Measurement of Anti-TNF Biologics in Serum Samples of Pediatric Patients: Comparison of Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) with a Rapid and Automated Fluorescence-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients’ Samples
2.2. Enzyme-Linked Immunoassorbent Assays (ELISA)
2.3. Fluorescence-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay
2.4. Stability
2.5. Statistical Methods
3. Results
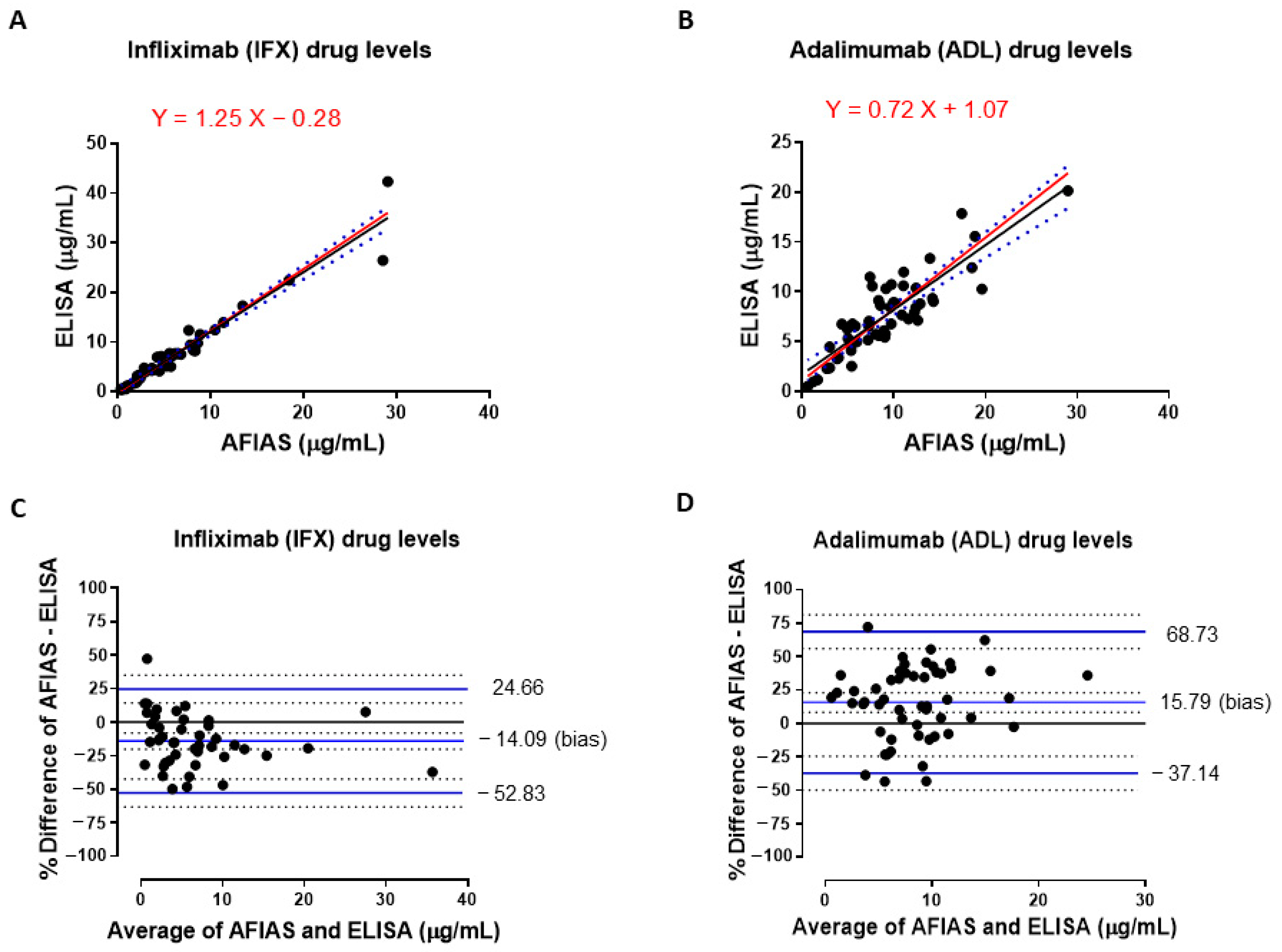
3.1. Comparison of IFX and ADL Serum Levels Measured with Both AFIAS and ELISA Assays
3.2. Comparison of Total Anti-Infliximab Concentrations in Serum Samples Obtained by Using AFIAS and ELISA Assays
3.3. Qualitative Evaluation of Agreement Between Drug Levels Measured with Both AFIAS and ELISA Assays
3.4. Evaluation of Stability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- D’Arcangelo, G.; Distante, M.; Raso, T.; Rossetti, D.; Catassi, G.; Aloi, M. Safety of Biological Therapy in Children with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2021, 72, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duijvestein, M.; Battat, R.; Vande Casteele, N.; D’Haens, G.R.; Sandborn, W.J.; Khanna, R.; Jairath, V.; Feagan, B.G. Novel Therapies and Treatment Strategies for Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Curr. Treat. Options Gastroenterol. 2018, 16, 129–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyams, J.; Crandall, W.; Kugathasan, S.; Griffiths, A.; Olson, A.; Johanns, J.; Liu, G.; Travers, S.; Heuschkel, R.; Markowitz, J.; et al. Induction and maintenance infliximab therapy for the treatment of moderate-to-severe Crohn’s disease in children. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyams, J.S.; Griffiths, A.; Markowitz, J.; Baldassano, R.N.; Faubion, W.A., Jr.; Colletti, R.B.; Dubinsky, M.; Kierkus, J.; Rosh, J.; Wang, Y.; et al. Safety and efficacy of adalimumab for moderate to severe Crohn’s disease in children. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 365–374.e362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rheenen, P.F.; Aloi, M.; Assa, A.; Bronsky, J.; Escher, J.C.; Fagerberg, U.L.; Gasparetto, M.; Gerasimidis, K.; Griffiths, A.; Henderson, P.; et al. The Medical Management of Paediatric Crohn’s Disease: An ECCO-ESPGHAN Guideline Update. J. Crohns Colitis 2020, 15, 171–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, S.R.; Bernardo, S.; Simoes, C.; Goncalves, A.R.; Valente, A.; Baldaia, C.; Moura Santos, P.; Correia, L.A.; Tato Marinho, R. Proactive Infliximab Drug Monitoring Is Superior to Conventional Management in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2020, 26, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bots, S.J.; Kuin, S.; Ponsioen, C.Y.; Gecse, K.B.; Duijvestein, M.; D’Haens, G.R.; Lowenberg, M. Relapse rates and predictors for relapse in a real-life cohort of IBD patients after discontinuation of anti-TNF therapy. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 54, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paolo, A.; Luci, G. Personalized Medicine of Monoclonal Antibodies in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Pharmacogenetics, Therapeutic Drug Monitoring, and Beyond. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 610806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naviglio, S.; Lacorte, D.; Lucafo, M.; Cifu, A.; Favretto, D.; Cuzzoni, E.; Silvestri, T.; Pozzi Mucelli, M.; Radillo, O.; Decorti, G.; et al. Causes of Treatment Failure in Children with Inflammatory Bowel Disease Treated with Infliximab: A Pharmacokinetic Study. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2019, 68, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazonovs, A.; Kennedy, N.A.; Moutsianas, L.; Heap, G.A.; Rice, D.L.; Reppell, M.; Bewshea, C.M.; Chanchlani, N.; Walker, G.J.; Perry, M.H.; et al. HLA-DQA1*05 Carriage Associated with Development of Anti-Drug Antibodies to Infliximab and Adalimumab in Patients with Crohn’s Disease. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curci, D.; Lucafo, M.; Cifu, A.; Fabris, M.; Bramuzzo, M.; Martelossi, S.; Franca, R.; Decorti, G.; Stocco, G. Pharmacogenetic variants of infliximab response in young patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2021, 14, 2184–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atiqi, S.; Hooijberg, F.; Loeff, F.C.; Rispens, T.; Wolbink, G.J. Immunogenicity of TNF-Inhibitors. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roda, G.; Jharap, B.; Neeraj, N.; Colombel, J.F. Loss of Response to Anti-TNFs: Definition, Epidemiology, and Management. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2016, 7, e135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.S.; Chon, H.; Kwon, Y.; Lee, M.; Kim, M.J.; Choe, Y.H. Fluorescence-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay for Quantification of Infliximab: Analytical and Clinical Performance Evaluation. Ther. Drug Monit. 2024, 46, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papamichael, K.; Cheifetz, A.S. Therapeutic drug monitoring in patients on biologics: Lessons from gastroenterology. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2020, 32, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, F.I.; Lichtenstein, G.R. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Anti-TNF Therapy in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Curr. Treat. Options Gastroenterol. 2014, 12, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeoli, R.; Dorlo, T.P.C.; Hanff, L.M.; Huitema, A.D.R.; Dreesen, E. Editorial: Therapeutic Drug Monitoring (TDM): A Useful Tool for Pediatric Pharmacology Applied to Routine Clinical Practice. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 931843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franca, R.; Curci, D.; Lucafo, M.; Decorti, G.; Stocco, G. Therapeutic drug monitoring to improve outcome of anti-TNF drugs in pediatric inflammatory bowel disease. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2019, 15, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakase, H.; Motoya, S.; Matsumoto, T.; Watanabe, K.; Hisamatsu, T.; Yoshimura, N.; Ishida, T.; Kato, S.; Nakagawa, T.; Esaki, M.; et al. Significance of measurement of serum trough level and anti-drug antibody of adalimumab as personalised pharmacokinetics in patients with Crohn’s disease: A subanalysis of the DIAMOND trial. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 46, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodini, G.; Giannini, E.G.; Savarino, V.; Del Nero, L.; Lo Pumo, S.; Brunacci, M.; De Bortoli, N.; Jain, A.; Tolone, S.; Savarino, E. Infliximab trough levels and persistent vs transient antibodies measured early after induction predict long-term clinical remission in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Dig. Liver Dis. 2018, 50, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papamichael, K.; Juncadella, A.; Wong, D.; Rakowsky, S.; Sattler, L.A.; Campbell, J.P.; Vaughn, B.P.; Cheifetz, A.S. Proactive Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Adalimumab Is Associated with Better Long-term Outcomes Compared with Standard of Care in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Crohns Colitis 2019, 13, 976–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vande Casteele, N. Assays for measurement of TNF antagonists in practice. Frontline Gastroenterol. 2017, 8, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regazzi, M.; Golay, J.; Molinaro, M. Monoclonal Antibody Monitoring: Clinically Relevant Aspects, A Systematic Critical Review. Ther. Drug Monit. 2020, 42, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeire, S.; Dreesen, E.; Papamichael, K.; Dubinsky, M.C. How, When, and for Whom Should We Perform Therapeutic Drug Monitoring? Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 1291–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ates, H.C.; Roberts, J.A.; Lipman, J.; Cass, A.E.G.; Urban, G.A.; Dincer, C. On-Site Therapeutic Drug Monitoring. Trends Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 1262–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curci, D.; Lucafo, M.; Cifu, A.; Bramuzzo, M.; Martelossi, S.; Favretto, D.; De Pellegrin, F.; Fabris, M.; Vascotto, F.; Naviglio, S.; et al. Determination of Serum Infliximab Concentration by Point-of-care Devices in Children with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2019, 69, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez Perez, J.; Inda-Landaluce, M.; Nocito-Colon, M.; Martinez-Lostao, L. Comparative Analysis of 2 Commercially Available Assays for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Infliximab and Adalimumab. Ther. Drug Monit. 2025, 00, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iniesta-Navalón, C.; Ríos-Saorín, M.; Añez-Castaño, R.; Rentero-Redondo, L.; Ortíz-Fernandez, P.; Martínez, E.; Urbieta-Sanz, E. Evaluating the Accuracy and Clinical Utility of AFIAS-10 Point of Care Versus Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay in Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Infliximab and Adalimumab. Ther. Drug Monit. 2024, 00, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.; Corbett, G.; Moss, A.C. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis: Serum Infliximab Levels During Maintenance Therapy and Outcomes in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Crohns Colitis 2016, 10, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Moreau, A.C.; Del Tedesco, E.; Rinaudo, M.; Phelip, J.M.; Genin, C.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Roblin, X. Pharmacokinetics of adalimumab in inflammatory bowel diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2014, 20, 1288–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Afonso, J.; Lopes, S.; Goncalves, R.; Caldeira, P.; Lago, P.; Tavares de Sousa, H.; Ramos, J.; Goncalves, A.R.; Ministro, P.; Rosa, I.; et al. Proactive therapeutic drug monitoring of infliximab: A comparative study of a new point-of-care quantitative test with two established ELISA assays. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 44, 684–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherry, M.; Dutzer, D.; Nasser, Y.; Berger, A.E.; Roblin, X.; Paul, S. Point-of-Care Assays Could Be Useful for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of IBD Patients in a Proactive Strategy with Adalimumab. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facchin, S.; Buda, A.; Cardin, R.; Agbariah, N.; Zingone, F.; De Bona, M.; Zaetta, D.; Bertani, L.; Ghisa, M.; Barberio, B.; et al. Rapid point-of-care anti-infliximab antibodies detection in clinical practice: Comparison with ELISA and potential for improving therapeutic drug monitoring in IBD patients. Therap. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2021, 14, 1756284821999902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novakovic, V.; Abdija, S.; Larsen, P.B.; Fenger, M.; Gredal, L.; Jacobsen, K.K. Comparison of the Quantum Blue(R) reader Point-of-Care system versus ELISA technique for therapeutic drug monitoring of Infliximab levels. Clin. Biochem. 2019, 74, 73–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasser, Y.; Labetoulle, R.; Harzallah, I.; Berger, A.E.; Roblin, X.; Paul, S. Comparison of Point-of-Care and Classical Immunoassays for the Monitoring Infliximab and Antibodies Against Infliximab in IBD. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2018, 63, 2714–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdes-Delgado, T.; Aguado-Paredes, A.; Merino-Bohorquez, V.; Martin-Manzanares, J.; Alonso, M.M.; Maldonado, B.; Castro, L.; Belvis, M.; Benitez, B.; Caunedo, A.; et al. Performance of a New Rapid Point-of-Care Test for Infliximab Levels in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Comparison to ELISA. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2024, 69, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jannetto, P.J. Chapter 8-Therapeutic drug monitoring using mass spectrometry. In Mass Spectrometry for the Clinical Laboratory; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 165–179. [Google Scholar]
- Velikova, T.; Sekulovski, M.; Peshevska-Sekulovska, M. Immunogenicity and Loss of Effectiveness of Biologic Therapy for Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients Due to Anti-Drug Antibody Development. Antibodies 2024, 13, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual-Salcedo, D.; Plasencia, C.; Ramiro, S.; Nuno, L.; Bonilla, G.; Nagore, D.; Ruiz Del Agua, A.; Martinez, A.; Aarden, L.; Martin-Mola, E.; et al. Influence of immunogenicity on the efficacy of long-term treatment with infliximab in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2011, 50, 1445–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartelds, G.M.; Krieckaert, C.L.; Nurmohamed, M.T.; van Schouwenburg, P.A.; Lems, W.F.; Twisk, J.W.; Dijkmans, B.A.; Aarden, L.; Wolbink, G.J. Development of antidrug antibodies against adalimumab and association with disease activity and treatment failure during long-term follow-up. JAMA 2011, 305, 1460–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeire, S.; Gils, A.; Accossato, P.; Lula, S.; Marren, A. Immunogenicity of biologics in inflammatory bowel disease. Therap Adv. Gastroenterol. 2018, 11, 1756283X17750355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steenholdt, C.; Brynskov, J.; Thomsen, O.O.; Munck, L.K.; Fallingborg, J.; Christensen, L.A.; Pedersen, G.; Kjeldsen, J.; Jacobsen, B.A.; Oxholm, A.S.; et al. Individualised therapy is more cost-effective than dose intensification in patients with Crohn’s disease who lose response to anti-TNF treatment: A randomised, controlled trial. Gut 2014, 63, 919–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steenholdt, C.; Ainsworth, M.A.; Tovey, M.; Klausen, T.W.; Thomsen, O.O.; Brynskov, J.; Bendtzen, K. Comparison of techniques for monitoring infliximab and antibodies against infliximab in Crohn’s disease. Ther. Drug Monit. 2013, 35, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloem, K.; van Leeuwen, A.; Verbeek, G.; Nurmohamed, M.T.; Wolbink, G.J.; van der Kleij, D.; Rispens, T. Systematic comparison of drug-tolerant assays for anti-drug antibodies in a cohort of adalimumab-treated rheumatoid arthritis patients. J. Immunol. Methods 2015, 418, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, F.B.; Morand, E.F.; Murphy, K.; Mackay, F.; Mariette, X.; Marcelli, C. Antidrug antibodies (ADAb) to tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-specific neutralising agents in chronic inflammatory diseases: A real issue, a clinical perspective. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Reference ELISA | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| (IDKmonitor® Infliximab Drug Levels) | |||
| <3 µg/mL | ≥3 to <7 µg/mL | ≥7 µg/mL | |
| AFIAS Infliximab | |||
| <3 µg/mL | 13 | 5 | 0 |
| ≥3 to <7 µg/mL | 0 | 8 | 6 |
| ≥7 µg/mL | 0 | 0 | 12 |
| Reference ELISA | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| (IDKmonitor® Adalimumab Drug Levels) | |||
| <5 µg/mL | ≥5 to <10 µg/mL | ≥10 µg/mL | |
| AFIAS Adalimumab | |||
| <5 µg/mL | 8 | 2 | 0 |
| ≥5 to <10 µg/mL | 4 | 18 | 4 |
| ≥10 µg/mL | 0 | 9 | 9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rossi, C.; Simeoli, R.; Angelino, G.; Cairoli, S.; Bracci, F.; Knafelz, D.; Romeo, E.F.; Faraci, S.; Tarantino, G.; Mancini, A.; et al. Measurement of Anti-TNF Biologics in Serum Samples of Pediatric Patients: Comparison of Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) with a Rapid and Automated Fluorescence-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040421
Rossi C, Simeoli R, Angelino G, Cairoli S, Bracci F, Knafelz D, Romeo EF, Faraci S, Tarantino G, Mancini A, et al. Measurement of Anti-TNF Biologics in Serum Samples of Pediatric Patients: Comparison of Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) with a Rapid and Automated Fluorescence-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(4):421. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040421
Chicago/Turabian StyleRossi, Chiara, Raffaele Simeoli, Giulia Angelino, Sara Cairoli, Fiammetta Bracci, Daniela Knafelz, Erminia Francesca Romeo, Simona Faraci, Giusyda Tarantino, Alessandro Mancini, and et al. 2025. "Measurement of Anti-TNF Biologics in Serum Samples of Pediatric Patients: Comparison of Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) with a Rapid and Automated Fluorescence-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 4: 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040421
APA StyleRossi, C., Simeoli, R., Angelino, G., Cairoli, S., Bracci, F., Knafelz, D., Romeo, E. F., Faraci, S., Tarantino, G., Mancini, A., Vitale, A., Vici, C. D., Manzoni, S. M., De Angelis, P., & Goffredo, B. M. (2025). Measurement of Anti-TNF Biologics in Serum Samples of Pediatric Patients: Comparison of Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) with a Rapid and Automated Fluorescence-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay. Pharmaceutics, 17(4), 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040421








