Abstract
With data transparency and immutability, the blockchain can provide trustless and decentralized services for Internet of Things (IoT) applications. However, most blockchain-IoT networks, especially those with a private blockchain, are built on top of an infrastructure-based wireless network (i.e., using Wi-Fi access points or cellular base stations). Hence, they are still under the risk of Single-Point-of-Failure (SPoF) on the network layer, hindering the decentralization merit, for example, when the access points or base stations get failures. This paper presents an Optimized Link State Routing (OLSR) protocol-based solution for that issue in a private blockchain-IoT application. By decentralizing the underlying network with OLSR, the private blockchain network can avoid SPoF and automatically recover after a failure. Single blockchain connections can be extended to multiple ad hoc hops. Services over blockchain become flexible to fit various IoT scenarios. We show the effectiveness of our solution by constructing a private Ethereum blockchain network running on IoT devices (i.e., Raspberry Pi model 4) with environmental data sensing (i.e., Particular Matter (PM)). The IoT devices use OLSR to form an ad hoc network. The environment data are collected and propagated in transactions to a pre-loaded smart contract periodically. We then evaluate the IoT blockchain network’s recovery time when facing a link error. The evaluation results show that OLSR can automatically recover after the failure. We also evaluate the transaction-oriented latency and block-oriented latency, which indicates the blocks have a high transmission quality, while transactions are transferred individually.
1. Introduction
Blockchain technology was first introduced in the cryptocurrency application, which has been gaining more and more interest and popularity with Bitcoin [1], Ethereum [2], etc. After that, with various features of decentralization, immutability, data transparency, etc., the blockchain has shown its potential in many other fields beyond cryptocurrency, including data sharing in healthcare [3], access control in cloud storage [4], vehicles communication [5], and the Internet of Things (IoT) [6]. Notably, there is an increasing number of works aiming to bring the decentralization nature of blockchain to strengthen IoT systems [7]. For example, in [8], by achieving distributed consensuses among participants in IoT systems, the blockchain can provide a transparent and immutable communication and storage platform. As a result, with blockchain, IoT services can be provided in a trustless and decentralized manner.
Ethereum is one of the most popular blockchains, which is open source and suitable for IoT. Ethereum notably supports the smart contract, which is automatically executable code in the blockchain. Hence, IoT devices can perform uploaded functions or modify store variables in a smart contract following triggering transactions. When a blockchain node launches a transaction, instructions and/or data are propagated to all nodes among the network, each of them executes or stores data correspondingly. In Ethereum, all legal transactions are packaged into blocks by consensus algorithms (e.g., Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Authority (PoA)). After that, a complete copy of historical blocks is shared among all participating nodes. Ultimately, IoT devices communicate and cooperate over the Ethereum blockchain platform without a centralized authority. For example, the smart home in [9] uses Ethereum in a home-area IoT devices management system. In [10], the authors proposed an Ethereum-based smart edge contract, which is a computational power trading system for edge computing.
However, although not discussed in detail, most of the previous blockchain-IoT systems normally run on a wireless infrastructure network using Wi-Fi [11], cellular [12], LoRa [13], or other wireless technologies. As a result, all IoT devices in a particular area utilize blockchain services over wireless communication through a centralized node, such as Wi-Fi access points or cellular base stations. Moreover, in the previous works, the blockchains are carried out to assume that the underlying infrastructure-based transmission is reliable. The assumption may not hold since the IoT network infrastructure is vulnerable and at high risks of failure [14]. Most likely, the blockchain with all decentralization merit in the application layer still incurs the Single Point of Failure (SPoF) at the network level, bringing the whole blockchain-IoT system disfunction. Therefore, it is necessary to improve the underlying network of blockchain-IoT to avoid SPoF. The ad hoc routing protocols show a lot of potential to bypass the issue. The nodes with ad hoc routing can flexibly communicate with others to form a network, enhancing resilience compared to the infrastructure ones.
This work proposes and implements a decentralized private blockchain-IoT system over an ad hoc network [15] with the Optimized Link State Routing (OLSR) protocol [16]. With OLSR, IoT devices in the blockchain application can directly communicate with others without wireless infrastructures. In other words, the blockchain-IoT systems thoroughly perform in a decentralized method in the application and network layers. We show the effectiveness of our proposal in an environmental monitoring application with four Raspberry Pi model 4 (RPi4) nodes as IoT devices and a PM sensor. Each RPi is equipped with an OLSR daemon (OLSRd) and an Ethereum client (Geth). One RPi with the sensor performs as a sender that collects and submits PM data to a pre-loaded smart contract. Another RPi is involved as a receiver and in charge of mining blocks and monitoring if the PM data exceed an alert value. The sender keeps streaming transactions to the receiver directly via a blockchain connection. First, we evaluate the IoT blockchain system with underlying network failures. The results show that the blockchain connection could recover from the failures, eliminating the SPoF issue on the network layer. Second, we evaluate the latency performance of blocks and transactions using the characterizing method in [11]. The results show nodes in the ad hoc network transfer blocks more smoothly than transactions since transactions are transferred individually. Meanwhile, the infrastructure network propagated the information more efficiently than the ad hoc network.
The remainder of the paper is organized as follows. Section 2 presents related works, while Section 3 introduces the background of Ethereum blockchain and OLSR protocol. In Section 4, we present our decentralized system over an ad hoc network. Section 5 describes the evaluation results. Finally, Section 6 concludes the paper.
2. Related Work
Blockchain essentially is a distributed ledger based on peer-to-peer (P2P) communication, which significantly improves the traditional centralized models. One of the most representative applications that benefit from decentralization is voting as in [17]. The authors proposed an online blockchain-based voting platform that enforces immutability and transparency. In [18,19], the blockchain technology is used for the Internet of Vehicles (IoV). The results show significant advantages in security, data storage, and real-time response. The authors of [20,21] discussed adopting different blockchains for healthcare services. They showed that the private blockchain is a popular trust-preserving solution within the healthcare ecosystem. The authors of [22] introduced an Ethereum blockchain-based healthcare management for a large amount of medical data and different workflows for medical procedures. A blockchain-based healthcare framework in [23] allows local networks to submit transactions to a blockchain network. The local networks stretch from IoT devices encircling patients, established as the Internet of Medical Things, to the local healthcare service provider.
In the IoT field, many works use the private blockchain in decentralized IoT systems. However, the underlying network is commonly omitted or regarded as an infrastructure-based wireless network. For example, in the blockchain-based smart home in [24], the system’s backbone comprises several cluster headers, which manage private blockchains for their cluster. The underlying network in each cluster is not discussed, while IoT devices in each cluster are connected to a Wi-Fi access point or a cellular base station as default. In another smart home with blockchain [9], the Raspberry Pi Model 3B and DHT11 sensor are used to monitor temperature and humidity with a DHT11 sensor. The monitoring results are presented to the Blynk App on the smartphone. However, the system runs over a Wi-Fi access point, according to the smartphone screenshot. The blockchain-based healthcare systems described above are usually built over infrastructure networks, as illustrated. In [12], the authors considered different underlying networks in a real-world private Ethereum application. In this work, the Wi-Fi and 3G cellular networks are involved in a blockchain-based flood monitoring and detection system. A comparison work in [25,26] indicates that decentralized generated mesh networks have a higher efficiency to cover irregular spaces than centralized generated ones. A decentralized network could automatically adapt according to local information, which is capable of avoiding SPoF. Thus, decentralized ad hoc networks may be an alternative to build blockchain networks with higher robustness.
Several works in the literature consider a combination of ad hoc networks and blockchains. In [27], a self-managed vehicular ad hoc network that uses routing with smart contracts is proposed. The authors found the feasibility of performing various applications, such as traffic regulation, vehicle tax, and vehicle insurance, on blockchain platforms with proper routing. The work in [28] manages group keys dynamically with blockchain for an unmanned aerial vehicles ad hoc network. The keys can be recovered from neighbors when lost or attacked. In that sense, blockchain provides immutable storage here. Moreover, a smart contract-based contractual routing protocol is proposed in [29] for the ad hoc network. The proposed protocol has a higher tolerance on the transmission delay or malicious nodes in a decentralized manner. The authors of [30] proposed a blockchain-enabled Stackelberg competition mechanism to improve the performance of the QoS-OLSR protocol. On-chain smart contract is integrated into off-chain QoS-OLSR protocol to motivate participants, utilizing the monetary feature. A blockchain-embedded OLSR protocol is presented in [31,32] to solve security problems on routing issues. A policy- and reputation-based trust management framework is constructed with smart contracts for identifying malicious attackers and trusted nodes. Probably, the closest work to ours was presented by Laube et al. [33], who improved the underlying network of IoT-blockchain with a mobile node. They defined a so-called network splitting and merging problems in the ad hoc networks. Our work is similar in terms of the integration of ad hoc routing and blockchain. However, we concentrate on recovery capability against failure over ad hoc network with OLSR protocol. Moreover, we uniquely consider the integration on a real system with real hardware, sensing, and blockchain. An overview of related works with their main contributions is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Overview of the related works and ours.
3. Background
3.1. Ad Hoc Network and OLSR
In the IoT blockchain applications, the IoT devices majorly communicate over wireless infrastructure networks. In such cases, the blockchain and non-blockchain traffic is usually sent/received on infrastructures including Wi-Fi networks, cellular, or LoRa. As a result, the performance and sustainability entirely depend on a central point, such as Wi-Fi access points, cellular base stations, or LoRa gateways. That is because all the packets are routed to the central devices before arriving at the final destinations. Moreover, the communication range of the whole network is limited to the radio coverage range of the devices. On the other hand, as defined in the popular IEEE 802.11 [34], wireless communications are not merely driven as infrastructure but also ad hoc networks. Ad hoc networks can be formed by a group of nodes, which directly communicate with each other. In the opposite of the wireless infrastructure, the ad hoc network drives the data packet between nodes without the central point. Since the wireless communication range limits a wireless node, the node needs to participate in the routing activity to reach others. This can be realized with an ad hoc routing protocol. In such a case, the nodes can cooperate to expand the coverage of the network.
The OLSR protocol is a table-driven, proactive routing protocol for ad hoc networks. An OLSR node discerns links, detects neighbors, and decides Multipoint Relays (MPR) nodes with HELLO messages before establishing the routing table. It periodically broadcasts HELLO messages with its neighbors’ information to reachable nodes. Upon receiving the HELLO messages with attached parameters, the receiver divides associated links into asymmetric link (ASYM_LINK), symmetric link (SYM_LINK), and lost link (LOST_LINK). The node records the sender to their one-hop neighbor set with an asymmetric link sensed. By sending back a HELLO message, the sender acknowledges the receiver with the symmetric link discerned. Similarly, the receiver’s one-hop neighbors become the two-hop neighbors of the sender. By constantly discerning neighbors, each node detects two sets, indicating the one-hop and two-hop neighbors locally. Furthermore, each node selects a set of Multipoint Relays (MPR) from its one-hop neighbors to cover all two-hop neighbors. Only selected MPR nodes are responsible for forwarding network traffic. Consequently, the OLSR protocol minimizes the overhead of flooding messages by reducing redundant retransmission [35]. The selected MPRs shape the backbone of the information propagation topology. Finally, the routing table is calculated based on the topology information. IETF RFC 3626 defines the protocol and a set of parameters for an OLSR node [16]. We present the time parameters and their definition in Table 2. Several important parameters related to HELLO messages are as follow.

Table 2.
OLSR time parameters.
- HELLO_INTERVAL or determines the time interval of HELLO message emission for each node. This parameter is included in a HELLO message. is set to 2 s by default.
- REFRESH_INTERVAL: Each known neighbor node has to be mentioned at least once during a REFRESH_INTERVAL to keep track of the latest connectivity changes. is equal to by default.
- NEIGHB_HOLD_TIME or specifies until when the information provided in the latest HELLO message is considered to be valid. The by default.
- Validity Time determines the time when the messages (including HELLO messages) will expire from reception.
After receiving a HELLO message, the local links will be updated according to the attached information. All symmetric links and asymmetric links are restricted with a timer to show when the links are expired, namely L_SYM_time and L_ASYM_time, respectively. Both timers are set to the current time plus Validity Time. A node loss response comes from a regular pace of disseminating HELLO messages. The link is restricted by another time L_LOST_LINK_time, which is defined as the current time plus NEIGHB_HOLD_TIME. The link is still regarded as SYM_LINK or ASYM_LINK since a packet loss may cause it. The timer will be revoked on the arrival of a HELLO message. On the contrary, if L_LOST_LINK_time expires without a standard message received, the link will be regarded as lost marked as LOST_LINK. The lost links are advertised in messages rather than dropped immediately, allowing nodes to detect link breakages. After the expiration of SYM_LINK or ASYM_LINK timers, the link is finally removed.
3.2. Ethereum
Ethereum is well-known in the form of a cryptocurrency over a public blockchain network, namely Mainnet. At the same time, Ethereum also supports private blockchain, which can be deployed and edited by users. The private blockchain networks are isolated to the public Ethereum. Only the blockchain nodes with permissions can access the private blockchain. The nodes in the Ethereum blockchain construct their P2P communication entirely in the transport and application layers of the networking stack. More specifically, they use Recursive Length Prefix transport protocol (RLPx) and Ethereum Wire Protocol (ETH) [2]. RLPx is responsible for serializing messages transmitted in blockchain connections. ETH defines how peers are enabled to interact with different messages. The synchronization of transactions and blocks is one of the most significant parts during the interaction [36]. The nodes propagate transactions and blocks to keep synchronizing the latest actions and events. Moreover, transactions that have not been admitted into blocks are propagated and managed with the TxPool module (https://github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/blob/master/core/tx_pool.go (accessed on 24 June 2021)). The received transactions are arranged in TxPool that is located on every node and further propagated to cover the entire network as rapidly as possible. The blocks, which contain block headers and various admitted transactions in block bodies, are disseminated according to the protocol defined in the Downloader package (https://github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/blob/master/eth/downloader/downloader.go (accessed on 24 June 2021)). Using an ad hoc routing protocol such as OLSR, a blockchain connection could leverage the multi-hop characteristic in the ad hoc network. Directed by the routing protocol, each node could reach more peers rather than in the case of infrastructure restriction. It may accelerate information propagation to the entire blockchain network [37].
4. Decentralization of IoT Blockchain System
4.1. Motivation
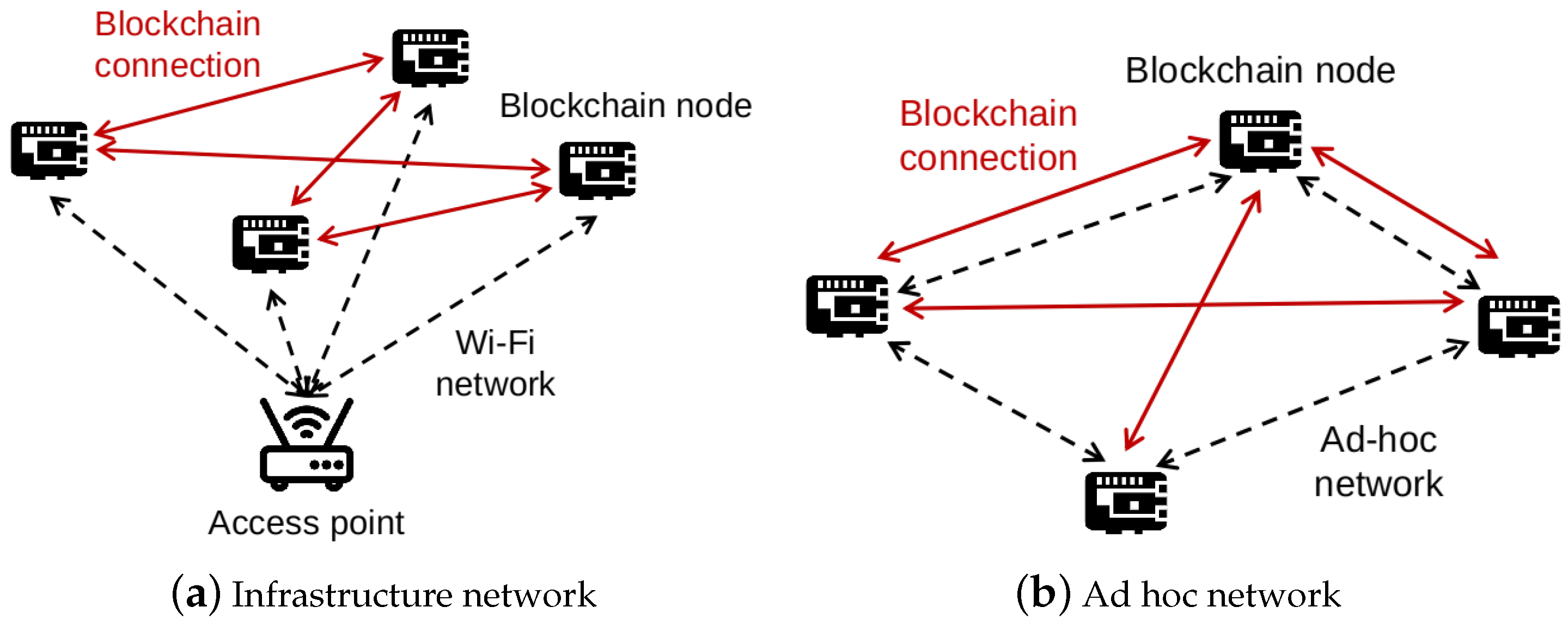
As mentioned, blockchain technology brings decentralization to IoT systems. However, the underlying network is normally built on top of the wireless infrastructure network. For example, Figure 1 shows a typical private blockchain-IoT, which runs over a Wi-Fi network. It is obvious that all the communication of blockchain nodes in the system relies on the access point. Hence, all packets generated by blockchain connections are transmitted and received via the access point. When a link failure happens, the associated blockchain node will be removed (from the system) even though it is still fully functional. If the access point fails due to power shortage or damage, the whole system is corrupted. Consequently, all the decentralization merits disappear. Hence, this system incurs the single point of failure issue in the network layer. To further enhance the adoption capability of IoT blockchain, it is necessary to solve this problem.
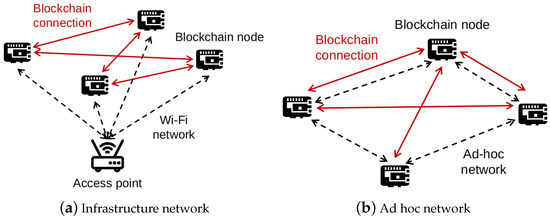
Figure 1.
Blockchain-IoT system over an infrastructure network and an ad hoc network.
Turning the underlying network of IoT blockchain into ad hoc one is a potential method to handle the issue. The ad hoc network does not have a centralized point as in the infrastructure one. Moreover, each node in an ad hoc mode can receive and forward messages, facilitating decentralization. By dispatching packets by network nodes rather than a specific centralized point, the blockchain connections become self-organized. Another merit is that the blockchain-IoT network, which is normally limited by the access point’s communication range, can be extended by adding new IoT nodes. However, all the packets traverse through several nodes to a destination require an ad hoc routing protocol. More importantly, the routing may allow IoT nodes to search for adaptable, dynamic routing paths, recovering from network failure. Since the ad hoc routing is lightweight and low performance, it is important to investigate its operation with blockchains. In the next sections, we present our approach with OLSR.
4.2. Decentralizing Underlying Blockchain Network
In this paper, we investigate the decentralization of the underlying network in a blockchain-IoT application. In our approach, we aim to build a blockchain system close to the actual applications, in which sensors normally sense the environment and push to the blockchain. For that purpose, we emulate an environment monitoring application with the particulate matter (PM) sensor that can report the PM data. The skeleton of the whole system is IoT devices, which can run blockchain and the OLSR protocol. In our previous work, we confirmed that the popular IoT device RPi4 is powerful enough to operate Proof of Work (PoW) or mining task [38]. On the other hand, RPi4 supports Linux-based operating systems, which can host the OLSR implementation code. Furthermore, RPi4’s Wi-Fi implementation also well supports the ad hoc mode. Therefore, RPi4 was selected as the hardware to build our system. Each RPi4 node works in a wireless ad hoc mode with OLSR protocol and participates in the Ethereum blockchain’s operation. We also leverage the smart contract technology to record the PM data into the blockchain automatically. In our investigation, we consider the blockchain communication between a sender and a receiver. A sender is a node with the sensor that disseminates its collected PM data with transactions, which then are mined into blocks. The data are stored on the blockchain through transaction execution. Our written smart contract can monitor the logged data and perform a processing task. More specifically, it emits events once the PM data exceed an alerting value. The receiver receives the transactions, produces blocks with the PoW algorithm, and listens to the smart contract events. The blockchain decentralizes the application in the system, which delivers and processes data without a centralized authority. The functionalities of the underlying network are distributed by the ad hoc mode and OLSR protocol at every node. The system is evaluated with the following metrics when transactions are streaming from the sender to the receiver.
Recovery time: A blockchain connection over multiple hops in an OLSR ad hoc network depends on the MPRs, which form the backbone. When a sender propagates transactions to the receiver, the data packets are forwarded by the MPR nodes. If a middle forwarding MPR node fails, the transactions will be accumulated in the sender’s TxPool. Moreover, the receiver temporarily loses the synchronization with the sender. After a failure happens in OLSR, the nodes first need to realize the failure and MPR in the transmission path by the expiration of the latest HELLO message. If the is greater than , the HELLO messages expire after waiting for . The link of a failed node is marked as LOST_LINK. Otherwise, if the is smaller than the (i.e., three times of ), the HELLO messages expire after . Second, the nodes select a new candidate for MPR from the one-hop neighbor set and disseminate the selection result to the targeted node in the next following HELLO message. Upon receiving the message, the new node starts forwarding packets and notifies them to perform as an MPR (in a HELLO message). When the route is successfully rebuilt, the overlying blockchain connection is consequently resumed after the processing at the transport and application layers (denoted as ). In Ethereum blockchain, by default, the client Geth will drop peers without responses after the inactive period of 30 s (https://github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/blob/master/p2p/server.go (accessed on 25 June 2021)). We build a simple equation to capture the recovery time in Equation (1). After recovery, the receiver resumes synchronization to the sender, the group of accumulated transactions is synchronized to the receiver immediately. We can define the recovery time (i.e., on the blockchain level) as the period from when the blockchain synchronization is lost to the moment it resumes.
Latency performance: With more peers related, a node could disseminate information directly with more blockchain connections. Over a decentralized network, a node could reach peers which are beyond their radio range, through multiple ad hoc hops. It allows information directly propagated to more peers and a shorter latency to cover the entire network [39]. According to our previous work [40], the transaction and block propagation latency from end to end in a blockchain connection could be evaluated as transaction-oriented latency (TOL) and block-oriented latency (BOL). In transaction propagation, TOL describes the latency from transaction submission to transaction arrival. BOL describes the latency from block generation to block arrival. We evaluate both TOL and BOL in information propagation from sender to receiver of a two-hop ad hoc connection associated with a MPR. Both types of latency are highly related to the network link condition and could be measured from the log file of both clients.
5. Evaluation
5.1. Experiment Setup
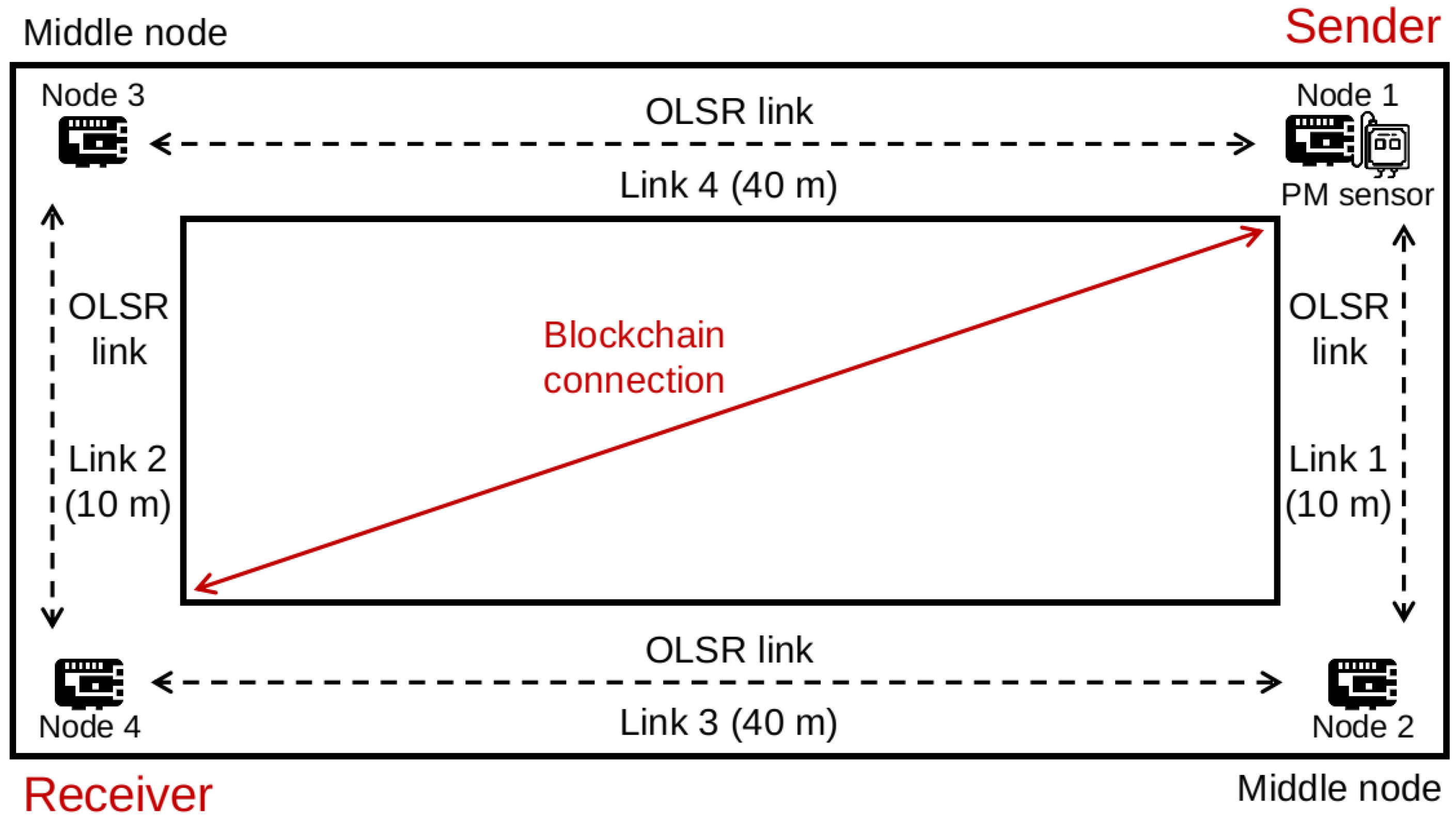
In our evaluation, we deployed four RPi4 nodes on the fifth floor of the first building in the Faculty of Engineering, Chiba University, with the topology shown in Figure 2. The distances between nodes are illustrated in the figure. The figure also illustrates the distances between the nodes. The hardware configurations of each RPi and software are listed in Table 3. Since RPi4 is capable of mining blocks, a centralized, powerful mining node is not necessary in this case. The wireless adapters were configured in the ad hoc mode to run the OLSR protocol. We adopted the OLSR implementation from the OLSRd package (http://www.olsr.org/mediawiki/index.php/Releases (accessed on 21 June 2021)). In each RPi node, the OLSRd module was configured with the default Willingness value (equalling 3), indicating the willingness to become an MPR. The nodes ran the Ethereum client, the unmodified version of Geth (https://geth.ethereum.org/downloads/ (accessed on 22 June 2021)), to form a private blockchain that starts with a custom genesis file in Geth. The Nova PM Sensor SDS011 air quality sensor was used, which can detect the 0.3–10 m particle concentration in the air. The output data of Nova Sensor include the PM2.5 and PM10 indexes. The sensor could be programmed with the sds011-client module (https://github.com/ivkos/sds011-client (accessed on 21 June 2021)) for Node.js. We allowed the sensor work to be in active or query mode. In the former, the sensor actively released data as soon as they were available, while, in the latter, the sensor passively responded to requests at a periodic pace.
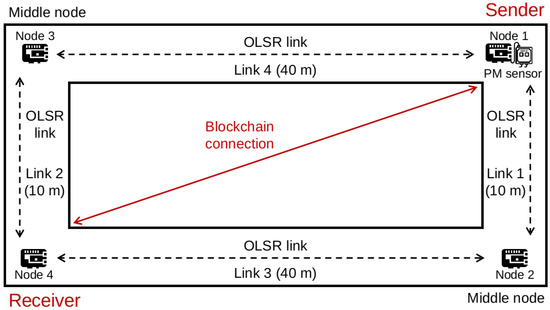
Figure 2.
Evaluation topology.

Table 3.
RPi4 Configuration.
We conducted the experiments over RPi4 nodes as the following. First, we deployed a smart contract to the blockchain, which recorded PM2.5 and PM10 data as state variables. Moreover, the contract emitted events when any of them exceeded a pre-defined value. Second, the sender RPi4 ran a script (with sds011-client library) requesting PM data every second. It then wrapped the data into transactions and submitted them to the blockchain with the Web3 library via Remote Procedure Call (RPC) to the local Ethereum client. The transactions were automatically disseminated to any reachable blockchain peers. Third, the receiver collected propagated transactions and mined them into blocks. Once a block was accepted, the block’s inside transactions were executed. Then, the state variables were modified in the smart contract. If the state variable exceeded the pre-defined value, the blockchain emitted an event logged in the block header. The receiver listened to the event with Web3 library and readied an alert. Finally, we synchronized the system time of the RPi4 nodes for more accurate latency measurements with the ntpdate utility (i.e., using Network Time Protocol).
In the experiment environment, the sender was out of the receiver’s communication range. Hence, they could not communicate with each other without a relaying or forwarding node (e.g., an access point or an MPR node). When the OLSR protocol was enabled in the network, Nodes 1 and 4 discerned the reachable one-hop neighbors, Nodes 2 and 3, with HELLO messages. They selected one of them as an MPR node to transmit data and control packets. After forming a reachable path, they could build a blockchain connection via Links 1 and 3 (marked as Path 1) or Links 2 and 4 (marked as Path 2). Since there are two available paths, the blockchain connection could recover from the MPR node failure by selecting a new MPR node following the procedure of OLSR routing protocol.
5.2. Recovery Time
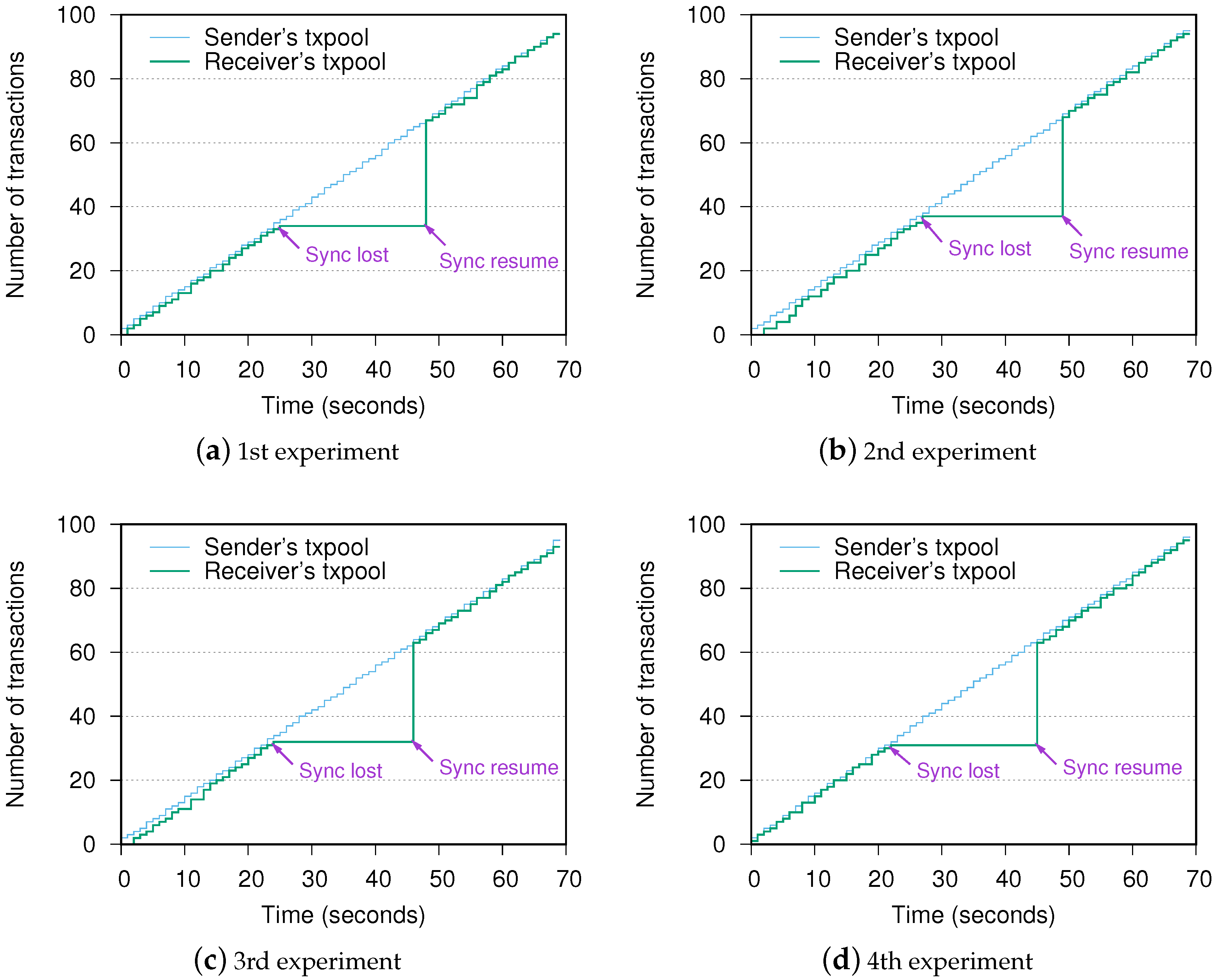
This section evaluates and quantifies the performance of blockchain connection when it recovers from a failure in the underlying network. More specifically, there is an MPR failure during the blockchain operation. The sender keeps requesting data and streaming transactions at the speed of one transaction per second (tps). Transactions are propagated to the receiver via a selected MPR (Node 2 or Node 3), which can be observed with tcptraceroute tool. We then force the MPR node to shut down. On the collapse, the blockchain connection and transaction stream to the receiver are interrupted, thus the receiver loses synchronization with the sender. However, the network is not recovered immediately. The sender initially needs to confirm the MPR is out of connection by the expiration of the latest HELLO message according to Equation (1). Second, the sender selects a new MPR (the left alive node) and notifies the new MPR to start packets forwarding within the following HELLO messages. After acknowledgment of the new MPR node, packets including OLSR and blockchain messages finally get their destinations. The blockchain re-certifies the connection and resumes the transaction synchronization. In our experiment settings, equals to 2 s, thus becomes 6 s. is set to 20 s in the configuration file. is greater than , which means the sender needs to wait for the expiration of the last legal HELLO message for over 20 s. Then, it calls for a new MPR node in the next 2 s with the pace of HELLO message dissemination. The entire recovery time is reflected in the number of transactions in both sender and receiver’s Txpool. We record the accumulated number of transactions in the Txpool of both sides via inter-process communication (IPC) and show the cumulative curve of four measurements in Figure 3. We can see that the trend in the four subfigures is similar. After the failure, the transactions are queued at the sender’s txpool (the “Sync lost” mark). When OLSR finds a new route, the operation is back to normal at the “Sync resume” mark. From the experiment results, the recovery time from when the synchronization is lost to resumed has an average value of 22.3 s, which proves the blockchain is recoverable from the underlying network failures.
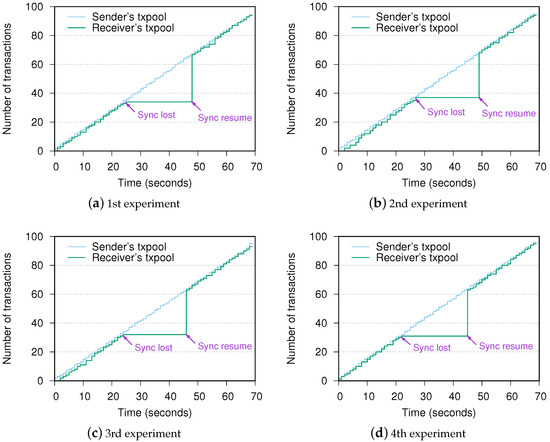
Figure 3.
Experimental results of recovery time.
5.3. Latency Performance
In an ad hoc network, nodes can directly communicate with peers in their wireless communication range. Deploying the OLSR protocol will provide paths to other nodes in the network. In our experiment, the connections between peers are marked as OLSR links, as shown in Figure 2. The distances of Links 1 and 2 are 10 m, while those of Links 3 and 4 are 40 m. As a result, the blockchain communication between the sender and the receiver can go through two paths denoted as Paths 1 and 2. First, we evaluate the performance of each path with Ping time, packet loss rate, and throughput. We use the iperf3 tool to measure those performance metrics, and the results are shown in Table 4. It is obvious that the OLSR link has a better performance when the nodes are between a shorter distance. The table also shows the comparison of wireless link performance in an infrastructure network with Wi-Fi. We replace Node 3 with an access point; hence, Path 2 becomes the infrastructure-based links. We let the packets pass through the same path for comparison. We can see that the transmission delay is smaller in the infrastructure mode, and the loss rate is lower, which lead to a shorter propagation latency in the later measurements.

Table 4.
Link evaluation.
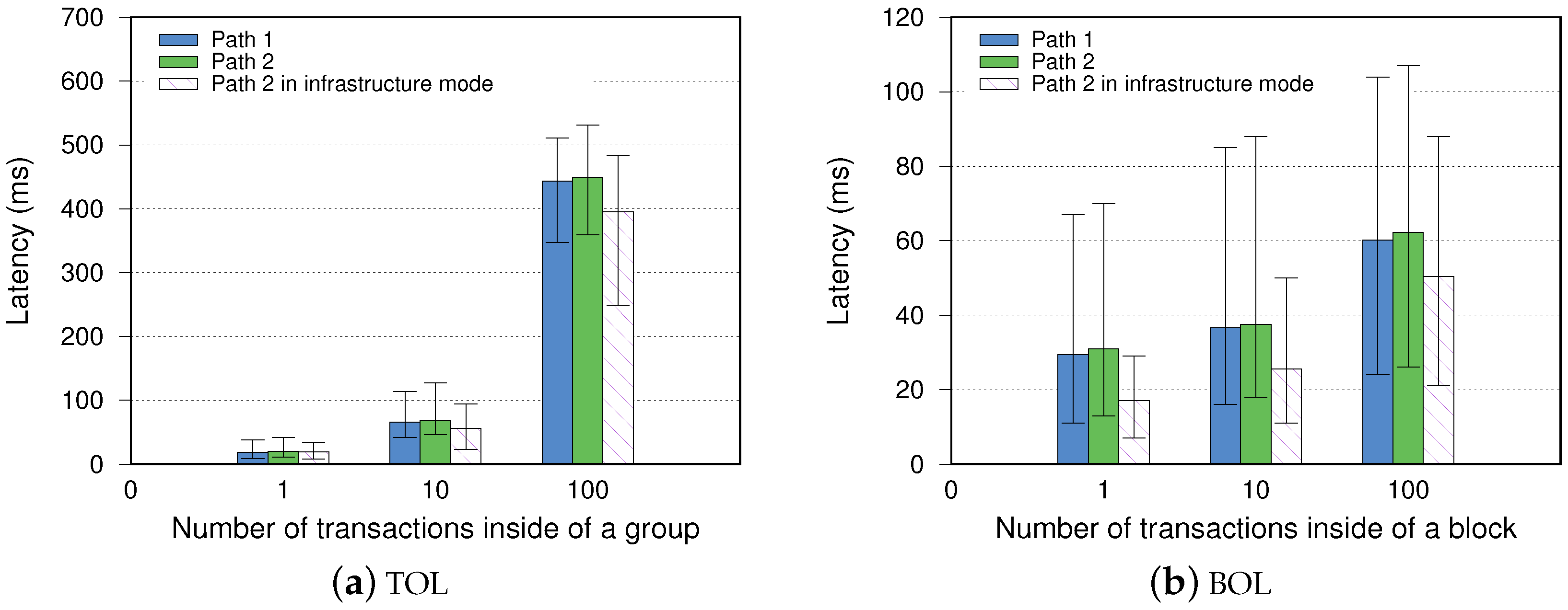
In the following, we present the latency measurement in our IoT blockchain network. During the data streaming, submitted transactions are propagated to the receiver through one path from the sender to the server. The receiver then loads a JavaScript file, which starts the mining process to admit and execute transactions into blocks when the Txpool is not empty. The generated blocks are propagated to every participates in confirming their uploaded transactions. We collect both Geth logs and measure Transaction-Oriented Latency (TOL) and Block-Oriented Latency (BOL) with different groups of transactions. The TOL results are shown in Figure 4. We can see that the TOL of a single transaction propagation is on average 18.9 and 19.1 ms for the two-hop paths. When sending multiple transactions in groups, transactions are propagated continuously without waiting to confirm previous transactions. Consequently, propagating ten transactions consumes 66.7 and 68.2 ms for both paths, while 100 transactions averages 443.4 and 449.3 ms, respectively. Propagated transactions are mined into blocks by the receiver, which is disseminated back to the sender. With more transactions inside, a block becomes more extensive and has a greater BOL. The blocks with a single transaction have a similar BOL an TOL. However, as the transaction number grows, BOL becomes smaller than TOL. The results indicate blockchain over an ad hoc network has a better experience on block propagation than transaction propagation. Because transactions are transferred individually, each transaction is divided into three or more TCP packets, while blocks are serialized before transmission. In comparison with infrastructure mode, the packets are re-transmitted by the access point. Hence, it is reasonable that information dissemination is commonly quicker than ad hoc mode.
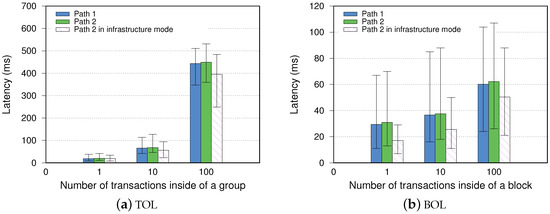
Figure 4.
Latency performance between the sender and the receiver.
6. Conclusions and Future Works
This paper introduces a method of decentralizing the underlying network of the private blockchain-IoT system using OLSR. The private blockchain-IoT networks will benefit from the flexibility of the routing protocol by operating over multiple ad hoc IoT nodes. Moreover, the blockchain connection well recovers from failures, which may happen in various IoT application scenarios. We built a real Ethereum blockchain-IoT network that works as a monitoring application. The network collects PM monitoring data and transfers them over the ad hoc network with the OLSR protocol. The evaluation results show that the blockchain connection recovers from the underlying network failures within 22.3 s on average. Besides, we also evaluated and compared the latency performance in ad hoc and infrastructure networks. The results show that the blockchain connection over an ad hoc network has a better latency for block propagation than transaction propagation. Meanwhile, the infrastructure network disseminates information more quickly than the ad hoc network through the same path.
In the future, we will investigate and evaluate the recovery time when varying other parameters such as different validity time, traffic conditions, etc., aiming to find the optimal recovery time. Moreover, we plan to conduct a comparative study of different ad hoc routing protocols in blockchain-IoT networks.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.C. and K.N.; methodology, X.C. and K.N.; software, X.C.; validation, X.C. and K.N.; formal analysis, X.C.; investigation, X.C., S.T. and K.N.; resources, X.C.; writing—original draft preparation, X.C. and K.N.; writing—review and editing, S.T., K.N. and H.S.; supervision, K.N. and H.S.; project administration, K.N.; funding acquisition, K.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Numbers 19K20251 and 20H04174. Additionally, Kien Nguyen is supported by the Leading Initiative for Excellent Young Researchers (LEADER) program from MEXT, Japan.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Nakamoto, S. Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System; Technical Report; Manubot: Seocho-gu, Seoul, Korea, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, G. Ethereum: A secure decentralised generalised transaction ledger. Ethereum Proj. Yellow Pap. 2014, 151, 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Q.; Sifah, E.B.; Asamoah, K.O.; Gao, J.; Du, X.; Guizani, M. MeDShare: Trust-less medical data sharing among cloud service providers via blockchain. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 14757–14767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y. A blockchain-based framework for data sharing with fine-grained access control in decentralized storage systems. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 38437–38450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Zhu, L.; Shen, M.; Sharif, K.; Wan, Z.; Ren, K. A blockchain-based privacy-preserving payment mechanism for vehicle-to-grid networks. IEEE Netw. 2018, 32, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kshetri, N. Can blockchain strengthen the internet of things? IT Prof. 2017, 19, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, S.K.; Liu, Y.; Chia, S.Y.; Xu, X.; Lu, Q.; Zhu, L.; Ning, H. Analysis of blockchain solutions for IoT: A systematic literature review. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 58822–58835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingxiao, D.; Xiaofeng, M.; Zhe, Z.; Xiangwei, W.; Qijun, C. A review on consensus algorithm of blockchain. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), Banff, AB, Canada, 5–8 October 2017; pp. 2567–2572. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.; He, Z.; Li, Z.; Xiao, M. Building an ethereum-based decentralized smart home system. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Parallel and Distributed Systems (ICPADS), Singapore, 11–13 December 2017; pp. 1004–1009. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, K.L.; Martinez, M.; Chadha, U.; Krishnamachari, B. SmartEdge: A smart contract for edge computing. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Internet of Things (iThings), Halifax, NS, Canada, 30 July–3 August 2018; pp. 1685–1690. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Nguyen, K.; Sekiya, H. Characterizing Latency Performance in Private Blockchain Network. In International Conference on Mobile Networks and Management; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 238–255. [Google Scholar]
- Alrubei, S.M.; Ball, E.A.; Rigelsford, J.M.; Willis, C.A. Latency and Performance Analyses of Real-World Wireless IoT-Blockchain Application. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 7372–7383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozyilmaz, K.R.; Yurdakul, A. Designing a Blockchain-Based IoT With Ethereum, Swarm, and LoRa: The Software Solution to Create High Availability With Minimal Security Risks. IEEE Consum. Electron. Mag. 2019, 8, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modarresi, A.; Sterbenz, J.P. Towards a model and graph representation for smart homes in the IoT. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Smart Cities Conference (ISC2), Kansas City, MO, USA, 16–19 September 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Anastasi, G.; Borgia, E.; Conti, M.; Gregori, E. IEEE 802.11 b ad hoc networks: Performance measurements. Clust. Comput. 2005, 8, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausen, T.; Jacquet, P. RFC3626: Optimized Link State Routing Protocol (OLSR). 2003. Available online: https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc3626 (accessed on 23 June 2021).
- Khoury, D.; Kfoury, E.F.; Kassem, A.; Harb, H. Decentralized voting platform based on ethereum blockchain. In Proceedings of the International Multidisciplinary Conference on Engineering Technology (IMCET), Beirut, Lebanon, 14–16 November 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, T.; Fang, H.; Wang, H. Blockchain-based internet of vehicles: Distributed network architecture and performance analysis. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 6, 4640–4649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, S.; Li, Y. Electric vehicle power trading mechanism based on blockchain and smart contract in V2G network. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 160546–160558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasselgren, A.; Kralevska, K.; Gligoroski, D.; Pedersen, S.A.; Faxvaag, A. Blockchain in healthcare and health sciences—A scoping review. Int. J. Med Inform. 2020, 134, 104040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razdan, S.; Sharma, S. Internet of Medical Things (IoMT): Overview, Emerging Technologies, and Case Studies. IETE Tech. Rev. 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatoon, A. A blockchain-based smart contract system for healthcare management. Electronics 2020, 9, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdellatif, A.A.; Al-Marridi, A.Z.; Mohamed, A.; Erbad, A.; Chiasserini, C.F.; Refaey, A. ssHealth: Toward secure, blockchain-enabled healthcare systems. IEEE Netw. 2020, 34, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorri, A.; Kanhere, S.S.; Jurdak, R.; Gauravaram, P. Blockchain for IoT security and privacy: The case study of a smart home. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications Workshops (PerCom Workshops), Kona, HI, USA, 13–17 March 2017; pp. 618–623. [Google Scholar]
- Derr, K.; Manic, M. Wireless sensor network configuration—Part I: Mesh simplification for centralized algorithms. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2013, 9, 1717–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derr, K.; Manic, M. Wireless sensor network configuration—Part II: Adaptive coverage for decentralized algorithms. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2013, 9, 1728–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiding, B.; Memarmoshrefi, P.; Hogrefe, D. Self-managed and blockchain-based vehicular ad-hoc networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing: Adjunct, Heidelberg, Germany, 12–16 September 2016; pp. 137–140. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Vijayakumar, P.; He, D.; Kumar, N.; Ma, J. Blockchain-based mutual-healing group key distribution scheme in unmanned aerial vehicles ad-hoc network. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 11309–11322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezan, G.; Leung, C. A blockchain-based contractual routing protocol for the internet of things using smart contracts. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2018, 2018, 4029591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadadha, M.; Otrok, H. A blockchain-enabled relay selection for QoS-OLSR in urban VANET: A Stackelberg game model. Ad Hoc Networks 2021, 117, 102502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lwin, M.T.; Ko, Y.B.; Kim, D. When Blockchain Takes Care of the OLSR Network. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Communication and Networks (ICCCN), Valencia, Spain, 29 July–1 August 2019; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Lwin, M.T.; Yim, J.; Ko, Y.B. Blockchain-based lightweight trust management in mobile ad-hoc networks. Sensors 2020, 20, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laube, A.; Martin, S.; Al Agha, K. A solution to the split & merge problem for blockchain-based applications in ad hoc networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 8th International Conference on Performance Evaluation and Modeling in Wired and Wireless Networks (PEMWN), Paris, France, 26–28 November 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Crow, B.P.; Widjaja, I.; Kim, J.G.; Sakai, P.T. IEEE 802.11 wireless local area networks. IEEE Commun. Mag. 1997, 35, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.; Minet, P. Analysis of MPR Selection in the OLSR Protocol. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications Workshops (AINAW’07), Niagara Falls, ON, Canada, 21–23 May 2007; Volume 2, pp. 887–892. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Zhao, C.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Liew, S.C. Ethna: Analyzing the Underlying Peer-to-Peer Network of Ethereum Blockchain. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäffer, M.; Di Angelo, M.; Salzer, G. Performance and scalability of private Ethereum blockchains. In International Conference on Business Process Management; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 103–118. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Nguyen, K.; Sekiya, H. Investigating Dynamic Mining Time of Private Ethereum Blockchain on IoT Devices. In Proceedings of the IEICE General Conference, Online, 9–12 March 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Premsankar, G.; Di Francesco, M.; Taleb, T. Edge computing for the Internet of Things: A case study. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 5, 1275–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Nguyen, K.; Sekiya, H. An experimental study on performance of private blockchain in IoT applications. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 2021, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).