Vedolizumab Clearance as a Surrogate Marker for Remission in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients: Insights from Real-World Pharmacokinetics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Treatment and Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Vedolizumab
2.3. Data Source
2.4. Population Pharmacokinetic Modelling
2.5. Statistical Analysis
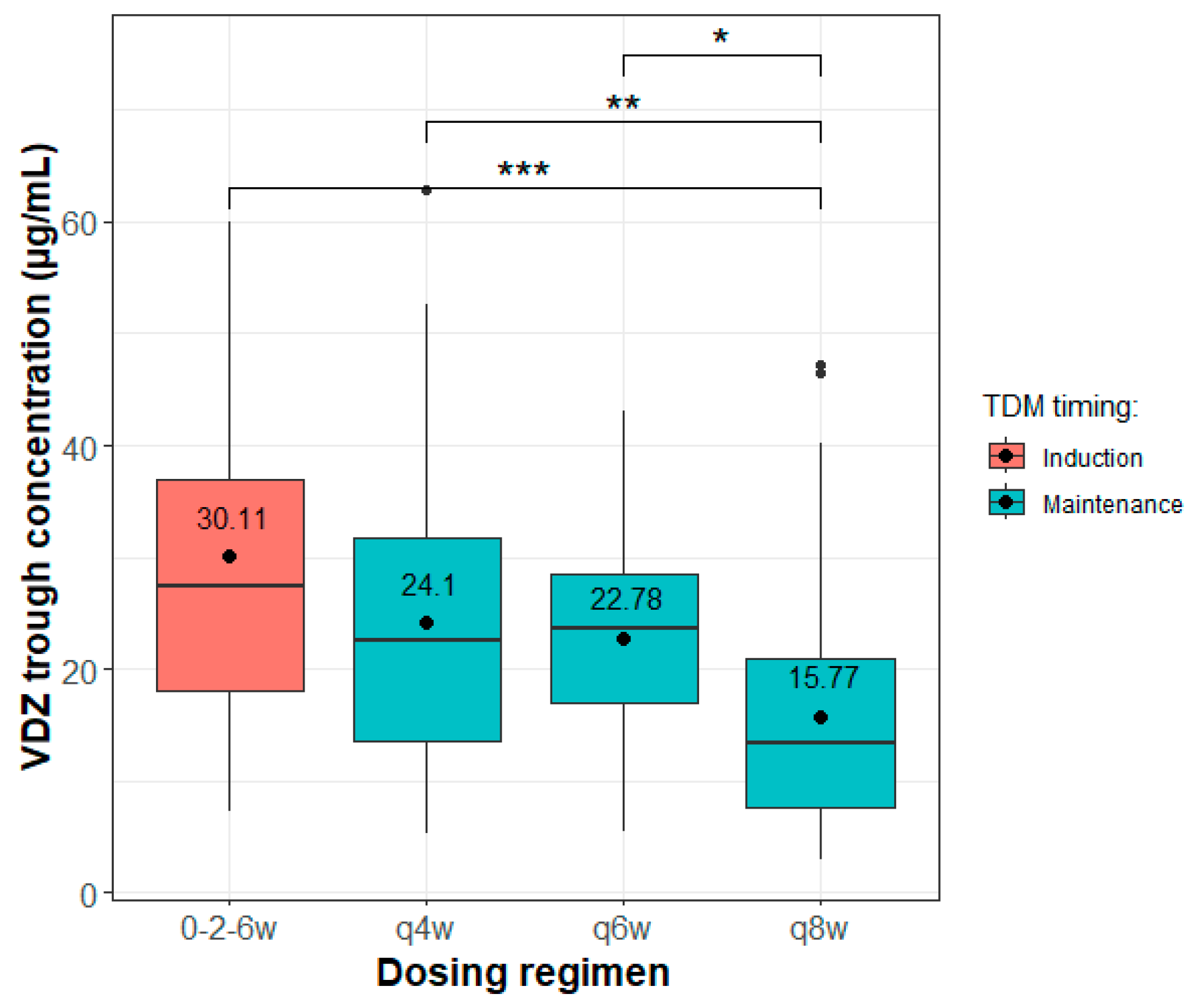
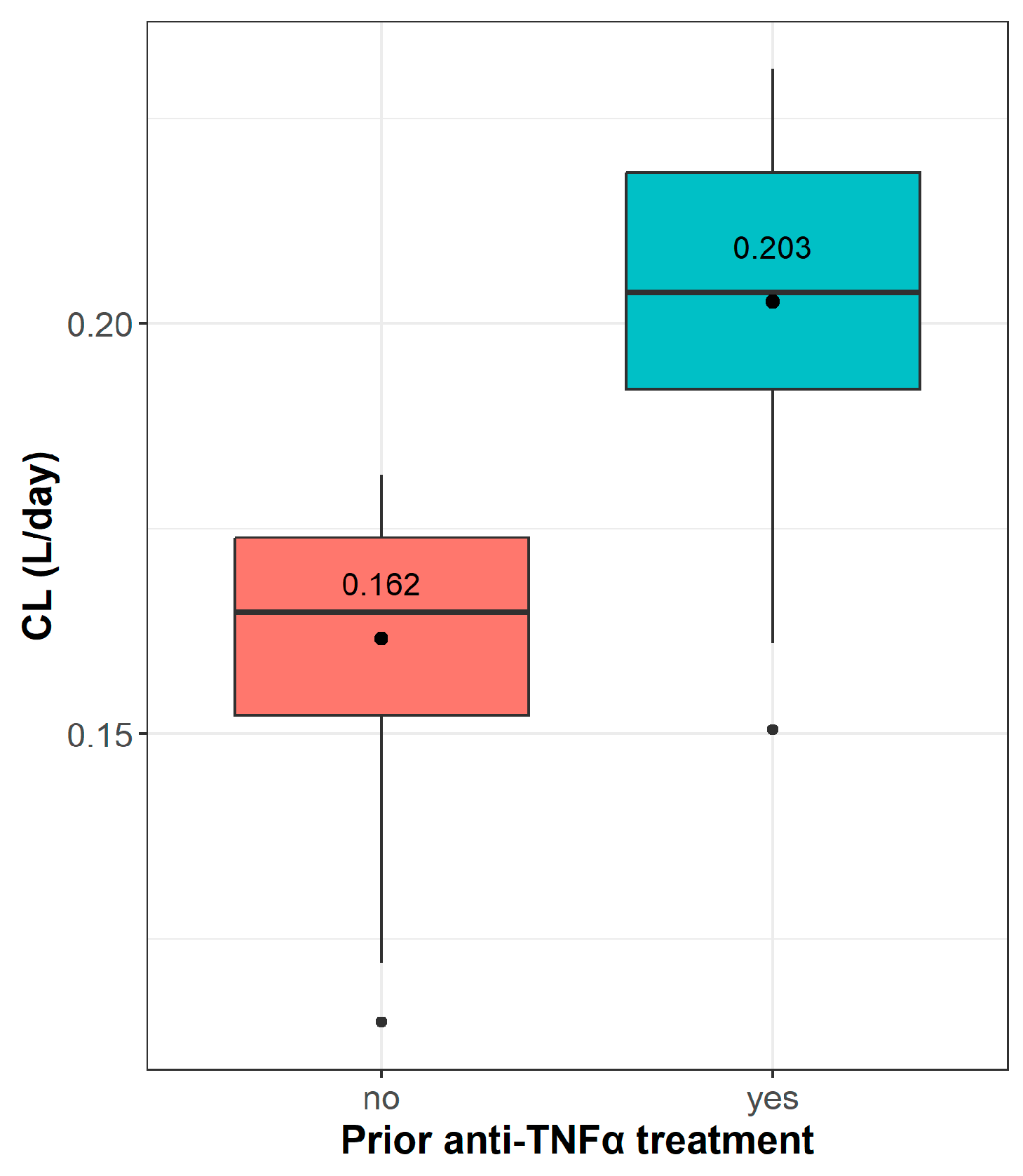
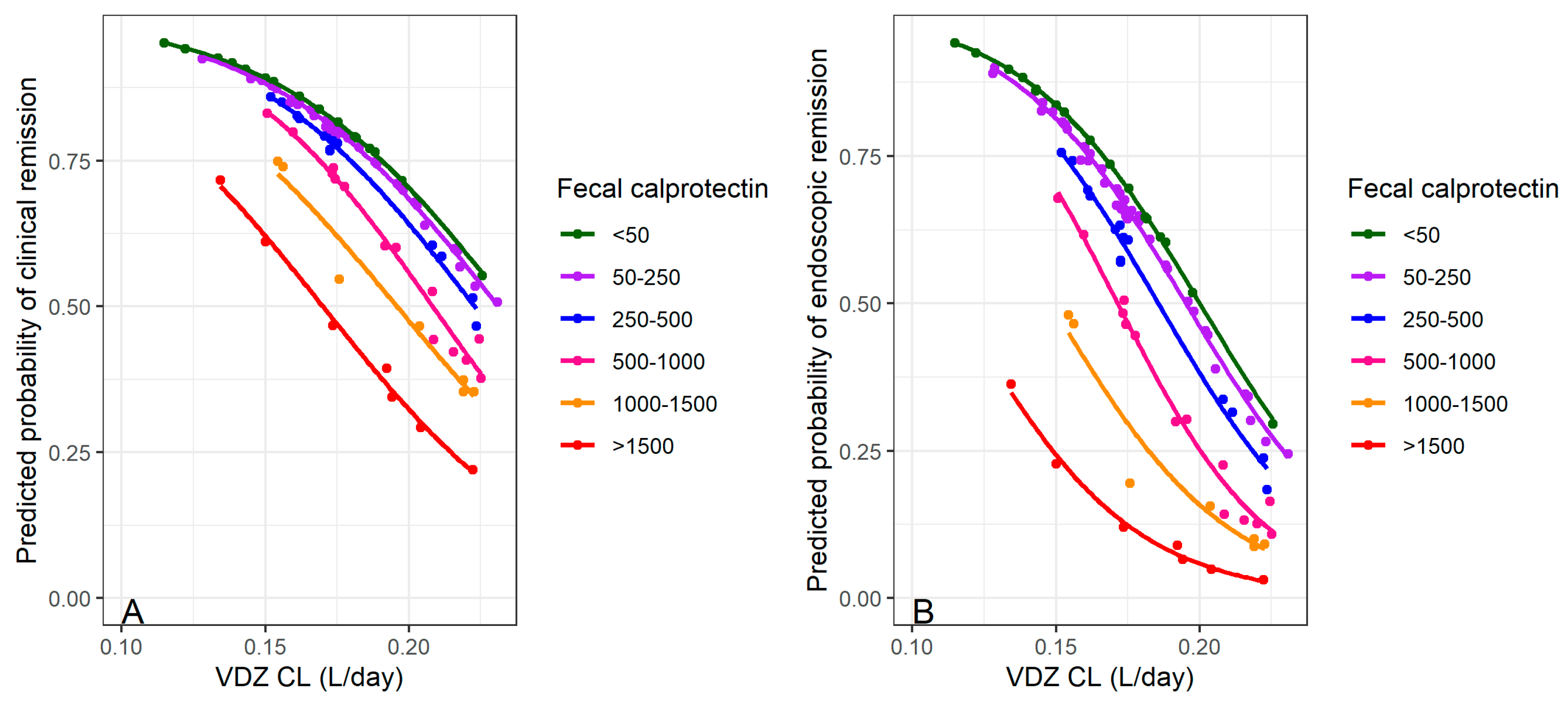
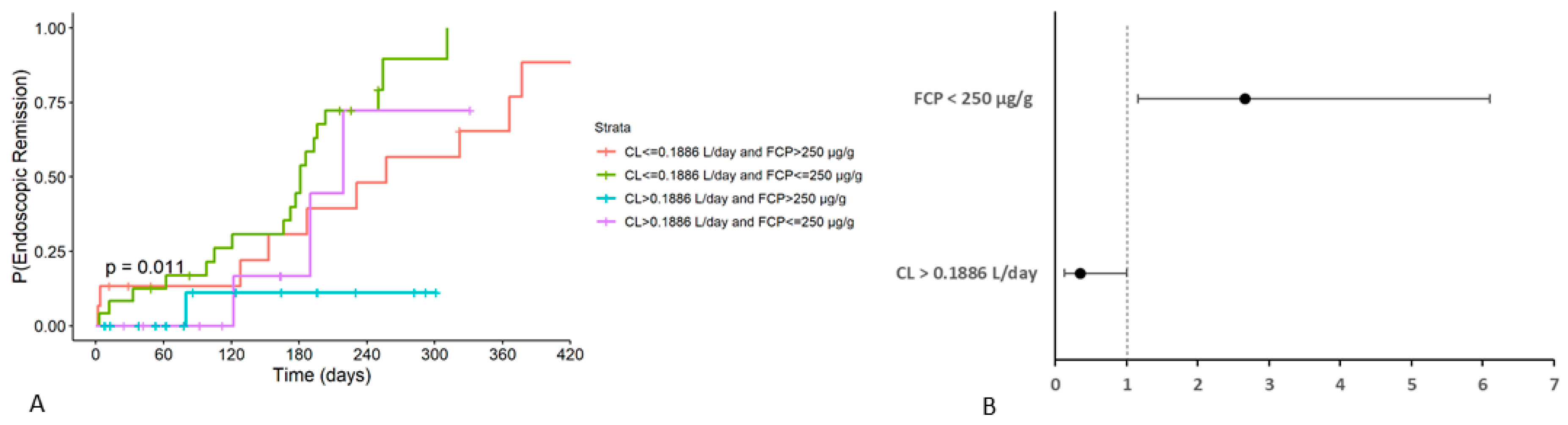
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- SmPC Entyvio. Summary of Product Characteristics for Entyvio 300 mg Powder for Concentrate for Solution for Infusion. Last Updated on the eMC: 02/15/2024. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/5442/smpc#gref (accessed on 1 October 2024).
- Rosario, M.; Dirks, N.L.; Milch, C.; Parikh, A.; Bargfrede, M.; Wyant, T.; Fedyk, E.; Fox, I. A review of the clinical pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and immunogenicity of vedolizumab. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2017, 56, 1287–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosario, M.; Wyant, T.; Leach, T.; Sankoh, S.; Scholz, C.; Parikh, A.; Fox, I.; Feagan, B.G. Vedolizumab pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, safety, and tolerability following administration of a single, ascending, intravenous dose to healthy volunteers. Clin. Drug Investig. 2016, 36, 913–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, M.G.; Sparrow, M.P.; Roblin, X. Therapeutic drug monitoring of vedolizumab in inflammatory bowel disease: Current data and future directions. Therap Adv. Gastroenterol. 2018, 11, 1756284818772786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosario, M.; Dirks, N.L.; Gastonguay, M.R.; Fasanmade, A.A.; Wyant, T.; Parikh, A.; Sandborn, W.J.; Feagan, B.G.; Reinisch, W.; Fox, I. Population pharmacokinetics-pharmacodynamics of vedolizumab in patients with ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 42, 188–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feagan, B.G.; Rutgeerts, P.; Sands, B.E.; Hanauer, S.; Colombel, J.F.; Sandborn, W.J.; Van Assche, G.; Axler, J.; Kim, H.J.; Danese, S.; et al. Vedolizumab as induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 699–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandborn, W.J.; Feagan, B.G.; Rutgeerts, P.; Hanauer, S.; Colombel, J.F.; Sands, B.E.; Lukas, M.; Fedorak, R.N.; Lee, S.; Bressler, B.; et al. Vedolizumab as induction and maintenance therapy for Crohn’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roganovic, M.; Homsek, A.; Jovanovic, M.; Topić Vučenović, V.; Ćulafić, M.; Miljković, B.; Vučićević, K. Concept and utility of population pharmacokinetic and pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic models in drug development and clinical practice. Arh. Farm. 2021, 71, 336–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, H.; Dirks, N.L.; Rosario, M.; Hori, T.; Hibi, T. Population pharmacokinetics of vedolizumab in Asian and non-Asian patients with ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Intest. Res. 2021, 19, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauwels, R.W.M.; Proietti, E.; van der Woude, C.J.; Oudijk, L.; Crombag, M.B.S.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Grohmann, U.; Fuhler, G.M.; de Vries, A.C. Vedolizumab tissue concentration correlates to mucosal inflammation and objective treatment response in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2021, 27, 1813–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyant, T.; Yang, L.; Rosario, M. Comparison of the ELISA and ECL Assay for vedolizumab anti-drug antibodies: Assessing the impact on pharmacokinetics and safety outcomes of the phase 3 GEMINI trials. AAPS 2020, 23, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanzel, J.; Dreesen, E.; Vermeire, S.; Lowenberg, M.; Hoentjen, F.; Bossuyt, P.; Clasquin, E.; Baert, F.J.; D’Haens, G.R.; Mathot, R. Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic model of vedolizumab for targeting endoscopic remission in patients with crohn disease: Posthoc analysis of the LOVE-CD study. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2022, 28, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colman, R.J.; Mizuno, T.; Fukushima, K.; Haslam, D.B.; Hyams, J.S.; Boyle, B.; Noe, J.D.; D’Haens, G.R.; Van Limbergen, J.; Chun, K.; et al. Real world population pharmacokinetic study in children and young adults with inflammatory bowel disease discovers novel blood and stool microbial predictors of vedolizumab clearance. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 57, 524–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreesen, E.; Verstockt, B.; Bian, S.; de Bruyn, M.; Compernolle, G.; Tops, S.; Noman, M.; Van Assche, G.; Ferrante, M.; Gils, A.; et al. Evidence to support monitoring of vedolizumab trough concentrations in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 16, 1937–1946.e1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusato, J.; Ribaldone, D.G.; Falzone, M.H.; Manca, A.; Antonucci, M.; Palermiti, A.; Saracco, G.M.; Ceccarelli, L.; Costa, F.; Bottari, A.; et al. Therapeutic drug monitoring as a tool for the clinical outcome prediction in vedolizumab-treated patients: An italian pilot study. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steenholdt, C.; Lorentsen, R.D.; Petersen, P.N.; Widigson, E.S.; Kloft, C.; Klaasen, R.A.; Brynskov, J. Therapeutic drug monitoring of vedolizumab therapy in inflammatory bowel disease. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 39, 1088–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Restellini, S.; Afif, W. Update on TDM (Therapeutic Drug Monitoring) with Ustekinumab, Vedolizumab and Tofacitinib in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosario, M.; French, J.L.; Dirks, N.L.; Sankoh, S.; Parikh, A.; Yang, H.; Danese, S.; Colombel, J.F.; Smyth, M.; Sandborn, W.J.; et al. Exposure-efficacy relationships for vedolizumab induction therapy in patients with ulcerative colitis or crohn’s disease. J. Crohns Colitis 2017, 11, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osterman, M.T.; Rosario, M.; Lasch, K.; Barocas, M.; Wilbur, J.D.; Dirks, N.L.; Gastonguay, M.R. Vedolizumab exposure levels and clinical outcomes in ulcerative colitis: Determining the potential for dose optimisation. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 49, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williet, N.; Boschetti, G.; Fovet, M.; Di Bernado, T.; Claudez, P.; Del Tedesco, E.; Jarlot, C.; Rinaldi, L.; Berger, A.; Phelip, J.M.; et al. Association between low trough levels of vedolizumab during induction therapy for inflammatory bowel diseases and need for additional doses within 6 months. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, 1750–1757.e1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bawardy, B.; Ramos, G.P.; Willrich, M.A.V.; Jenkins, S.M.; Park, S.H.; Aniwan, S.; Schoenoff, S.A.; Bruining, D.H.; Papadakis, K.A.; Raffals, L.; et al. Vedolizumab drug level correlation with clinical remission, biomarker normalization, and mucosal healing in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2019, 25, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yacoub, W.; Williet, N.; Pouillon, L.; Di-Bernado, T.; De Carvalho Bittencourt, M.; Nancey, S.; Lopez, A.; Paul, S.; Zallot, C.; Roblin, X.; et al. Early vedolizumab trough levels predict mucosal healing in inflammatory bowel disease: A multicentre prospective observational study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 47, 906–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungaro, R.C.; Yarur, A.; Jossen, J.; Phan, B.L.; Chefitz, E.; Sehgal, P.; Kamal, K.; Bruss, A.; Beniwal-Patel, P.; Fox, C.; et al. Higher trough vedolizumab concentrations during maintenance therapy are associated with corticosteroid-free remission in inflammatory bowel disease. J. Crohns Colitis 2019, 13, 963–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouillon, L.; Rousseau, H.; Busby-Venner, H.; De Carvalho Bittencourt, M.; Choukour, M.; Gauchotte, G.; Zallot, C.; Danese, S.; Baumann, C.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L. Vedolizumab trough levels and histological healing during maintenance therapy in ulcerative colitis. J. Crohns Colitis 2019, 13, 970–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarur, A.J.; Bruss, A.; Naik, S.; Beniwal-Patel, P.; Fox, C.; Jain, A.; Berens, B.; Patel, A.; Ungaro, R.; Bahur, B.; et al. Vedolizumab concentrations are associated with long-term endoscopic remission in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2019, 64, 1651–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Dulai, P.S.; Vande Casteele, N.; Battat, R.; Fumery, M.; Boland, B.S.; Sandborn, W.J. Systematic review with meta-analysis: Association between vedolizumab trough concentration and clinical outcomes in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 50, 848–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouillon, L.; Vermeire, S.; Bossuyt, P. Vedolizumab trough level monitoring in inflammatory bowel disease: A state-of-the-art overview. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaughn, B.P.; Yarur, A.J.; Graziano, E.; Campbell, J.P.; Bhattacharya, A.; Lee, J.Y.; Gheysens, K.; Papamichael, K.; Osterman, M.T.; Cheifetz, A.S.; et al. Vedolizumab serum trough concentrations and response to dose escalation in inflammatory bowel disease. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosario, M.; Abhyankar, B.; Sankoh, S.; Dirks, N.; Lasch, K.; Sandborn, W. Relationship between vedolizumab pharmacokinetics and endoscopic outcomes in patients with ulcerative colitis. J. Crohns Colitis 2015, 9, S46. [Google Scholar]
- Jairath, V.; Yarur, A.; Osterman, M.T.; James, A.; Balma, D.; Mehrotra, S.; Yang, L.; Yajnik, V.; Qasim Khan, R.M. ENTERPRET: A randomized controlled trial of vedolizumab dose optimization in patients with ulcerative colitis who have early nonresponse. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 22, 1077–1086.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, S.; Dias, S.; Kumar, A.; Blackwell, J.; Brookes, M.J.; Segal, J.P. Meta-analysis: The efficacy of therapeutic drug monitoring of anti-tnf-therapy in inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 57, 1362–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheifetz, A.S.; Abreu, M.T.; Afif, W.; Cross, R.K.; Dubinsky, M.C.; Loftus, E.V., Jr.; Osterman, M.T.; Saroufim, A.; Siegel, C.A.; Yarur, A.J.; et al. A comprehensive literature review and expert consensus statement on therapeutic drug monitoring of biologics in inflammatory bowel disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 116, 2014–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Paolo, A.; Luci, G. Personalized medicine of monoclonal antibodies in inflammatory bowel disease: Pharmacogenetics, therapeutic drug monitoring, and beyond. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 610806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beal, S.L.; Sheiner, L.B.; Boeckmann, A.J.; Bauer, R.J. NONMEM 7.5 Users Guides; Icon Development Solutions: Ellicott City, MD, USA, 1989–2024. [Google Scholar]
- Chan Kwong, A.H.P.; Calvier, E.A.M.; Fabre, D.; Gattacceca, F.; Khier, S. Prior information for population pharmacokinetic and pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic analysis: Overview and guidance with a focus on the NONMEM PRIOR subroutine. J. Pharmacokinet. Pharmacodyn. 2020, 47, 431–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisleskog, P.O.; Karlsson, M.O.; Beal, S.L. Use of prior information to stabilize a population data analysis. J. Pharmacokinet. Pharmacodyn. 2002, 29, 473–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sands, B.E.; Feagan, B.G.; Rutgeerts, P.; Colombel, J.F.; Sandborn, W.J.; Sy, R.; D’Haens, G.; Ben-Horin, S.; Xu, J.; Rosario, M.; et al. Effects of vedolizumab induction therapy for patients with Crohn’s disease in whom tumor necrosis factor antagonist treatment failed. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 618–627.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauwels, R.W.M.; van der Woude, C.J.; Erler, N.S.; de Vries, A.C. Fecal calprotectin is an early predictor of endoscopic response and histologic remission after the start of vedolizumab in inflammatory bowel disease. Therap Adv. Gastroenterol. 2020, 13, 1756284820979765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauwels, R.W.M.; de Vries, A.C.; van der Woude, C.J. Fecal calprotectin is a reliable marker of endoscopic response to vedolizumab therapy: A simple algorithm for clinical practice. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 35, 1893–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; de Lannoy, I.A. Pharmacokinetics. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 87, 93–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magro, F.; Fernandes, S.; Patita, M.; Arroja, B.; Lago, P.; Rosa, I.; de Sousa, H.T.; Ministro, P.; Mocanu, I.; Vieira, A.; et al. The influence of subclinical active inflammation on IFX pharmacokinetic modeling and disease progression assessment: Findings from a prospective real-world study in inflammatory bowel disease patients. J. Crohns Colitis 2024, 18, 1102–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamedi, J.A.; Thomas, D.; Rahier, J.F.; Louis, E.; Baert, F.; Dewint, P.; Lambrecht, G.; Vermeire, S.; Bossuyt, P.; Franchimont, D.; et al. Cumulative Exposure to Infliximab During Induction Therapy Predict Remission in Patients with Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis. PAGE 32 (2024) Abstr. 11125. 2024. Available online: www.page-meeting.org/?abstract=11125 (accessed on 1 October 2024).
| Ulcerative Colitis (N = 62) | Crohn’s Disease (N = 44) | Total (N = 106) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | |||
| Mean (SD) | 49.81 (17.56) | 49.71 (17.44) | 49.76 (17.43) |
| Range | 21–78 | 21–76 | 21–78 |
| Sex | |||
| Male | 36 (58.1%) | 19 (43.2%) | 55 (51.9%) |
| Female | 26 (41.9%) | 25 (56.8%) | 51 (48.1%) |
| Body weight (kg) | |||
| Mean (SD) | 74.29 (11.57) | 68.64 (13.74) * | 71.94 (12.76) |
| Range | 50–110 | 44–103 | 44–110 |
| Haemoglobin (g/L) | |||
| N-Miss | 3 | 2 | 5 |
| Mean (SD) | 126.83 (23.06) | 126.74 (18.85) | 126.79 (21.31) |
| Range | 75–171 | 68–161 | 68–171 |
| Erythrocytes (·1012/L) | |||
| N-Miss | 5 | 1 | 6 |
| Mean (SD) | 4.50 (0.71) | 4.41 (0.49) | 4.46 (0.63) |
| Range | 2.45–5.84 | 3.08–5.50 | 2.45–5.84 |
| Iron (µmol/L) | |||
| N-Miss | 10 | 6 * | 16 |
| Mean (SD) | 8.47 (5.84) | 11.62 (6.74) | 9.80 (6.39) |
| Range | 2.0–24.8 | 2.8–28.2 | 2.0–28.2 |
| CRP (mg/L) | |||
| N-Miss | 3 | 0 | 3 |
| Mean (SD) | 21.80 (42.97) | 8.94 (13.04) | 16.31 (34.10) |
| Range | 0.1–205.0 | 0.1–66.2 | 0.1–205.0 |
| Albumin (g/L) | |||
| N-Miss | 29 | 13 | 42 |
| Mean (SD) | 39.03 (5.75) | 40.55 (6.10) | 39.77 (5.92) |
| Range | 28–49 | 26–52 | 26–52 |
| Platelets (·109/L) | |||
| N-Miss | 8 | 1 | 9 |
| Mean (SD) | 332.37 (130.65) | 324.86 (118.60) | 329.04 (124.87) |
| Range | 123–797 | 120–701 | 120–797 |
| Leukocytes (·109/L) | |||
| N-Miss | 6 | 3 | 9 |
| Mean (SD) | 9.07 (3.54) | 9.01 (3.50) | 9.05 (3.50) |
| Range | 2.4–18.4 | 2.8–16.7 | 2.4–18.4 |
| Ferritin (ng/mL) | |||
| N-Miss | 15 | 6 | 21 |
| Mean (SD) | 58.83 (88.51) | 45.58 (47.62) | 52.91 (73.03) |
| Range | 3–495 | 4–164 | 3–495 |
| Faecal calprotectin (µg/g) | |||
| N-Miss | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Mean (SD) | 608.63 (573.21) | 544.19 (602.01) | 582.24 (583.17) |
| Range | 16–1801 | 12–2055 | 12–2055 |
| Immunomodulatory drug (azathioprine, 6-mercaptopurine, methotrexate, calcineurin inhibitors) | |||
| No | 14 (22.6%) | 6 (13.6%) | 20 (18.9%) |
| Yes | 48 (77.4%) | 39 (86.4%) | 86 (81.1%) |
| Prior anti-TNFα therapy | |||
| No | 39 (62.9%) | 23 (52.3%) | 62 (58.5%) |
| Yes | 23 (37.1%) | 21 (47.7%) | 44 (41.5%) |
| Parameter (Units) | Estimated Value (%RSE) | Bootstrap Median (2.5–97.5th Percentile) |
|---|---|---|
| CL (L/day) | 0.159 (4.8) | 0.160 (0.143–0.177) |
| Vc (L) | 3.19 (1) | 3.19 (3.191–3.192) |
| Q (L/day) | 0.120 (3.8) | 0.120 (0.119–0.120) |
| Vp (L) | 1.66 (1.8) | 1.66 (1.65–1.66) |
| ATNF | 0.264 (28.3) | 0.263 (0.105–0.453) |
| IIVCL (%) | 16.4 (25.3) | 15.9 (7.91–32.3) |
| IIVVc (%) | 18.9 (2.8) | 18.9 (18.9–18.9) |
| Proportional residual error | 0.458 (11.1) | 0.453 (0.226–0.520) |
| Dosing Regimen | prior Anti-TNFα | Ctrough (5–95% CI) [ng/mL] | AUC0-last (5–95% CI) [ng·day/mL] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0–2–6w + 10w + q4w | no | 36.6 (20.4–59.8) | 16,534 (13,191–22,415) |
| yes | 25.7 (14.7–39.1) | 13,851 (11,069–17,585) | |
| 0–2–6w + 14w + q6w | no | 20.5 (12.4–35.9) | 12,925 (9834–16,107) |
| yes | 13.4 (5.46–20.4) | 10,236 (6877–12,993) | |
| 0–2–6w + q8w | no | 11.6 (5.92–20.9) | 10,860 (7856–14,551) |
| yes | 6.82 (2.86–13.9) | 8531 (6723–12,305) | |
| 0–2–6w + 10w + q8w | no | 26.4 (14.4–42.4) | 11,816 (9279–16,496) |
| yes | 18.2 (11.4–31.8) | 9879 (7380–13,386) |
| Predictor Variable | Remission | p-Value | AUROC (95% CI) | Youden’s Index | Optimal Threshold |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plt (109/L) | Clinical | <0.05 | 57.8 (44.9–70.7) | 0.249 | 392 |
| Endoscopic | <0.001 | 70.6 (60.6–80.6) | 0.313 | 257.5 | |
| FCP (µg/g) | Clinical | <0.01 | 74.4 (64.4–84.2) | 0.427 | 164.5 |
| Endoscopic | <0.001 | 73.0 (63.6–82.5) | 0.347 | 190.5 | |
| VDZ Ctrough (ng/mL) | Clinical | n.s. | 54.0 (42.5–65.5) | 0.155 | 19.84 |
| Endoscopic | n.s. | 49.4 (38.7–60.1) | 0.0887 | 35.71 | |
| VDZ CL (L/day) | Clinical | <0.01 | 67.2 (56.1–78.2) | 0.287 | 0.1886 |
| Endoscopic | <0.001 | 72.7 (63.0–82.4) | 0.442 | 0.1886 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marković, S.; Kralj, Đ.; Svorcan, P.; Knežević Ivanovski, T.; Odanović, O.; Obradović, S.; Homšek, A.; Jovanović, M.; Savić, R.; Vučićević, K.M. Vedolizumab Clearance as a Surrogate Marker for Remission in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients: Insights from Real-World Pharmacokinetics. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1629. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16121629
Marković S, Kralj Đ, Svorcan P, Knežević Ivanovski T, Odanović O, Obradović S, Homšek A, Jovanović M, Savić R, Vučićević KM. Vedolizumab Clearance as a Surrogate Marker for Remission in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients: Insights from Real-World Pharmacokinetics. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(12):1629. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16121629
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarković, Srđan, Đorđe Kralj, Petar Svorcan, Tamara Knežević Ivanovski, Olga Odanović, Sanja Obradović, Ana Homšek, Marija Jovanović, Rada Savić, and Katarina M. Vučićević. 2024. "Vedolizumab Clearance as a Surrogate Marker for Remission in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients: Insights from Real-World Pharmacokinetics" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 12: 1629. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16121629
APA StyleMarković, S., Kralj, Đ., Svorcan, P., Knežević Ivanovski, T., Odanović, O., Obradović, S., Homšek, A., Jovanović, M., Savić, R., & Vučićević, K. M. (2024). Vedolizumab Clearance as a Surrogate Marker for Remission in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients: Insights from Real-World Pharmacokinetics. Pharmaceutics, 16(12), 1629. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16121629







