Therapeutic Effects of Intranasal Administration of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Secretome in Rats Exposed to Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Outline of the Study
2.3. Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress (CUMS) Procedure
2.4. Behavioral Tests
2.5. Determination of Global Depression Score
2.6. Isolation, Expansion and Characterization of Human AD-MSCs
2.7. Preconditioning of hAD-MSCs and Secretome Generation
2.8. Evaluation of mRNA Levels of Neuroprotective and Anti-Inflammatory Factors in Preconditioned hAD-MSCs
2.9. MSC-Secretome Intranasal Administration
2.10. Immunohistofluorescense and Microscopy Image Analysis
2.11. Gene Expression Analysis
2.12. Statistical Analysis and Sample Size Determination
3. Results
3.1. hAD-MSC Preconditioning to Improve the Production of Neuroprotective and Anti-Inflammatory Factors
3.2. Neurovegetative and Behavioral Evaluations
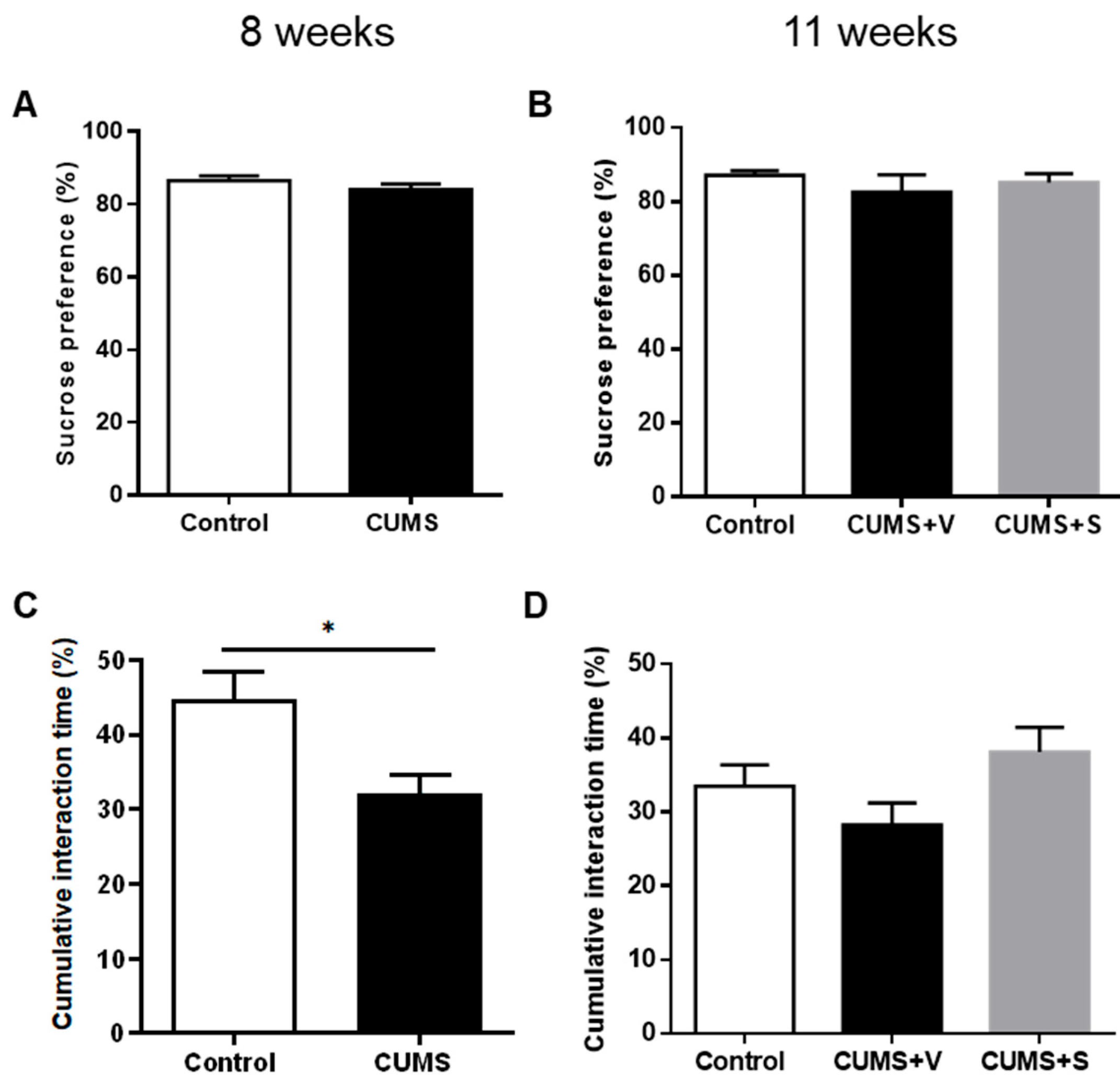
3.3. Changes in Hedonic-Driven Behaviors
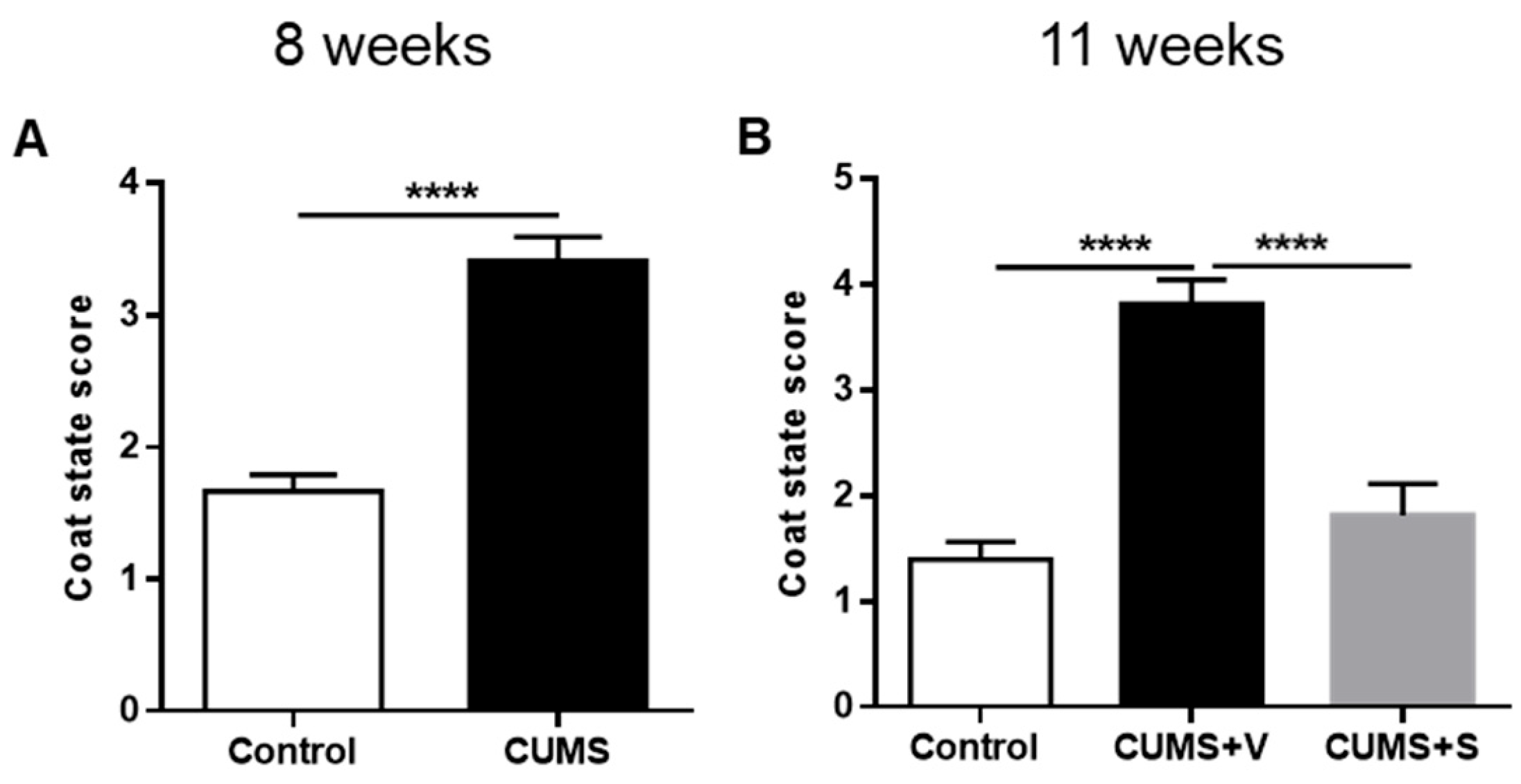
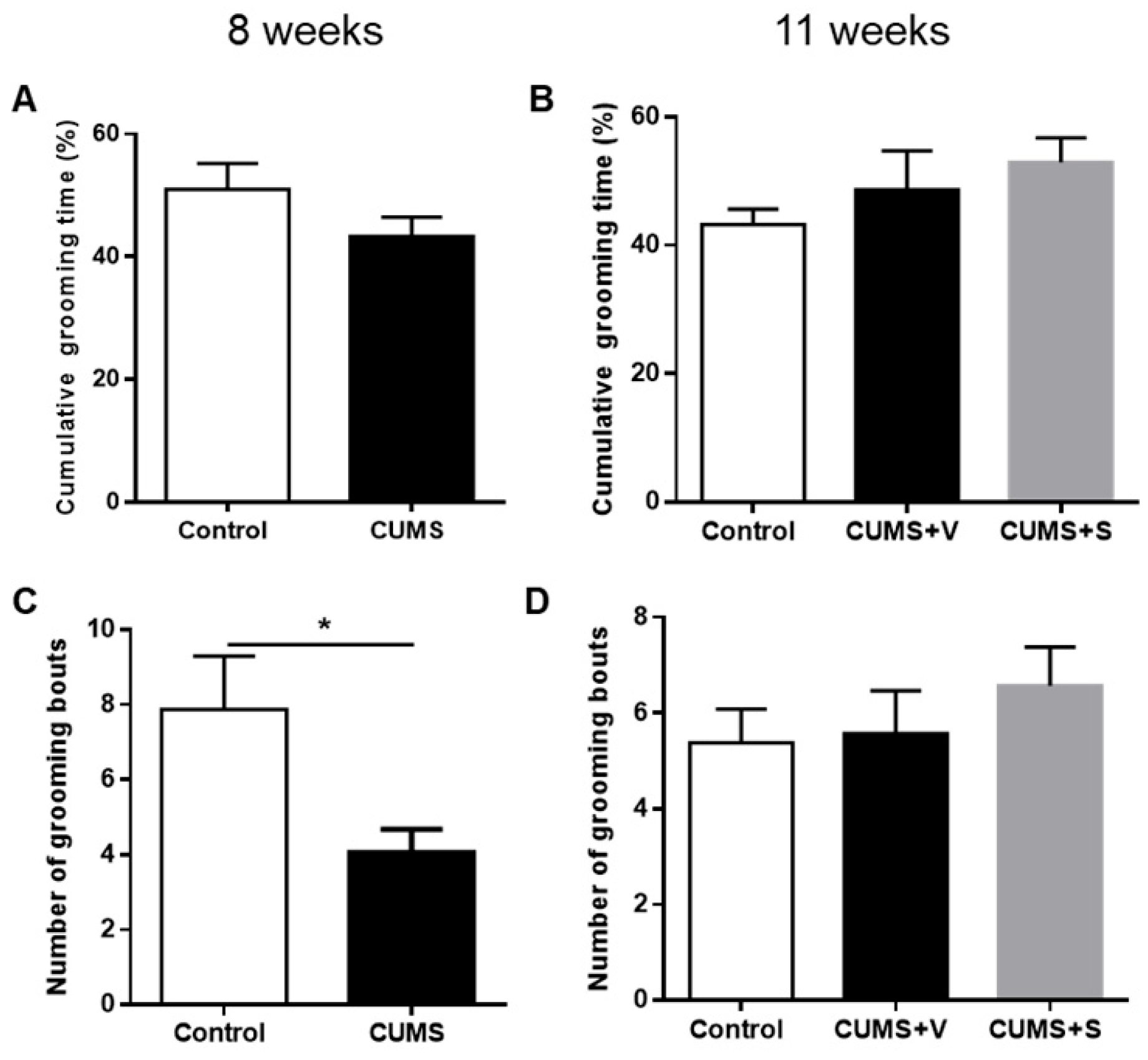
3.4. Changes in Self-Care-Related Outcomes
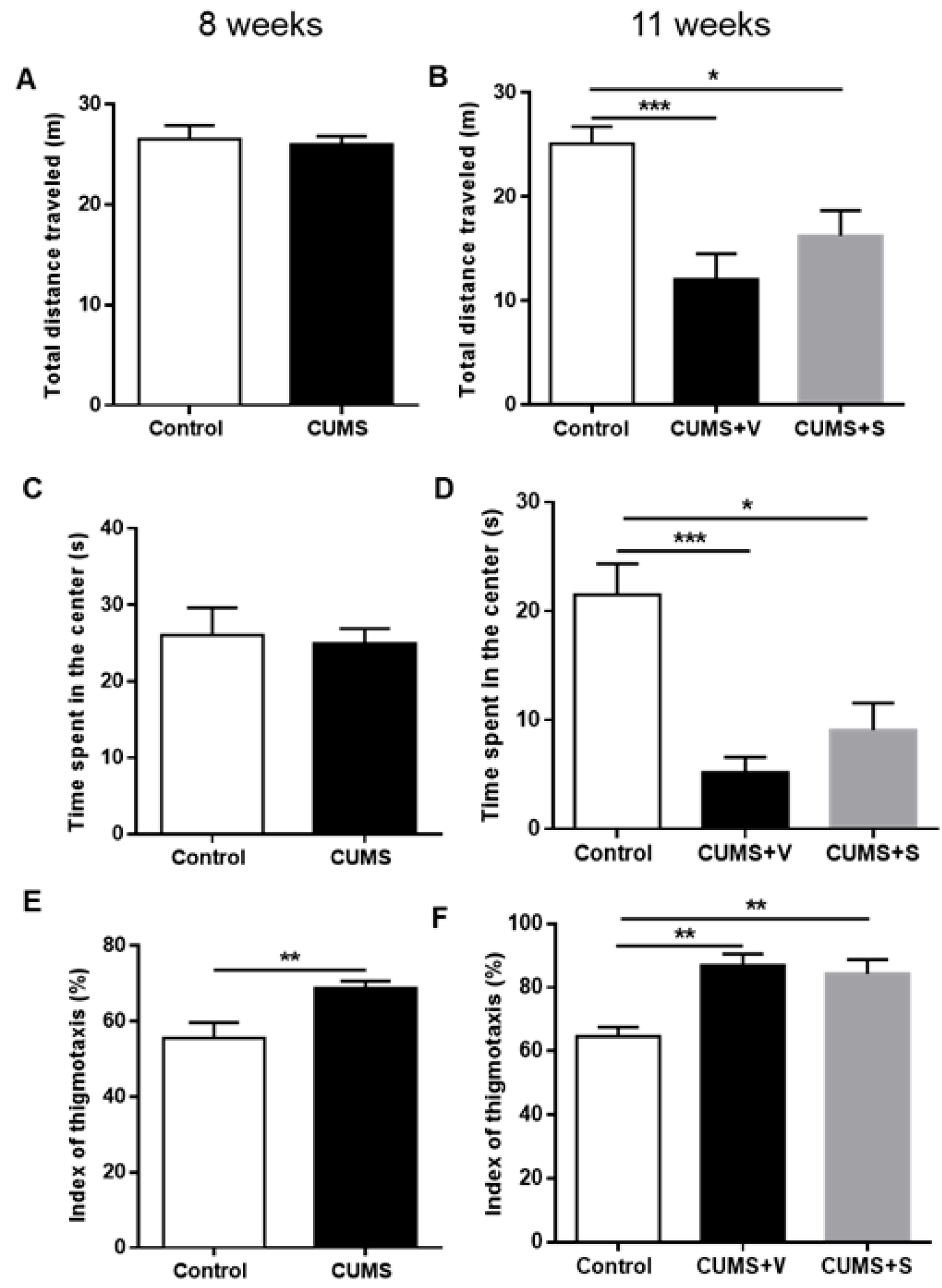
3.5. Changes in Anxiety-Related Outcomes
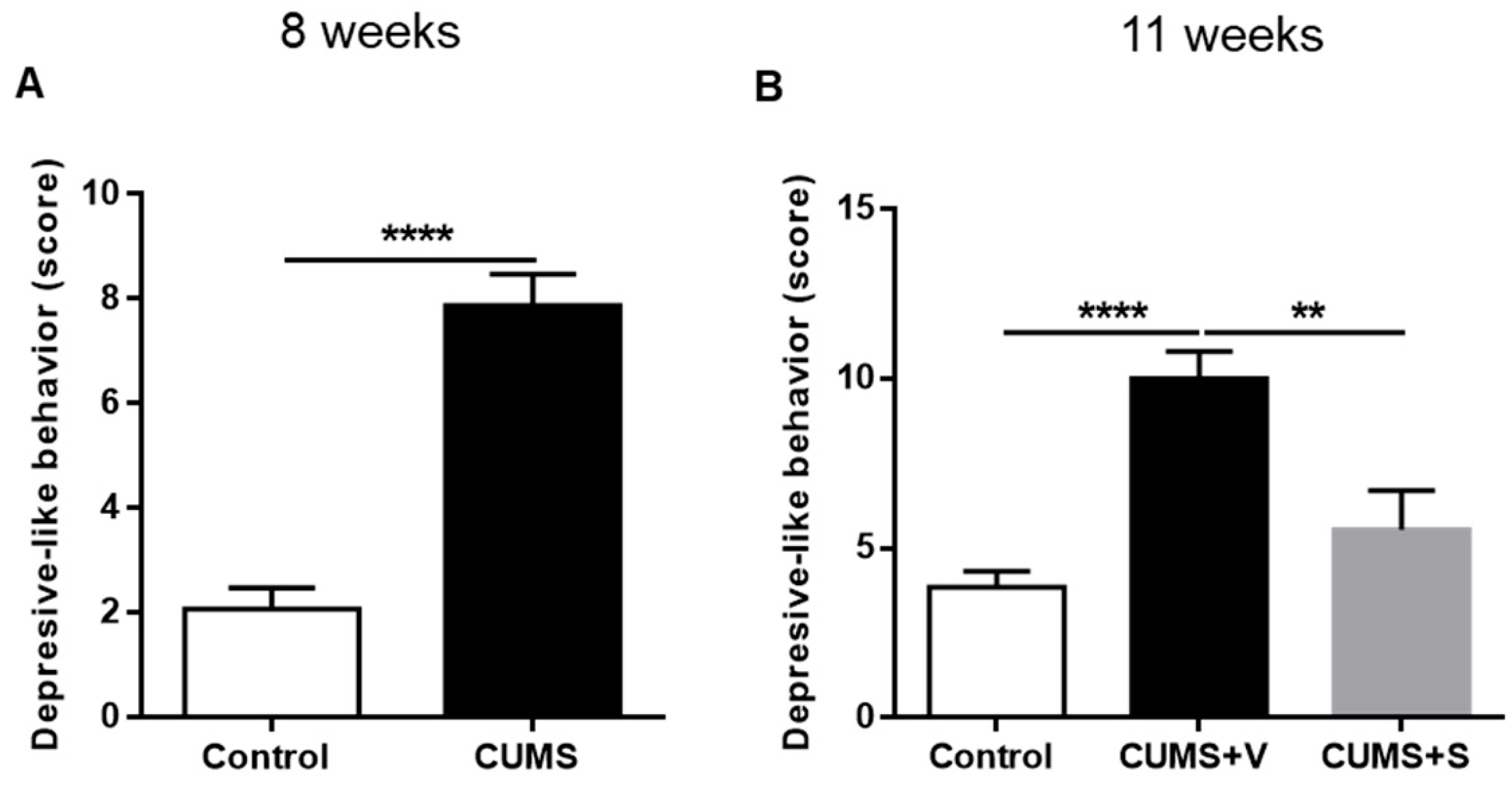
3.6. Global Score of Depression-Related Behavior
3.7. Evaluation of Proinflammatory Factor Levels in the Frontal Cortex and the Hippocampus
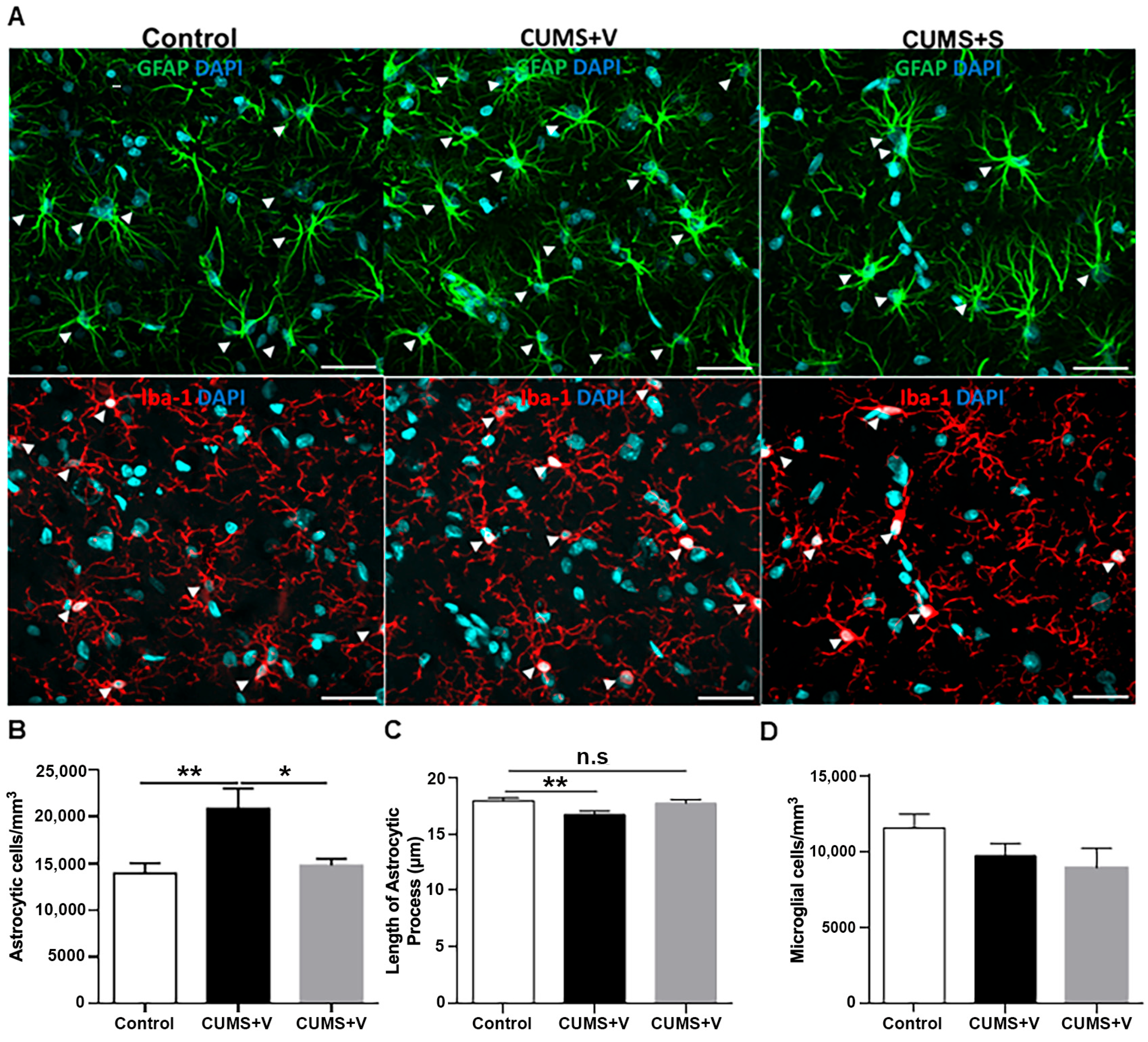
3.8. Evaluation of Astrocytic Density, Microglial Density and Astrocyte Processes in the CA1 Region of the Hippocampus
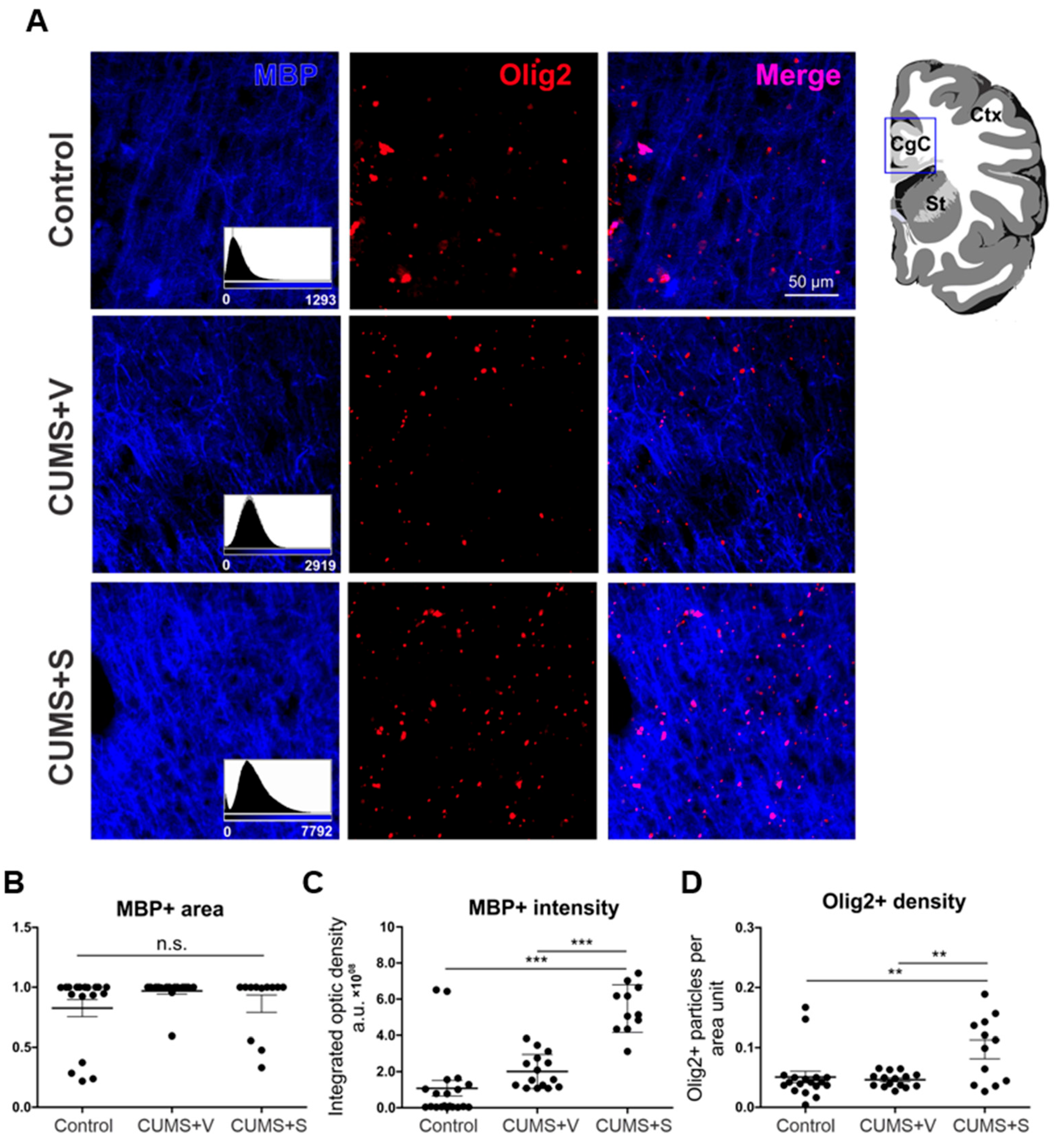
3.9. Myelination Evaluation
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BDNF | Brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| BSA | Bobine serum albumin |
| bFGF | Basic fibroblast growth factor |
| CS | Coat status |
| CUMS | Chronic unpredictable mild stress |
| DAPI | 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| FUST | Female urine sniffing test |
| GFAP | Glial fibrillary acidic protein |
| h-AD-MSC | Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells |
| HP | Hippocampus |
| Iba-1 | Ionized calcium-binding adaptor molecule-1 |
| IDO | Indoleamine 2-3 dioxygenase |
| IFN-γ | Interferon gamma |
| IL-1b | Interleukin 1b |
| IL-5 | Interleukin 5 |
| IL-6 | Interleukin 6 |
| IL-10 | Interleukin 10 |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| MBP | Myelin binding protein |
| MSCs | Mesenchymal stem cells |
| NGF | Neural growth factor |
| NGS | Normal goat serum |
| OFT | Open field test |
| OPC | Oligodendrocyte precursor cell |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| PFA | Paraformaldehyde |
| PFC | Prefrontal cortex |
| SPT | Sucrose preference test |
| SST | Sucrose splash test |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor alfa |
| TSG-6 | Tumor necrosis factor-stimulated gene 6 |
| VEGF-a | Vascular endothelial growth factor a |
| vmPFC | Ventromedial prefrontal cortex |
References
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders; American Psychiatric Association Publishing: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, T.; Barber, R.M.; Bell, B.; Bertozzi-Villa, A.; Biryukov, S.; Bolliger, I.; Charlson, F.; Davis, A.; Degenhardt, L.; Dicker, D.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Incidence, Prevalence, and Years Lived with Disability for 301 Acute and Chronic Diseases and Injuries in 188 Countries, 1990–2013: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2015, 386, 743–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K. Mental Health: A World of Depression. Nature 2014, 515, 180–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteford, H.A.; Degenhardt, L.; Rehm, J.; Baxter, A.J.; Ferrari, A.J.; Erskine, H.E.; Charlson, F.J.; Norman, R.E.; Flaxman, A.D.; Johns, N.; et al. Global Burden of Disease Attributable to Mental and Substance Use Disorders: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2013, 382, 1575–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Undurraga, J.; Baldessarini, R.J. Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trials of Antidepressants for Acute Major Depression: Thirty-Year Meta-Analytic Review. Neuropsychopharmacology 2012, 37, 851–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schildkraut, J.J. The catecholamine hypothesis of affective Disorders: A review of supporting evidence. Am. J. Psychiatry 1965, 122, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirschfeld, R.M. History and Evolution of the Monoamine Hypothesis of Depression. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2000, 61 (Suppl. 6), 4–6. [Google Scholar]
- Mahar, I.; Rodriguez Bambico, F.; Mechawar, N.; Nobrega, J.N. Stress, Serotonin, and Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Relation to Depression and Antidepressant Effects. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2014, 38, 173–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micheli, L.; Ceccarelli, M.; D’Andrea, G.; Tirone, F. Depression and Adult Neurogenesis: Positive Effects of the Antidepressant Fluoxetine and of Physical Exercise. Brain Res. Bull. 2018, 143, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliwa, H.; Belzung, C.; Surget, A. Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis: Is It the Alpha and Omega of Antidepressant Action? Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 141, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santarelli, L.; Saxe, M.; Gross, C.; Surget, A.; Battaglia, F.; Dulawa, S.; Weisstaub, N.; Lee, J.; Duman, R.; Arancio, O.; et al. Requirement of Hippocampal Neurogenesis for the Behavioral Effects of Antidepressants. Science 2003, 301, 805–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surget, A.; Saxe, M.; Leman, S.; Ibarguen-Vargas, Y.; Chalon, S.; Griebel, G.; Hen, R.; Belzung, C. Drug-Dependent Requirement of Hippocampal Neurogenesis in a Model of Depression and of Antidepressant Reversal. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 64, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bierhaus, A.; Wolf, J.; Andrassy, M.; Rohleder, N.; Humpert, P.M.; Petrov, D.; Ferstl, R.; von Eynatten, M.; Wendt, T.; Rudofsky, G.; et al. A Mechanism Converting Psychosocial Stress into Mononuclear Cell Activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 1920–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slavich, G.M.; Irwin, M.R. From Stress to Inflammation and Major Depressive Disorder: A Social Signal Transduction Theory of Depression. Psychol. Bull. 2014, 140, 774–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beurel, E.; Toups, F.; Nemeroff, C.B. The Bidirectional Relationship of Depression and Inflammation: Double Trouble. Neuron 2020, 107, 234–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumeister, D.; Akhtar, R.; Ciufolini, S.; Pariante, C.M.; Mondelli, V. Childhood Trauma and Adulthood Inflammation: A Meta-Analysis of Peripheral C-Reactive Protein, Interleukin-6 and Tumour Necrosis Factor-α. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Ji, M.-H.; Li, S.-M.; Li, B.; Mei, L.; Yang, J.-J. Systemic Inflammation Impairs Mood Function by Disrupting the Resting-State Functional Network in a Rat Animal Model Induced by Lipopolysaccharide Challenge. Mediat. Inflamm. 2019, 2019, 6212934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felger, J.C.; Li, Z.; Haroon, E.; Woolwine, B.J.; Jung, M.Y.; Hu, X.; Miller, A.H. Inflammation Is Associated with Decreased Functional Connectivity within Corticostriatal Reward Circuitry in Depression. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 1358–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Xu, X.; Chen, G.; Mehta, N.D.; Haroon, E.; Miller, A.H.; Luo, Y.; Li, Z.; Felger, J.C. Inflammation and Decreased Functional Connectivity in a Widely-Distributed Network in Depression: Centralized Effects in the Ventral Medial Prefrontal Cortex. Brain Behav. Immun. 2019, 80, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prockop, D.J.; Youn Oh, J. Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells (MSCs): Role as Guardians of Inflammation. Mol. Ther. 2012, 20, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezquer, F.; Morales, P.; Quintanilla, M.E.; Santapau, D.; Lespay-Rebolledo, C.; Ezquer, M.; Herrera-Marschitz, M.; Israel, Y. Intravenous Administration of Anti-Inflammatory Mesenchymal Stem Cell Spheroids Reduces Chronic Alcohol Intake and Abolishes Binge-Drinking. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrowska, S.; Andrzejewska, A.; Lukomska, B.; Janowski, M. Neuroinflammation as a Target for Treatment of Stroke Using Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Extracellular Vesicles. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doeppner, T.R.; Herz, J.; Görgens, A.; Schlechter, J.; Ludwig, A.-K.; Radtke, S.; de Miroschedji, K.; Horn, P.A.; Giebel, B.; Hermann, D.M. Extracellular Vesicles Improve Post-Stroke Neuroregeneration and Prevent Postischemic Immunosuppression. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2015, 4, 1131–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomi, G.; Surbek, D.; Haesler, V.; Joerger-Messerli, M.; Schoeberlein, A. Exosomes Derived from Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Reduce Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation in Perinatal Brain Injury. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farfán, N.; Carril, J.; Redel, M.; Zamorano, M.; Araya, M.; Monzón, E.; Alvarado, R.; Contreras, N.; Tapia-Bustos, A.; Quintanilla, M.E.; et al. Intranasal Administration of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome Reduces Hippocampal Oxidative Stress, Neuroinflammation and Cell Death, Improving the Behavioral Outcome Following Perinatal Asphyxia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzini, L.; Vescovi, A.; Cantello, R.; Gelati, M.; Vercelli, A. Stem Cells Therapy for ALS. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2016, 16, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, M.; Mayilsamy, K.; Mohapatra, S.S.; Mohapatra, S. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for the Treatment of Traumatic Brain Injury: Progress and Prospects. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 30, 839–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genc, B.; Bozan, H.R.; Genc, S.; Genc, K. Stem Cell Therapy for Multiple Sclerosis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1084, 145–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Liu, N.; Sun, N.; Zhang, K.; Yu, L. Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Their Exosomes: Promising Therapeutics for Chronic Pain. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 14, 644–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Huang, W.; Yi, J.; Deng, Y.; Li, R.; Chen, J.; Shi, J.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, T.; Chen, X.; et al. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Alleviate Depressive and Anxiety-like Behaviors via a Lung Vagal-to-Brain Axis in Male Mice. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICD-10 Version: 2016. Available online: https://icd.who.int/browse10/2016/en#/F32.0 (accessed on 16 August 2025).
- Mieske, P.; Hobbiesiefken, U.; Fischer-Tenhagen, C.; Heinl, C.; Hohlbaum, K.; Kahnau, P.; Meier, J.; Wilzopolski, J.; Butzke, D.; Rudeck, J.; et al. Bored at Home?—A Systematic Review on the Effect of Environmental Enrichment on the Welfare of Laboratory Rats and Mice. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 899219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardi, Z.; Albrecht, A.; Richter-Levin, A.; Saha, R.; Richter-Levin, G. Behavioral Profiling as a Translational Approach in an Animal Model of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder. Neurobiol. Dis. 2016, 88, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oses, C.; Olivares, B.; Ezquer, M.; Acosta, C.; Bosch, P.; Donoso, M.; Léniz, P.; Ezquer, F. Preconditioning of Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells with Deferoxamine Increases the Production of pro-Angiogenic, Neuroprotective and Anti-Inflammatory Factors: Potential Application in the Treatment of Diabetic Neuropathy. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintanilla, M.E.; Ezquer, F.; Morales, P.; Santapau, D.; Berríos-Cárcamo, P.; Ezquer, M.; Herrera-Marschitz, M.; Israel, Y. Intranasal Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome Administration Markedly Inhibits Alcohol and Nicotine Self-Administration and Blocks Relapse-Intake: Mechanism and Translational Options. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz, F.C.; Habermacher, C.; Graciarena, M.; Houry, P.Y.; Nishiyama, A.; Oumesmar, B.N.; Angulo, M.C. Neuronal Activity in Vivo Enhances Functional Myelin Repair. JCI Insight 2019, 5, e123434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.L.; De Gregorio, C.; Silva, V.; Elorza, Á.A.; Léniz, P.; Aliaga-Tobar, V.; Maracaja-Coutinho, V.; Budini, M.; Ezquer, F.; Ezquer, M. Administration of Secretome Derived from Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Induces Hepatoprotective Effects in Models of Idiosyncratic Drug-Induced Liver Injury Caused by Amiodarone or Tamoxifen. Cells 2023, 12, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gregorio, C.; Contador, D.; Diáz, D.; Cárcamo, C.; Santapau, D.; Lobos-Gonzalez, L.; Acosta, C.; Campero, M.; Carpio, D.; Gabriele, C.; et al. Human Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Conditioned Medium Ameliorates Polyneuropathy and Foot Ulceration in Diabetic BKS Db/Db Mice. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Reekum, R.; Donald, F.R.C.P.C.; Stuss, T.L.; Ostrander, R.N. Apathy: Why Care? J. Neuropsychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2005, 17, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhi, G.S.; Mann, J.J. Depression. Lancet 2018, 392, 2299–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faries, D.; Herrera, J.; Rayamajhi, J.; Debrota, D.; Demitrack, M.; Potter, W.Z. The Responsiveness of the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2000, 34, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.-Y.; Wang, H.-Q.; Wang, Z.-Z.; Chen, N.-H. Linking Depression and Neuroinflammation: Crosstalk between Glial Cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2025, 995, 177408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Fang, Z.; Wu, C.; Xu, H.; Huang, Q.J. Changes in Proinflammatory Cytokines and White Matter in Chronically Stressed Rats. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2015, 11, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sahel, A.; Ortiz, F.C.; Kerninon, C.; Maldonado, P.P.; Angulo, M.C.; Nait-Oumesmar, B. Alteration of Synaptic Connectivity of Oligodendrocyte Precursor Cells Following Demyelination. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortolani, D.; Manot-Saillet, B.; Orduz, D.; Ortiz, F.C.; Angulo, M.C. In Vivo Optogenetic Approach to Study Neuron-Oligodendroglia Interactions in Mouse Pups. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noronha Nc, N.D.C.; Mizukami, A.; Caliári-Oliveira, C.; Cominal, J.G.; Rocha, J.L.M.; Covas, D.T.; Swiech, K.; Malmegrim, K.C.R. Priming Approaches to Improve the Efficacy of Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Based Therapies. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-García, L.; Castro-Manrreza, M.E. TNF-α and IFN-γ Participate in Improving the Immunoregulatory Capacity of Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells: Importance of Cell–Cell Contact and Extracellular Vesicles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezquer, F.; Quintanilla, M.E.; Morales, P.; Santapau, D.; Ezquer, M.; Kogan, M.J.; Salas-Huenuleo, E.; Herrera-Marschitz, M.; Israel, Y. Intranasal Delivery of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Reduces Oxidative Stress and Markedly Inhibits Ethanol Consumption and Post-Deprivation Relapse Drinking. Addict. Biol. 2019, 24, 994–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrowska, S.; Andrzejewska, A.; Janowski, M.; Lukomska, B. Immunomodulatory and Regenerative Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Extracellular Vesicles: Therapeutic Outlook for Inflammatory and Degenerative Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 591065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drobiova, H.; Sindhu, S.; Ahmad, R.; Haddad, D.; Al-Mulla, F.; Al Madhoun, A. Wharton’s Jelly Mesenchymal Stem Cells: A Concise Review of Their Secretome and Prospective Clinical Applications. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1211217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quezada, M.; Ponce, C.; Berríos-Cárcamo, P.; Santapau, D.; Gallardo, J.; De Gregorio, C.; Quintanilla, M.E.; Morales, P.; Ezquer, M.; Herrera-Marschitz, M.; et al. Amelioration of Morphine Withdrawal Syndrome by Systemic and Intranasal Administration of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Secretome in Preclinical Models of Morphine Dependence. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2024, 30, e14517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carragher, N.; Adamson, G.; Bunting, B.; McCann, S. Subtypes of Depression in a Nationally Representative Sample. J. Affect. Disord. 2009, 113, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juruena, M.F.; Bocharova, M.; Agustini, B.; Young, A.H. Atypical Depression and Non-Atypical Depression: Is HPA Axis Function a Biomarker? A Systematic Review. J. Affect. Disord. 2018, 233, 45–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, F.; Riglin, L.; Lomax, T.; Souter, E.; Potter, R.; Smith, D.J.; Thapar, A.K.; Thapar, A. Adolescent and Adult Differences in Major Depression Symptom Profiles. J. Affect. Disord. 2019, 243, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willner, P.; Gruca, P.; Lason, M.; Tota-Glowczyk, K.; Litwa, E.; Niemczyk, M.; Papp, M. Validation of Chronic Mild Stress in the Wistar-Kyoto Rat as an Animal Model of Treatment-Resistant Depression. Behav. Pharmacol. 2019, 30, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payne, J.L.; Palmer, J.T.; Joffe, H. A Reproductive Subtype of Depression: Conceptualizing Models and Moving toward Etiology. Harv. Rev. Psychiatry 2009, 17, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinzmann, J.M.; Kloiber, S.; Ebling-Mattos, G.; Bielohuby, M.; Schmidt, M.V.; Palme, R.; Holsboer, F.; Uhr, M.; Ising, M.; Touma, C. Mice Selected for Extremes in Stress Reactivity Reveal Key Endophenotypes of Major Depression: A Translational Approach. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2014, 49, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilloux, J.P.; Seney, M.; Edgar, N.; Sibille, E. Integrated Behavioral Z-Scoring Increases the Sensitivity and Reliability of Behavioral Phenotyping in Mice: Relevance to Emotionality and Sex. J. Neurosci. Methods 2011, 197, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraeuter, A.K. The Use of Integrated Behavioural Z-Scoring in Behavioural Neuroscience—A Perspective Article. J. Neurosci. Methods 2023, 384, 109751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequeira-Cordero, A.; Salas-Bastos, A.; Fornaguera, J.; Brenes, J.C. Behavioural Characterisation of Chronic Unpredictable Stress Based on Ethologically Relevant Paradigms in Rats. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batt, M.M.; Duffy, K.A.; Novick, A.M.; Metcalf, C.A.; Epperson, C.N. Is Postpartum Depression Different From Depression Occurring Outside of the Perinatal Period? A Review of the Evidence. Focus (Am. Psychiatr. Publ.) 2020, 18, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thom, R.; Silbersweig, D.A.; Boland, R.J. Major Depressive Disorder in Medical Illness: A Review of Assessment, Prevalence, and Treatment Options. Psychosom. Med. 2019, 81, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vares, E.A.; Salum, G.A.; Spanemberg, L.; Caldieraro, M.A.; De Souza, L.H.; Borges, R.D.P.; Fleck, M.P. Childhood Trauma and Dimensions of Depression: A Specific Association with the Cognitive Domain. Braz. J. Psychiatry 2015, 38, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacerda-Pinheiro, S.F.; Pinheiro Junior, R.F.F.; De Lima, M.A.P.; Da Silva, C.G.L.; Dos Santos, M.D.S.V.; Teixeira Júnior, A.G.; De Oliveira, P.N.L.; Ribeiro, K.D.B.; Rolim-Neto, M.L.; Bianco, B.A.V. Are There Depression and Anxiety Genetic Markers and Mutations? A Systematic Review. J. Affect. Disord. 2014, 168, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnevali, L.; Montano, N.; Tobaldini, E.; Thayer, J.F.; Sgoifo, A. The Contagion of Social Defeat Stress: Insights from Rodent Studies. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2020, 111, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angst, J. Sexual Problems in Healthy and Depressed Persons. Int. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 1998, 13 (Suppl. 6), S1–S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atmaca, M. Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor-Induced Sexual Dysfunction: Current Management Perspectives. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2020, 16, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serretti, A.; Chiesa, A. Treatment-Emergent Sexual Dysfunction Related to Antidepressants: A Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2009, 29, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Luo, Y.; Wang, H.; Kuang, S.; Liang, G.; Yang, Y.; Mai, S.; Yang, J. Re-Evaluation of the Interrelationships among the Behavioral Tests in Rats Exposed to Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, A.Q.; Gao, B.; Fan, J.J.; Zhu, Y.J.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Y.L.; Xu, L.Z.; Wu, W.N.; Wu, W.N. NLRP1 Inflammasome Contributes to Chronic Stress-Induced Depressive-like Behaviors in Mice. J. Neuroinflam. 2020, 17, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beurel, E.; Jope, R.S. Inflammation and Lithium: Clues to Mechanisms Contributing to Suicide-Linked Traits. Transl. Psychiatry 2014, 4, e488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troubat, R.; Barone, P.; Leman, S.; Desmidt, T.; Cressant, A.; Atanasova, B.; Brizard, B.; El Hage, W.; Surget, A.; Belzung, C.; et al. Neuroinflammation and Depression: A Review. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2021, 53, 151–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzog, S.; Bartlett, E.A.; Zanderigo, F.; Galfalvy, H.C.; Burke, A.; Mintz, A.; Schmidt, M.; Hauser, E.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Melhem, N.; et al. Neuroinflammation, Stress-Related Suicidal Ideation, and Negative Mood in Depression. JAMA Psychiatry 2025, 82, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamberlain, S.R.; Cavanagh, J.; De Boer, P.; Mondelli, V.; Jones, D.N.C.; Drevets, W.C.; Cowen, P.J.; Harrison, N.A.; Pointon, L.; Pariante, C.M.; et al. Treatment-Resistant Depression and Peripheral C-Reactive Protein. Br. J. Psychiatry 2019, 214, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Björkholm, C.; Monteggia, L.M. BDNF—A Key Transducer of Antidepressant Effects. Neuropharmacology 2016, 102, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Gao, L.N.; Song, X.J.; Dong, Q.W.; Chen, Y.B.; Cui, Y.L.; Wang, Q. Enhanced Antidepressant Effects of BDNF-Quercetin Alginate Nanogels for Depression Therapy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Xu, C.; Cheng, W.; Zhao, Y.; Sui, L.; Zhao, Y. Pretreated Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Their Secretome: Enhanced Immunotherapeutic Strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wihadmadyatami, H.; Zulficar, M.A.; Herewati, H.; Karnati, S.; Saragih, G.R.; Aliffia, D.; Pratama, D.A.O.A.; Handayani, N.; Kustiati, U.; Tirtosari, D.R.; et al. Neuroprotection Effect of Bovine Umbilical Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Conditioned Medium on the Rat Model of Alzheimer’s Disease Mediated by Upregulation of BDNF and NGF and Downregulation of TNF-α and IL-1β. Open Vet. J. 2025, 15, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantin, A.; Comarița, I.K.; Alexandru, N.; Filippi, A.; Bojin, F.; Gherghiceanu, M.; Vîlcu, A.; Nemecz, M.; Niculescu, L.S.; Păunescu, V.; et al. Stem Cell-derived Extracellular Vesicles Reduce the Expression of Molecules Involved in Cardiac Hypertrophy—In a Model of Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1003684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meservey, L.M.; Topkar, V.V.; Fu, M. meng MRNA Transport and Local Translation in Glia. Trends Cell Biol. 2021, 31, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Yang, J. Astrocyte-Mediated Neuroinflammation in Neurological Conditions. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saur, L.; Baptista, P.P.A.; Bagatini, P.B.; Neves, L.T.; de Oliveira, R.M.; Vaz, S.P.; Ferreira, K.; Machado, S.A.; Mestriner, R.G.; Xavier, L.L. Experimental Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Decreases Astrocyte Density and Changes Astrocytic Polarity in the CA1 Hippocampus of Male Rats. Neurochem. Res. 2016, 41, 892–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, J.; Guerra-Gomes, S.; Serra, S.C.; Baltazar, G.; Oliveira, J.F.; Teixeira, F.G.; Salgado, A.J. Astrocyte Signaling Impacts the Effects of Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Secretome Application into the Hippocampus: A Proliferation and Morphometrical Analysis on Astrocytic Cell Populations. Brain Res. 2020, 1732, 146700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, E.G.; Orthmann-Murphy, J.L.; Langseth, A.J.; Bergles, D.E. Myelin Remodeling through Experience-Dependent Oligodendrogenesis in the Adult Somatosensory Cortex. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 696–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, E.G.; Kang, S.H.; Fukaya, M.; Bergles, D.E. Oligodendrocyte Progenitors Balance Growth with Self-Repulsion to Achieve Homeostasis in the Adult Brain. Nat. Neurosci. 2013, 16, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slavich, G.M.; Sacher, J. Stress, Sex Hormones, Inflammation, and Major Depressive Disorder: Extending Social Signal Transduction Theory of Depression to Account for Sex Differences in Mood Disorders. Psychopharmacology 2019, 236, 3063–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willner, P. The Chronic Mild Stress (CMS) Model of Depression: History, Evaluation and Usage. Neurobiol. Stress 2017, 6, 78–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planchez, B.; Surget, A.; Belzung, C. Animal Models of Major Depression: Drawbacks and Challenges. J. Neural Transm. 2019, 126, 1383–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belzung, C.; Lemoine, M. Criteria of Validity for Animal Models of Psychiatric Disorders: Focus on Anxiety Disorders and Depression. Biol. Mood Anxiety Disord. 2011, 1, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czéh, B.; Fuchs, E.; Wiborg, O.; Simon, M. Animal Models of Major Depression and Their Clinical Implications. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 64, 293–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ávila, A.; Riveros, M.E.; Adasme, S.; Guevara, C.; Del Rio, R.; Ortiz, F.C.; Leibold, N.; Ezquer, F. Therapeutic Effects of Intranasal Administration of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Secretome in Rats Exposed to Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17091129
Ávila A, Riveros ME, Adasme S, Guevara C, Del Rio R, Ortiz FC, Leibold N, Ezquer F. Therapeutic Effects of Intranasal Administration of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Secretome in Rats Exposed to Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(9):1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17091129
Chicago/Turabian StyleÁvila, Alba, María Eugenia Riveros, Sofía Adasme, Coram Guevara, Rodrigo Del Rio, Fernando C. Ortiz, Nicole Leibold, and Fernando Ezquer. 2025. "Therapeutic Effects of Intranasal Administration of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Secretome in Rats Exposed to Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 9: 1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17091129
APA StyleÁvila, A., Riveros, M. E., Adasme, S., Guevara, C., Del Rio, R., Ortiz, F. C., Leibold, N., & Ezquer, F. (2025). Therapeutic Effects of Intranasal Administration of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Secretome in Rats Exposed to Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress. Pharmaceutics, 17(9), 1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17091129








