Evaluation of Blockchain Networks’ Scalability Limitations in Low-Powered Internet of Things (IoT) Sensor Networks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
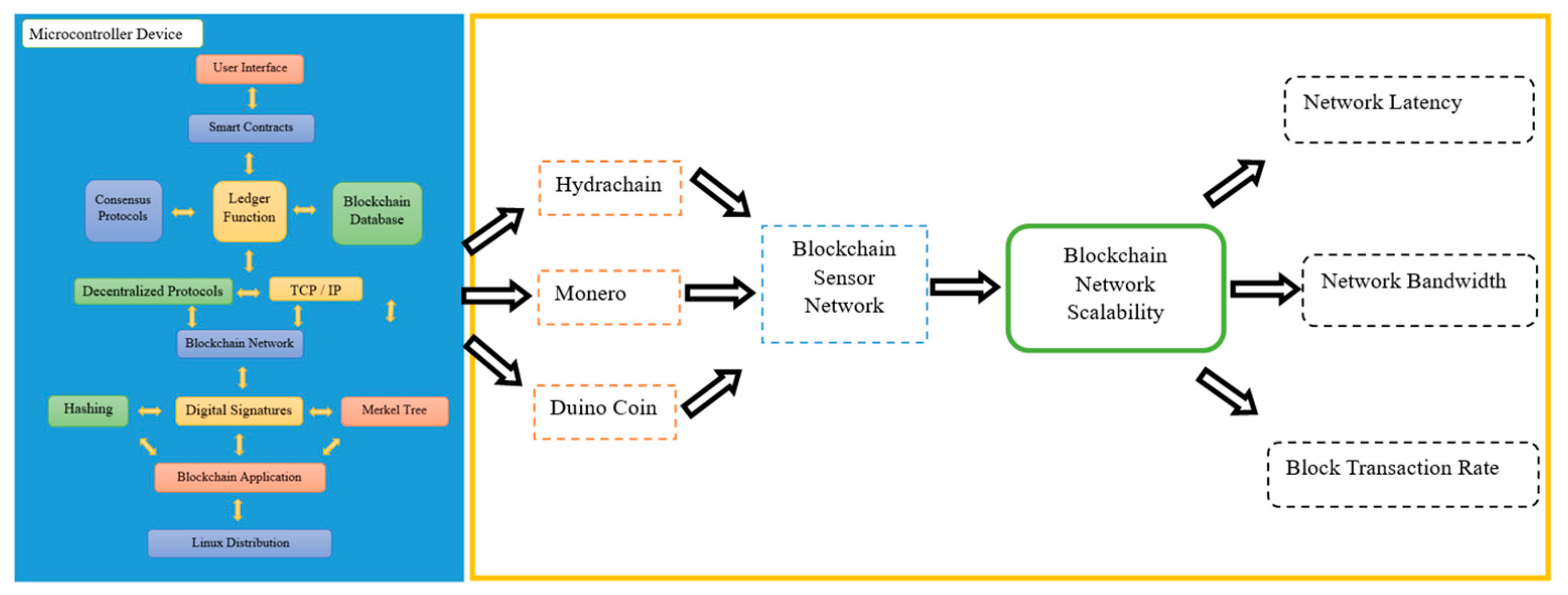
1.1. Research Architecture
1.2. Research Contributions
- We identify the scalability limitations of blockchain-based sensor networks using real test bed experiments.
- We evaluate the scalability variations of different blockchain networks that can be applied to avoid scalability bottlenecks of blockchain-based sensor networks.
- We provide an overview of real test results using three key blockchain network scalability parameters. The parameters are network latency, block transaction rate, and network bandwidth.
2. Blockchain Technology
2.1. Public Blockchain Networks
2.2. Private Blockchain Networks
2.3. Hybrid Blockchain Networks
3. Blockchain Technology in Healthcare
4. Related Work
5. Research Methodology
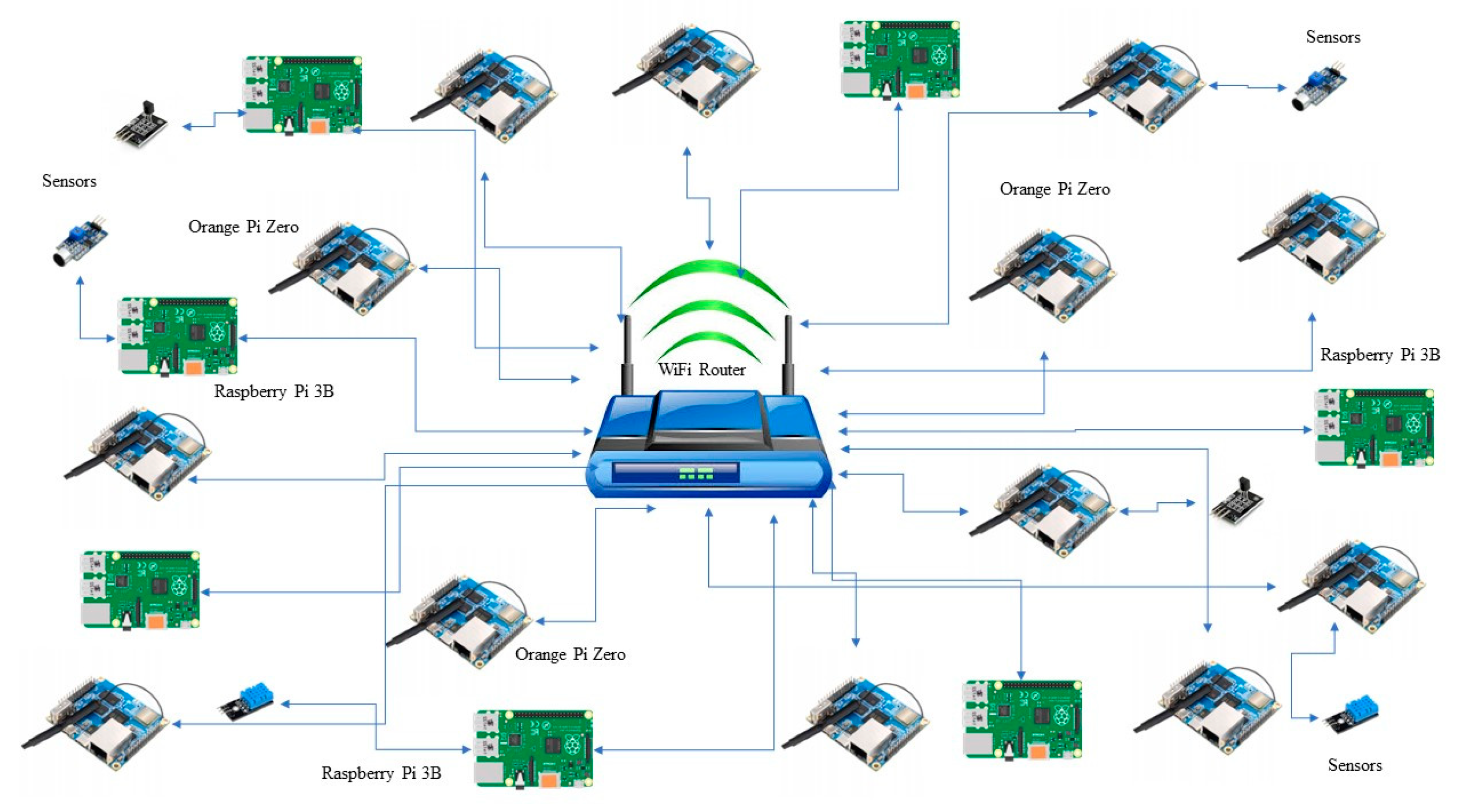
5.1. Blockchain Network Prototype
5.2. Resources
5.2.1. Orange Pi
5.2.2. Raspberry Pi
5.2.3. Hydrachain Blockchain
5.2.4. Monero Blockchain
5.2.5. Duino Coin Blockchain
5.3. Data Collection Parameters
5.3.1. Network Latency
5.3.2. Bandwidth Usage
5.3.3. Data Transaction Rate
6. Results and Evaluation
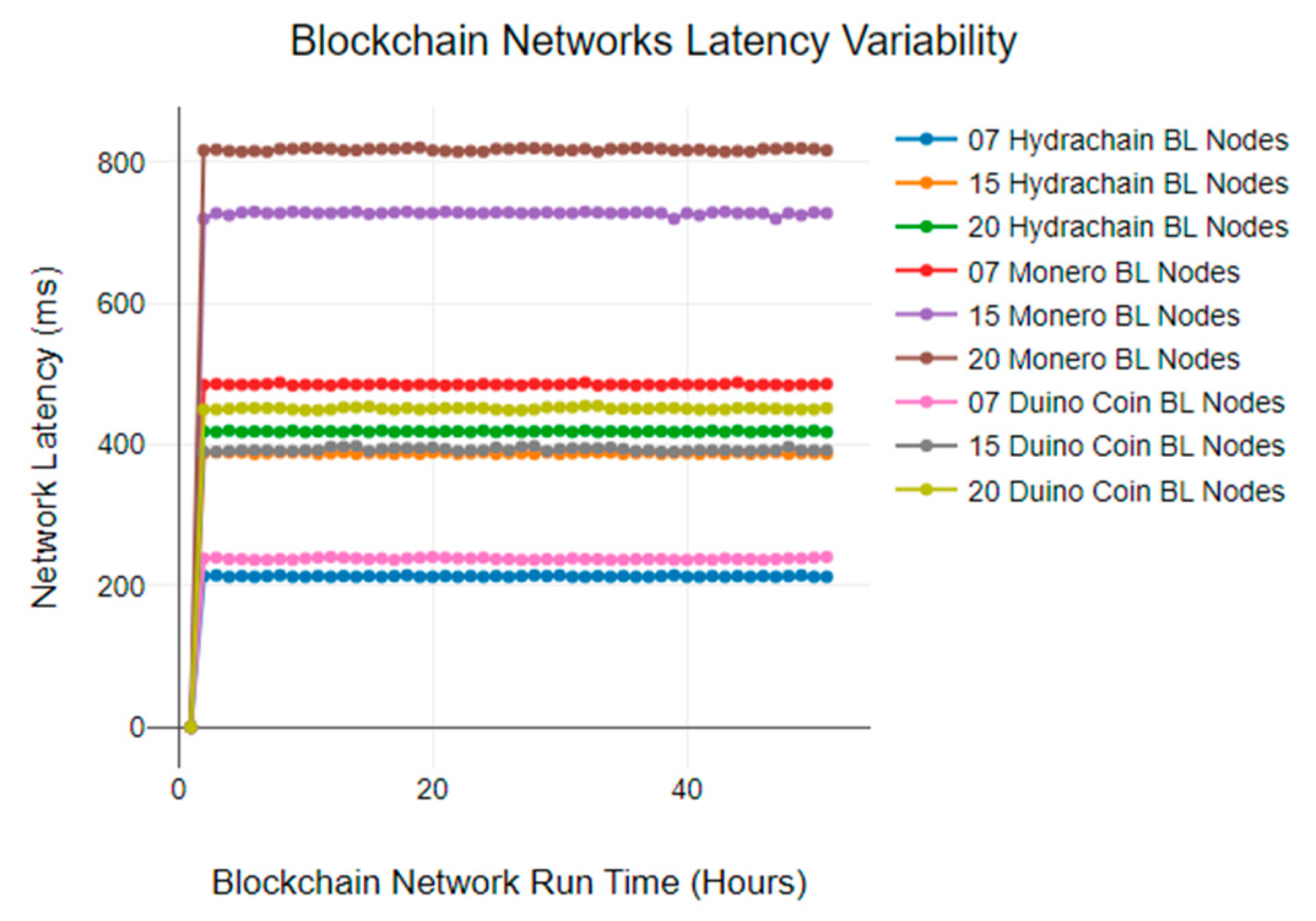
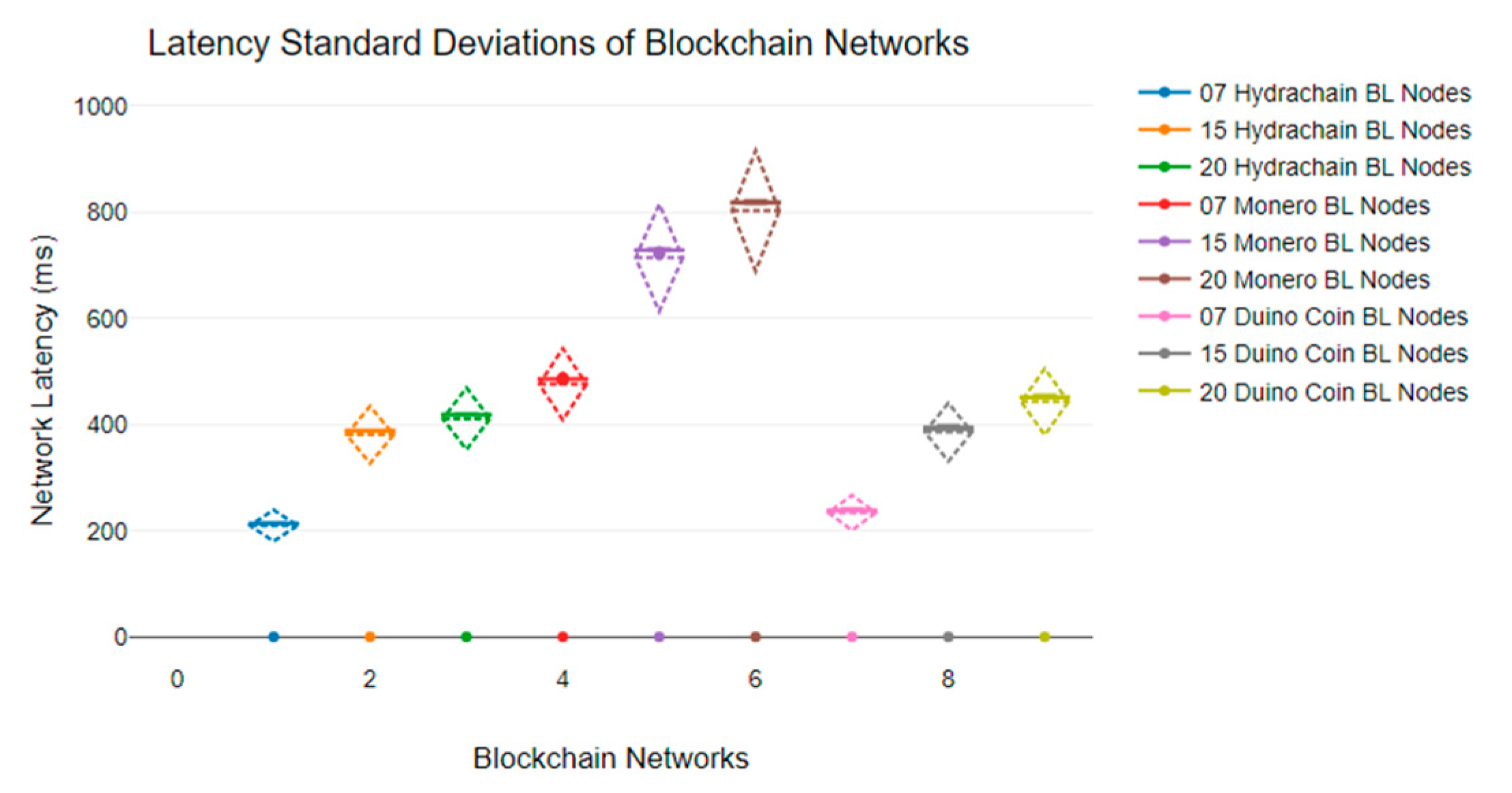
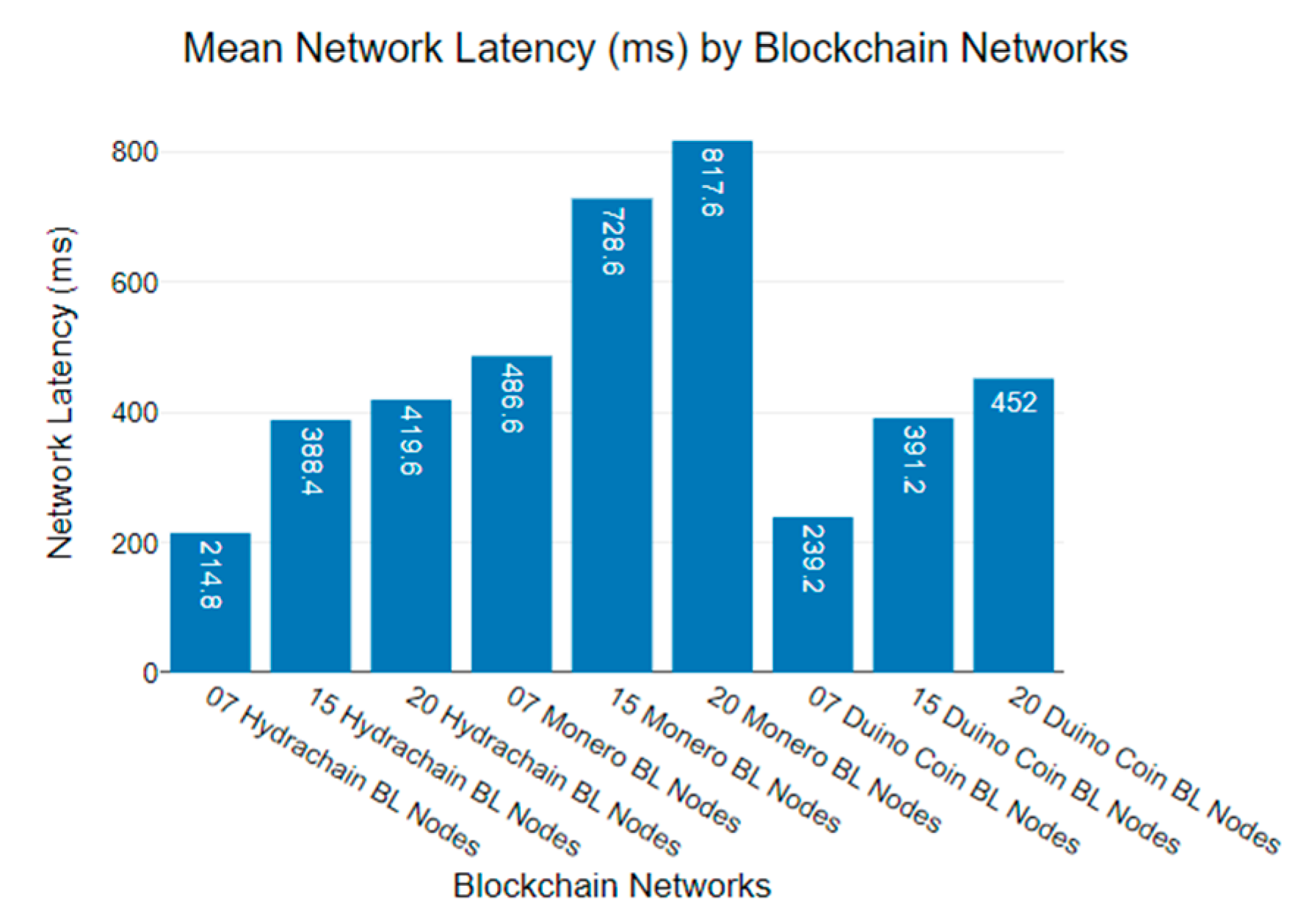
6.1. Blockchain Network Latency Analysis
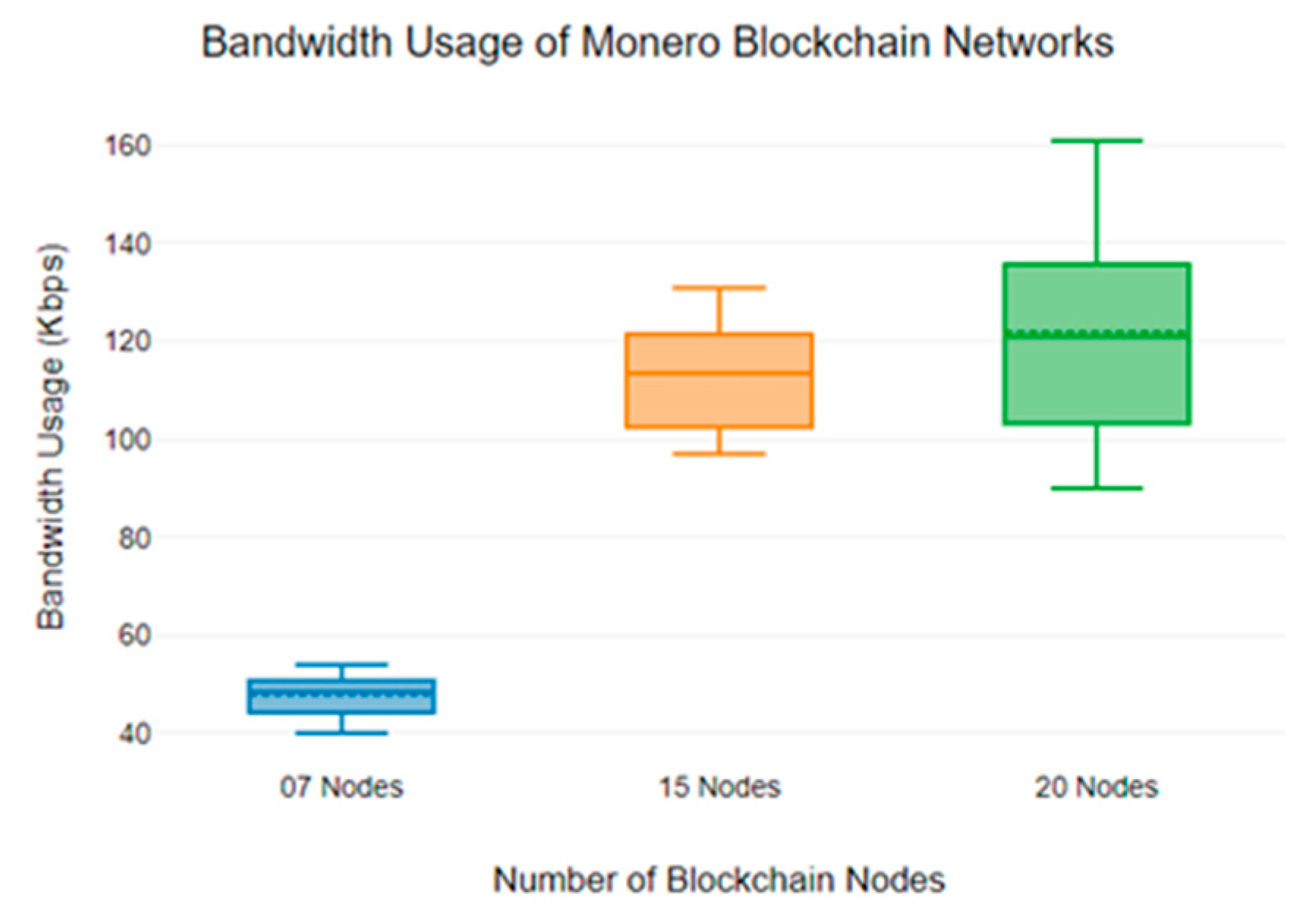
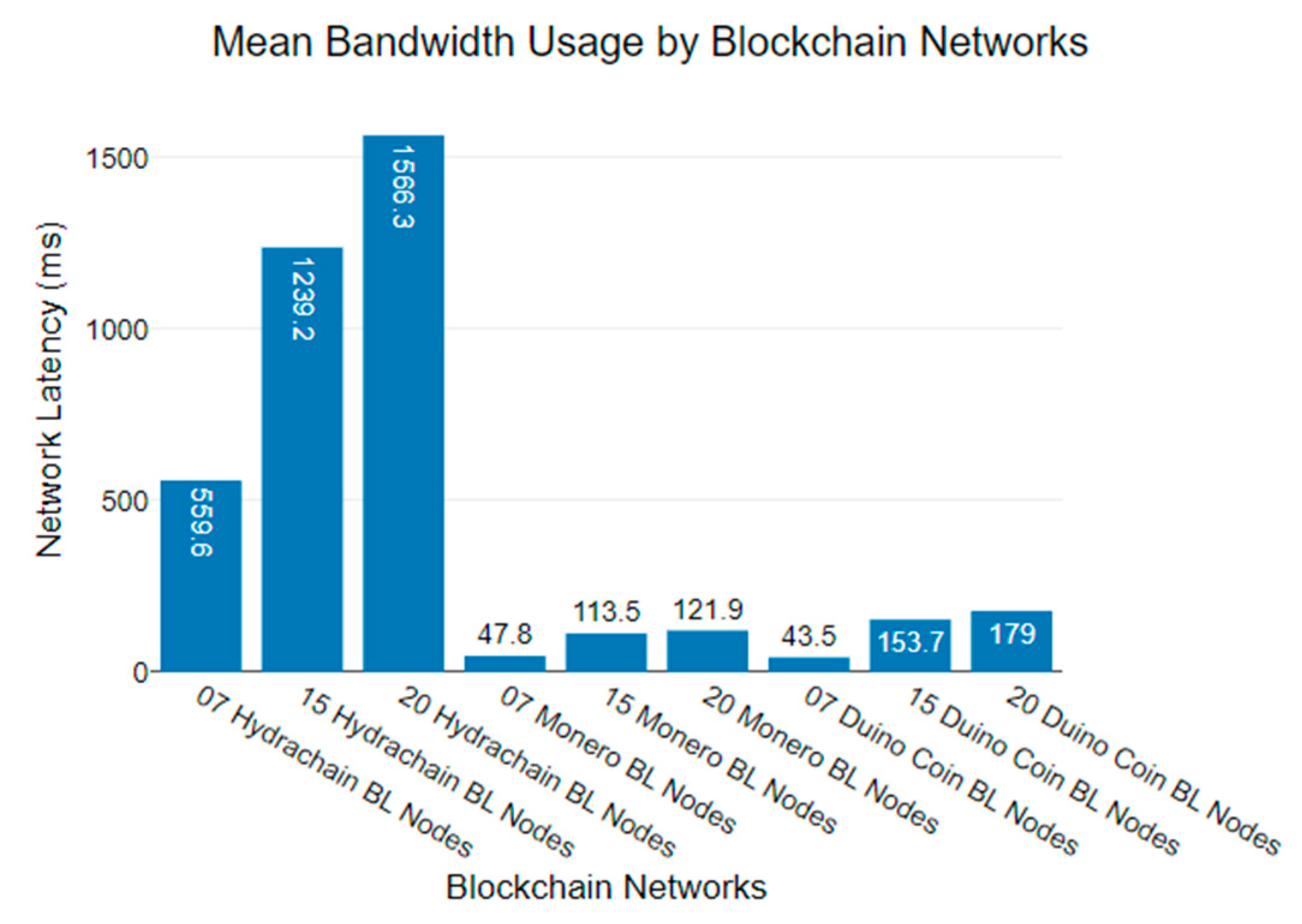
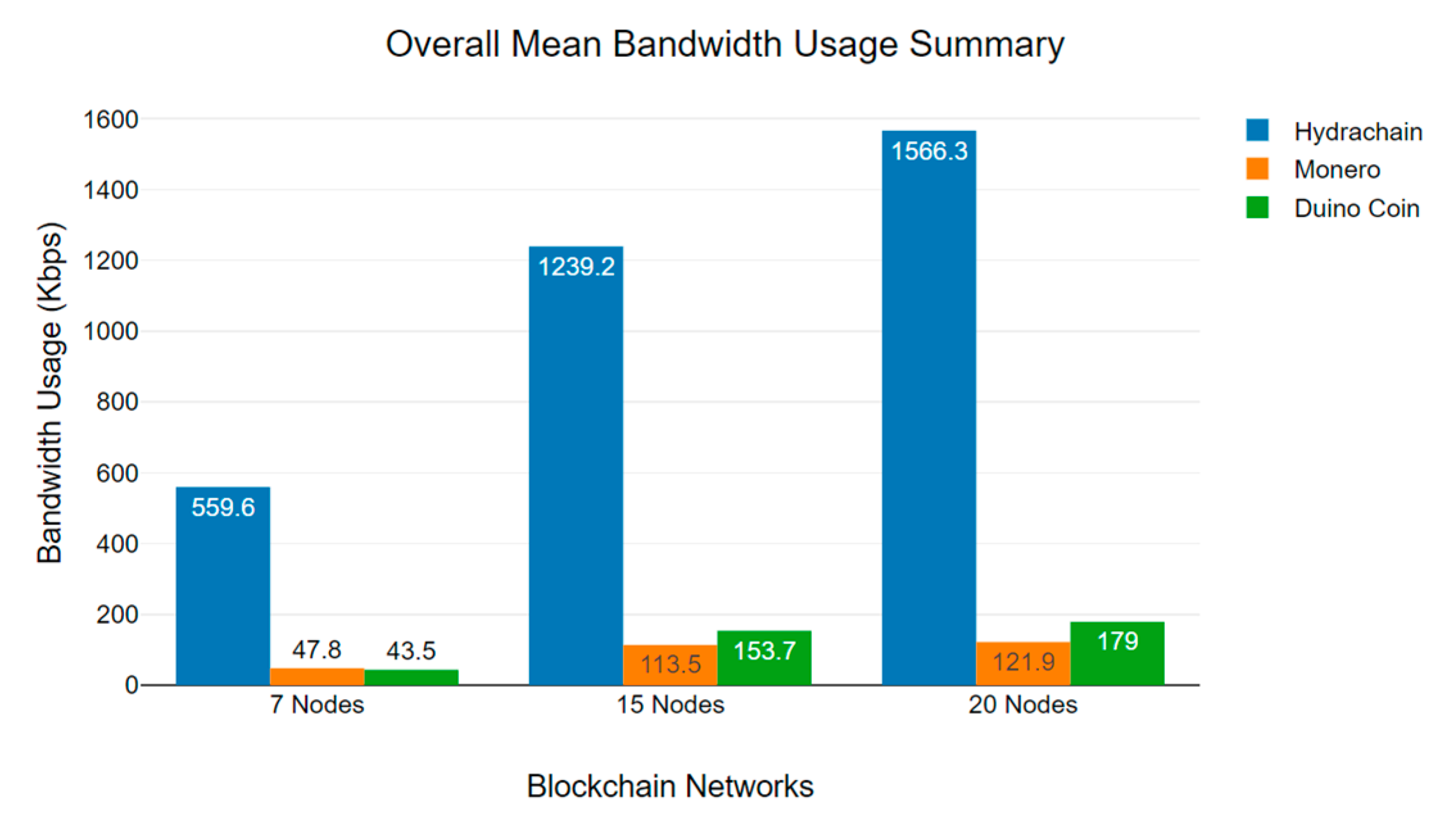
6.2. Blockchain Network Bandwidth Usage Analysis
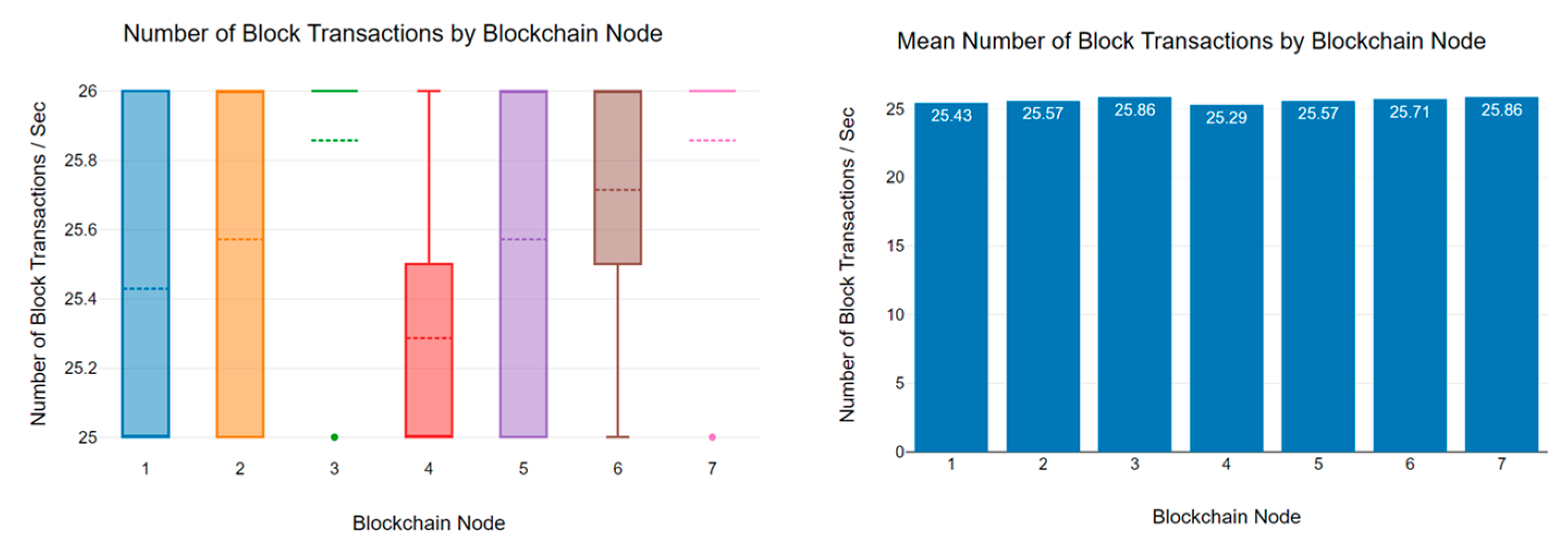
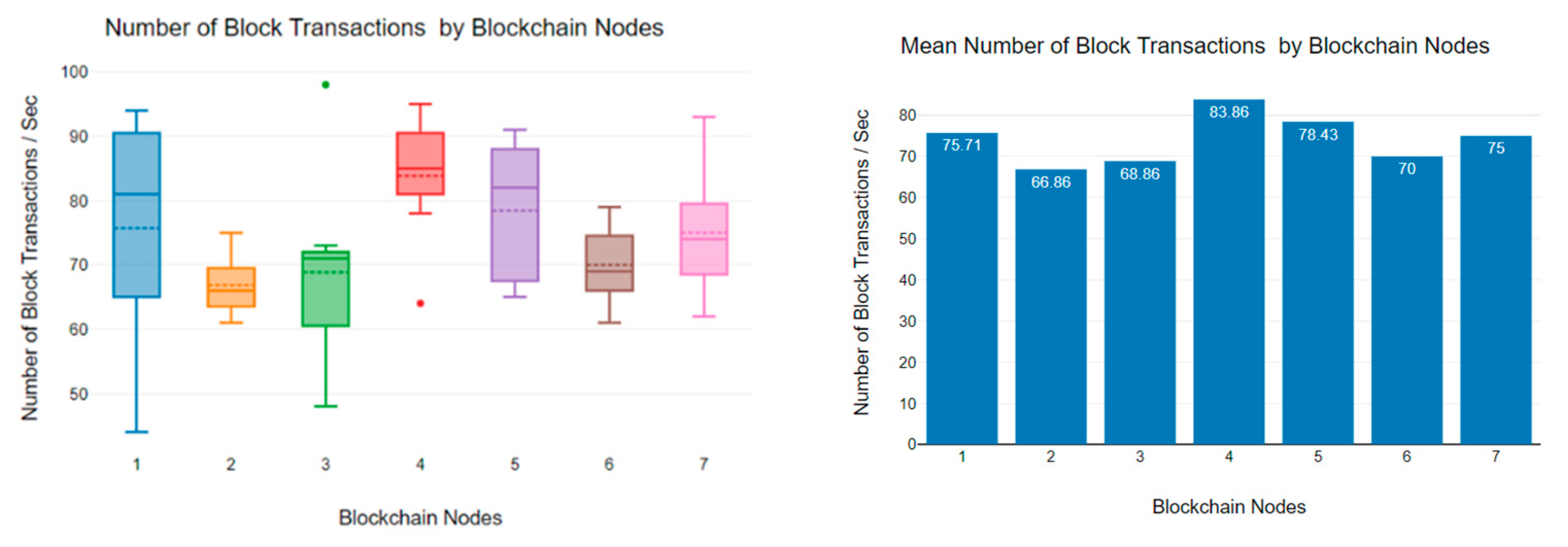
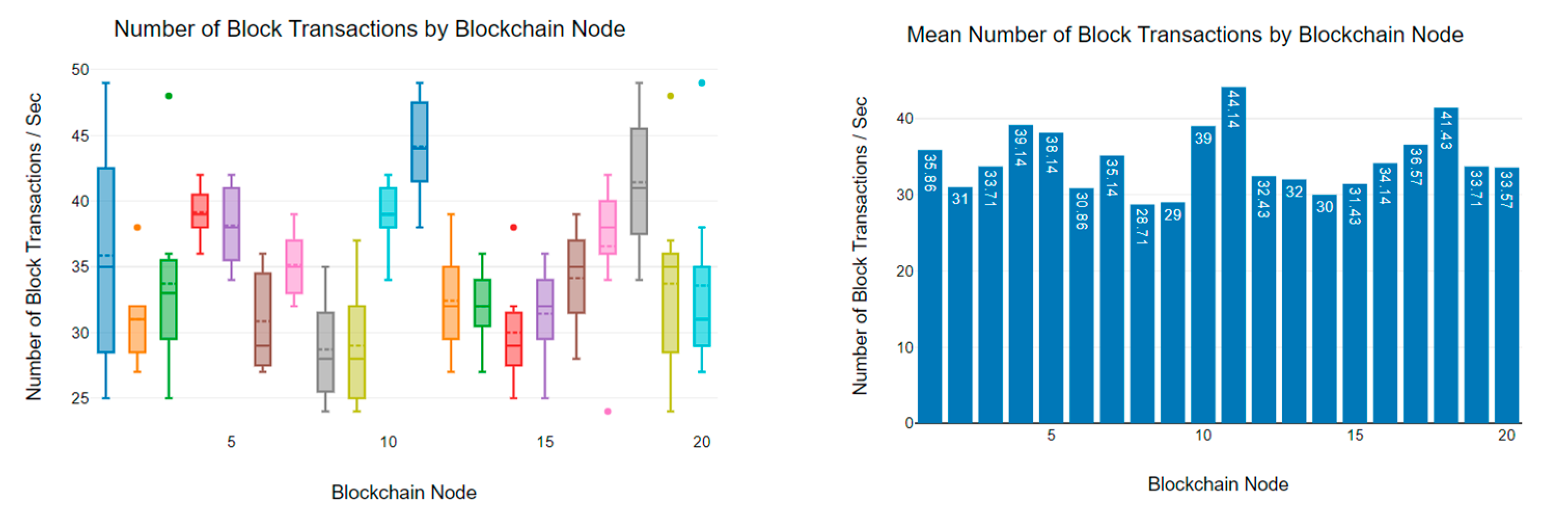
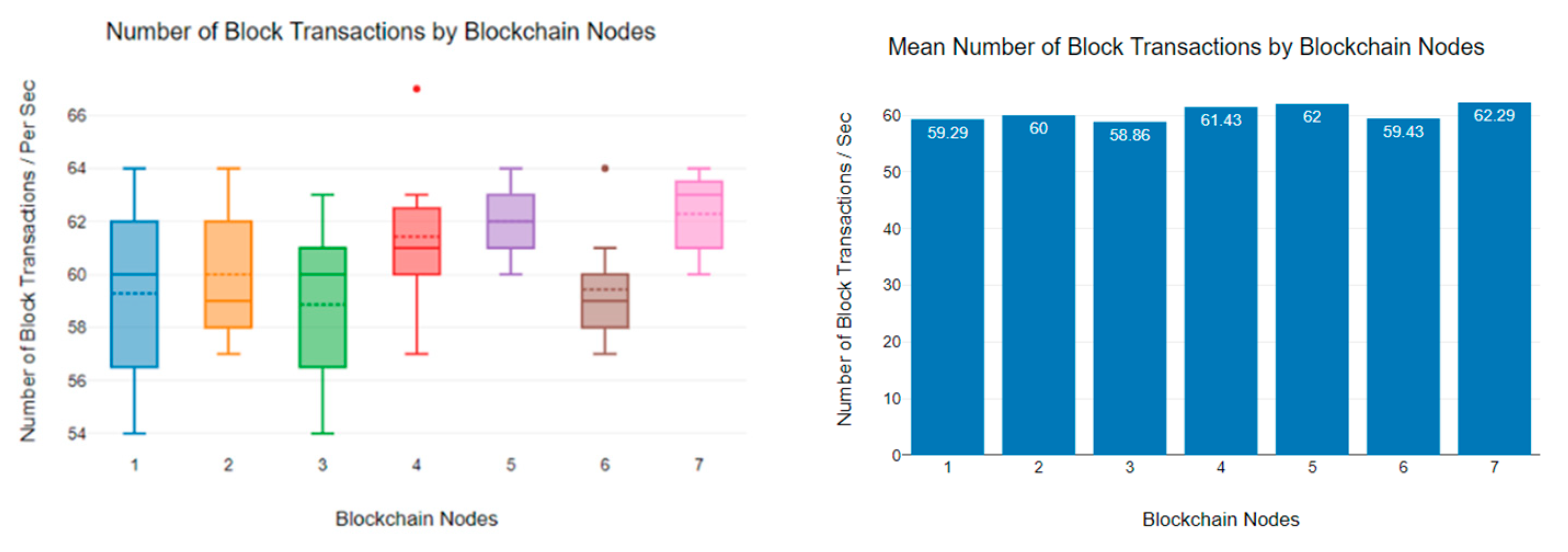
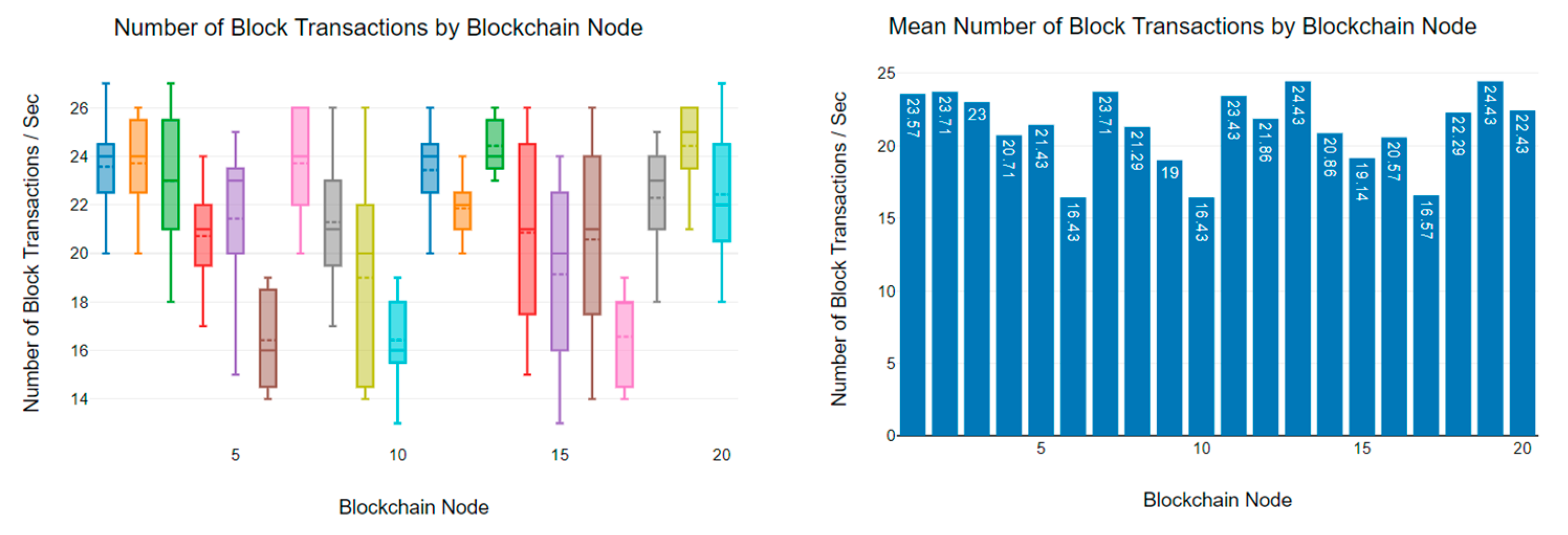
6.3. Block Transaction Rate Analysis
7. Conclusions and Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alam, S.; De, D. Analysis of Security Threats in Wireless Sensor Network. Int. J. Wirel. Mob. Netw. 2014, 6, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharani, A.; Khaliq-ur-Rehman Raazi, S.M. Integrating Blockchain with IoT for Mitigating Cyber Threat In Corporate Environment. In Proceedings of the 2022 Mohammad Ali Jinnah University International Conference on Computing (MAJICC), Karachi, Pakistan, 27–28 October 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Alazzawi, L.; Elkateeb, A. Performance Evaluation of the WSN Routing Protocols Scalability. J. Comput. Syst. Netw. Commun. 2008, 2008, 481046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Brito Gonçalves, J.P.; Spelta, G.; da Silva Villaça, R.; Gomes, R.L. IoT Data Storage on a Blockchain Using Smart Contracts and IPFS. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Blockchain (Blockchain), Espoo, Finland, 22–25 August 2022; pp. 508–511. [Google Scholar]
- Godawatte, K.; Branch, P.; But, J. Use of blockchain in health sensor networks to secure information integrity and accountability. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2022, 210, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, V.; Ordieres-Mere, J. [WiP] IoT Blockchain Technologies for Smart Sensors Based on Raspberry Pi. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 11th Conference on Service-Oriented Computing and Applications (SOCA), Paris, France, 20–22 November 2018; pp. 216–220. [Google Scholar]
- Forkan, A.R.M.; Branch, P.; Jayaraman, P.P.; Ferretto, A. An Internet-of-Things Solution to Assist Independent Living and Social Connectedness in Elderly. Trans. Soc. Comput. 2019, 2, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, M.; Sardaraz, M.; Muhammad, S.; Saud Khan, M. A Lightweight Authentication and Authorization Framework for Blockchain-Enabled IoT Network in Health-Informatics. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewa, T.; Gür, G.; Kalla, A.; Ylianttila, M.; Bracken, A.; Liyanage, M. The Role of Blockchain in 6G: Challenges, Opportunities and Research Directions. In Proceedings of the 2nd 6G Wireless Summit (6G SUMMIT), Levi, Finland, 17–20 March 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yiyang, C.; Takashio, K. A Floating Calculation Revamp For the Ethereum Blockchain-Based IoT Systems. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 8th World Forum on Internet of Things (WF-IoT), Yokohama, Japan, 26 October–11 November 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Su, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, C.; Zhang, H.; Xie, L. A Decentralized Solution for IoT Data Trusted Exchange Based-on Blockchain. In Proceedings of the 3rd IEEE International Conference on Computer and Communications, Chengdu, China, 13–16 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zha, X.; Ni, W.; Liu, R.P.; Guo, Y.J.; Niu, X.; Zheng, K. Survey on blockchain for Internet of Things. Comput. Commun. 2019, 136, 10–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, W.; Liu, Q.; Tian, Z.; Chen, J.-S.; Wang, B.; Liu, W. Blockchain Trust Model for Malicious Node Detection in Wireless Sensor Networks. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 38947–38956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, R.; Hasan, A.S.M.T.; Islam, M.R.; Watanobe, Y. A Blockchain-based Approach to Secure Cloud Connected IoT Devices. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Information and Communication Technology for Sustainable Development (ICICT4SD), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 27–28 February 2021; pp. 366–370. [Google Scholar]
- Moinet, A.; Darties, B.; Baril, J.-L. Blockchain based trust & authentication for decentralized sensor networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.01730. [Google Scholar]
- Panarello, A.; Tapas, N.; Merlino, G.; Longo, F.; Puliafito, A. Blockchain and IoT Integration: A Systematic Survey. Sensors 2018, 18, 2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Shetty, S.; Tosh, D.; Bowden, D.; Njilla, L.; Kamhoua, C. Towards Blockchain Empowered Trusted and Accountable Data Sharing and Collaboration in Mobile Healthcare Applications. EAI Endorsed Trans. Pervasive Health Technol. 2018, 4, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novo, O. Scalable Access Management in IoT Using Blockchain: A Performance Evaluation. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 6, 4694–4701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, S.K.; Roy, P.; Karda, C.; Agrawal, S.; Amin, R. Blockchain-Based Internet of Things and Industrial IoT: A Comprehensive Survey. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2021, 2021, 7142048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.N.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, Y. Blockchain for Internet of Things: A Survey. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 6, 8076–8094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amreen Ashraf, W.E. Authentication in IoT devices using blockchain technology: A Review. In Proceedings of the 4th IET International Smart Cities Symposium, Online Conference, Bahrain, 21–23 November 2021; p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Tao, X.; Zhao, M.; Wu, T.; Zhang, C.; Xue, J.; Zhu, L. Decentralized Policy-Hidden Fine-Grained Redaction in Blockchain-Based IoT Systems. Sensors 2023, 23, 7105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eklund, P.W.; Beck, R. Factors that Impact Blockchain Scalability. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Management of Digital EcoSystems, Limassol, Cyprus, 12–14 November 2019; pp. 126–133. [Google Scholar]
- Corradini, E.; Nicolazzo, S.; Nocera, A.; Ursino, D.; Virgili, L. A two-tier Blockchain framework to increase protection and autonomy of smart objects in the IoT. Comput. Commun. 2022, 181, 338–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyla, T.; Pejaś, J. eHealth Integrity Model Based on Permissioned Blockchain. Future Internet 2019, 11, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, A.D.; Srivastava, G.; Dhar, S.; Singh, R. A Decentralized Privacy-Preserving Healthcare Blockchain for IoT. Sensors 2019, 19, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellahi, R.M.; Wood, L.C.; Bekhit, A.E.-D.A. Blockchain-Based Frameworks for Food Traceability: A Systematic Review. Foods 2023, 12, 3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, F.; Ahmad, S.; Iqbal, N.; Kim, D.-H. Towards a Remote Monitoring of Patient Vital Signs Based on IoT-Based Blockchain Integrity Management Platforms in Smart Hospitals. Sensors 2020, 20, 2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arachchige, K.G.; Branch, P.; But, J. Evaluation of Correlation between Temperature of IoT Microcontroller Devices and Blockchain Energy Consumption in Wireless Sensor Networks. Sensors 2023, 23, 6265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orange Pi—Orange Pi Official Website—Orange Pi Development Board, Open Source Hardware, Open Source Software, Open Source Chip, Computer Keyboard. Available online: http://www.orangepi.org/ (accessed on 22 August 2023).
- Raspberry Pi. Available online: https://www.raspberrypi.com/ (accessed on 22 August 2023).
- Solving the “Total Supply Problem”. Available online: https://hydrachain.org/ (accessed on 17 August 2023).
- The Monero Project. Available online: https://www.getmonero.org/ (accessed on 17 August 2023).
- Coin—A Simple, Eco-Friendly, Centralized Coin. Available online: https://duinocoin.com/ (accessed on 17 August 2023).
- Guerrero-Sanchez, A.E.; Rivas-Araiza, E.A.; Gonzalez-Cordoba, J.L.; Toledano-Ayala, M.; Takacs, A. Blockchain Mechanism and Symmetric Encryption in A Wireless Sensor Network. Sensors 2020, 20, 2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, W.; Zhang, W.; Chen, W.; Pan, T.; Ni, Y.; Yang, Y. Trust-Based Attack and Defense in Wireless Sensor Networks: A Survey. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2020, 2020, 2643546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhusudan Singh, A.S. Shiho Kim Blockchain: A Game Changer for Securing IoT Data. In Proceedings of the IEEE 4th World Forum on Internet of Things (WF-IoT), Singapore, 5–8 February 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, X.; Yeoh, P.L.; Wu, T.; Yu, Y.; Li, Y.; Vucetic, B. Scalable Double Blockchain Architecture for IoT Information and Reputation Management. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 7th World Forum on Internet of Things (WF-IoT), New Orleans, LA, USA, 14 June–31 July 2021; pp. 171–176. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, S. Secure caching scheme by using blockchain for information-centric network-based wireless sensor networks. J. Signal Process. 2018, 22, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikram, A.; Kumar, S. Mohana, Blockchain Technology and its Impact on Future of Internet of Things (IoT) and Cyber Security. In Proceedings of the 2022 6th International Conference on Electronics, Communication and Aerospace Technology, Coimbatore, India, 1–3 December 2022; pp. 444–447. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, X.; Wang, H.; Jin, D.; Li, M.; Jiang, W. Healthcare Data Gateways: Found Healthcare Intelligence on Blockchain with Novel Privacy Risk Control. J. Med. Syst. 2016, 40, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaga, D.; Mell, P.; Roby, N.; Scarfone, K. Blockchain Technology Overview; NIST: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2018.
- Stamatellis, C.; Papadopoulos, P.; Pitropakis, N.; Katsikas, S.; Buchanan, W.J. A Privacy-Preserving Healthcare Framework Using Hyperledger Fabric. Sensors 2020, 20, 6587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truong, H.T.T.; Almeida, M.; Karame, G.; Soriente, C. Towards Secure and Decentralized Sharing of IoT Data. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Blockchain (Blockchain), Atlanta, GA, USA, 14–17 July 2019; pp. 176–183. [Google Scholar]
- Premkumar, R.; Sathya, P.S. A Blockchain based Framework for IoT Security. In Proceedings of the 2021 5th International Conference on Computing Methodologies and Communication (ICCMC), Erode, India, 8–10 April 2021; pp. 409–413. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, C.; Chai, K.K.; Poslad, S. A Challenge-Response Assisted Authorisation Scheme for Data Access in Permissioned Blockchains. Sensors 2020, 20, 4681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Tang, H.; Du, R. A Novel Blockchain-Based IoT Data Provenance Model. In Proceedings of the 2022 2nd International Conference on Computer Science and Blockchain (CCSB), Wuhan, China, 28–30 October 2022; pp. 46–52. [Google Scholar]
- Peral, J.; Gallego, E.; Gil, D.; Tanniru, M.; Khambekar, P. Using Visualization to Build Transparency in a Healthcare Blockchain Application. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyna, A.; Martín, C.; Chen, J.; Soler, E.; Díaz, M. On blockchain and its integration with IoT. Challenges and opportunities. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2018, 88, 173–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Hydrachain | Monero | Duino Coin | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 07 Nodes | 15 Nodes | 20 Nodes | 07 Nodes | 15 Nodes | 20 Nodes | 07 Nodes | 15 Nodes | 20 Nodes |
| 214 ms | 388 ms | 419 ms | 485 ms | 720 ms | 817 ms | 239 ms | 390 ms | 450 ms |
| 215 ms | 389 ms | 418 ms | 486 ms | 728 ms | 818 ms | 240 ms | 390 ms | 450 ms |
| 213 ms | 389 ms | 420 ms | 485 ms | 725 ms | 816 ms | 238 ms | 391 ms | 451 ms |
| 214 ms | 389 ms | 418 ms | 485 ms | 729 ms | 815 ms | 238 ms | 392 ms | 452 ms |
| 213 ms | 387 ms | 419 ms | 485 ms | 730 ms | 816 ms | 237 ms | 392 ms | 452 ms |
| 214 ms | 388 ms | 419 ms | 486 ms | 728 ms | 815 ms | 237 ms | 392 ms | 452 ms |
| 215 ms | 389 ms | 418 ms | 488 ms | 728 ms | 819 ms | 238 ms | 391 ms | 452 ms |
| 213 ms | 389 ms | 420 ms | 484 ms | 730 ms | 819 ms | 237 ms | 391 ms | 450 ms |
| 213 ms | 389 ms | 418 ms | 485 ms | 729 ms | 820 ms | 239 ms | 392 ms | 449 ms |
| 214 ms | 387 ms | 419 ms | 485 ms | 728 ms | 820 ms | 240 ms | 392 ms | 449 ms |
| Hydrachain | Monero | Duino Coin | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 07 Nodes | 15 Nodes | 20 Nodes | 07 Nodes | 15 Nodes | 20 Nodes | 07 Nodes | 15 Nodes | 20 Nodes |
| 410 Kbps | 1125 Kbps | 1655 Kbps | 43 Kbps | 112 Kbps | 120 Kbps | 51 Kbps | 100 Kbps | 155 Kbps |
| 628 Kbps | 1245 Kbps | 1548 Kbps | 49 Kbps | 119 Kbps | 128 Kbps | 49 Kbps | 112 Kbps | 143 Kbps |
| 553 Kbps | 1157 Kbps | 1577 Kbps | 53 Kbps | 124 Kbps | 136 Kbps | 49 Kbps | 128 Kbps | 115 Kbps |
| 498 Kbps | 1148 Kbps | 1471 Kbps | 48 Kbps | 120 Kbps | 154 Kbps | 48 Kbps | 147 Kbps | 149 Kbps |
| 673 Kbps | 1302 Kbps | 1470 Kbps | 46 Kbps | 127 Kbps | 138 Kbps | 50 Kbps | 140 Kbps | 144 Kbps |
| 768 Kbps | 1024 Kbps | 1489 Kbps | 46 Kbps | 110 Kbps | 133 Kbps | 50 Kbps | 143 Kbps | 78 Kbps |
| 728 Kbps | 1268 Kbps | 1602 Kbps | 51 Kbps | 111 Kbps | 158 Kbps | 51 Kbps | 157 Kbps | 280 Kbps |
| 612 Kbps | 1459 Kbps | 1631 Kbps | 52 Kbps | 133 Kbps | 155 Kbps | 49 Kbps | 159 Kbps | 245 Kbps |
| 558 Kbps | 1468 Kbps | 1624 Kbps | 47 Kbps | 128 Kbps | 157 Kbps | 48 Kbps | 166 Kbps | 251 Kbps |
| 790 Kbps | 1520 Kbps | 1659 Kbps | 45 Kbps | 131 Kbps | 129 Kbps | 49 Kbps | 154 Kbps | 267 Kbps |
| Hydrachain | Monero | Duino Coin | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 07 Nodes | 15 Nodes | 20 Nodes | 07 Nodes | 15 Nodes | 20 Nodes | 07 Nodes | 15 Nodes | 20 Nodes |
| 25 | 21 | 13 | 53 | 39 | 28 | 61 | 15 | 14 |
| 25 | 21 | 19 | 51 | 45 | 33 | 56 | 21 | 18 |
| 25 | 20 | 17 | 67 | 38 | 30 | 63 | 17 | 15 |
| 25 | 20 | 18 | 73 | 61 | 31 | 60 | 13 | 14 |
| 26 | 22 | 14 | 62 | 64 | 28 | 64 | 15 | 23 |
| 25 | 21 | 14 | 65 | 55 | 40 | 58 | 28 | 16 |
| 25 | 21 | 14 | 81 | 52 | 34 | 57 | 19 | 26 |
| 26 | 21 | 15 | 70 | 59 | 32 | 62 | 24 | 15 |
| 25 | 19 | 18 | 74 | 60 | 44 | 55 | 21 | 22 |
| 25 | 22 | 18 | 66 | 64 | 31 | 62 | 20 | 22 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Godewatte Arachchige, K.; Branch, P.; But, J. Evaluation of Blockchain Networks’ Scalability Limitations in Low-Powered Internet of Things (IoT) Sensor Networks. Future Internet 2023, 15, 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi15090317
Godewatte Arachchige K, Branch P, But J. Evaluation of Blockchain Networks’ Scalability Limitations in Low-Powered Internet of Things (IoT) Sensor Networks. Future Internet. 2023; 15(9):317. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi15090317
Chicago/Turabian StyleGodewatte Arachchige, Kithmini, Philip Branch, and Jason But. 2023. "Evaluation of Blockchain Networks’ Scalability Limitations in Low-Powered Internet of Things (IoT) Sensor Networks" Future Internet 15, no. 9: 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi15090317
APA StyleGodewatte Arachchige, K., Branch, P., & But, J. (2023). Evaluation of Blockchain Networks’ Scalability Limitations in Low-Powered Internet of Things (IoT) Sensor Networks. Future Internet, 15(9), 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi15090317







