Optimal Mobility-Aware Wireless Edge Cloud Support for the Metaverse
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
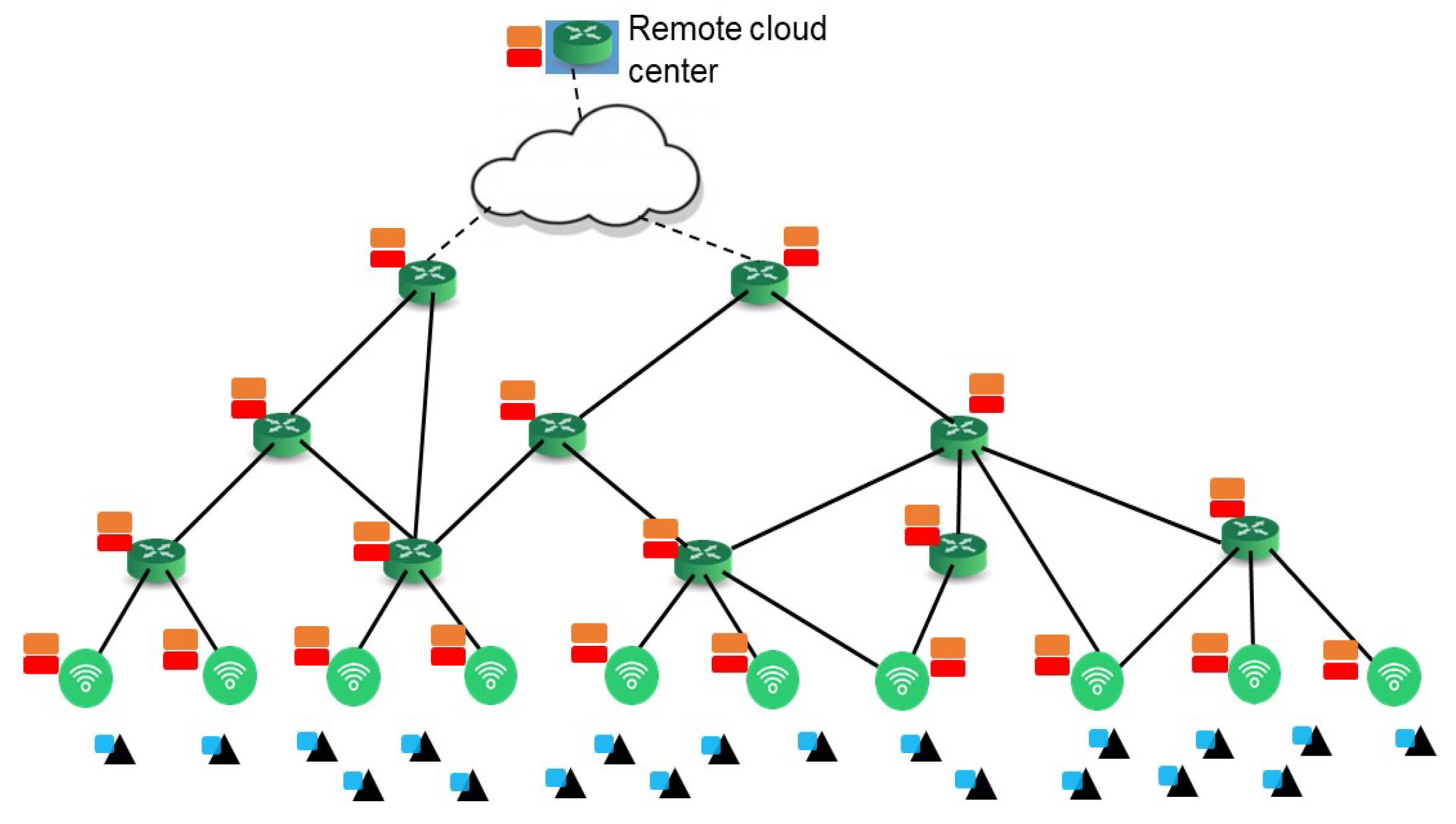
3. System Model
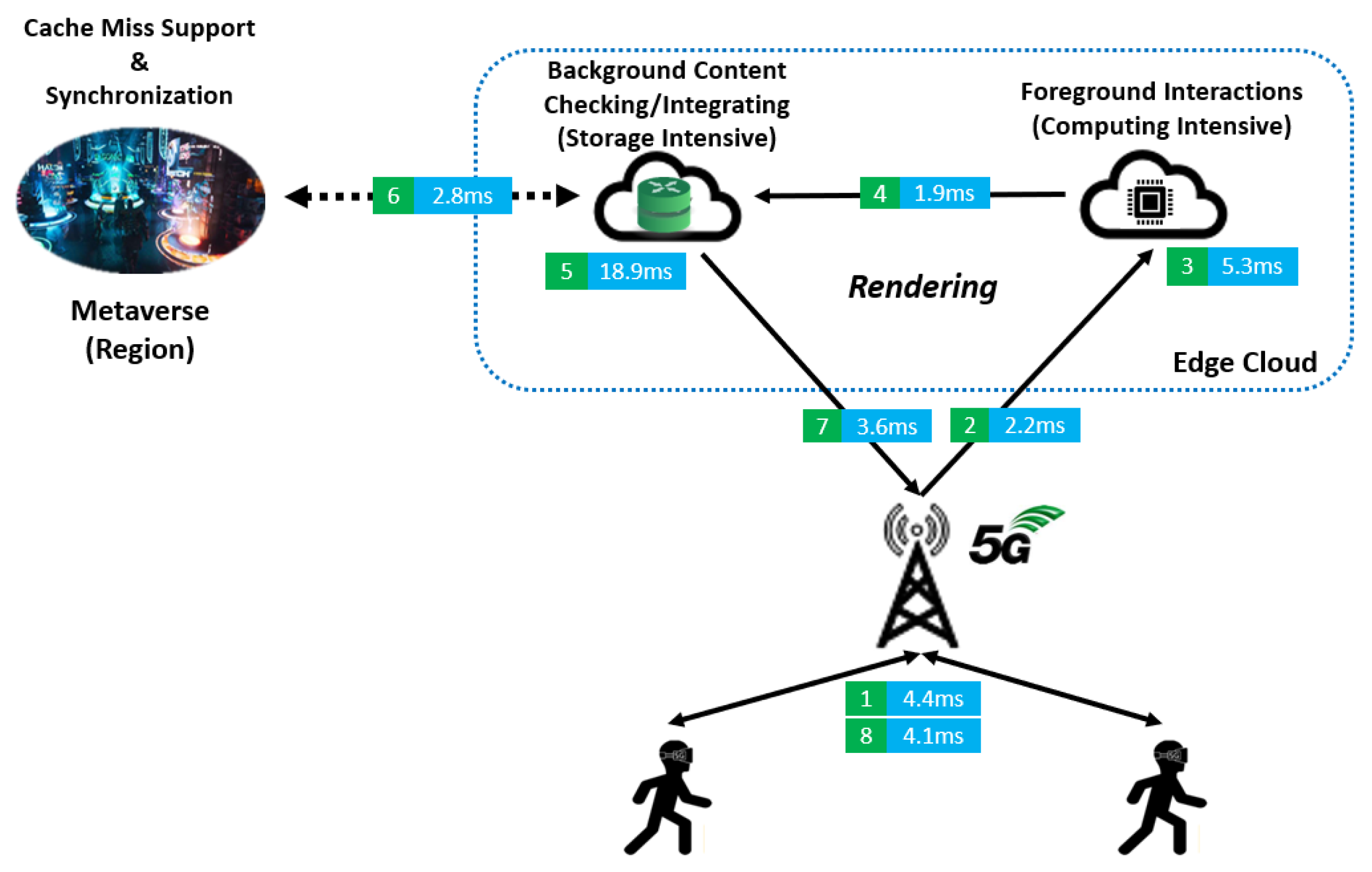
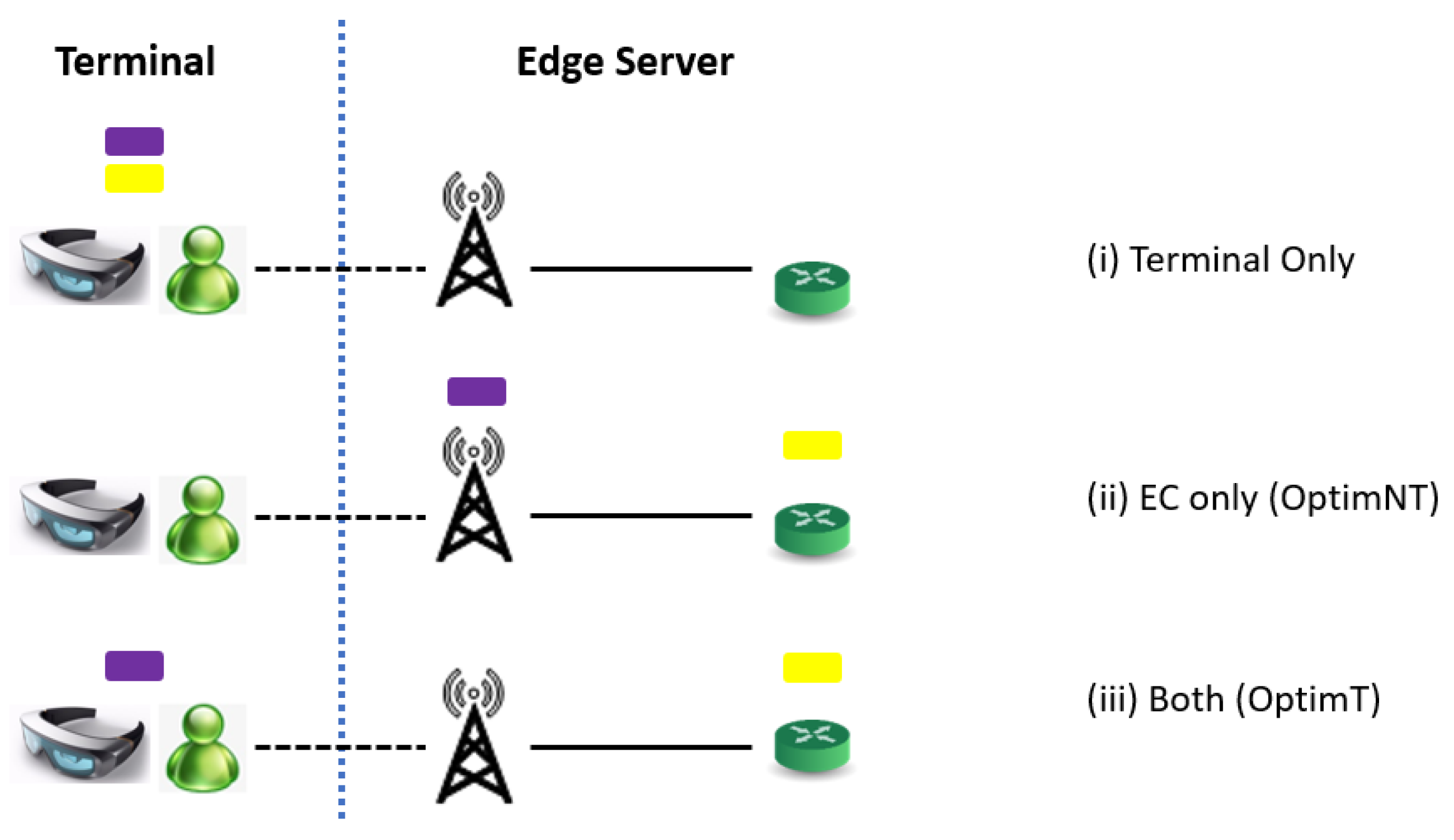
3.1. Multirendering in Metaverse AR
3.2. Wireless Resource Allocation and Channel Model
3.3. Latency, Energy Consumption and Quality of Perception Experience
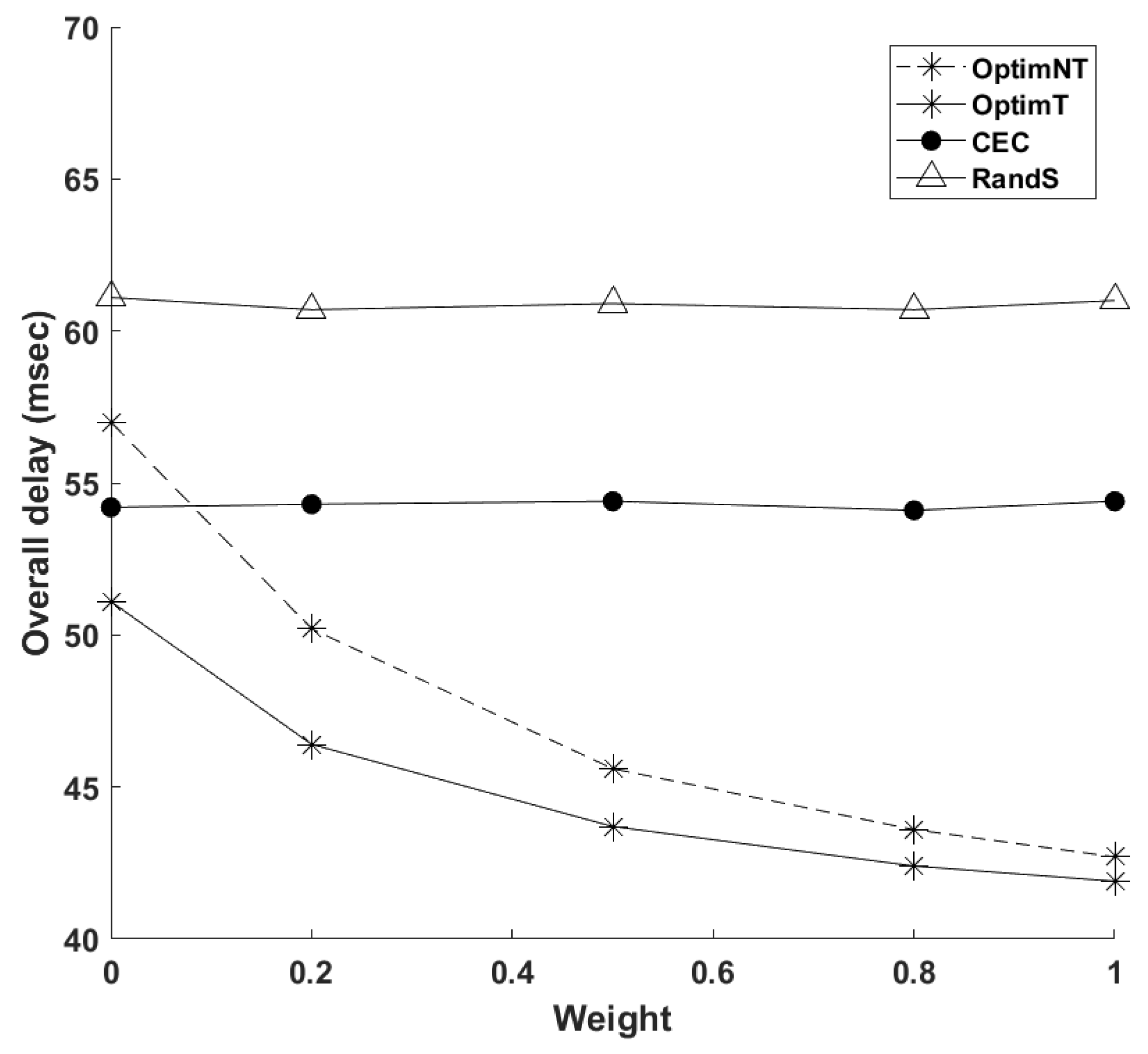
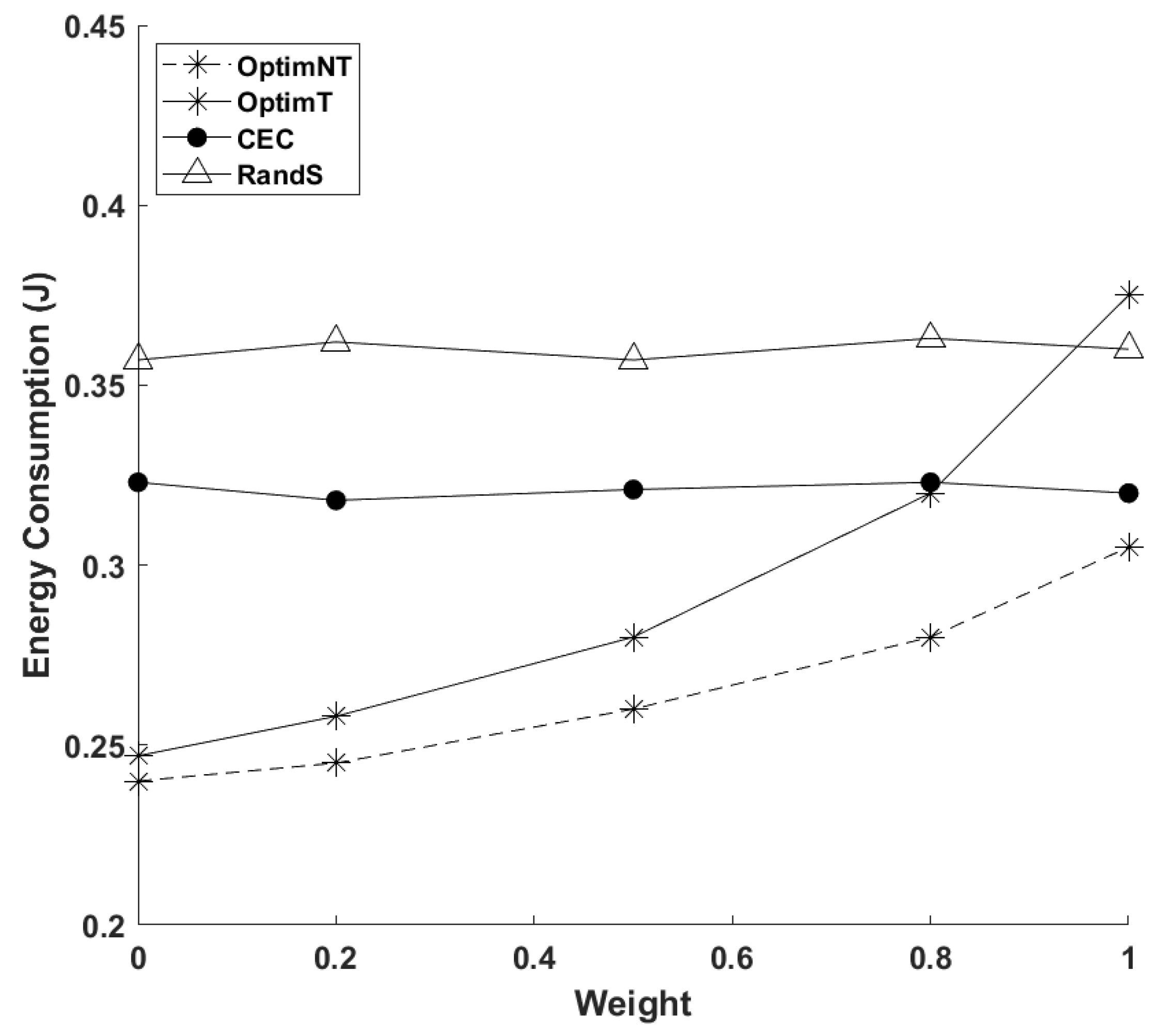
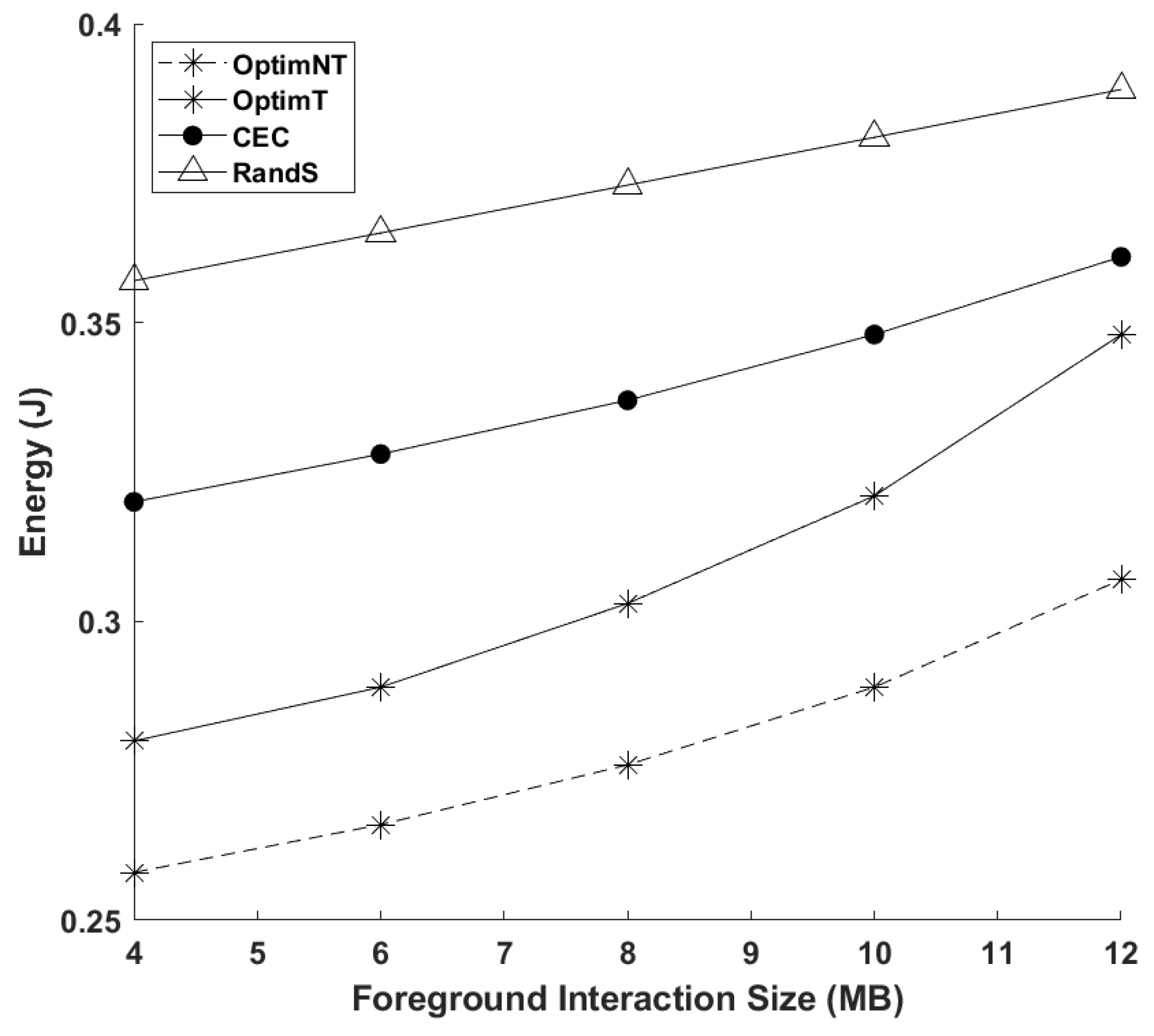
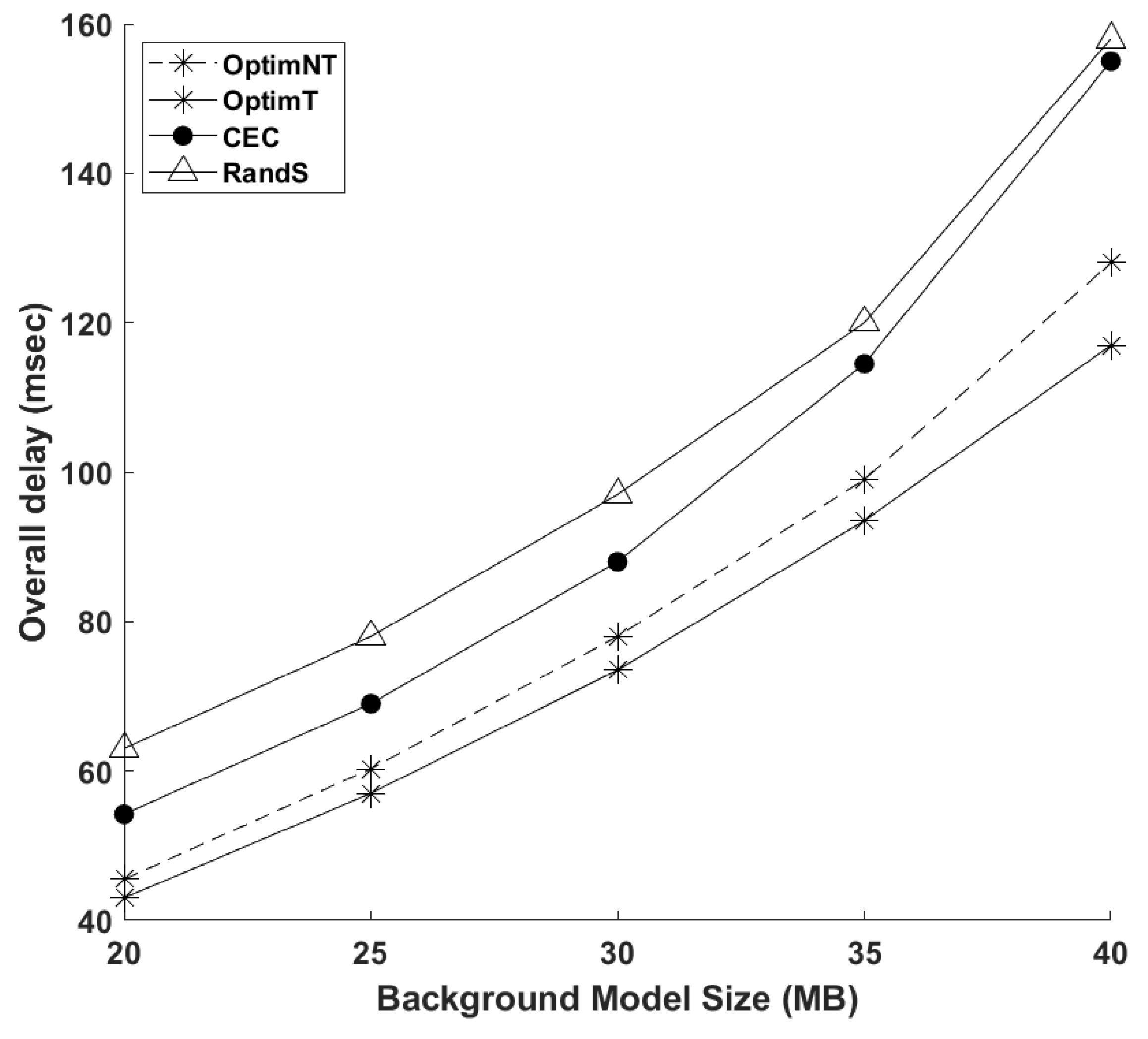
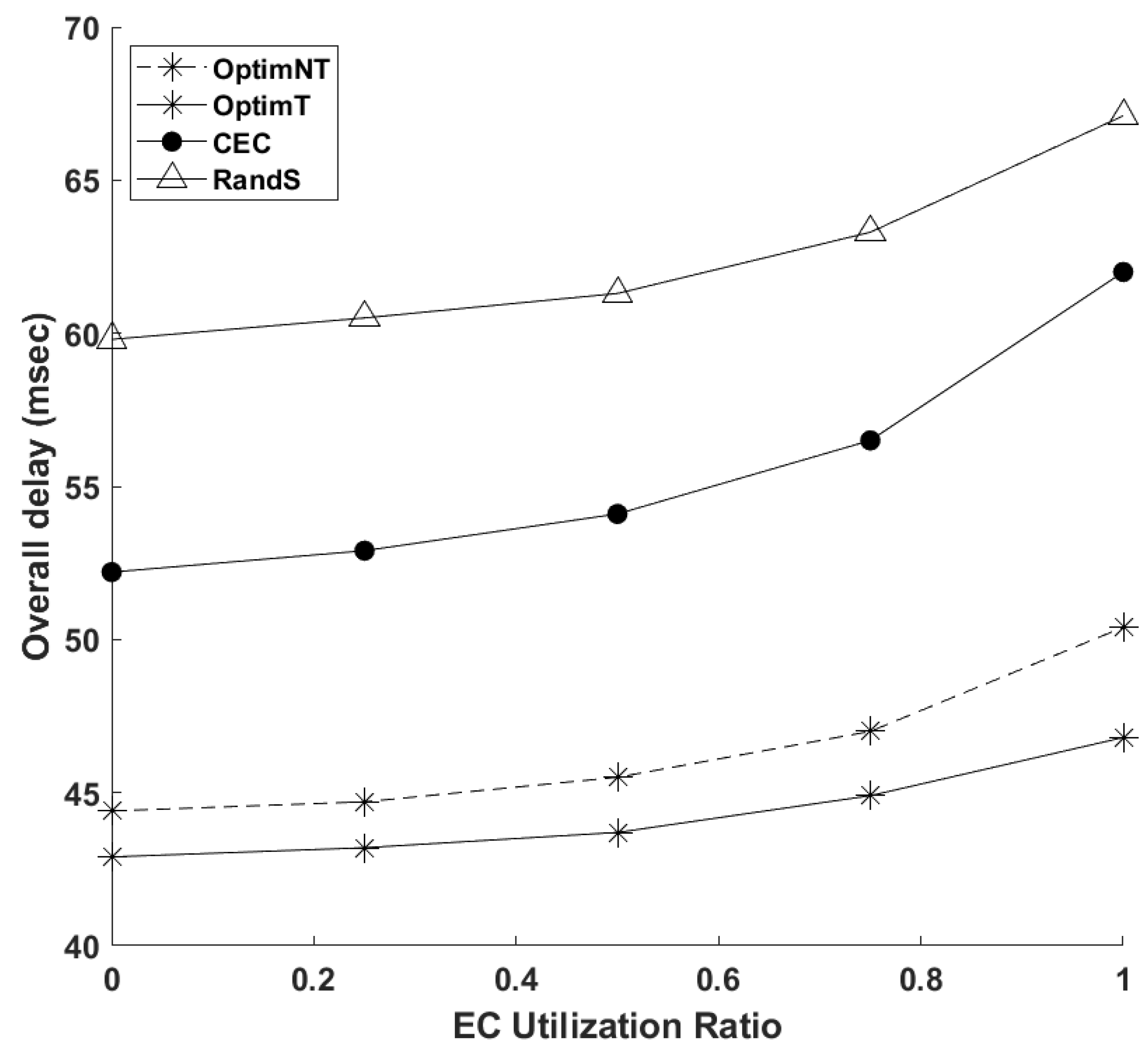
4. Numerical Investigations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ball, M. The Metaverse: And How It Will Revolutionize Everything; Liveright Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Rauschnabel, P.A.; Felix, R.; Hinsch, C. Augmented reality marketing: How mobile AR-apps can improve brands through inspiration. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2019, 49, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauschnabel, P.A.; Felix, R.; Hinsch, C.; Shahab, H.; Alt, F. What is XR? Towards a framework for augmented and virtual reality. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2022, 133, 107289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Niyato, D.; Kang, J.; Xiong, Z.; Miao, C.; Kim, D.I. Wireless Edge-Empowered Metaverse: A Learning-Based Incentive Mechanism for Virtual Reality. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.03776. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, R.; She, C.; Hardjawana, W.; Li, Y.; Vucetic, B. Deep learning for hybrid 5G services in mobile edge computing systems: Learn from a digital twin. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2019, 18, 4692–4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Ng, W.C.; Lim, W.Y.B.; Kang, J.; Xiong, Z.; Niyato, D.; Yang, Q.; Shen, X.S.; Miao, C. A Full Dive into Realizing the Edge-enabled Metaverse: Visions, Enabling Technologies, and Challenges. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.05471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chylinski, M.; Heller, J.; Hilken, T.; Keeling, D.I.; Mahr, D.; de Ruyter, K. Augmented reality marketing: A technology-enabled approach to situated customer experience. Australas. Mark. J. (AMJ) 2020, 28, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Qiao, X.; Lu, Q.; Ren, P.; Lin, R. Rendering Optimization for Mobile Web 3D Based on Animation Data Separation and On-Demand Loading. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 88474–88486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Yu, F.R.; Zhang, H.; Ji, H.; Leung, V.C.; Li, X. An adaptive wireless virtual reality framework in future wireless networks: A distributed learning approach. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 8514–8528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, H.; Kobayashi, T.; Sugano, M.; Naito, S. Split Rendering of the Transparent Channel for Cloud AR. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 23rd International Workshop on Multimedia Signal Processing (MMSP), Tampere, Finland, 6–8 October 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Chen, Z.; Li, K.; Sun, Y.; Liu, N.; Xie, W.; Zhao, Y. Communication-constrained mobile edge computing systems for wireless virtual reality: Scheduling and tradeoff. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 16665–16677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Friderikos, V. Proactive edge cloud optimization for mobile augmented reality applications. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Nanjing, China, 29 March–1 April 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hertzmann, A.; Perlin, K. Painterly rendering for video and interaction. In Proceedings of the 1st international Symposium on Non-Photorealistic Animation and Rendering, Annecy, France, 5–7 June 2000; pp. 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Dai, Y.; Meng, H.; Chen, Y.; Li, T. Understanding the characteristics of mobile augmented reality applications. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Symposium on Performance Analysis of Systems and Software (ISPASS), Belfast, UK, 2–4 April 2018; pp. 128–138. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Friderikos, V. Mobility Aware Optimization in the Metaverse. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 4–8 December 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Song, S.; Kim, J.; Chung, J.M. Energy consumption minimization control for augmented reality applications based on multi-core smart devices. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics (ICCE), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 11–13 January 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Li, T.; Kim, H.S.; Culler, D.E.; Katz, R.H. Marvel: Enabling mobile augmented reality with low energy and low latency. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 16th ACM Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems, Shenzhen, China, 4–7 November 2018; pp. 292–304. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, Y.J.; Lee, J.; Hwang, J.; Niyato, D.; Park, H.S.; Choi, J.K. A novel joint mobile cache and power management scheme for energy-efficient mobile augmented reality service in mobile edge computing. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2021, 10, 1061–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Niyato, D.; Leung, C.; Miao, C.; Kim, D.I. A dynamic resource allocation framework for synchronizing metaverse with iot service and data. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.00431. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Kang, J.; Niyato, D.; Ge, X.; Xiong, Z.; Miao, C. Reliable coded distributed computing for metaverse services: Coalition formation and incentive mechanism design. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.10548. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, N.H.; Hoang, D.T.; Nguyen, D.N.; Phan, K.T.; Dutkiewicz, E. MetaSlicing: A Novel Resource Allocation Framework for Metaverse. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.11087. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, W.C.; Lim, W.Y.B.; Ng, J.S.; Xiong, Z.; Niyato, D.; Miao, C. Unified resource allocation framework for the edge intelligence-enabled metaverse. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.14325. [Google Scholar]
- Gemici, Ö.F.; Hökelek, İ.; Çırpan, H.A. Modeling Queuing Delay of 5G NR With NOMA Under SINR Outage Constraint. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2021, 70, 2389–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.S.; Kim, J.; Yang, W.Y.; Kang, C.G. MIMO-OFDM Wireless Communications with MATLAB; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Haenggi, M.; Tan, Z. The meta distribution of the SIR for cellular networks with power control. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2017, 66, 1745–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wen, Y.; Guan, K.; Kilper, D.; Luo, H.; Wu, D.O. Energy-optimal mobile cloud computing under stochastic wireless channel. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2013, 12, 4569–4581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miettinen, A.P.; Nurminen, J.K. Energy efficiency of mobile clients in cloud computing. In Proceedings of the 2nd USENIX Workshop on Hot Topics in Cloud Computing (HotCloud 10), Boston, MA, USA, 22 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Amdahl, G.M. Validity of the single processor approach to achieving large scale computing capabilities. In Proceedings of the Spring Joint Computer Conference, Atlantic City, NJ, USA, 18–20 April 1967; pp. 483–485. [Google Scholar]
- Cozzolino, V.; Tonetto, L.; Mohan, N.; Ding, A.Y.; Ott, J. Nimbus: Towards Latency-Energy Efficient Task Offloading for AR Services. IEEE Trans. Cloud Comput. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, G.; Chen, Q. Learning an video frame-based face detection system for security fields. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2018, 55, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naman, A.T.; Xu, R.; Taubman, D. Inter-frame prediction using motion hints. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 15–18 September 2013; pp. 1792–1796. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Huang, S.; Opadere, J.; Han, T. An edge network orchestrator for mobile augmented reality. In Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM, Honolulu, HI, USA, 16–19 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, A.; Jacobs, J.; Sra, M.; Höllerer, T. Multi-View AR Streams for Interactive 3D Remote Teaching. In Proceedings of the 27th ACM Symposium on Virtual Reality Software and Technology, Osaka, Japan, 8–10 December 2021; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Korrai, P.K.; Lagunas, E.; Sharma, S.K.; Chatzinotas, S.; Ottersten, B. Slicing based resource allocation for multiplexing of eMBB and URLLC services in 5G wireless networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 24th International Workshop on Computer Aided Modeling and Design of Communication Links and Networks (CAMAD), Limassol, Cyprus, 11–13 September 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Lin, P.; Song, J.; Song, Q. Computing-Assisted Task Offloading and Resource Allocation for Wireless VR Systems. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 6th International Conference on Computer and Communications (ICCC), Chengdu, China, 11–14 December 2020; pp. 368–372. [Google Scholar]
- Chettri, L.; Bera, R. A comprehensive survey on Internet of Things (IoT) toward 5G wireless systems. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 7, 16–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toczé, K.; Nadjm-Tehrani, S. ORCH: Distributed orchestration framework using mobile edge devices. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Fog and Edge Computing (ICFEC), Larnaca, Cyprus, 14–17 May 2019; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]




| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of available ECs | 6 |
| Number of available VMs per EC (EC capacity) | 14 |
| Number of requests | 30 |
| Number of available models per user | 4 |
| AR object size | MByte |
| Total moving probability | |
| Cell radius | 250 m |
| Remained cache capacity per EC | MByte |
| EC CPU frequency | [4,8] GHz |
| EC CPU cores | [4,8] |
| EC CPU core portion per VM | 0.25–0.5 |
| Remained cache capacity per terminal | MByte |
| Terminal CPU frequency | 1 GHz |
| Terminal CPU cores | 4 |
| CPU architecture coefficient | |
| Foreground-interaction computational load | 4 cycles/bit |
| Background-content-checking computational load | 10 cycles/bit |
| Carrier frequency | 2 GHz |
| Transmission power | 20 dBm |
| Path loss exponent | 4 |
| Noise power | W |
| Number of resource blocks | 100 |
| Frame resolution | 1280 × 720 |
| Average latency per hop | 2 ms |
| Cache miss penalty | 25 ms |
| Scheme | OptimT | OptimNT | CFS | RandS |
| Delay (ms) | 38.8 | 40.1 | 40.7 | 60.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Z.; Friderikos, V. Optimal Mobility-Aware Wireless Edge Cloud Support for the Metaverse. Future Internet 2023, 15, 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi15020047
Huang Z, Friderikos V. Optimal Mobility-Aware Wireless Edge Cloud Support for the Metaverse. Future Internet. 2023; 15(2):47. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi15020047
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Zhaohui, and Vasilis Friderikos. 2023. "Optimal Mobility-Aware Wireless Edge Cloud Support for the Metaverse" Future Internet 15, no. 2: 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi15020047
APA StyleHuang, Z., & Friderikos, V. (2023). Optimal Mobility-Aware Wireless Edge Cloud Support for the Metaverse. Future Internet, 15(2), 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi15020047






