Polysaccharide-Based Micelles for Drug Delivery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Advantages of Polysaccharide-Based Materials in Drug Delivery
2.1. Biodegradability and Biocompatibility
2.2. Solubility
2.3. Ease of Modification
2.4. Bioactivity
3. Polysaccharide-Based Micelle Drug Delivery Systems
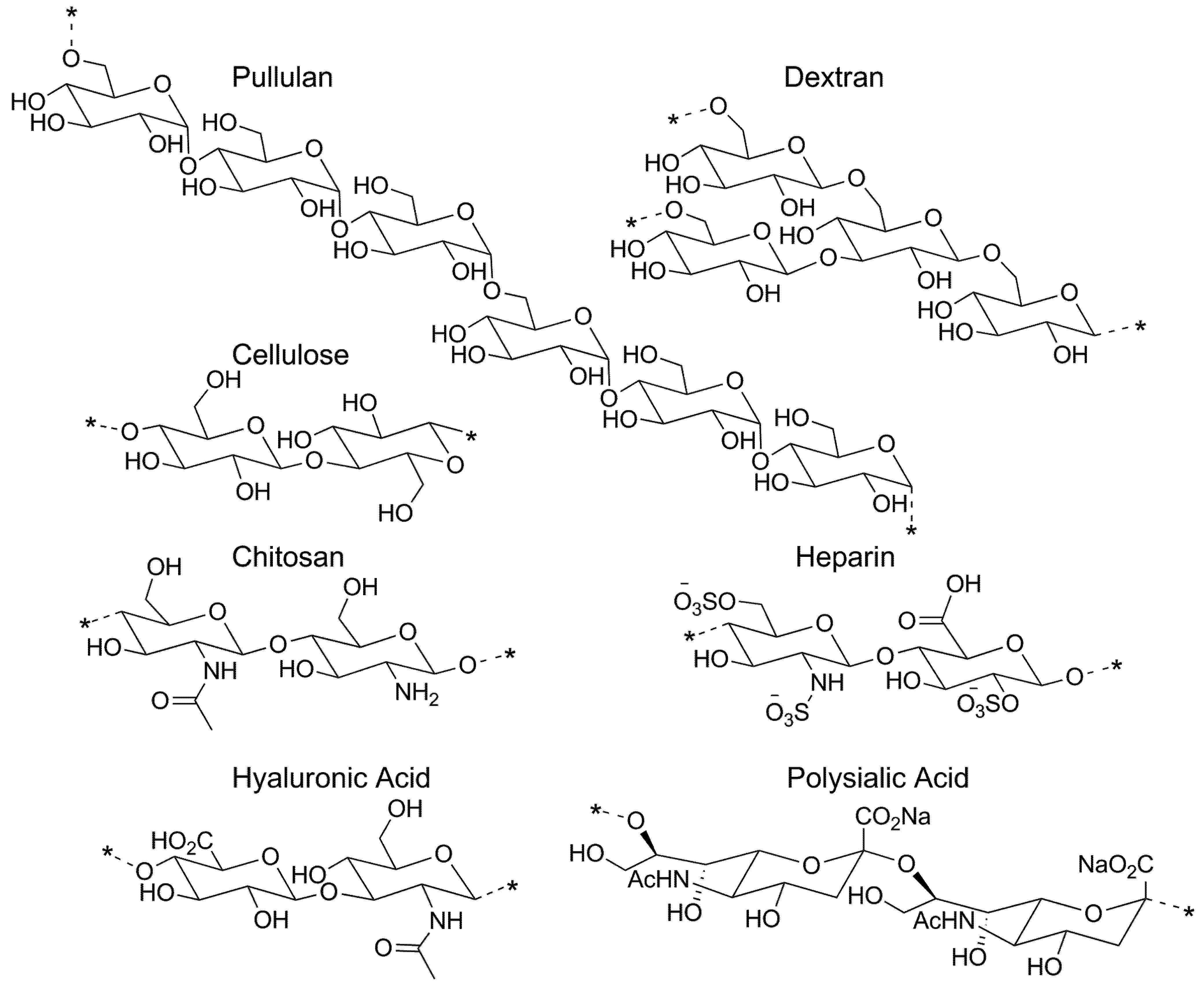
3.1. Pullulan-Based Systems
| Name | Structure | References |
|---|---|---|
| Cholesterol | 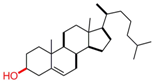 | [38,39,40,46,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57] |
| Cholic Acid | 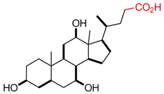 | [43,58,59,60] |
| Deoxycholic Acid | 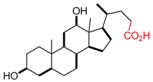 | [43,44,58,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70] |
| Poly(lactide) | 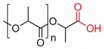 | [71,72,73,74,75,76] |
| Poly(lactide-co-glycolide) | 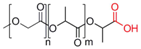 | [55,77,78,79,80,81,82] |
| Pluronic | 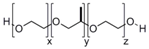 | [83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93] |
| Polycaprolactone |  | [93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100] |
| Stearic Acid | 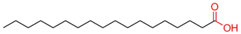 | [58,79,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111] |
3.2. Cellulose-Based Systems
3.3. Dextran-Based Systems
3.4. Chitosan-Based Systems
3.5. Heparin-Based Micelle Systems
3.6. Hyaluronan-Based Systems
3.7. Other Polysaccharide-Based Micelle Systems
4. “Smart” Polysaccharide-Based Micelle Drug Delivery Systems
4.1. Stealth Coating
4.2. Stimuli-Sensitive Systems
4.3. Active Targeting Agents
5. Conclusions and Outlook
Conflict of Interest
References
- Torchilin, V.P. Micellar nanocarriers: Pharmaceutical perspectives. Pharma. Res. 2007, 24, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R. Water-Insoluble Drug Formulation, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; p. 669. [Google Scholar]
- Torchilin, V.P. Nanoparticulates as Drug Carriers, 1st ed.; World Scientific Publishing Company: London, UK/Hackensack, NJ, USA, 2006; p. 724. [Google Scholar]
- Torchilin, V.P. Targeted polymeric micelles for delivery of poorly soluble drugs. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2004, 61, 2549–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, H.; Ringsdorf, H.; Schmidt, B. Watersoluble Polymers in Medicine. Angew. Makromol. Chem. 1984, 123, 457–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torchilin, V.P. Drug targeting. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2000, 11, S81–S91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.B.; Falamarzian, A.; Garg, S.M.; Lavasanifar, A. Engineering of amphiphilic block copolymers for polymeric micellar drug and gene delivery. J. Contr. Release 2011, 155, 248–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Ba, K.; Mao, R.Y.; Lai, W.L.; Lin, Y.F. Toxicity of Biodegradable Nanoscale Preparations. Curr. Drug Metabol. 2012, 13, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.N.; Muzzarelli, R.A.; Muzzarelli, C.; Sashiwa, H.; Domb, A.J. Chitosan chemistry and pharmaceutical perspectives. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 6017–6084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.H.; Jones, S.A.; Forbes, B.; Martin, G.P.; Brown, M.B. Hyaluronan: Pharmaceutical characterization and drug delivery. Drug Deliv. 2005, 12, 327–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, R.K.; Tiwari, A. Carbohydrate polymers: Applications and recent advances in delivering drugs to the colon. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 88, 399–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, Z. Polysaccharides-based nanoparticles as drug delivery systems. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1650–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanakumar, G.; Jo, D.G.; Park, J.H. Polysaccharide based nanoparticles: A versatile Platform for Drug Delivery and Biomedical Imaging. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 3212–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, J.M.; Leong, K.W. Natural polymers for gene delivery and tissue engineering. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2006, 58, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratner, B.D.; Bryant, S.J. Biomaterials: Where we have been and where we are going. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2004, 6, 41–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Jo, S.; Park, K. Polysaccharide hydrogels for protein drug delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 1995, 28, 69–76. [Google Scholar]
- Mizrahy, S.; Peer, D. Polysaccharides as building blocks for nanotherapeutics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2623–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coviello, T.; Matricardi, P.; Marianecci, C.; Alhaique, F. Polysaccharide hydrogels for modified release formulations. J. Contr. Release 2007, 119, 5–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadée, J.A.; Brouwer, L.A.; den Otter, W.; Hennick, W.E.; van Luyn, M.J. A comparative biocompatibiltiy study of microspheres based on crosslinked dextran or poly(lactic-co-glycolic)acid after subcutaneous injection in rats. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2001, 56, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Gupta, Y.; Jain, S.K. Perspectives of biodegradable natural polysaccharides for site specific drug delivery to the colon. J.Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 10, 86–128. [Google Scholar]
- Rempel, B.P.; Withers, S.G. Covalent inhibitors of glycosidases and their applications in biochemistry and biology. Glycobiology 2008, 18, 570–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehvar, R. Recent trends in the use of polysaccharides for improved delivery of therapeutic agents: Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic perspectives. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2003, 4, 283–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.M.; Song, D.K.; Oh, S.H.; Lee-Yoon, D.S.; Bae, E.H.; Lee, J.H. In vitro and in vivo degradation behavior of acetylated chitosan porous beads. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2008, 19, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, M.; Chiellini, F.; Ottenbrite, R.M.; Chiellini, E. Chitosan—A versatile semi-synthetic polymer in biomedical applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 981–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.A. Polysaccharide drug delivery systems based on pectin and chitosan. Biotechnol. Genet. Eng. Rev. 2010, 27, 257–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Sande, M.; Teijeiro-Osorio, D.; Remuñán-López, C.; Alonso, M.J. Glucomannan, a promising polysaccharide for biopharmaceutical purposes. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009, 72, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourya, V.K.; Inamdar, N.N. Trimethyl chitosan and its application in drug delivery. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2009, 20, 1057–1079. [Google Scholar]
- Thanou, M.; Verhoef, J.C.; Junginger, H.E. Oral drug absorption enhancement by chitosan and its derivatives. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 52, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanou, M.; Verhoef, J.C.; Junginger, H.E. Chitosan and its derivatives as intestinal absorption enhancers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 50, S91–S101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernkop-Schnürch, A.; Dünnhaupt, S. Chitosan-based drug delivery systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 81, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boddhoi, S.; Killingsworth, C.E.; Kipper, M.J. Polyelectrolyte multilayer assembly as a function of pH and ionic strength using the polysaccharides chitosan and heparin. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 2021–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonferoni, M.C.; Sandri, G.; Ferrari, F.; Rossi, S.; Larghi, V.; Zambito, Y.; Caramella, C. Comparison of different in vitro and ex vivo methods to evaluate mucoadhesion of glycol-palmitoyl chitosan micelles. J. Drug Del. Sci. Tech. 2010, 20, 419–424. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, K.; Mohan, G.K.; Satla, S.; Gaikwad, S. Natural Polysaccharides: Versatile Excipients for controlled drug delivery systems. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 6, 275–286. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, T.; Tanaka, M.; Huang, Y.Y.; Hamblin, M.R. Chitosan preparations for wounds and burns: Antimicrobial and wound healing effects. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2011, 9, 857–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, E. The anti-inflammatory effects of heparin and related compounds. Thromb. Res. 2008, 122, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, S.T.; Srinivasan, K.R.; Bjork, I.; Shore, J.D. Binding of high affinity heparin to antithrombin III. Stopped flow kinetic studies of the binding interaction. J. Biol. Chem. 1981, 256, 11073–11079. [Google Scholar]
- Olson, S.T.; Shore, J.D. Binding of high affinity heparin to antithrombin III. Characterization of the protein fluorescence enhancement. J. Biol. Chem. 1981, 256, 11065–11072. [Google Scholar]
- Akiyoshi, K.; Sasaki, Y.; Sunamoto, J. Molecular chaperone-like activity of hydrogel nanoparticles of hydrophobized pullulan: Thermal stabilization with refolding of carbonic anhydrase B. Bioconjug. Chem. 1999, 10, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunamoto, J.; Akiyoshi, K.; Deguchi, S.; Kato, Y.; Taniguchii, I.; Sasaki, Y.; Kuroda, K. Hydrogel nanoparticles formed by self-aggregation of hydrophobized polysaccharides. Abstr. Pap. Am. Chem. S 1998, 216, U831–U831. [Google Scholar]
- Akiyoshi, K.; Deguchi, S.; Moriguchi, N.; Yamaguchi, S.; Sunamoto, J. Self-aggregates of hydrophobized polysaccharides in water. Formation and characteristics of nanoparticles. Macromolecules 1993, 26, 3062–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, N.; Nomura, S.I.M.; Miyazawa, N.; Akiyoshi, K. Nanogel engineered designs for polymeric drug delivery. ACS Sym. Ser. 2006, 924, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabanov, A.V.; Vinogradov, S.V. Nanogels as Pharmaceutical Carriers: Finite Networks of Infinite Capabilities. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2009, 48, 5418–5429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Jo, W.H.; Kwon, I.C.; Kim, Y.H.; Jeong, S.Y. Structural determination and interior polarity of self-aggregates prepared from deoxycholic acid-modified chitosan in water. Macromolecules 1998, 31, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichifor, M.; Lopes, A.; Carpov, A.; Melo, E. Aggregation in water of dextran hydrophobically modified with bile acids. Macromolecules 1999, 32, 7078–7085. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, K.C.; Demirci, A.; Catchmark, J.M. Pullulan: Biosynthesis, production, and application. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 92, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyoshi, K.; Yamaguchi, S.; Sunamoto, J. Self-aggregates of hydrophobic polysaccharide derivatives. Chem. Lett. 1991, 1263–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyoshi, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Shichibe, S.; Mix, D.; Baudys, M.; Kim, S.W.; Sunamoto, J. Self-assembled hydrogel nanoparticle of cholesterol-bearing pullulan as a carrier of protein drugs: Complexation and stabilization of insulin. J. Contr. Release 1998, 54, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyoshi, K.; Nishikawa, T.; Shichibe, S.; Sunamoto, J. Stabilization of insulin upon supramolecular complexation with hydrophobized polysaccharide nanoparticle. Chem. Lett. 1995, 24, 707–708. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, H.; Katakura, O.; Morimoto, N.; Akiyoshi, K.; Kasugai, S. Effects of cholesterol-bearing pullulan (CHP)-nanogels in combination with prostaglandin E1 on wound healing. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B 2009, 91B, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, K.; Chen, F.; Aoyama, A.; Date, H.; Akiyoshi, K. Nanoparticle of cholesterol-bearing pullulan as a carrier of anticancer drugs. EJC Suppl. 2008, 6, 139–139. [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu, T.; Kishida, T.; Hasegawa, U.; Ueda, Y.; Imanishi, J.; Yamagishi, H.; Akiyoshi, K.; Otsuji, E.; Mazda, O. Nanogel DDS enables sustained release of IL-12 for tumor immunotherapy. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 367, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kageyama, S.; Kitano, S.; Hirayama, M.; Nagata, Y.; Imai, H.; Shiraishi, T.; Akiyoshi, K.; Scott, A.M.; Murphy, R.; Hoffman, E.W.; et al. Humoral immune responses in patients vaccinated with 1–146 HER2 protein complexed with cholesteryl pullulan nanogel. Cancer Sci. 2008, 99, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyahara, T.; Nyan, M.; Shimoda, A.; Yamamoto, Y.; Kuroda, S.; Shiota, M.; Akiyoshi, K.; Kasugai, S. Exploitation of a novel polysaccharide nanogel cross-linking membrane for guided bone regeneration (GBR). J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2012, 6, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, E.; Morimoto, N.; Kujawa, P.; Ozawa, Y.; Winnik, F.M.; Akiyoshi, K. Self-assembled nanogels of cholesteryl-modified polysaccharides: Effect of the polysaccharide structure on their association characteristics in the dilute and semidilute regimes. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 2366–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagahama, K.; Ouchi, T.; Ohya, Y. Biodegradable nanogels prepared by self-assembly of poly(L-lactide)-grafted dextran: Entrapment and release of proteins. Macromol. Biosci. 2008, 8, 1044–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, N.; Hirano, S.; Takahashi, H.; Loethen, S.; Thompson, D.H.; Akiyoshi, K. Self-assembled pH-sensitive cholesteryl pullulan nanogel as a protein delivery vehicle. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujioka-Kobayashi, M.; Ota, M.S.; Shimoda, A.; Nakahama, K.; Akiyoshi, K.; Miyamoto, Y.; Iseki, S. Cholesteryl group- and acryloyl group-bearing pullulan nanogel to deliver BMP2 and FGF18 for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 7613–7620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.H.; Tian, Q.; Wang, W.; Zhang, C.N.; Wang, P.; Yuan, Z. In vitro evaluation of polymeric micelles based on hydrophobically-modified sulfated chitosan as a carrier of doxorubicin. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2012, 23, 1663–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngawhirunpat, T.; Wonglertnirant, N.; Opanasopit, P.; Ruktanonchai, U.; Yoksan, R.; Wasanasuk, K.; Chirachanchai, S. Incorporation methods for cholic acid chitosan-g-mPEG self-assembly micellar system containing camptothecin. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2009, 74, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Qi, J.; Yao, P. Amphiphilic cholic-acid-modified dextran sulfate and its application for the controlled delivery of superoxide dismutase. Macromol. Biosci. 2012, 12, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatun, Z.; Nurunnabi, M.; Cho, K.J.; Lee, Y.K. Oral delivery of near-infrared quantum dot loaded micelles for noninvasive biomedical imaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 3880–3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Kim, K.; Kwon, I.C.; Kim, S.K.; Lee, S.; Lee, D.Y.; Byun, Y. Preparation and characterization of self-assembled nanoparticles of heparin-deoxycholic acid conjugates. Langmuir 2004, 20, 11726–11731. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Huo, M.; Wang, J.; Zhou, J.; Mohammad, J.M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Waddad, A.Y.; Zhang, Q. Redox-sensitive micelles self-assembled from amphiphilic hyaluronic acid-deoxycholic acid conjugates for targeted intracellular delivery of paclitaxel. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 2310–2320. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.H.; Zhang, D.R.; Duan, C.X.; Jia, L.J.; Feng, F.F.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.C.; Hao, L.L.; Zhang, Q.A. Preparation and characterizations of a novel deoxycholic acid-O-carboxymethylated chitosan-folic acid conjugates and self-aggregates. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 1192–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, M.R.; Zou, A.F.; Yao, C.L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.P.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Q.N.; Li, J.; Zhang, Q. Somatostatin receptor-mediated tumor-targeting drug delivery using octreotide-PEG-deoxycholic acid conjugate-modified N-deoxycholic acid-O,N-hydroxyethylation chitosan micelles. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 6393–6407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.H.; Hu, H.Y.; Qiao, M.X.; Zhu, J.; Qi, J.W.; Hu, C.J.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, D.W. pH-Sensitive chitosan-derived nanoparticles as doxorubicin carriers for effective anti-tumor activity: Preparation and in vitro evaluation. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 94, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, C.; Kim, T.H.; Lee, E.S.; Shin, B.S.; Chi, S.C.; Park, E.S.; Lee, K.C.; Youn, Y.S. Self-assembled glycol chitosan nanogels containing palmityl-acylated exendin-4 peptide as a long-acting anti-diabetic inhalation system. J. Contr. Release 2012, 161, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, D.; Hao, L.; Liu, Y.; Duan, C.; Jia, L.; Liu, G. Folate-mediated targeted and intracellular delivery of paclitaxel using a novel deoxycholic acid-O-carboxymethylated chitosan-folic acid micelles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 325–337. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Huo, M.; Zhou, J.; Dai, Y.; Deng, Y.; Shi, X.; Masoud, J. Enhanced oral absorption of paclitaxel in N-deoxycholic acid-N,O-hydroxyethyl chitosan micellar system. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 4543–4553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Gihm, S.H.; Park, C.R.; Lee, K.Y.; Kim, T.W.; Kwon, I.C.; Chung, H.; Jeong, S.Y. Structural characteristics of size-controlled self-aggregates of deoxycholic acid-modified chitosan and their application as a DNA delivery carrier. Bioconjug. Chem. 2001, 12, 932–938. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, S.; Lee, C.S.; Jung, Y.S.; Na, K. Thermo-sensitivity and triggered drug release of polysaccharide nanogels derived from pullulan-g-poly(l-lactide) copolymers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 1105–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Xu, Q.; Li, Y.; Mo, S.; Cai, S.; Liu, L. The synthesis of biodegradable graft copolymer cellulose-graft-poly(l-lactide) and the study of its controlled drug release. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2008, 66, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.T.; Huang, C.P.; Lee, Y.D. Preparation of amphiphilic poly(l-lactide)-graft-chondroitin sulfate copolymer self-aggregates and its aggregation behavior. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 1179–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagahama, K.; Mori, Y.; Ohya, Y.; Ouchi, T. Biodegradable nanogel formation of polylactide-grafted dextran copolymer in dilute aqueous solution and enhancement of its stability by stereocomplexation. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 2135–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, X.; Shu, X.; Shen, Z.; Sun, R.C. Self-assembly and paclitaxel loading capacity of cellulose-graft-poly(lactide) nanomicelles. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 3900–3908. [Google Scholar]
- Ouchi, T.; Minari, T.; Ohya, Y. Synthesis of poly(l-lactide)-grafted pullulan through coupling reaction between amino end-capped poly(l-lactide) and carboxymethyl pullulan and its aggregation behavior in water. J. Polym. Sci. A Polym. Chem. 2004, 42, 5482–5487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.I.; Na, H.S.; Oh, J.S.; Choi, K.C.; Song, C.E.; Lee, H.C. Adriamycin release from self-assembling nanospheres of poly(dl-lactide-co-glycolide)-grafted pullulan. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 322, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.I.; Kim, O.H.; Chung, C.-W.; Yoo, J.-J.; Choi, K.H.; Kim, C.H.; Ha, S.H.; Kang, D.H. Doxorubicin-incorporated polymeric micelles composed of dextran-b-poly(dl-lactide-co-glycolide) copolymer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 1415–1427. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.Y.; Du, Y.Z.; Wang, L.; Yuan, H.; Zhou, J.P.; Hu, F.Q. Preparation and pharmacodynamics of stearic acid and poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) grafted chitosan oligosaccharide micelles for 10-hydroxycamptothecin. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 393, 143–151. [Google Scholar]
- Bang, J.Y.; Song, C.E.; Kim, C.; Park, W.D.; Cho, K.R.; Kim, P.I.; Lee, S.R.; Chung, W.T.; Choi, K.C. Cytotoxicity of amphotericin B-incorporated polymeric micelles composed of poly(dl-lactide-co-glycolide)/dextran graft copolymer. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2008, 31, 1463–1469. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.; Ahn, C.H.; Park, T.G. Poly[lactic-co-(glycolic acid)]-grafted hyaluronic acid copolymer micelle nanoparticles for target-specific delivery of doxorubicin. Macromol. Biosci. 2009, 9, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.I.; Kim, O.H.; Chung, C.W.; Yoo, J.J.; Choi, K.H.; Kim, C.H.; Ha, S.H.; Kang, D.H. Self-assembled nanoparticles of hyaluronic acid/poly(dl-lactide-co-glycolide) block copolymer. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 90, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahmani, F.Z.; Yang, H.; Zhou, J.P.; Yao, J.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Q. Enhanced oral bioavailability of paclitaxel in pluronic/LHR mixed polymeric micelles: Preparation, in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 47, 179–189. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.H.; Jang, J.Y.; Joung, Y.K.; Kwon, M.H.; Park, K.D. Intracellular delivery and anti-cancer effect of self-assembled heparin-Pluronic nanogels with RNase A. J. Contr. Release 2010, 147, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malingre, M.M.; Beijnen, J.H.; Schellens, J.H.M. Oral delivery of taxanes. Investig. New Drugs 2001, 19, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiappetta, D.A.; Sosnik, A. Poly(ethylene oxide)-poly(propylene oxide) block copolymer micelles as drug delivery agents: Improved hydrosolubility, stability and bioavailability of drugs. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharma. 2007, 66, 303–317. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, J.L.; Zhao, Y.Z.; Jin, Z.; Lu, C.T.; Tang, Q.Q.; Xiang, Q.; Sun, C.Z.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Y.Y.; Gao, H.S.; et al. Synthesis and characterization of Poloxamer 188-grafted heparin copolymer. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2010, 36, 832–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.M.; Bae, J.W.; Joung, Y.K.; Shin, J.W.; Park, K.D. Nanoaggregate of thermosensitive chitosan-Pluronic for sustained release of hydrophobic drug. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2008, 63, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.H.; Joung, Y.K.; Choi, J.H.; Moon, H.T.; Park, K.D. Targeting ligand-functionalized and redox-sensitive heparin-Pluronic nanogels for intracellular protein delivery. Biomed. Mater. 2011, 6, 055004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.J.; Sun, S.L.; Feng, T.H.; Sung, K.H.; Lui, W.L.; Wang, L.F. Folate-mediated chondroitin sulfate-Pluronic 127 nanogels as a drug carrier. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 38, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, H.; Joung, Y.K.; Jung, K.H.; Choi, J.H.; Lee, D.H.; Park, K.D.; Hong, S.S. The use of low molecular weight heparin-pluronic nanogels to impede liver fibrosis by inhibition the TGF-beta/Smad signaling pathway. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 1438–1445. [Google Scholar]
- Manaspon, C.; Viravaidya-Pasuwat, K.; Pimpha, N. Preparation of folate-conjugated pluronic f127/chitosan core-shell nanoparticles encapsulating doxorubicin for breast cancer treatment. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 593878:1–593878:11. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.W.; Cai, G.Q.; Tang, G.P.; Wang, L.Q.; Jiang, H.L. Synthesis, self-assembly, and cytotoxicity of well-defined trimethylated chitosan-O-poly(epsilon-caprolactone): Effect of chitosan molecular weight. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B 2011, 98B, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Cai, G.Q.; Zhang, H.W.; Jiang, H.L.; Wang, L.Q. Chitosan-poly(epsilon-caprolactone)-poly(ethylene glycol) graft copolymers: Synthesis, self-assembly, and drug release behavior. Jo. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2011, 96A, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Y.; Zhang, L.M. Preparation of a polysaccharide-polyester diblock copolymer and its micellar characteristics. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 69, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.W.; Burt, H.M. Synthesis and characterization of amphiphilic hydroxypropylcellulose-graft-poly(epsilon-caprolactone). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 89, 718–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.J.; Liu, Y.S.; Yeh, H.H.; Cheng, T.L.; Wang, L.F. Self-assembled poly(epsilon-caprolactone)-g-chondroitin sulfate copolymers as an intracellular doxorubicin delivery carrier against lung cancer cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 4169–4183. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.H.; Cuong, N.V.; Chen, Y.T.; So, R.C.; Liau, I.; Hsieh, M.F. Overcoming multidrug resistance of breast cancer cells by the micellar doxorubicin nanoparticles of mPEG-PCL-graft-cellulose. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2011, 11, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, K.; Zhang, X.; Tang, X.; Yu, J.; Liu, S.; Wang, D.; Li, Y.; Huang, J. Fabrication of cationic nanomicelle from chitosan-graft-polycaprolactone as the carrier of 7-ethyl-10-hydroxy-camptothecin. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 76, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, M.F.; Cuong, N.V.; Chen, C.H.; Chen, Y.T.; Yeh, J.M. Nano-sized micelles of block copolymers of methoxy poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(epsilon-caprolactone)-graft-2-hydroxyethyl cellulose for doxorubicin delivery. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2008, 8, 2362–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, S.K.; Maiti, S.; Maiti, T.K.; Ghosh, S.K.; Pramanik, P. Hydrophobically modified carboxymethyl chitosan nanoparticles targeted delivery of paclitaxel. J. Drug Target. 2011, 19, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Jiang, X.H.; Hu, F.Q.; Du, Y.Z.; Zhu, Q.F.; Jin, C.S. In vitro antitumour activity of stearic acid-g-chitosan oligosaccharide polymeric micelles loading podophyllotoxin. J. Microencapsul. 2012, 29, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.T.; Du, Y.Z.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, X.G.; Miao, J.; Cui, F.D.; Hu, F.Q. Synthesis and anti-hepatitis B virus activity of acyclovir conjugated stearic acid-g-chitosan oligosaccharide micelle. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 1715–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Lu, L.J.; Du, Y.Z.; Hu, F.Q. Stearic acid-g-chitosan polymeric micelle for oral drug delivery: In vitro transport and in vivo absorption. Mol. Pharma. 2011, 8, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.Z.; Cai, L.L.; Liu, P.; You, J.; Yuan, H.; Hu, F.Q. Tumor cells-specific targeting delivery achieved by A54 peptide functionalized polymeric micelles. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 8858–8867. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.T.; Du, Y.Z.; Yuan, H.; Hu, F.Q. Brain-targeting study of stearic acid-grafted chitosan micelle drug-delivery system. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 3235–3244. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.Z.; Cai, L.L.; Li, J.; Zhao, M.D.; Chen, F.Y.; Yuan, H.; Hu, F.Q. Receptor-mediated gene delivery by folic acid-modified stearic acid-grafted chitosan micelles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 1559–1568. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, F.Q.; Jiang, X.H.; Huang, X.; Wu, X.L.; Yuan, H.; Wei, X.H.; Du, Y.Z. Enhanced cellular uptake of chlorine e6 mediated by stearic acid-grafted chitosan oligosaccharide micelles. J. Drug Target. 2009, 17, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.Q.; Wu, X.L.; Du, Y.Z.; You, J.; Yuan, H. Cellular uptake and cytotoxicity of shell crosslinked stearic acid-grafted chitosan oligosaccharide micelles encapsulating doxorubicin. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 69, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.Q.; Chen, W.W.; Zhao, M.D.; Yuan, H.; Du, Y.Z. Effective antitumor gene therapy delivered by polyethylenimine-conjugated stearic acid-g-chitosan oligosaccharide micelles. Gene Ther. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.Q.; Liu, L.N.; Du, Y.Z.; Yuan, H. Synthesis and antitumor activity of doxorubicin conjugated stearic acid-g-chitosan oligosaccharide polymeric micelles. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 6955–6963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.W.; Jeong, Y.I.; Kim, S.H. Characterization of hydrophobized pullulan with various hydrophobicities. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 254, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.X.; Wen, X.T.; Liang, J.; Gu, Z.W.; Zhang, X.D.; Fan, Y.J. A pH-sensitive nano drug delivery system derived from pullulan/doxorubicin conjugate. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl Biomater. 2009, 89B, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.H.; Kang, D.; Na, K. Physicochemical characterization and carcinoma cell interaction of self-organized nanogels prepared from polysaccharide/biotin conjugates for development of anticancer drug carrier. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 16, 1369–1376. [Google Scholar]
- Kamel, S.; Ali, N.; Jahangir, K.; Shah, S.M.; El-Gendy, A.A. Pharmaceutical significance of cellulose: A review. Exp. Polym. Lett. 2008, 2, 758–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, M.F.; Piredda, M.; Winnik, F.M. Solubilization of poorly water soluble drugs in micelles of hydrophobically modified hydroxypropylcellulose copolymers. J. Contr. Release 2003, 93, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chayed, S.; Winnik, F.M. In vitro evaluation of the mucoadhesive properties of polysaccharide-based nanoparticulate oral drug delivery systems. Eur. J. Pharma. Biopharm. 2007, 65, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, M.F.; Cristea, M.; Yang, Y.L.; Winnik, F.M. Engineering polysaccharide-based polymeric micelles to enhance permeability of cyclosporin a across Caco-2 cells. Pharma. Res. 2005, 22, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enomoto-Rogers, Y.; Kamitakahara, H.; Yoshinaga, A.; Takano, T. Synthesis of diblock copolymers with cellulose derivatives 4. Self-assembled nanoparticles of amphiphilic cellulose derivatives carrying a single pyrene group at the reducing-end. Cellulose 2011, 18, 1005–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clagett, G.P.; Anderson, F.A.; Geerts, W.; Heit, J.A.; Knudson, M.; Lieberman, J.R.; Merli, G.J.; Wheeler, H.B. Prevention of venous thromboembolism. Chest 1998, 114, 531S–560S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, M.F.; Lavoie, L.; Winnik, F.M.; Leroux, J.C. Solubilization of cyclosporin A in dextran-g-polyethyleneglycolalkyl ether polymeric micelles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2003, 56, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, M.F.; Cristea, M.; Winnik, F.M. Exploiting the vitamin B-12 pathway to enhance oral drug delivery via polymeric micelles. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 2462–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Discher, D.E.; Ahmed, F. Polymersomes. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2006, 8, 323–341. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, X.B.; Li, H.; Zhu, X.X.; Woo, H.G. Self-aggregated nanoparticles composed of periodate-oxidized dextran and cholic acid: Preparation, stabilization and in-vitro drug release. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2006, 81, 746–754. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.G.; Yuan, X.B.; Chang, J. Self-aggregates of cholic acid hydrazide-dextran conjugates as drug carriers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 95, 487–493. [Google Scholar]
- Houga, C.; Giermanska, J.; Lecommandoux, S.; Borsali, R.; Taton, D.; Gnanou, Y.; Le Meins, J.F. Micelles and polymersomes obtained by self-assembly of dextran and polystyrene based block copolymers. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 32–40. [Google Scholar]
- Daoud-Mahammed, S.; Couvreur, P.; Bouchemal, K.; Cheron, M.; Lebas, G.; Amiel, C.; Gref, R. Cyclodextrin and polysaccharide-based nanogels: Entrapment of two hydrophobic molecules, benzophenone and tamoxifen. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 547–554. [Google Scholar]
- Krasznai, D.J.; McKenna, T.F.L.; Cunningham, M.F.; Champagne, P.; Smeets, N.M.B. Polysaccharide-stabilized core cross-linked polymer micelle analogues. Polym. Chem. 2012, 3, 992–1001. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Q.; Wang, X.H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, C.N.; Wang, P.; Yuan, Z. Self-assembly and liver targeting of sulfated chitosan nanoparticles functionalized with glycyrrhetinic acid. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2012, 8, 870–879. [Google Scholar]
- Mo, R.; Jin, X.; Li, N.; Ju, C.Y.; Sun, M.J.; Zhang, C.; Ping, Q.N. The mechanism of enhancement on oral absorption of paclitaxel by N-octyl-O-sulfate chitosan micelles. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 4609–4620. [Google Scholar]
- Lian, H.; Sun, J.; Yu, Y.P.; Liu, Y.H.; Cao, W.; Wang, Y.J.; Sun, Y.H.; Wang, S.L.; He, Z.G. Supramolecular micellar nanoaggregates based on a novel chitosan/vitamin E succinate copolymer for paclitaxel selective delivery. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 3323–3334. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.Z.; Wang, L.; Yuan, H.; Hu, F.Q. Linoleic acid-grafted chitosan oligosaccharide micelles for intracellular drug delivery and reverse drug resistance of tumor cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 48, 215–222. [Google Scholar]
- Srinophakun, T.; Boonmee, J. Preliminary study of conformation and drug release mechanism of doxorubicin-conjugated glycol chitosan, via cis-aconityl linkage, by molecular modeling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 1672–1683. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.G.; Li, X.Y.; Cao, Z.X.; Xu, Y.Z.; Lin, H.J.; Zhao, Y.L.; Wei, Y.Q.; Qian, Z.Y. Camptothecin nanocolloids based on N,N,N-trimethyl chitosan: Efficient suppression of growth of multiple myeloma in a murine model. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 27, 1035–1040. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, G.B.; Lin, Z.T.; Xu, X.J.; Zhang, H.; Song, K. Stable nanomicelles based on chitosan derivative: In vitro antiplatelet aggregation and adhesion properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 88, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonaje, K.; Lin, K.J.; Tseng, M.T.; Wey, S.P.; Su, F.Y.; Chuang, E.Y.; Hsu, C.W.; Chen, C.T.; Sung, H.W. Effects of chitosan-nanoparticle-mediated tight junction opening on the oral absorption of endotoxins. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 8712–8721. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Z.T.; Song, K.; Bin, J.P.; Liao, Y.L.; Jiang, G.B. Characterization of polymer micelles with hemocompatibility based on N-succinyl-chitosan grafting with long chain hydrophobic groups and loading aspirin. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 19153–19165. [Google Scholar]
- Niers, T.M.H.; Klerk, C.P.W.; DiNisio, M.; van Noorden, C.J.F.; Buller, H.R.; Reitsma, P.H.; Richel, D.J. Mechanisms of heparin induced anti-cancer activity in experimental cancer models. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2007, 61, 195–207. [Google Scholar]
- Karti, S.S.; Ovali, E.; Ozgur, O.; Yilmaz, M.; Sonmez, M.; Ratip, S.; Ozdemir, F. Induction of apoptosis and inhibition of growth of human hepatoma HepG2 cells by heparin. HepatoGastroenterology 2003, 50, 1864–1866. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Xin, D.C.; Liu, K.J.; Zhu, M.Q.; Xiang, J.N. Heparin-paclitaxel conjugates as drug delivery system: Synthesis, self-assembly property, drug release, and antitumor activity. Bioconjug. Chem. 2009, 20, 2214–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.K.; Kim, Y.J.; Tran, T.H.; Huh, K.M.; Lee, Y.K. Water-soluble heparin-PTX conjugates for cancer targeting. Polymer 2010, 51, 3387–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Moon, H.T.; Park, J.Y.; Heo, Y.J.; Choi, Y.; Tran, T.H.; Lee, Y.K.; Kim, S.Y.; Huh, K.M. Heparin-based self-assembled nanoparticles for photodynamic therapy. Macromol. Res. 2011, 19, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.J.; Yoon, I.S.; Yoon, H.Y.; Koo, H.; Jin, Y.J.; Ko, S.H.; Shim, J.S.; Kim, K.; Kwon, I.C.; Kim, D.D. Polyethylene glycol-conjugated hyaluronic acid-ceramide self-assembled nanoparticles for targeted delivery of doxorubicin. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 1190–1200. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.L.; Liu, C.G.; Wang, X.L.; Huang, Z.H. Preparation and characterization of nanoparticles based on histidine-hyaluronic acid conjugates as doxorubicin carriers. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2012, 23, 1921–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.J.; Termsarasab, U.; Ko, S.H.; Shim, J.S.; Chong, S.; Chung, S.J.; Shim, C.K.; Cho, H.J.; Kim, D.D. Hyaluronic acid derivative-based self-assembled nanoparticles for the treatment of melanoma. Pharma. Res. 2012, 29, 3443–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.H.; Sun, J.; Cao, W.; Yang, J.H.; Lian, H.; Li, X.; Sun, Y.H.; Wang, Y.J.; Wang, S.L.; He, Z.G. Dual targeting folate-conjugated hyaluronic acid polymeric micelles for paclitaxel delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 421, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanakumar, G.; Choi, K.Y.; Yoon, H.Y.; Kim, K.; Park, J.H.; Kwon, I.C.; Park, K. Hydrotropic hyaluronic acid conjugates: Synthesis, characterization, and implications as a carrier of paclitaxel. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 394, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Wang, B.H.; Lu, Y.; Ouahab, A.; Li, Q.; Tu, J.S. A novel tumor-targeted delivery system with hydrophobized hyaluronic acid-spermine conjugates (HHSCs) for efficient receptor-mediated siRNA delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 414, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manju, S.; Sreenivasan, K. Conjugation of curcumin onto hyaluronic acid enhances its aqueous solubility and stability. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 359, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.Y.; Min, K.H.; Yoon, H.Y.; Kim, K.; Park, J.H.; Kwon, I.C.; Choi, K.; Jeong, S.Y. PEGylation of hyaluronic acid nanoparticles improves tumor targetability in vivo. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 1880–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, R.A.; Silvers, A.L.; Zhang, N. Polysialic acid-based micelles for encapsulation of hydrophobic drugs. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Li, X.R.; Zhou, Y.X.; Li, W.J.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, S.J.; Li, J.W.; Gao, Y.J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.L.; et al. The use of polyion complex micelles to enhance the oral delivery of salmon calcitonin and transport mechanism across the intestinal epithelial barrier. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 8881–8892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, W.; Wu, H.; Wang, X.L.; Peng, S.L.; Ding, L.S.; Zhang, S.; Li, B.J. Self-aggregates of cholesterol-modified carboxymethyl konjac glucomannan conjugate: Preparation, characterization, and preliminary assessment as a carrier of etoposide. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.A.; Pereira, P.; Sampaio, P.; Coutinho, P.J.G.; Gama, F.M. Supramolecular assembled nanogel made of mannan. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 361, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.A.; Coutinho, P.J.G.; Gama, F.M. Self-assembled nanogel made of mannan: Synthesis and characterization. Langmuir 2010, 26, 11413–11420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Medeiros Modolon, S.; Otsuka, I.; Fort, S.; Minatti, E.; Borsali, R.; Halila, S. Sweet block copolymer nanoparticles: Preparation and self-assembly of fully oligosaccharide-based amphiphile. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 1129–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.X.; Su, Z.G.; Xiao, Y.Y.; Huang, A.W.; Li, H.Y.; Bao, X.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.A.; Sun, M.J.; Ping, Q.N. Octreotide-modified and pH-triggering polymeric micelles loaded with doxorubicin for tumor targeting delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 45, 216–226. [Google Scholar]
- Caliceti, P.; Veronese, F.M. Pharmacokinetic and biodistribution properties of poly(ethylene glycol)-protein conjugates. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2003, 55, 1261–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregoriadis, G.; Jain, S.; Papaioannou, I.; Laing, P. Improving the therapeutic efficacy of peptides and proteins: A role for polysialic acids. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 300, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knop, K.; Hoogenboom, R.; Fischer, D.; Schubert, U.S. Poly(ethylene glycol) in drug delivery: Pros and cons as well as potential alternatives. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6288–6308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, R.L.; Huang, C.J.; Tseng, Y.L.; Pang, V.F.; Chen, S.T.; Liu, J.J.; Chang, F.H. Direct comparison of liposomal doxorubicin with or without polyethylene glycol coating in C-26 tumor-bearing mice: Is surface coating with polyethylene glycol beneficial? Clin. Cancer Res. 1999, 5, 3645–3652. [Google Scholar]
- Holland, J.W.; Hui, C.; Cullis, P.R.; Madden, T.D. Poly(ethylene glycol)—Lipid conjugates regulate the calcium-induced fusion of liposomes composed of phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylserine. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 2618–2624. [Google Scholar]
- Erbacher, P.; Bettinger, T.; Belguise-Valladier, P.; Zou, S.; Coll, J.L.; Behr, J.P.; Remy, J.S. Transfection and physical properties of various saccharide, poly(ethylene glycol), and antibody-derivatized polyethylenimines (PEI). J. Gene Med. 1999, 1, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Hreczuk-Hirst, D.H.; McCormack, B.; Mital, M.; Epenetos, A.; Laing, P.; Gregoriadis, G. Polysialylated insulin: Synthesis, characterization and biological activity in vivo. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2003, 1622, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.I.; Gregoriadis, G. Polysialylated asparaginase: Preparation, activity and pharmacokinetics. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1997, 1341, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.I.; Gregoriadis, G. The effect of polysialylation on the immunogenicity and antigenicity of asparaginase: Implication in its pharmacokinetics. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 217, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.G. G FC41 catalase-polysialic acid conjugates. Eur. J. Pharma. Sci. 1994, 2, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.I.; Gregoriadis, G. Synthesis, characterization and properties of sialylated catalase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1996, 1293, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.K.; Won, Y.W.; Lim, K.S.; Kim, Y.H. Low-molecular-weight methylcellulose-based thermo-reversible gel/pluronic micelle combination system for local and sustained docetaxel delivery. Pharma. Res. 2012, 29, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, C.J.; Huo, D.; Qian, H.Q.; Ding, Y.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, X.Q. Synthesis of beta-cyclodextrin modified chitosan-poly(acrylic acid) nanoparticles and use as drug carriers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 90, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, K.; Lee, K.H.; Bae, Y.H. pH-Sensitivity and pH-dependent interior structural change of self-assembled hydrogel nanoparticles of pullulan acetate/oligo-sulfonamide conjugate. J. Contr. Release 2004, 97, 513–525. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, X.Y.; Yin, Y.H.; Huang, Z.J.; Lu, B.; Xu, P.H.; Zheng, H.; Xiong, F.L.; Xu, H.X.; Xiong, X.; Gu, X.B. Preparation, characterization and in vitro release study of a glutathione-dependent polymeric prodrug cis-3-(9H-purin-6-ylthio)-acrylic acid-graft-carboxymethyl chitosan. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 436, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Rao, Y.; Yin, Y.H.; Xiong, X.O.; Xu, P.H.; Lu, B. Preparation, characterization, and in vitro drug release behavior of 6-mercaptopurine-carboxymethyl chitosan. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 1952–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirakura, T.; Nomura, Y.; Aoyama, Y.; Akiyoshi, K. Photoresponsive nanogels formed by the self-assembly of spiropyrane-bearing pullulan that act as artificial molecular chaperones. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 1804–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patnaik, S.; Sharma, A.K.; Garg, B.S.; Gandhi, R.P.; Gupta, K.C. Photoregulation of drug release in azo-dextran nanogels. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 342, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.L.; Liu, P.; Li, X.; Huang, X.; Ye, Y.Q.; Chen, F.Y.; Yuan, H.; Hu, F.Q.; Du, Y.Z. RGD peptide-mediated chitosan-based polymeric micelles targeting delivery for integrin-overexpressing tumor cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 3499–3508. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Y.L.; Liu, C.G. Preparation and characterization of self-assemblied nanoparticles based on folic acid modified carboxymethyl chitosan. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2011, 22, 1213–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.Y.; Liu, F.; Guo, J.; Xue, J.P.; Qian, Z.Y.; Gu, Y.Q. Folate-modified chitosan micelles with enhanced tumor targeting evaluated by near infrared imaging system. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 1118–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayebsadrian, M.; Varshosaz, J.; Hassanzadeh, F.; Sadeghi, H.; Banitalebi, M.; Rostami, M. Screening the most effective variables on physical properties of folate-targeted dextran/retinoic acid micelles by taguchi design. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 860691:1–860691:7. [Google Scholar]
- Dionisio, M.; Cordeiro, C.; Remunan-Lopez, C.; Seijo, B.; Rosa da Costa, A.M.; Grenha, A. Pullulan-based nanoparticles as carriers for transmucosal protein delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, N.; Wardwell, P.R.; Bader, R.A. Polysaccharide-Based Micelles for Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2013, 5, 329-352. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics5020329
Zhang N, Wardwell PR, Bader RA. Polysaccharide-Based Micelles for Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics. 2013; 5(2):329-352. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics5020329
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Nan, Patricia R. Wardwell, and Rebecca A. Bader. 2013. "Polysaccharide-Based Micelles for Drug Delivery" Pharmaceutics 5, no. 2: 329-352. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics5020329
APA StyleZhang, N., Wardwell, P. R., & Bader, R. A. (2013). Polysaccharide-Based Micelles for Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics, 5(2), 329-352. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics5020329




