically Suspected Brugada Syndrome. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 758903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranchuk, A.; Nguyen, T.; Ryu, M.H.; Femenia, F.; Zareba, W.; Wilde, A.A.; Shimizu, W.; Brugada, P.; Pérez-Riera, A.R. Brugada phenocopy: New terminology and proposed classification. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2012, 17, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campuzano, O.; Sarquella-Brugada, G.; Cesar, S.; Arbelo, E.; Brugada, J.; Brugada, R. Update on Genetic Basis of Brugada Syndrome: Monogenic, Polygenic or Oligogenic? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Agustin, A.; Pinsach-Abuin, M.L.; Pagans, S. Role of Non-Coding Variants in Brugada Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, R.; Mauleekoonphairoj, J.; Mengarelli, I.; Bosada, F.M.; Verkerk, A.O.; van Duijvenboden, K.; Poovorawan, Y.; Wongcharoen, W.; Sutjaporn, B.; Wandee, P.; et al. A Rare Noncoding Enhancer Variant in SCN5A Contributes to the High Prevalence of Brugada Syndrome in Thailand. Circulation 2024, 151, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezzina, C.R.; Barc, J.; Mizusawa, Y.; Remme, C.A.; Gourraud, J.B.; Simonet, F.; Verkerk, A.O.; Schwartz, P.J.; Crotti, L.; Dagradi, F.; et al. Common variants at SCN5A-SCN10A and HEY2 are associated with Brugada syndrome, a rare disease with high risk of sudden cardiac death. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1044–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barc, J.; Tadros, R.; Glinge, C.; Chiang, D.Y.; Jouni, M.; Simonet, F.; Jurgens, S.J.; Baudic, M.; Nicastro, M.; Potet, F.; et al. Genome-wide association analyses identify new Brugada syndrome risk loci and highlight a new mechanism of sodium channel regulation in disease susceptibility. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, T.; Masuda, T.; Hachiya, T.; Dina, C.; Simonet, F.; Nagata, Y.; Tanck, M.W.T.; Sonehara, K.; Glinge, C.; Tadros, R.; et al. Brugada syndrome in Japan and Europe: A genome-wide association study reveals shared genetic architecture and new risk loci. Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, 2320–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moras, E.; Gandhi, K.; Narasimhan, B.; Brugada, R.; Brugada, J.; Brugada, P.; Krittanawong, C. Genetic and Molecular Mechanisms in Brugada Syndrome. Cells 2023, 12, 1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mascia, G.; Brugada, J.; Barca, L.; Benenati, S.; Della Bona, R.; Scarà, A.; Russo, V.; Arbelo, E.; Di Donna, P.; Porto, I. Prognostic significance of electrophysiological study in drug-induced type-1 Brugada syndrome: A brief systematic review. J. Cardiovasc. Med. 2024, 25, 775–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
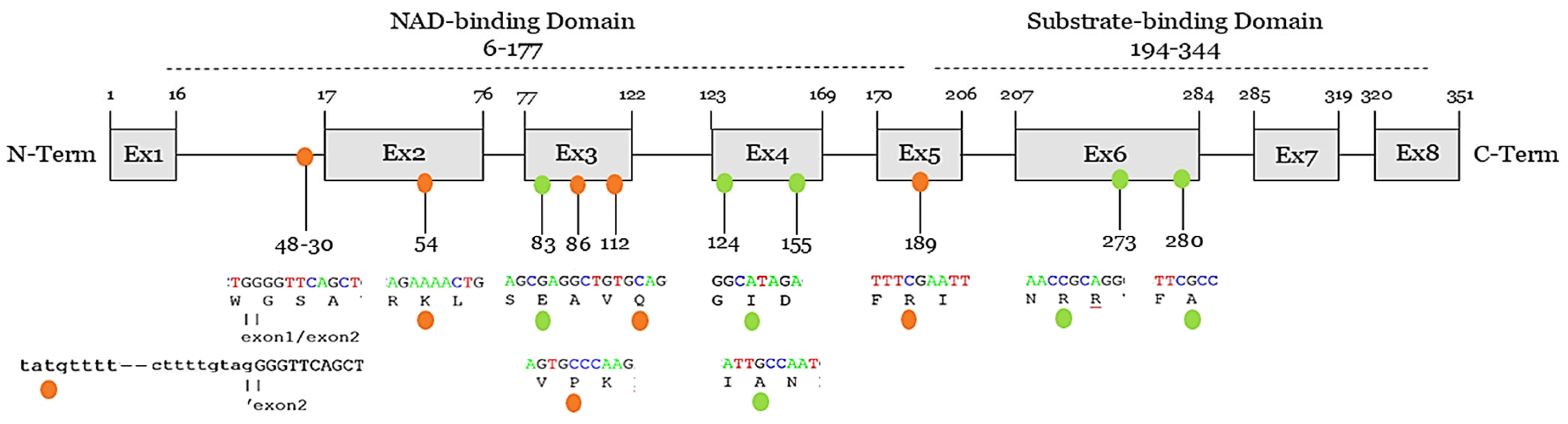
| Nucleotide | Protein | dbSNP/ClinVar | GnomAD (%) | ACMG/AMP | Reported |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c.48-30T>C | NA | rs1700537085/NA | 8/1367436 (0.0005%) | VUS | Makiyama, 2008 |
| c.161A>T | p.(Asp54Val) | NA | NA | VUS | Yuan, 2021 |
| c.247G>A | p.(Glu83Lys) | rs72552292/ VUS | 245/1461762 (0.016%) | LB | Van Norstrand, 2007 Valdivia, 2009 Hedley, 2009 Paludan-Müller, 2019 Chen, 2019 |
| c.257A>G | p.(Gln86Arg) | rs755240955/ VUS | 6/1461764 (0.0004%) | VUS | Marshall, 2019 |
| c.335C>T | p.(Pro112Leu) | rs1201810677/NA | 5/1461802 (0.0003%) | VUS | Fan, 2020 |
| c.370A>G | p.(Ile124Val) | rs72552293/ LB | 2412/1461798 (0.16%) | LB | Van Norstrand, 2007 Hedley, 2009 Hasdemir, 2015 Paludan-Müller, 2019 Sahlin, 2019 |
| c.465C>T | p.(Ala155Ala) | rs113645050/ LB | 1276/1461858 (0.08%) | LB | Makiyama, 2008 |
| c.565C>T | p.(Arg189Ter) | rs982730623/ VUS | NA | VUS | Huang, 2018 |
| c.817C>T | p.(Arg273Cys) | rs72552294/ VUS | 87/1461446 (0.005%) | LB | Van Norstrand, 2007 Hedley, 2009 |
| c.839C>T | p.(Ala280Val) | rs72552291/ VUS | 117/1461050 (0.008%) | LB | London, 2007 Hedley, 2009 Liu, 2009 Chen, 2019 Campuzano, 2019 Fan, 2020 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Greco, A.; Martínez-Barrios, E.; Cruzalegui, J.; Cesar, S.; Chipa, F.; Díez-Escuté, N.; Cerralbo, P.; Zschaeck, I.; Loredo, P.; Sarquella-Brugada, G.; et al. Brugada Syndrome and GPD1L: Definite Genotype-Phenotype Association? Cardiogenetics 2025, 15, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/cardiogenetics15010009
Greco A, Martínez-Barrios E, Cruzalegui J, Cesar S, Chipa F, Díez-Escuté N, Cerralbo P, Zschaeck I, Loredo P, Sarquella-Brugada G, et al. Brugada Syndrome and GPD1L: Definite Genotype-Phenotype Association? Cardiogenetics. 2025; 15(1):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/cardiogenetics15010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleGreco, Andrea, Estefanía Martínez-Barrios, José Cruzalegui, Sergi Cesar, Fredy Chipa, Nuria Díez-Escuté, Patricia Cerralbo, Irene Zschaeck, Paula Loredo, Georgia Sarquella-Brugada, and et al. 2025. "Brugada Syndrome and GPD1L: Definite Genotype-Phenotype Association?" Cardiogenetics 15, no. 1: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/cardiogenetics15010009
APA StyleGreco, A., Martínez-Barrios, E., Cruzalegui, J., Cesar, S., Chipa, F., Díez-Escuté, N., Cerralbo, P., Zschaeck, I., Loredo, P., Sarquella-Brugada, G., & Campuzano, O. (2025). Brugada Syndrome and GPD1L: Definite Genotype-Phenotype Association? Cardiogenetics, 15(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/cardiogenetics15010009







