Tannic Acid/Fe(III)-Coated Curcumin Self-Assembled Nanoparticles for Combination Therapy to Treat Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Processes for CUR@TA-Fe(III) NPs
2.3. Drug Encapsulation Rate and Drug Loading Capacity
2.4. Characterization of CUR@TA-Fe(III) NPs
2.5. Photothermal Properties of CUR@TA-Fe(III) NPs
2.6. Cellular Uptake
2.7. In Vitro Cytotoxicity
2.7.1. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.7.2. Live/Dead Cell Assay
2.8. In Vitro Ferroptosis Mechanism and Photothermal–Ferroptosis Therapy
2.8.1. Intracellular Fe(II) Detection
2.8.2. Intracellular ROS Detection
2.8.3. Intracellular LPO Detection
2.8.4. Intracellular Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Detection
2.8.5. GSH Level Detection
2.9. In Vivo Antitumor Effects
2.9.1. In Vivo Photothermal Efficacy
2.9.2. Antitumor Effect
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Processes for CUR@TA-Fe(III) NPs
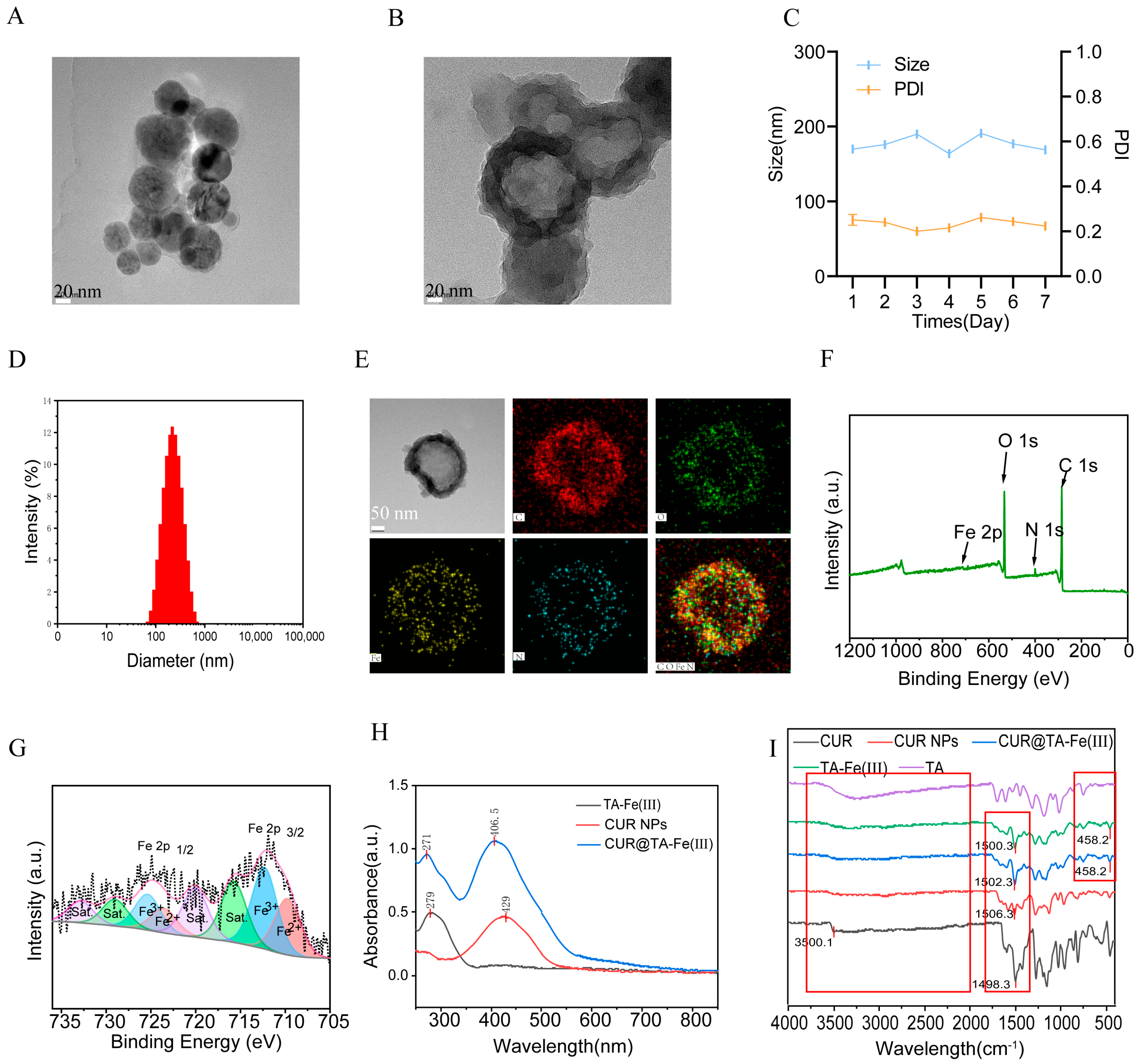
3.2. Characterization of CUR@Fe-TA(III) NPs
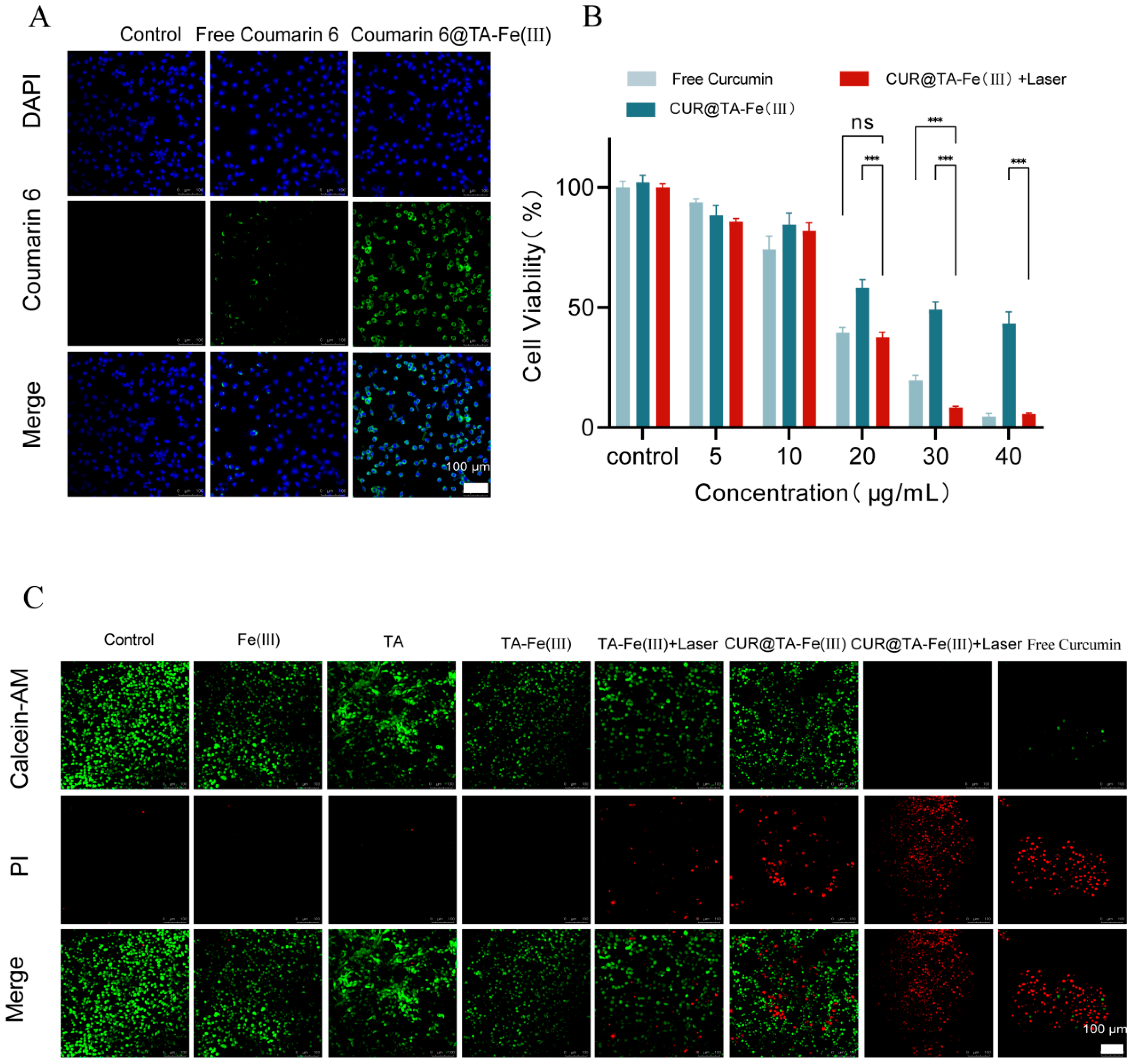
3.3. Cellular Uptake
3.4. In Vitro Cytotoxicity
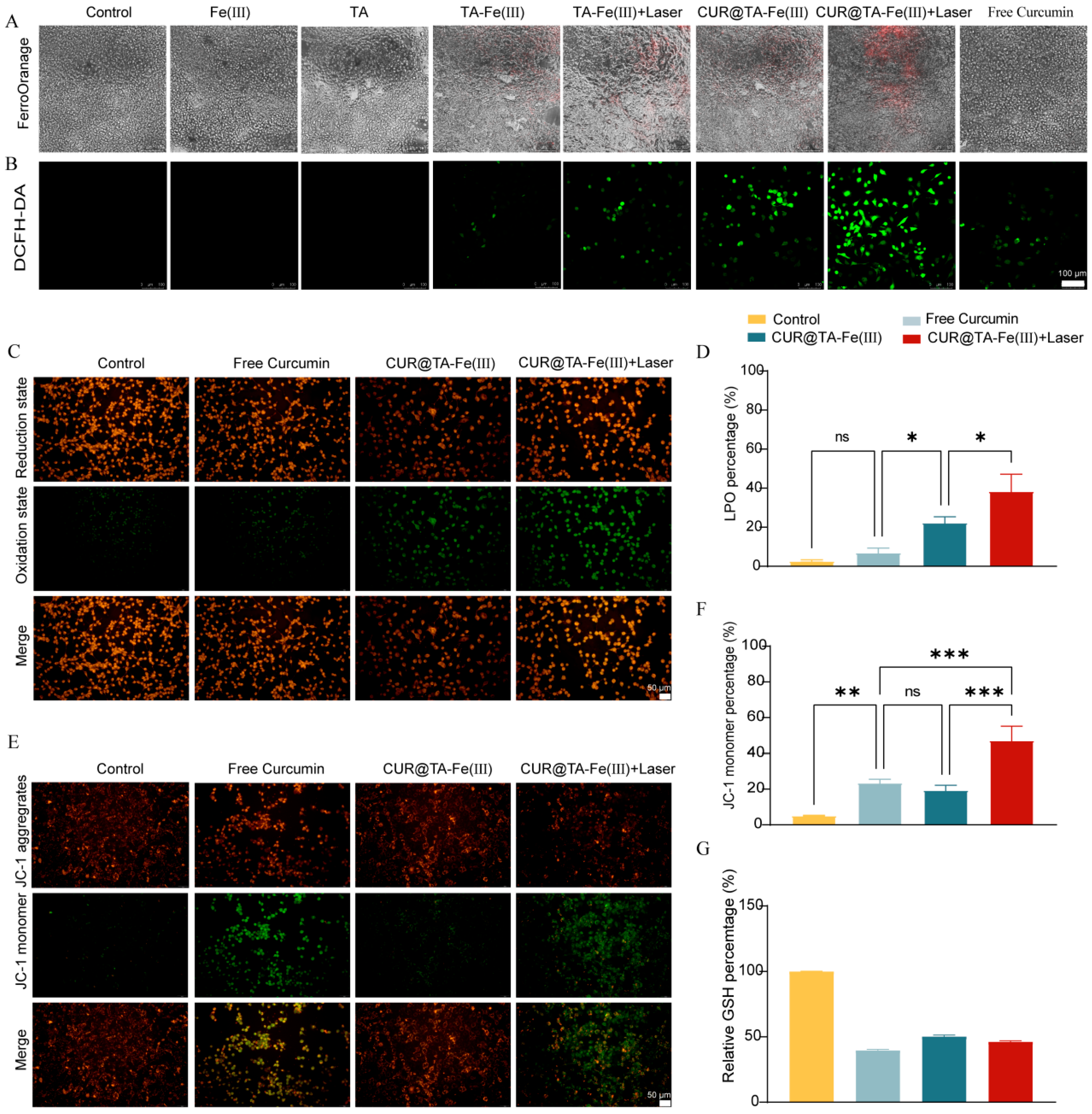
3.5. In Vitro Ferroptosis Mechanism and Photothermally Strengthened Ferroptosis
3.6. Antitumor Activity In Vivo
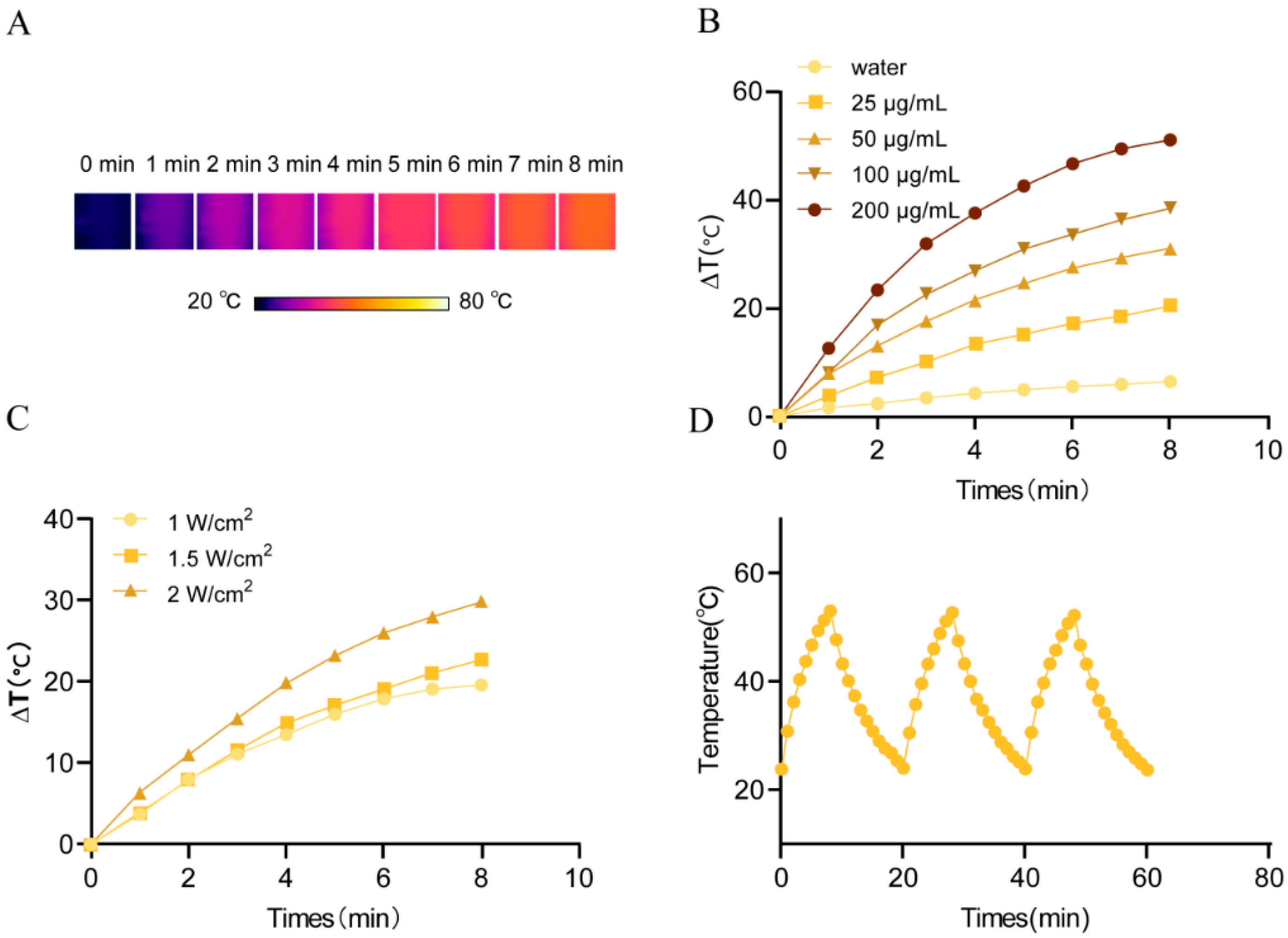
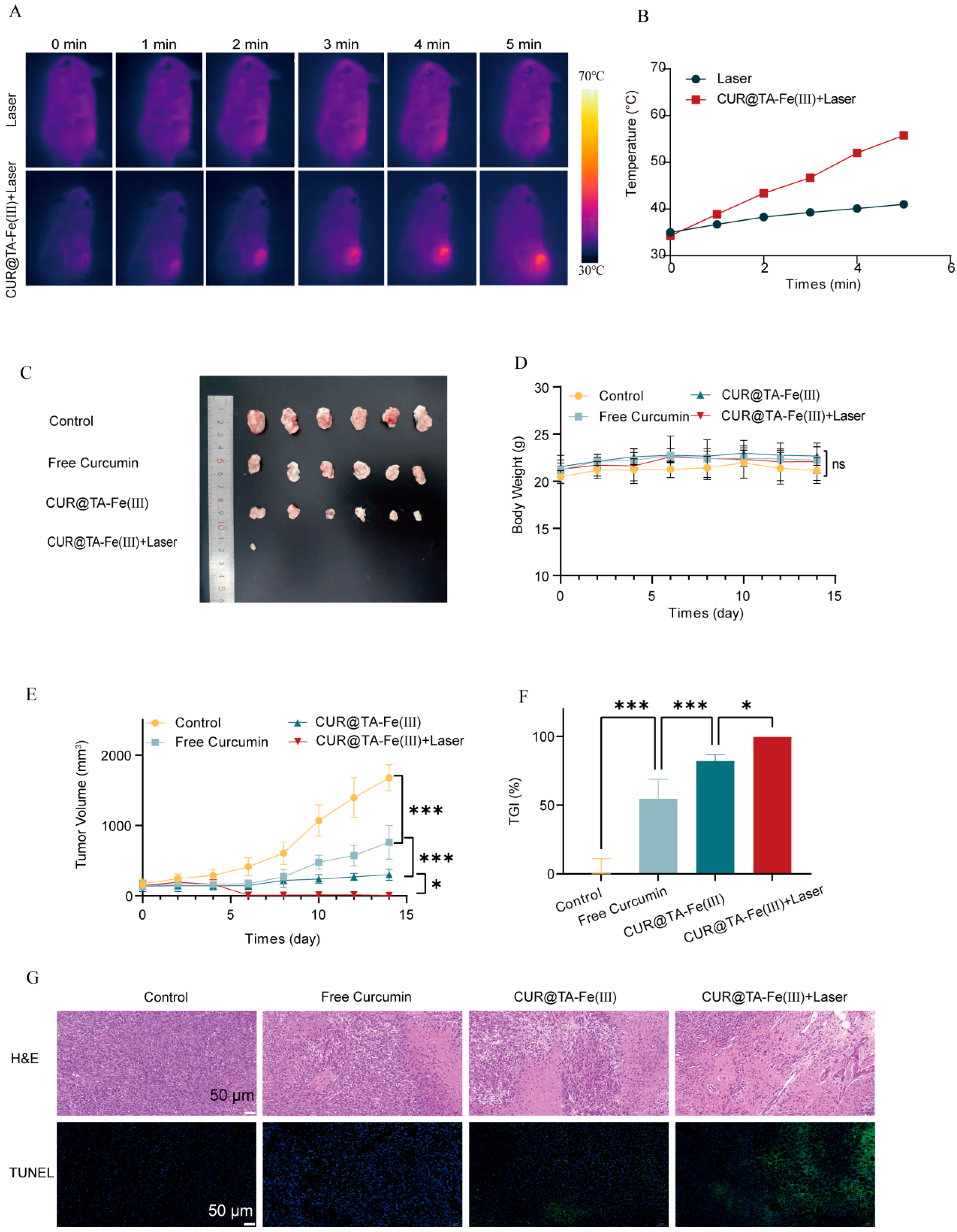
3.6.1. In Vivo Photothermal Warming Effect
3.6.2. In Vivo Antitumor Effects
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Society of Breast Cancer China Anti-Cancer Association; International Medical Exchange Society, China Anti-Cancer Association; Breast Cancer Group, Branch of Oncologist, Chinese Medical Doctor Association; International Medical Exchange Society, China Anti-Cancer Association. Guidelines for clinical diagnosis and treatment of advanced triple negative breast cancer in China (2024 edition). Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi 2024, 46, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnatilaka Na Bhuket, P.; El-Magboub, A.; Haworth, I.S.; Rojsitthisak, P. Enhancement of curcumin bioavailability via the prodrug approach: Challenges and prospects. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2017, 42, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Shi, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, R. Curcumin alleviates d-galactose-induced cardiomyocyte senescence by promoting autophagy via the sirt1/ampk/mtor pathway. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2022, 2022, 2990843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Liu, K.; Li, Y.; Xie, T.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Tong, H.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, H.; et al. Intrinsically bioactive manganese-eumelanin nanocomposites mediated antioxidation and anti-neuroinflammation for targeted theranostics of traumatic brain injury. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2022, 11, 2200517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doghish, A.S.; Mageed, S.S.A.; Zaki, M.B.; Abd-Elmawla, M.A.; Sayed, G.A.; Hatawsh, A.; Aborehab, N.M.; Moussa, R.; Mohammed, O.A.; Abdel-Reheim, M.A.; et al. Role of long non-coding RNAs and natural products in prostate cancer: Insights into key signaling pathways. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2025, 25, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Ding, H.; Liang, M.; Chen, X.; Yan, Y.; Wan, N.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, J.; Cao, J. Curcumin induces ferroptosis in non-small-cell lung cancer via activating autophagy. Thorac. Cancer 2021, 12, 1219–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.; Deka, D.; Kondaveeti, S.B.; Ayyadurai, P.; Siripragada, S.; Philip, N.; Pathak, S.; Duttaroy, A.K.; Banerjee, A. An overview of potential of natural compounds to regulate epigenetic modifications in colorectal cancer: A recent update. Epigenetics 2025, 20, 2491316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firouzjaei, A.A.; Aghaee-Bakhtiari, S.H.; Tafti, A.; Sharifi, K.; Abadi, M.; Rezaei, S.; Mohammadi-Yeganeh, S. Impact of curcumin on ferroptosis-related genes in colorectal cancer: Insights from in-silico and in-vitro studies. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2023, 41, 1488–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.F.; Xie, Y.; Malhotra, A. Potential of curcumin and quercetin in modulation of premature mitochondrial senescence and related changes during lung carcinogenesis. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol. 2021, 40, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.H.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Y.F.; Gao, Q.; Wang, R.; Fu, Y.R.; Zheng, L.W.; Yu, H. Transcriptome investigation and in vitro verification of curcumin-induced ho-1 as a feature of ferroptosis in breast cancer cells. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 3469840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, T.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, X.; Guan, J. Curcumin suppresses tumorigenesis by ferroptosis in breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0261370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Li, X.; Gu, P.; Cheng, W.; Zhang, R.; Hu, K. Curcumin-loaded zein/pectin nanoparticles: Caco-2 cellular uptake and the effects on cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of human hepatoma cells (hepg2). J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 74, 103497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.J.; Wang, B.H.; Chen, Y.; Facchetti, A.; Marks, T.J.; Balogun, O. Cross-plane thermal conductance of phosphonate-based self-assembled monolayers and self-assembled nanodielec-trics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 34901–34909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanii, T.; Hosaka, T.; Miyake, T.; Ohdomari, I. Electron beam lithography on organosilane self-assembled monolayer resist. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. Part 1-Regul. Pap. Short Notes Rev. Pap. 2004, 43, 4396–4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejima, H.; Richardson, J.J.; Liang, K.; Best, J.P.; van Koeverden, M.P.; Such, G.K.; Cui, J.; Caruso, F. One-step assembly of coordination complexes for versatile film and particle engineering. Science 2013, 341, 154–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.T.; Cheng, B.H.; Wang, C.Y.; Richardson, J.J.; Naito, M.; Miyata, K.; Ejima, H. Surface-initiated synergistic disassembly of metal-phenolic networks by redox and hydrolytic reactions. Chem. Mater. 2024, 36, 9646–9657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liao, L.F.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Lei, L.T.Y.; Tao, Z.H.; Zhang, J.Y.; Peng, D.D.; Wang, J.Q.; Yu, C.Y.; et al. A poss-based metal-phenolic network with coupled hardness and softness for photodynamic-immunotherapy of tri-ple-negative breast cancer. ACS Mater. Lett. 2024, 6, 2369–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.H.; Yang, S.C.; Zhu, M.H.; Zhu, X.D.; Luan, X.; Liu, X.L.; Lai, X.; Yuan, Y.H.; Lu, Q.; Sun, P.; et al. Metal phenolic network-integrated multistage nanosystem for enhanced drug delivery to solid tumors. Small 2021, 17, 2100789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Jiang, W.X.; Luo, Y.L.; Wan, L.; Guo, X.; Xie, Z.Y.; Tang, R.; Huang, T.; Wang, J.X.; Du, C.R.; et al. Nir activated multimodal therapeutics based on metal-phenolic networks-functionalized nanoplatform for combating against multidrug resistance and metastasis. Small 2023, 19, 2206174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Z.M.; Zhang, Y.F.; Chen, X.L.; Wang, N.; Ma, R.Y.; Luo, X.Y.; Pan, X.; Yang, Y.; Xue, W. A versatile nanoplatform based on metal-phenolic networks inhibiting tumor growth and metastasis by combined star-vation/chemodynamic/immunotherapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2211869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardajee, G.R.; Mahmoodian, H.; Rouhi, M. Tailoring a salep-g-p(vp-co-aa)/ag nps superabsorbent single network hydrogel for enhanced ph-responsive delivery of deferasirox. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2025, 112, 107222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Shi, X.Y.; Peng, Y.; Hu, J.M.; Ding, J.S.; Zhou, W.H. Anti-pd-l1 dnazyme loaded photothermal Mn2+/Fe3+ hybrid metal-phenolic networks for cyclically amplified tumor ferroptosis-immunotherapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2022, 11, 2102315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.R.; Wang, Y.R.; Du, J.Y.; Meng, Y.L.; Liu, X.Y.; Zhang, X.L.; Kang, Y.F. pH-responsive metal-phenolic network nanoparticles for synergistic chemo-photodynamic antibacterial therapy. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 28408–28418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.L.; Chen, J.J.; Li, R.H.; Wei, L.Z.; Xiong, H.T.; Wang, C.H.; Chai, K.K.; Chen, M.Y.; Zhu, Z.N.; Yao, T.M.; et al. Metal-polyphenol-network coated prussian blue nanoparticles for synergistic ferroptosis and apoptosis via triggered gpx4 inhibition and concurrent in situ bleomycin toxification. Small 2021, 17, 2103919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.M.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, J.Q.; Yang, X.T.; Zhang, K.; Lei, L.; Hu, H.L.; Zhang, H.L.; Ouyang, L.; Gao, H.L. Metal-phenolic networks with ferroptosis to deliver NIR-responsive CO for synergistic therapy. J. Control. Release 2022, 352, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, M.J.; Nóbrega, C.; Andrade, S.; Lima, J.; Loureiro, J.A.; Pereira, M.C. Targeted fluoxetine delivery using folic acid-modified plga nanoparticles for selective uptake by glioblastoma cells. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, S.A.M.; Fouad, G.I.; Beherei, H.H.; Shehata, M.R.; Mabrouk, M. Palladium complex-loaded magnetite nanoparticles as drug delivery systems for targeted liver cancer therapy. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Jia, D.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Rao, Z.; Lei, X.; Zhao, J.; Zeng, K.; Xu, Z.; Ming, J. Promotion of the anticancer activity of curcumin based on a metal–polyphenol networks delivery system. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 602, 120650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Eerdenbrugh, B.; Taylor, L.S. An ab initio polymer selection methodology to prevent crystallization in amorphous solid dispersions by application of crystal engineering principles. Crystengcomm 2011, 13, 6171–6178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegiel, L.A.; Zhao, Y.H.; Mauer, L.J.; Edgar, K.J.; Taylor, L.S. Curcumin amorphous solid dispersions: The influence of intra and intermolecular bonding on physical stability. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2014, 19, 976–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowding, P.J.; Atkin, R.; Vincent, B.; Bouillot, P. Oil core/polymer shell microcapsules by internal phase separation from emulsion droplets. Ii: controlling the release profile of active molecules. Langmuir 2005, 21, 5278–5284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prosapio, V.; De Marco, I.; Reverchon, E. Supercritical antisolvent coprecipitation mechanisms. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2018, 138, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Chen, W.; Feng, J.; Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Wang, C.; Yang, W.; Du, X. Facile, smart, and degradable metal–organic framework nanopesticides gated with feiii-tannic acid networks in re-sponse to seven biological and environmental stimuli. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 19507–19520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; He, Y.; Pan, X.; Yi, G.; Ouyang, X.K.; Wang, N. Encapsulation of dihydroartemisinin with tannic acid/Fe coated hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles for tumor therapy. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 38, 107951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.S.; Li, J.; Wang, L.Y.; Dai, Y.L. Engineering metal-phenolic networks for enhancing cancer therapy by tumor microenvironment modulation. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev.-Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 15, e1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.M.; Ding, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.F.; Sun, Z.Y.; Liu, J.; Dai, M.X.; Feng, J.Y.; Li, B.; Wang, C.Z.; Wei, Y.M.; et al. An engineered cascade-sensitized red-emitting upconversion nanoplatform with a tandem hydrophobic hydration-shell and metal-phenolic network decoration for single 808 nm triggered simultaneous tumor PDT and PTT enhanced CDT. Nanoscale 2023, 15, 10067–10078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Yang, X.J.; Li, H.R.; Wu, X.Y.; Wu, W.; Chen, J.Z.; Wu, A.M.; Wang, X.X. Self-assembled fe-phenolic acid network synergizes with ferroptosis to enhance tumor nanotherapy. Small 2024, 20, 2402073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vos, F.Y.F.L.; Willemse, P.H.B.; de Vries, E.G.E.; Gietema, J.A. Endothelial cell effects of cytotoxics: Balance between desired and unwanted effects. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2004, 30, 495–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.P.; Guo, Y.X.; Liu, X.Y.; Wu, S.Y.; Zhu, Y.X.; Wang, S.Z.; Duan, Q.Y.; Xu, K.F.; Li, Z.H.; Zhu, X.Y.; et al. A metal-phenolic network-assembled nanotrigger evokes lethal ferroptosis via self-supply loop-based cytotoxic reactions. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 479, 147084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.-C.; Chuang, J.-Y.; Ko, C.-Y.; Kao, T.-J.; Yang, P.-Y.; Yu, C.-H.; Liu, M.-S.; Hu, S.-L.; Tsai, Y.-T.; Chan, H.; et al. AR ubiquitination induced by the curcumin analog suppresses growth of temozolomide-resistant glioblastoma through disrupting GPX4-Mediated redox homeostasis. Redox Biol. 2020, 30, 101413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Li, Y.; Wei, Q.; Liu, J. Degradable bifunctional phototherapy composites based on upconversion nanoparticle-metal phenolic network for multimodal tumor therapy in the near-infrared biowindow. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 663, 436–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.Y.; Dai, L.Q.; Liu, J.; Lu, Y.; Pan, M.; Pan, L.L.; Ye, L.; Yuan, L.P.; Li, X.C.; Bei, Z.W.; et al. Metal-phenolic-network-coated gold nanoclusters for enhanced photothermal/chemodynamic/immunogenic cancer therapy. Bioact. Mater. 2025, 44, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Stabilizer | Particle Size (nm) | PDI | EE (%) | LE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5% PVA | 188.8 ± 0.6 | 0.157 ± 0.009 | 41.33 ± 2.80 | 13.53 ± 0.63 |
| 0.5% PVP | 124.7 ± 0.8 | 0.178 ± 0.007 | 60.24 ± 1.04 | 9.49 ± 0.17 |
| 0.5% HPMC | 343.7 ± 3.6 | 0.219 ± 0.008 | 43.83 ± 7.67 | 10.09 ± 1.06 |
| Stabilizer | Particle Size (nm) | PDI | EE (%) | LE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1% PVP | 124.2 ± 0.7 | 0.227 ± 0.039 | 52.09 ± 0.21 | 21.97 ± 0.36 |
| 0.5% PVP | 124.7 ± 0.8 | 0.178 ± 0.007 | 60.24 ± 1.04 | 9.49 ± 0.17 |
| 1% PVP | 203.8 ± 1.5 | 0.181 ± 0.009 | 46.70 ± 2.99 | 7.98 ± 0.22 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Han, N.; Ruan, M.; Wei, H.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, H.; Guo, Z.; Du, S.; Li, P. Tannic Acid/Fe(III)-Coated Curcumin Self-Assembled Nanoparticles for Combination Therapy to Treat Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1257. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101257
Li J, Han N, Ruan M, Wei H, Dong Y, Zhang H, Guo Z, Du S, Li P. Tannic Acid/Fe(III)-Coated Curcumin Self-Assembled Nanoparticles for Combination Therapy to Treat Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(10):1257. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101257
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jialing, Ning Han, Mingyue Ruan, Hongmei Wei, Yunan Dong, Haitong Zhang, Zishuo Guo, Shouying Du, and Pengyue Li. 2025. "Tannic Acid/Fe(III)-Coated Curcumin Self-Assembled Nanoparticles for Combination Therapy to Treat Triple-Negative Breast Cancer" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 10: 1257. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101257
APA StyleLi, J., Han, N., Ruan, M., Wei, H., Dong, Y., Zhang, H., Guo, Z., Du, S., & Li, P. (2025). Tannic Acid/Fe(III)-Coated Curcumin Self-Assembled Nanoparticles for Combination Therapy to Treat Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Pharmaceutics, 17(10), 1257. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101257






