Enteric Coating Enhances the Biopharmaceutical Performance of a Silica–Lipid Formulation of Abiraterone Acetate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Formulation Preparation
2.3. Particle Characterisation
2.4. In Vitro Gastrointestinal Lipolysis
2.5. In Vivo Rat Pharmacokinetic Study
2.6. Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry
2.7. Pharmacokinetic Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Formulation Characteristics and Particle Size Analysis
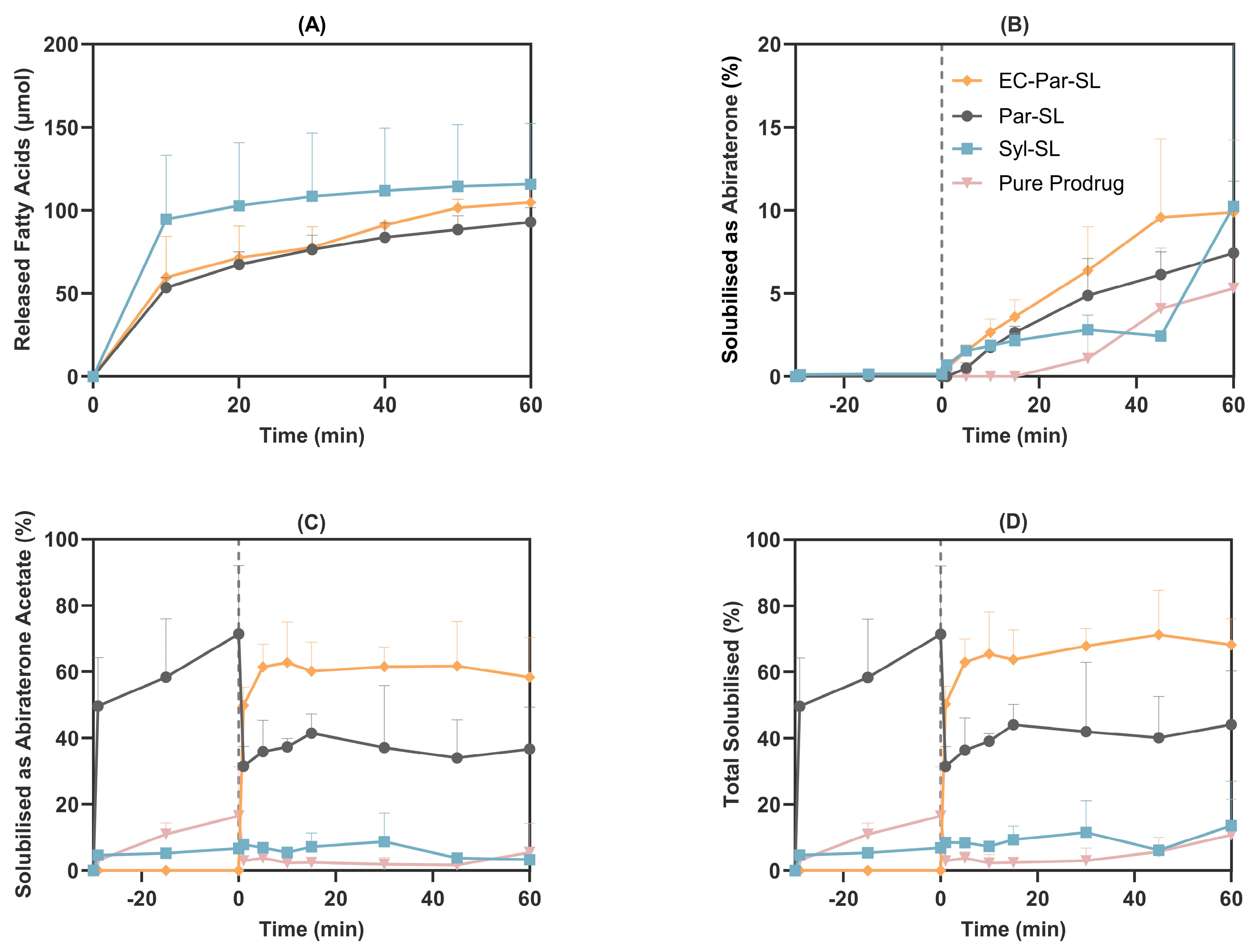
3.2. In Vitro Gastrointestinal Lipolysis
3.3. In Vivo Rat Pharmacokinetics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| APC | Australian Prostate Cancer |
| ASDs | Amorphous Solid Dispersions |
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| BCS | Biopharmaceutics Classification System |
| Cmax | Maximum Plasma Concentration |
| CYP17A1 | Cytochrome P450 17A1 |
| EC | Enteric Coated |
| FaSSGF | Fasted State Simulated Gastric Fluid |
| FaSSIF | Fasted State Simulated Intestinal Fluid |
| Frel | Relative Bioavailability |
| MADLS | Multi-Angle Dynamic Light Scattering |
| NHMRC | National Health and Medical Research Council |
| Par-SL | Parteck Silica–lipid |
| PDI | Polydispersity Index |
| SD | Standard Deviation, |
| Syl-SL | Syloid Silica–lipid |
| THRF | The Hospital Research Foundation |
| tmax | Time to Maximum Plasma Concentration |
References
- Shan, X.; Gong, X.; Li, J.; Wen, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z. Current approaches of nanomedicines in the market and various stage of clinical translation. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 3028–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza-Oliver, M.; Santander-Ortega, M.J.; Lozano, M.V. Current approaches in lipid-based nanocarriers for oral drug delivery. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2021, 11, 471–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, S.T.; Frank, K.J.; Fricker, G.; Brandl, M. Biopharmaceutical classification of poorly soluble drugs with respect to “enabling formulations”. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 50, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, C.J.; Williams, H.D.; Trevaskis, N.L. Recent advances in lipid-based formulation technology. Pharm. Res. 2013, 30, 2971–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, H.; Holm, R.; Müllertz, A. Lipid-based formulations for oral administration of poorly water-soluble drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 453, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janjua, T.I.; Cao, Y.; Yu, C.; Popat, A. Clinical translation of silica nanoparticles. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2021, 6, 1072–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janjua, T.I.; Cao, Y.; Kleitz, F.; Linden, M.; Yu, C.; Popat, A. Silica nanoparticles: A review of their safety and current strategies to overcome biological barriers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2023, 203, 115115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremmell, K.E.; Prestidge, C.A. Enhancing oral bioavailability of poorly soluble drugs with mesoporous silica based systems: Opportunities and challenges. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2019, 45, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, M.B.; Wüst, M.; Kuentz, M.; Wagner, K.G. High loading of lipophilic compounds in mesoporous silica for improved solubility and dissolution performance. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 654, 123946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramarczyk, D.; Knapik-Kowalczuk, J.; Smolka, W.; Monteiro, M.F.; Tajber, L.; Paluch, M. Inhibition of celecoxib crystallization by mesoporous silica–Molecular dynamics studies leading to the discovery of the stabilization origin. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 171, 106132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, P.; Dening, T.J.; Meola, T.R.; Schultz, H.B.; Holm, R.; Thomas, N.; Prestidge, C.A. Solidification to improve the biopharmaceutical performance of SEDDS: Opportunities and challenges. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 142, 102–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Møller, A.; Schultz, H.B.; Meola, T.R.; Müllertz, A.; Prestidge, C.A. The influence of solidification on the in vitro solubilisation of blonanserin loaded supersaturated lipid-based oral formulations. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 157, 105640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, H.B.; Joyce, P.; Thomas, N.; Prestidge, C.A. Supersaturated-silica lipid hybrids improve in vitro solubilization of abiraterone acetate. Pharm. Res. 2020, 37, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almasri, R.; Joyce, P.; Schultz, H.B.; Thomas, N.; Bremmell, K.E.; Prestidge, C.A. Porous nanostructure, lipid composition, and degree of drug supersaturation modulate in vitro fenofibrate solubilization in silica-lipid hybrids. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, H.B.; Kovalainen, M.; Peressin, K.F.; Thomas, N.; Prestidge, C.A. Supersaturated silica-lipid hybrid oral drug delivery systems: Balancing drug loading and in vivo performance. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2019, 370, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meola, T.R.; Schultz, H.B.; Peressin, K.F.; Prestidge, C.A. Enhancing the oral bioavailability of simvastatin with silica-lipid hybrid particles: The effect of supersaturation and silica geometry. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 150, 105357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almasri, R.; Schultz, H.B.; Møller, A.; Bremmell, K.E.; Garcia-Bennett, A.; Joyce, P.; Prestidge, C.A. Role of Silica Intrawall Microporosity on Abiraterone acetate solubilization and in vivo oral absorption. Mol. Pharm. 2022, 19, 1091–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meola, T.R.; Abuhelwa, A.Y.; Joyce, P.; Clifton, P.; Prestidge, C.A. A safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetic study of a novel simvastatin silica-lipid hybrid formulation in healthy male participants. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2021, 11, 1261–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, A.; Eskandar, N.G.; Rao, S.; Prestidge, C.A. First in man bioavailability and tolerability studies of a silica–lipid hybrid (Lipoceramic) formulation: A Phase I study with ibuprofen. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2014, 4, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.-H.; Tan, A.; Santos, L.; Ngo, D.; Edwards, G.A.; Porter, C.J.; Prestidge, C.A.; Boyd, B.J. Silica–lipid hybrid (SLH) formulations enhance the oral bioavailability and efficacy of celecoxib: An in vivo evaluation. J. Control. Release 2013, 167, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, E.J.Y.; Chin, S.Y.; Ng, Z.W.; Yap, T.J.; Cheong, E.Z.B.; Wang, Z.; Chan, E.C.Y. Unraveling complexities in the absorption and Disposition Kinetics of Abiraterone via Iterative PBPK Model Development and Refinement. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2023, 62, 1243–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, A.; Almasri, R.; Wignall, A.; Schultz, H.B.; Elz, A.S.; Ariaee, A.; Bremmell, K.E.; Joyce, P.; Prestidge, C.A. Enhancing the pharmacokinetics of abiraterone acetate through lipid-based formulations: Addressing solubility and food effect challenges. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.; Famta, P.; Vambhurkar, G.; Sharma, A.; Mourya, A.; Srinivasarao, D.A.; Shinde, A.; Prasad, S.B.; Pandey, G.; Madan, J. Exploration of Abiraterone acetate loaded Nanostructured lipid carriers for bioavailability improvement and circumvention of fast-fed variability. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2025, 15, 1074–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, H.B.; Meola, T.R.; Thomas, N.; Prestidge, C.A. Oral formulation strategies to improve the bioavailability and mitigate the food effect of abiraterone acetate. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 577, 119069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, H.B.; Wignall, A.D.; Thomas, N.; Prestidge, C.A. Enhancement of abiraterone acetate oral bioavailability by supersaturated-silica lipid hybrids. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 582, 119264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, A.T.; Ohlsson, A.G.; Polentarutti, B.; Barker, R.A.; Phillips, A.R.; Abu-Rmaileh, R.; Dickinson, P.A.; Abrahamsson, B.; Østergaard, J.; Müllertz, A. Oral bioavailability of cinnarizine in dogs: Relation to SNEDDS droplet size, drug solubility and in vitro precipitation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 48, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogmann, B.; Beckert, T. Enteric targeting through enteric coating. Drugs Pharm. Sci. 2001, 115, 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Joyce, P.; Tan, A.; Whitby, C.P.; Prestidge, C.A. The role of porous nanostructure in controlling lipase-mediated digestion of lipid loaded into silica particles. Langmuir 2014, 30, 2779–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, P.; Dening, T.J.; Gustafsson, H.; Prestidge, C.A. Modulating the Lipase-Mediated Bioactivity of Particle-Lipid Conjugates Through Changes in Nanostructure and Surface Chemistry. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2017, 119, 1700213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, P.; Kempson, I.; Prestidge, C.A. QCM-D and ToF-SIMS investigation to deconvolute the relationship between lipid adsorption and orientation on lipase activity. Langmuir 2015, 31, 10198–10207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, P.; Kempson, I.; Prestidge, C.A. Orientating lipase molecules through surface chemical control for enhanced activity: A QCM-D and ToF-SIMS investigation. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 142, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stappaerts, J.; Geboers, S.; Snoeys, J.; Brouwers, J.; Tack, J.; Annaert, P.; Augustijns, P. Rapid conversion of the ester prodrug abiraterone acetate results in intestinal supersaturation and enhanced absorption of abiraterone: In vitro, rat in situ and human in vivo studies. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 90, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, M.; Gonzalez, M.; Mannens, G.; De Vries, R.; Lopez, C.; Griffin, T.; Tran, N. A phase I, open-label, single-dose, mass balance study of 14C-labeled abiraterone acetate in healthy male subjects. Xenobiotica 2013, 43, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Speybroeck, M.; Mellaerts, R.; Mols, R.; Do Thi, T.; Martens, J.A.; Van Humbeeck, J.; Annaert, P.; Van den Mooter, G.; Augustijns, P. Enhanced absorption of the poorly soluble drug fenofibrate by tuning its release rate from ordered mesoporous silica. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 41, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, C.N.; Priya, R.; Swain, S.; Jena, G.K.; Panigrahi, K.C.; Ghose, D. Pharmaceutical significance of Eudragit: A review. Future J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 3, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Van Duong, T.; Taylor, L.S. Impact of gastric pH variations on the release of amorphous solid dispersion formulations containing a weakly basic drug and enteric polymers. Mol. Pharm. 2023, 20, 1681–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Van Duong, T.; Taylor, L.S. Enteric coating of tablets containing an amorphous solid dispersion of an enteric polymer and a weakly basic drug: A strategy to enhance in vitro release. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 642, 123139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Xiao, C.; Li, X.; Huang, J.; Si, L.; Sun, M. Enteric polymer–based amorphous solid dispersions enhance oral absorption of the weakly basic drug Nintedanib via stabilization of Supersaturation. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angi, R.; Jordán, T.; Basa-Dénes, O.; Solymosi, T.; Ötvös, Z.; Glavinas, H.; Filipcsei, G. Complexes of abiraterone acetate, process for the preparation thereof and pharmaceutical compositions containing them. U.S. Patent No. 10,668,016, 2 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Won, J.-H.; Jin, M.; Na, Y.-G.; Song, B.; Yun, T.-S.; Hwang, Y.-R.; Lee, S.-R.; Je, S.; Kim, J.-Y.; Lee, H.-K. The combinative strategy for improving the intestinal stability and cellular absorption of curcumin by enteric coating of the optimized nanostructured lipid carriers. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 89, 105108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosny, K.M. Alendronate sodium as enteric coated solid lipid nanoparticles; preparation, optimization, and in vivo evaluation to enhance its oral bioavailability. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, K.K.; Kaurav, M.; Pandey, R.S. Chylomicron mimicking solid lipid nanoemulsions encapsulated enteric minicapsules targeted to colon for immunization against hepatitis B. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 66, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhou, K.; Chen, D.; Xu, W.; Tao, Y.; Pan, Y.; Meng, K.; Shabbir, M.A.B.; Liu, Q.; Huang, L. Solid lipid nanoparticles with enteric coating for improving stability, palatability, and oral bioavailability of enrofloxacin. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 1619–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Liu, W.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Zhang, R.; He, H.; Lu, Y.; Wu, W.; Qi, J. Translation of ionic liquids to be enteric nanoparticles for facilitating oral absorption of cyclosporine A. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2023, 8, e10405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, P.; Allen, C.J.; Alonso, M.J.; Ashford, M.; Bradbury, M.S.; Germain, M.; Kavallaris, M.; Langer, R.; Lammers, T.; Peracchia, M.T. A translational framework to DELIVER nanomedicines to the clinic. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2024, 19, 1597–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameter | EC-Par-SL 6 mg/kg n = 4 |
Par-SL 6 mg/kg n = 4 |
Pure Prodrug a 25 mg/kg n = 4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| AUC0–8 h (ng·h/mL) | 840 (113) | 321 (86) | 122 (27) |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 178 (46) | 88 (59) | 47 (9) |
| Tmax (h) | 4 [1–6] | 3 [1.5, 4] | 2 [2, 2] |
| Frel (fold) | 28.7 | 11.0 | 1.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Taheri, A.; Almasri, R.; Wignall, A.; Feltrin, F.; Bremmell, K.E.; Joyce, P.; Prestidge, C.A. Enteric Coating Enhances the Biopharmaceutical Performance of a Silica–Lipid Formulation of Abiraterone Acetate. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101289
Taheri A, Almasri R, Wignall A, Feltrin F, Bremmell KE, Joyce P, Prestidge CA. Enteric Coating Enhances the Biopharmaceutical Performance of a Silica–Lipid Formulation of Abiraterone Acetate. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(10):1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101289
Chicago/Turabian StyleTaheri, Ali, Ruba Almasri, Anthony Wignall, Felicia Feltrin, Kristen E. Bremmell, Paul Joyce, and Clive A. Prestidge. 2025. "Enteric Coating Enhances the Biopharmaceutical Performance of a Silica–Lipid Formulation of Abiraterone Acetate" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 10: 1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101289
APA StyleTaheri, A., Almasri, R., Wignall, A., Feltrin, F., Bremmell, K. E., Joyce, P., & Prestidge, C. A. (2025). Enteric Coating Enhances the Biopharmaceutical Performance of a Silica–Lipid Formulation of Abiraterone Acetate. Pharmaceutics, 17(10), 1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101289









