Quality by Design (QbD)-Based Development of a Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery System for the Ocular Delivery of Flurbiprofen
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. HPLC Conditions
2.3. Solubility Test
2.4. Pseudo-Ternary Phase Diagrams
2.5. Optimization of the FLU-SNE Formulation Using a Box–Behnken Design (BBD) Approach
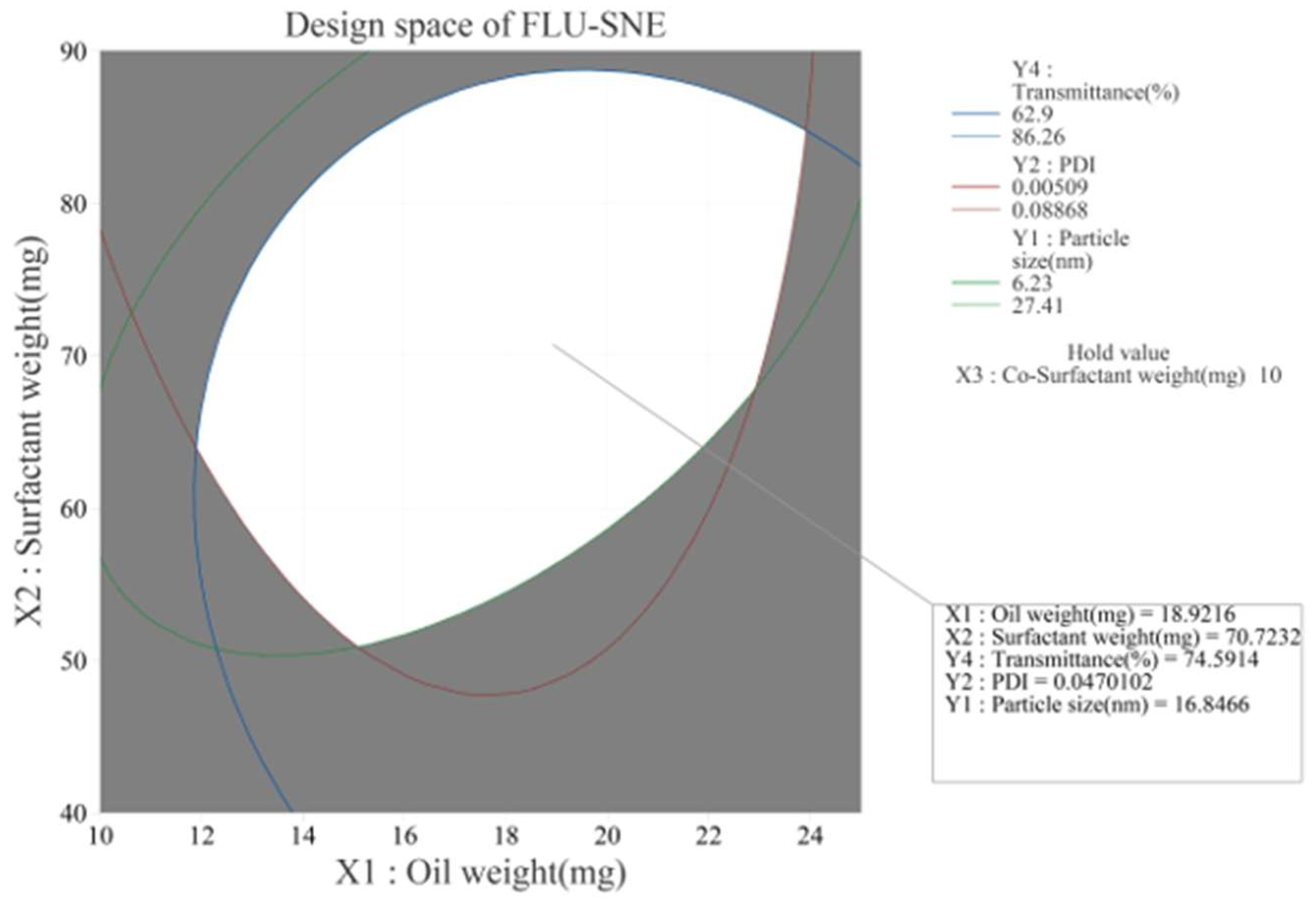
2.6. Response Optimization and Design Space Development
2.7. Particle Size and Zeta Potential Analyses
2.8. pH Test
2.9. Transmission Electron Microscopy
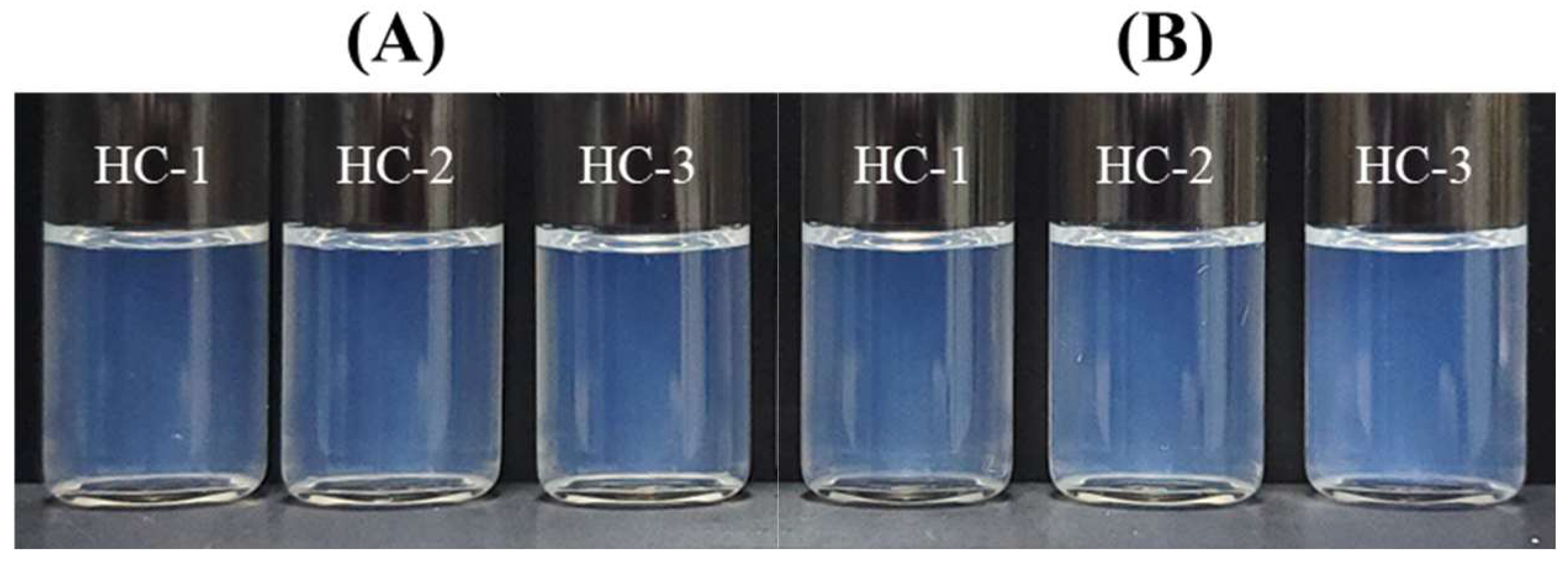
2.10. Heating and Cooling Cycles
2.11. In Vitro and Ex Vivo Diffusion Tests
3. Results
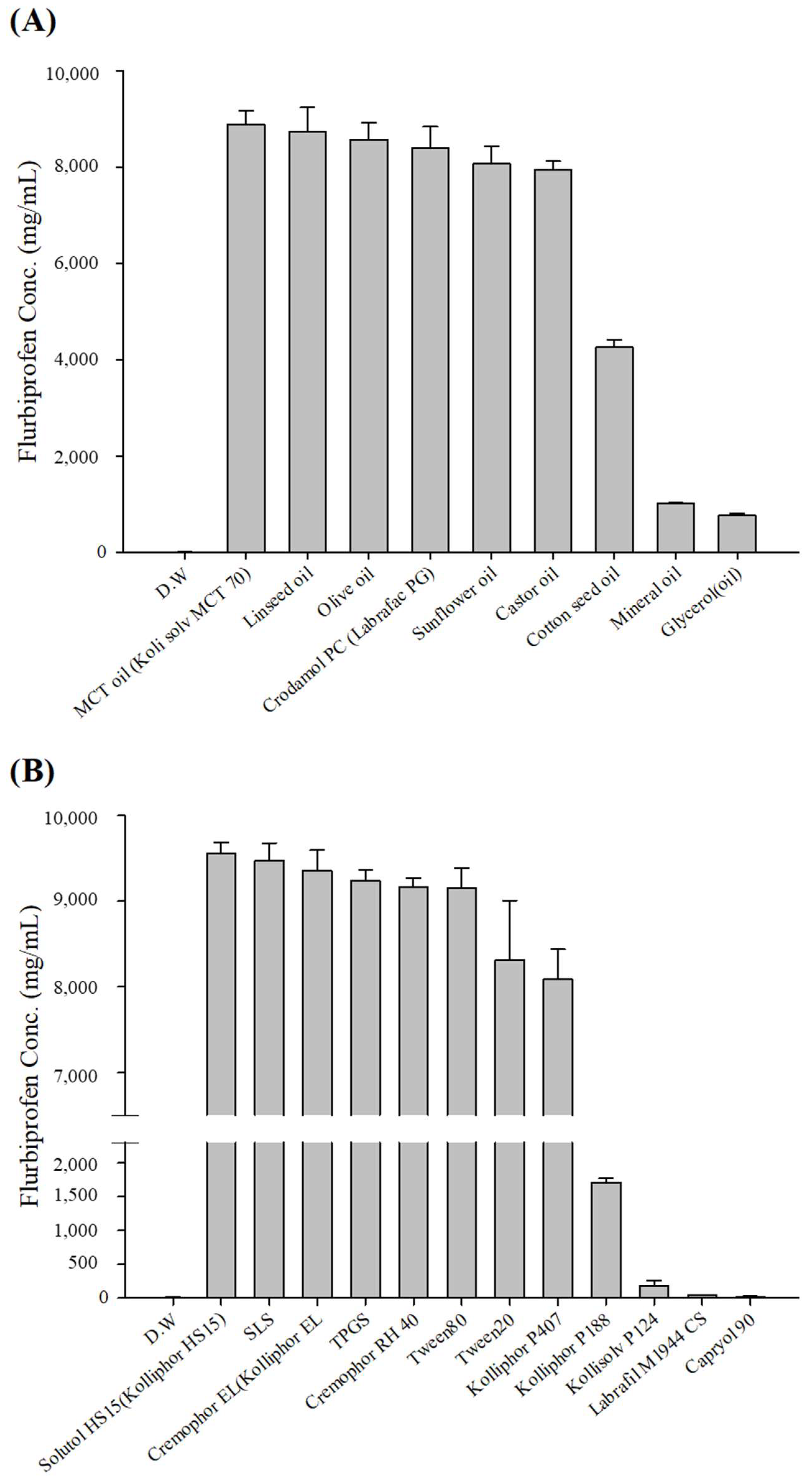
3.1. Solubility of FLU
3.2. Pseudo-Ternary Phase Diagrams
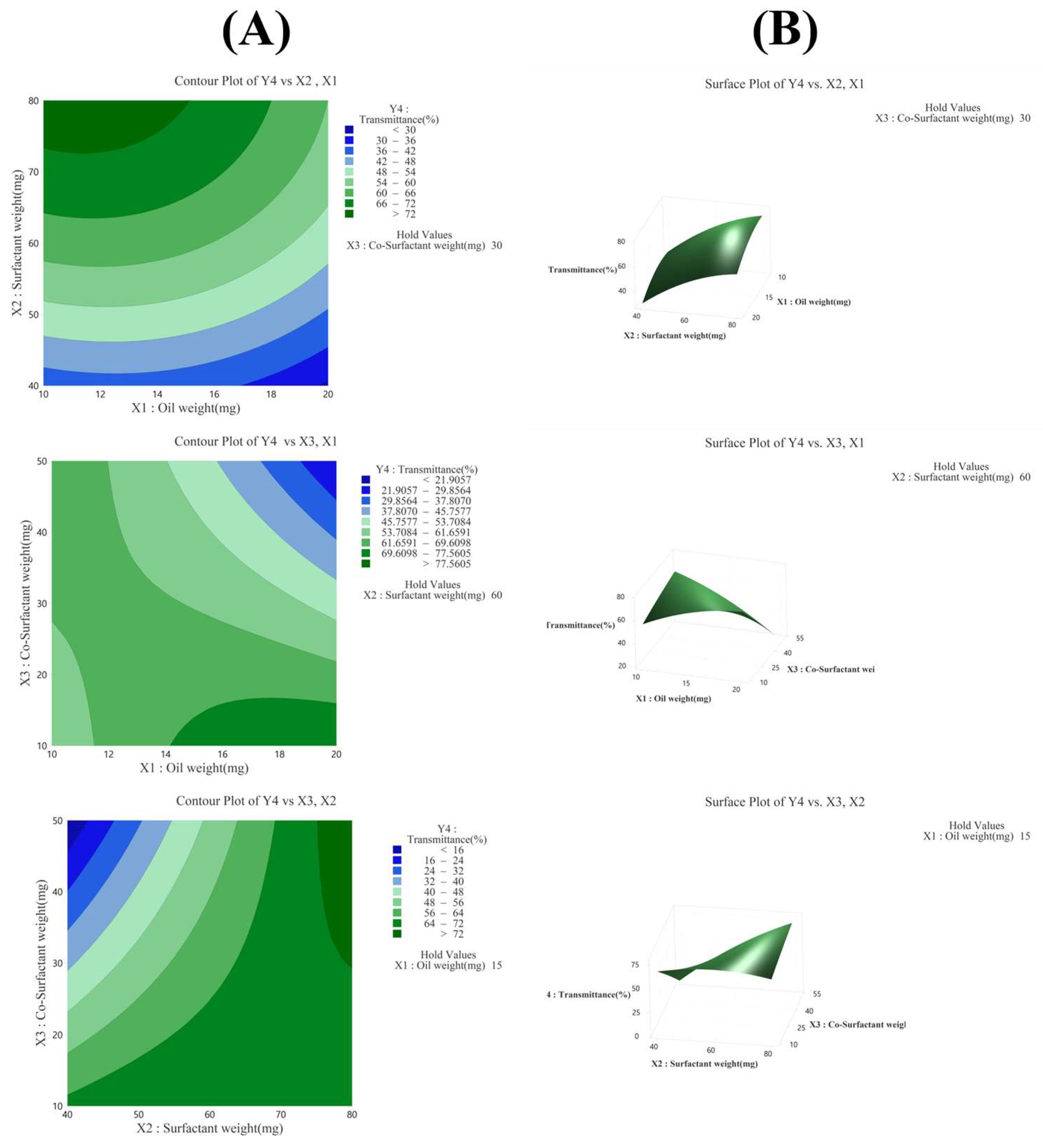
3.3. Optimization of the FLU-SNE Formulation Using a Box–Behnken Design (BBD)
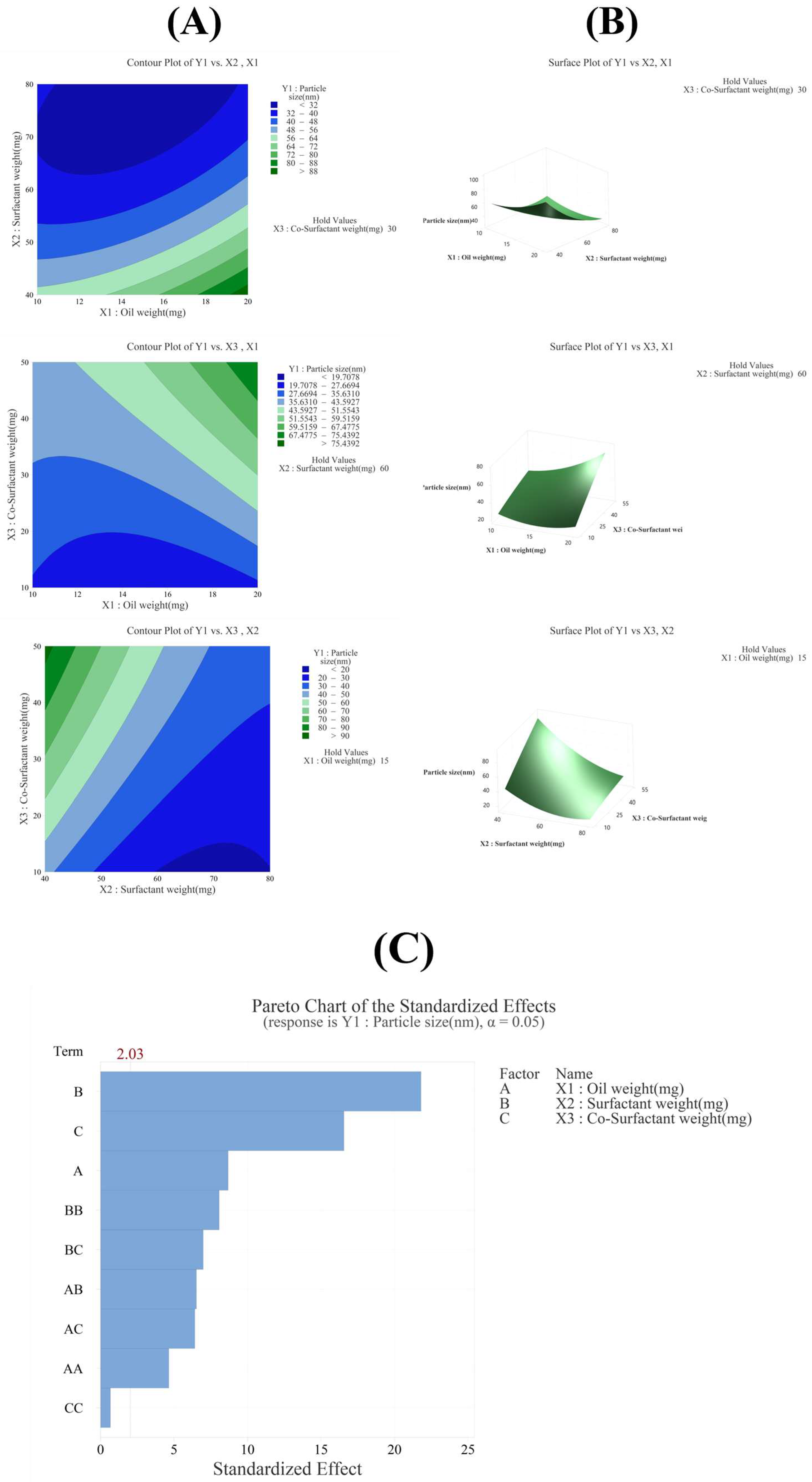
3.3.1. Effect of Variables on Particle Size (Y1)
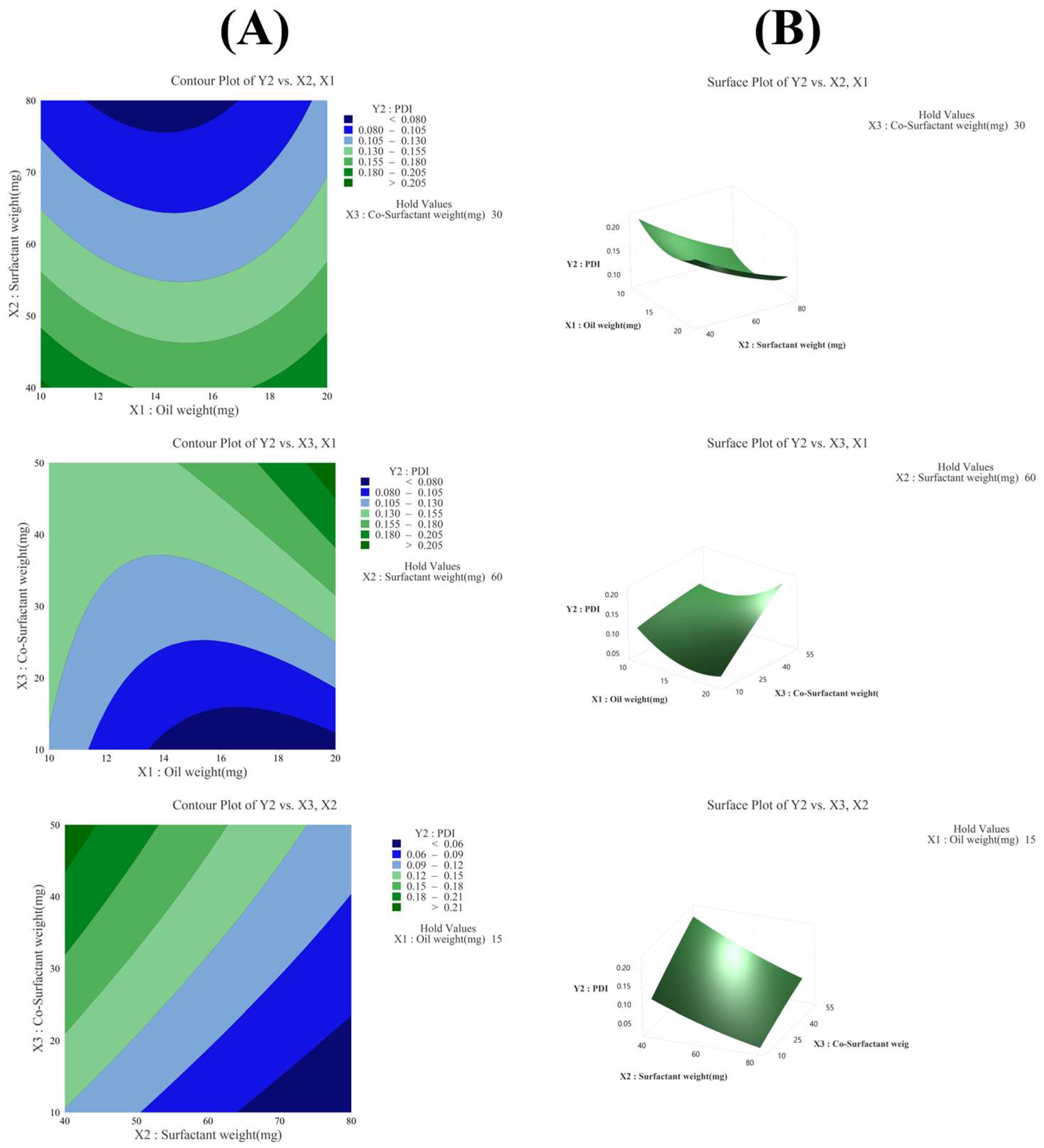
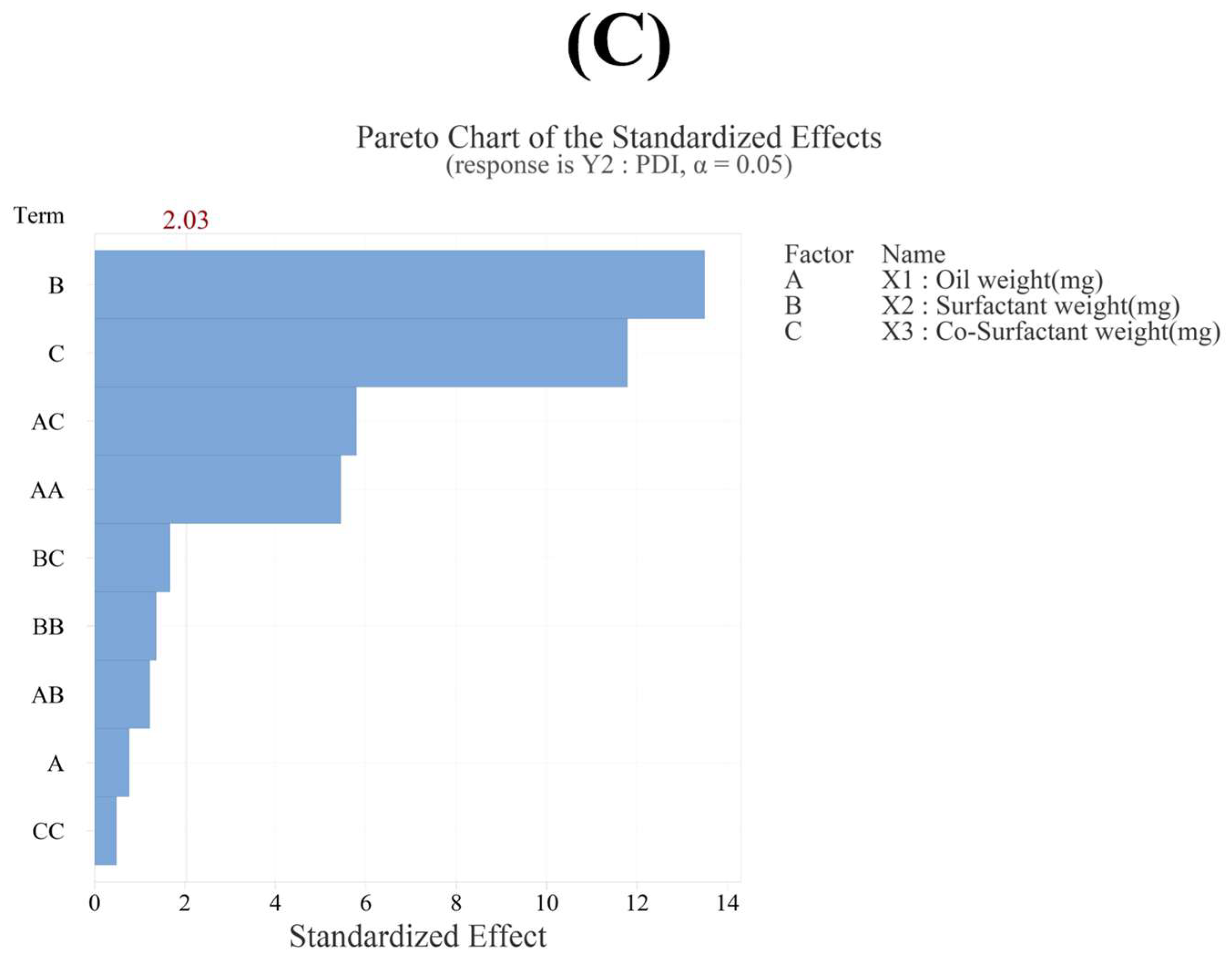
3.3.2. Effect of Variables on PDI (Y2)
3.3.3. Effect of Variables on Zeta Potential (Y3)
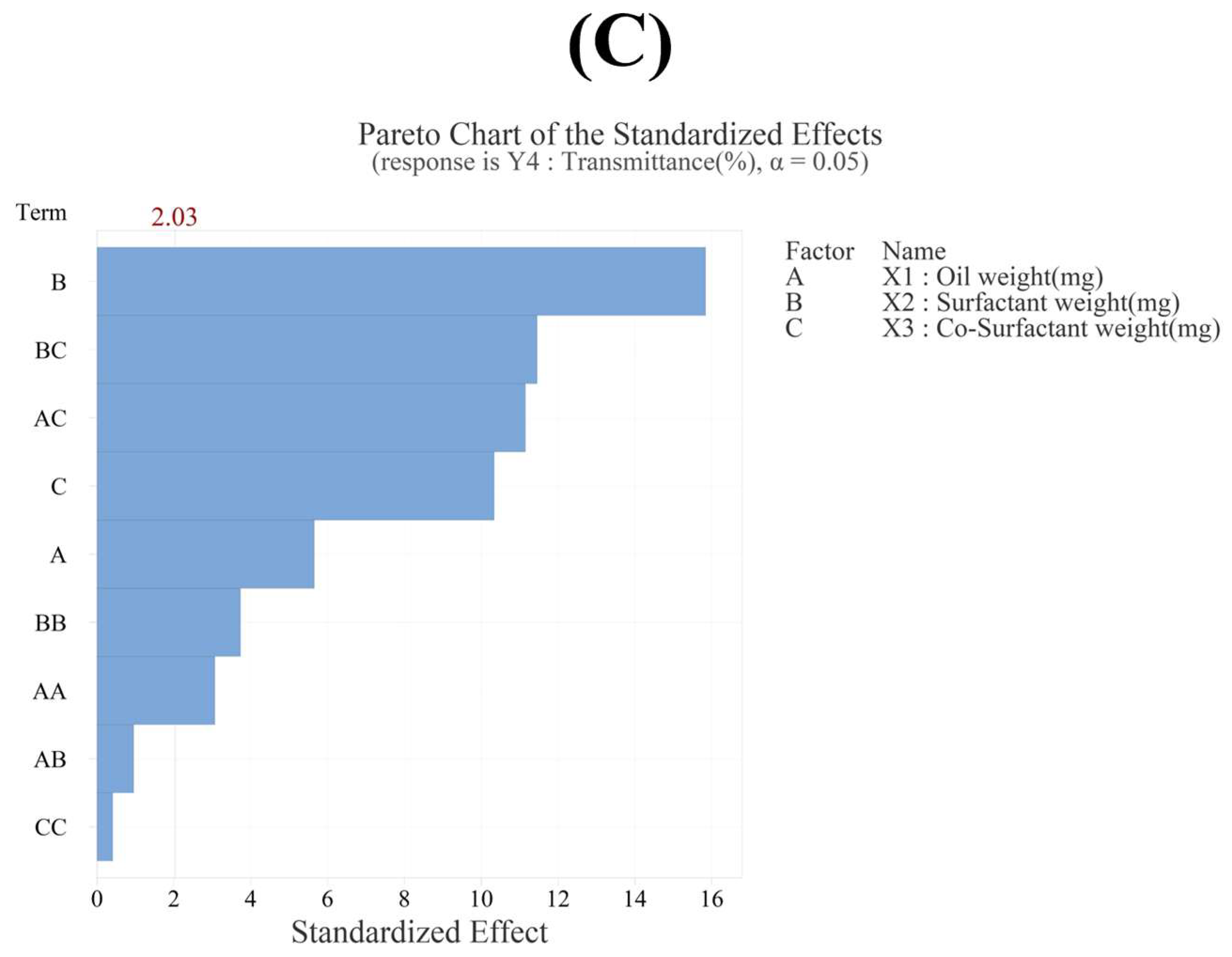
3.3.4. Effect of Variables on Transmittance (Y4)
3.4. Characterization of Optimized FLU-SNE
3.5. Evaluation of Optimized FLU-SNE
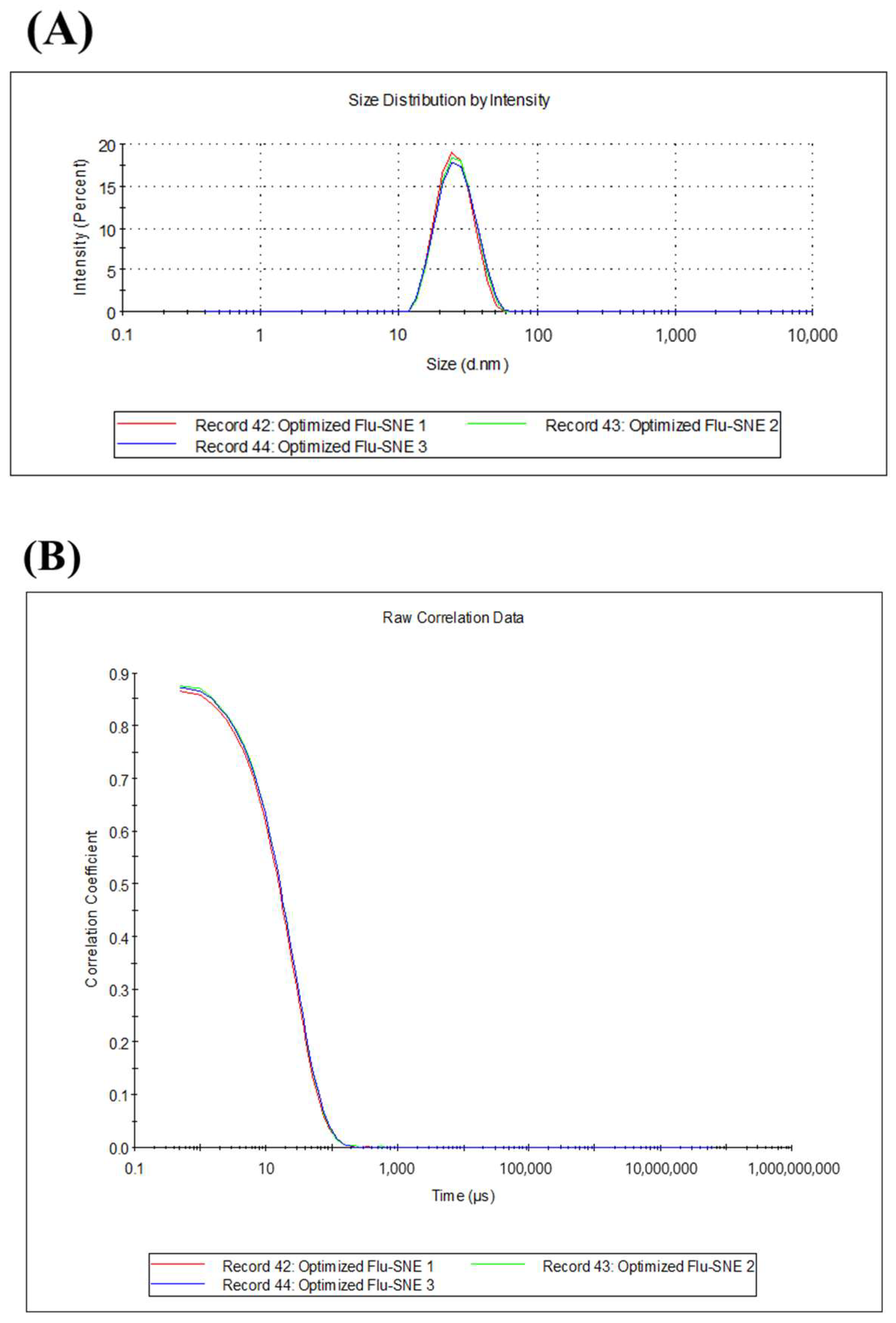
3.5.1. Evaluation of Reproducibility of Optimized FLU-SNE
3.5.2. Thermodynamic Stability of FLU-SNE
3.5.3. pH of FLU-SNE
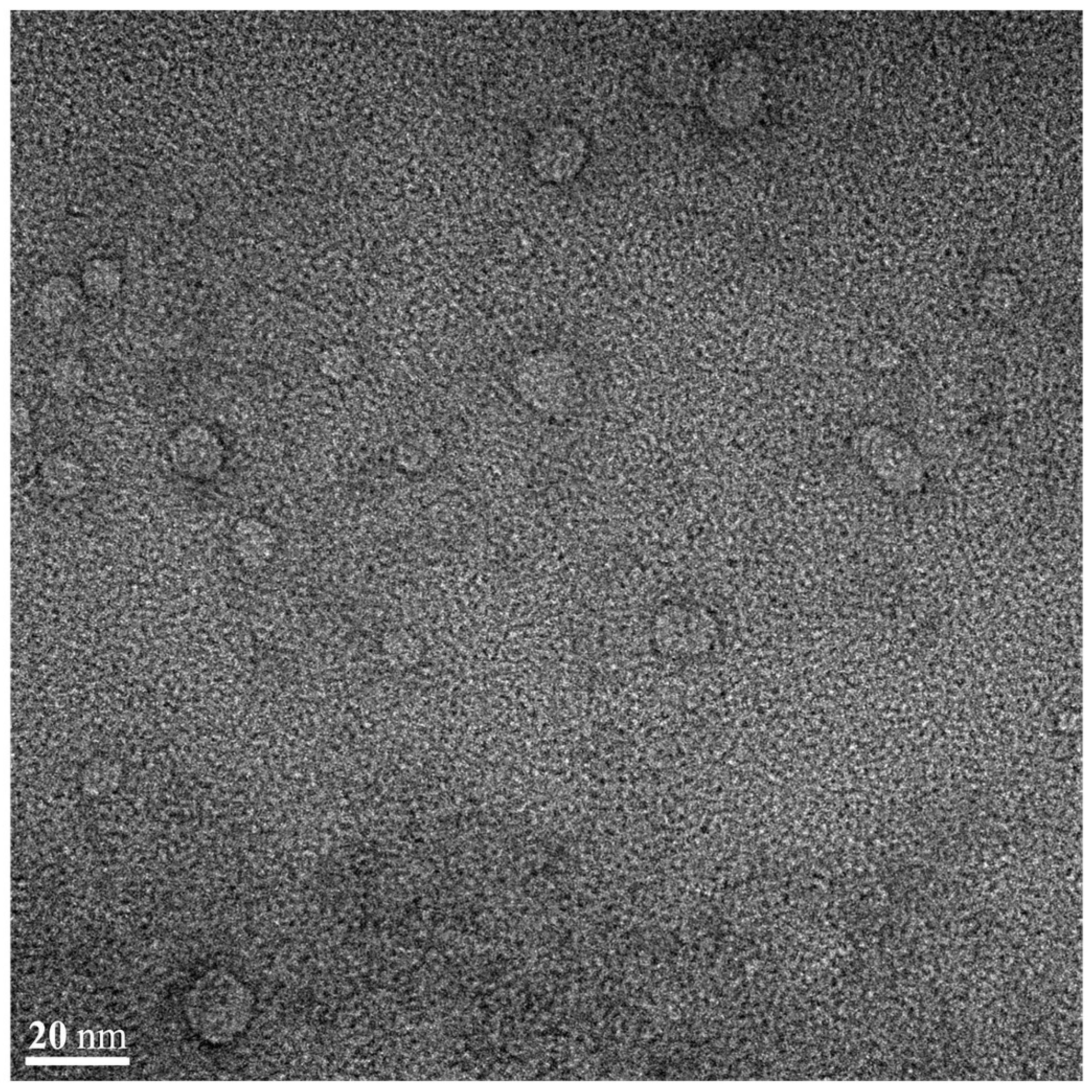
3.5.4. Morphological Evaluation of FLU-SNE
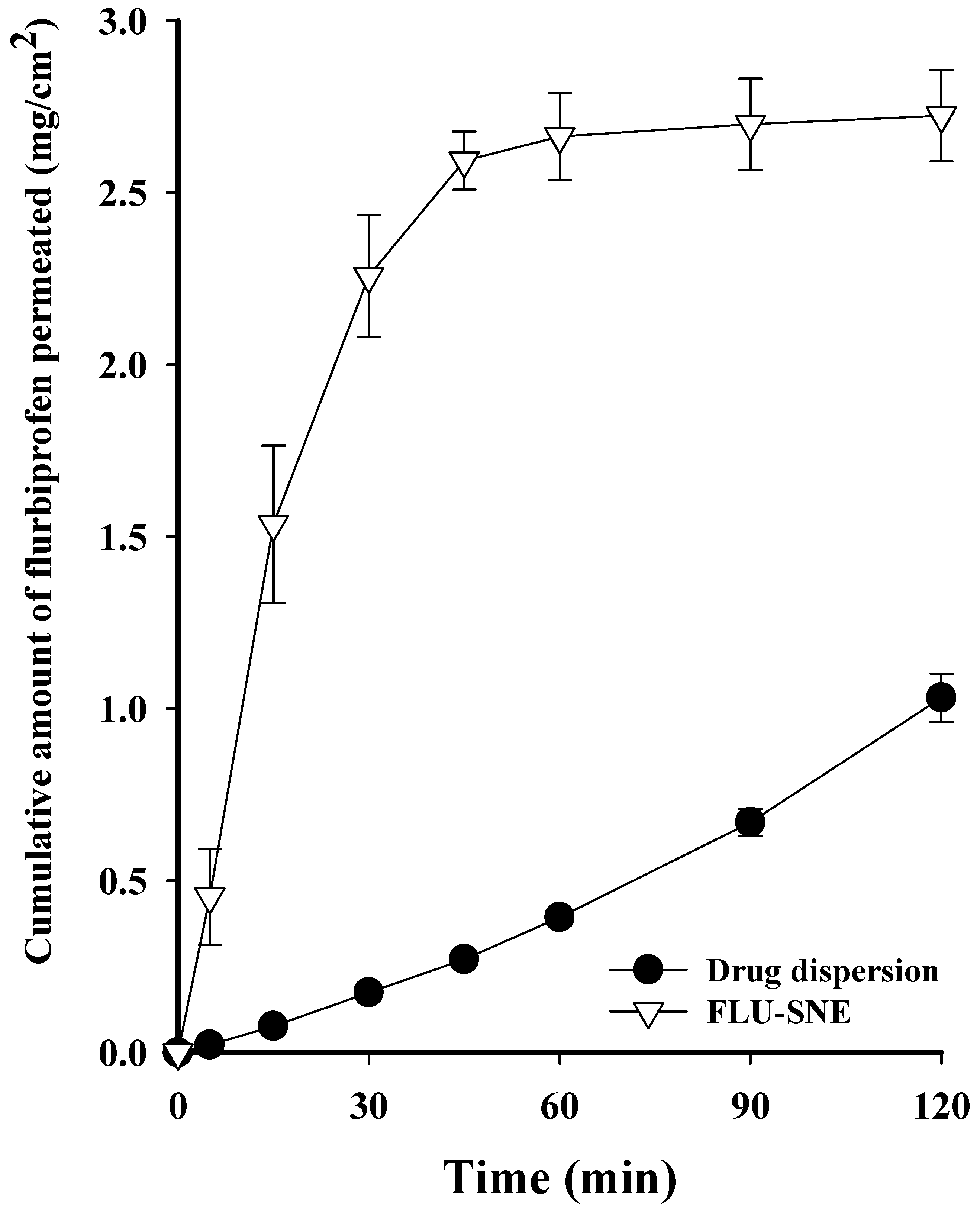
3.6. In Vitro Diffusion Test
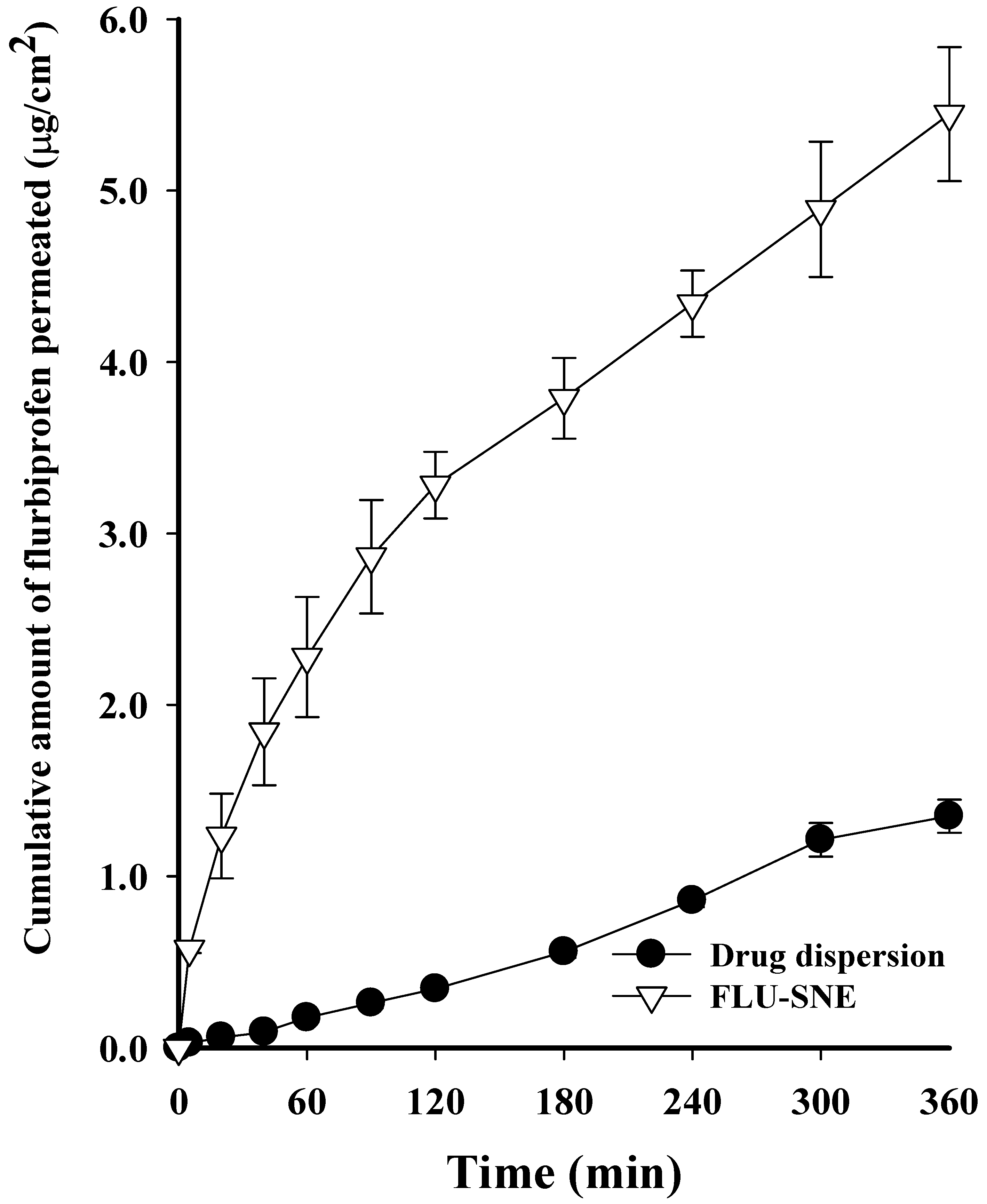
3.7. Ex Vivo Diffusion Test
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krishna, U.; Ajanaku, D.; Denniston, A.K.; Gkika, T. Uveitis: A sight-threatening disease which can impact all systems. Postgrad. Med. J. 2017, 93, 766–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, M.; Dhake, A.S.; Sharma, S.K.; Majumdar, D.K. Topical ocular delivery of NSAIDs. AAPS J. 2008, 10, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blazaki, S.; Tsika, C.; Tzatzarakis, M.; Naoumidi, E.; Tsatsakis, A.; Tsatsanis, C.; Tsilimbaris, M.K. Pharmacokinetics and efficacy of intraocular flurbiprofen. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2017, 255, 2375–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginsburg, A.P.; Cheetham, J.K.; DeGryse, R.E.; Abelson, M. Effects of flurbiprofen and indomethacin on acute cystoid macular edema after cataract surgery: Functional vision and contrast sensitivity. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 1995, 21, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignatello, R.; Bucolo, C.; Spedalieri, G.; Maltese, A.; Puglisi, G. Flurbiprofen-loaded acrylate polymer nanosuspensions for ophthalmic application. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 3247–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.Y.; Akbar, D.; Giunta, M.; Kalevar, A.; Tran, S.D. Hydrogels in ophthalmology: Novel strategies for overcoming therapeutic challenges. Materials 2023, 17, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vane, J.R.; Botting, R.M. Mechanism of action of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Am. J. Med. 1998, 104, 2S–8S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zhuang, C.; Wang, M.; Sun, X.; Nie, S.; Pan, W. Liposome coated with low molecular weight chitosan and its potential use in ocular drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 379, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zingale, E.; Bonaccosrso, A.; D’Amico, A.G.; Lombardo, R.; D’Agata, V.; Rautio, J.; Pignatello, R. Formulating Resveratrol and Melatonin Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery Systems (SNEDDS) for Ocular Administration Using Design of Experiments. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.F.; Yin, C.M.; Ouyang, T.; Sun, S.D.; Chen, W.G.; Yang, X.L.; He, X.; Zhang, C.F. Self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system of genkwanin: A novel approach for anti-colitis-associated colorectal cancer. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2021, 15, 557–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasoanirina, B.N.V.; Lassoued, M.A.; Miladi, K.; Razafindrakoto, Z.; Chaâbane-Banaoues, R.; Ramanitrahasimbola, D.; Cornet, M.; Sfar, S. Self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system to improve transcorneal permeability of voriconazole: In-vivo studies. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2020, 72, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, R.R.; Verma, A.; Ghosh, A. Microemulsion: New insights into the ocular drug delivery. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2013, 2013, 826798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zingale, E.; Masuzzo, S.; Lajunen, T.; Reinisalo, M.; Rautio, J.; Consoli, V.; D’amico, A.G.; Vanella, L.; Pignatello, R. Protective Role and Enhanced Intracellular Uptake of Curcumin in Retinal Cells Using Self-Emulsifying Drug Delivery Systems (SNEDDS). Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Dong, J.; Chen, J.; Eastoe, J.; Li, X. Design and optimization of a new self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 330, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, B.; Bayrak, B.; Kadıoğlu, Y. Development and validation of HPLC method for the determination of Flurbiprofen in pharmaceutical preparations. Int. J. PharmATA 2022, 2, 72–81. [Google Scholar]
- Bachu, R.D.; Chowdhury, P.; Al-Saedi, Z.H.; Karla, P.K.; Boddu, S.H. Ocular drug delivery barriers—Role of nanocarriers in the treatment of anterior segment ocular diseases. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Haydar, M.; Abid, H.R.; Sunderland, B.; Wang, S. Metal organic frameworks as a drug delivery system for flurbiprofen. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2017, 11, 2685–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikash, B.; Pandey, N.K.; Kumar, B.; Wadhwa, S.; Goutam, U.; Alam, A.; Al-Otaibi, F.; Chaubey, P.; Mustafa, G.; Gupta, G. Formulation and evaluation of ocular self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system of brimonidine tartrate. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 81, 104226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassem, A.A.; Salama, A.; Mohsen, A.M. Formulation and optimization of cationic nanoemulsions for enhanced ocular delivery of dorzolamide hydrochloride using Box-Behnken design: In vitro and in vivo assessments. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 68, 103047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Mira, E.; Egea, M.; Garcia, M.; Souto, E. Design and ocular tolerance of flurbiprofen loaded ultrasound-engineered NLC. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 81, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, N.F.; Abdel-Halim, S.A.; Elassasy, A.I. Solutol HS15 based binary mixed micelles with penetration enhancers for augmented corneal delivery of sertaconazole nitrate: Optimization, in vitro, ex vivo and in vivo characterization. Drug Deliv. 2018, 25, 1706–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, J.; Tang, J.; Bu, M.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, L.; Liu, H. A novel eye drop of alpha tocopherol to prevent ocular oxidant damage: Improve the stability and ocular efficacy. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2016, 42, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auriol, S.; Mahieu, L.; Brousset, P.; Malecaze, F.; Mathis, V. Safety of medium-chain triglycerides used as an intraocular tamponading agent in an experimental vitrectomy model rabbit. Retina 2013, 33, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangri, P.; Khurana, S. Basics of ocular drug delivery systems. Int. J. Res. Pharm. Biomed. Sci. 2011, 2, 1541–1552. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, H.J.; Kim, K.S. Development of a novel ticagrelor solid dispersion-loaded tablet with enhanced solubility. Yakhak Hoeji 2020, 64, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.A.; Park, E.J.; Lee, J.H.; Min, K.A.; Kim, S.T.; Jang, D.J.; Maeng, H.J.; Jin, S.G.; Cho, K.H. Preparation and Characterization of Pazopanib Hydrochloride-Loaded Four-Component Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery Systems Preconcentrate for Enhanced Solubility and Dissolution. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.J.; Kim, K.S. Development of Solid Self-nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery Systems of Ticagrelor Using Porous Carriers. J. Life Sci. 2021, 31, 502–510. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.S.; Cho, J.H.; Park, J.H.; Kim, J.S.; Song, E.S.; Kwon, J.; Giri, B.R.; Jin, S.G.; Kim, K.S.; Choi, H.G. Self-microemulsifying drug delivery system (SMEDDS) for improved oral delivery and photostability of methotrexate. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 4949–4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinteros, D.A.; Tártara, L.I.; Palma, S.D.; Manzo, R.H.; Allemandi, D.A. Ocular delivery of flurbiprofen based on Eudragit® E-flurbiprofen complex dispersed in aqueous solution: Preparation, characterization, in vitro corneal penetration, and ocular irritation. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 103, 3859–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Kim, S.B.; Choi, S.H.; Nguyen, T.T.L.; Ahn, S.H.; Moon, K.S.; Moon, K.S.; Cho, K.H.; Sim, T.Y.; Heo, E.J.; et al. Development and evaluation of self-microemulsifying drug delivery system for improving oral absorption of poorly water-soluble Olaparib. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bali, V.; Ali, M.; Ali, J. Nanocarrier for the enhanced bioavailability of a cardiovascular agent: In vitro, pharmacodynamic, pharmacokinetic and stability assessment. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 403, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajitha, P.; Shammika, P.; Aiswarya, S.; Gopikrishnan, A.; Jayakumar, R.; Sabitha, M. Chaulmoogra oil based methotrexate loaded topical nanoemulsion for the treatment of psoriasis. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasoanirina, B.N.V.; Lassoued, M.A.; Kamoun, A.; Bahloul, B.; Milaki, K.; Sfar, S. Voriconazole-loaded self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system (SNEDDS) to improve transcorneal permeability. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2020, 25, 694–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracy, P.; Dasgupta, D.; More, S. Challenges and opportunities for production of C5 sugar fatty acid esters (SFAEs) from renewable resources. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 193, 116170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar, A.M.S.; Naveros, B.C.; Campmany, A.C.C.; Trenchs, M.A.; Rocabert, C.B.; Bellowa, L.H. Design and optimization of self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems (SNEDDS) for enhanced dissolution of gemfibrozil. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 431, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Chaurasiya, A.; Singh, M.; Upadhyay, S.C.; Mykherjee, R.; Khar, R.K. Exemestane loaded self-microemulsifying drug delivery system (SMEDDS): Development and optimization. Aaps Pharmscitech 2008, 9, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beg, S.; Sandhu, P.S.; Batra, R.S.; Khurana, R.K.; Singh, B. QbD-based systematic development of novel optimized solid self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems (SNEDDS) of lovastatin with enhanced biopharmaceutical performance. Drug Deliv. 2015, 22, 765–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, A.R.; Rajput, S.J.; Patel, S.G. Preparation and bioavailability assessment of SMEDDS containing valsartan. AAPS Pharmscitech 2010, 11, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Tiwary, A.K.; Bedi, N. Canagliflozin loaded SMEDDS: Formulation optimization for improved solubility, permeability and pharmacokinetic performance. J. Pharm. Investig. 2019, 49, 67–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traul, K.; Driedger, A.; Ingle, D.; Nakhasi, D. Review of the toxicologic properties of medium-chain triglycerides. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2000, 38, 79–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smail, S.S.; Ghareeb, M.M.; Omer, H.K.; Al-Kinani, A.A.; Alany, R.G. Studies on surfactants, cosurfactants, and oils for prospective use in formulation of ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic nanoemulsions. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, I.J.; Kim, K.J. An interactive desirability function method to multiresponse optimization. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2009, 195, 412–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasniyati, M.R.; Zuhailawati, H.; Ramakrishnan, S. A statistical prediction of multiple responses using overlaid contour plot on hydroxyapatite coated magnesium via cold spray deposition. Procedia Chem. 2016, 19, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Khor, C.; Jaafar, M.B.; Ramakrishnan, S. Optimization of conductive thin film epoxy composites properties using desirability optimization methodology. J. Optim. 2016, 2016, 1652928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuk, D.-H.; Ha, E.-S.; Ha, D.-H.; Sim, W.-Y.; Lee, S.-K.; Jeong, J.-S.; Kim, J.-S.; Baek, I.-H.; Park, H.; Choi, D.H. Development of a resveratrol nanosuspension using the antisolvent precipitation method without solvent removal, based on a quality by design (QbD) approach. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakumar, K.; Raghavan, C.V.; Abdu, S. Self nanoemulsifying drug delivery system (SNEDDS) of rosuvastatin calcium: Design, formulation, bioavailability and pharmacokinetic evaluation. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 112, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leone, G.; Pepi, S.; Consumi, M.; Mahdizadeh, F.F.; Lamponi, S.; Magnani, A. Phosphorylated xanthan gum-Ag (I) complex as antibacterial viscosity enhancer for eye drops formulation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 267, 118196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Nagai, N.; Saijo, S.; Kaji, H.; Nishizawa, M.; Abe, T. In situ formation of injectable chitosan-gelatin hydrogels through double crosslinking for sustained intraocular drug delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 88, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resch, M.D.; Resch, B.E.; Csizmazia, E.; Imre, L.; Németh, J.; Révész, P.; Csányi, E. Permeability of human amniotic membrane to ofloxacin in vitro. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 1024–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Level | ||
|---|---|---|
| Factor | −1 (Low) | +1 (High) |
| X1: Oil weight (mg) | 10 | 20 |
| X2: Surfactant weight (mg) | 40 | 80 |
| X3: Co-surfactant weight (mg) | 10 | 50 |
| X1 | X2 | X3 | Y1 | Y2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oil (mg) | Surfactant (mg) | Co-Surfactant (mg) | Particle Size (nm) | PDI | ||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |||
| 20 | 80 | 30 | 34.38 | 32.98 | 32.33 | 0.100 | 0.089 | 0.091 |
| 20 | 60 | 50 | 72.67 | 70.12 | 69.98 | 0.237 | 0.231 | 0.239 |
| 20 | 60 | 10 | 23.16 | 22.58 | 22.56 | 0.071 | 0.047 | 0.047 |
| 20 | 40 | 30 | 105.40 | 99.55 | 97.09 | 0.214 | 0.213 | 0.226 |
| 15 | 80 | 50 | 37.93 | 36.62 | 36.41 | 0.123 | 0.110 | 0.101 |
| 15 | 80 | 10 | 23.71 | 22.34 | 22.14 | 0.061 | 0.072 | 0.053 |
| 15 | 60 | 30 | 38.08 | 36.55 | 36.30 | 0.111 | 0.114 | 0.111 |
| 15 | 60 | 30 | 35.01 | 35.31 | 35.25 | 0.114 | 0.117 | 0.120 |
| 15 | 60 | 30 | 38.80 | 37.49 | 37.14 | 0.135 | 0.110 | 0.111 |
| 15 | 40 | 50 | 93.57 | 90.06 | 88.48 | 0.204 | 0.200 | 0.189 |
| 15 | 40 | 10 | 39.20 | 38.01 | 37.63 | 0.112 | 0.117 | 0.108 |
| 10 | 80 | 30 | 27.61 | 26.24 | 25.96 | 0.067 | 0.082 | 0.083 |
| 10 | 60 | 50 | 45.34 | 44.01 | 43.65 | 0.159 | 0.16 | 0.174 |
| 10 | 60 | 10 | 32.30 | 30.82 | 30.49 | 0.111 | 0.116 | 0.116 |
| 10 | 40 | 30 | 59.42 | 58.08 | 57.76 | 0.229 | 0.230 | 0.225 |
| X1 | X2 | X3 | Y3 | Y4 | ||||
| Oil (mg) | Surfactant (mg) | Co-Surfactant (mg) | Zeta Potential (mV) (Absolute Value) | Transmittance (%) | ||||
| 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | |||
| 20 | 80 | 30 | 1.310 | 0.444 | 1.310 | 0.444 | 1.310 | 0.444 |
| 20 | 60 | 50 | 4.220 | 6.270 | 4.220 | 6.270 | 4.220 | 6.270 |
| 20 | 60 | 10 | 3.270 | 1.250 | 3.270 | 1.250 | 3.270 | 1.250 |
| 20 | 40 | 30 | 0.483 | 0.113 | 0.483 | 0.113 | 0.483 | 0.113 |
| 15 | 80 | 50 | 2.580 | 0.286 | 2.580 | 0.286 | 2.580 | 0.286 |
| 15 | 80 | 10 | 0.178 | 0.951 | 0.178 | 0.951 | 0.178 | 0.951 |
| 15 | 60 | 30 | 1.880 | 2.390 | 1.880 | 2.390 | 1.880 | 2.390 |
| 15 | 60 | 30 | 2.150 | 3.050 | 2.150 | 3.050 | 2.150 | 3.050 |
| 15 | 60 | 30 | 0.373 | 0.258 | 0.373 | 0.258 | 0.373 | 0.258 |
| 15 | 40 | 50 | 0.275 | 0.215 | 0.275 | 0.215 | 0.275 | 0.215 |
| 15 | 40 | 10 | 0.766 | 3.840 | 0.766 | 3.840 | 0.766 | 3.840 |
| 10 | 80 | 30 | 0.893 | 0.600 | 0.893 | 0.600 | 0.893 | 0.600 |
| 10 | 60 | 50 | 1.270 | 1.800 | 1.270 | 1.800 | 1.270 | 1.800 |
| 10 | 60 | 10 | 0.724 | 1.410 | 0.724 | 1.410 | 0.724 | 1.410 |
| 10 | 40 | 30 | 5.820 | 2.900 | 5.820 | 2.900 | 5.820 | 2.900 |
| DF * | Adj SS * | Adj MS * | F-Value | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 9 | 23,321.3 | 2591.3 | 115.60 | 0.000 |
| Linear Model | 3 | 18,477.5 | 6159.2 | 274.77 | 0.000 |
| X1: Oil (mg) | 1 | 1685.4 | 1685.4 | 75.19 | 0.000 |
| X2: Surfactant (mg) | 1 | 10,651.3 | 10,651.3 | 475.17 | 0.000 |
| X3: Co-Surfactant (mg) | 1 | 6140.8 | 6140.8 | 273.95 | 0.000 |
| Quadratic Model | 3 | 1878.8 | 626.3 | 27.94 | 0.000 |
| X1: Oil2 | 1 | 483 | 483.0 | 21.55 | 0.000 |
| X2: Surfactant2 | 1 | 1457.6 | 1457.6 | 65.03 | 0.000 |
| X3: Co-Surfactant2 | 1 | 10.1 | 10.1 | 0.45 | 0.506 |
| Two-Factor Interaction | 3 | 2965 | 988.3 | 44.09 | 0.000 |
| X1: Oil · X2: Surfactant | 1 | 952.3 | 952.3 | 42.48 | 0.000 |
| X1: Oil · X3: Co-Surfactant | 1 | 920.2 | 920.2 | 41.05 | 0.000 |
| X2: Surfactant · X3: Co-Surfactant | 1 | 1092.5 | 1092.5 | 48.74 | 0.000 |
| S | R2 | R2 (Retouch) | R2 (Prediction) | ||
| 4.73451 | 96.75% | 95.91% | 94.24% | ||
| DF | Adj SS | Adj MS | F-Value | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 9 | 0.136459 | 0.015162 | 43.43 | 0.000 |
| Linear Model | 3 | 0.112265 | 0.037422 | 107.18 | 0.000 |
| X1: Oil (mg) | 1 | 0.000204 | 0.000204 | 0.58 | 0.450 |
| X2: Surfactant (mg) | 1 | 0.063551 | 0.063551 | 182.03 | 0.000 |
| X3: Co-Surfactant (mg) | 1 | 0.048510 | 0.048510 | 138.94 | 0.000 |
| Quadratic Model | 3 | 0.010983 | 0.003661 | 10.49 | 0.000 |
| X1: Oil2 | 1 | 0.010342 | 0.010342 | 29.62 | 0.000 |
| X2: Surfactant2 | 1 | 0.000646 | 0.000646 | 1.85 | 0.182 |
| X3: Co-Surfactant2 | 1 | 0.000080 | 0.000080 | 0.23 | 0.634 |
| Two-Factor Interaction | 3 | 0.013211 | 0.004404 | 12.61 | 0.000 |
| X1: Oil · X2: Surfactant | 1 | 0.000520 | 0.000520 | 1.49 | 0.230 |
| X1: Oil · X3: Co-Surfactant | 1 | 0.011719 | 0.011719 | 33.57 | 0.000 |
| X2: Surfactant · X3: Co-Surfactant | 1 | 0.000972 | 0.000972 | 2.78 | 0.104 |
| S | R2 | R2 (Retouch) | R2 (Prediction) | ||
| 0.0186851 | 91.78% | 89.67% | 85.56% | ||
| DF | Adj SS | Adj MS | F-Value | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 9 | 18,204.7 | 2022.75 | 74.21 | 0.000 |
| Linear Model | 3 | 10,620.8 | 3540.28 | 129.88 | 0.000 |
| X1: Oil (mg) | 1 | 870.1 | 870.11 | 31.92 | 0.000 |
| X2: Surfactant (mg) | 1 | 6838.0 | 6838.02 | 250.86 | 0.000 |
| X3: Co-Surfactant (mg) | 1 | 2912.7 | 2912.72 | 106.86 | 0.000 |
| Quadratic Model | 3 | 591.2 | 197.08 | 7.23 | 0.001 |
| X1: Oil2 | 1 | 256.1 | 256.06 | 9.39 | 0.004 |
| X2: Surfactant2 | 1 | 379.5 | 379.46 | 13.92 | 0.001 |
| X3: Co-Surfactant2 | 1 | 4.5 | 4.49 | 0.16 | 0.687 |
| Two-Factor Interaction | 3 | 6992.6 | 2330.88 | 85.51 | 0.000 |
| X1: Oil · X2: Surfactant | 1 | 24.7 | 24.71 | 0.91 | 0.348 |
| X1: Oil · X3: Co-Surfactant | 1 | 3391.3 | 3391.28 | 124.41 | 0.000 |
| X2: Surfactant · X3: Co-Surfactant | 1 | 3576.7 | 3576.65 | 131.21 | 0.000 |
| S | R2 | R2 (Retouch) | R2 (Prediction) | ||
| 5.22092 | 95.02% | 93.74% | 91.15% | ||
| Factor | Setting | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1: Oil Weight (mg) | 18.9 | |||
| X2: Surfactant Weight (mg) | 70.7 | |||
| X3: Co-Surfactant Weight (mg) | 10.0 | |||
| Response | Suitable Value | SE Suitable Value | 95% CI | 95% PI |
| Y1: Particle Size (nm) | 16.82 | 2.19 | (12.37, 21.26) | (6.23, 27.41) |
| Y2: PDI | 0.047 | 0.009 | (0.029, 0.064) | (0.005, 0.089) |
| Y4: Transmittance (%) | 74.58 | 2.42 | (69.68, 79.48) | (62.90, 86.26) |
| Particle Size (nm) | PDI | Transmittance (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 24.89 ± 0.28 | 0.068 ± 0.008 | 74.85 ± 5.69 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, J.-H.; Yoon, T.-H.; Ryu, S.-W.; Kim, M.-G.; Kim, G.-H.; Oh, Y.-J.; Lee, S.-J.; Kwak, N.-W.; Bang, K.-H.; Kim, K.-S. Quality by Design (QbD)-Based Development of a Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery System for the Ocular Delivery of Flurbiprofen. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17050629
Jeong J-H, Yoon T-H, Ryu S-W, Kim M-G, Kim G-H, Oh Y-J, Lee S-J, Kwak N-W, Bang K-H, Kim K-S. Quality by Design (QbD)-Based Development of a Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery System for the Ocular Delivery of Flurbiprofen. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(5):629. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17050629
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Ju-Hwan, Tae-Han Yoon, Si-Won Ryu, Min-Gyeong Kim, Gu-Hae Kim, Ye-Jin Oh, Su-Jeong Lee, Na-Woon Kwak, Kyu-Ho Bang, and Kyeong-Soo Kim. 2025. "Quality by Design (QbD)-Based Development of a Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery System for the Ocular Delivery of Flurbiprofen" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 5: 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17050629
APA StyleJeong, J.-H., Yoon, T.-H., Ryu, S.-W., Kim, M.-G., Kim, G.-H., Oh, Y.-J., Lee, S.-J., Kwak, N.-W., Bang, K.-H., & Kim, K.-S. (2025). Quality by Design (QbD)-Based Development of a Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery System for the Ocular Delivery of Flurbiprofen. Pharmaceutics, 17(5), 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17050629







