A Framework for Optimal Sizing of Heavy-Duty Electric Vehicle Charging Stations Considering Uncertainty
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- This study introduces a dedicated framework for simultaneously sizing multiple HDEV CSs. The framework utilizes historical commuting data for different depots and their rollout plans for deploying HDEVs in place of ICE HDVs. It proposes a multi-period expansion plan for CSs and is designed to adapt to various scenarios for modeling HDEV behavior. The framework provides a comprehensive overview of HDEV SOCs as well as energy/power at all times.
- (2)
- Two types of HDEV CSs are demonstrated and analyzed: utility-based and RE-based CSs. Utility-based CSs rely entirely on grid power, while RE-based CSs are exclusively supplied by onsite PV generation and local BS. For each type, queue-based energy management algorithms are proposed to assign chargers to HDEVs and manage the charging or discharging processes. These algorithms can manage the interaction between the CS and the utility grid or RE sources and storage systems. They consider arrival time, departure time, SOC, and priority of HDEVs. Utility-based CSs also consider the charging model of the corresponding utilities, while RE-based CSs consider the availability of PV generation and the SOC of local BS in their management algorithm.
- (3)
- A two-layer uncertainty model is proposed to address issues associated with PV systems, HDEV behavior, and charger failure. In the first layer, the model simulates worst-case scenarios using depot-specific HDEV schedules and PV generation profiles through a deterministic approach. The second layer resizes the CS components to add a safety margin based on the outputs of the optimization loop, ensuring any charger failures do not hinder the operation of CSs.
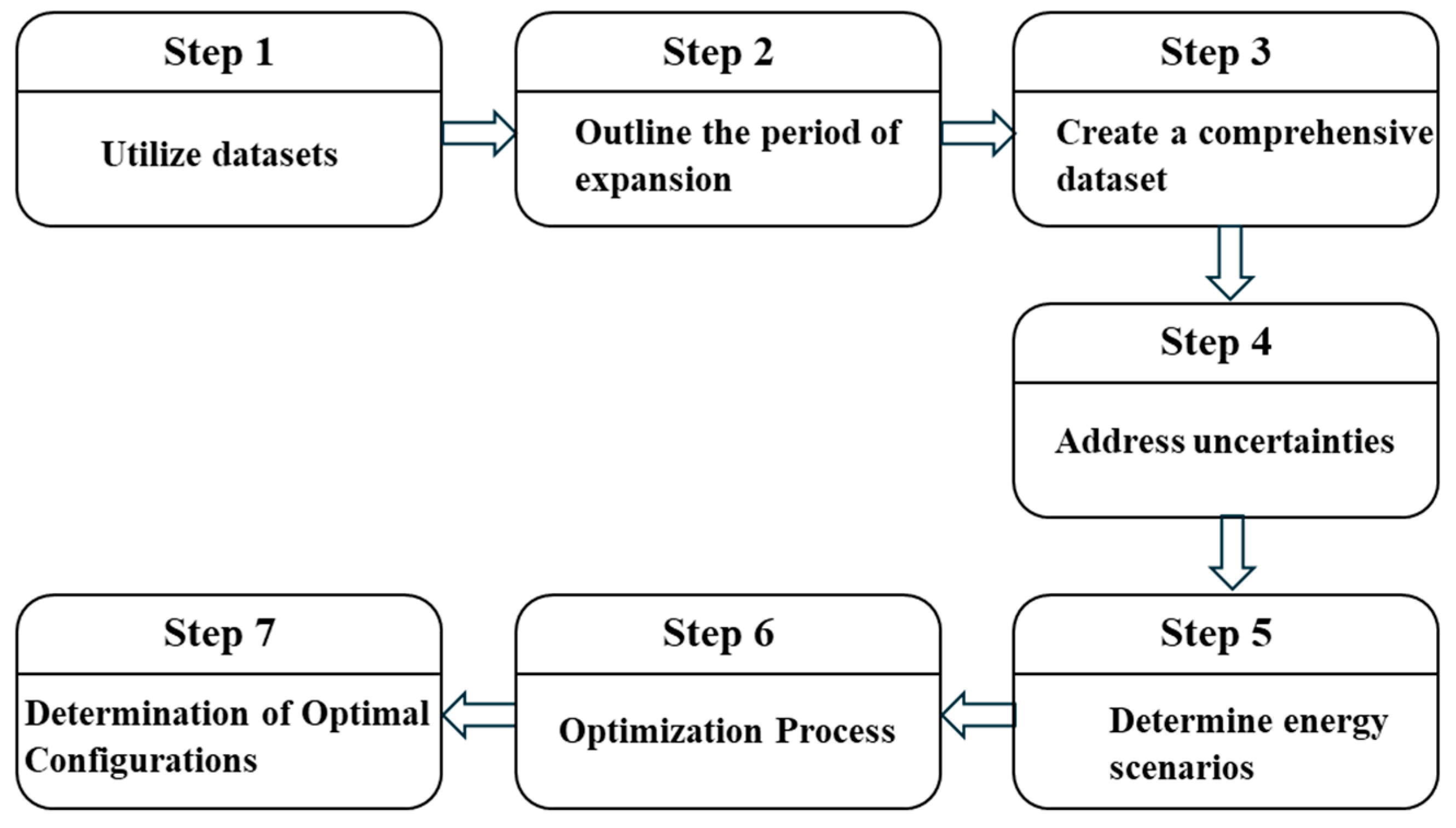
2. Framework of the Planning
2.1. Utilize Datasets
2.2. Outline the Period of Expansion
2.3. Create a Comprehensive Dataset
2.4. Address Uncertainties
2.5. Determine Energy Scenarios
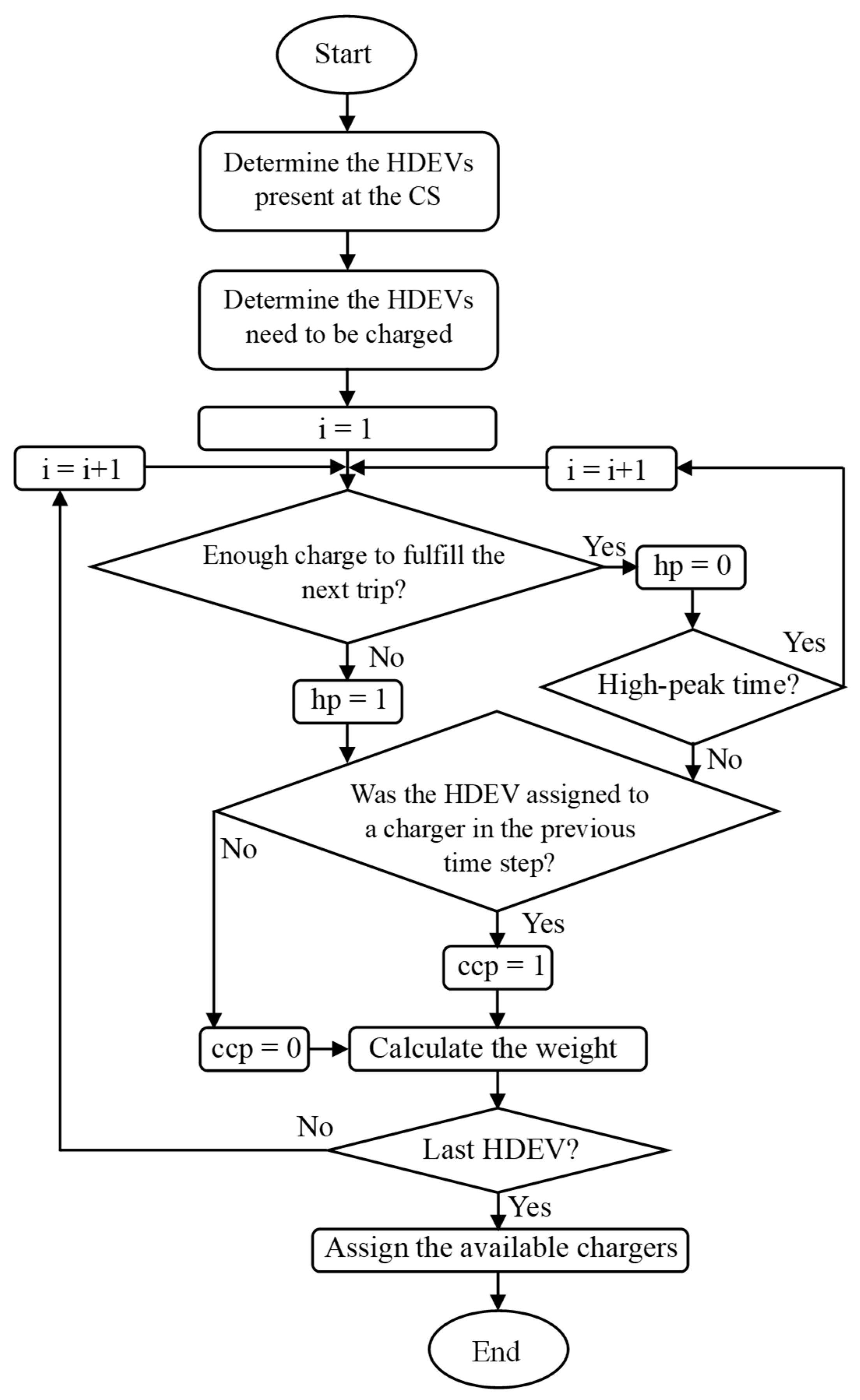
2.5.1. Utility-Based CSs Energy Scenario
2.5.2. RE-Based CS Energy Scenario
2.5.3. On the Road Energy Scenario
2.6. Optimization Process
2.7. Determination of Optimal Configurations
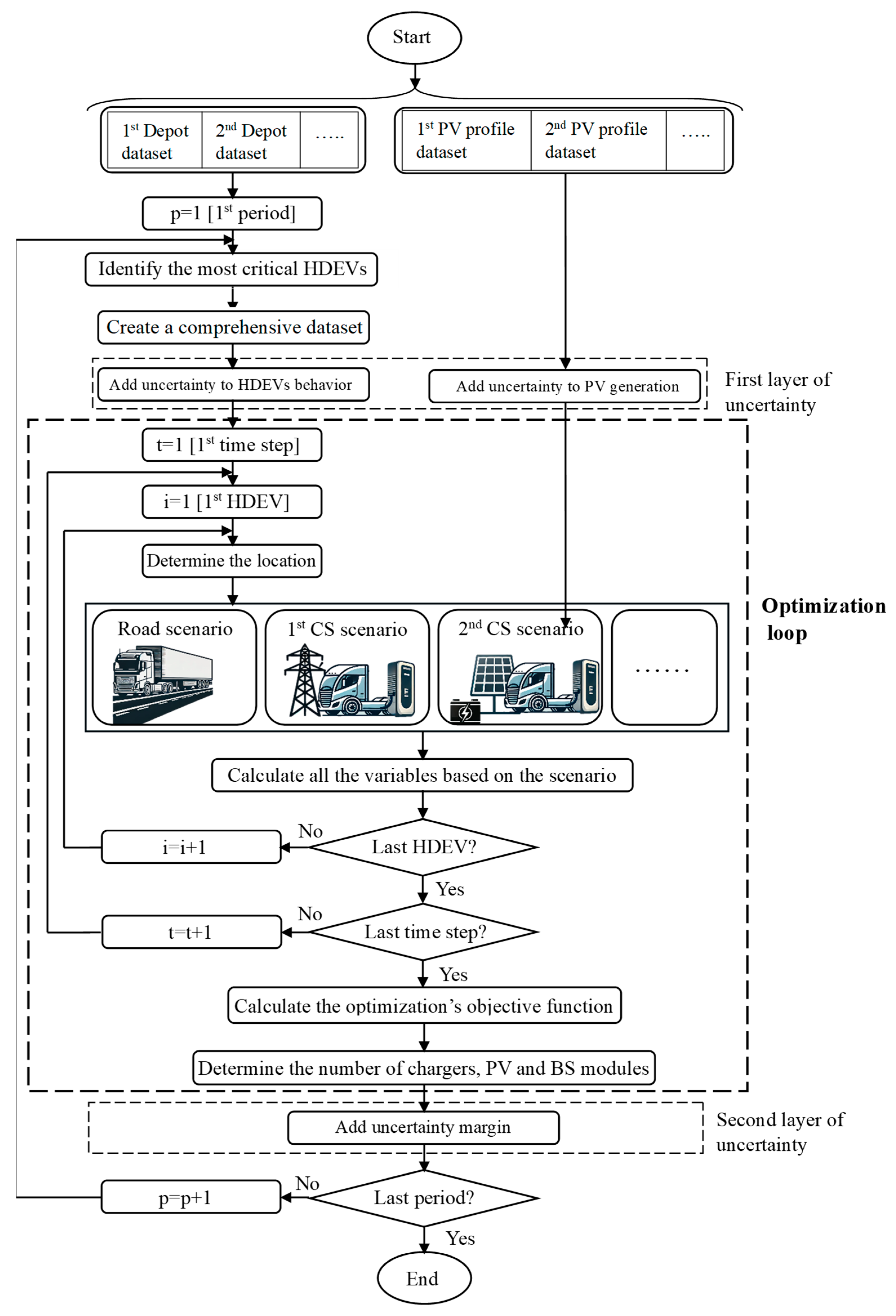
3. Uncertainty Modeling
3.1. First Layer of Uncertainty Modeling
3.1.1. Photovoltaic Generation
3.1.2. HDEV Activity
3.2. Second Layer of Uncertainty Modeling
4. Optimization Procedure
4.1. Objective Function
4.1.1. Annual Capital Cost
4.1.2. Annual Operation and Maintenance Cost
4.2. Design Constraints
4.3. Optimization Method
5. Case Study
5.1. Adding the First Layer of Uncertainty
5.1.1. PV Generation
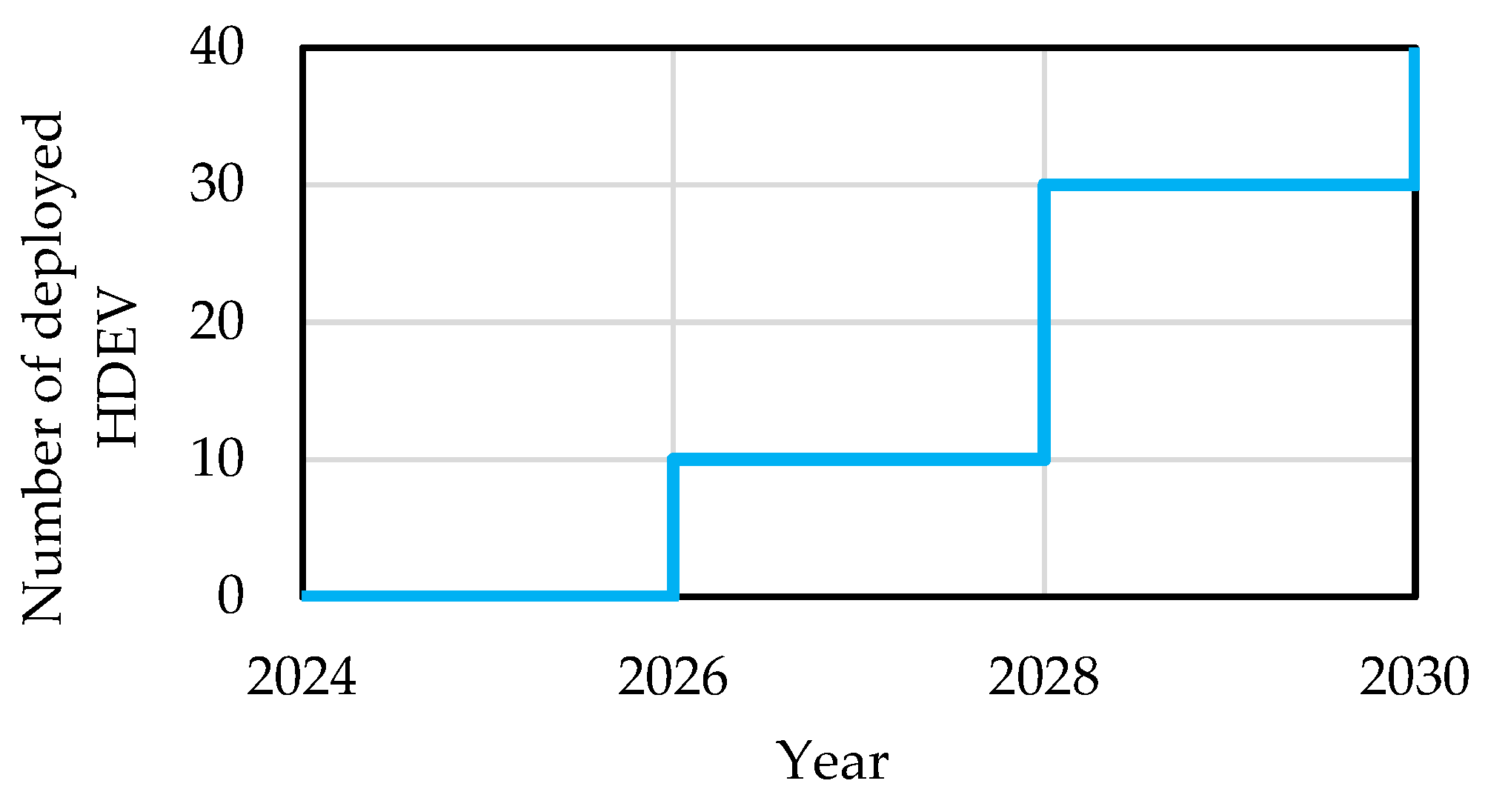
5.1.2. HDEV Activity
5.2. Optimization Results of Sizing for Each Expansion Period
5.3. Evaluation Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABC | Artificial bee colony |
| BS | Battery storage |
| CS | Charging station |
| EV | Electric vehicle |
| GA | Genetic algorithm |
| HDEV | Heavy-duty electric vehicle |
| HDV | Heavy-duty vehicle |
| HOMER | Hybrid optimization model for electric renewables |
| ICE | Internal combustion engine |
| LDEVs | Low-duty electric vehicles |
| OM | Annual operation and maintenance |
| PSO | Particle swarm algorithm |
| PV | Photovoltaic |
| RE | Renewable energy |
| SCE | Southern California Edison |
| SOC | State of charge |
| Variables | |
| APV | PV module surface area (m2) |
| CRF | Capital recovery factor |
| Cbill | The monthly electricity bill (USD) |
| CC,BS | Capital cost of a BS module (USD) |
| CC,CH | Capital cost of a charger (USD) |
| CC,PV | Capital cost of a PV module (USD) |
| CHigh | Utility billing rates during high peak (USD/kWh) |
| Cinit,BS | Initial capital cost of BS (USD) |
| CLow | Utility billing rates during low peak (USD/kWh) |
| CMid | Utility billing rates during mid peak (USD/kWh) |
| CCap | Annual capital cost |
| COM | Annual OM cost |
| COM,BS | OM cost of a BS module (USD/yr) |
| COM,CH | OM cost of a charger (USD/yr) |
| COM,PV | OM cost of a PV module (USD/yr) |
| Ccrate | Maximum charging C-rate of BS |
| Maximum discharging C-rate of BS | |
| EBS,j | Total BS capacity (kWh) at the jth CS |
| EBS,module | Capacity of each BS module (kWh) |
| EHigh | The amount of energy consumed during high peak (kWh) |
| ELow | The amount of energy consumed during low peak (kWh) |
| EMid | The amount of energy consumed during mid peak (kWh) |
| EVBt,i | Battery size of ith HDEV (kWh) |
| F | Total annual cost (USD) |
| i | Index for HDEV |
| int | Interest rate |
| I | Solar irradiation (W/m2) |
| j | Index for CS |
| Lnext,trip,i | Next trip distance of ith HDEV (miles) |
| Lpremile,i | Mileage covered since the previous time step by ith HDEV (miles) |
| n | Lifespan of the project (yr) |
| NBS,j | Number of assigned BS modules at the jth CS |
| Nchar,j | Number of available chargers at the jth CS |
| NCH,before | Total number of chargers before incorporating non-functioning chargers’ impact |
| NCH,after | Total number of chargers after incorporating non-functioning chargers’ impact |
| NCH,j | Number of physically assigned chargers at the jth CS |
| NCH,BS,j | Float number of chargers that can be supplied by the BS at jth CS |
| NCH,PV,j | Float number of chargers that can be supplied by the PV system at jth CS |
| NCS | Number of CSs |
| NRECS | Number of RE-based CSs |
| NH | Number of HDEVs |
| NP,j | Number of HDEVs present at the jth CS |
| NPV,j | Number of assigned PV modules at the jth CS |
| NTC,j | Number of HDEVs that need charging at the jth CS |
| PBS,j | Charge/discharge power of BS at the jth CS (kW) |
| PCH,rated | Rated power of each charger (kW) |
| Pload,j | Total power required by the active chargers at the jth CS (kW) |
| Pmax,BS,j | Maximum possible throughput power of BS at the jth CS (kW) |
| PPV,j | Total PV capacity (kW) |
| PPV,module | Capacity of each PV module (kW) |
| SOCBS,j | SOC of BS at the jth CS |
| SOCH | Maximum allowable limit SOC for each BS |
| SOCL | Minimum allowable limit SOC for each BS |
| SOCnext,trip,i | Required charge for the ith HDEV to complete the next trip (%) |
| SOCVBt,i | SOC of ith HDEV’s battery |
| SPPWFBS | Single payment present worth factor of BS |
| t | Index for step time |
| tarr,i | Arrival time of ith HDEV |
| tdep,i | Departure time of ith HDEV |
| T | Number of time steps |
| BS energy conversion efficiency (%) | |
| Non-functioning charger proxy | |
| Overall PV module efficiency | |
| Fuel efficiency of ith HDEV (kWh/mile) | |
| Time step duration (h) |
References
- Clar-Garcia, D.; Campello-Vicente, H.; Fabra-Rodriguez, M.; Velasco-Sanchez, E. Research on Battery Electric Vehicles’ DC Fast Charging Noise Emissions: Proposals to Reduce Environmental Noise Caused by Fast Charging Stations. World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, E.; Johnston, J.; McConnell, R.; Palinkas, L.; Eckel, S.P. California’s Early Transition to Electric Vehicles: Observed Health and Air Quality Co-Benefits. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 867, 161761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, P. Electric Vehicle Projections 2024: Update to the 2022 Projections Report 2024. Available online: https://aemo.com.au/-/media/files/major-publications/isp/2025/stage-2/electric-vehicle-projections-2024.pdf (accessed on 4 May 2025).
- Tietz, T.; Fay, T.-A.; Schlenther, T.; Göhlich, D. Electric Long-Haul Trucks and High-Power Charging: Modelling and Analysis of the Required Infrastructure in Germany. World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryanpur, V.; Rogan, F. Decarbonising Road Freight Transport: The Role of Zero-Emission Trucks and Intangible Costs. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- California Air Resources Board. California Meets Its Target for Zero-Emissions Truck Sales Two Years Ahead of Schedule; California Air Resources Board: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2023.
- United States Joint Economic Committee. Electrifying Heavy-Duty Vehicles Will Benefit the U.S. Economy, Environment, and Public Health; United States Joint Economic Committee: Washington, DC, USA, 2024.
- Danese, A.; Torsæter, B.N.; Sumper, A.; Garau, M. Planning of High-Power Charging Stations for Electric Vehicles: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Ji, X.; Li, K. Optimal Planning of Charging Station for Electric Vehicle Based on Particle Swarm Optimization. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies (ISGT), Washington, DC, USA, 16–20 January 2012; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Borlaug, B.; Muratori, M.; Gilleran, M.; Woody, D.; Muston, W.; Canada, T.; Ingram, A.; Gresham, H.; McQueen, C. Heavy-Duty Truck Electrification and the Impacts of Depot Charging on Electricity Distribution Systems. Nat. Energy 2021, 6, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, A. Assessment of Requirements, Costs, and Benefits of Providing Charging Facilities for Battery-Electric Heavy-Duty Trucks at Safety Roadside Rest Areas; Institute of Transportation Studies: Davis, CA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Bruchon, M.; Borlaug, B.; Liu, B.; Jonas, T.; Sun, J.; Le, N.; Wood, E. Depot-Based Vehicle Data for National Analysis of Medium- and Heavy-Duty Electric Vehicle Charging; National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL): Golden, CO, USA, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Shariatio, O.; Coker, P.J.; Smith, S.T.; Potter, B.; Holderbaum, W. An Integrated Techno-Economic Approach for Design and Energy Management of Heavy Goods Electric Vehicle Charging Station with Energy Storage Systems. Appl. Energy 2024, 369, 123596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Miller, E.; Santhanagopalan, S.; Bennion, K.; Meintz, A. A Framework to Analyze the Requirements of a Multiport Megawatt-Level Charging Station for Heavy-Duty Electric Vehicles. Energies 2022, 15, 3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Helou, R.; Sivaranjani, S.; Kalathil, D.; Schaper, A.; Xie, L. The Impact of Heavy-Duty Vehicle Electrification on Large Power Grids: A Synthetic Texas Case Study. Adv. Appl. Energy 2022, 6, 100093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrest, K.; Mac Kinnon, M.; Tarroja, B.; Samuelsen, S. Estimating the Technical Feasibility of Fuel Cell and Battery Electric Vehicles for the Medium and Heavy Duty Sectors in California. Appl. Energy 2020, 276, 115439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borlaug, B.; Chaudhari, K.; Fitzgerald, R.; Garikapati, V.; Ge, Y.; Moniot, M.; Rames, C.; Reinicke, N.; Wang, J.; Wood, E. Autonomous Energy Systems: Transportation. 2020. Available online: https://www.nrel.gov/grid/autonomous-energy (accessed on 4 May 2025).
- Ugirumurera, J.; Haas, Z.J. Optimal Capacity Sizing for Completely Green Charging Systems for Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2017, 3, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, S.N.; Ahmadian, A.; Anantharaman, V.; Chu, C.-C.; Gadh, R. Power Management via Integration of Battery Energy Storage Systems with Electric Bus Charging. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Power & Energy Society Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Conference (ISGT), New Orleans, LA, USA, 24–28 April 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zahedi, R.; Ahmadian, A.; SedghiSigarchi, K.; Gadh, R. An Optimal Methodology for Mitigating the Impacts of EVs and Solar Systems on the Grid by Utilizing Existing Residential Battery Storage Capacity with No Further Grid Upgrades. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference & Expo (ITEC), Detroit, MI, USA, 21–23 June 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, W.; Li, N.; Chu, C.-C.; Gadh, R. Real-Time Energy Management in Microgrids. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2015, 8, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Home|JETSI. Available online: https://www.jetsiproject.com/ (accessed on 27 June 2024).
- Hu, D.; Huang, L.; Liu, C.; Liu, Z.-W. Locating and Sizing Charging Station in Multi-Period to Promote Electric Vehicles Adoption in Urban Areas. Energy Rep. 2024, 11, 3581–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Cao, Y.; Wang, B.; Wu, J. Multi-Stage Adaptive Expansion of EV Charging Stations Considering Impacts from the Transportation Network and Power Grid. Appl. Energy 2025, 386, 125544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Li, J.; Shu, H.; Cai, Z.; Tang, B.; Huang, X.; Zhu, M. Recent Advances of Optimal Sizing and Location of Charging Stations: A Critical Overview. Int. J. Energy Res. 2022, 46, 17899–17925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Sedghisigarchi, K.; Sheinberg, R.; Gowda, S.N.; Gadh, R. Enhancing Voltage Stability in Distribution Networks through Metaheuristic Algorithm-Based Reactive Power Compensation from MDHD EVs. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE Power & Energy Society Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Conference (ISGT), Washington, DC, USA, 19–22 February 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zahedi, R.; Lord, N.; SedghiSigarchi, K.; Gadh, R. Simultaneous Optimal Sizing of Multi Heavy-Duty Electric Charging Infrastructures Connected to Different Electric Utilities Considering Demand Charges. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Smart Mobility (SM), Niagara Falls, ON, Canada, 16–18 September 2024; pp. 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Zahedi, R.; Gharehpetian, G.B. Optimal Sizing of Floating Photovoltaic System Equipped with Hydrogen Tank and Battery ESS. In Proceedings of the 2019 Smart Grid Conference (SGC), Tehran, Iran, 18–19 December 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, A.K.V.K.; Narayana, K.V.L. Meta-Heuristics Optimization in Electric Vehicles-an Extensive Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 160, 112285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.S. Review of Meta-Heuristics and Generalised Evolutionary Walk Algorithm. Int. J. Bio-Inspired Comput. 2011, 3, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.; Chandel, S.S. Review of Software Tools for Hybrid Renewable Energy Systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 32, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahramara, S.; Moghaddam, M.P.; Haghifam, M.R. Optimal Planning of Hybrid Renewable Energy Systems Using HOMER: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 62, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Javaid, N. Jaya Learning-Based Optimization for Optimal Sizing of Stand-Alone Photovoltaic, Wind Turbine, and Battery Systems. Engineering 2020, 6, 812–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaki, B.; Chung, Y.-W.; Chu, C.; Gadh, R. Probabilistic Electric Vehicle Load Management in Distribution Grids. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo (ITEC), Detroit, MI, USA, 19–21 June 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Khaki, B.; Chung, Y.-W.; Chu, C.; Gadh, R. Nonparametric User Behavior Prediction for Distributed Ev Charging Scheduling. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM), Portland, OR, USA, 05–10 August 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- An, K. Battery Electric Bus Infrastructure Planning under Demand Uncertainty. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2020, 111, 572–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Du, B.; Liu, W.; Perez, P. A Joint Optimisation Model for Charger Locating and Electric Bus Charging Scheduling Considering Opportunity Fast Charging and Uncertainties. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2022, 141, 103732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.; Wei, W.; Khodayar, M.E.; Wang, J.; Mei, S. Planning Fully Renewable Powered Charging Stations on Highways: A Data-Driven Robust Optimization Approach. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2018, 4, 817–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmali, L.P.; Gholami, A.; Nezamoddini, N. Integrated Optimization of Production Planning and Electric Trucks Charging and Discharging Scheduling. Sustain. Energy Grids Netw. 2024, 39, 101397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rempel, D.; Cullen, C.; Bryan, M.M.; Cezar, G.V. Reliability of Open Public Electric Vehicle Direct Current Fast Chargers. Hum. Factors 2023, 66, 2528–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashkezari, L.S.; Mouli, G.R.C.; Yorke-Smith, N.; Bauer, P. Multiobjective System Sizing for Heavy-Duty Electric Vehicle Charging Stations. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Electrical Systems for Aircraft, Railway, Ship Propulsion and Road Vehicles and International Transportation Electrification Conference (ESARS-ITEC), Naples, Italy, 26–29 November 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, D.; Cao, Y.; Beil, I. Bi-Level Optimization Framework for Heavy-Duty Electric Truck Charging Station Design. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference & Expo (ITEC), Anaheim, CA, USA, 15–17 June 2022; pp. 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.A.S.; Ingalalli, A.; Ur Rehman, W.; Bhavaraju, V. Sizing of Fast Charging Infrastructure Site for Commercial Electric Vehicle Fleet Considering Smart Charge Management. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference & Expo (ITEC), Chicago, IL, USA, 19–21 June 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danese, A.; Garau, M.; Sumper, A.; Torsæter, B.N. Electrical Infrastructure Design Methodology of Dynamic and Static Charging for Heavy and Light Duty Electric Vehicles. Energies 2021, 14, 3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheri, A. A Critical Evaluation of Deterministic Methods in Size Optimisation of Reliable and Cost Effective Standalone Hybrid Renewable Energy Systems. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2014, 130, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferris, D. Politico. 2023. Available online: https://www.politico.com/live-updates/2023/11/14/congress/house-passes-johnson-bill-to-avert-shutdown-00127099 (accessed on 4 May 2025).
- California Air Resources Board. Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment Standards Technology Review; California Air Resources Board: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2022.
- Maleki, A.; Ameri, M.; Keynia, F. Scrutiny of Multifarious Particle Swarm Optimization for Finding the Optimal Size of a PV/Wind/Battery Hybrid System. Renew. Energy 2015, 80, 552–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tervo, E.; Agbim, K.; DeAngelis, F.; Hernandez, J.; Kim, H.K.; Odukomaiya, A. An Economic Analysis of Residential Photovoltaic Systems with Lithium Ion Battery Storage in the United States. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 94, 1057–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RATE SCHEDULES TOU-EV-7, TOU-EV-8, TOU-EV-9. Available online: https://www.sce.com/sites/default/files/inline-files/TOU-EV-7_8_9%20Rate%20Fact%20Sheet_WCAG%20(2).pdf (accessed on 7 July 2024).
- Li, J.; He, S.; Yang, Q.; Ma, T.; Wei, Z. Optimal Design of the EV Charging Station with Retired Battery Systems against Charging Demand Uncertainty. IEEE Trans. Industr. Inform. 2022, 19, 3262–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-H.; Lee, W.-C.; Ke, J.-C.; Liu, T.-H. Optimization Analysis of an Unreliable Multi-Server Queue with a Controllable Repair Policy. Comput. Oper. Res. 2014, 49, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Advanced Clean Fleets Regulation Summary. California Air Resources Board. 2023. Available online: https://ww2.arb.ca.gov/our-work/programs/advanced-clean-fleets (accessed on 4 May 2025).
- Sbordone, D.; Bertini, I.; Di Pietra, B.; Falvo, M.C.; Genovese, A.; Martirano, L. EV Fast Charging Stations and Energy Storage Technologies: A Real Implementation in the Smart Micro Grid Paradigm. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2015, 120, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liimatainen, H.; van Vliet, O.; Aplyn, D. The Potential of Electric Trucks–An International Commodity-Level Analysis. Appl. Energy 2019, 236, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alternative Fuels Data Center: Operation and Maintenance for Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure. Available online: https://afdc.energy.gov/fuels/electricity-infrastructure-maintenance-and-operation (accessed on 8 July 2024).
- Cole, W.; Frazier, A.W.; Augustine, C. Cost Projections for Utility-Scale Battery Storage: 2021 Update; National Renewable Energy Lab.(NREL): Golden, CO, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- IRENA. Renewable Power Generation Costs in 2020; eBook Partnership; International Renewable Energy Agency: Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2022; ISBN 9292603795. [Google Scholar]

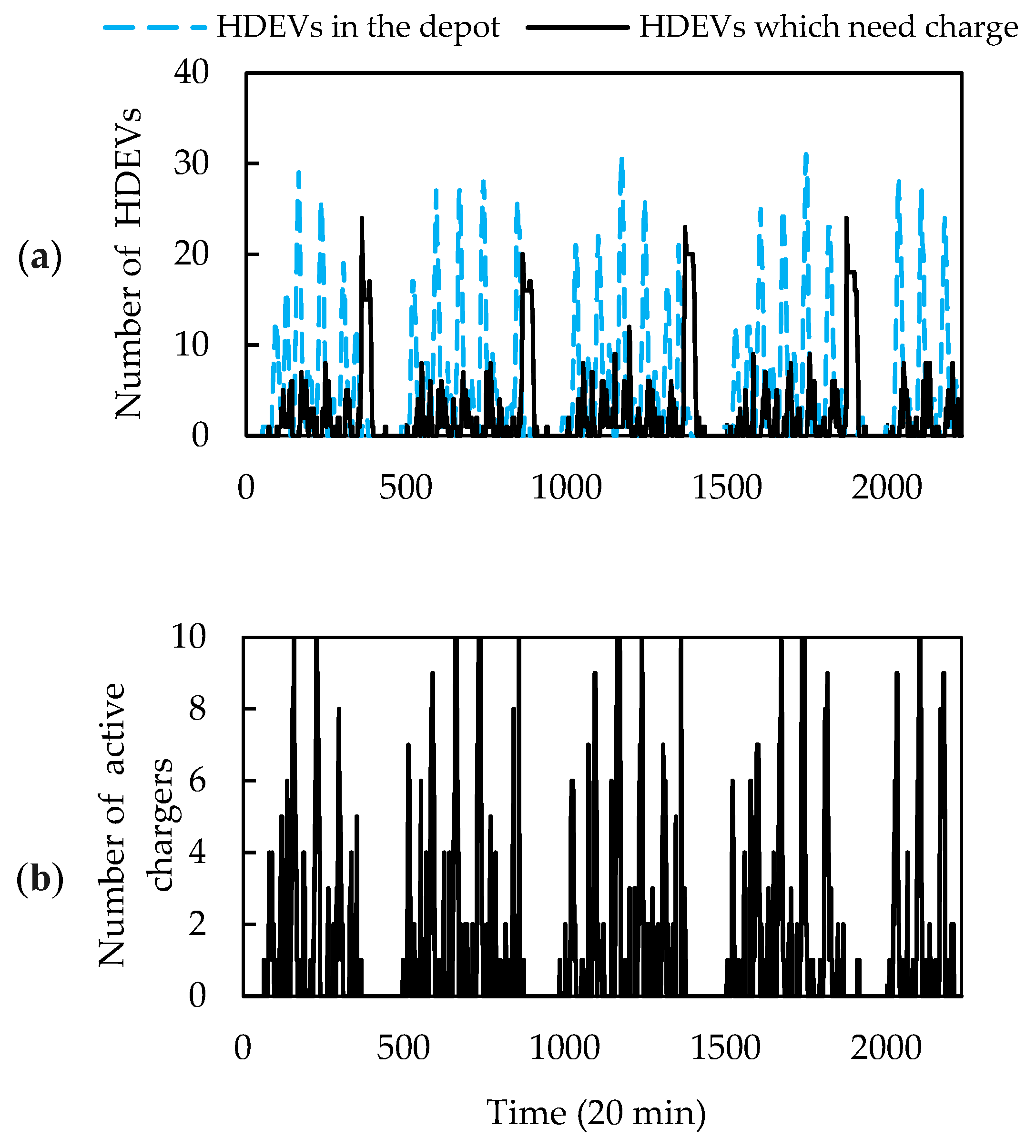

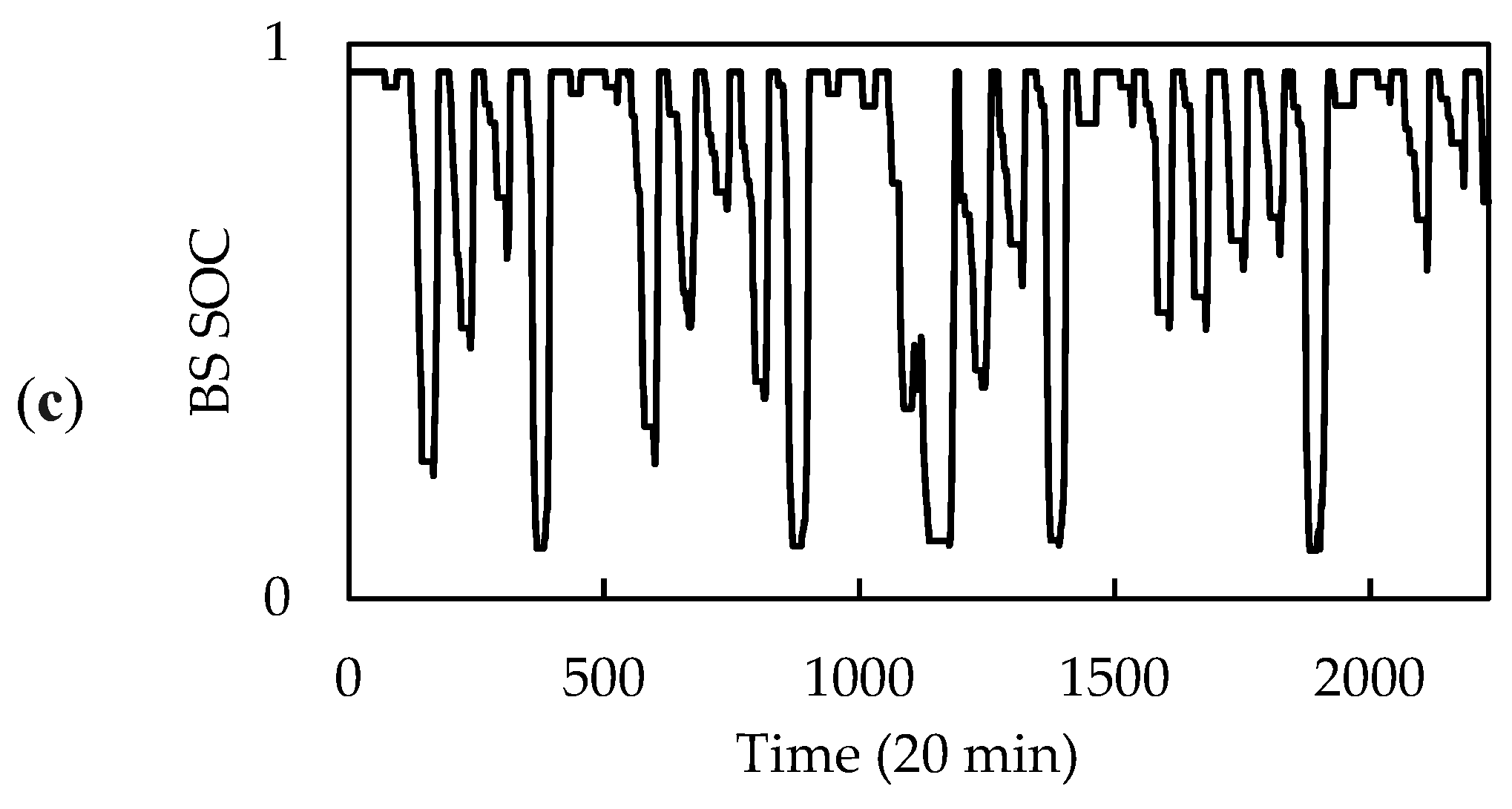

| Symbol | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| CC,BS | 626 | USD/kWh |
| CC,CH | 960 | USD/unit |
| CC,PV | 111.9 | USD/kW |
| COM,BS | 2.5%* CC,BS | USD |
| COM,CH | 800 | USD/unit/yr |
| COM,PV | 13 | USD/kW/yr |
| 1 | - | |
| CHigh | 0.16799 | USD/kWh |
| CMid | 0.09729 | USD/kWh |
| CLow | 0.04595 | USD/kWh |
| 100 | kWh | |
| EVBt | 550 | kWh |
| j | 4 | % |
| n | 20 | Yr |
| PCH,rated | 180 | kW |
| 100 | kW | |
| 0.95 | - | |
| 0.05 | - | |
| 0.9 | - | |
| 1.27 | - | |
| 2.22 | kWh/mil | |
| 20 | min |
| Period 1 | Period 2 | Period 3 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | |
| Chargers at CS1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 10 |
| Chargers at CS2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 7 | 7 | 11 |
| PV modules | 6 | 6 | 8 | 15 | 16 | 16 | 20 | 20 | 35 |
| BS modules | 6 | 6 | 6 | 11 | 12 | 19 | 15 | 24 | 36 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the World Electric Vehicle Association. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zahedi, R.; Sheinberg, R.; Gowda, S.N.; SedghiSigarchi, K.; Gadh, R. A Framework for Optimal Sizing of Heavy-Duty Electric Vehicle Charging Stations Considering Uncertainty. World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16, 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16060318
Zahedi R, Sheinberg R, Gowda SN, SedghiSigarchi K, Gadh R. A Framework for Optimal Sizing of Heavy-Duty Electric Vehicle Charging Stations Considering Uncertainty. World Electric Vehicle Journal. 2025; 16(6):318. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16060318
Chicago/Turabian StyleZahedi, Rafi, Rachel Sheinberg, Shashank Narayana Gowda, Kourosh SedghiSigarchi, and Rajit Gadh. 2025. "A Framework for Optimal Sizing of Heavy-Duty Electric Vehicle Charging Stations Considering Uncertainty" World Electric Vehicle Journal 16, no. 6: 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16060318
APA StyleZahedi, R., Sheinberg, R., Gowda, S. N., SedghiSigarchi, K., & Gadh, R. (2025). A Framework for Optimal Sizing of Heavy-Duty Electric Vehicle Charging Stations Considering Uncertainty. World Electric Vehicle Journal, 16(6), 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16060318








