Taste-Masked Diclofenac Sodium Microparticles Prepared by Polyelectrolyte Complexation: Formulation Using Different Fatty Acids and Taste Evaluation by Human Panel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of Polyelectrolyte Complexes
2.2.2. Storage Stability Assessment
2.2.3. Diclofenac Sodium Content Analysis
2.2.4. In Vitro Drug Dissolution Profile
2.2.5. Taste Evaluation
2.2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
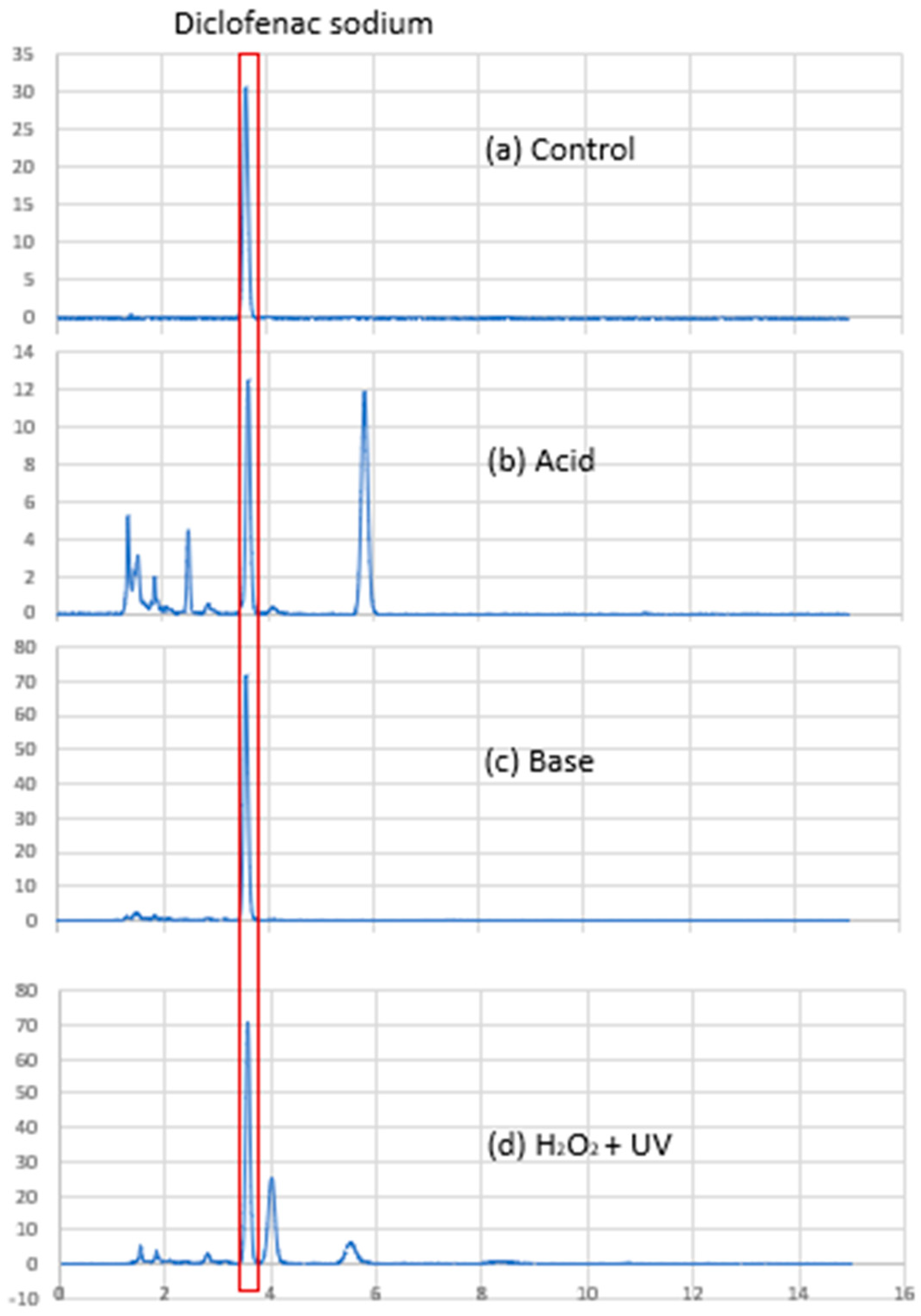
3.1. Stability Assessment: Diclofenac Sodium Content
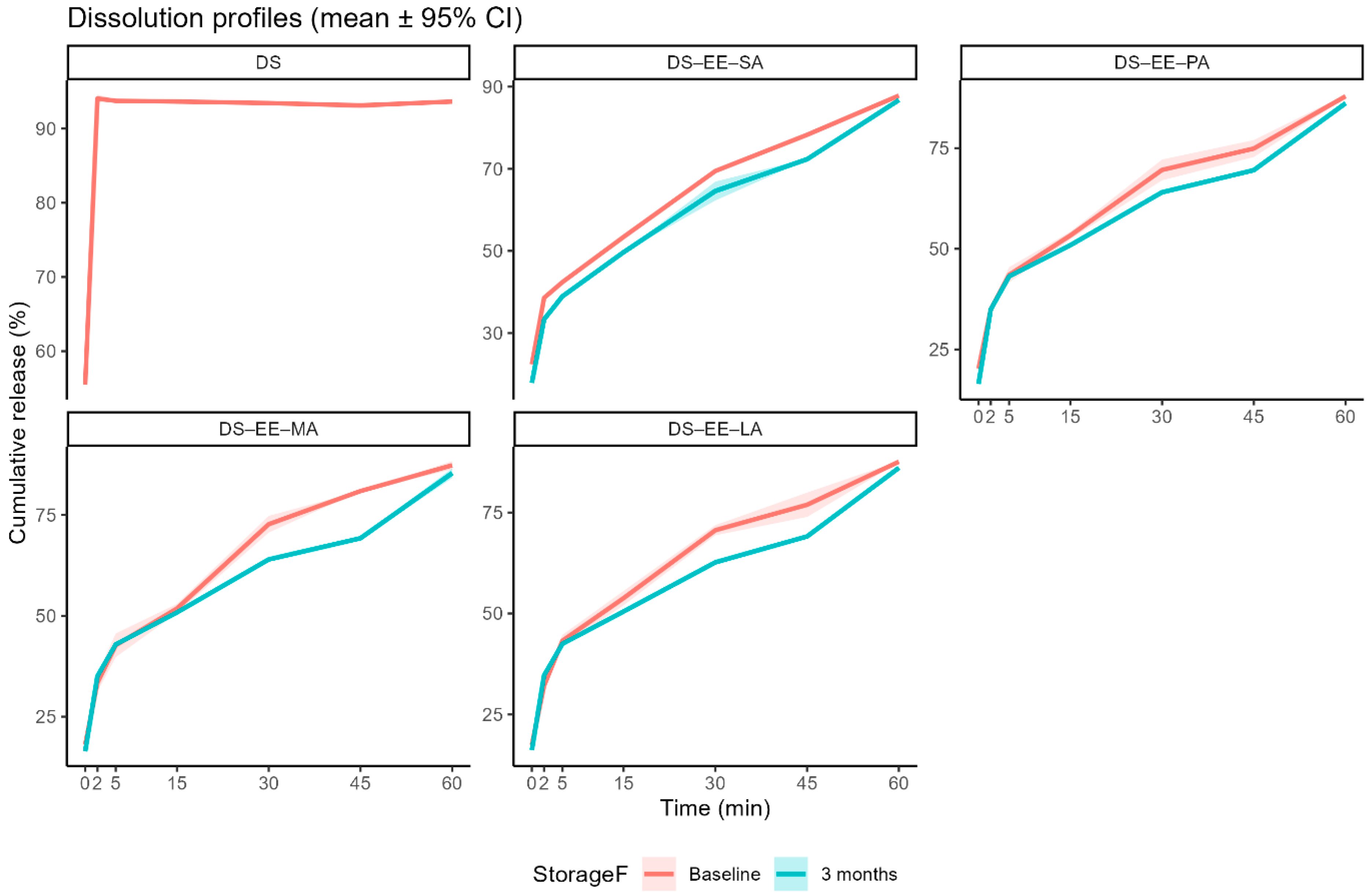
3.2. Stability Assessment: In Vitro DS Dissolution Profile
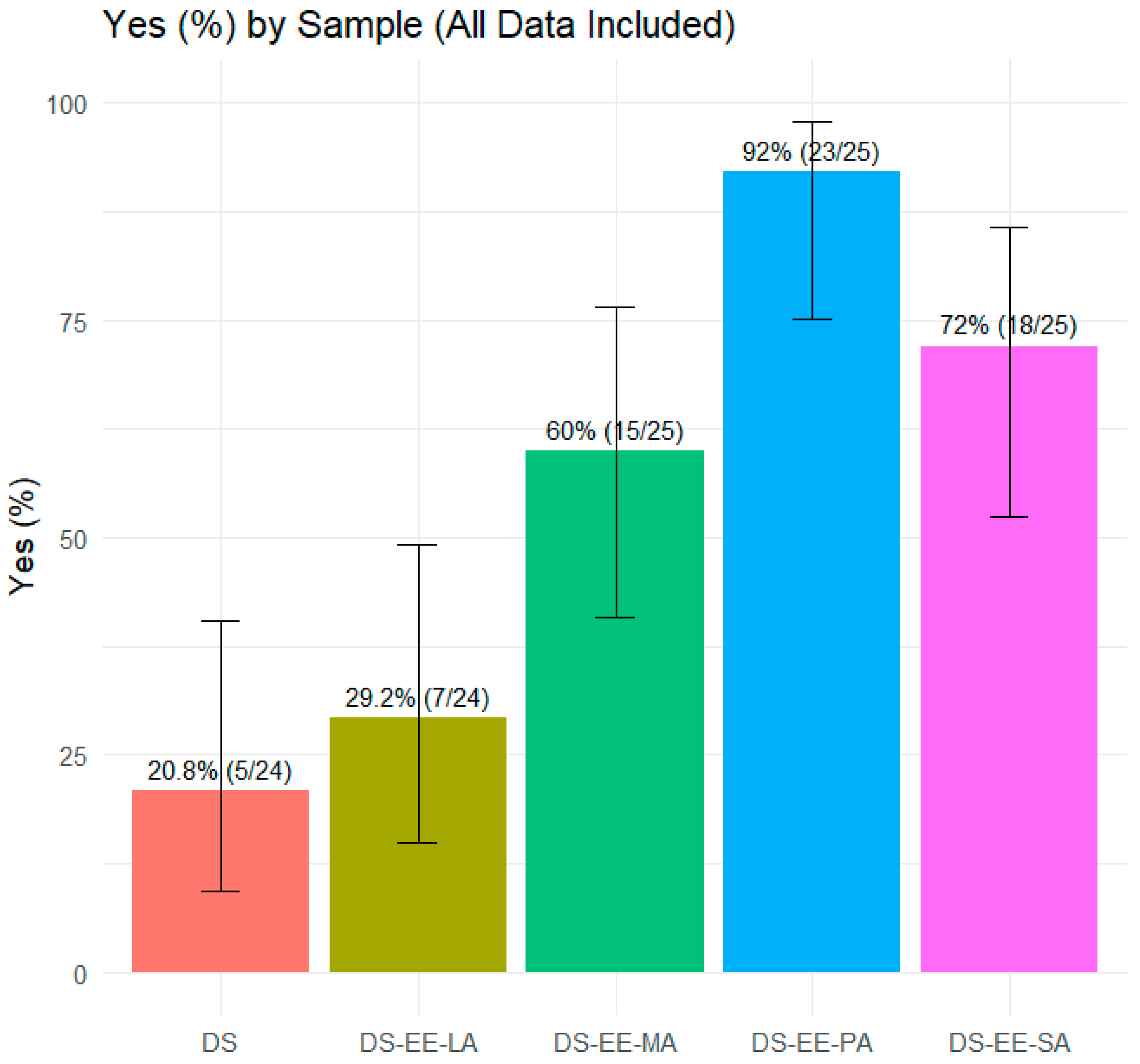
3.3. Taste Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schrier, L.; Hadjipanayis, A.; Stiris, T.; Ross-Russell, R.I.; Valiulis, A.; Turner, M.A.; Zhao, W.; De Cock, P.; de Wildt, S.N.; Allegaert, K.; et al. Off-Label Use of Medicines in Neonates, Infants, Children, and Adolescents: A Joint Policy Statement by the European Academy of Paediatrics and the European Society for Developmental Perinatal and Pediatric Pharmacology. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2020, 179, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahn, J.; Hoerning, A.; Trollmann, R.; Rascher, W.; Neubert, A. Manipulation of Medicinal Products for Oral Administration to Paediatric Patients at a German University Hospital: An Observational Study. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venables, R.; Batchelor, H.; Hodson, J.; Stirling, H.; Marriott, J. Determination of Formulation Factors That Affect Oral Medicines Acceptability in a Domiciliary Paediatric Population. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 480, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, O.; Salman, S.; von Ungern-Sternberg, B.S.; Lim, L.Y. Taste-Masked Flucloxacillin Powder Part 1: Optimisation of Fabrication Process Using a Mixture Design Approach. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, O.; Salman, S.; von Ungern-Sternberg, B.S.; Lim, L.Y. Taste-Masked Flucloxacillin Powder Part 2: Formulation Optimisation Using the Mixture Design Approach and Storage Stability. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuoss, R.M.; Sadek, H. Mutual Interaction of Polyelectrolytes. Science 1949, 110, 552–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.-D.; Woo, J.S.; Kang, J.H.; Yong, C.S.; Choi, H.-G. Preparation and Evaluation of Taste-Masked Donepezil Hydrochloride Orally Disintegrating Tablets. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 33, 1364–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burapapadh, K.; Warintaksa, P.; Ruksapram, S.; Saokham, P. Development of Taste-Masked Enteric Granules Containing Diclofenac Sodium Utilizing Eudragit® E PO as a Taste-Masking Agent. Sci. Eng. Health Stud. 2024, 18, 24050016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, O. Development and Evaluation of Taste Masked Paediatric Medicinal Formulations. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Western Australia, Perth, Australia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pratap Singh, A.; Siddiqui, J.; Diosady, L.L. Characterizing the pH-Dependent Release Kinetics of Food-Grade Spray Drying Encapsulated Iron Microcapsules for Food Fortification. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2018, 11, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringsten, M.; Kredo, T.; Hohlfeld, A.; Bruschettini, M. Diclofenac for Acute Postoperative Pain in Children. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2022, 2022, CD015087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evonik Nutrition & Care GmbH Technical Information EUDRAGIT® E 100, EUDRAGIT® E PO and EUDRAGIT® E 12,5. Available online: https://www.pharmaexcipients.com/wp-content/uploads/attachments/TI-EUDRAGIT-E-100-E-PO-E-12-5-EN.pdf?t=1508413942 (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- European Medicines Agency. ICH Q2(R2) Guideline on Validation of Analytical Procedures—Step 5. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/ich-q2r2-guideline-validation-analytical-procedures-step-5-revision-1_en.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- Kincl Skube, M.; Meleh, M.; Veber, M.; Vrecer, F. Study of Physicochemical Parameters Affecting the Release of Diclofenac Sodium from Lipophilic Matrix Tablets. Acta Chim. Slov. 2004, 51, 409–425. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Vienna, Austria:R Foundation for Statistical Computing. 2023. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- Lagerlöf, F.; Dawes, C. The Volume of Saliva in the Mouth before and after Swallowing. J. Dent. Res. 1984, 63, 618–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiffman, S.S.; Zervakis, J.; Westall, H.L.; Graham, B.G.; Metz, A.; Bennett, J.L.; Heald, A.E. Effect of Antimicrobial and Anti-Inflammatory Medications on the Sense of Taste. Physiol. Behav. 2000, 69, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, G.; Wang, Q.; Shang, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, R.; Jing, B.; Fu, Q. Preparation and Characterization of Diclofenac Sodium-Purolite A430MR Complexes for Taste Masking. AAPS PharmSciTech 2025, 26, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheela, D.L.; Nazeem, P.A.; Narayanankutty, A.; Shylaja, R.M.; Davis, S.P.; James, P.; Valsalan, R.; Babu, T.D.; Raghavamenon, A.C. Coconut Phytocompounds Inhibits Polyol Pathway Enzymes: Implication in Prevention of Microvascular Diabetic Complications. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2017, 127, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheon, E.; Mattes, R.D. Perceptual Quality of Nonesterified Fatty Acids Varies with Fatty Acid Chain Length. Chem. Senses 2021, 46, bjab023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, O.; Stanford, D.; von Ungern-Sternberg, B.S.; Lim, L.Y. Net Promoter Score Model for Evaluating Paediatric Medicine Acceptability: Validation and Feasibility Study. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Formulation | Ingredients | Fatty Acid Chain Length | Diclofenac Sodium (g) | Eudragit EPO (g) | Fatty Acid (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DS-EE-LA | Diclofenac–Eudragit EPO–Lauric acid | C12 | 0.3181 | 0.3181 | 0.2003 |
| DS-EE-MA | Diclofenac–Eudragit EPO–Myristic acid | C14 | 0.3181 | 0.3181 | 0.2284 |
| DS-EE-PA | Diclofenac–Eudragit EPO–Palmitic acid | C16 | 0.3181 | 0.3181 | 0.2564 |
| DS-EE-SA | Diclofenac–Eudragit EPO–Stearic acid | C18 | 0.3181 | 0.3181 | 0.2845 |
| Actual Concentration of DS (µg/mL) | Run 1 | Run 2 | Run 3 | % Mean Recovery (n = 3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| % Recovery | % Recovery | % Recovery | ||
| 12.5 | 103.26 | 103.47 | 103.26 | 103.33 |
| 25 | 101.36 | 101.47 | 101.36 | 101.40 |
| 47.5 | 98.93 | 98.30 | 98.59 | 98.60 |
| Actual Concentration (µg/mL) | Intra-Day | Inter-Day | ||
| Predicted Concentration (µg/mL, Mean ± SD, n = 3) | %RSD | Predicted Concentration (µg/mL, Mean ± SD, n = 3) | %RSD | |
| 10 | 9.98 ± 0.02 | 0.16 | 9.85 ± 0.10 | 1.05 |
| 20 | 19.48 ± 0.04 | 0.21 | 19.30 ± 0.12 | 0.61 |
| 30 | 29.62 ± 0.06 | 0.19 | 29.03 ± 0.46 | 1.58 |
| 40 | 39.72 ± 0.04 | 0.11 | 39.14 ± 0.47 | 1.19 |
| 50 | 50.45 ± 0.06 | 0.11 | 49.26 ± 1.01 | 2.05 |
| Polyelectrolyte Complex Formulation | Drug Content (% Labelled Content, n = 3, mean ± SD) After Storage at Ambient Conditions for Specified Periods | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 1 Month | 3 Months | |
| DS-EE-LA | 95.3 ± 0.3 | 99.0 ± 0.6 | 99.0 ± 0.5 |
| DS-EE-MA | 103.9 ± 1.5 | 102.0 ± 0.9 | 102.7 ± 0.2 |
| DS-EE-PA | 101.0 ± 0.2 | 95.7 ± 0.8 | 95.9 ± 0.4 |
| DS-EE-SA | 99.4 ± 0.3 | 97.5 ± 0.1 | 96.6 ± 0.2 |
| (a) ‘Taste’ Data | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | % Detractors | % Passive | % Promoters | MAS | % ‘Yes’ | % ‘No’ |
| DS | 92 | 8 | 0 | −92 | 20.8 | 79 |
| DS-EE-LA | 92 | 8 | 0 | −92 | 29.2 | 71 |
| DS-EE-MA | 52 | 36 | 12 | −40 | 60.0 | 40 |
| DS-EE-PA | 8 | 14 | 3 | −5 | 92.0 | 8 |
| DS-EE-SA | 52 | 40 | 8 | −44 | 72.0 | 28 |
| (b) ‘Willingness to Take Again’ Data | ||||||
| Sample | % Detractors | % Passive | % Promoters | MAS | % ‘Yes’ | % ‘No’ |
| DS | 84 | 12 | 4 | −80 | 20.8 | 79 |
| DS-EE-LA | 84 | 16 | 0 | −84 | 29.2 | 71 |
| DS-EE-MA | 40 | 40 | 20 | −20 | 60.0 | 40 |
| DS-EE-PA | 24 | 52 | 24 | 0 | 92.0 | 8 |
| DS-EE-SA | 32 | 52 | 16 | −16 | 72.0 | 28 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoo, O.; Sultana, S.; von Ungern-Sternberg, B.S.; Lim, L.Y. Taste-Masked Diclofenac Sodium Microparticles Prepared by Polyelectrolyte Complexation: Formulation Using Different Fatty Acids and Taste Evaluation by Human Panel. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17111411
Yoo O, Sultana S, von Ungern-Sternberg BS, Lim LY. Taste-Masked Diclofenac Sodium Microparticles Prepared by Polyelectrolyte Complexation: Formulation Using Different Fatty Acids and Taste Evaluation by Human Panel. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(11):1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17111411
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoo, Okhee, Sharmin Sultana, Britta S. von Ungern-Sternberg, and Lee Yong Lim. 2025. "Taste-Masked Diclofenac Sodium Microparticles Prepared by Polyelectrolyte Complexation: Formulation Using Different Fatty Acids and Taste Evaluation by Human Panel" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 11: 1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17111411
APA StyleYoo, O., Sultana, S., von Ungern-Sternberg, B. S., & Lim, L. Y. (2025). Taste-Masked Diclofenac Sodium Microparticles Prepared by Polyelectrolyte Complexation: Formulation Using Different Fatty Acids and Taste Evaluation by Human Panel. Pharmaceutics, 17(11), 1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17111411







