Injectable In Situ Thermoreversible Gel Depot System of Lidocaine Nanoemulsion for Prolonged Anesthetic Activity in Dental and Operative Procedures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
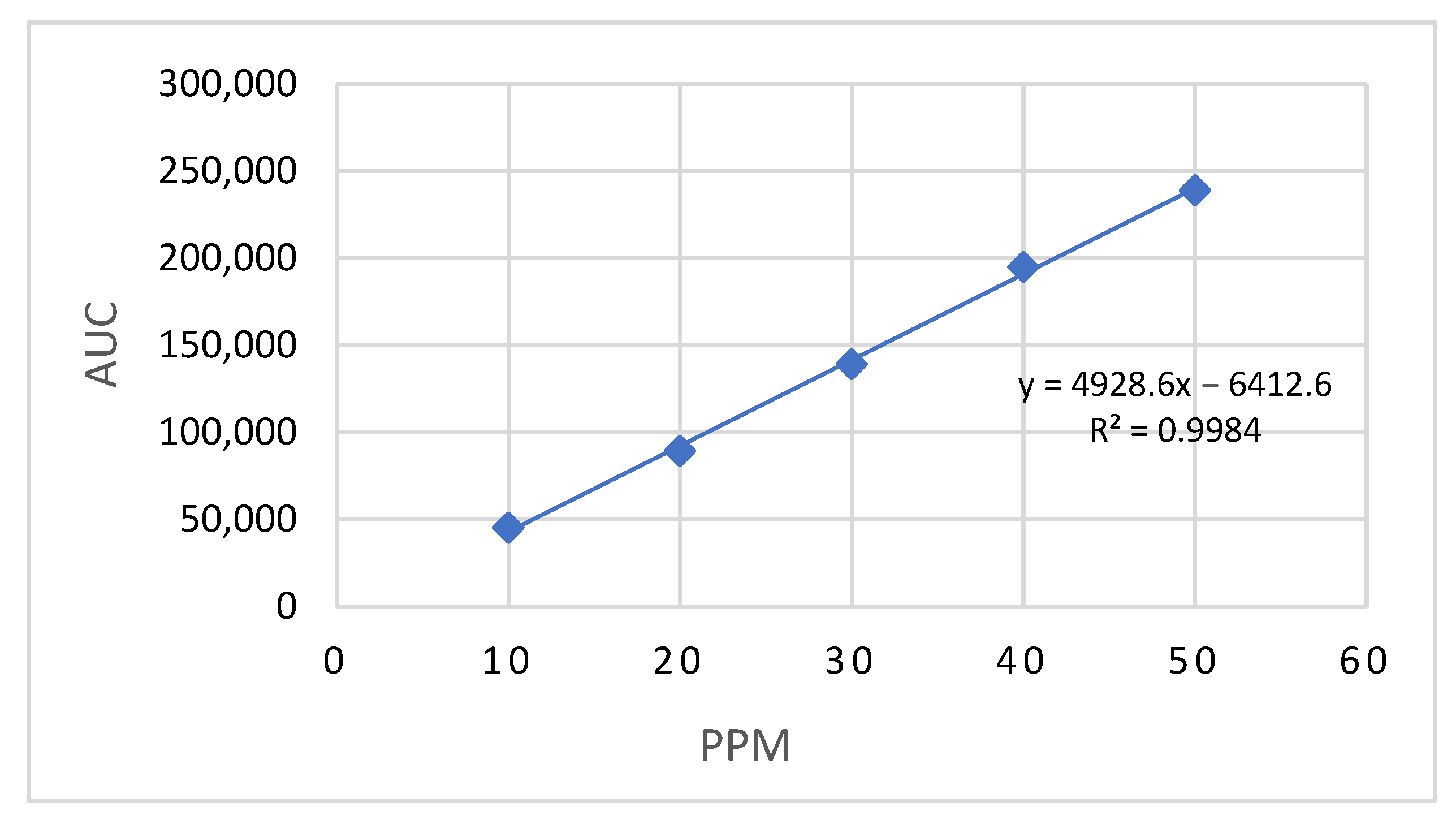
2.2. HPLC Analysis of Lidocaine
2.3. Screening of Oil
2.4. Selection of Surfactants and Co-Surfactants
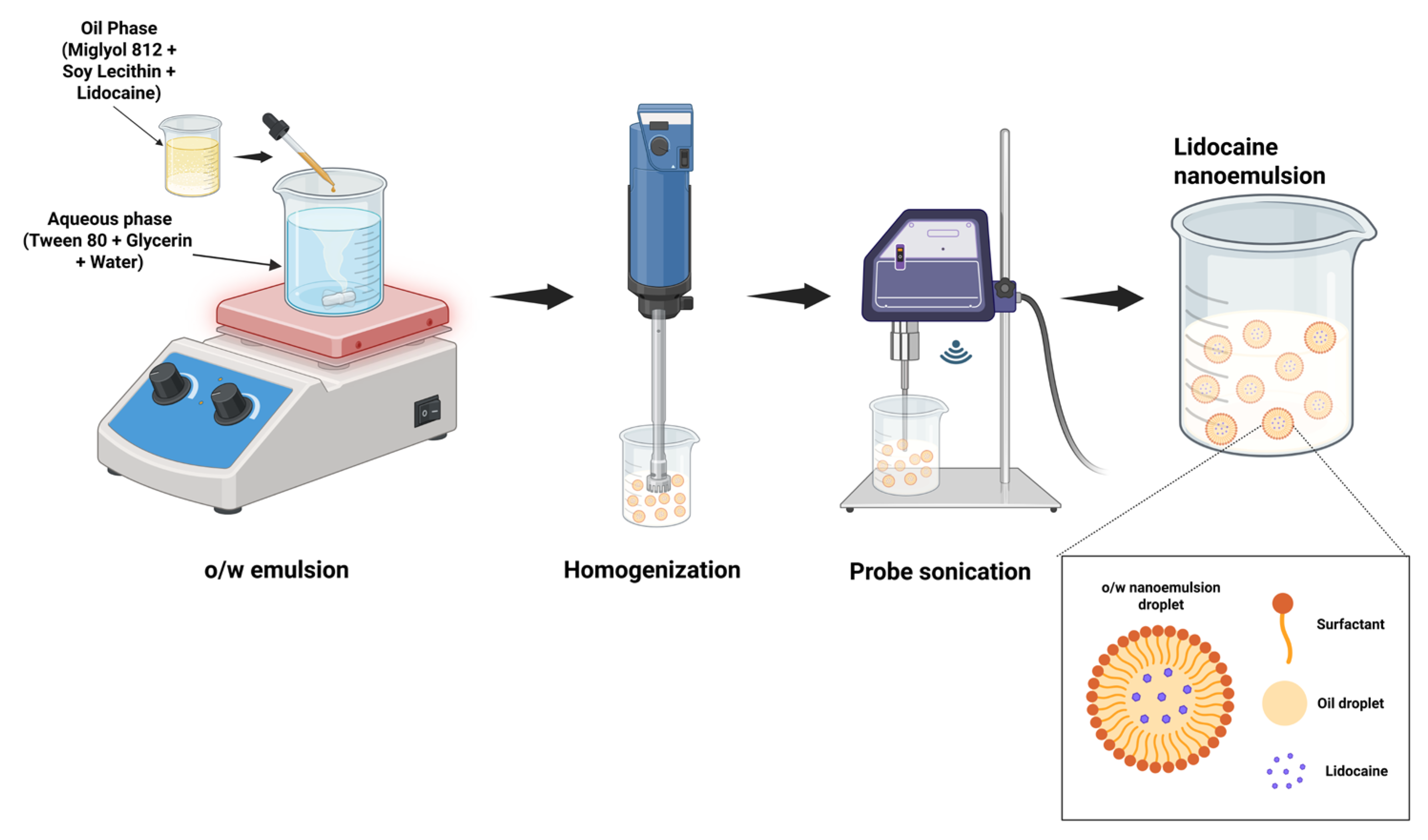
2.5. Preparation of Lidocaine-Loaded Nanoemulsion
2.6. Characterization of LD-Loaded Nanoemulsion
2.6.1. Drug Content
2.6.2. Percentage Transmittance and pH
2.6.3. Dilution Potential
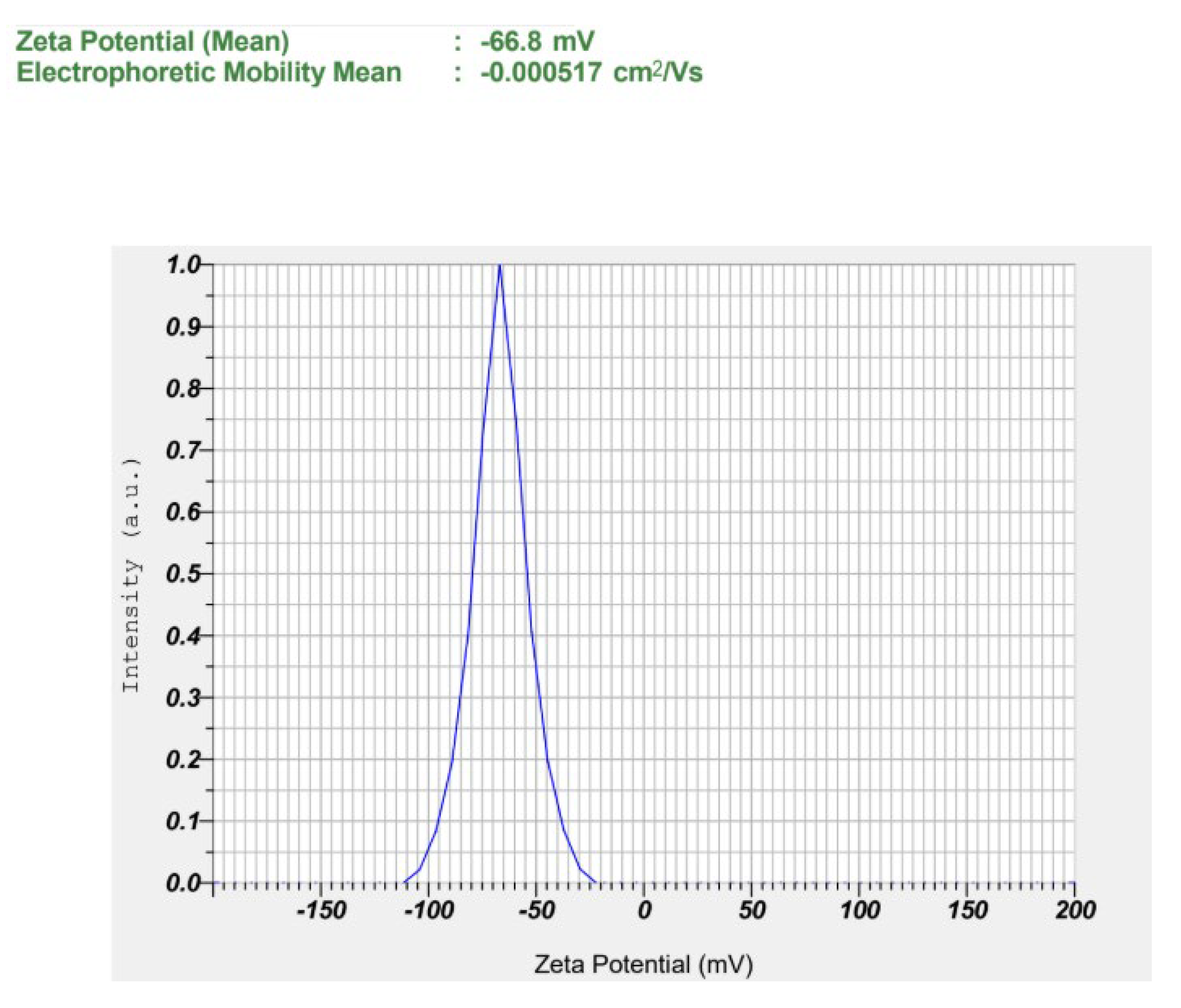
2.6.4. Particle Size and Zeta (ζ) Potential
2.6.5. Viscosity
2.6.6. Kinetic Stability Studies
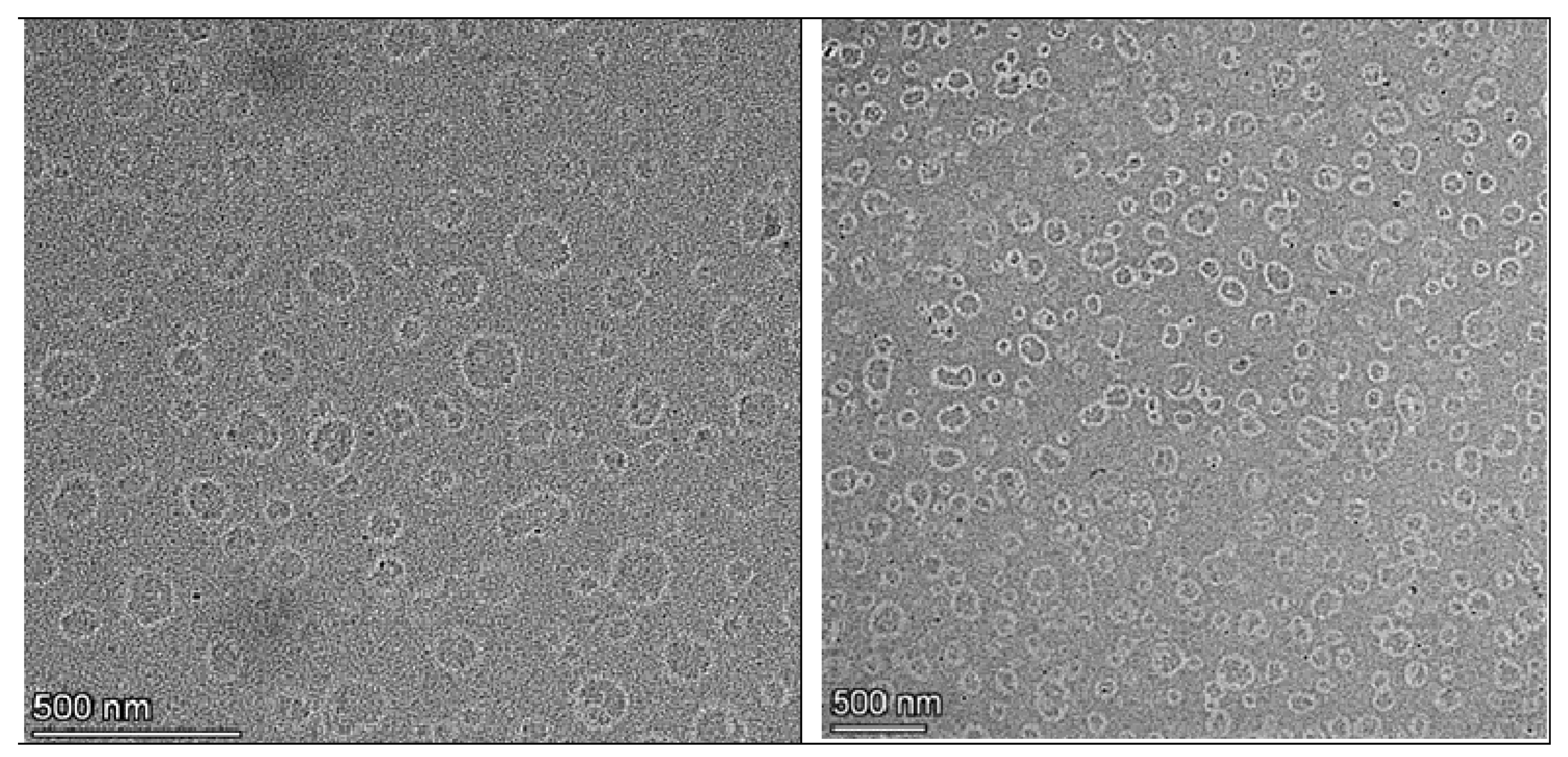
2.6.7. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.7. Preparation of Lidocaine Loaded Nanoemulgel
2.8. Characterization of Nanoemulgel
2.8.1. pH and Drug Content
2.8.2. Viscosity
2.8.3. Sol–Gel Transition and Injectability Testing
2.9. In Vitro Release
2.10. Stability Assessment
2.11. Animal Studies
2.11.1. Radiant Heat Tail-Flick Latency (TFL) Test
2.11.2. Thermal Hind Paw Hyperalgesia Study
2.11.3. Cardiovascular Safety Studies
2.12. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. HPLC Analysis of Lidocaine
3.2. Solubility Assessment and Selection of Excipients
3.3. Development of LD-Loaded Nanoemulsion
3.4. Characterization of Nanoemulsion
3.5. Kinetic Stability Studies
3.6. TEM
3.7. Characterization of Nanoemulgel
3.7.1. pH and Drug Content
3.7.2. Viscosity
3.7.3. Sol–Gel Transition and Injectability Testing
3.8. In Vitro Drug Release
3.9. Radiant Heat Tail-Flick Latency Test
3.10. Thermal Hind Paw Hyperalgesia Study
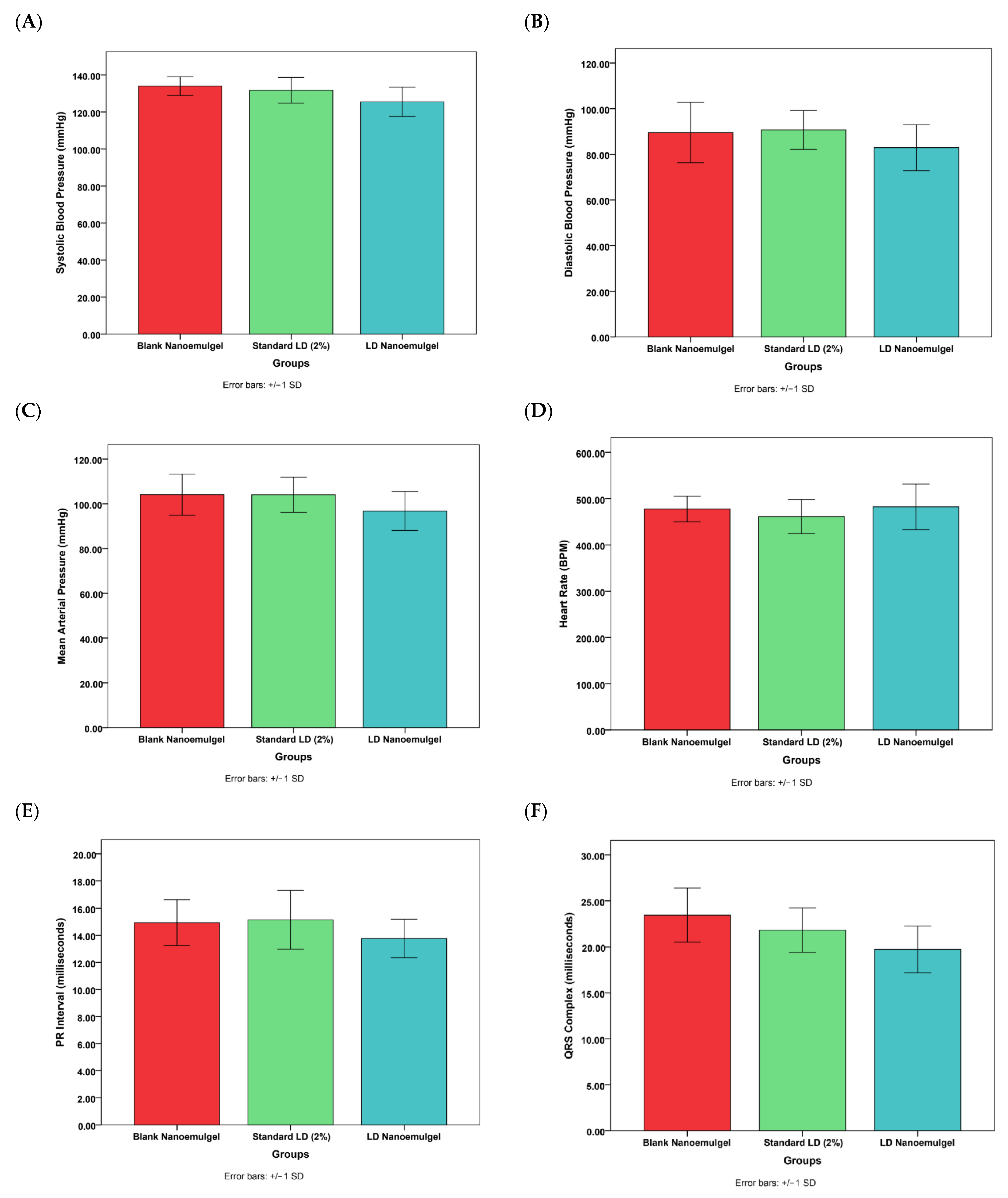
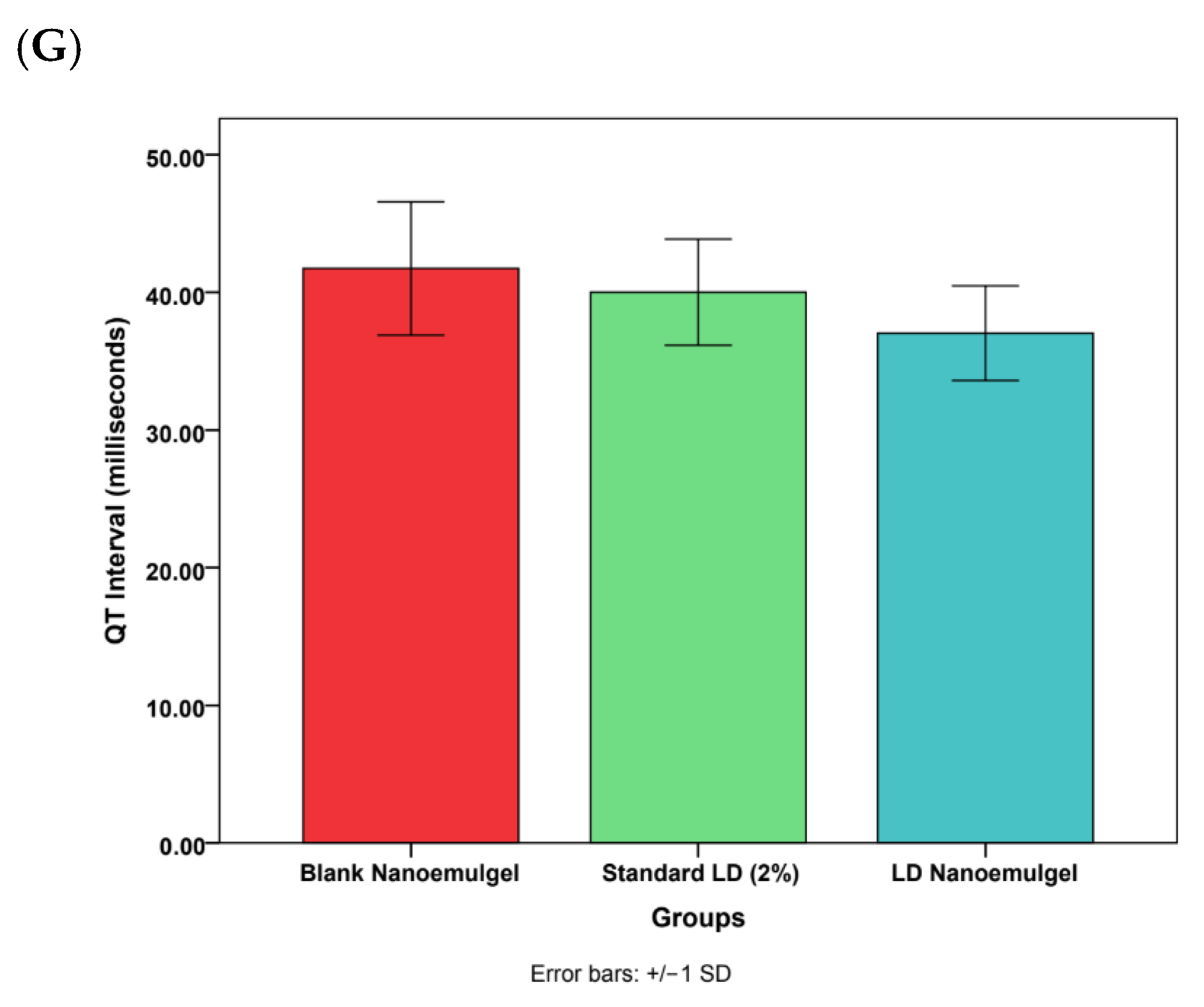
3.11. Cardiovascular Safety Studies
3.12. Stability Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shipton, E.A. New formulations of local anaesthetics-part I. Anesthesiol. Res. Pract. 2012, 2012, 546409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipton, E.A. New delivery systems for local anaesthetics-part 2. Anesthesiol. Res. Pract. 2012, 2012, 289373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Nedley, M.P.; Bhaduri, S.B.; Bredzinski, X.; Boddu, S.H. Masking the bitter taste of injectable lidocaine HCl formulation for dental procedures. AAPS PharmSciTech 2015, 16, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decloux, D.; Ouanounou, A. Local anaesthesia in dentistry: A review. Int. Dent. J. 2020, 71, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, J.O.; Kim, M.; Kim, S.; Lee, K.K.; Choi, H. Advanced Hydrogel Systems for Local Anesthetic Delivery: Toward Prolonged and Targeted Pain Relief. Gels 2025, 11, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.C.; Kohane, D.S.; Park, Y.J.; Bartlett, R.H.; Langer, R.; Yang, V.C. Injectable microparticle-gel system for prolonged and localized lidocaine release. II. In vivo anesthetic effects. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2004, 70, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiany, F.; Meshkati Yazd, S.M.; Shahriarirad, R.; Kamran, H.; Karoobi, M.; Shabani Mofrad, N.; Kamali, M. Evaluation of post laparoscopic cholecystectomy pain after subcutaneous injection of lidocaine at port site versus lidocaine spray on gallbladder bed after cholecystectomy: A randomized controlled trial. Langenbeck’s Arch. Surg. 2022, 407, 2853–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kau, Y.C.; Liao, C.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Liu, S.J. Sustained Release of Lidocaine from Solvent-Free Biodegradable Poly[(d,l)-Lactide-co-Glycolide] (PLGA): In Vitro and In Vivo Study. Materials 2014, 7, 6660–6676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danaei, M.; Dehghankhold, M.; Ataei, S.; Hasanzadeh Davarani, F.; Javanmard, R.; Dokhani, A.; Khorasani, S.; Mozafari, M.R. Impact of Particle Size and Polydispersity Index on the Clinical Applications of Lipidic Nanocarrier Systems. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, S.; Kather, F.S.; Boddu, S.H.S.; Shah, J.; Nair, A.B. Innovations in Nanoemulsion Technology: Enhancing Drug Delivery for Oral, Parenteral, and Ophthalmic Applications. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirtallo, J.M.; Ayers, P.; Boullata, J.; Gura, K.M.; Plogsted, S.; Anderson, C.R.; Worthington, P.; Seres, D.S.; Nicolai, E.; Alsharhan, M.; et al. ASPEN Lipid Injectable Emulsion Safety Recommendations, Part 1: Background and Adult Considerations. Nutr. Clin. Pract. Off. Publ. Am. Soc. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2020, 35, 769–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norouzi, P.; Rastegari, A.; Mottaghitalab, F.; Farokhi, M.; Zarrintaj, P.; Saeb, M.R. 24—Nanoemulsions for intravenous drug delivery. In Nanoengineered Biomaterials for Advanced Drug Delivery; Mozafari, M., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 581–601. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, M.; Karkanitsa, M.; Christman, K.L. Design and translation of injectable biomaterials. Nat. Rev. Bioeng. 2024, 2, 810–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Dong, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, Q.; Wang, B. Determination and correlation of solubility with thermodynamic analysis of lidocaine hydrochloride in pure and binary solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 265, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Song, Y.; Wang, X.; Hao, J. Design and Development of Lidocaine Microemulsions for Transdermal Delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech 2019, 20, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.; Tahir, N.; Sohail, M.F.; Qadri, M.U.; Duarte, S.O.D.; Brandão, P.; Esteves, T.; Javed, I.; Fonte, P. Lipid-Based Nanoformulations for Drug Delivery: An Ongoing Perspective. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Lian, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Ye, H.; Liu, M.; Li, J. Depot lidocaine-loaded microemulsion for prolonged local anesthesia: Different efficacy model studies. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 101404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical Guidelines for the Use of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition in Adult and Pediatric Patients, 2009. JPEN. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2009, 33, 255–259. [CrossRef]
- United States Pharmacopeia. USP <729> Globule Size Distribution in Lipid Injectable Emulsions; United States Pharmacopeia: Rockville, MD, USA, 2009; pp. 314–316. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Zhong, Y.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, J.; Pan, J. Physiology of pregnancy and oral local anesthesia considerations. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bani-Hani, T.; Al-Fodeh, R.; Tabnjh, A.; Leith, R. The Use of Local Anesthesia in Pediatric Dentistry: A Survey of Specialists’ Current Practices in Children and Attitudes in Relation to Articaine. Int. J. Dent. 2024, 2024, 2468502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehata, T.M.; Nair, A.B.; Al-Dhubiab, B.E.; Shah, J.; Jacob, S.; Alhaider, I.A.; Attimarad, M.; Elsewedy, H.S.; Ibrahim, M.M. Vesicular emulgel based system for transdermal delivery of insulin: Factorial design and in vivo evaluation. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, S.; Abdullahi, J.O.; Usman, S.; Boddu, S.H.S.; Khan, S.N.; Saad, M.A.; Nair, A.B. Preparation and Evaluation of Tadalafil-Loaded Nanoemulgel for Transdermal Delivery in Cold-Induced Vasoconstriction: A Potential Therapy for Raynaud’s Phenomenon. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vichare, R.; Crelli, C.; Liu, L.; Das, A.C.; McCallin, R.; Zor, F.; Kulahci, Y.; Gorantla, V.S.; Janjic, J.M. A Reversibly Thermoresponsive, Theranostic Nanoemulgel for Tacrolimus Delivery to Activated Macrophages: Formulation and In Vitro Validation. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabery, A.M.; Widodo, R.T.; Chik, Z. Formulation and In Vivo Pain Assessment of a Novel Niosomal Lidocaine and Prilocaine in an Emulsion Gel (Emulgel) of Semisolid Palm Oil Base for Topical Drug Delivery. Gels 2023, 9, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popescu, I.; Constantin, M.; Bercea, M.; Coșman, B.P.; Suflet, D.M.; Fundueanu, G. Poloxamer/Carboxymethyl Pullulan Aqueous Systems—Miscibility and Thermogelation Studies Using Viscometry, Rheology and Dynamic Light Scattering. Polymers 2023, 15, 1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Zhu, Z.; Cao, X.; Pan, F.; Li, F.; Xue, M.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zeng, J.; Liu, Y.; et al. Evaluation the injectability of injectable microparticle delivery systems on the basis of injection force and discharged rate. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2023, 190, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algahtani, M.S.; Ahmad, M.Z.; Nourein, I.H.; Albarqi, H.A.; Alyami, H.S.; Alyami, M.H.; Alqahtani, A.A.; Alasiri, A.; Algahtani, T.S.; Mohammed, A.A.; et al. Preparation and Characterization of Curcumin Nanoemulgel Utilizing Ultrasonication Technique for Wound Healing: In Vitro, Ex Vivo, and In Vivo Evaluation. Gels 2021, 7, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, A.; Gupta, R.; Vasanti, S. In vitro controlled release of alfuzosin hydrochloride using HPMC-based matrix tablets and its comparison with marketed product. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2007, 12, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maded, Z.K.; Sfar, S.; Taqa, G.A.A.; Lassoued, M.A.; Ben Hadj Ayed, O.; Fawzi, H.A. Development and Optimization of Dipyridamole- and Roflumilast-Loaded Nanoemulsion and Nanoemulgel for Enhanced Skin Permeation: Formulation, Characterization, and In Vitro Assessment. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durgapal, S.; Goswami, L.; Nair, A.B.; Juyal, V.; Verma, A. Enhanced anti-cataract effect of microemulsion containing Cineraria maritima: Formulation, optimization and in vivo evaluation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 77, 103872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council (US) Committee for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. The National Academies Collection: Reports Funded by National Institutes of Health; National Academy of Sciences: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Çakırgöz, E.; Durdağı, G.; Öz Oyar, E. Enhanced analgesia: Synergistic effects of melatonin and tramadol on acute thermal nociception in Wistar rats via tail-flick and hot-plate tests. Behav. Brain Res. 2025, 490, 115641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaee-Asl, M.; Sabour, M.; Nikoui, V.; Ostadhadi, S.; Bakhtiarian, A. The Study of Analgesic Effects of Leonurus cardiaca L. in Mice by Formalin, Tail Flick and Hot Plate Tests. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2014, 2014, 687697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheah, M.; Fawcett, J.W.; Andrews, M.R. Assessment of Thermal Pain Sensation in Rats and Mice Using the Hargreaves Test. Bio-Protocol 2017, 7, e2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapsdorferová, V.; Grešová, S.; Švorc, P. Measurement of blood pressure in rats: Invasive or noninvasive methods? Physiol. Rep. 2024, 12, e70041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warhol, A.; George, S.A.; Obaid, S.N.; Efimova, T.; Efimov, I.R. Differential cardiotoxic electrocardiographic response to doxorubicin treatment in conscious versus anesthetized mice. Physiol. Rep. 2021, 9, e14987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhusal, P.; Sharma, M.; Harrison, J.; Procter, G.; Andrews, G.; Jones, D.S.; Hill, A.G.; Svirskis, D. Development, Validation and Application of a Stability Indicating HPLC Method to Quantify Lidocaine from Polyethylene-co-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) Matrices and Biological Fluids. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2017, 55, 832–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermer, J. ICH Q2 (R2): Validation of analytical procedures. In Method Validation in Pharmaceutical Analysis: A Guide to Best Practic; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2025; pp. 351–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalkowsky, S.H.; He, Y.; Jain, P. Handbook of Aqueous Solubility Data; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Koroleva, M.Y.; Yurtov, E.V. Ostwald ripening in macro-and nanoemulsions. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2021, 90, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P. Ostwald ripening in emulsions: Estimation of solution thermodynamics of the disperse phase. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 106, 261–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alliod, O.; Messager, L.; Fessi, H.; Dupin, D.; Charcosset, C. Influence of viscosity for oil-in-water and water-in-oil nanoemulsions production by SPG premix membrane emulsification. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2019, 142, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liang, Y.; Yuhong, J.; Xin, P.; Han, J.L.; Du, Y.; Yu, X.; Zhu, R.; Zhang, M.; Chen, W.; et al. Advances in Nanotechnology for Enhancing the Solubility and Bioavailability of Poorly Soluble Drugs. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2024, 18, 1469–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanarova, E.; Lantsova, A.; Nikolaeva, L.; Oborotova, N. Using polysorbates to create parenteral dosage forms of hydrophobic substances (a review). Pharm. Chem. J. 2022, 56, 974–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlschwede, K.M.; Ofori, E.; Andey, T.; Osei, A.; Somberg, J.S. Formulation, Characterization, and the Diuretic Effects of a New Intravenous Metolazone Emulsion. Drug Res. 2022, 72, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Peng, Y.; Liu, Q. Interactions of NaCl with frother surfactants in producing microbubbles through modifying air/water interfacial energy and interfacial charge. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 389, 122889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Li, M.; Xu, X.; Sun, C. Coupling Effects of Ionic Surfactants and Electrolytes on the Stability of Bulk Nanobubbles. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariyaprakai, S.; Tananuwong, K. Freeze–thaw stability of edible oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by sucrose esters and Tweens. J. Food Eng. 2015, 152, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, J.M.; Masbernat, O.; Roger, K. Emulsions stabilized by phospholipids. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2025, 678, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerniel, J.; Gostyńska-Stawna, A.; Sommerfeld-Klatta, K.; Przybylski, T.; Krajka-Kuźniak, V.; Stawny, M. Development and Validation of In Vitro Assessment Protocol of Novel Intravenous Nanoemulsions for Parenteral Nutrition. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, S.K.; Kaur, G.; Bhasin, K.K. Tween-embedded microemulsions--physicochemical and spectroscopic analysis for antitubercular drugs. AAPS PharmSciTech 2010, 11, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakar, K.; Afzal, S.M.; Surender, G.; Kishan, V. Tween 80 containing lipid nanoemulsions for delivery of indinavir to brain. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2013, 3, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeem, A.; Rizwan, M.; Ahmad, F.J.; Iqbal, Z.; Khar, R.K.; Aqil, M.; Talegaonkar, S. Nanoemulsion components screening and selection: A technical note. AAPS PharmSciTech 2009, 10, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varelis, P.; Melton, L.; Shahidi, F. Encyclopedia of Food Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kentish, S.; Wooster, T.; Ashokkumar, M.; Balachandran, S.; Mawson, R.; Simons, L. The use of ultrasonics for nanoemulsion preparation. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2008, 9, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratap-Singh, A.; Guo, Y.; Lara Ochoa, S.; Fathordoobady, F.; Singh, A. Optimal ultrasonication process time remains constant for a specific nanoemulsion size reduction system. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, J.; Fernandes, C.; Patravale, V. Formulation development of parenteral phospholipid-based microemulsion of etoposide. AAPS PharmSciTech 2010, 11, 826–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehmood, T.; Ahmed, A. Tween 80 and Soya-Lecithin-Based Food-Grade Nanoemulsions for the Effective Delivery of Vitamin D. Langmuir 2020, 36, 2886–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Kong, B.; Liu, Q.; Xia, X.; Liu, H. Characterization of Nanoemulsions Stabilized with Different Emulsifiers and Their Encapsulation Efficiency for Oregano Essential Oil: Tween 80, Soybean Protein Isolate, Tea Saponin, and Soy Lecithin. Foods 2023, 12, 3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Mandal, A. Thermodynamic and physicochemical properties evaluation for formation and characterization of oil-in-water nanoemulsion. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 266, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.; Li, Y.; Yang, G.; Zhao, C. Nanoemulsions for drug delivery. Particuology 2022, 64, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usach, I.; Martinez, R.; Festini, T.; Peris, J.E. Subcutaneous Injection of Drugs: Literature Review of Factors Influencing Pain Sensation at the Injection Site. Adv. Ther. 2019, 36, 2986–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Davis, S.S.; Washington, C. Physical properties and stability of two emulsion formulations of propofol. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 215, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, X. Chapter 12—Nanoemulsions-Based Drug Delivery for Brain Tumors. In Nanotechnology-Based Targeted Drug Delivery Systems for Brain Tumors; Kesharwani, P., Gupta, U., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 327–358. [Google Scholar]
- Allmendinger, A.; Fischer, S.; Huwyler, J.; Mahler, H.C.; Schwarb, E.; Zarraga, I.E.; Mueller, R. Rheological characterization and injection forces of concentrated protein formulations: An alternative predictive model for non-Newtonian solutions. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 87, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Rousseau, D. Freeze-thaw stability of water-in-oil emulsions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 339, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanatkaran, N.; Masalova, I. Interfacial behavior of oil/oil and oil/water soluble binary surfactants and their effect on stability of highly concentrated W/O emulsions. Colloid J. 2015, 77, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.S.; Alam, M.S.; Alam, N.; Siddiqui, M.R. Preparation, characterization and stability study of dutasteride loaded nanoemulsion for treatment of benign prostatic hypertrophy. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. IJPR 2014, 13, 1125–1140. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gué, E.; Since, M.; Ropars, S.; Herbinet, R.; Le Pluart, L.; Malzert-Fréon, A. Evaluation of the versatile character of a nanoemulsion formulation. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 498, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Gu, Y.; Yang, D.; Tang, X.; Liu, J. Development of triptolide-nanoemulsion gels for percutaneous administration: Physicochemical, transport, pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic characteristics. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 15, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mfoafo, K.; Kwon, Y.; Omidi, Y.; Omidian, H. Contemporary applications of thermogelling PEO-PPO-PEO triblock copolymers. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 70, 103182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, A.B.; Chaudhary, S.; Shah, H.; Jacob, S.; Mewada, V.; Shinu, P.; Aldhubiab, B.; Sreeharsha, N.; Venugopala, K.N.; Attimarad, M.; et al. Intranasal Delivery of Darunavir-Loaded Mucoadhesive In Situ Gel: Experimental Design, In Vitro Evaluation, and Pharmacokinetic Studies. Gels 2022, 8, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, T.; Chen, Y.; Li, N.; Liao, X.; Heng, Y.; Guo, Y.; Hu, K. A Comprehensive Review of Thermosensitive Hydrogels: Mechanism, Optimization Strategies, and Applications. Gels 2025, 11, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klouda, L. Thermoresponsive hydrogels in biomedical applications: A seven-year update. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 97, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, E.J.; Lunardi, L.O.; Nanclares, D.M.; Marchetti, J.M. Sustained release of lidocaine from Poloxamer 407 gels. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 288, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Wang, S.; Li, C.; Zeng, B.; Wu, H.; Liu, C.; Chen, L.; Jin, M.; Huang, W.; Zang, Y.; et al. LA67 Liposome-Loaded Thermo-Sensitive Hydrogel with Active Targeting for Efficient Treatment of Keloid via Peritumoral Injection. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, V.M.; Nguyen, D.X.; Rao, D.A.; Alany, R.G.; Alani, A.W. Thermogel polymers for injectable drug delivery systems. In Temperature-Responsive Polymers: Chemistry, Properties and Applications; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 313–327. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, I.C.; Su, C.Y.; Chen, P.Y.; Hoang, T.C.; Tsou, Y.S.; Fang, H.W. Investigation and Characterization of Factors Affecting Rheological Properties of Poloxamer-Based Thermo-Sensitive Hydrogel. Polymers 2022, 14, 5353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeswani, G.; Paul, S.D.; Deshmukh, R. Design of vincristine sulfate loaded poloxamer in situ nanogel: Formulation and in vitro evaluation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Ali, A.; Rahman, M.A.; Warsi, M.H.; Yusuf, M.; Alam, P. Development of Nanogel Loaded with Lidocaine for Wound-Healing: Illustration of Improved Drug Deposition and Skin Safety Analysis. Gels 2022, 8, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yam, M.F.; Loh, Y.C.; Oo, C.W.; Basir, R. Overview of Neurological Mechanism of Pain Profile Used for Animal “Pain-Like” Behavioral Study with Proposed Analgesic Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasidharan, S.; Kaveri, A.N.; Sithara, M.S.; Nair, J.H. Pharmacological Evaluation of the Anesthetic and Analgesic Potential of Injection Harsha 22: A Novel Polyherbal Local Anesthetic Formulation Intended for Parenteral Administration in Wistar Albino Rats. J. Exp. Pharmacol. 2023, 15, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catterall, W.A.; Mackie, K. Local anesthetics. In Goodman and Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 11th ed.; Brunton, L.L., Lazo, J.S., Parker, K.L., Eds.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 369–386. [Google Scholar]
- de Araújo, D.R.; Ribeiro, L.N.M.; de Paula, E. Lipid-based carriers for the delivery of local anesthetics. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 701–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Pan, Z.; Lai, B.; Zan, C.; Liu, H. Recent Research Advances in Nano-Based Drug Delivery Systems for Local Anesthetics. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2023, 17, 2639–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getachew, M.; Tesfaye, H.; Yihunie, W.; Ayenew, T.; Alemu, S.; Dagnew, E.M.; Biyazin, Y.; Abebe, D.; Degefu, N.; Abebaw, A. Sustained release local anesthetics for pain management: Relevance and formulation approaches. Front. Pain Res. 2024, 5, 1383461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, D.E.; Reed, K.L. Local anesthetics: Review of pharmacological considerations. Anesth. Prog. 2012, 59, 90–101; quiz 102–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, S.; Ghosh, V.; Jain, P.; Ajazuddin. Recent Advancement of Novel Drug Delivery Systems for Topical Anaesthesia Formulations. Curr. Nanomed. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Component | S1 | S2 | S3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oil phase (%) | 7.5 | 8.0 | 8.5 |
| Surfactant (%) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Co-surfactant (%) | 3.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 |
| Stabilizer (%) | 2.25 | 2.25 | 2.25 |
| Aqueous phase (%) | qs to 100 | qs to 100 | qs to 100 |
| Evaluation Parameters | |||
| Drug content (%) | 97.61 ± 1.48 | 96.90 ± 1.13 | 96.04 ± 2.97 |
| Entrapment efficiency (%) | 98.91 ± 0.48 | 98.90 ± 0.13 | 98.75 ± 0.27 |
| Drug loading (%) | 9.32 ± 0.67 | 9.28 ± 0.58 | 9.23 ± 0.56 |
| pH | 5.78 ± 0.42 | 5.77 ± 0.12 | 5.76 ± 0.29 |
| Transmittance (%) | 96.80 ± 0.89 | 95.00 ± 0.76 | 97.03 ± 1.63 |
| Dilution potential | >20 folds | >20 folds | >20 folds |
| Droplet size (nm) | 206.00 ± 7.50 | 293.73 ± 6.27 | 227.00 ± 3.99 |
| Polydispersity index | 0.40 ± 0.04 | 0.51 ± 0.03 | 0.49 ± 0.01 |
| ζ potential (mV) | −66.67 ± 0.42 | −61.73 ± 3.96 | −67.13 ± 0.06 |
| Viscosity (cP) | 33.13 ± 0.80 | 36.93 ± 0.25 | 38.03 ± 0.63 |
| Batches | Centrifugation | Heat–Cool | Freeze–Thaw |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | √ | √ | √ |
| S2 | √ | √ | √ |
| S3 | √ | √ | √ |
| Polaxamer 407 Concentration % | Gelation Temperature (°C) | Gelation Time (min) |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | 60 | 15 |
| 12 | 50 | 15 |
| 14 | 45 | 12 |
| 16 | 40 | 10 |
| 18 | 37 | 5 |
| 20 | 35 | 3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jacob, S.; Kather, F.S.; Satyam, S.M.; Boddu, S.H.S.; Assaf, F.; Allam, T.H.A.; Nair, A.B. Injectable In Situ Thermoreversible Gel Depot System of Lidocaine Nanoemulsion for Prolonged Anesthetic Activity in Dental and Operative Procedures. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1355. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101355
Jacob S, Kather FS, Satyam SM, Boddu SHS, Assaf F, Allam THA, Nair AB. Injectable In Situ Thermoreversible Gel Depot System of Lidocaine Nanoemulsion for Prolonged Anesthetic Activity in Dental and Operative Procedures. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(10):1355. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101355
Chicago/Turabian StyleJacob, Shery, Fathima Sheik Kather, Shakta Mani Satyam, Sai H. S. Boddu, Firas Assaf, Tasnem H. Abdelfattah Allam, and Anroop B. Nair. 2025. "Injectable In Situ Thermoreversible Gel Depot System of Lidocaine Nanoemulsion for Prolonged Anesthetic Activity in Dental and Operative Procedures" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 10: 1355. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101355
APA StyleJacob, S., Kather, F. S., Satyam, S. M., Boddu, S. H. S., Assaf, F., Allam, T. H. A., & Nair, A. B. (2025). Injectable In Situ Thermoreversible Gel Depot System of Lidocaine Nanoemulsion for Prolonged Anesthetic Activity in Dental and Operative Procedures. Pharmaceutics, 17(10), 1355. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101355








