A Modified Triaxial Electrospinning for a High Drug Encapsulation Efficiency of Curcumin in Ethylcellulose
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
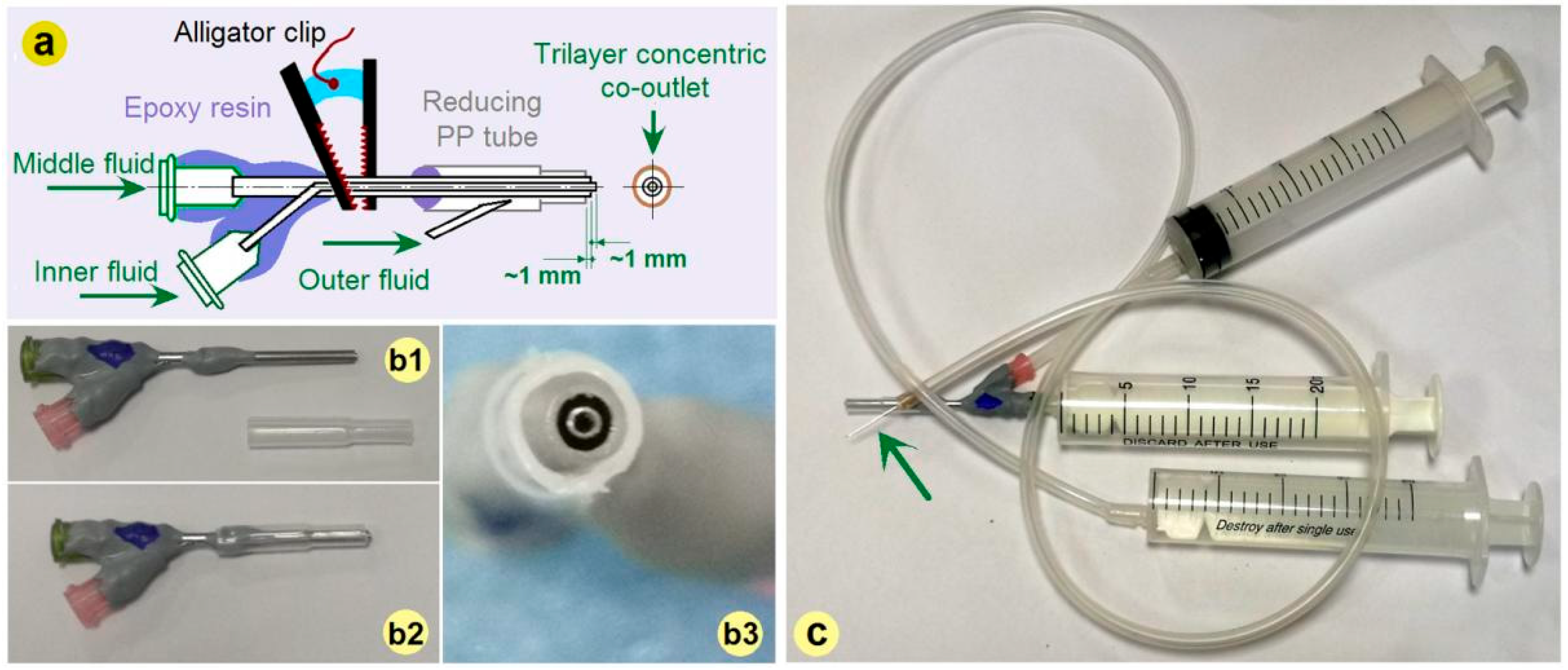
2.2. Electrospinning
2.3. Characterizations of Physical Properties
2.3.1. Morphology
2.3.2. Inner Structure
2.3.3. Physical State
2.3.4. Compatibility
2.4. Characterizations of Functional Performances
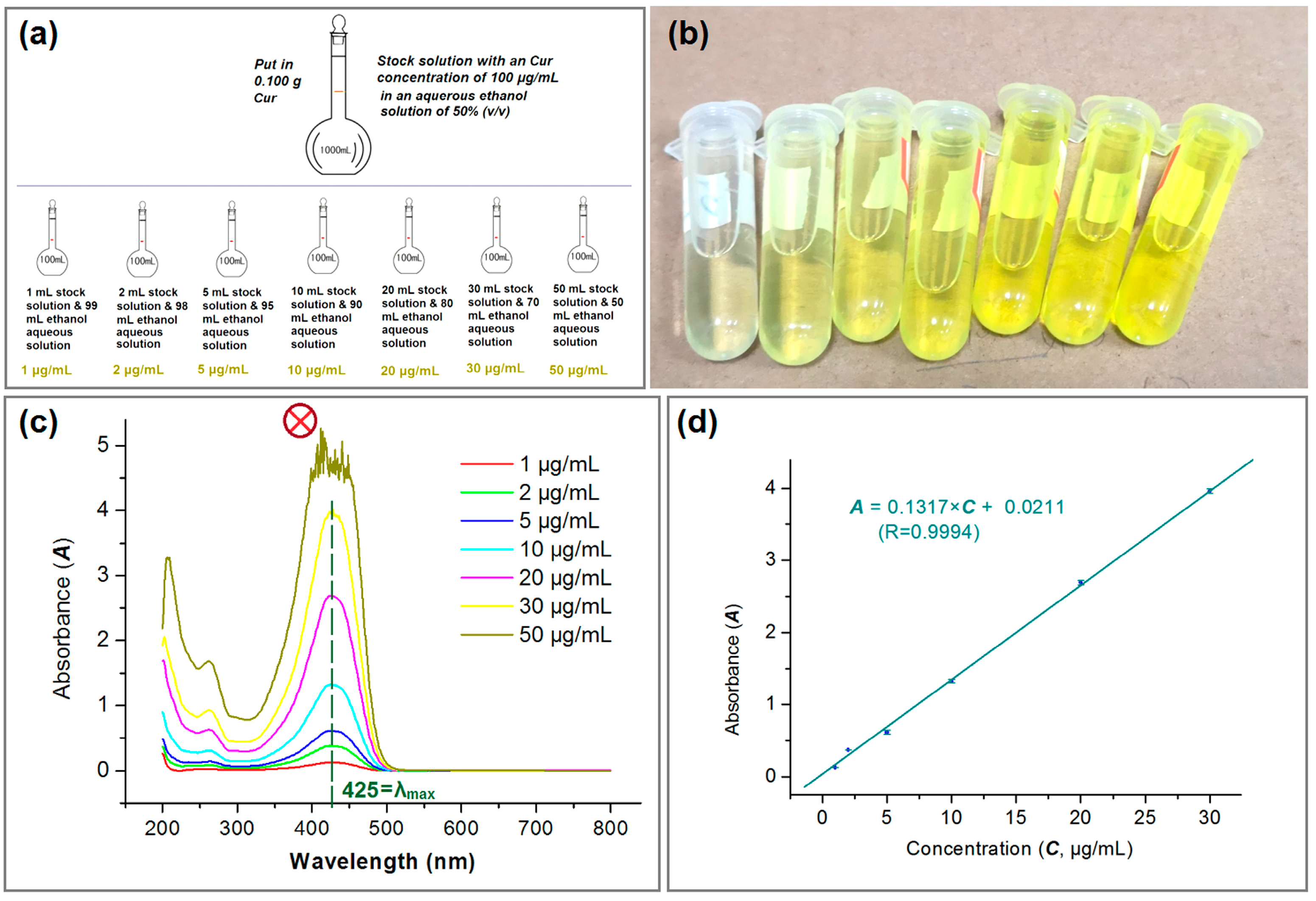
2.4.1. Encapsulation Efficiency (DEE %)
2.4.2. In Vitro Release Studies
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
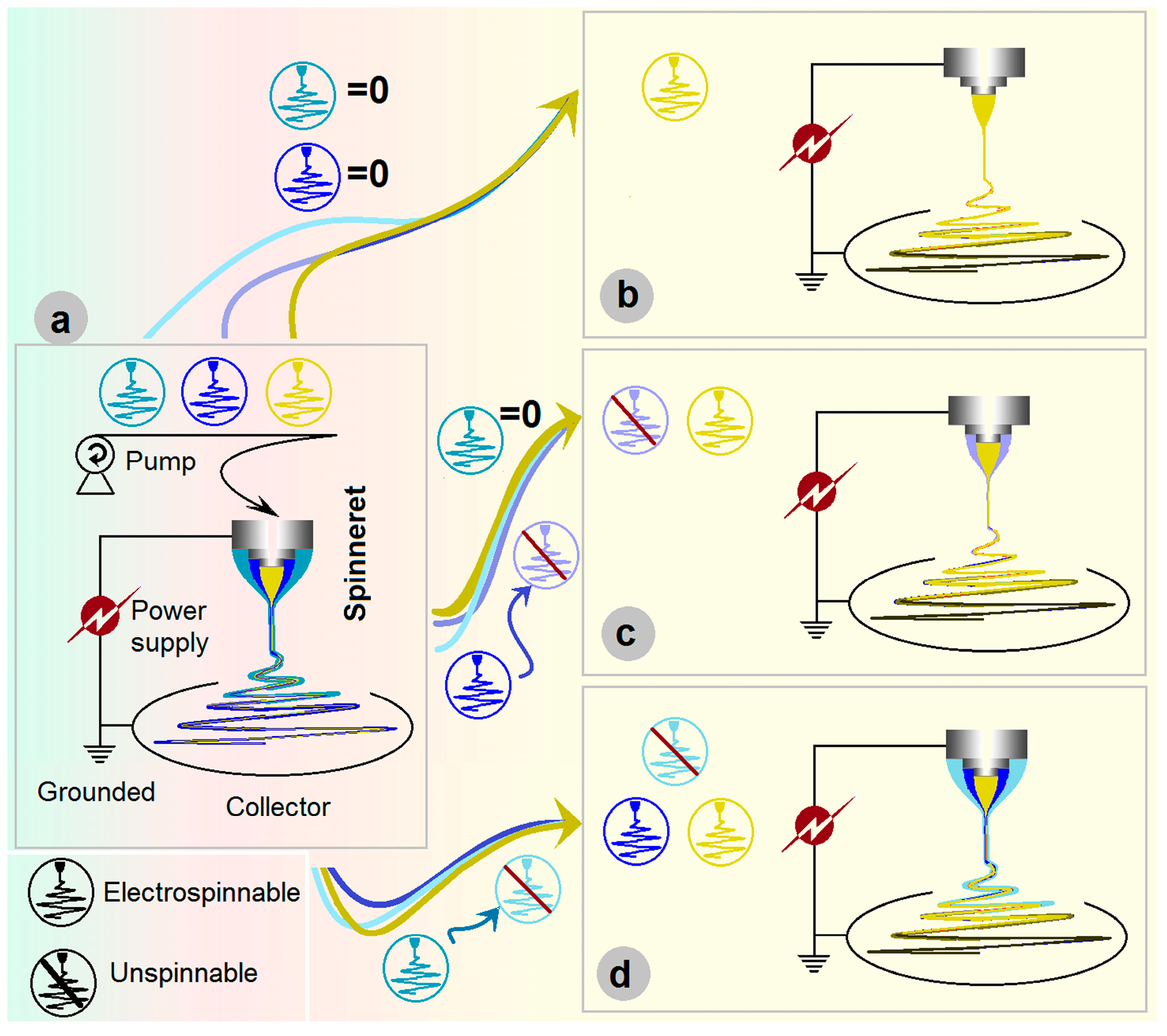
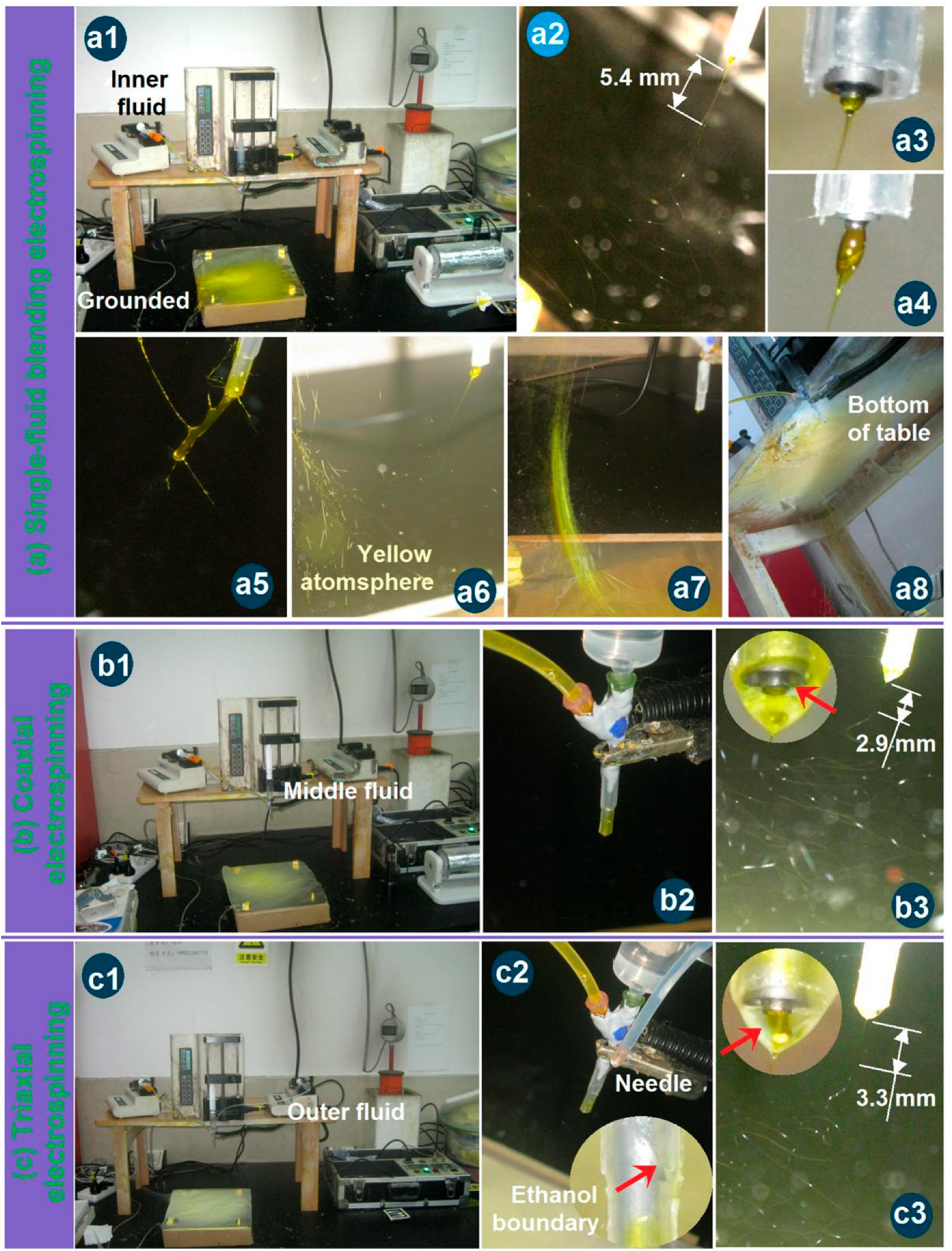
3.1. New EHDA Processes and Their Apparatus
3.2. Working Processes
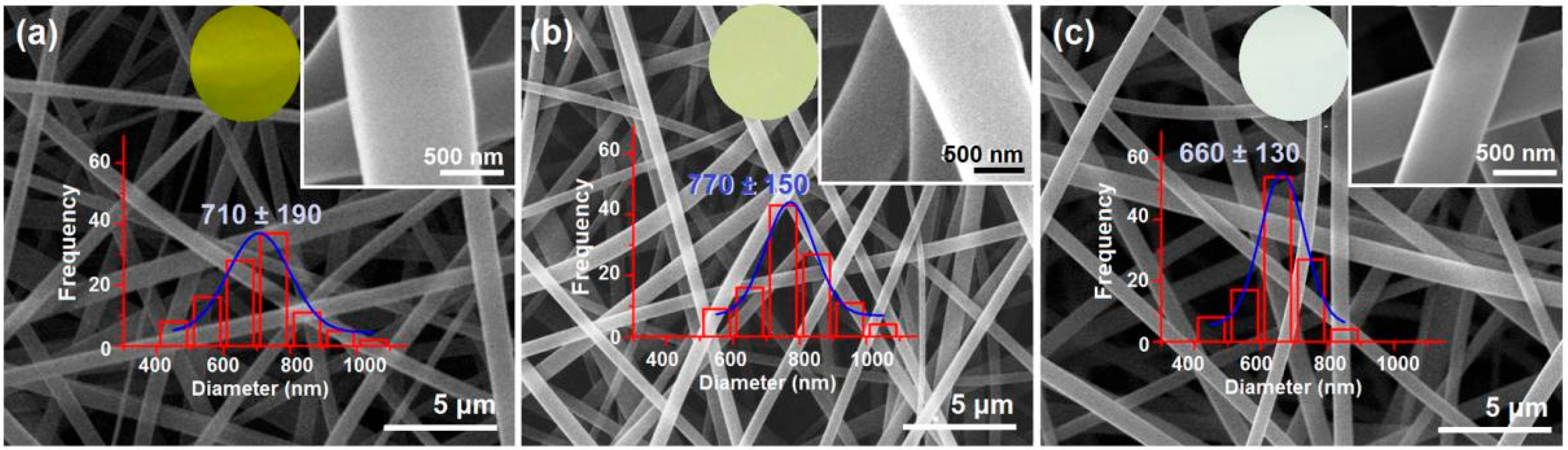
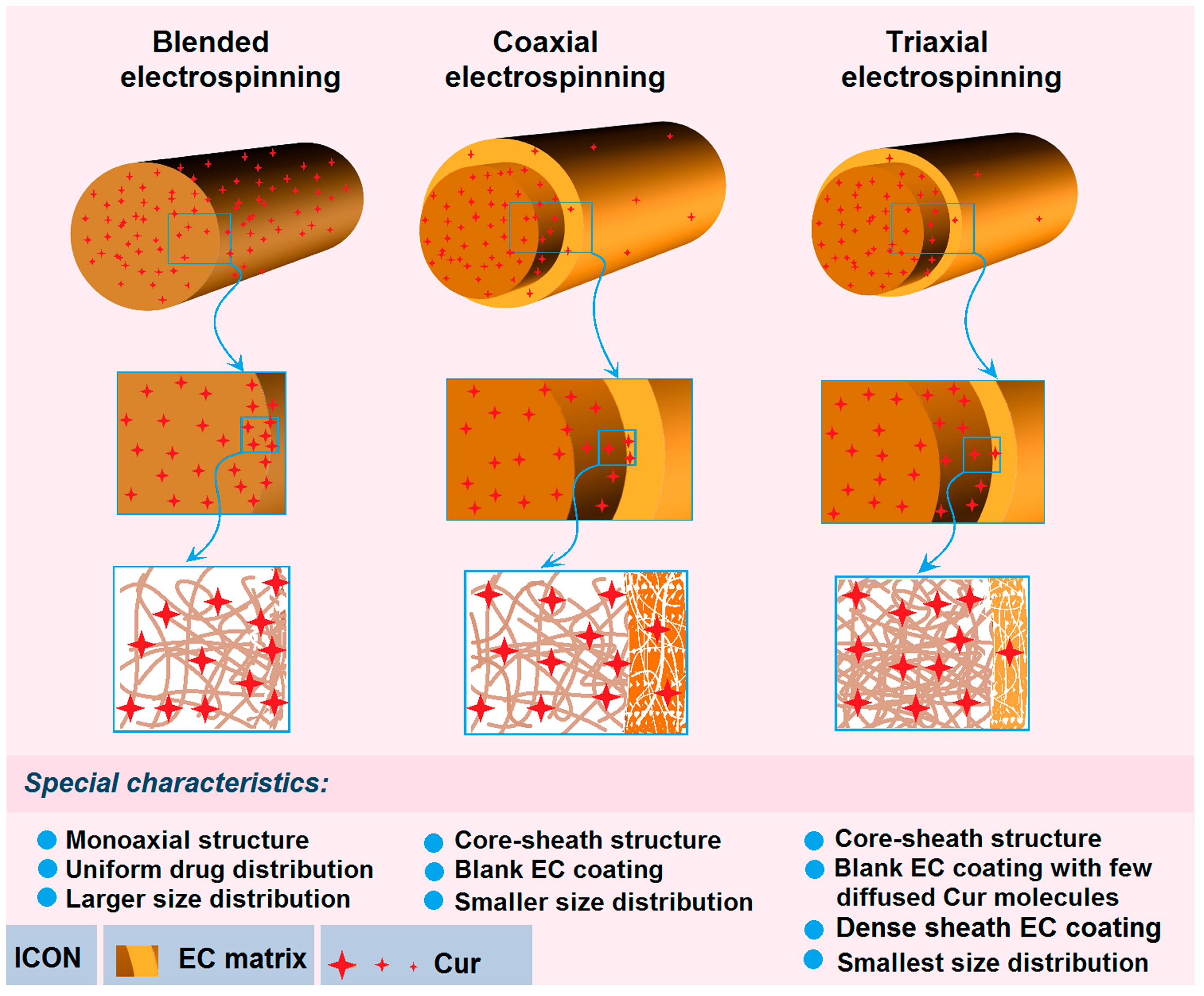
3.3. Morphologies and Inner Structures
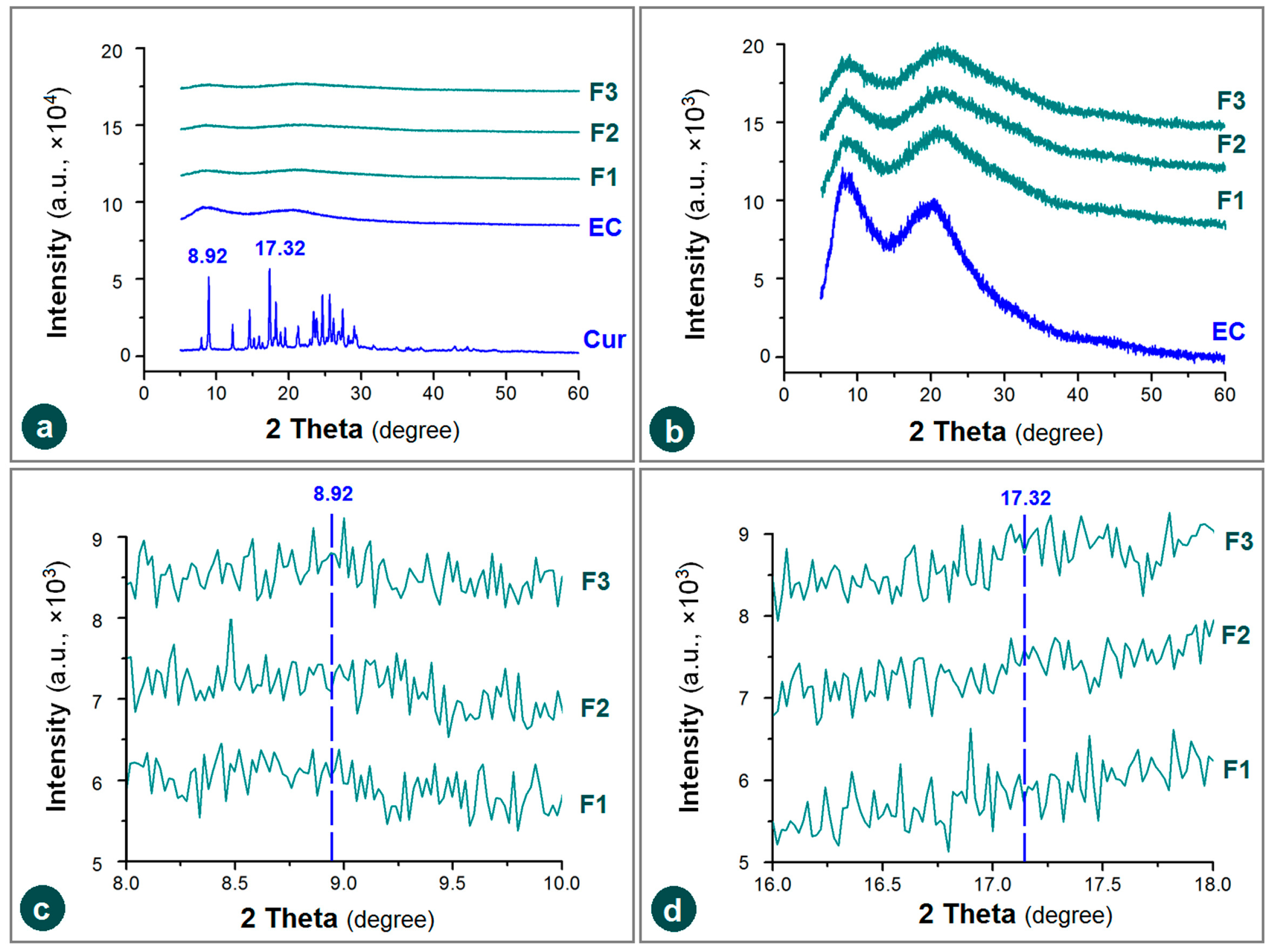
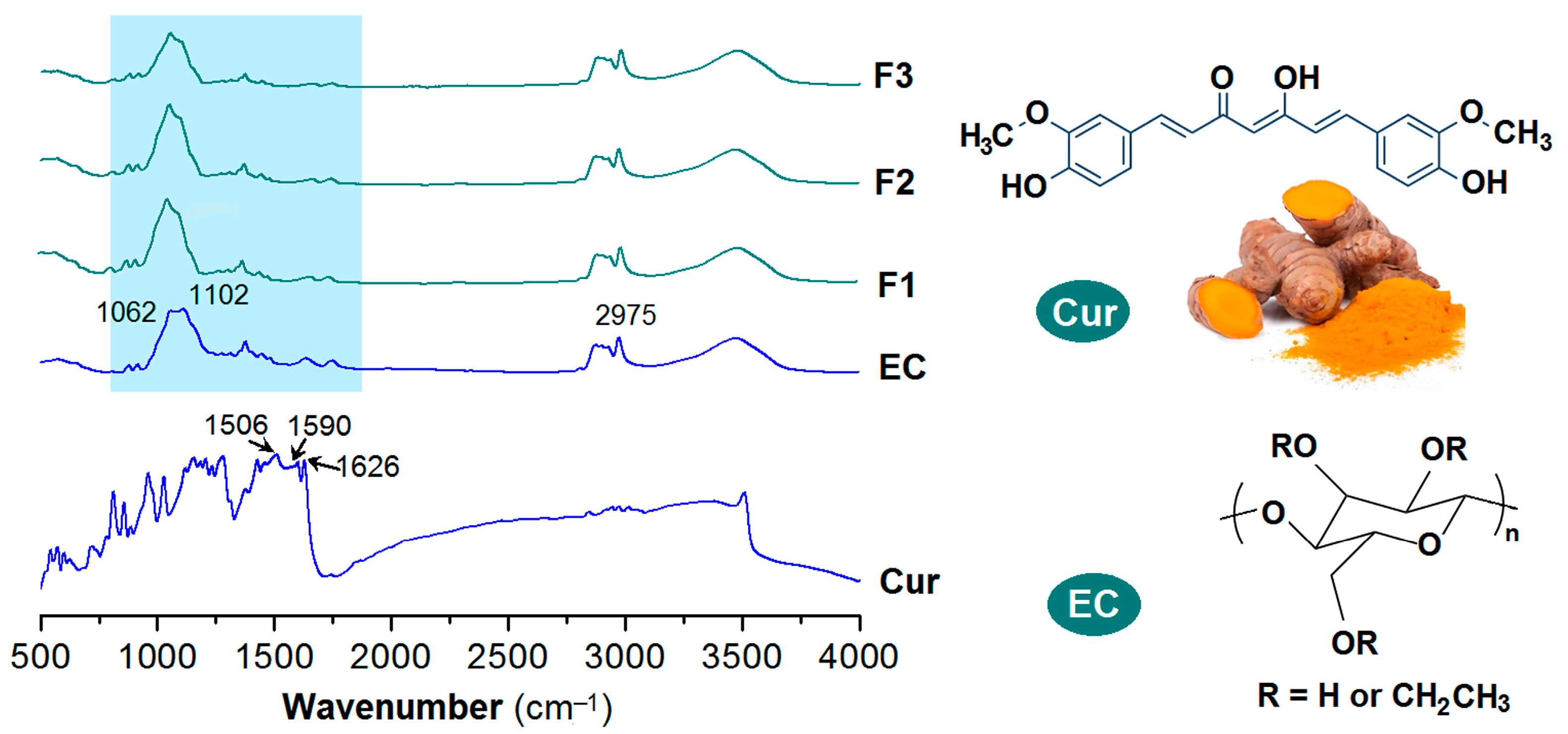
3.4. Physical State and Compatibility
3.5. Encapsulation Efficiency
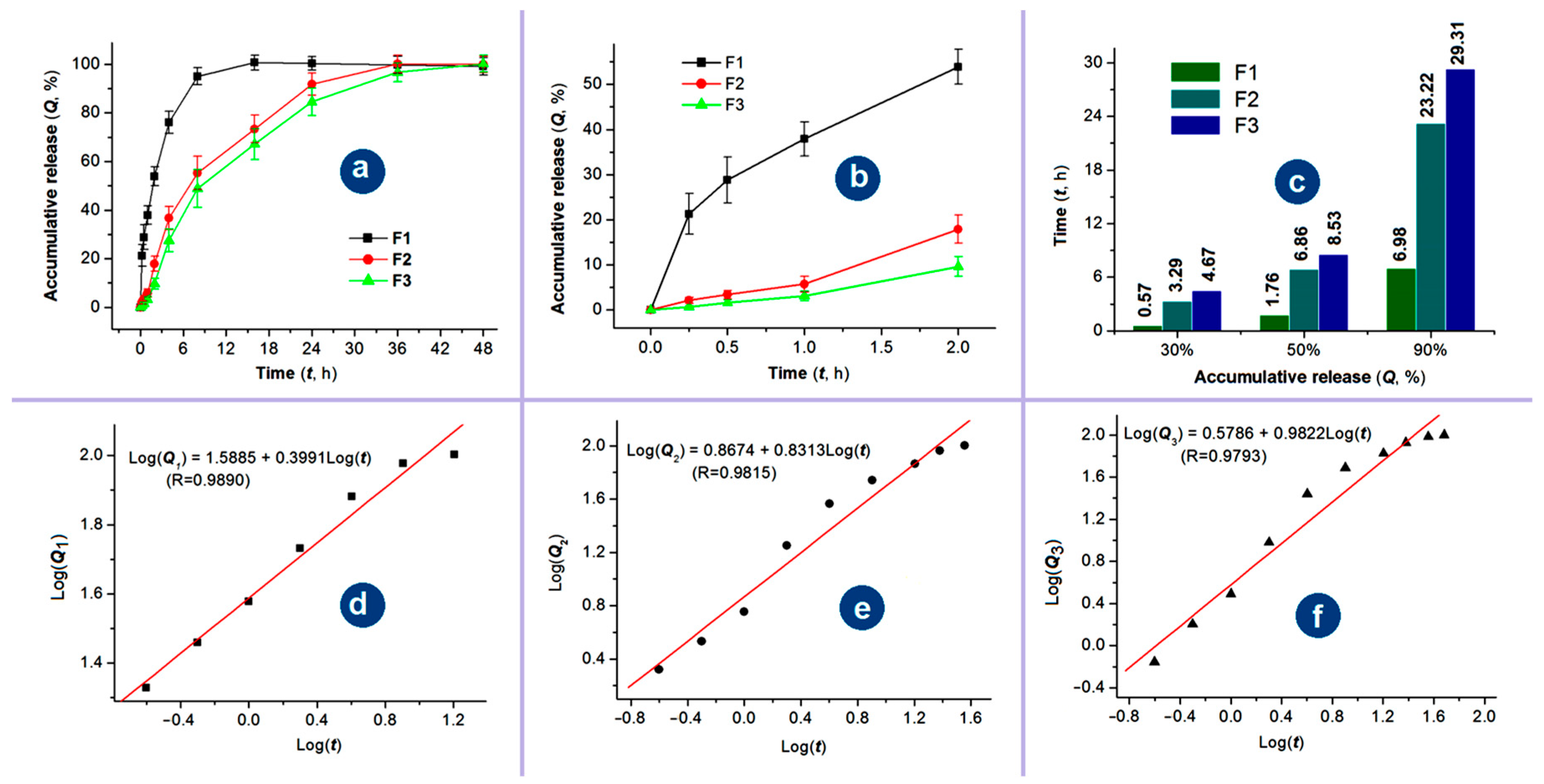
3.6. Sustained Release Profiles
3.7. Mechanisms of Sustained Release and the Related Process-Structure-Performance Relationship
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cruz-Maya, I.; Cirillo, V.; Serrano-Bello, J.; Serri, C.; Alvarez-Perez, M.A.; Guarino, V. Optimization of Diclofenac-Loaded Bicomponent Nanofibers: Effect of Gelatin on In Vitro and In Vivo Response. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaj, D.-A.; Peptu, C.A.; Danu, M.; Harabagiu, V.; Peptu, C.; Bujor, A.; Ochiuz, L.; Tuchilus, C.G. Enrofloxacin Pharmaceutical Formulations through the Polymer-Free Electrospinning of β-Cyclodextrin–oligolactide Derivatives. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Lu, P.; Li, P.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, J.; Hou, Y.; Han, X.; Ji, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Li, D.; et al. Multi-Level Resource Utilization of Food-Grade Nanomaterials from Brewing Residues: Synergistic Polyphenol-Pullulan Membranes for Litchi Preservation. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 519, 165226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, D.R.; Ramani, V.D.; Shah, D.P.; Vaishnav, D.; Kapoor, D.U. A synoptic examination of commercially viable nanofiber-based products. J. Drug. Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 102, 106323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Jin, X.; Guo, J.; Kou, B.; Chai, M.; Dou, S.; Jin, G.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, X.; Ma, J.; et al. A Biomimetic Asymmetric Structured Intelligent Wound Dressing with Dual-Modality Humidity-Pressure Sensing for Non-Invasive and Real-Time Wound Healing Monitoring. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2025, 7, 156–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Zhang, T.; Yuan, B.; Rohani, S. Local Delivery of Ginger Extract via A Nanofibrous Membrane Suppresses Human Skin Melanoma B16F10 Cells Growth via Targeting Ras/ERK and PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathways: An In Vitro Study. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2024; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumal, V.; Sujatha, K.; Dhanush, R.; Sowmya, C. Electrospun Nanofiber Films Containing Hesperidin and Ofloxacin for the Inhibition of Inflammation and Psoriasis: A Potential In vitro Study. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2025, 22, 1358–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agiba, A.M.; Elsayyad, N.; ElShagea, H.N.; Metwalli, M.A.; Mahmoudsalehi, A.O.; Beigi-Boroujeni, S.; Lozano, O.; Aguirre-Soto, A.; Arreola-Ramirez, J.L.; Segura-Medina, P.; et al. Advances in Light-Responsive Smart Multifunctional Nanofibers: Implications for Targeted Drug Delivery and Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Limaye, A.; Osorno, L.; Alheib, O.; Wang, Z.; Ievlev, A.V.; Domingo, N.; Arinzeh, T.; Foston, M. Spatial Distribution and Clustering of Glycosaminoglycans in Electrospun Gelatin-Based Scaffolds. ACS Omega 2025, 10, 25405–25414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirzad, M.; Salahvarzi, A.; Fathi-karkan, S.; Rahdar, A.; Guettari, M.; Pandey, S. Green Nanocarriers and Biodegradable Systems for Sustainable Drug Delivery Solutions. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2025, 111, 107208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakran, M.; Antipina, M.N. Emulsion-Based Techniques for Encapsulation in Biomedicine, Food and Personal Care. Curr. Opinion Pharmacol. 2014, 18, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, S.; Ijaz, M.; Rafique, S.; Yasin, H.; Mushtaq, M.; Khan, A.K.; Khan, M.; Nasir, B.; Murtaza, G. Cefadroxil-Mupirocin Integrated Electrospun Nanofiber Films for Burn Wound Therapy. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, W.; Wang, M.-L.; Liu, Y.; Yu, D.-G.; Bligh, S.W.A. Shell Distribution of Vitamin K3 within Reinforced Electrospun Nanofibers for Improved Photo-Antibacterial Performance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbar, Z.; Zahoor, T.; Huma, N.; Jamil, A.; Ayesha, H.; Kumar-Irudayaraj, J.M. Electrospun Probiotics: An Alternative for Encapsulation. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2018, 32, 1551–1556. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Topuz, F.; Uyar, T. Recent Developments in Nanofiber-Based Fast-Disintegrating Drug Delivery Systems. Expert Opin. Drug Del. 2025, 1, 957–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, P.; Yusufu, R.; Guan, Z.; Chen, T.; Li, S.; Feng, Y.; Zeng, X.; Lu, J.; Luo, M.; Wei, F. Multifunctional Bioactivity Electrospinning Nanofibers Encapsulating Emodin Provide A Potential Postoperative Management Strategy for Skin Cancer. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, S.; Nagy, N.; Pinke, B.; Mészáros, L.; Kazsoki, A.; Zelkó, R. Development and Evaluation of Different Electrospun Cysteamine-Loaded Nanofibrous Webs: A Promising Option for Treating A Rare Lysosomal Storage Disorder. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Pandey, G.; Kumar, A.; Kapoor, A.; Wagh, S.; Kolipaka, T.; Famta, P.; Mishra, A.; Srivastava, S.; Misra, S.K. Harnessing Electrospun Nanofibers for Comprehensive Oral Disease Management: Current Trends and Future Perspectives. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2025, 106, 106681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, Q.; Huang, Q.; Cao, L. Transfluthrin-Loaded Electrospun Nanohybrids for Long-Term Mosquito Control and Efficient Air Filtration. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 516, 163889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Wu, W.; Cui, Z.; Li, Q.; Li, X.; Zhou, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, J.; Jiao, T. Self-Assembled Janus Structure Nanofiber Membranes for Skin Wound Healing: Synergistic Photothermal and Chemical Antibacterial Strategies. Colloid Surf. A 2025, 718, 136921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Wang, P.; Lv, Y.; Dong, L.; Li, L.; Xu, M.; Fu, L.; Yue, B.; Yu, D. Piezo-Photocatalytic Degradation of Ciprofloxacin Based on Flexible BiVO4 PVDF Nanofibers Membrane. Catalysts 2025, 15, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhu, T.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, K.-Y.; Meng, Z.-Y.; Huang, J.-J.; Cai, W.-L.; Lai, Y. Recent Advances in Functional Cellulose-Based Materials: Classification, Properties, and Applications. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2024, 6, 1343–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehcheshmeh, M.A.; Fathi, M. Production of Core-shell Nanofibers from Zein and Tragacanth for Encapsulation of Saffron Extract. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 122, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, A.; Lawson, D.; Onyekuru, L.; Dziemidowicz, K.; Angkawinitwong, U.; Costa, P.F.; Radacsi, N.; Williams, G.R. Protein Encapsulation by Electrospinning and Electrospraying. J. Control. Release. 2021, 329, 1172–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Liu, Y.; He, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, J.; Yu, D.-G. Coaxial Electrospun ZIF-8@PAN Nanofiber Membranes for Tetracycline and Doxycycline Adsorption in Wastewater: Kinetic, Isothermal and Thermodynamic Studies. Adv. Mater. Interf. 2025, 12, e00364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, W.; Yang, X.; Yu, D.-G.; Liu, P. Electrospun Gelatin/Tea Polyphenol@pullulan Nanofibers for Fast-Dissolving Antibacterial and Antioxidant Applications. J. Food Sci. 2024, 89, 7803–7818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfadhel, M. Nanofiber-Based Drug Delivery Systems: A Review on Its Applications, Challenges, and Envisioning Future Perspectives. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2024. in press. Available online: https://www.x-mol.com/paperRedirect/1834266114278010880 (accessed on 14 June 2025).
- Wang, M.; Huang, C.; Chen, Y.; Ji, Y.; Yu, D.-G.; Bligh, S.W.A. Medicated Tri-Layer Fibers Based on Cellulose Acetate and Polyvinylpyrrolidone for Enhanced Antibacterial and Wound Healing Properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 348, 122856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.-G.; He, W.; He, C.; Liu, H.; Yang, H. Versatility of Electrospun Janus Wound Dressings. Nanomedicine 2025, 20, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.-G.; Zhou, J. Electrospun Multi-Chamber Nanostructures for Sustainable Biobased Chemical Nanofibers. Next Mater. 2024, 2, 100119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Jiao, T. Recent Progress in the Strategies and Applications of Electrospinning Electroactive Tissue Engineering Scaffolds. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2025, 11, 3182–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, P.; Zong, M.-H.; Linhardt, R.J.; Feng, K.; Wu, H. Electrospinning: A Novel Nano-encapsulation Approach for Bioactive Compounds. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 70, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, P.; Wen, Y.; Zong, M.-H.; Linhardt, R.J.; Wu, H. Encapsulation of Bioactive Bompound in Electrospun Fibers and Its Potential Application. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 9161–9179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, S.C.; Estevinho, B.N.; Rocha, F. Encapsulation in Food Industry with Emerging Electrohydrodynamic Techniques: Electrospinning and Electrospraying-A Review. Food Chem. 2021, 339, 127850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.X.; Wang, M.; Lin, Y.; Xu, Q.; Kaplan, D.-L. Hydrophobic drug-triggered self-assembly of nanoparticles from silk-elastin-like protein polymers for drug delivery. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 908–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, R.; Guo, R.; Shen, M.; Cao, X.; Zhang, L.; Xu, J.; Yu, J.; Shi, X. Electrospun poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid)/halloysite nanotube composite nanofibers for drug encapsulation and sustained release. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 133, 10622–10629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Liu, Y.; He, C.; Xiong, X.; Zhang, R.; Yan, T.; Shi, S.; Yu, D.G.; Yang, H. Synergistic Improvements of Properties of Cellulose Acetate Based Curcumin@ TiO2 Nanofibers via Triaxial Electrospinning. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 506, 160117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliabbasi, N.; Mehrabi, S.; Kheirandish, M.; Gashtasbi, S.; Mokhtarian, M.; Hosseini-Isfahani, M.; Vakilinezami, A.; Vakilinezami, P.; Mostaghim, T.; Rezaeinia, H. The Novel Nano-Electrospray Delivery of Curcumin via Ultrasound Assisted Balangu (Lallemantia Royleana) Hydrocolloid-Chickpea Protein Interaction. Food Chem. 2025, 484, 144388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.-Y.; Meng, X.; Li, S.; Gan, R.-Y.; Li, Y.; Li, H.-B. Bioactivity, Health Benefits, and Related Molecular Mechanisms of Curcumin: Current Progress, Challenges, and Perspectives. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheshwari, R.K.; Singh, A.K.; Gaddipati, J.; Srimal, R.C. Multiple Biological Activities of Curcumin: A Short Review. Life Sci. 2006, 78, 2081–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xia, Y.; Gong, W.; Zhou, J.; Yu, D.-G.; Xie, Y. Electrospun Chitosan//Ethylcellulose-Vitamin E//Ethylcellulose-Curcumin Tri-Chamber Eccentric Janus Nanofibers for a Joint Antibacterial and Antioxidant Performance. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 281, 135753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, H.Y.; Williams, G.R.; Yang, H.H.; Tao, L.; Zhu, L.M. Electrospun poly (N-isopropylacrylamide)/ethyl cellulose nanofibers as thermoresponsive drug delivery systems. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 1104–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Wang, Q.; Li, G.; Qiu, Y.; Wei, Q. Electrospun water-stable zein/ethyl cellulose composite nanofiber and its drug release properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 74, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paarakh, M.P.; Jose, P.A.; Setty, C.M.; Peterchristoper, G.V. Release kinetics–concepts and applications. Int. J. Pharm. Res. Technol. 2018, 8, 12–20. [Google Scholar]
- Blaj, D.-A.; Peptu, C.A.; Balan-Porcarasu, M.; Peptu, C.; Tuchilus, C.G.; Ochiuz, L. Polymer-Free Electrospinning of β-Cyclodextrin–Oligolactide for Magnolol and Honokiol Pharmaceutical Formulations. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaskólski, M.; Paczkowska-Walendowska, M.; Miklaszewski, A.; Cielecka-Piontek, J. Ashwagandha: Optimizing the Extraction and Electrospun Nanofiber Production. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlMotawa, R.Y.; Alhamid, G.; Badran, M.M.; Orfali, R.; Alomrani, A.H.; Tawfik, E.A.; Alzahrani, D.A.; Alfassam, H.A.; Ghaffar, S.; Fathaddin, A.; et al. Co-Delivery of Dragon’s Blood and Alkanna Tinctoria Extracts Using Electrospun Nanofibers: In Vitro and In Vivo Wound Healing Evaluation in Diabetic Rat Model. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, T.; Nemadea, A.; Kumar, V. Unlocking the Power of Electrospinning: A Review of Cutting-Edge Polymers and Their Impact on Scaffold Design and Performance. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhoundiyal, S.; Sharma, A.; Alam, M.A. Fiber Technology in Drug Delivery and Pharmaceuticals. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2025, 22, 261–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, B.S.; Khan, M.; Ibrahim, N.A.; Khan, A.K.; Liaqat, R.; Ijaz, M. Smart Nanofibers in Wound Healing: Exploring Novel Combinations and Applications. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, W.; Gong, W.; Lu, Y.; Yu, D.-G.; Liu, P. Recent Progress of Electrospun Nanofibers as Burning Dressings. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 14374–14391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Freitas, C.F.; Souza, P.R.; Jacinto, G.S.; Braga, T.L.; Ricken, Y.S.; Souza, G.K.; Caetano, W.; Radovanovic, E.; Arns, C.W.; Rai, M.; et al. Silver Nanoparticles In Situ Synthesized and Incorporated in Uniaxial and Core–Shell Electrospun Nanofibers to Inhibit Coronavirus. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-S.; Huang, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, W.; Yu, D.-G.; He, H.; Liu, P.; Du, K. Electrospun Nanofibers and Their Application As Sensors for Healthcare. Front. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2025, 13, 1533367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Hou, J.; Yu, D.-G.; Li, S.; Zhu, J.; Chen, Z. Electrospun Tri-Layer Nanodepots for Sustained Release of Acyclovir. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 846, 156471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yang, X.; Yin, H.; Lu, Y.; Dou, H.; Liu, Y.; Yu, D.-G. Polymeric Nanofibers via Green Electrospinning for Safe Food Engineering. Macromol. Rapid Comm. 2025, 46, 2401152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, L.; Yu, D.-G.; Liu, L.-y. Tri-Layer Core–Shell Fibers from Coaxial Electrospinning for a Modified Release of Metronidazole. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, S.; Sahoo, J.K.; Sahoo, S.K. Electrospun MXene Based Functionalized Nanofibers for Water Pollutants Adsorption: Potentials, Challenges and Future Perspective. J. Mol. Liq. 2025, 433, 127871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, P.M.; Torres-Giner, S.; Vicente, A.A.; Cerqueira, M.A. Management of operational parameters and novel spinneret configurations for the electrohydrodynamic processing of functional polymers. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2022, 307, 2100858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghe, A.K.; Gupta, B.S. Co-axial electrospinning for nanofiber structures: Preparation and applications. Polym. Rev. 2008, 48, 353–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.G.; Li, X.Y.; Chian, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. Influence of sheath solvents on the quality of ethyl cellulose nanofibers in a coaxial electrospinning process. Bio-Med. Mater. Eng. 2014, 24, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Yu, D.-G.; Pan, D.; Liu, X.-K.; Wang, X.; Annie Bligh, S.W.; Williams, G.R. Electrospun pH-Sensitive Core–Shell Polymer Nanocomposites Fabricated Using A Triaxial Process. Acta Biomater. 2016, 35, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.Y.; Kim, J.I.; Lee, I.H. Fabrication and characterization of antimicrobial ethyl cellulose nanofibers using electrospinning techniques. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 5672–5675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wang, X.; Jiang, J.; Hou, J.; Li, Q. Internal structure of amorphous electrospun nanofiber: Oriented molecular chains. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2017, 302, 1700054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Tsai, C.W.; Hashimoto, T. Poly (vinyl alcohol) fibrils with highly oriented amorphous chains developed in electrospun nanofibers. Macromolecules 2024, 57, 2191–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Pyda, M.; Mao, B.; Cebe, P. Relationship between the rigid amorphous phase and mesophase in electrospun fibers. Polymer 2013, 54, 2544–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, S.; Bahners, T.; Gutmann, J.S.; Gao, S.L.; Mäder, E.; Fuchsluger, T.A. Characterization of Structural, Mechanical and Nano-Mechanical Properties of Electrospun PGS/PCL Fibers. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 16951–16957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, F.L.; Shearman, G.C.; Gaisford, S.; Williams, G.R. Amorphous Formulations of Indomethacin and Griseofulvin Prepared by Electrospinning. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 4327–4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.F.; Wang, L.Z.; Gong, W.J.; Wang, B.; Yu, D.G.; Zhu, Y.J. Correction: Zhou et al. Integrating Chinese Herbs and Western Medicine for New Wound Dressings Through Handheld Electrospinning. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, M.; Yu, D.G.; Geraldes, C.F.G.C.; Williams, G.R.; Bligh, S.W.A. Correction to Theranostic Fibers for Simultaneous Imaging and Drug Delivery. Mol. Pharm. 2025, 22, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Vazquez, B.; Amaral, A.J.R.; Yu, D.G.; Pasparakis, G.; Williams, G.R. Correction: Electrosprayed Janus Particles for Combined Photo-Chemotherapy. AAPS PharmSciTech 2025, 26, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, H.; Zhou, J.; Yan, L.; Zhang, S.; Yu, D.-G. Correction: Hybrid Films Loaded with 5-Fuorouracil and Reglan for Synergistic Treatment of Colon Cancer via Asynchronous Dual-Drug Delivery. Front. Bioeng. Biotech. 2025, 13, 1597014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Dai, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, P.; Zhou, W.; Yu, D.-G.; Ge, R. Corrigendum: Fast and Convenient Delivery of Fluidextracts Liquorice Through Electrospun Core-shell Nanohybrids. Front. Bioeng. Biotech. 2025, 13, 1596937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paaver, U.; Heinämäki, J.; Laidmäe, I.; Lust, A.; Kozlova, J.; Sillaste, E.; Kogermann, K. Electrospun nanofibers as a potential controlled-release solid dispersion system for poorly water-soluble drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 479, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.M.; Mondal, M.I.H. Carboxymethyl cellulose/polyvinylpyrrolidone bio-composite hydrogels enriched with clove bud extracts for enhanced wound healing. Arab. J. Chem. 2024, 17, 105945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Gong, W.; Guo, Q.; Liu, H.; Yu, D.-G. Synergistic Effects of Radical Distributions of Soluble and Insoluble Polymers within Electrospun Nanofibers for an Extending Release of Ferulic Acid. Polymers 2024, 16, 2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Guo, S.; Hong, S.; Piao, J.; Piao, M. Transdermal Drug Delivery System of Linagliptin Sustained-Release Microparticle Gels: In Vitro Characterization and In Vivo Evaluation. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2024, 21, 1536–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Gong, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Yu, D.-G.; Yi, T. Reverse Gradient Distributions of Drug and Polymer Molecules within Electrospun Core–Shell Nanofibers for Sustained Release. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Zhu, S.; Song, J.; Li, X.; Li, C.; Hou, G.; Gao, Z. Cirsium Setosum Extract-Loaded Hybrid Nanostructured Scaffolds Incorporating A Temperature-Sensitive Polymer for Mechanically Assisted Wound Healing. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodoulou, E.; Chondromatidou, A.; Bikiaris, N.D.; Balla, E.; Vlachou, M.; Barmpalexis, P.; Bikiaris, D.N. PLA-Based Electrospun Nanofibrous Mats Towards Application as Antibiotic Carriers: Processing Parameters, Fabrication and Characterization. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Yang, W.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, S.; Yu, D.-G.; Liu, P. Engineered Beads-on-A-String Nanocomposites for An Improved Drug Fast-Sustained Bi-Stage Release. Nanocomposites 2024, 10, 240–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhuang, J.; Wu, X.; Shen, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W. Preparation of the Chitosan/Poly-γ-Glutamic Acid/Glabrid in Hybrid Sanoparticles and Study on Its Releasing Property. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2023, 20, 1195–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcuello, C.; Chabbert, L.F.B.; Aguié-Béghin, V.; Molinari, M. Atomic Force Microscopy Reveals How Relative Humidity Impacts the Young’s Modulus of Lignocellulosic Polymers and Their Adhesion with Cellulose Nanocrystals At the Nanoscale. Int. J. Biolog. Macromol. 2020, 147, 1064–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Zhang, M.; Shen, J.; He, Z.; Fatehi, P.; Ni, Y. Applications of Cellulose-based Materials in Sustained Drug Delivery Systems. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 2485–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doustgani, A. Doxorubicin Release from Optimized Electrospun Polylactic Acid Nanofibers. J. Ind. Text. 2017, 47, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hathout, R.M.; Kassem, D.H. Positively Charged Electroceutical Spun Chitosan Nanofibers Can Protect Health Care Providers From COVID-19 Infection: An Opinion. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, S.; Xiang, C.; Liu, Z.; Tong, G.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, X. Bio-Inspired, Robust, and Anti-Swelling Hydrogel Sensors for Underwater Information Transmission. J. Mater. Chem. C 2024, 12, 8813–8824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wu, L.; Ge, M.; Wang, X.; Ren, N.; Sun, H.; Zhu, X. Reactive Molecular Simulation with Size Extrapolation to Bridge the Polymerization Mechanism and Kinetics. Macromolecules 2024, 57, 4285–4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wu, X.; Ding, X. One-Step Side-by-Side Electrospraying of Janus Particles for Durable Multifunctional Coatings on Cotton Textiles. Colloid. Surf. A 2025, 710, 136227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Yue, G.; Li, S.; Liu, J.; Li, H.; Gao, Y.; Liu, J.; Hou, L.; Liu, X.; Cui, Z.; et al. Fabrication and Applications of Multi-Fluidic Electrospinning Multi-Structure Hollow and Core–Shell Nanofibers. Engineering 2022, 13, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brimo, N.; Serdaroğlu, D.Ç.; Uyar, T.; Uysal, B.; Çakıcı, E.B.; Dikmen, M.; Canturk, Z. Novel Electrospun Polymeric Nanofibers Loaded Different Medicaments as Drug Delivery Systems for Regenerative Endodontics. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2023, 20, 992–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, I.S. Controlled Drug Release from Nanoengineered Polysaccharides. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, J.; Fang, B.; Ying, Y.; Yu, D.G.; He, H. Three EHDA Processes from a Detachable Spinneret for Fabricating Drug Fast Dissolution Composites. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2024, 309, 2300361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
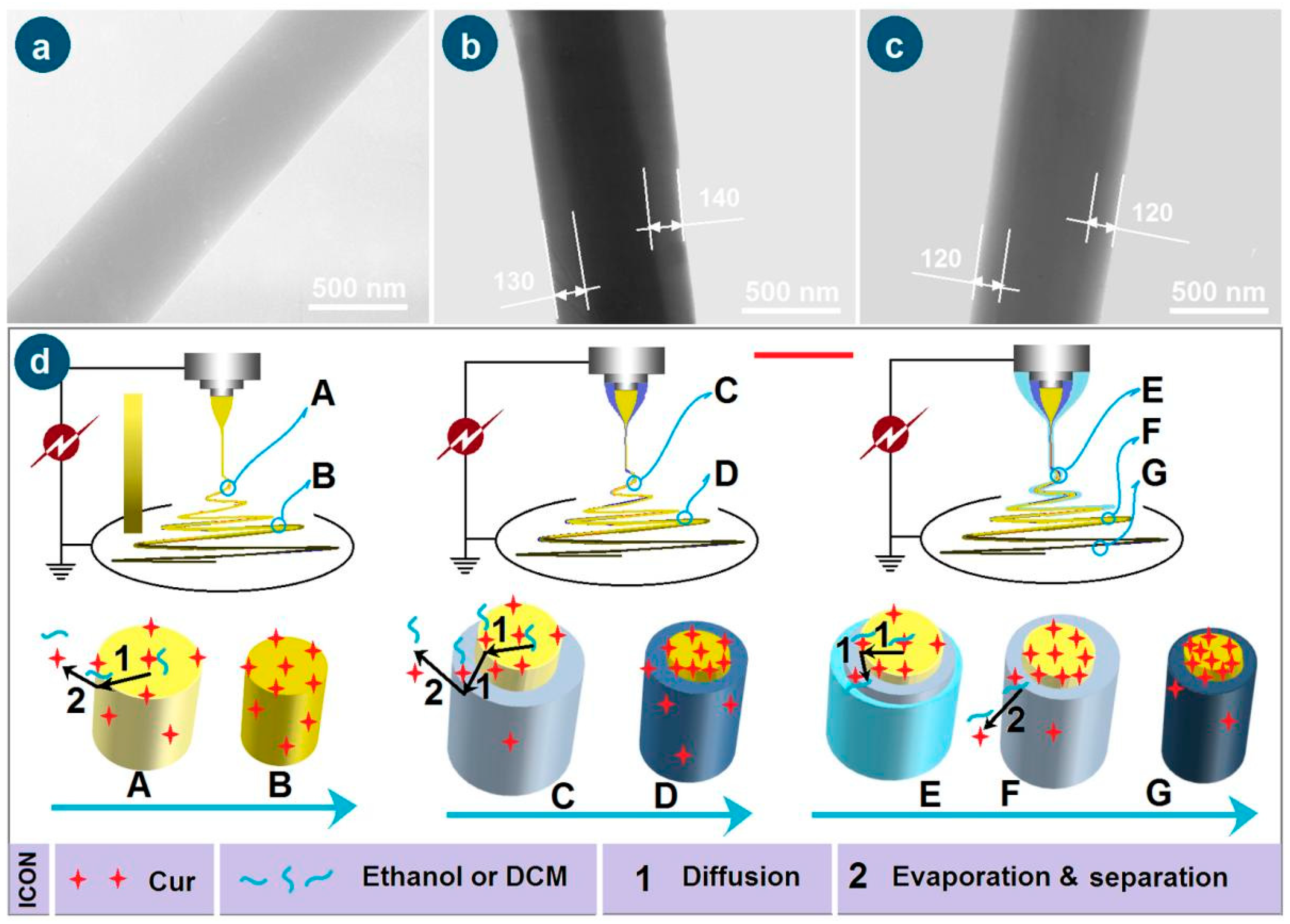
| No. | Working Process | Working Fluid/Flow Rate (mL/h) | Cur Content a (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outer | Middle | Inner | |||
| F1 | Single-fluid blending | ---- | ---- | Fluid 1/3.0 | 11.1% |
| F2 | Coaxial | ---- | Fluid 2/1.2 | Fluid 1/3.0 | 9.0% |
| F3 | Modified triaxial | Ethanol/0.5 | Fluid 3/0.8 | Fluid 1/3.0 | 9.0% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Lu, Y.; Liu, H.; Yu, D.-G.; Bligh, S.-W.A. A Modified Triaxial Electrospinning for a High Drug Encapsulation Efficiency of Curcumin in Ethylcellulose. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1152. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17091152
Yang X, Wang Q, Zhu Z, Lu Y, Liu H, Yu D-G, Bligh S-WA. A Modified Triaxial Electrospinning for a High Drug Encapsulation Efficiency of Curcumin in Ethylcellulose. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(9):1152. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17091152
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Xingjian, Qiling Wang, Zhirun Zhu, Yi Lu, Hui Liu, Deng-Guang Yu, and Sim-Wan Annie Bligh. 2025. "A Modified Triaxial Electrospinning for a High Drug Encapsulation Efficiency of Curcumin in Ethylcellulose" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 9: 1152. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17091152
APA StyleYang, X., Wang, Q., Zhu, Z., Lu, Y., Liu, H., Yu, D.-G., & Bligh, S.-W. A. (2025). A Modified Triaxial Electrospinning for a High Drug Encapsulation Efficiency of Curcumin in Ethylcellulose. Pharmaceutics, 17(9), 1152. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17091152









