Design and Sensorless Control in Dual Three-Phase PM Vernier Motors for 5 MW Ship Propulsion
Abstract
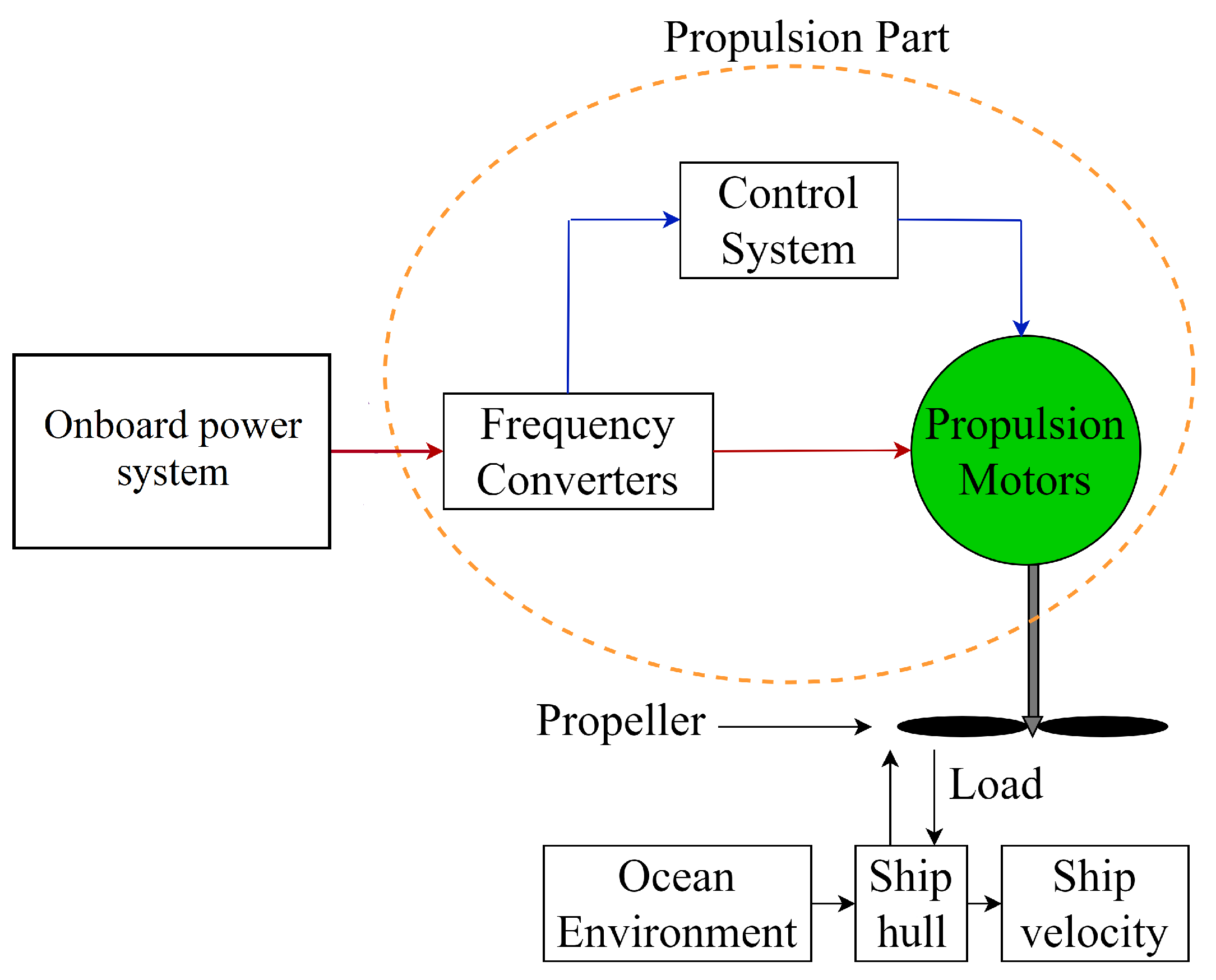
1. Introduction
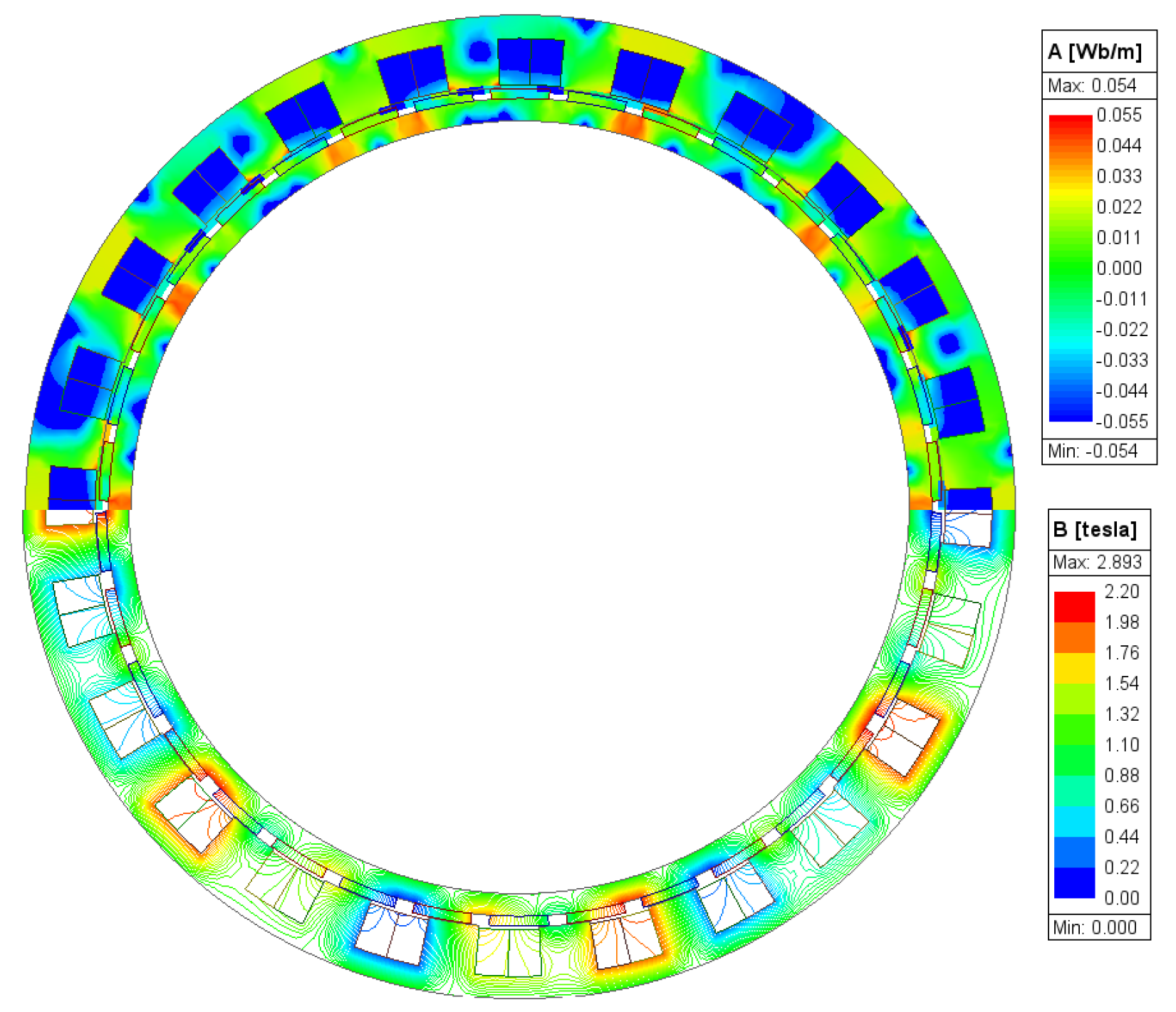
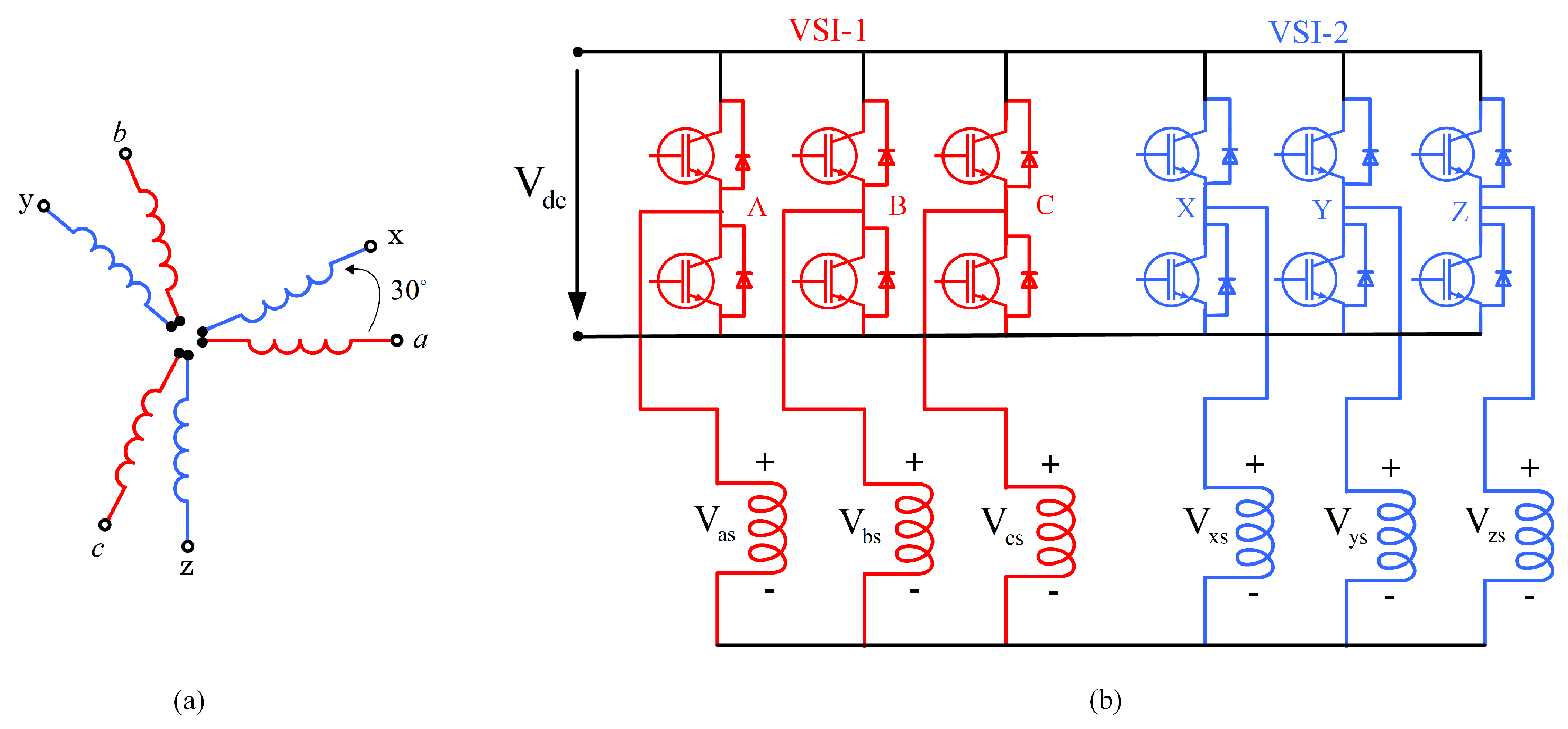
2. Operation Principle and Proposed Design
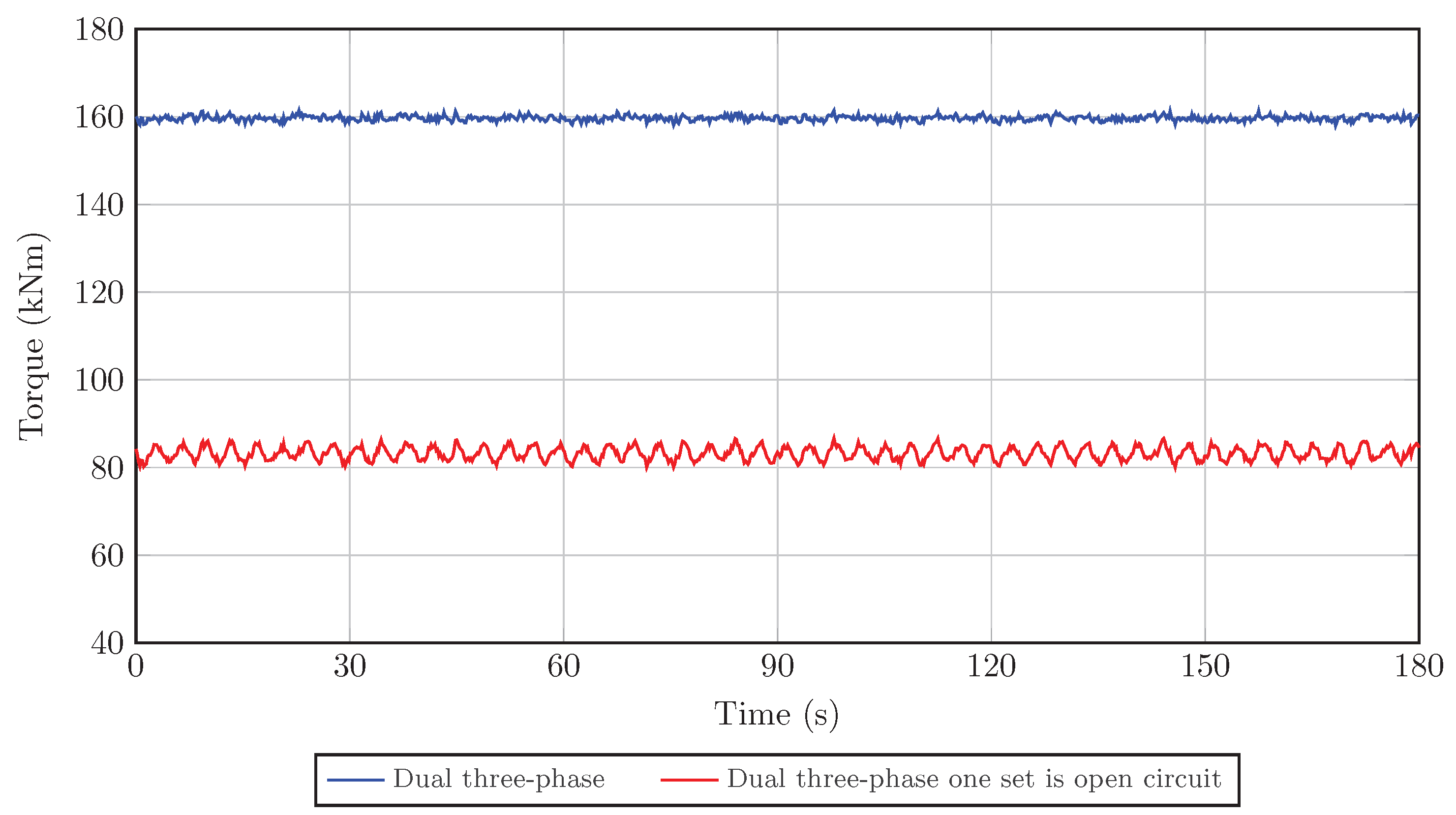
No Load and Full Load Test
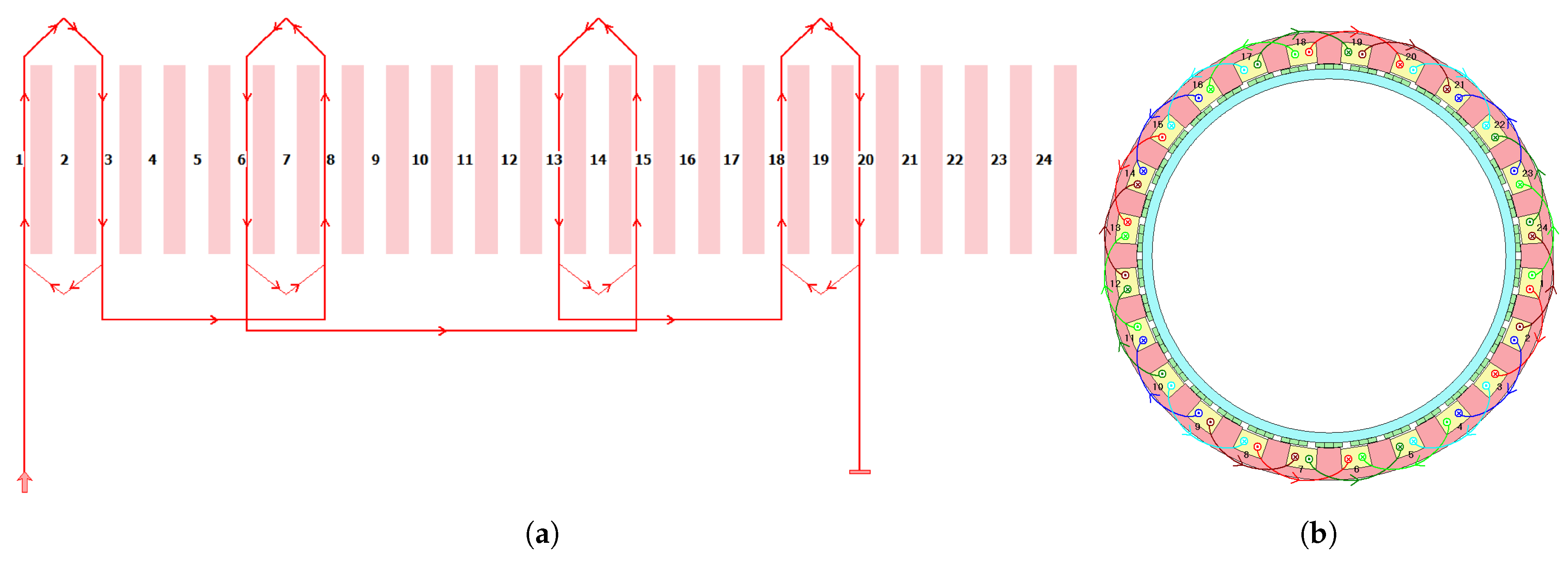
3. Dual Three-Phase Machine Modelling Methods
3.1. Modeling of MITP
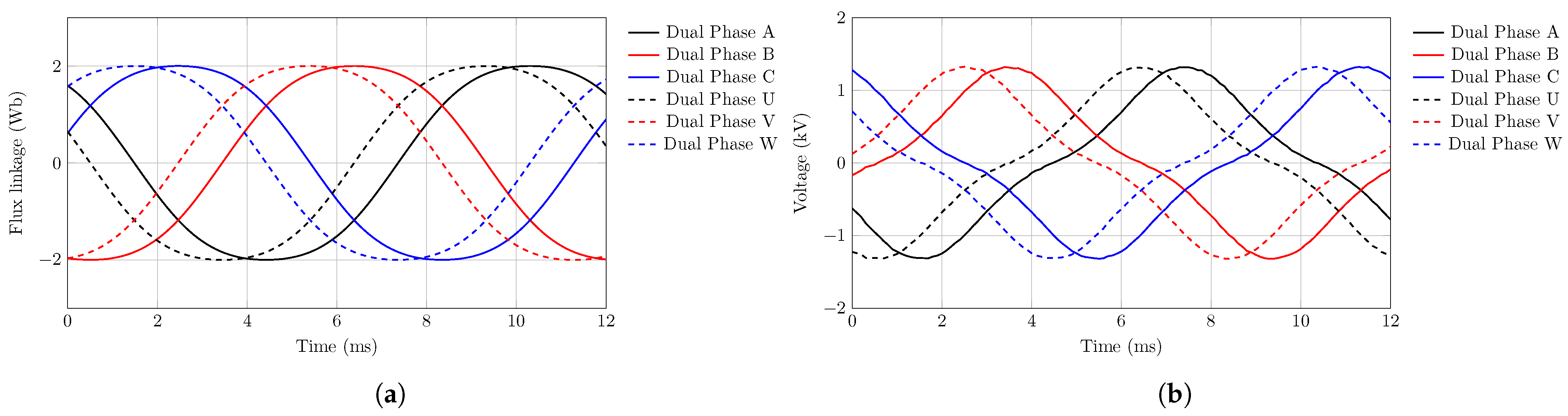
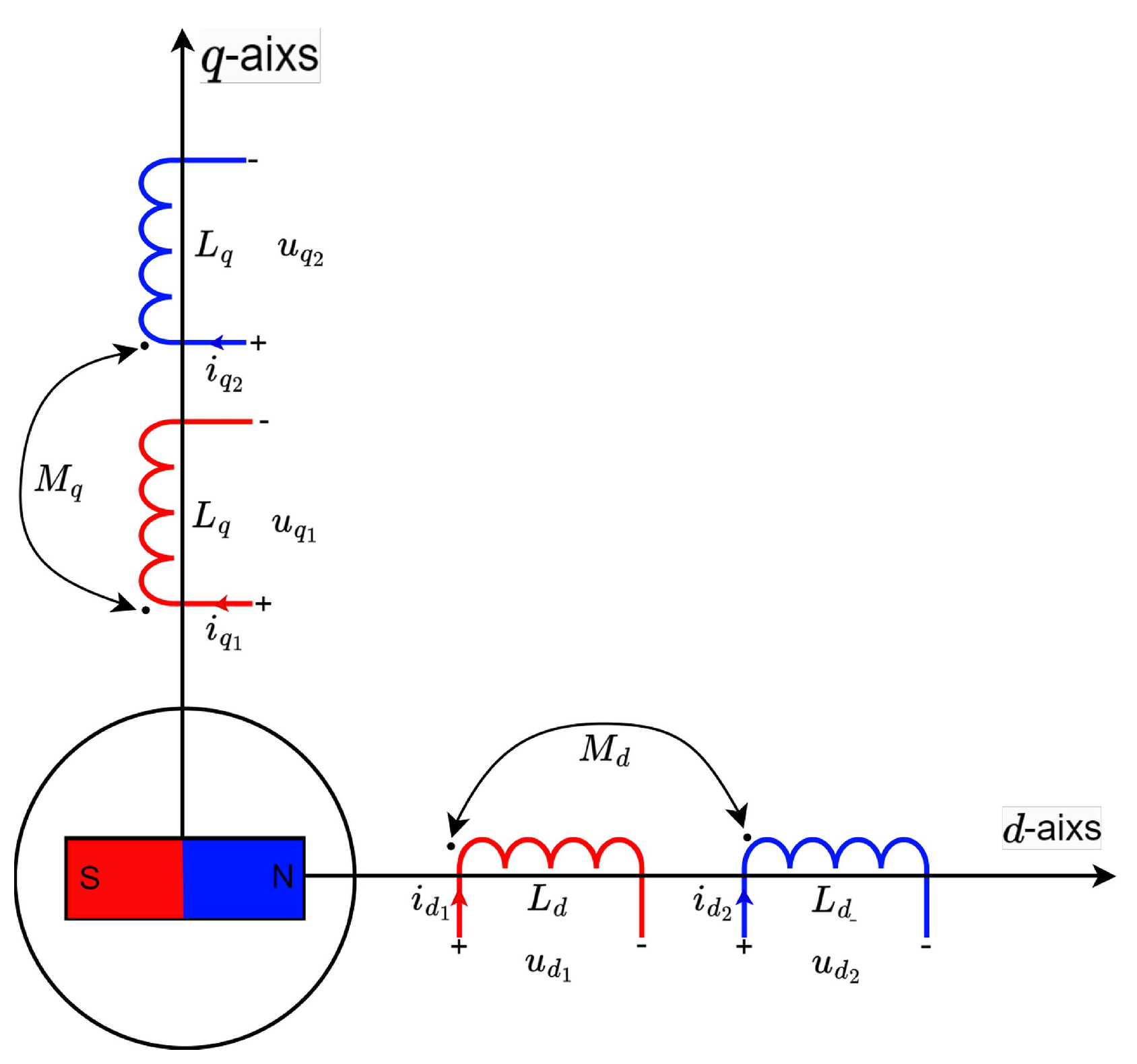
3.2. VSD Machine Model
4. Model of Propeller Load Torque
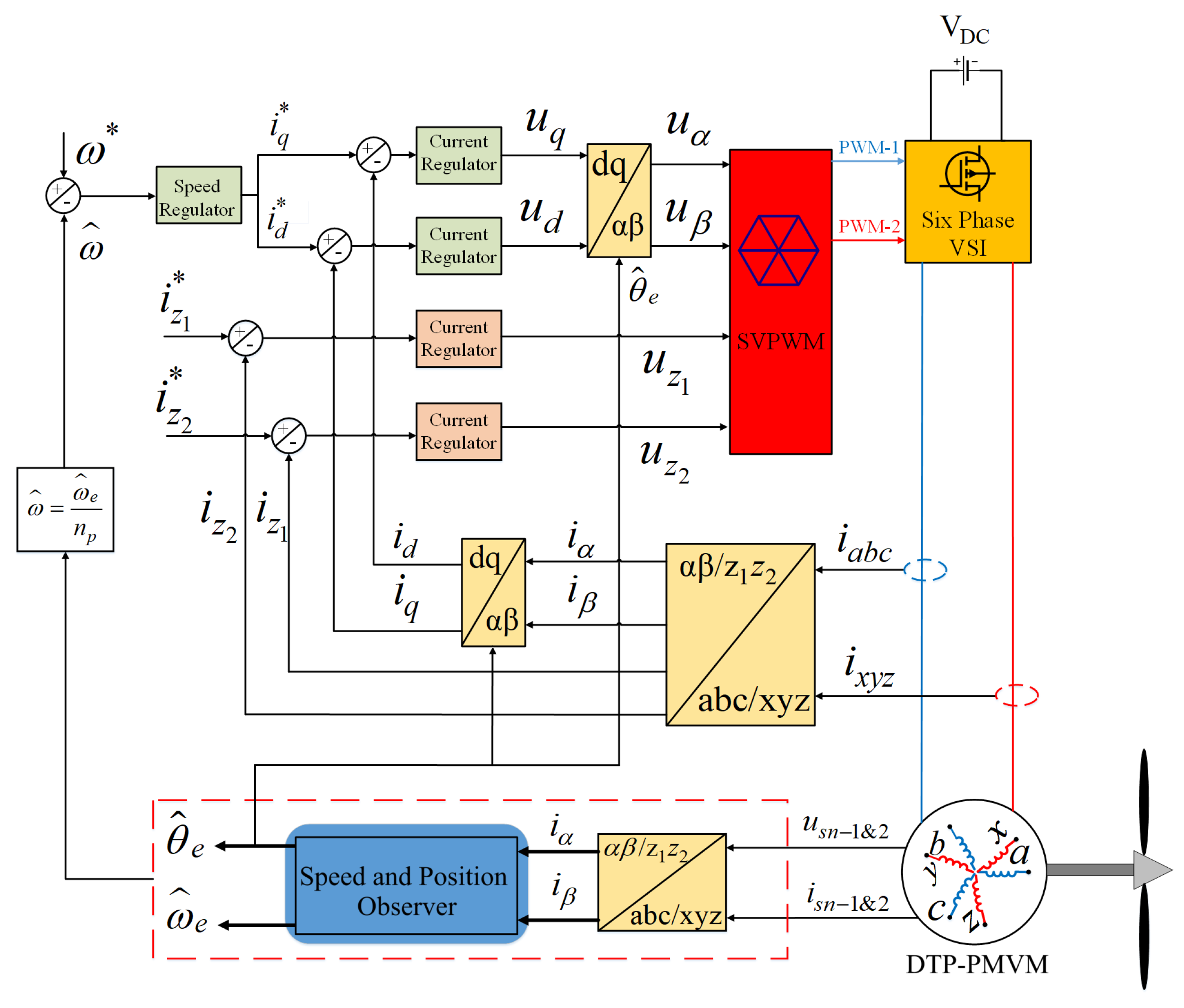
5. Sensorless Control of DTP-PMVM
5.1. Prescribed-Time Sliding Mode Observer
- ;
- monotonically as .
5.2. PT-SMO for Speed and Position Estimation of DTP-PMVM with Known Parameters
5.3. Neural Network Based Adaptive PT-SMO for Speed and Position Estimation of DTP-PMVM with Unknown Variable Parameters
- Since the optimal weights are unknown a priori, we utilize adaptation laws derived from the Lyapunov function to train these neural networks online. The specific adaptation laws will be formulated subsequently. Let us define the sliding surface as (24). Based on (22), (23) and (24); one has
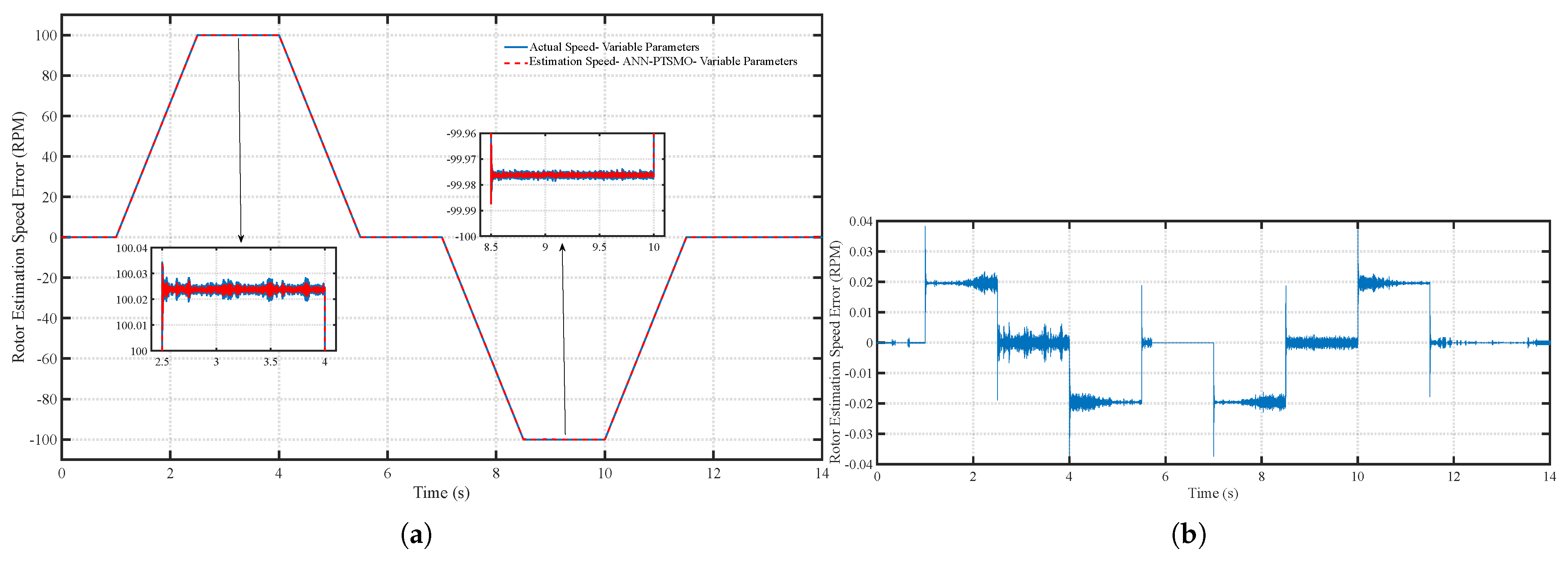
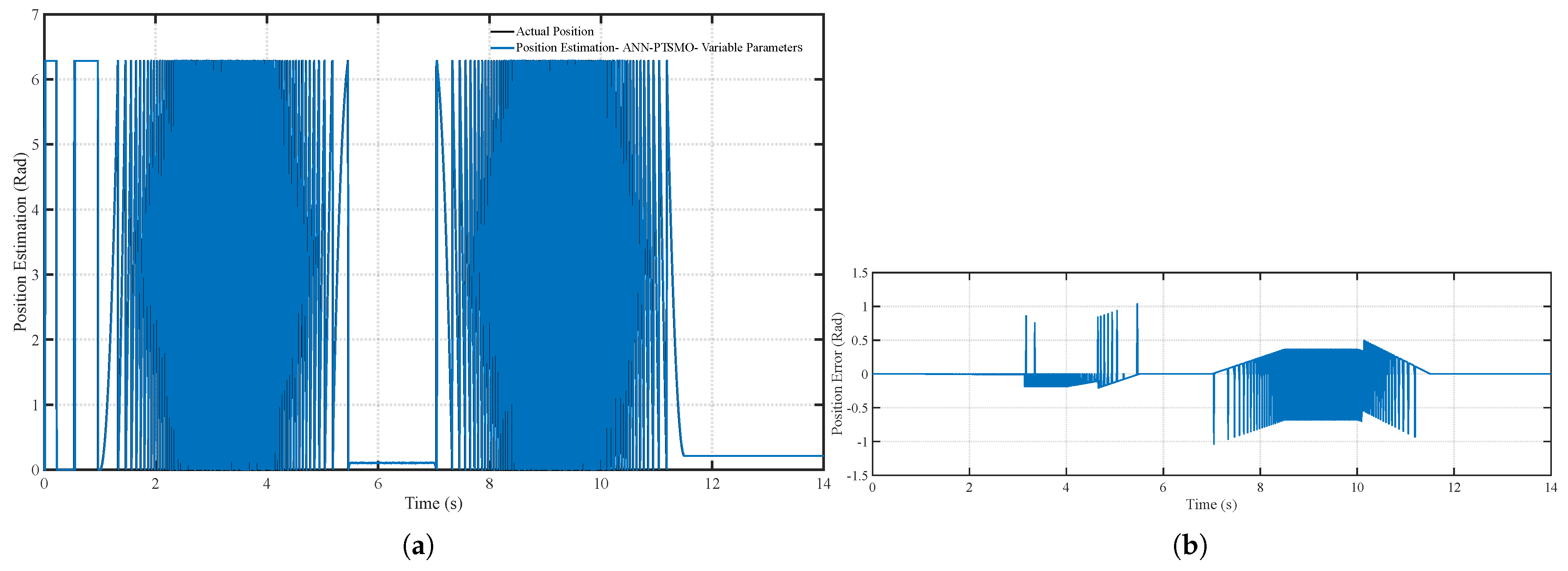
6. Simulation Results and Analysis
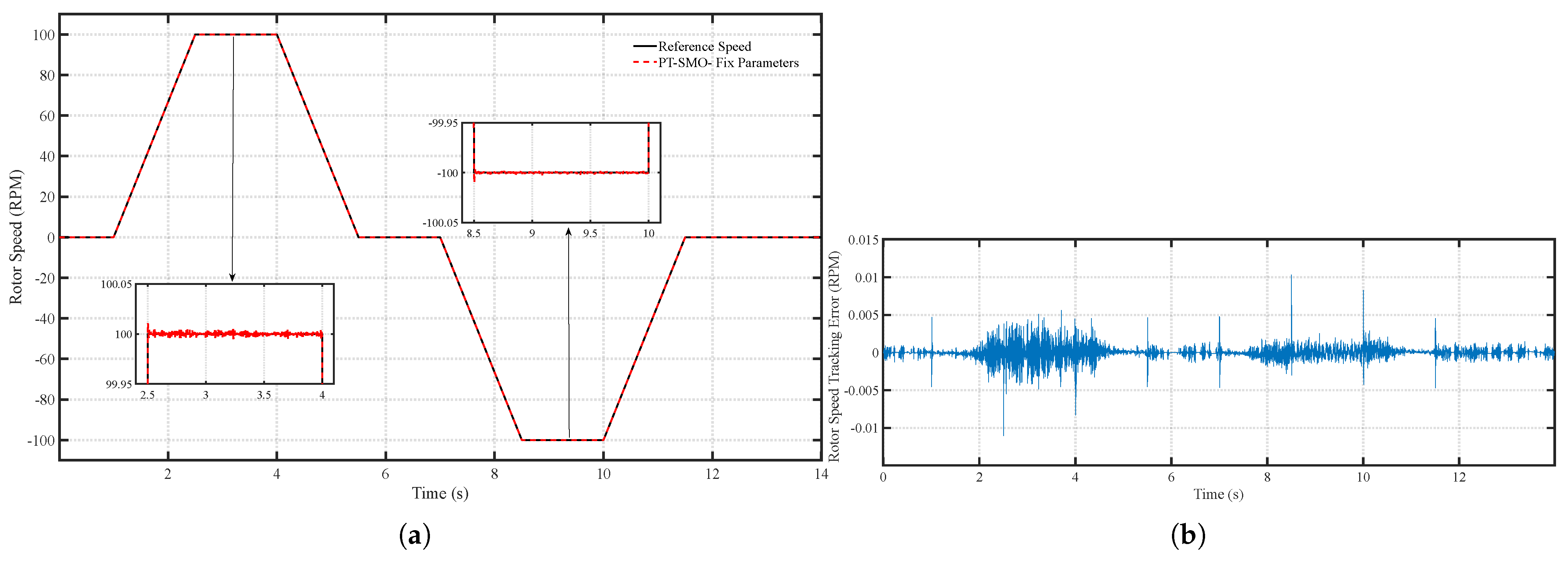
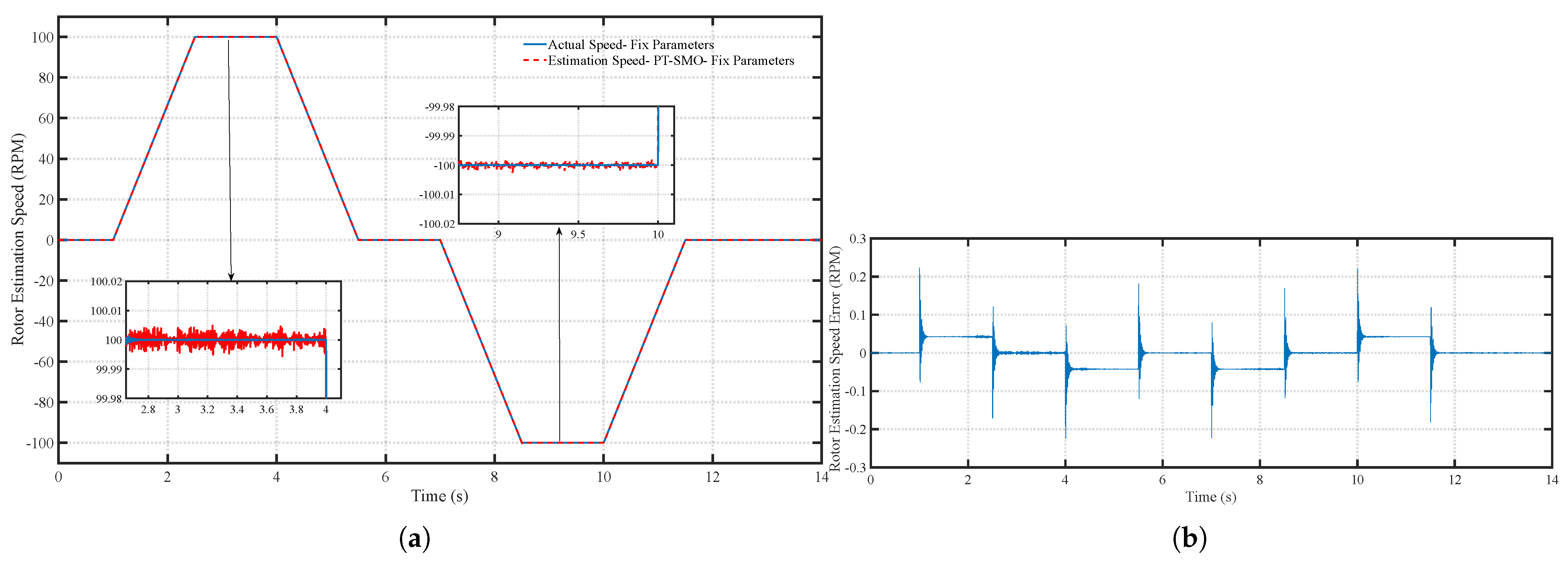
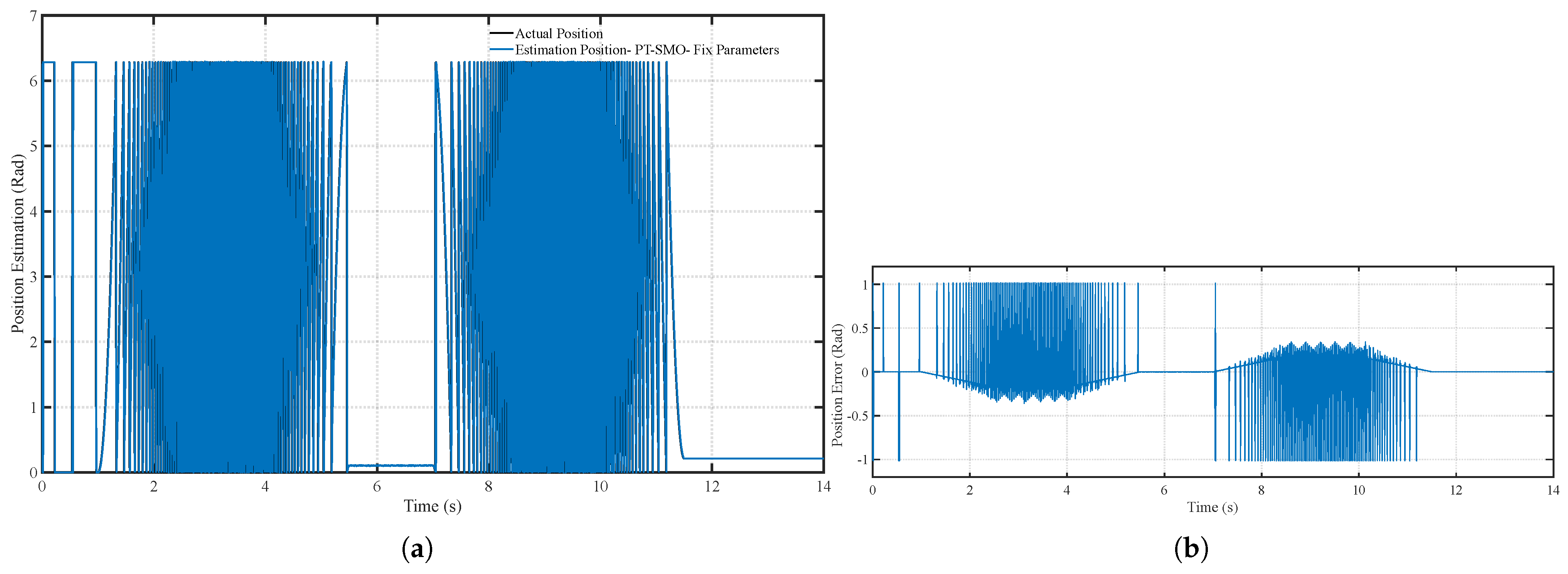
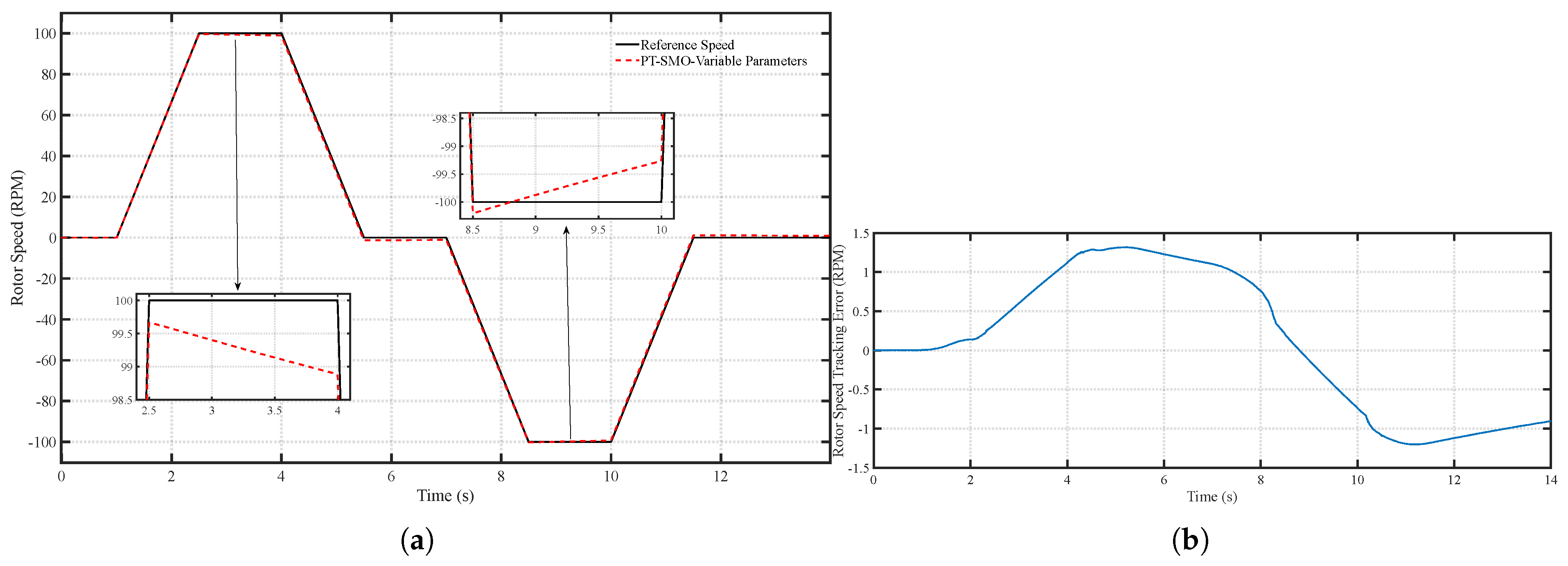
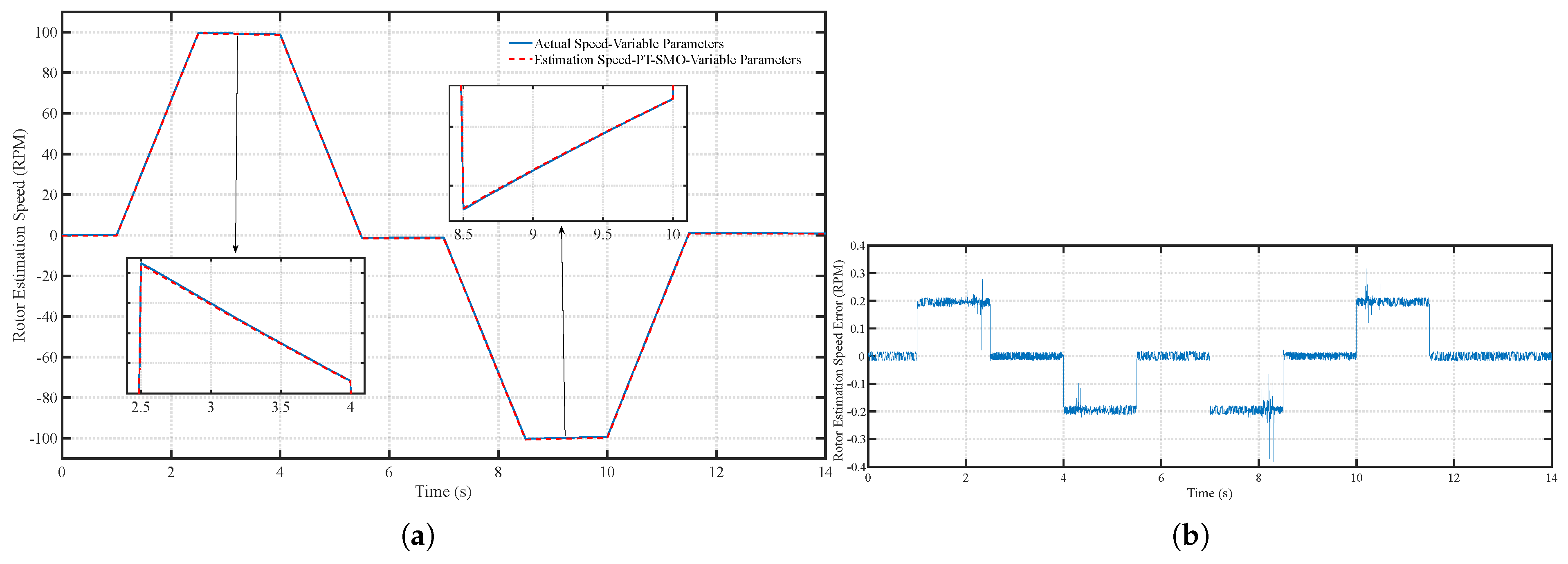
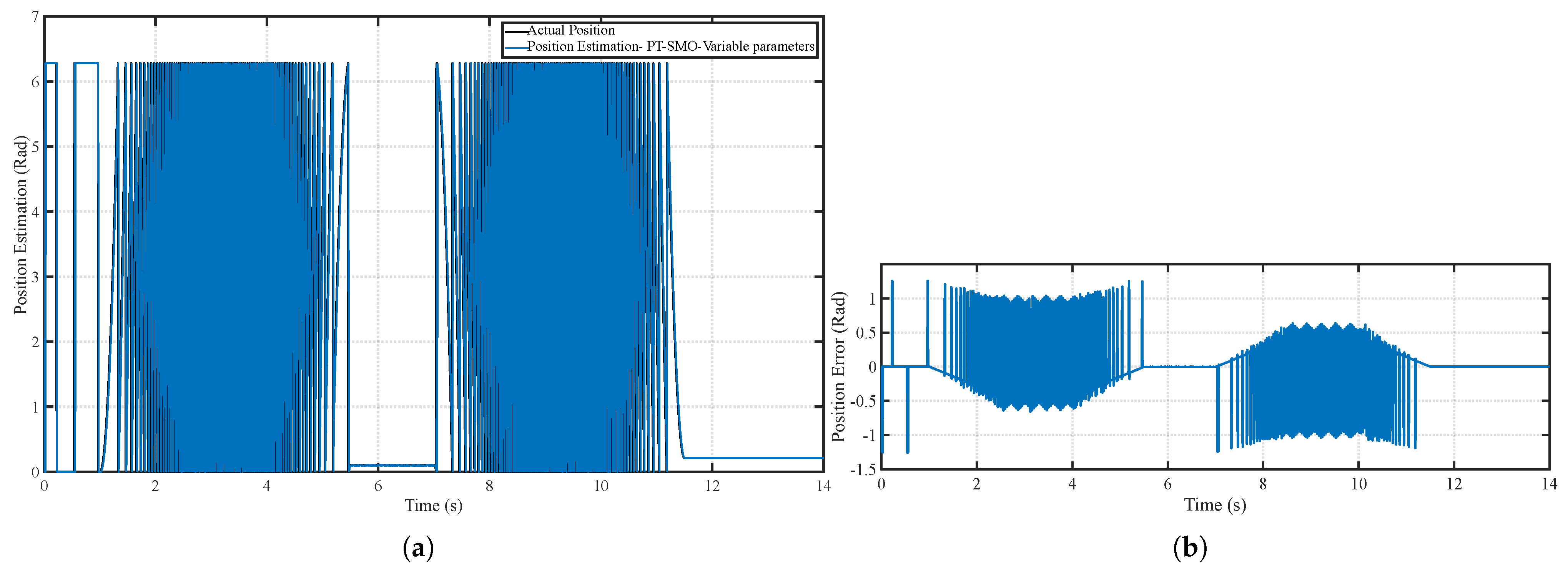
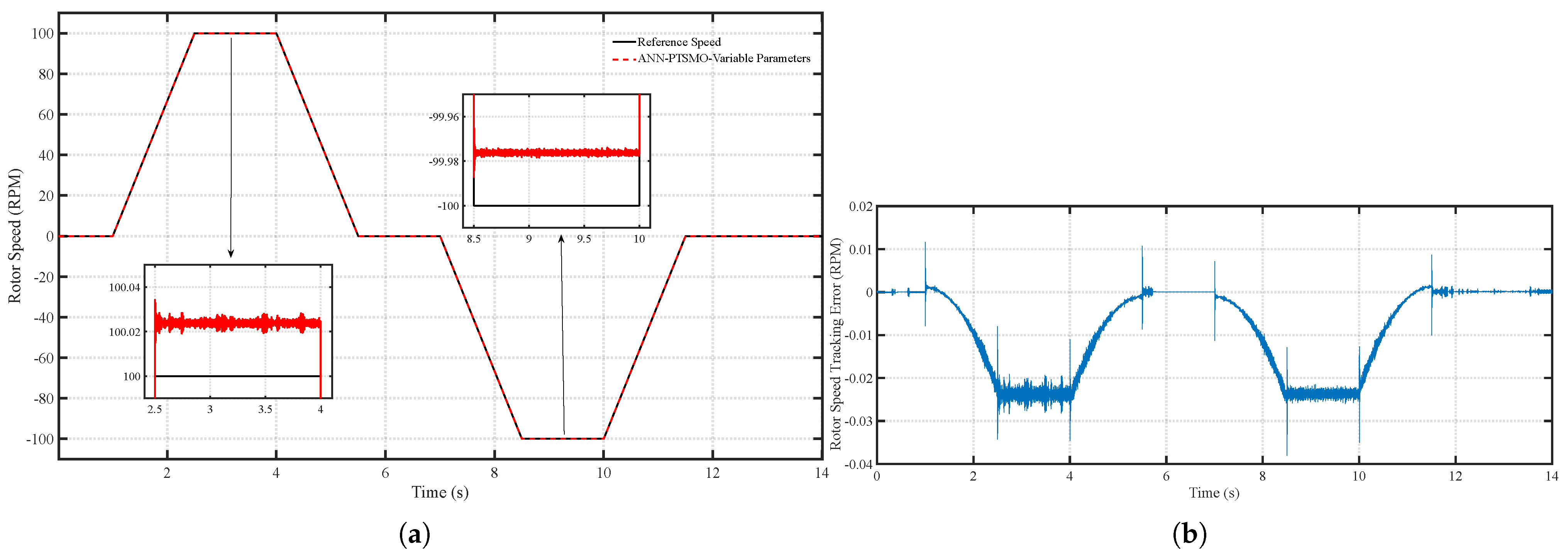
6.1. Scenario 1: Fixed Motor Parameters
6.2. Scenario 2: Time-Varying Motor Parameters
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANN | Artificial Neural Network |
| ANN-PTSMO | Artificial Neural Network Prescribed-Time Sliding Mode Observer |
| DTC | Direct Torque Control |
| DTP | Dual Three-Phase |
| DTP-PMSM | Dual Three-Phase Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor |
| DTP-PMVM | Dual Three-Phase Permanent Magnet Vernier Motor |
| FEM | Finite Element Method |
| NN | Neural Network |
| PM | Permanent Magnet |
| PMVM | Permanent Magnet Vernier Motor |
| PMSM | Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor |
| PTSMO | Prescribed-Time Sliding Mode Observer |
| PWM | Pulse Width Modulation |
| SMO | Sliding Mode Observer |
| SPMSM | Surface-mounted Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor |
Appendix A. Theorem 1 Proof
Appendix B. Theorem 2 Proof
References
- Burzanowska, H.; Sario, P.; Stulz, C. Redundant Drive with Direct Torque Control (DTC) and Dual-Star Synchronous Machine, Simulations and Verifications. In Proceedings of the EPE 2007—12th European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications, Aalborg, Denmark, 2–5 September 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Nanoty, A.; Chudasama, A. Design of multiphase induction motor for electric ship propulsion. In Proceedings of the Electric Ship Technologies Symposium (ESTS), Alexandria, VA, USA, 10–13 April 2011; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 283–287. [Google Scholar]
- Barcaro, M.; Bianchi, N.; Magnussen, F. Analysis and Tests of a Dual Three-Phase 12-Slot 10-Pole Permanent-Magnet Motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2010, 46, 2355–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Ren, Y.; Ombach, G. Torque Improvement of Dual Three-Phase Permanent-Magnet Machine with Third-Harmonic Current Injection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 6833–6844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teymoori, V.; Kamper, M.J.; Wang, R.-J.; Kennel, R. Sensorless Control of Dual Three-Phase Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines—A Review. Energies 2023, 16, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, S.; Song, Y.; Qi, W.; Guo, Q.; Li, X.; Kong, L.; Chen, J. Real-Time Global Optimal Energy Management Strategy for Connected PHEVs Based on Traffic Flow Information. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024, 25, 20032–20042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallio, S.; Andriollo, M.; Tortella, A.; Karttunen, J. Decoupled d-q model of double-star interior-permanent-magnet synchronous machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 2486–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, Y.; Aydin, M. Design, analysis and validation of a dual three-phase 72-slot, 12-pole permanent magnet synchronous motor. In Proceedings of the 2016 XXII International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), Lausanne, Switzerland, 4–7 September 2016; pp. 1598–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Xu, J.; Wu, S.; Xie, X.; Wang, H. Analysis and Design of Dual Three-Phase Fractional-Slot Permanent Magnet Motor With Low Space Harmonic. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2022, 58, 8100112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrero, F.; Duran, M.J. Recent advances in the design, modeling, and control of multiphase machines—Part I. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayati, M.; Rezaei, P.; Aghakhani, H. Modeling, fault detection, and stabilization of quadrotor unmanned aerial vehicle with rotor thrust deviation fault. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part I J. Syst. Control Eng. 2023, 237, 415–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia, D.F.; Taylor, J.; Mohamadian, M.; Luedtke, D.; Emadi, A.; Bilgin, B. A comparative analysis for six-phase motor configurations. In Proceedings of the WCX SAE World Congress Experience, Detroit, MI, USA, 21–23 April 2020; p. 2020-01-0465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, E. Multiphase electric machines for variable-speed applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 1893–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.Q.; Xia, Z.P.; Wu, L.J.; Jewell, G.W. Analytical modeling and finite-element computation of radial vibration force in fractional-slot permanent-magnet brushless machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2010, 46, 1908–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Odavic, M.; Zhu, Z. An Advanced Harmonic Compensation Strategy for Dual Three-Phase Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines Considering Different Angle Displacements. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition, Baltimore, MD, USA, 29 September–3 October 2019; pp. 1797–1803. [Google Scholar]
- Arish, N.; Kamper, M.J.; Wang, R.-J. Electromagnetic analysis of flux barrier U-shaped permanent magnet vernier motor. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Aegean Conference on Electrical Machines and Power Electronics (ACEMP) and 2021 International Conference on Optimization of Electrical and Electronic Equipment (OPTIM), Brasov, Romania, 2–3 September 2021; pp. 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonysamy, R.P.; Lee, S.R.; Jung, S.Y.; Joo, Y.H. Performance enhancement using robust sliding mode approach-based current control for PMVG-WECS. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 70, 10156–10166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Wang, S.; Shao, B.; Yan, L.; Xu, P.; Ren, Y. Advances in Dual-Three-Phase Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines and Control Techniques. Energies 2021, 14, 7508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, Q.; Ma, R. A Novel Luenberger Observer for the Sensorless Speed Control of PMSM. PCIM Asia 2021. In Proceedings of the International Exhibition and Conference for Power Electronics, Intelligent Motion, Renewable Energy and Energy Management, Shenzhen, China, 9–11 September 2021; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Elbuluk, M. A sliding mode observer for sensorless control of permanent magnet synchronous motors. In Proceedings of the Conference Record of the 2001 IEEE Industry Applications Conference. 36th IAS Annual Meeting (Cat. No.01CH37248), Chicago, IL, USA, 30 September–4 October 2001; Volume 2, pp. 1273–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Lai, C.; Iyer, K.L.V. A Review of Sliding Mode Observer Based Sensorless Control Methods for PMSM Drive. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 11352–11367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Yang, T.; Rashed, M.; Bozhko, S. Sensorless control of dual-three phase PMSM based aircraft electric starter/generator system using model reference adaptive system method. In Proceedings of the CSAA/IET International Conference on Aircraft Utility Systems (AUS 2018), Guiyang, China, 19–22 June 2018; pp. 787–794. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Hu, W.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, Z. Speed and Position Sensorless Control for Dual-Three-Phase PMSM Drives. In Proceedings of the 2009 Twenty-Fourth Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition, Washington, DC, USA, 15–19 February 2009; pp. 945–950. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, X.; Ji, J.; Zhou, D.; Zhao, W.; Chen, Y.; Huang, L. A Modified Flux Observer for Sensorless Direct Torque Control of Dual Three-Phase PMSM Considering Open-Circuit Fault. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 15356–15369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teymoori, V.; Dastres, H.; Kamper, M.J.; Wang, R.J.; Arish, N. Enhanced Fast Terminal Sliding Mode Observer for Wide-Speed Sensorless Control of PM Vernier Ship Propulsion Machine Drives. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Aegean Conference on Electrical Machines and Power Electronics (ACEMP) and 2023 International Conference on Optimization of Electrical and Electronic Equipment (OPTIM), Istanbul, Turkiye, 1 September 2023; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, P.; Lee, S.Y.; Cho, K.; Hahn, J.O. Robust control of Exo-Abs, a wearable platform for ubiquitous respiratory assistance. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2025, 147, 021005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, D.; Liu, L. Adaptive Second-Order Disturbance Observer-Based Position Sensorless Drive Strategy for PMSM. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2024, 39, 16415–16428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Shi, T.; Li, C.; Yan, Y.; Xia, C. High-Precision Sensorless Control of High-Speed Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Based on the Prediction Methodology. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2024, 39, 11386–11397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Xu, P.; Wu, X.; Yuan, K.; Wu, T.; Yu, X.; Yang, D.; Rong, F.; Huang, S. Sensorless Control for Bearingless Permanent Magnet Vernier Motor with Special Windings Based on Decoupling Sliding-Mode Observer. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Liu, X. Sensorless Control of PMSM With Improved Adaptive Super-Twisting Sliding Mode Observer and IST-QSG. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2025, 11, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, H.; Tang, C.; Wang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, S. Sensorless Control Strategy for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Based on Adaptive Non-Singular Fast Terminal Sliding Mode Observer. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2024, 34, 5208905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, F.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, X.; Hang, J.; Ding, S. New Sliding Mode Predictive Observer for Variable-Leakage-Flux PMSM Sensorless Drive System. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2025, 72, 11130–11140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, Q.; Ma, R.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, H.; Zhang, G. Improved Sliding-mode Observer for PMSM Sensorless Indirect Field-Oriented Control. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2025, 11, 13789–13801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Huang, J.; Wang, P.; Li, Y.; Qi, G.; Wu, Y.; He, Y.; Zhang, Y. An Improved Sliding Model Observer Sensorless Control for PMSM Based on Fuzzy Logic Controller and DSOGI-FLL. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2025, 11, 823–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wang, N.; Yao, M.; Lei, G. Position Sensorless Control of SRMs Based on Improved Sliding Mode Speed Controller and Position Observer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2025, 72, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Li, B.; Zhao, Y. An Adaptive SMO Approach for Low-Chattering Sensorless Control of PMSM. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2025, 40, 15329–15338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Hu, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, C.; Sun, X. A Gain-Adaptive High-Order Terminal Sliding Mode Observer Under SPMSM Sensorless Control. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2025, 40, 6555–6565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.-P.; Cheng, M.-Y. Rotor Position Estimation for a Position-Sensorless FOC PMSM Drive—A Super-Twisting-Based Sliding Mode Observer Approach. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 164540–164551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Li, K.; Yu, C.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Luo, B. Sensorless Control of Permanent magnet in-wheel motor for EVs Using Global Fast Terminal Sliding Mode Observer. ISA Trans. 2025, 160, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Su, H. Adaptive Robust Sensorless Control for PMSM Based on Improved Back EMF Observer and Extended State Observer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2024, 71, 16635–16643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teymoori, V.; Dastres, H.; Kamper, M.J.; Wang, R.-J.; Arish, N. Sensorless Control of DTP-PMSM Ship-Propulsion Drives by Using Nonsingular Fast Terminal Sliding Mode Observer. In Proceedings of the 2023 26th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Zhuhai, China, 5–8 November 2023; pp. 4257–4262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Wang, J.; Guo, X.; Li, S.; Guerrero, J.M. Fixed-Time Sliding-Mode Disturbance Observer-Based Finite-Time Backstepping Control for Current Source Rectifier. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2024, 12, 4767–4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Shao, Y.; Yu, Y.; Dong, Q.; Yun, Z.; Xu, D. High-Order Terminal Sliding-Mode Observer for Chattering Suppression and Finite-Time Convergence in Sensorless SPMSM Drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 11910–11920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arish, N.; Kamper, M.J.; Wang, R.-J. Performance Comparison of 5-MW Normal and Dual Three-Phase PM Vernier Motors for Ship Propulsion. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Aegean Conference on Electrical Machines and Power Electronics (ACEMP) and 2023 International Conference on Optimization of Electrical and Electronic Equipment (OPTIM), Istanbul, Turkiye, 1 September 2023; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Lan, P.; Yang, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.; Peng, F.; Hong, J. Multi-U-Style micro-channel in liquid cooling plate for thermal management of power batteries. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2024, 256, 123984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karttunen, J.; Kallio, S.; Peltoniemi, P.; Silventoinen, P.; Pyrhonen, O. Dual three-phase permanent magnet synchronous machine supplied by two independent voltage source inverters. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Power Electronics, Electrical Drives, Automation and Motion, Sorrento, Italy, 20–22 June 2012; pp. 741–747. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, G.K.; Nam, K.; Lim, S.K. A simple indirect field-oriented control scheme for multiphase induction machine. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2005, 52, 1177–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojoi, R.; Lazzari, M.; Profumo, F.; Tenconi, A. Digital field-oriented control for dual three-phase induction motor drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2003, 39, 752–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slunjski, M.; Dordevic, O.; Jones, M.; Levi, E. Symmetrical/Asymmetrical Winding Reconfiguration in Multiphase Machines. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 12835–12844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Feng, Y.; Liu, J. A simple current sharing scheme for dual three-phase permanent-magnet synchronous motor drives. In Proceedings of the Annual IEEE Conference on Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), Palm Springs, CA, USA, 21–25 February 2010; pp. 1093–1096. [Google Scholar]
- Tessarolo, A.; Bortolozzi, M.; Contin, A. Modeling of split-phase machines in Park’s coordinates. Part II: Equivalent circuit representation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Euro Conference, Zagreb, Croatia, 1–4 July 2013; pp. 1314–1319. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.J.; Liu, Y.C.; Wang, N.; Liu, S.Y. Sensorless control of ship propulsion interior permanent magnet synchronous motor based on a new sliding mode observer. ISA Trans. 2015, 54, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulligoi, G.; Vicenzutti, A.; Menis, R. All electric ship design: From electrical propulsion to integrated electrical and electronic power systems. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2016, 2, 507–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, Y.; Krstic, M. Time-varying feedback for stabilization in prescribed finite time. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2019, 29, 618–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.-Q.; Krstic, M. Stochastic nonlinear prescribed-time stabilization and inverse optimality. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2021, 67, 1179–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.X. Command filter adaptive asymptotic tracking of uncertain nonlinear systems with time-varying parameters and 577 disturbances. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2021, 67, 2973–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
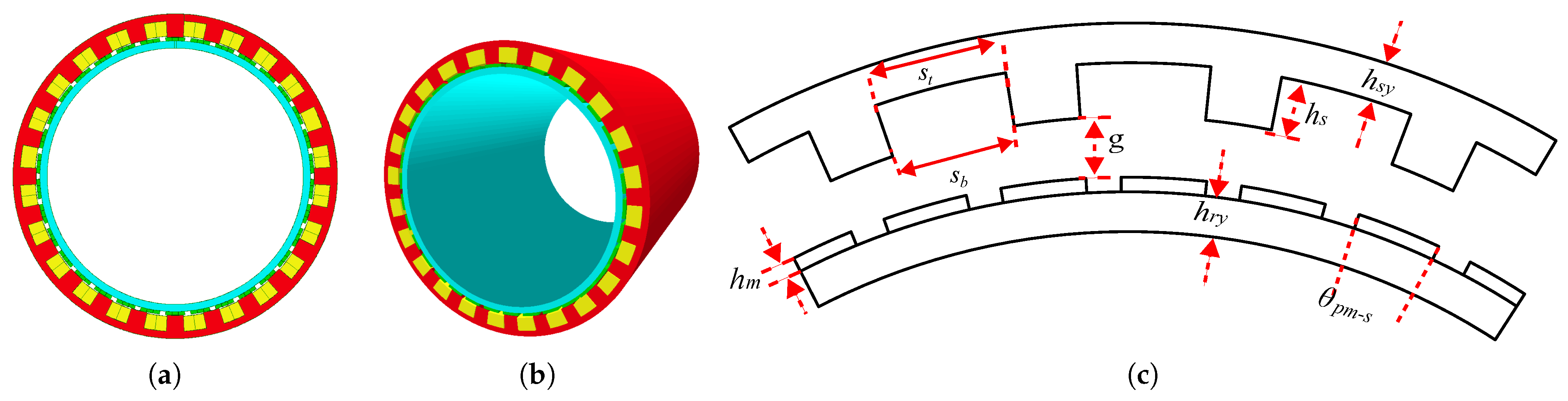

| Stator Parameters | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Slot number | 24 | - |
| 7 | - | |
| Slot area | 5130 | mm2 |
| Outer diameter | 1300 | mm |
| Stack length | 1400 | mm |
| Stator bore | 1113.5 | mm |
| Slot width bottom () | 89 | mm |
| Slot width top () | 80 | mm |
| Slot depth () | 64.25 | mm |
| Slot opening | 80 | mm |
| Stator yoke thickness () | 4.2 | mm |
| Rotor Parameters | Value | Unit |
| 17 | - | |
| Magnet segments (radial) | 3 | - |
| Magnet segments (axial) | 2 | - |
| Magnet arc () | 140 | degrees |
| Magnet thickness () | 13.8 | mm |
| Airgap (g) | 1.3 | mm |
| Inner rotor diameter | 1025.5 | mm |
| Rotor yoke thickness () | 5.1 | mm |
| Winding Parameters | Value | Unit |
| Winding factor | 0.975 | - |
| Fill factor | 0.6 | - |
| Stator resistance | 3 | m |
| End winding length | 3 | mm |
| Number of phases | 6 | - |
| Winding layer | 2 | - |
| Winding type | Overlap | - |
| Coil pitch | 2 | - |
| Parameters | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Rated Power | 5 | MW |
| Rated Voltage | 3.3 | kV |
| Rated Torque | 160 | kN.m |
| Rated Speed | 300 | rpm |
| q-axis inductance | 0.9 | mH |
| d-axis inductance | 1.1 | mH |
| PM magnetic flux linkage | 3.89 | Wb |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Propeller diameter, | 3.5 m |
| Wake fraction, w | 0.136 |
| Water density, | 1030 kg/m3 |
| Adhesion coefficient, k | 1.09 |
| Mass of the ship, | 15,527 ton |
| Force reduction factor, t | 0.1551 |
| Performance Metric | PT-SMO | ANNPT-SMO | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average speed tracking error (RPM) | 0.65 | 0.01 | 98.5% reduction |
| Maximum speed estimation error (RPM) | 1.20 | 0.04 | 96.7% reduction |
| Average position estimation error (rad) | 0.90 | 0.12 | 86.7% reduction |
| Maximum position estimation error (rad) | 1.50 | 0.35 | 76.7% reduction |
| Convergence time (s) | 0.45 | 0.18 | 60% faster |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the World Electric Vehicle Association. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Teymoori, V.; Arish, N.; Dastres, H.; Kamper, M.J.; Wang, R.-J. Design and Sensorless Control in Dual Three-Phase PM Vernier Motors for 5 MW Ship Propulsion. World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16, 670. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16120670
Teymoori V, Arish N, Dastres H, Kamper MJ, Wang R-J. Design and Sensorless Control in Dual Three-Phase PM Vernier Motors for 5 MW Ship Propulsion. World Electric Vehicle Journal. 2025; 16(12):670. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16120670
Chicago/Turabian StyleTeymoori, Vahid, Nima Arish, Hossein Dastres, Maarten J. Kamper, and Rong-Jie Wang. 2025. "Design and Sensorless Control in Dual Three-Phase PM Vernier Motors for 5 MW Ship Propulsion" World Electric Vehicle Journal 16, no. 12: 670. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16120670
APA StyleTeymoori, V., Arish, N., Dastres, H., Kamper, M. J., & Wang, R.-J. (2025). Design and Sensorless Control in Dual Three-Phase PM Vernier Motors for 5 MW Ship Propulsion. World Electric Vehicle Journal, 16(12), 670. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16120670











