Longitudinal Exploration of Regularity and Variability in Electric Car Charging Patterns
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data
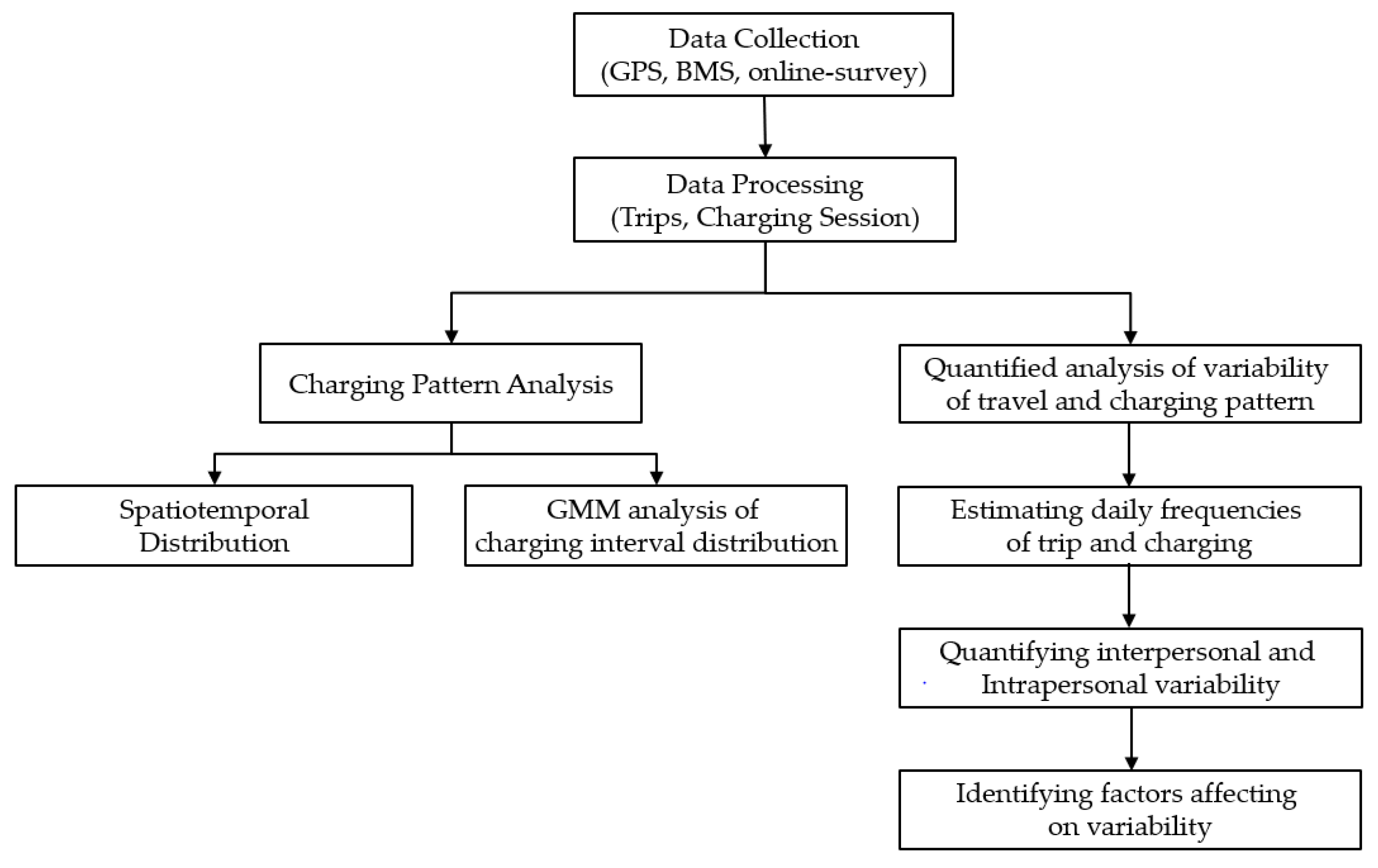
2.2. Method
2.2.1. Spatiotemporal Charging Patterns and Charging Interval Distributions
2.2.2. Quantified Analysis of Variability in Travel and Charging Patterns
3. Results
3.1. Charging Pattern Analysis
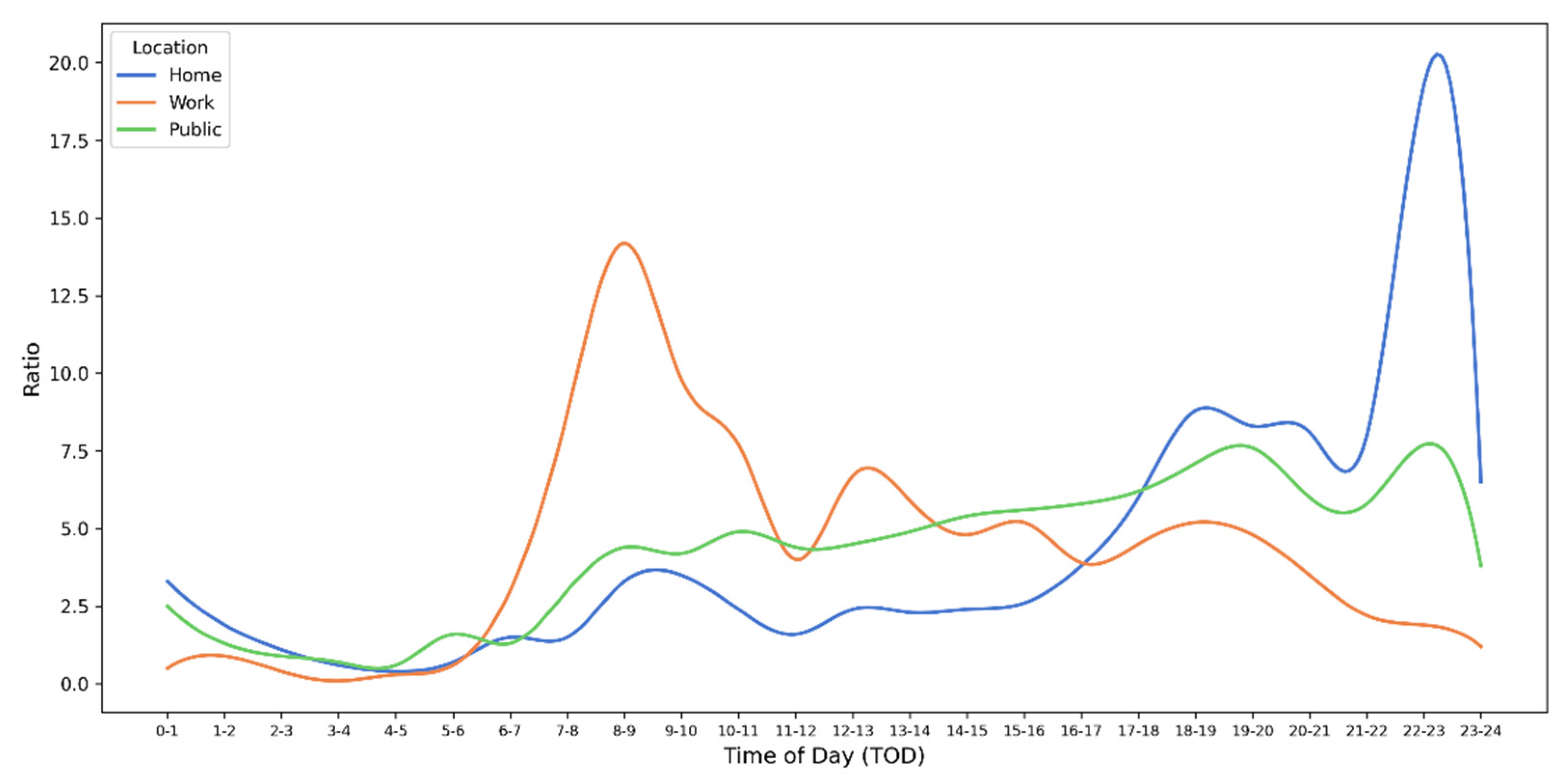
3.1.1. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Charging Behaviors
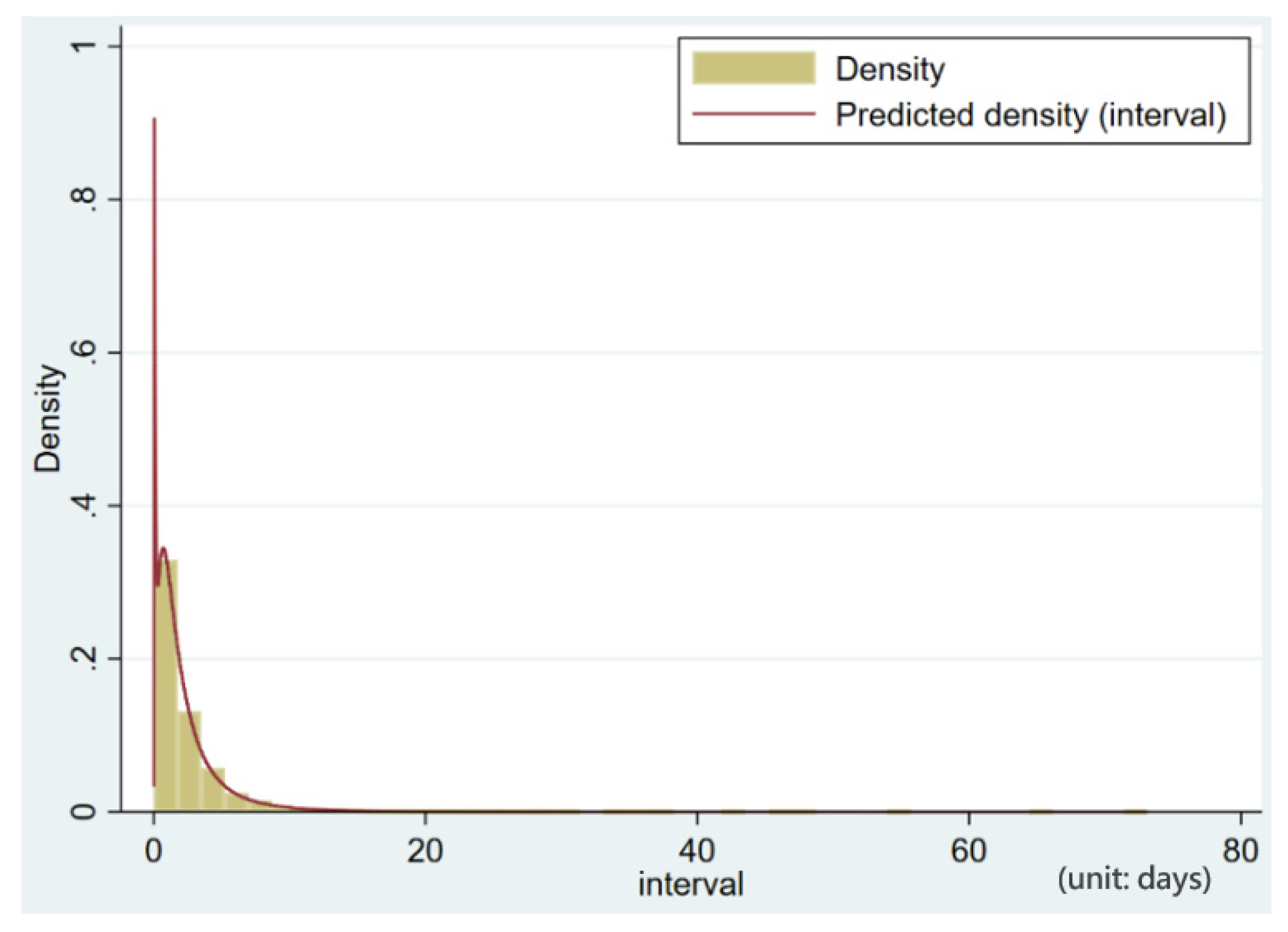
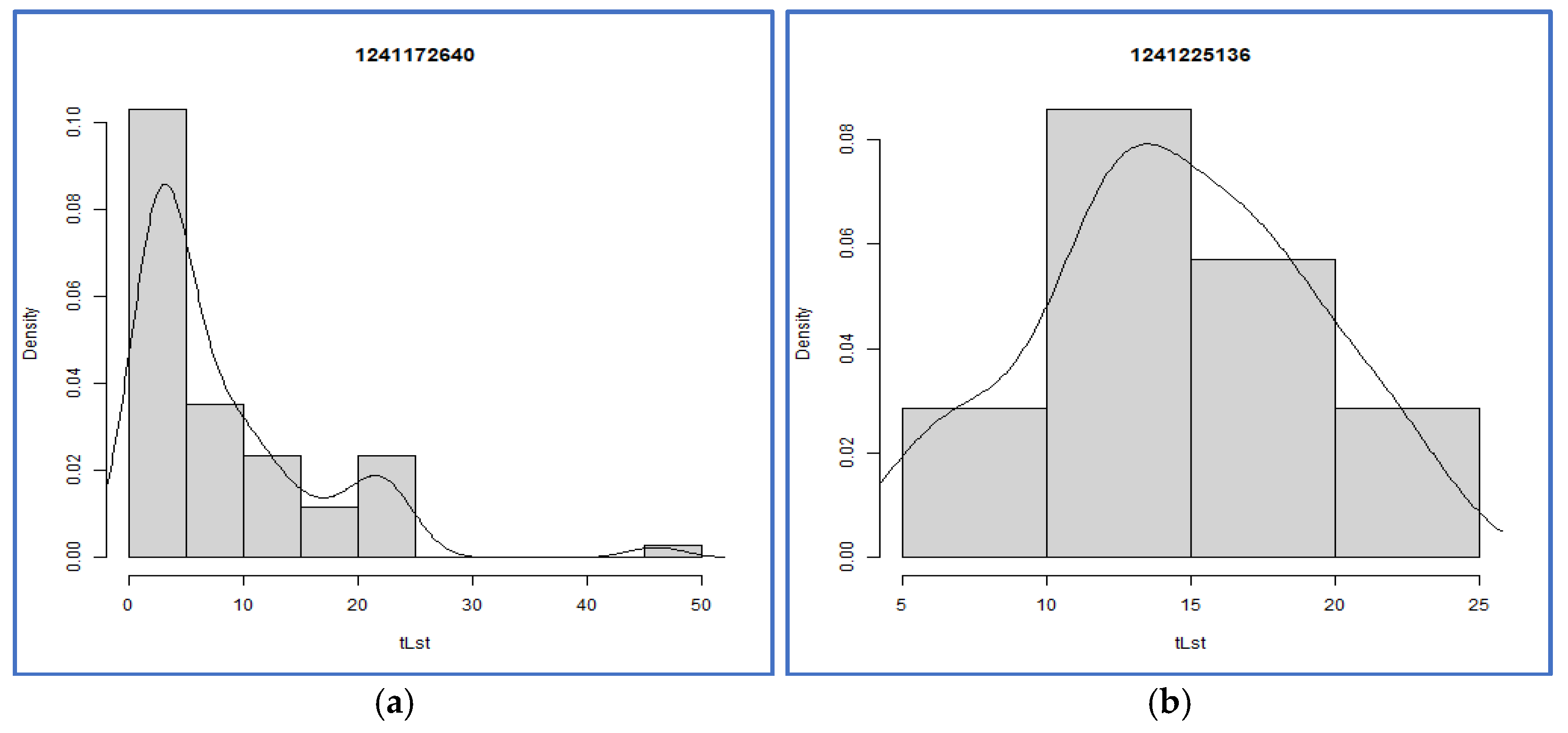
3.1.2. Distributions of Charging Interval: Aggregated Versus Individual
3.2. Analysis of Variability in Charging Patterns
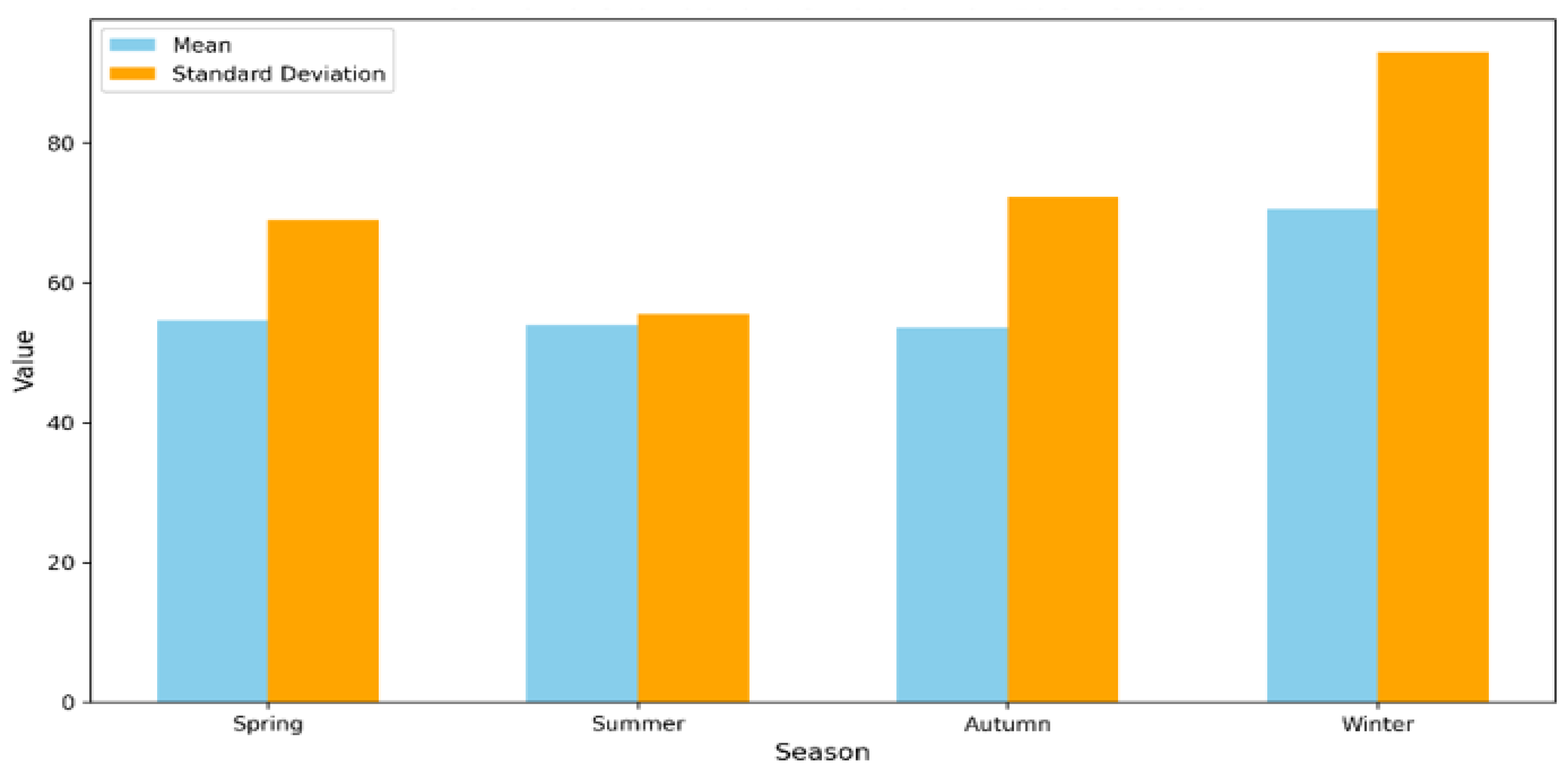
3.2.1. Trips and Charging Frequencies per Day
3.2.2. Quantified Variability in Trips and Charging Frequencies
3.2.3. Factors Affecting Intrapersonal Variability in Charging Patterns
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Energy Agency (IEA). Global EV Outlook 2024. Moving Towards Increased Affordability. Available online: https://iea.blob.core.windows.net/assets/a9e3544b-0b12-4e15-b407-65f5c8ce1b5f/GlobalEVOutlook2024.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- Cao, Y.; Tang, S.; Li, C.; Zhang, P.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J. An optimized EV charging model considering TOU price and SOC curve. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2011, 3, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, T.; Krems, J.F. Understanding charging behaviour of electric vehicle users. Transp. Res. Part F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2013, 21, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, N.; Sivakumar, A.; Polak, J.W. Electric vehicle charging choices: Modelling and implications for smart charging services. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2017, 81, 36–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potoglou, D.; Song, R.; Santos, G. Public charging choices of electric vehicle users: A review and conceptual framework. Transp. Res. Part D 2023, 121, 103824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Yang, D.; Rasoulli, S.; Timmermans, H. Heterogeneous hazard model of PEV users charging intervals: Analysis of four year charging transactions data. Transp. Res. Part C 2017, 82, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Song, Y.; Hu, X.; Guardiola, I.G. Analysis of electric vehicle charging behavior patterns with function principal component analysis approach. J. Adv. Transp. 2020, 2020, 8850654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahriar, S.; Al-Ali, A.R.; Osman, A.H.; Dhou, S.; Nijim, M. Machine learning approaches for EV charging behavior: A review. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 168980–168993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortimer, B.J.; Hecht, C.; Goldbeck, R.; Sauer, D.U.; De Doncker, R.W. Electric Vehicle Public Charging Infrastructure Planning Using Real-World Charging Data. World Electr. Veh. J. 2022, 13, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munshi, A.; Mohamed, Y.A.-R.I. Extracting and Defining Flexibility of Residential Electrical Vehicle Charging Loads. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 14, 448–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crozier, C.; Morstyn, T.; McCulloch, M. Capturing diversity in electric vehicle charging behaviour for network capacity estimation. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2021, 93, 102762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Ma, Z. Unveiling electric vehicle (EV) charging patterns and their transformative role in electricity balancing and delivery: Insights from real-world data in Sweden. Renew. Energy 2024, 236, 121511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, S.; Cezar, G.V.; Rajagopal, V. Scalable probabilistic estimates of electric vehicle charging given observed driver behavior. Appl. Energy 2022, 309, 118382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martz, A.; Langenmayr, U.; Ried, S.; Seddig, K.; Jochem, P. Charging behavior of electric vehicles: Temporal clustering based on real-world data. Energies 2022, 15, 6575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Shao, C.; Zhuge, C.; Wang, P.; Yang, X.; Wang, S. Uncovering travel and charging patterns of private electric vehicles with trajectory data: Evidence and policy implications. Transportation 2021, 49, 1409–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axhausen, K.W.; Zimmermann, A.; Schönfelder, S.; Rindsfüser, G.; Haupt, T. Observing the rhythms of daily life: A six-week travel diary. Transportation 2002, 29, 95–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pas, E.I. Intrapersonal variability and model goodness-of-fit. Transp. Res. 1987, 21, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlich, R.; Axhausen, K.W. Habitual travel behaviour: Evidence from a six-week travel diary. Transportation 2003, 30, 13–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, R.; Yamamoto, T.; Susilo, Y.O.; Axhausen, K.W. How routine is a routine? An analysis of the day-to-day variability in prism vertex location. Transp. Res. Part A 2006, 40, 259–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmus, J.R.; Lees, M.H.; van den Hoed, R. A data driven typology of electric vehicle user types and charging sessions. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2020, 115, 102637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hong, Y.; Hu, C. Research on Big Data Mining Technology of Electric Vehicle Charging Behaviour. Elektron. Elektrotechnika 2019, 25, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, P.; Kazemzadeh, K.; Bansal, P. Integration of charging behavior into infrastructure planning and management of electric vehicles: A systematic review and framework. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 88, 104265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, C. Charging pattern of Electric Vehicle User and Affecting Facotrs: Latent Class Analysis Approach. Trans. Korean Inst. Electr. Eng. 2022, 71, 1639–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- StataCorp. Finite Mixture Model (FMMs). Available online: https://www.stata.com/features/overview/finite-mixture-models/ (accessed on 1 October 2024).
- Raux, C.; Ma, T.Y.; Cornelis, E. Variability in daily activity-travel patterns: The case of a one-week travel diary. Eur. Transp. Res. Rev. 2016, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Park, J.; Yoo, J.; Park, J. An empirical study on spatiotemporal distribution of charge load by electric vehicle driver in Kora. In Proceedings of the EVS 37, International Electric Vehicles Symposium and Exhibition, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 23–26 April 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Chakraborty, D.; Hardman, S.J.; Tal, G. Exploring electric vehicle charging patterns: Mixed usage of charging infrastructure. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2020, 79, 102249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adenaw, L.; Lienkamp, M. Multi-Criteria, Co-Evolutionary Charging Behavior: An Agent-Based Simulation of Urban Electromobility. World Electr. Veh. J. 2021, 12, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herfindahl, O.C. Concentration in the Steel Industry. Ph.D. Thesis, Columbia University, New York, NY, USA, 1950. [Google Scholar]
- Susilo, Y.O.; Axhausen, K.W. Repetitions in individual daily activity–travel–location patterns: A study using the Herfindahl–Hirschman Index. Transportation 2014, 41, 995–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, F.; Watling, D.P.; Connors, R.D. Analysing Spatial Intrapersonal Variability of Road Users Using Point-to-Point Sensor Data. Netw. Spat. Econ. 2023, 23, 373–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristics | Ratio (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male driver | 90.9 |
| Female driver | 9.1 | |
| Age | Under 40 | 30.5 |
| 40 to 60 | 63.5 | |
| Above 60 | 6.0 | |
| EV model | IONIQ | 28.2 |
| BOLT | 22.2 | |
| EV6 | 19.4 | |
| KONA | 14.2 | |
| Others | 16.0 | |
| Battery capacity | Under 70 kwh | 52.1 |
| Above 70 kwh | 47.9 | |
| Description of family | Single family | 14.5 |
| Dual family | 36.7 | |
| Multi family | 48.7 | |
| Occupation | Office worker | 40.7 |
| Others | 59.3 | |
| Average monthly income | Low income | 19.1 |
| Middle income | 63.0 | |
| High income | 17.9 | |
| Region | Metropolitan area | 32.2 |
| Others | 67.8 | |
| Home charging availability | Available | 70.1 |
| Unavailable | 29.9 | |
| Classification | Average of Charging Interval (Day) | Standard Deviation of Charging Interval (Day) |
|---|---|---|
| Aggregated average | 2.25 | 2.88 |
| Disaggregated average | 3.65 | 3.30 |
| Home charging only | 2.86 | 3.56 |
| Workplace charging only | 1.58 | 1.08 |
| Public charging only | 2.53 | 2.88 |
| Mixed charging * | 2.14 | 2.83 |
| Component Type | Ratio (%) | Average (Day) | Variance (Day Square) | Information Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Component 1 | 13.3 | −2.30 | −0.18 | Log-likelihood = −29,341.8, AIC *= 58,693.6, BIC **= 58,732.1 |
| Component 2 | 86.7 | 0.52 | −0.09 |
| Classification | Mean | Standard Deviation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Individual averages | Trips | 3.55 | 1.39 |
| Charging frequency | 0.62 | 0.54 | |
| Daily averages | Trips | 3.56 | 0.38 |
| Charging frequency | 0.54 | 0.10 | |
| Variability | Trips | Charging Frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total variability | TSS | 794,552 | 115,203 |
| Interpersonal variability | BPSS | 203,410 | 26,665 |
| Intrapersonal variability | WPSS (C = A + B) | 591,142 | 88,538 |
| BDSS (A) | 15,154 | 946 | |
| WDSS (B) | 575,988 | 87,592 | |
| Ratio of (A) to (B) | 2.56% | 1.07% | |
| Ratio of BPSS to TSS | 25.6% | 23.15% | |
| Key Variables | Specific Variables | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | If (gender = male), 1, otherwise 0 |
| Age | Age30 | If (age < 30), age30 = 1, otherwise age30 = 0 |
| Age4050 | If (age >= 30 and age < 50), age4050 =1, otherwise age4050 = 0 | |
| Age60 | If (age >= 60), age60 = 1, otherwise age60=0 | |
| EV model | IONIQ | If (EV model = IONIQ), 1, otherwise 0 |
| BOLT | If (EV model = BOLT), 1, otherwise 0 | |
| EV6 | If (EV model = EV6), 1, otherwise 0 | |
| KONA | If (EV model = KONA), 1, otherwise 0 | |
| Others | If (EV model is not above type), 1, otherwise 0 | |
| Battery capacity | Battery capacity | Battery capacity of EV |
| Number of family | Single family | If (number of family = 1), 1, otherwise 0 |
| Dual family | If (number of family = 2), 1, otherwise 0 | |
| Multi family | If (number of family = 3), 1, otherwise 0 | |
| Occupation | Office worker | If (occupation = office worker), 1, otherwise 0 |
| Average monthly income | Low income | If (average monthly income of the respondent’s household (KRW 10,000) < 300), 1, otherwise 0 |
| Middle income | If (average monthly income of the respondent’s household (KRW 10,000) > 300 & income < 1000), 1, otherwise 0 | |
| High income | If (average monthly income of the respondent’s household (KRW 10,000) >= 1000), 1, otherwise 0 | |
| Region | Region | If (Region of residence is metropolitan area), 1, otherwise 0 |
| Home charging | Home charging availability | If (Home charging is available) 1, otherwise 0 |
| Trip | Average number of trips | Average number of trips per day |
| Charging | Average number of charging | Average number of charging frequencies per day |
| Variables | Coefficient | Standard Error | z | P > │z│ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | −0.022 | 0.138 | −0.16 | 0.871 |
| Age60 | −0.227 | 0.167 | −1.36 | 0.174 |
| IONIQ base | ||||
| BOLT | −0.615 (***) | 0.211 | −2.92 | 0.004 |
| EV6 | −0.061 | 0.112 | −0.55 | 0.586 |
| KONA | −0.093 | 0.245 | −0.38 | 0.704 |
| Others | −0.487 (**) | 0.237 | −2.06 | 0.040 |
| Battery capacity | −0.027 (*) | 0.016 | −1.74 | 0.083 |
| Multi family | 0.083 | 0.076 | 1.10 | 0.274 |
| Office worker | 0.004 | 0.110 | 0.04 | 0.967 |
| High income | −0.375 (**) | 0.162 | −2.31 | 0.022 |
| Region | 0.080 | 0.080 | 1.01 | 0.312 |
| Home charging availability | 0.031 | 0.132 | 0.24 | 0.814 |
| Average number of trips | 0.061 (**) | 0.029 | 2.08 | 0.038 |
| Average number of charges | 1.047 (***) | 0.077 | 13.66 | 0.000 |
| Constant | 6.329 | 0.2154 | 0.79 | 0.431 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the World Electric Vehicle Association. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, C.; Park, J. Longitudinal Exploration of Regularity and Variability in Electric Car Charging Patterns. World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16, 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16050256
Kim C, Park J. Longitudinal Exploration of Regularity and Variability in Electric Car Charging Patterns. World Electric Vehicle Journal. 2025; 16(5):256. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16050256
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Chansung, and Jiyoung Park. 2025. "Longitudinal Exploration of Regularity and Variability in Electric Car Charging Patterns" World Electric Vehicle Journal 16, no. 5: 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16050256
APA StyleKim, C., & Park, J. (2025). Longitudinal Exploration of Regularity and Variability in Electric Car Charging Patterns. World Electric Vehicle Journal, 16(5), 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16050256








