Abstract
Leishmaniasis is a group of parasitic diseases with the potential to infect more than 1 billion people; however, its treatment is still old and inadequate. In order to contribute to changing this view, this work consisted of the development of complexes derived from MI metal ions with thioureas, aiming to obtain potential leishmanicidal agents. The thiourea ligands (HLR) were obtained by reactions of p-toluenesulfohydrazide with R-isothiocyanates and were used in complexation reactions with AgI and AuI, leading to the formation of complexes of composition [M(HLR)2]X (M = Ag or Au; X = NO3− or Cl−). All compounds were characterized by FTIR, 1H NMR, UV-vis, emission spectroscopy and elemental analysis. Some representatives were additionally studied by ESI-MS and single-crystal XRD. Their properties were further analyzed by DFT calculations. Their cytotoxicity on Vero cells and the extracellular leishmanicidal activity on Leishmania infantum and Leishmania braziliensis cells were evaluated. Additionally, the interaction of the complexes with the Old Yellow enzyme of the L. braziliensis (LbOYE) was examined. The biological tests showed that some compounds present remarkable leishmanicidal activity, even higher than that of the standard drug Glucantime, with different selectivity for the two species of Leishmania. Finally, the interaction studies with LbOYE revealed that this enzyme could be one of their biological targets.
1. Introduction
Leishmaniasis is considered one of the most neglected tropical and subtropical parasitic diseases and a problem of public health in almost 90 countries [1,2,3,4]. An increasing number of cases per year have been pointed out (700 thousand to 1 million), which is related to the migratory flow of refugees from regions of conflicts to tropical and subtropical countries [1,2]. The transmission of Leishmaniasis occurs mainly in endemic areas, where the protozoa are spread when female phlebotomine sandflies bite infected animals and then humans [5,6]. Among the hosts of these parasites, domestic animals, mostly dogs, are the main source of infection for people who are in close contact with them [7,8,9]. The most common prescriptions for the treatment of Leishmaniasis are based on pentavalent antimonials (SbV), like Glucantime and Pentostam, which have in their composition meglumine antimoniate and sodium stibogluconate, respectively [2,10,11]. However, this is not a good alternative since, although offering a relatively low toxicity, these drugs are not effective in many cases; in addition, the growing incidence of resistance limits their use in endemic areas [10,11]. Therapy with the second-line drugs paromomycin, amphotericin B and miltefosine presents even more problems, which comprises the need of parenteral applications and severe side effects, including teratogenic potential in the case of miltefosine [10]. Although a lot of effort has been made, so far there is no effective vaccine in clinical trials [12]. Therefore, new therapeutic alternatives for treating leishmaniasis are truly needed. In an effort to change this situation, several metal-based compounds, including silver and gold complexes (Figure 1B), have been studied and identified as antileishmanial drug prototypes and some of them have shown in vivo activity [13,14,15]. Despite these recent advances in antileishmanial drug discovery, to our knowledge, no metallodrug has passed clinical trials.
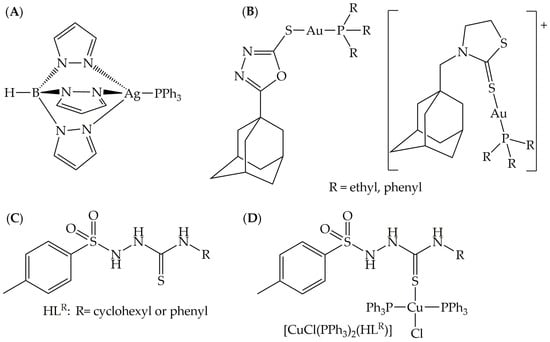
Figure 1.
Promising silver(I) (A) and gold(I) (B) antileishmanial agents; HLR ligands (C) and their copper complexes [CuCl(PPh3)2(HL1R)] (D).
In order to have a good metallodrug candidate, the choice of the ligand is very important since the organic molecule is responsible for stabilizing the metal center, avoiding losing the compounds for non-target biomolecules, which in many cases are also responsible for the activity. Thioureas and sulfonamides are two classes of compounds with a broad spectrum of pharmacological applications, among which the following stand out: antibacterial, antitumor, antiparasitic, antiviral and anticonvulsant [16,17,18]. The union of these classes of compounds in a single molecule by a covalent bond allows one, therefore, to obtain hybrid molecules. In addition to enhancing activity, these hybrid molecules can lead to a synergistic effect between two classes in the same compound and to a mechanism of action on more than one target. Our research uses, as a strategy, the development of hybrid molecules by the combination of bioactive groups such as sulfonamides, thioureas, oximes, carbazates, thiosemicarbazides and other classes of molecules with known biological activity [19,20,21,22]. Additionally, in order to achieve multiple mechanisms of action against the parasite, the coordination of these bioactive ligands to metal ions has been accomplished, producing compounds with enhanced biological activity when compared to the free ligands [23]. This hypothesis was confirmed in a previous work, where CuI complexes derived from the HLR ligands (Figure 1C,D) presented better trypanocidal activity against the amastigote form of the Tulahuen LacZ strain of Trypanosoma cruzi, the causative agent of Chagas disease [24]. Notably, the cytotoxicity of the compounds on LLC-MK2 cells did not increase upon complexation. In addition to our work, only a few complexes containing such type of ligands have been reported up to now, which were not structurally characterized [25,26].
The promising findings found for silver and gold complexes during the last decade, together with our previous encouraging results for the HLR derivatives, gave us the interest in seeking to verify the influence of changing the peripheral structure of organic molecules and also the metal center on antiparasitic activity. In this context, herein, new ligands were prepared, coordinated to AgI and AuI ions and evaluated against leishmania strains. Many mechanisms of action have been proposed for transition metal complexes [27,28]; however, the trypanothione reductase system is the most studied for such type of compounds [15,29,30,31]. Herein, we decided to investigate the LbOYE as a molecular target of the new coordination compounds, including both experimental and theoretical methods.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
All solvents were obtained commercially and used without prior treatment. The reagents, p-toluenesulfohydrazide, cyclohexyl isothiocyanate, phenyl isothiocyanate, 4-fluorophenyl isothiocyanate, 4-chlorophenyl isothiocyanate, 4-nitrophenyl isothiocyanate, allyl isothiocyanate, AgNO3 and [AuCl(DMS)] were obtained commercially (Sigma Aldrich, Cotia, Brazil). HL1Ch, HL2Ph, [Ag(HL1Ch)2]NO3 (Ag1) and [Ag(HL2Ph)2]NO3 (Ag2) were obtained as previously reported [22].
2.2. General Methods
The melting points were determined using a PF1500 FARMA-GEHAKA instrument (São Paulo, Brazil). The elemental analyses (CHNS) were determined using Heraeus vario EL equipment (Langenselbold, Germany). The conductivities of the complexes were measured with an CG1800-GEHAKA conductometer (São Paulo, Brazil). The vibrational spectra were carried out using a PerkinElmer spectrophotometer model FT-IR Frontier Single Range (Waltham, MA, USA) in the region between 4000 and 200 cm−1. The sample analyzes were performed in the solid state using the Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR) accessory with diamond crystal. The NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker Ascend 400 (Ettlingen, Germany) or on a JEOL 400 MHz multinuclear spectrometer (Tokyo, Japan), operating at 400 and 377 MHz for 1H and 19F{1H}, respectively. The electronic spectra were measured with a Shimadzu UV-2501 spectrophotometer (Tokyo, Japan) in methanol or acetonitrile solutions. The emission spectra were obtained in a Horiba Fluoromax-4 fluorimeter (Kyoto, Japan) at room temperature. The excitation and emission slits were set to 6 nm. Solutions were purged with argon for five minutes before the measurements. The measurements at 77 K glass medium were performed in a Dewar flask with liquid nitrogen in a solvent mixture of 4:1 ethanol/methanol (v/v). The positive-mode electrospray ionization mass spectra (ESI-MS) were recorded with an Agilent 6210 ESI-TOF (Agilent Technologies Santa Clara, CA, USA). All MS results are given in the form: m/z, assignment.
2.3. Preparation of the Compounds
2.3.1. Synthesis of HLR Ligands
The HLR (R = F, Cl, NO2 and allyl) ligands were formed by a method adopted from procedures in the literature [32,33,34]. Briefly, 3.80 mmol of the desired R-isothiocyanate were added to a solution containing 1 equivalent of p-toluenesulfohydrazide 708 mg (3.80 mmol) dissolved in 10 mL of ethanol. The reaction mixtures were left under stirring at 60 °C for 3 h until the formation of colorless precipitates was observed. After keeping the reaction mixtures in the freezer for 3 days, the solids were filtered, washed with n-hexane and dried under vacuum. The solids were recrystallized from a dichloromethane:ethanol mixture in a 2:1 (v/v) ratio. Crystals were obtained after slow evaporation of the resulting solutions for all compounds.
N-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-tosylhydrazinocarbothioamide (HL3FPh)–Color: Colorless. Yield: 85% (1.09 g). M.P.: 185–186 °C. Elemental Analysis calculated for C14H14FN3O2S2 (339.41 g mol−1): C: 49.54; H: 4.16; N: 12.38; S: 18.89%. Found: C: 49.58; H: 4.17; N: 12.43; S: 18.57%. IR (ATR/cm–1): 3320, 3240, 3133 ν(N-H), 1596 ν(C=N), 1543 ν(C=C), 1333 ν(S=O), 1156 ν(S=O) and 814 ν(C=S). 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6, δ/ppm): 2.40 (s, 3H, CH3), 7.10–7.14 (m, 2H, CH-FPh), 7.28–7.31 (m, 2H, CH-FPh), 7.42 (d, 3J = 8 Hz, 2H, CH-p-toluene), 7.76 (d, 3J = 8 Hz, 2H, CH-p-toluene), 9.66 (s, 1H, NH), 9.75 (s, 1H, NH) and 9.94 (s, 1H, NH). 19F NMR (377 MHz, DMSO-d6, δ/ppm): −118.43 (s). UV-vis, solution of CH3OH concentration 10−5 mol L−1 [λmax/ε (L mol−1 cm−1)]: 227 nm (69,185) and 265 nm (29,711).
N-(4-chlorophenyl)-2-tosylhydrazinocarbothioamide (HL4ClPh)–Color: Colorless. Yield: 87% (1.17 g). M.P.: 183–184 °C. Elemental Analysis calculated for C14H14ClN3O2S2 (355.86 g mol−1): C: 47.25; H: 3.97; N: 11.81; S: 18.02%. Found: C: 47.24; H: 3.96; N: 11.91; S: 17.71%. IR (ATR/cm–1): 3306, 3290, 3145 ν(N-H), 1600, 1584 ν(C=N), 1532, 1510 ν(C=C), 1341 ν(S=O), 1161 ν(S=O) and 806 ν(C=S). 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6, δ/ppm): 2.39 (s, 3H, CH3), 7.31–7.39 (m, 4H, CH-ClPh), 7.41 (d, 3J = 8 Hz, 2H, CH-p-toluene), 7.75 (d, 3J = 8 Hz, 2H, CH-p-toluene), 9.72 (s, 1H, NH), 9.82 (s, 1H, NH) and 9.96 (s, 1H, NH). UV-vis, solution of CH3OH concentration 10−5 mol L−1 [λmax/ε (L mol−1 cm−1)]: 228 nm (65,744) and 273 nm (26,616).
N-(4-nitrophenyl)-2-tosylhydrazinocarbothioamide (HL5NO2Ph)–Color: Colorless. Yield: 80% (1.11 g). M.P.: 181–183 °C. Elemental Analysis calculated for C14H14N4O4S2 (366.41 g mol−1): C: 45.89; H: 3.85; N: 15.29; S: 17.50 %. Found: C: 45.89; H: 3.87; N: 15.64; S: 17.63%. IR (ATR/cm–1): 3308, 3240, 3136 ν(N-H), 1615, 1597 ν(C=N), 1548 ν(C=C), 1424 ν(N-O), 1331 ν(S=O), 1158 ν(S=O) and 807 ν(C=S). 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6, δ/ppm): 2.35 (s, 3H, CH3), 7.39 (d, 3J = 8 Hz, 2H, CH-p-toluene), 7.75 (d, 3J = 8 Hz, 2H, CH-p-toluene), 7.80 (d, 3J = 8 Hz, 2H, CH-NO2Ph), 8.17 (d, 3J = 12 Hz, 2H, CH-NO2Ph), 10.06 (s, 1H, NH), 10.10 (s, 1H, NH) and 10.17 (s, 1H, NH). UV-vis, solution of CH3OH concentration 10−5 mol L−1 [λmax/ε (L mol−1 cm−1)]: 227 nm (46,030), 270 nm (19,579) and 331 nm (13,099).
N-allyl-2-tosylhydrazinocarbothioamide (HL6Al)–Color: Colorless. Yield: 69 % (0.74 g). M.P.: 166–167 °C. Elemental Analysis calculated for C11H15N3O2S2 (285.39 g mol−1): C: 46.29; H: 5.30; N: 14.72; S: 22.47 %. Found: C: 46.15; H: 5.35; N: 14.85; S: 22.51 %. IR (ATR/cm–1): 3358, 3160 ν(N-H), 1600 ν(C=N), 1557 ν(C=C), 1348 ν(S=O), 1170 ν(S=O) and 809 ν(C=S). 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6, δ/ppm): 2.41 (s, 3H, CH3), 4.06 (t, 2H, CH2-NH), 5.00–5.11 (m, 2H, CH2-CH), 5.69–5.79 (m, 1H, CH-CH2), 7.41 (d, 3J = 8 Hz, 2H, CH-p-toluene), 7.70 (d, 3J = 8 Hz, 2H, CH-p-toluene), 8.18 (t, 1H, NH-CH2), 9.35 (s, 1H, NH) and 9.82 (s, 1H, NH). UV-vis, solution of CH3OH concentration 10−5 mol L−1 [λmax/ε (L mol−1 cm−1)]: 228 nm (53,510) and 246 nm (41,523).
2.3.2. Synthesis of [Ag(HLR)2]NO3 Complexes
The desired ligand (0.20 mmol) was added to a solution containing the precursor AgNO3 (0.10 mmol, 17 mg) dissolved in ethanol (4 mL). The solution was maintained under stirring for 24 h, forming colorless precipitates. The solids were filtered, washed with n-hexane and dried under vacuum.
[Ag(HL3FPh)2]NO3 (Ag3): Color: Colorless. Yield: 59% (50 mg). M.P.: 159–160 °C. Elemental Analysis calculated for C28H28AgF2N7O7S4 (848.69 g mol−1): C: 39.63; H: 3.33; N: 11.55; S: 15.11%. Found: C: 39.73; H: 3.34; N: 11.58; S: 15.19%. IR (ATR/cm–1): 3233, 3183, 3156 ν(N-H), 1609 ν(C=N), 1559 ν(C=C), 1416 ν(N-O), 1332 ν(S=O), 1160 ν(S=O) and 786 ν(C=S). 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, δ/ppm): 2.38 (s, 6H, CH3), 7.13 (d, J = 8 Hz, 4H, CH-p-toluene), 7.22–7.41 (m, 12H, CH-FPh), 7.73 (d, J = 8 Hz, 4H, CH-p-toluene), 10.29 (s, 2H, NH), 10.35 (s, 2H, NH) and 10.44 (s, 2H, NH). 19F NMR (377 MHz, DMSO-d6, δ/ppm): −115.15 (s). ESI/MS (m/z): 785.0040, [M]+ (calcd. 785.0074). UV-vis, solution of CH3CN concentration 10−6 mol L−1 [λmax/ε (L mol−1 cm−1)]: 228 nm (22,532) and 265 nm (9229). Molar Conductivity: (10−3 M, DMSO): 4.48 μS cm−1 mol−1.
[Ag(HL4ClPh)2]NO3 (Ag4): Color: Colorless. Yield: 76% (67 mg). M.P.: 162–164 °C. Elemental Analysis calculated for C28H28AgCl2N7O7S4 (881.60 g mol−1): C: 38.15; H: 3.20; N: 11.12; S: 14.55%. Found: C: 40.67; H: 3.30; N: 10.54; S: 15.75%. IR (ATR/cm–1): 3228, 3184, 3166 ν(N-H), 1593 ν(C=N), 1550 ν(C=C), 1409 ν(N-O), 1332 ν(S=O), 1160 ν(S=O) and 784 ν(C=S). 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, δ/ppm): 2.37 (s, 6H, CH3), 7.04–7.47 (m, 12H, CH-ClPh + CH-p-toluene), 7.76 (d, J = 8 Hz, 4H, CH-p-toluene), 8.32 (s, 1H, NH), 8.93 (s, 1H, NH) and 10.14 (s, 4H, NH). UV-vis, solution of CH3CN concentration 10−6 mol L−1 [λmax/ε (L mol−1 cm−1)]: 228 nm (26,078) and 278 nm (9379). Molar Conductivity: (10−3 M, DMSO): 4.25 μS cm−1 mol−1.
[Ag(HL5NO2Ph)2]NO3 (Ag5): Color: Colorless. Yield: 79% (71 mg). M.P.: 158–160 °C. Elemental Analysis calculated for C28H28AgN9O11S4 (902.70 g mol−1): C: 37.25; H: 3.13; N: 13.96; S: 14.21%. Found: C: 36.95; H: 3.00; N: 13.62; S: 13.84%. IR (ATR/cm–1): 3385, 3306, 3217, 3155 ν(N-H), 1619, 1596 ν(C=N), 1570 ν(C=C), 1418, 1400 ν(N-O), 1318 ν(S=O), 1154 ν(S=O) and 760 ν(C=S). 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, δ/ppm): 2.37 (s, 6H, CH3), 7.42 (d, J = 8 Hz, 4H, CH-p-toluene), 7.51 (d, J = 8 Hz, 4H, CH-p-toluene), 7.71–8.30 (m, 8H, CH-NO2Ph), 9.16 (s, 1H, NH), 9.30 (s, 1H, NH) and 10.26–10.82 (m, 4H, NH). UV-vis, solution of CH3CN concentration 10−6 mol L−1 [λmax/ε (L mol−1 cm−1)]: 227 nm (37,436), 280 nm (16,203) and 332 nm (15,907). Molar Conductivity: (10−3 M, DMSO): 20.4 μS cm−1 mol−1.
[Ag(HL6Al)2]NO3 (Ag6): Color: Colorless. Yield: 68% (50 mg). M.P.: 183–187 °C. Elementary Analysis calculated for C22H30AgN7O7S4 (740.64 g mol−1): C: 35.68; H: 4.08; N: 13.24; S: 17.32%. Found: C: 35.92; H: 4.21; N: 13.26; S: 17.33 %. IR (ATR/cm–1): 3265, 3225 ν(N-H), 1646 ν(C=N), 1568 ν(C=C), 1418 ν(N-O), 1327 ν(S=O), 1134 ν(S=O) and 781 ν(C=S). 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, δ/ppm): 2.38 (s, 6H, CH3), 4.05 (m, 4H, CH2-NH), 4.94–5.22 (m, 4H, CH2-CH), 5.61–5.90 (m, 2H, CH-CH2), 7.37 (d, J = 8 Hz, 4H, CH-p-toluene), 7.68 (d, J = 8 Hz, 4H, CH-p-toluene), 8.31 (s, 2H, NH) and 9.48 (s, 2H, NH). UV-vis, solution of CH3CN concentration 10−6 mol L−1 [λmax/ε (L mol−1 cm−1)]: 228 nm (72,213) and 251 nm (56,659). Molar Conductivity: (10−3 M, DMSO): 6.60 μS cm−1 mol−1.
2.3.3. Synthesis of [Au(HLR)2]Cl Complexes
A total of 0.20 mmol of the desired ligand was added to a solution containing 0.10 mmol (30 mg) of the precursor [AuCl(DMS)] dissolved in acetonitrile (4 mL). The reactions were maintained under stirring for 24 h, leading to the formation of colorless precipitates which were filtered, washed with n-hexane and dried under vacuum. Then, the solids were recrystallized in a dichloromethane/acetonitrile mixture in a 2:1 (v/v) ratio. Colorless crystals were obtained by slow evaporation of the solutions at room temperature in the absence of light.
[Au(HL1Ch)2]Cl (Au1): Color: Colorless. Yield: 73% (65 mg). M.P.: 183–187 °C. Elemental Analysis calculated for C28H42AuClN6O4S4 (887.35 g mol−1): C: 37.90; H: 4.77; N: 9.47; S: 14.45%. Found: C: 37.90; H: 4.86; N: 9.48; S: 14.61%. IR (ATR/cm–1): 3307, 3286, 3193 ν(N-H), 1600 ν(C=N), 1575 ν(C=C), 1330 ν(S=O), 1164 ν(S=O) and 789 ν(C=S). 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, δ/ppm): 1.09–1.68 (m, 20H, CH2), 2.40 (s, 6H, CH3), 3.91–3.99 (m, 2H, CH-CH2), 7.43 (d, J = 8 Hz, 4H, CH-p-toluene), 7.73 (d, J = 8 Hz, 4H, CH-p-toluene), 8.26 (s, 1H, H) and 9.96 (s, 3H, NH). ESI+ MS (m/z): 851.1810, [M]+ (calcd. 851.1816); 1374.2460 [M + AuL1Ch]+ (calcd. 1374.2479). UV-vis, solution of MeOH concentration 10−6 mol L−1 [λmax/ε (L mol−1 cm−1)]: 227 nm (78,234) and 255 nm (40,522). Molar Conductivity: (10−3 M, CH3OH): 65.1 μS cm−1 mol−1.
[Au(HL2Ph)2]Cl (Au2): Color: Colorless. Yield: 89% (78 mg). M.P.: 171–173 °C. Analysis calculated for C28H30AuClN6O4S4 (875.25 g mol−1): C: 38.42; H: 3.45; N: 9.60; S: 14.65 %. Found: C: 38.69; H: 3.55; N: 9.64; S: 14.68%. IR (ATR/cm–1): 3233, 3161, 3131 ν(N-H), 1597 ν(C=N), 1563 ν(C=C), 1352 ν(S=O), 1162 ν(S=O) and 798 ν(C=S). 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, δ/ppm): 2.40 (s, 6H, CH3), 7.12–7.40 (m, 10H, CH-phenyl), 7.43 (d, 3J = 8 Hz, 4H, CH-p-toluene), 7.78 (d, 3J = 8 Hz, 4H, CH-p-toluene) and 10.23 (sa, 5H, NH). ESI+ MS (m/z): 839.0767, [M]+ (calcd. 839.0877); 1356.0880, [M + AuL2Ph]+ (calcd. 1356.1070). UV-vis, solution of MeOH concentration 10−6 mol L−1 [λmax/ε (L mol−1 cm−1)]: 227 nm (91,320) and 270 nm (53,975). Molar Conductivity: (10−3 M, CH3OH): 74.9 μS cm−1 mol−1.
[Au(HL3FPh)2]Cl (Au3): Color: Colorless. Yield: 81% (74 mg). M.P.: 192–193 °C. Analysis calculated for C28H28AuClF2N6O4S4 (911.24 g mol−1): C: 36.91; H: 3.10; N: 9.22; S: 14.08%. Found: C: 36.98; H: 3.18; N: 9.24; S: 14.07%. IR (ATR/cm–1): 3235, 3202, 3160 ν(N-H), 1613, 1598 ν(C=N), 1571 ν(C=C), 1324 ν(S=O), 1156 ν(S=O) and 773 ν(C=S). 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, δ/ppm): 2.41 (s, 6H, CH3), 7.10–7.28 (m, 8H, CH-FPh), 7.44 (d, 3J = 8 Hz, 4H, CH-p-toluene), 7.78 (d, 3J = 8 Hz, 4H, CH-p-toluene) and 10.26 (sa, 6H, NH). ESI/MS (m/z): 875.0760, [M]+ (calcd. 875.0688); 1410.0908, [M + AuL3FPh]+ (calcd 1410.0788). UV-vis, solution of MeOH concentration 10−6 mol L−1 [λmax/ε (L mol−1 cm−1)]: 227 nm (32,697) and 264 nm (14,506). Molar Conductivity: (10−3 M, CH3OH): 84.3 μS cm−1 mol−1.
[Au(HL4ClPh)2]Cl (Au4): Color: Colorless. Yield: 87% (82 mg). M.P.: 194–195 °C. Elemental analysis calculated for C28H28AuCl3N6O4S4 (944.14 g mol−1): C: 35.62; H: 2.99; N: 8.90; S: 13.58%. Found: C: 35.67; H: 2.99; N: 8.95; S: 13.58%. IR (ATR/cm–1): 3222, 3158, 3119 ν(N-H), 1591 ν(C=N), 1552 ν(C=C), 1351 ν(S=O), 1160 ν(S=O) and 798 ν(C=S). 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, δ/ppm): 2.40 (s, 6H, CH3), 7.13–7.51 (m, 12H, CH-ClPh + CH-p-toluene), 7.77 (d, 2H, 3J = 8 Hz, CH-p-toluene) and 10.26 (sa, 6H, NH). ESI+ MS (m/z): 907.0080, [M]+ (calcd. 907.0097). UV-vis, solution of MeOH concentration 10−6 mol L−1 [λmax/ε (L mol−1 cm−1)]: 225 nm (33,535) and 270 nm (13,702). Molar Conductivity: (10−3 M, DMSO): 5.98 μS cm−1 mol−1.
[Au(HL5NO2Ph)2]Cl (Au5): Color: Colorless. Yield: 86% (83 mg). M.P.: 192–193 °C. Elemental analysis calculated for C28H28AuClN8O8S4 (965.25 g mol−1): C: 34.84; H: 2.92; N: 11.61; S: 13.29%. Found: C: 34.52; H: 2.89; N: 11.80; S: 13.54%. IR (ATR/cm–1): 3222, 3194, 3156 ν(N-H), 1618, 1596 ν(C=N), 1570 ν(C=C), 1426 ν(N-O), 1341 ν(S=O), 1158 ν(S=O) and 773 ν(C=S). 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, δ/ppm): 2.37 (s, 6H, CH3), 7.25–7.73 (m, 8H, CH-NO2Ph + CH-p-toluene), 7.77 (d, 3J = 8 Hz, 4H, CH-p-toluene), 7.93–8.31 (m, 4H, CH-phenyl) and 10.26 (sa, 4H, NH). UV-vis, solution of MeOH concentration 10−6 mol L−1 [λmax/ε (L mol−1 cm−1)]: 223 nm (29,670), 268 (17,210) and 364 nm (7623). Molar Conductivity: (10−3 M, DMSO): 30.4 μS cm−1 mol−1.
[Au(HL6Al)2]Cl (Au6): Color: Colorless. Yield: 83% (67 mg). M.P.: 197–198 °C. Elemental analysis calculated for C22H30AuClN6O4S4 (803.19 g mol−1): C: 32.90; H: 3.76; N: 10.46; S: 15.97%. Found: C: 32.97; H: 3.79; N: 10.46; S: 15.97%. IR (ATR/cm–1): 3261, 3192 ν(N-H), 1641 ν(C=N), 1584 ν(C=C), 1350 ν(S=O), 1160 ν(S=O) and 795 ν(C=S). 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, δ/ppm): 2.41 (s, 6H, CH3), 4.09 (t, 4H, CH2-NH), 5.06–5.16 (m, 4H, CH2-CH), 5.70–5.82 (m, 2H, CH-CH2), 7.43 (d, J = 8 Hz, 4H, CH-p-toluene), 7.73 (d, J = 8 Hz, 4H, CH-p-toluene), 8.98 (sa, 2H, NH) and 10.06 (sa, 4H, NH). ESI+ MS (m/z): 767.0784, [M]+ (calcd. 767.0877; 1248.0891, [M + AuL6Al]+ (calcd. 1248.1070). UV-vis, solution of MeOH concentration 10−6 mol L−1 [λmax/ε (L mol−1 cm−1)]: 225 nm (30,364) and 255 nm (10,471). Molar Conductivity: (10−3 M, CH3OH): 84.6 μS cm−1 mol−1.
2.4. Crystal Structure Determinations
The intensities for the X-ray determinations were collected at room temperature on a BRÜKER APEX II duo for HL3FPh, HL4ClPh, HL5NO2Ph and HL6Al; and on a STOE IPDS 2T diffractometer at 200 K for the Au1 and Au2 complexes, both instruments equipped with Mo-Kα radiation (λ = 0.71073 Å). Standard procedures were applied for data reduction and absorption correction [35,36]. The structures were predicted by direct methods using SHELXS97 [37] or SHELXT [38] and refined by using SHELXL2016 [39], programs included in the OLEX2 program package [40]. The positions of the hydrogen atoms were calculated at idealized positions and treated with the “riding model” option of the SHELXL2016 program [39]. The details regarding structure refinement can be found in Table 1, with the exception of HL4ClPh, whose data were not adequate. Since Au1 crystallized together with disordered solvent molecules (partially close to special positions), the refinement of its structure was undertaken with the removal of the disordered solvent molecules using the solvent mask option of OLEX2. Details are given in the Supplementary Materials. The representations of molecular and crystalline structures were prepared with the programs Mercury 4.3.1. [41] and DIAMOND 4 [42].

Table 1.
Refinement data for HL3FPh, HL5NO2Ph, HL6Al, Au1∙MeOH and Au2∙1.5MeOH.
2.5. Theoretical Calculations
2.5.1. DFT
The geometry optimizations and harmonic frequencies calculations of all complexes were conducted using Density Functional Theory (DFT) [43]; the Becke functional, B3LYP, was applied at first [44]. For the silver complexes, the D3-BJ correction for dispersion effects was enclosed [45].
For the gold complexes, we used a methodology that includes relativistic calculations as stated by the Douglas–Kroll–Hess (DKH) scheme [46]. The recontracted basis set functions were applied following the scheme displayed in the Supporting Information Materials. All calculations were conducted in the polarizable continuous medium considering the dielectric constant of the solvent (ε = 36.6, acetonitrile) in the CPCM model [47]. Calculations were performed using ORCA software version 4.2.1 [48].
For the silver complexes, the basis set functions of Ahlrichs [49] def2-SVP were used for all atoms, except sulfur and silver, for which a def2-TZVP set was applied. All calculations were conducted in continuous medium considering the dielectric constant of the solvent (ε = 36.6, acetonitrile) in the CPCM model [47]. Calculations were performed using ORCA software version 5.0.2 [50].
2.5.2. Molecular Docking
The docking simulations were performed using the optimized structures of the compounds in the enzyme active site with the GOLD (Genetic Optimization for Ligand Docking) suite version 5.5. All the water molecules and heteroatoms were removed from the enzyme and the flavin mononucleotide riboflavin monophosphate (FMN) prosthetic group was maintained in the catalytic site of enzyme structure. Only residues within 10.0 Å around His186 residue were used as a cavity site. Hermes was used for pre- and post-docking visualization, with the genetic algorithm (GA) method to run the calculations [51]. Full flexibility was allowed to the compounds. GA runs were conducted herein with a maximum of 100,000 GA operations were performed on a population size of 100 individuals. Diverse solutions were generated, ring corners were allowed to flip, conformations were explored and no constraint was applied to the protein or to the compounds. Redocking simulations of the FMN prosthetic group were executed in the enzyme active site with the available GOLD score functions and the best score (lowest rmsd to the X-ray conformation) was found with the GoldScore fitness function [51]. The enzyme used was based on the OLD Yellow protein from the protozoan Trypanosoma cruzi found in the database registered under the code PDB 4E2D [52].
2.6. Biological Studies
2.6.1. Cultivation of the Leishmania infantum and Leishmania braziliensis
The Leishmania infantum and Leishmania braziliensis strains were maintained in Schneider medium supplemented with 20% of SFB (Schneider 20%), cultivated in 25 mm3 bottles and stored at 28 °C in a BOD oven [53]. For the assays, parasites at the 5th day stationary growth phase were used.
The promastigotes metacyclic form of Leishmania infantum and Leishmania braziliensis were first filtered with an insulin syringe to break up rosettes and, then, were isolated from the culture in the stationary phase by centrifugation of 400× g for 4 min at a temperature of 4 °C [53]. The supernatant was subjected to a new centrifugation, heavier, of 2000× g for 30 min, also at 4 °C. The supernatant was discarded and the cell pallet formed from this centrifugation was resuspended in 10 mL of 10% Schneider medium. The process ensured the removal of cellular debris and dead parasites, as well as possible crystals from the culture medium, so that the quality of the experiment was guaranteed. Then, the promastigotes were diluted to 1:10 in paraformaldehyde (PFA) for counting in a Neubauer Chamber, with the concentrations adjusted for each experiment.
An amount of 1 × 107 parasites per well was used. The parasites were plated in 96-well plates. Then, the compounds were added in triplicate, starting at a concentration of 500 µM, with serial dilutions being performed up to a concentration of 3.9 µM [53]. The treatment was carried out for 24 h and, after adding 5 µL of resazurin, the fluorescence was read using a Enspire model spectrofluorometer (Perkin-Elmer, Waltham, MA, USA).
2.6.2. Cytotoxicity Assays (Vero Cells Culture)
For the experiment, Vero cells (ATCC CRL-1587) were used in Roswell Parl Memorial Institute (RPMI) medium with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) (RPMI 10%) and 20 μg/mL of Gentamicin. They were cultivated in culture bottles of 25 mm3 and kept in an oven at 37 °C with 5% carbon dioxide (CO2). When picked or used on the day of the experiment, the cells were detached from the wall of the bottles with saline and 1X trypsin/EDTA. To find out how many cells there were in the bottle, it was diluted in Turkey liquid and then we proceeded with the counting in the Neubauer Chamber to calculate the desired concentrations [54].
The Vero cells were plated at 5 × 105 cells per well, in 96-well plates, and kept in an incubator with 5% CO2 at 37 °C for 24 h. Then, the compounds were added in triplicate, starting at a concentration of 500 µM, with serial dilution being performed up to a concentration of 3.9 µM [54]. The treatment was carried out for 24 h, and, after adding 5 µL of resazurin, the fluorescence was read using a spectrofluorometer (EnSpire Perkin-Elmer, Waltham, MA, USA).
2.6.3. Infectivity Test
For the infection of RAW macrophages adhered to the plates, we used parasites in the promastigote form of Leishmania infantum, in the stationary phase, in a ratio of 10:1 (promastigotes/macrophages) [55].
Macrophages were plated in the amount of 5 × 104 cells per well, in 96-well plates, which were kept in a CO2 oven at 37 °C for 24 h. The parasites were plated at a concentration of 10:1. The plates were kept in a CO2 oven for 12 h until the parasites infected the cells. Then, we performed a cycle of 3 washes to remove the parasites that did not infect, with the treatment with the compounds being performed for 24 h. Plates were fixed with paraformol for further evaluation. Plaques were evaluated by counting parasites within 200 cells under the EVOS Cell Imaging System (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) microscope by staining with propidium iodide [55].
2.7. Enzymatic Studies
2.7.1. Expression and Purification of LbOYE
The recombinant LbOYE protein was produced using the methodology previously described [56]. Briefly, the protein was expressed in strains of bacterial Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) through induction by IPTG using the pET28a:LbOYE vector. The enzyme was purified through a chromatography step of capture by nickel affinity, as the pET28a vector allows the expression of a polyhistidine fusion peptide, located at the N-terminal end of the protein. After affinity purification, the polyhistidine tail was excised by “overnight” incubation with thrombin, and the second purification step was performed using size exclusion chromatography. Purification was evaluated by SDS-PAGE and protein concentration was estimated by spectrophotometry [56].
2.7.2. Suppression of Intrinsic Tryptophan Fluorescence
The emission spectra of the intrinsic fluorescence of the tryptophan were recorded using a Shimadzu F-4500 spectrofluorometer in the range of 310–420 nm, with opening of slits of excitation and emission at 5.0 nm and λex = 295 nm. Interaction analyzes between LbOYE and ligands were performed at λmax = 333 nm.
The compounds were solubilized in DMSO and then we made successive dilutions in a Tris-HCl 25 mmol L−1 buffer, pH 8.0, containing 100 mmol L−1 of NaCl. For all experiments, the final concentration of DMSO was kept constant and equal to 2.5%. Solutions with increasing concentrations of ligand and constant concentration of LbOYE (1 µmol L−1) were prepared, which were kept at 25 °C for a period of 1h before acquisition of fluorescence emission spectra.
The results were obtained from the fluorescence emission spectra of the intrinsic tryptophan probe in the presence of the compounds HL1Ch, HL3FPh, HL5NO2Ph, [Au(HL1Ch)2]Cl and [Ag(HL3FPh)2]NO3. The bonding parameters were determined by the Hill plot, obtaining the dissociation constant (Kd) through the non-linear adjustment of the saturation curve to the experimental data. The double-log plot was used to determine the bonding constant and the number of bonding sites (n). It also allows the calculation of the bonding constant (Kb) and Kd from 1/Kb. The Stern–Volmer plot at different temperatures demonstrates the static nature of the temper due to the increase in the temper with increasing temperature.
Equation (1)—Hill’s equation:
Reference: [21].
Equation (2)—Double-log:
Eeference: [57].
Equation (3)—Equation of Stern–Volmer:
Reference: [58].
In these equations, F0 is fluorescence in the absence of any quencher, [L] is the ligand concentration and [P0] is the protein concentration.
The methodology used to determine the Kd values presupposes the formation of the protein–ligand complex, which results in the suppression of fluorescence when compared to the protein in the absence of the suppressor.
The study of fluorescence quenching can be affected when the ligand has absorption bands that coincide with excitation and emission wavelengths of fluorescence [59]. This interference is called the internal filter effect, which can be minimized using the procedure described by Equation (4) [59,60]. Fobs and Fcor are the fluorescence intensities at 333 nm measured and corrected, respectively; l represents the optical step where the absorption and emission of light occurs and C0 is the concentration of the ligand.
For the correction of the internal filter effect, were used the molar absorptivity coefficient values in the excitation (295 nm) and emission (333 nm) lengths, [λ/ε (L mol−1 cm−1)]; HL1Ch (εex = 373 and εem = 117), HL3FPh (εex = 1191 and εem = 57), HL5NO2Ph (εex = 6162 and εem = 9124), Au1 (εex = 7045 and εem = 4008) and Ag3 (εex = 9431 and εem = 3281).
Equation (4)—Procedure to minimize the internal filter effect [59,60]:
2.7.3. Enzyme Kinetics
The initial rates were obtained through the decay of the band at 340 nm referring to the maximum absorption of the NADPH (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate) reducer, as previously reported [61]. Solutions containing 1 µmol L−1 of LbOYE, DMSO or 20 µmol L−1 of the tested compounds from a stock solution at a concentration of 5 mmol L−1 in DMSO were prepared in the presence and absence of the substrate N-Ethylmaleimide (NEM). These solutions were left for 30 min at room temperature. After 30 min, the NADPH reducer was added at a final concentration of 100 µmol L−1.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization
The synthesis and spectroscopic characterization of HLR ligands by FTIR and 1H NMR has already been reported and will not be the focus of the present work [22,32,33,34]. Herein, HLR (R = F, Cl, NO2 and Alil) were further analyzed by other methods, including crystallographic determination. Furthermore, four new silver(I) complexes of general composition [Ag(HLR)2]NO3 (Ag3–6) and six new gold(I) complexes of composition [Au(HLR)2]Cl (Au1–6) were obtained, as presented in Scheme 1. The reactions occurred in a 1:2 metal/ligand ratio in ethanol for the silver(I) complexes and in acetonitrile for the gold(I) complexes, under stirring at room temperature. The yields obtained were in the range of 54–76% for Ag3–Ag6, and around 80% for Au1–Au6. The colorless crystalline solids Ag3–Ag6 are soluble only in DMSO, while the complexes Au1–Au6 are partially soluble in a mixture of methanol or ethanol with dichloromethane (1:1) and fairly soluble in DMSO. The Ag3–Ag6 and Au1–Au6 complexes showed melting points in the range of 160–200 °C. The CHNS analyses were in accordance with the proposed structures of the Ag3–Ag6 and Au1–Au6 complexes. The poor solubility of Ag3–Ag6 in lower viscosity solvents resulted in inaccurate conductivity values [62], whereas the molar conductivity values for the Au1–Au3 and Au6 complexes were in accordance with the formation of cationic compounds, except for the Au4 complex, which differed from the other complexes due to the low solubility. The compounds were also studied by IR and 1H NMR; additional proof for the identity of the products is given by ESI+-MS for some representatives (see Supplementary Materials for details).
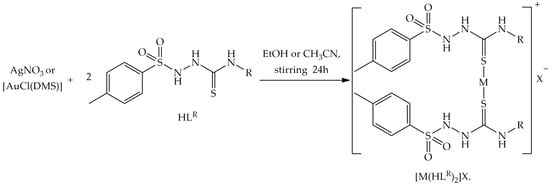
Scheme 1.
Synthesis reactions of silver(I) and gold(I) complexes of the type [M(HLR)2]X.
3.2. Crystal Structures
The HL3FPh, HL4ClPh, HL5NO2Ph and HL6Al ligands were studied by single crystal X-ray diffraction. The molecular structures can be seen in Figure 2. Selected experimental bond lengths and angles for the ligands can be seen in Table 2, except those of HL4ClPh as the data quality was not good enough to support a discussion about bond lengths and angles. HL3FPh, HL5NO2Ph and HL6Al were crystallized in the Triclinic crystal system and Pī space group. It was observed that the C(1)–N(2) and C(1)–N(3) bonds presented a shorter length (around 1.35 Å) when compared to C(9)–N(3) (around 1.43 Å), configuring an intermediate character between single and double bonds between the atoms N(2)−C(1)−N(3), while the S(2)−C(1) bond length had a double-bond character (around 1.67 Å).
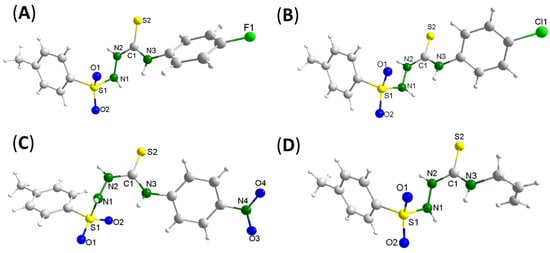
Figure 2.
Molecular structures of the free ligands HL3FPh (A), HL4ClPh (B), HL5NO2Ph (C) and HL6Al (D) obtained by single crystal X-ray diffraction.

Table 2.
Bond lengths (Å) and angles (°) selected from the structures of the HL3FPh, HL5NO2Ph and HL6Al.
The molecular structures for the gold complexes [Au(HL1Ch)2]Cl∙MeOH (Au1∙MeOH) and [Au(HL2Ph)2]Cl∙MeOH (Au2∙MeOH) were also determined using single crystal XRD. The representations of the Au1 and Au2 complexes can be seen in Figure 3. The ORTEP pictures may be observed in the Supplementary Materials (Figures S4.4 and S4.5). The selected experimental bond lengths and angles are presented in Table 3. The complexes crystallized in the Monoclinic space group I2/m. Two thiosemicarbazide ligands coordinated via the sulfur atom in monodentate mode to the gold(I) metal ion. The geometry around the metal center was described as linear, however, a small distortion of the angle S(11)−Au−S(21) was detected 176.73(13)° for Au1 and 175.16(9)° for Au2 A likely explanation is that there is an interaction forcing the distortion. With regard to the bond lengths, it was noticed that the sulfur–carbon bond length S(11)−C(11) and S(21)−C(21) showed a small elongation in relation to the free ligands. Still, this bond length retained its double-bond character.
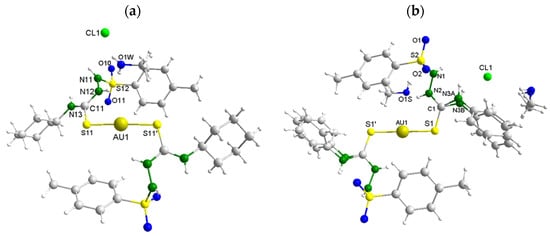
Figure 3.
Molecular structures of the Au1∙MeOH (a) and Au2∙MeOH (b) complexes. The MeOH molecules and NH-Ph group of Au2∙MeOH are disordered at two positions.

Table 3.
Selected bond lengths (Å) and angles (°) in the [Au(HL1Ch)2]Cl∙MeOH (Au1∙MeOH) and [Au(HL2Ph)2]Cl∙MeOH (Au2∙MeOH) complexes.
In the crystal lattice of the Au1 and Au2 complexes, hydrogen bonds involving N–H∙∙∙Cl, N–H∙∙∙O, O–H∙∙∙Cl and N–H∙∙∙O interactions can be found. For the Au1 complex (Figure 4), the interactions involved the nitrogen atoms N(11) and N(12) as hydrogen donors to the chloride Cl(1) and oxygen O(1W) atoms, respectively, in addition to the nitrogen atom N(13) as a hydrogen donor to the oxygen atom O(10) from a neighboring unit, and the oxygen atom O(1W) as hydrogen donor to the nitrogen atom N(12) of a second neighboring unit. For the Au2 complex (Figure S4.6), the interactions involved the nitrogen atom N(2) as a hydrogen donor to the oxygen atom O(1S), the nitrogen N(1) and oxygen O(1S) atoms with the chloride ion Cl(1), and the nitrogen N(3A) and N(3B) atoms as hydrogen donors to the oxygen atom O(1).
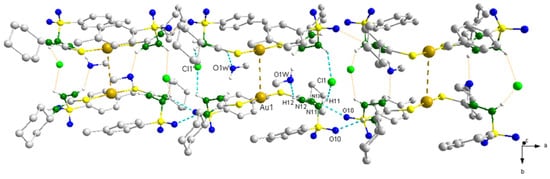
Figure 4.
Hydrogen bonds involved in the crystal structure of the Au1 complex. [N(13)···O(10) = 3.096(6) Å, N(13)-H(13)···O(10) = 157.4 °] and [O(1W)···N(12) = 2.889(6) Å, O(1W)-H(1W)···N(12) = 144.3°]. [N(11)···Cl(1) = 3.213(4) Å, N(11)-H(11)···Cl(1)= 113.4°] and [N(12)···O(1W) = 2.889(6) Å, N(12)-H(12)···O(1W) = 136.8°]. Symmetry operations used (′) −x, y, −z+1; (″) −x + 1, y, −z + 1; (‴) x, −y, z.
In addition to the hydrogen bonds, intermolecular interactions involving two Au(I) metal ions from different molecules were identified (see Figure 4). In the literature, many gold(I) complexes that present such type of interaction can be found [63,64]. According to the literature, the term “aurophilic interaction” was coined for this type of interaction, due to the high binding energy between Au∙∙∙Au ions, which resembles the energy found in intermolecular hydrogen bonds as well as to the low coordination number found for linear Au(I) complexes, which allows an opening in the coordination sphere of the metal ion for the approximation of another Au(I) metal ion [64]. Since there is no steric hindrance, the metal centers of different molecules were attracted by a distance equal to 3.8244(6) Å for Au1 and 3.5268(6) Å for Au2, being in accordance with the expected distance for a weak Au∙∙∙Au intermolecular interaction (between 3.50–3.80 Å) [64].
3.3. Photophysical Studies
The electronic spectra of the Ag3–Ag6 and Au1–A6 complexes were obtained from freshly prepared solutions in acetonitrile or methanol (Supplementary Materials, Part 5). The electronic spectra data can be found in Tables S2–S6 and in the experimental part. Two absorption bands with maximum of absorption around 230 and 260 nm were observed for the Ag3, Ag4, Ag6, Au1–Au4 and Au6 complexes, while the Ag5 and Au5 complexes presented three absorption bands around 220, 270 and 350 nm. There were no significant changes in the bands observed in relation to HL1-6 free ligands; however, the molar absorptivities registered were different after complexation. The first band observed in the spectra can be attributed to π→π* intraligand transitions, while the second band, according to theoretical calculations obtained for similar silver(I) complexes [22], is characteristic of charge transfer transitions MLTC (metal-to-ligand charge transfer), due to the electronic configurations of Ag(I) and Au(I).
The second part of the electronic studies was to obtain the fluorescence emission spectra of the Au1 and Au2 complexes (Figure S5.5). The measurement at room temperature of the complexes was performed in methanol solutions with and without the Ar atmosphere; however, no apparent change was verified for the two complexes in the different conditions, indicating that the Au1 and Au2 complexes do not show luminescence at room temperature. Then, the measurement of emission spectra at low temperature (Figure S5.6) was carried out, which showed bands with emission maxima at a relatively high intensity around 400 nm. As the non-radiative decay of the excited state was strongly suppressed, the luminescence of lower excited states could be detected. The characteristic of the extended bands observed is typical of MLTC emissions [65,66].
3.4. DFT Calculations
Aiming to better understand the properties of the compounds, theoretical calculations (DFT) were performed for the monomers of the AgI and AuI complexes. The following parameters were verified: the υ(C=S) band region, bond lengths and angles, the energy gap and composition of the orbitals (HOMO-LUMO) participating in the transitions that occurred from the state fundamental for the excited state of the complexes, as well as the AIM (Atoms in Molecules) data obtained by the optimized structures of the complexes.
Two different basis sets were used since gold and silver are classic examples of the importance of relativistic effects, as the difference between them is mainly due to these effects. Despite the use of an effective core potential to recover some of the relativistic effects for an element like gold, the use of a Hamiltonian with the inclusion of relativistic effects results in a better description of its properties [67,68,69,70]. In addition, in the case of the silver complexes the basis set def2-TZVP was used only for Ag and S, while def2-SVP was used for remaining atoms. The description of the metal with basis set functions of a triple-zeta character is important for a better description of its coordination chemistry, with several bonds being made. On the other hand, there are studies in the literature showing that the use of double-zeta character basis functions is sufficient for a good description of the ligands, in addition to resulting in a lower computational cost [71].
After optimizing the structures, the vibrational spectra were obtained. It was analyzed whether the assignment of the υ(C=S) band obtained by the experimental spectra of the AuI complexes was in accord with that expected by the theorical calculations. The attributions can be seen in Table S7. The frequencies presented in the table were not scaled in relation to the experimental spectra. There is no “pure” vibrational mode only for the υ(C=S) stretch, but conjugated modes as assigned in the table. According to theoretical data and experimental spectra, it is suggested that the stretching was within the expected region (730–800 cm−1), but with a variation between each complex. Then, from the optimized structures of the AgI and AuI complexes (Figures S6.1 and S6.2) the theoretical bond lengths and angles were obtained (Tables S8 and S9). For the Au1 and Au2 complexes, determined experimentally by X-ray diffraction and discussed earlier, the Au-S bond lengths and S-Au-S angle were consistent with the calculated values for both complexes.
The HOMO-LUMO orbitals of the AuI and AgI complexes (Figures S6.3 and S6.4, respectively), as well as the energy gap between the orbitals (Table 4) were also calculated. It was observed that in the AuI and AgI complexes with the HL1Ch and HL6Al ligands, the transition occurs from the HOMO orbital, with predominant composition in the C=S and N-H bonds, to the LUMO orbital, with the majority composition of the p-toluene group. On the other hand, the complexes derived from the HL2Ph, HL3FPh and HL4ClPh ligands, the peripheral groups compose the HOMO orbital, while the LUMO orbital remains primarily in the p-toluene group. In the case of the complexes with the HL5NO2Ph ligand, the nitrophenyl group participates in both the HOMO and LUMO orbitals.

Table 4.
The energy gap of the AgI and AuI complexes.
Regarding the energy gaps (between HOMO and LUMO) of the complexes, it was observed that the energies follow the same order of explanation of the orbitals. In descending order, the highest gap values were found for AgI and AuI complexes with HL1Ch and HL6Al ligands. Then, the values of the AgI and AuI complexes with the HL2Ph, HL3FPh and HL4ClPh ligands were found, and finally, the lowest values were observed for the AgI (Ag5) and AuI (Au5) complexes with the HL5NO2Ph ligand. The different energy gaps can be attributed to the different substituent groups of the ligands in the complexes, and therefore, the lowest gap energy value was found with the complexes that have the nitrate substituent group in the ligand, since it comes to a group more puller of electron density.
Finally, the AIM (Atoms in Molecules) data of the AuI complexes (Figure S6.5 and Table S10) were also obtained that comprise: the Bader charge (q), the delocalization index (DI), the electronic density at the relevant binding critical point (ρ), and the Laplacian of the density at this point (∇2ρ). The DI values are very indicative to say that each bond really has the characteristic of a single covalent bond.
The electron densities vary fairly between compounds due to the nature of each ligand, but the influence is relatively small on atoms on the coordination sphere of gold(I). With regard to the Bader charges, they evaluate the charges of metal ions and coordinated sulfur atoms. As expected, and according to the change in substituent on the ligands in each AuI complex, the charges show a small change from one complex to the other. The most positive charges were found for the Au5 complex (q = AuI: +0.1255, S3: +0.1277 and S4: +0.1269) with the HL5NO2Ph ligand, while the least positive charges were found for the complexes Au1 (q = AuI: +0.1028, S3: +0.0588 and S4: +0.0589) and Au6 (q = AuI: +0.1078, S3: +0.0610 and S4: +0.0606) with the HL1Ch and HL6Al ligands, respectively. It is noticed that the sulfur atoms suffer a much more significant decrease in the charge than the charges of the metal ions. In addition, the Bader charges follow an opposite trend in relation to the energy gaps of the orbitals. For the Au5 complex, a smaller energy gap and a more positive Bader charge was determined, while for the Au1 and Au6 complexes, a larger energy gap and a less positive Bader charge were calculated.
3.5. Biological Studies
3.5.1. Cytotoxicity on Vero Cells
Based on the interest in developing new drugs for Leishmaniasis, biological studies were initiated by carrying out in vitro tests to evaluate the cell viability (cytotoxicity) of free ligands (HL1-6) and Ag3–Ag4 and Au1–Au6 complexes against kidney cells of the African green monkey (Vero). In addition to these compounds, the [Ag(HL1Ch)2]NO3 (Ag1) and [Ag(HL2Ph)2]NO3 (Ag2) complexes, obtained in a previous work, were included in the test [22]. Through this test, it was possible to determine the CC50 values (inhibitory concentration for the viability of 50% of the cells). The higher the inhibitory concentration the greater the viability of the compound against the Vero cells. The CC50 values can be found in Table 5 and the graphs of viability in function of the concentrations are found in Figure S7.1. Analyzing the graphs obtained for all compounds, it was observed that the free ligands present good cytotoxicity indexes (between 200–300 μM), with the exception of the HL4ClPh and HL5NO2Ph ligands. Among the complexes tested, four silver(I) complexes, Ag3–Ag6, showed CC50 values close to or above 500 μM, while only one gold complex, [Au(HL2Ph)2]Cl (Au2), showed good cytotoxicity (295.6 µM). The Au2 complex was less toxic than its free ligand HL2Ph, while the Ag3–Ag6 complexes showed significantly better toxicities than their respective free ligands. For the other complexes, it was observed in general that the complexes presented a higher cytotoxicity than the free ligands.
3.5.2. Tests against Leishmania infantum and Leishmania braziliensis Parasites
The leishmanicidal activity of the compounds was evaluated against the promastigote form of L. infantum and L. braziliensis. Glucantime was used as reference drug. Figures S7.2 and S7.3 show the graphs referring to the results of the leishmanicidal activity versus tested concentrations of the compounds. The IC50 values can be seen in Table 5.
For the L. braziliensis, it was observed that the HL1Ch, HL4ClPh and HL5NO2Ph showed better activity than the reference drug (176.3–191.7 μM), and the HL5NO2Ph presented an excellent result with an IC50 value equal to 19.02 µM. Three silver(I) complexes Ag1, Ag4 and Ag5 were more active for this strain than reference drug, with Ag1 the most active among them (IC50 equal to 50.15 μM). Following the same trend, the gold(I) complex with the HL1Ch ligand, Au1, showed the best activity (IC50 = 77.38 μM).
For the L. infantum strain, it was possible to verify that the free ligands HL1Ch (11 μM) and HL2Ph (48.39 μM) presented the best activities when compared to the activity of Glucantime (113.2–130.2 μM). All Ag(I) complexes, with the exception of Ag2, showed a good activity, highlighting the Ag1 (57.42 μM) and Ag4 (72.17 μM) complexes. Regarding the Au(I) complexes, Au2, Au4 and Au6, with values of IC50 of 41.69, 38.18 and 62.54 µM, respectively, showed the most promising results. A similar activity was found for other antileishmanial compounds like primaquine (26.5 ± 1.2 μM), miltefosine (14.4 ± 1.1 μM), and [AuCl(PEt3)] (16.59 ± 1.03 μM) and auranofin (9.68 ± 1.02 μM), though conditions and methods vary [29,72].
The obtained data indicate that the peripheral groups of the ligands can influence the biological activity of the complexes, presenting different results from each other. Furthermore, the biological performance of the compounds is different between the two tested strains. A similar behavior was found for gold(I) complexes containing N-heterocyclic carbenes with L. amazonensis and L. braziliensis [73]. It is well-known that the properties of bioactive organic compounds are influenced by metal coordination. In most cases, an increased activity of the complexes is observed, which is assumed to be a modulation of pharmacokinetic parameters caused by a metal-assisted transport, while the complex dissociation inside the cell releases the ligands as the biologically active species [28].
In order to have a better toxicity response against the parasites, the IC50 should be as low as possible, while to have a better cytotoxicity response, the CC50 should be as high as possible. The ratio between the CC50 and IC50 values expresses the selectivity index (SI) of the compounds and indicates which of these are promising for the development of future drugs. Table 5 presents the IC50, CC50 and SI values of the compounds.

Table 5.
Values of CC50 (µM) on Vero cells, IC50 (µM) against the promastigote form of the L. braziliensis and L. infantum, and selectivity indexes (SI) obtained for the compounds.
Table 5.
Values of CC50 (µM) on Vero cells, IC50 (µM) against the promastigote form of the L. braziliensis and L. infantum, and selectivity indexes (SI) obtained for the compounds.
| Compound | CC50 (µM) | IC50 (µM) L. braziliensis | IC50 (µM) L. infantum | SI L. infantum | SI L. braziliensis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HL1Ch | 293.0 | 128.9 ± 0.051 | 11 ± 0.306 | 26.64 | 2.27 |
| HL2Ph | 268.0 | 273.5 ± 0.018 | 48.39 ± 0.189 | 5.54 | 0.98 |
| HL3FPh | 291.8 | 204.5 ± 0.018 | 201.2 ± 0.052 | 1.450 | 1.43 |
| HL4ClPh | 16.80 | 133.8 ± 0.036 | 108.4 ± 0.104 | 0.16 | 0.13 |
| HL5NO2Ph | 26.62 | 19.02 ± 0.012 | 286.9 ± 0.075 | 0.09 | 1.40 |
| HL6Al | 187.9 | 313.5 ± 0.063 | 812.8 ± 0.515 | 0.23 | 0.60 |
| Ag1 | 7.400 | 50.15 ± 0.020 | 57.42 ± 0.028 | 0.129 | 0.15 |
| Ag2 | 92.14 | 183.7 ± 0.027 | 280.5 ± 0.167 | 0.33 | 0.50 |
| Ag3 | >500 | 233.9 ± 0.031 | 92.83 ± 0.072 | >5.39 | >2.14 |
| Ag4 | >500 | 84.62 ± 0.116 | 72.17 ± 0.036 | >6.93 | >5.91 |
| Ag5 | 493.3 | 90.73 ± 0.236 | 78.79 ± 0.091 | 6.26 | 5.44 |
| Ag6 | >500 | 305.2 ± 0.032 | 78.59 ± 0.605 | >6.36 | >1.64 |
| Au1 | 19.94 | 77.38 ± 0.018 | 105.1 ± 3.139 | 0.19 | 0.26 |
| Au2 | 295.6 | 143.2 ± 0.085 | 41.69 ± 0.210 | 7.09 | 2.06 |
| Au3 | 28.77 | 194.9 ± 0.063 | 173.9 ± 0.087 | 0.17 | 0.15 |
| Au4 | 31.98 | 277.6 ± 0.163 | 38.18 ± 0.158 | 0.84 | 0.12 |
| Au5 | 58.59 | 284.0 ± 0.259 | 295.5 ± 0.259 | 0.198 | 0.21 |
| Au6 | 77.52 | 5554 ± 1.371 | 62.54 ± 0.151 | 1.24 | 0.01 |
| Glucantime | 1634 [74] | 176.3–191.7 | 113.2–130.2 | 14.43–12.55 | 9.26–8.52 |
Five compounds presented good SI values (HL1Ch = 26.6, HL2Ph = 5.5, Ag3 ≥ 5.39, Ag4 ≥ 6.93, Ag5 ≥ 6.36 and Au2 = 7.09) for the L. infantum promastigotes. Compared to the SI of Glucantime, the most promising result was for the HL1Ch. The Ag(I) complexes were in general more selective than the Au(I) complexes, with Au2 being the only one with a significant SI. In relation to the L. braziliensis promastigotes, only two compounds showed good SI values (Ag4 = >5.91 and Ag5 = 5.44). This result is comparable to that of amphotericin B, whose SI is 6.8 considering the activity against the same leishmania species and the cytotoxicity on macrophages [73]. On the other hand, the ligands did not display a good selectivity for L. braziliensis. Following the same trend of the tests against L. infantum, the silver(I) complexes were the most selective for this parasite. Generally, silver complexes display lower selectivity towards cancer cells compared to Au(I) complexes, as they present an increased lability resulting in a faster release of Ag+ ions; however, any assumption at this stage would be mere speculation [75,76].
In view of the data obtained, the six most promising compounds (HL1Ch, HL2Ph, Ag3, Ag4, Ag6 and Au2) were selected for carrying out the infection rate test against the L. infantum parasite. For this test, the L. infantum parasites and the compound to be evaluated in concentrations based on the IC50 values (the obtained value, one value below and one above) were plated with the Vero cells. This test was performed at four stages. The first step determined the percentage of the amount in 200 infected macrophages per parasite, the second determined the percentage of parasites that infects 100 cells/macrophages, the third determined the average percentage of parasites that infects 200 cells/macrophages and, finally, the fourth step indicated the infection rate, that is, the result of the amount of Leishmania per macrophage (obtained from the third step) multiplied by the percentage of infected macrophages. Figure 5 presents the graphs of the infection rates, while the other graphs can be found in Figure S7.4. From these graphs, it was observed that all compounds inhibited the parasite infection at the three concentrations (IC50<, IC50 and >IC50). The compound HL1Ch, in addition to inhibiting the infection, considerably lowered the infection rate of the parasite even at a concentration below its IC50. For HL2Ph, the infection index was not relevant for a concentration below its IC50. Regarding the complexes, Ag4 did not show a promising infection rate, while the Ag3, Ag6 and Au2 complexes were able to inhibit the parasite infection inside the cells even at lower concentrations than that determined by their IC50 values.
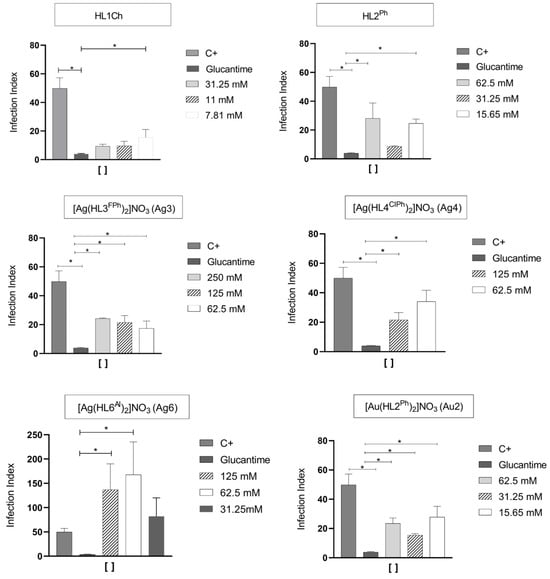
Figure 5.
Infection rate of selected compounds compared to Glucantime. Statistical analysis was conducted using the Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunn’s post-test, where * indicates significant differences, with a p-value < 0.05.
3.6. Enzymatic Studies
After the synthesis and structural characterization of the compounds, studies of interaction of the compounds and the recombinant LbOYE were carried out by fluorescence measurements. Initially, the solubility in buffer at the appropriate concentrations for carrying out the fluorescence experiments was evaluated; therefore, only the compounds that passed this stage were selected, them being HL1Ch, HL3FPh, HL5NO2Ph, Ag3 and Au1.
The fluorescence emission was obtained at increasing concentrations of HL1Ch, HL3FPh and HL5NO2Ph, which caused a decrease in the fluorescence emission intensity for all studied ligands. The quenching caused by the presence of the compound HL5NO2Ph (Figure S7.6) was more pronounced than when compared to HL1Ch and HL3FPh (Figure S7.7). This difference indicates a lower affinity of the LbOYE for the HL1Ch and HL3FPh.In this way, it was possible to adjust the Hill equation for the determination of Kd only for the ligand HL5NO2Ph. The Stern–Volmer relationship states that the kinetic study of the photophysical deactivation of the fluorophore can be performed. The nature of this deactivation can be static or dynamic [58,77]. The static deactivation occurs when the interaction results in the formation of the protein–compound complex, which is reflected in the decrease in fluorescence intensities. The fluorescence quenching can also result from deactivation by collision between molecules, which is called dynamic quenching, which is also favored by the increase in temperature [58]. In addition, the latter can occur together with static suppression when in the presence of high concentrations of the compound [58].
Figure 6 shows the results of the interaction between Ag3 and the LbOYE protein. The Ag3 complex showed interaction with Kd in the µM order and the Hill curve reaches its saturation which causes an increase in molecules in solution that do not interact with the protein, leading to a deviation from linearity in the Stern–Volmer graph and an increase in dynamic processes. Au1 shows interaction with the LbOYE enzyme as exposed in Figure S7.8. The temperature variation showed a slight increase in the suppression for higher concentrations where the sum of static and dynamic effects can be observed.
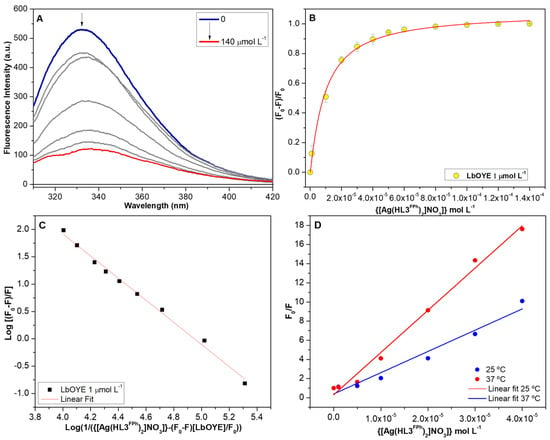
Figure 6.
(A) Fluorescence emission spectra (λex = 295 nm) of LbOYE protein in the concentration of 1 µmol L−1 in the presence of increasing concentrations of the [Ag(HL3FPh)2]NO3 (Ag3) complex. (B) Variation of maximum fluorescence intensities (λmax = 333 nm) and non-linear fit to the Hill equation (Equation (1)). (C) Logarithmic relationship to obtain the number of bonding sites according to Equation (2). (D) Comparison between the temperatures of 25 °C and 37 °C. The spectra were obtained in Tris-HCl buffer, pH 8.0; 100 mmol L−1 of NaCl and 2.5 % of DMSO.
The data obtained by the mathematical treatments applied to the experimental data (Table 6) demonstrate that, among the organic compounds, HL5NO2Ph presented the highest affinity. Among the complexes, Ag3 showed the highest affinity, although its ligand HL3FPh showed low affinity for the LbOYE protein. The same effect was observed for Au1, which showed an increase in the affinity in relation to the HL1Ch ligand.

Table 6.
Dissociation constant (Kd), number of bonding sites (n), association constant (Kb), Stern–Volmer constant (Ksv) for the interaction of the LbOYE enzyme with the HL1Ch, HL3FPh and HL5NO2Ph ligands, and their [Au(HL1Ch)2]Cl (Au1) and [Ag(HL3FPh)2]NO3 (Ag3) complex. Data for 25 °C.
After studying the interaction with the enzyme, the influence of the presence of the Au1 and Ag3 complexes on the LbOYE enzymatic activity was determined using two substrates, O2 and the N-Ethymaleimide (NEM). As a control, their HL1Ch and HL3FPh ligands were also tested.
The inhibition effect can be identified by the decrease in the initial velocity V0, which is obtained by the decay of the NADPH reducing band at 340 nm. Figure 7 evidences that the Ag3 was capable of inhibiting the reaction of the enzyme both with the NEM and for O2. The Au1 also demonstrates capacity of inhibition, although less than the Ag3. The respective free ligands did not influence the reaction velocity with the NADPH.
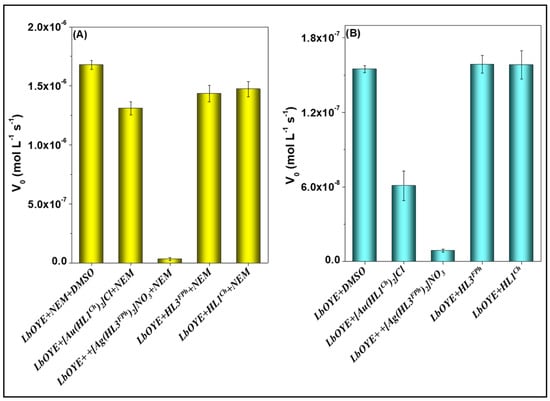
Figure 7.
Initial velocity (V0) for the reaction between 1 µmol L−1 of LbOYE and 100 µmol L−1 of NADPH in the presence of DMSO (control) or 20 µmol L−1 of the compounds tested. Using (A) 100 µmol L−1 of NEM in the presence of O2 and (B) absence of NEM in the presence of O2. Experiments carried out in phosphate buffer 25 mmol L−1 pH 7.0, NaCl 100 mmol L−1.
3.7. Molecular Docking Studies
With the purpose of finding new bioactive agents and providing a possible mechanism of action for the compounds described in this work, a Docking analysis with the OLD Yellow enzyme of the Leishmania braziliensis was performed. The enzyme used was based on the OLD Yellow protein from the protozoan Trypanosoma cruzi as they have the same structure, and can be found in the database registered under code PDB 4E2D [52]. The Old Yellow enzyme has a prosthetic group called Flavin Mononucleotide, known by its acronym FMN. In order to exert the activity of the enzyme, it is necessary for the FMN to pass from its oxidized form to the reduced form. For this, FMN uses as a cofactor NADPH, which reduces it to FMNH2 through electron transfer [21]. Our assumption is that the metal complex can target this enzyme by preventing this process to happen, capturing electrons from FMN or NADPH.
The purpose of the molecular docking performed was to identify the most favorable conformation of each compound (ligand) in the active site of the enzyme as well as the residues participating in the interactions, and thus determine the receptor–compound bond energies (score) [78,79]. In addition to comparing the activity between the silver(I) and gold(I) ions of the analogous complexes, the alteration of the peripheral groups of the ligands is also a factor that can influence the interaction between the molecule and the enzyme. In this way, representative figures of each molecule at the site of the LbOYE were obtained (Figure 8 and Figures S8.1–S8.15).
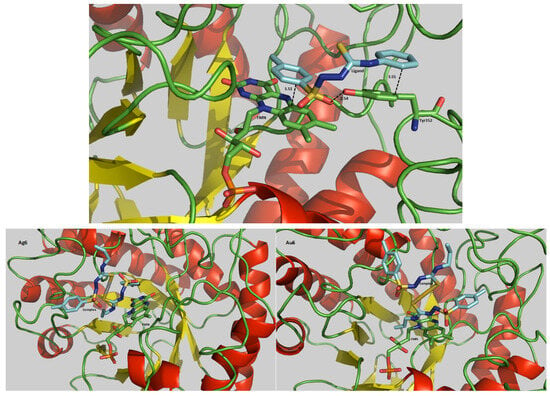
Figure 8.
Representative figure of the HL2Ph ligand (upper), [Ag(HL6Al)2]NO3 (Ag6) complex (bottom left) and [Au(HL6Al)2]Cl (Au6) complex (bottom right) at the site of the OLD Yellow enzyme of Leishmania braziliensis.
It was observed that some compounds are docked close to amino acid residues responsible for the enzyme–substrate interaction. All free ligands, the silver(I) complexes Ag1 and Ag2, and the gold complex Au3 were found next to the Tyr352 residue. The Ag1 complex is also close to residues Phe279 and Asp134, and the Ag2 complex close to the residue Thr32. In addition, it was observed that Ag4 and Au2 interact with the His135 and with Ser244 residues, respectively, while the other complexes did not interact with any residue. Thus, it was shown that the interaction does not depend only on the metal, but on the structure as a whole. Furthermore, the complexes fit into the space within the active site of the enzyme, almost parallel to the FMN structure. This indicates that they are in a suitable position to block the process of electron transfer from NADPH to FMN. It was verified that the HL1Ch and HL2Ph, Ag4 and Au4 were the closest to the FMN.
The energy corresponding to the interaction between the enzyme and the substrate is called bond energy [80]. From the most energetically favorable conformations within the site, the scoring values of the compounds (Table 7) were obtained. A lower bond energy (scoring) means a better interaction of the molecule with the enzyme. Thus, the compounds that energetically showed better interactions were HL6Al and its respective silver and gold complexes, Ag6 and Au6. Furthermore, the highest energy gap values (Table 4) were also found for the Ag6 and Au6 complexes. The energy gap obtained by DFT calculations determines the ability that a compound to donate or receive electrons [81]. If the difference is large, it is in principle a more stable complex in relation to the oxidation process. Thus, it is suggestive that these complexes are good at disrupting the electron transfer from the FMN group to the NADPH. However, there are cases in which the compound can only inhibit the protein by blocking the active site and still not participate in the electron transfer process with the FMN prosthetic group [80].

Table 7.
Free ligands, silver(I) and gold(I) complexes bond energies score with LbOYE.
4. Conclusions
Metal complexes of composition [M(HLR)2]X (M = Ag or Au; X = NO3− or Cl−) were successfully synthesized and characterized by different techniques, including the crystallographic determination of the Au1 and Au2 complexes and DFT calculations, which allowed us to not only confirm the structures of the molecules but also to understand their electronic properties.
The compounds were evaluated in vitro on Vero cells (Vero) in order to determine their cytotoxicity and against two Leishmaniasis strains, Leishmania infantum and Leishmania braziliensis. The activity tests showed a different behavior of the compounds against the two strains showing a dependence on both the metal center and peripheral groups of the ligands. The cytotoxicity tests showed that, in general, the gold(I) complexes are more toxic than the free ligands and silver(I) complexes. Overall, some compounds displayed good selectivity indexes for both strains. The infection rate of Leishmania infantum determined for the Ag3, Ag6 and Au2 complexes showed that all of them are able to inhibit the parasite infection even at lower concentrations than that of their IC50 values.
The enzymatic studies showed that the compounds have affinity with the target Old Yellow Enzyme from Leishmania braziliensis. Among the evaluated organic compounds, HL5NO2Ph showed the best interaction with the protein. The complexes [Ag(HL3FPh)2]NO3 (Ag3) and [Au(HL1Ch)2]Cl (Au1) showed a relatively higher affinity for the LbOYE protein when compared to free ligands, with the AgI complex having the best interaction. The enzymatic tests showed that the complex Ag3 was also the one that best inhibited the reaction responsible for the enzyme activity. Furthermore, the docking analysis showed that changing the peripheral groups of the ligands affects the interactions at the Old Yellow enzyme active site of L. braziliensis. The compound HL6Al and its complexes of AgI and AuI, Ag6 and Au6, presented the lowest score values and, consequently, the best interactions with the target enzyme, consistent with the highest energy gap values obtained for them, which indicates that these complexes are more suitable for preventing the electron transfer from the NADPH to FMN group. However, because they are not soluble in the buffer used for the experiment, it was not possible to carry out the test experimentally. Altogether, with the present data it is possible to say that the class of compounds studied here may be considered as a platform for the development of a new agent for Leishmaniasis treatment, particularly considering the Leishmania infantum species.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/pharmaceutics16040452/s1, Table S1: Selected absorption bands in the infrared region for free ligands and complexes; Table S2: Electronic spectra data obtained for the Ag3 and Ag4 complexes; Table S3: Electronic spectra data obtained for the Ag5 and Ag6 complexes; Table S4: Electronic spectra data obtained for the Au1 and Au2 complexes; Table S5: Electronic spectra data obtained for the Au3 and Au4 complexes; Table S6: Electronic spectra data obtained for the Au5 and Au6 complexes; Table S7. Basis set functions scheme used for the gold complexes; Table S8: Vibrational modes and their theoretical assignments related to the C=S bond; Table S9: Main theoretical structural data of the silver complexes; Table S10: Main theoretical structural data of the gold complexes; Table S11: Electronic properties of the gold(I) complexes. The values are shown, respectively, for each bond in the order they appear; Figure S1.1: IR (ATR) spectrum of HL3FPh; Figure S1.2: IR (ATR) spectrum of HL4ClPh; Figure S1.3: IR (ATR) spectrum of HL5NO2Ph; Figure S1.4: IR (ATR) spectrum of HL6Al; Figure S1.5: IR (ATR) spectrum of [Ag(HL3FPh)2]NO3 (Ag3); Figure S1.6: IR (ATR) spectrum of [Ag(HL4ClPh)2]NO3 (Ag4); Figure S1.7: IR (ATR) spectrum of [Ag(HL5NO2Ph)2]NO3 (Ag5); Figure S1.8: IR (ATR) spectrum of [Ag(HL6Al)2]NO3 (Ag6); Figure S1.9: IR (ATR) spectrum of [Au(HL1Ch)2]Cl (Au1); Figure S1.10: IR (ATR) spectrum of [Au(HL2Ph)2]Cl (Au2); Figure S1.11: IR (ATR) spectrum of [Au(HL3FPh)2]Cl (Au3); Figure S1.12: IR (ATR) spectrum of [Au(HL4ClPh)2]Cl (Au4); Figure S1.13: IR (ATR) spectrum of [Au(HL5NO2Ph)2]Cl (Au5); Figure S1.14: IR (ATR) spectrum of [Au(HL6Al)2]Cl (Au6); Table S1: Selected absorption bands in the infrared region for free ligands and complexes; Figure S2.1: 1H NMR spectrum of HL3FPh in DMSO-d6; Figure S2.2: 1H NMR spectrum of HL4ClPh in DMSO-d6; Figure S2.3: 1H NMR spectrum of HL5NO2Ph in DMSO-d6; Figure S2.4: 1H NMR spectrum of HL6Al in DMSO-d6; Figure S2.5: 19F NMR spectrum (377 MHz) of HL3FPh in DMSO-d6; Figure S2.6: 1H NMR spectrum of [Ag(HL3FPh)2]NO3 (Ag3) in DMSO-d6; Figure S2.7: 1H NMR spectrum of [Ag(HL4ClPh)2]NO3 (Ag4) in DMSO-d6; Figure S2.8: 1H NMR spectrum of [Ag(HL5NO2Ph)2]NO3 (Ag5) in DMSO-d6; Figure S2.9: 1H NMR spectrum of [Ag(HL6Al)2]NO3 (Ag6) in DMSO-d6; Figure S2.10: 1H NMR spectrum of [Au(HL1Ch)2]Cl (Au1) in DMSO-d6; Figure S2.11: 1H NMR spectrum of [Au(HL2Ph)2]Cl (Au2) in DMSO-d6; Figure S2.12: 1H NMR spectrum of [Au(HL3FPh)2]Cl (Au3) in DMSO-d6; Figure S2.13: 1H NMR spectrum of [Au(HL4ClPh)2]Cl (Au4) in DMSO-d6 Figure S2.14: 1H NMR spectrum of [Au(HL5NO2Ph)2]Cl(Au5) in DMSO-d6; Figure S2.15: 1H NMR spectrum of [Au(HL6Al)2]Cl (Au6) in DMSO-d6; Figure S2.16: 19F NMR spectrum (377 MHz) of [Ag(HL3FPh)2]NO3 (Ag3) in DMSO-d6; Figure S2.17: 19F NMR spectrum (377 MHz) of [Au(HL3FPh)2]Cl (Au3) in DMSO-d6; Figure S3.1: ESI(+) MS spectrum of [Ag(HL3FPh)2]NO3 (Ag3); Figure S3.2: ESI(+) MS spectrum of [Au(HL1Ch)2]Cl (Au1); Figure S3.3: ESI(+) MS spectrum of [Au(HL2Ph)2]Cl (Au2); Figure S3.4: ESI(+) MS spectrum of [Au(HL3FPh)2]Cl (Au3); Figure S3.5: ESI(+) MS spectrum of [Au(HL4ClPh)2]Cl (Au4); Figure S3.6: ESI(+) MS spectrum of [Au(HL6Al)2]Cl (Au6); Figure S4.1: Hydrogen bonds involved in the crystalline structure of the HL3FPh ligand. Intermolecular hydrogen bonds: [N(1)···O(1) = 2.910(3) Å, N(1)-H(1)···O(1) = 115.4°], [N(2)···S(1) = 3.311(2) Å, N(2)-H(2)···S(1) = 160.8°], [N(1)···O(2) = 3.420(3) Å, N(1)-H(1)···O(2) = 98.1°], [N(3)···O(2) = 2.959(2) Å, N(3)-H(3)···O(2) = 147.7°]. Intramolecular hydrogen bonding: [N(3)···N(1) = 2.659(3) Å, N(3)-H(3)···N(1) = 110.3°]. Used symmetry operations (′) x − 1, y, z, (″) −x, −y + 1, −z + 1 and (‴) −x, −y + 2, −z + 1. Red dotted lines (between donor and acceptor atoms) represent hydrogen bonds; Figure S4.2: Hydrogen bonds involved in the crystalline structure of the HL5NO2Ph ligand. Intermolecular hydrogen bonds: [N(1)···O(1′) = 2.887(4) Å, N(1)-H(1)···O(1′)= 117.4°], [N(2)···S(1″) = 3.347(3) Å, N(2)-H(2)···S(1″) = 165.2°], [N(3) ···O(2‴) = 3.040(4) Å, N(3)-H(3)···O(2‴) = 151.8 °]. Used symmetry operations (′) x − 1, y, z, (″) −x, −y + 1, −z + 1 and (‴) −x, −y, −z + 1. Blue dotted lines (between donor and acceptor atoms) represent; Figure S4.3: Hydrogen bonds involved in the crystalline structure of the HL6Al ligand. Intermolecular hydrogen bonds: [N(3)···O(2) = 3.024(3) Å, N(3)-H(3)···O(2) = 129.0°], [N(2)···S(1) = 3.3475(18) Å, N(2)-H(2)···S(1) = 159.0°], [N(1)···S(1) = 3.356(2) Å, N(1)-H(1)···S(1) = 118.4°]. Used symmetry operations (′) −x, −y, −z + 1, (″) −x + 1, −y + 1, −z + 1 and (‴) x − 1, y, z. Blue dotted lines (between donor and acceptor atoms) represent hydrogen bonds; Figure S4.4 Ellipsoid representation of [Au(HL1Ch)2]Cl∙CH3OH (Au1∙CH3OH). The hydrogen atoms have been omitted for clarity. A solvent mask was calculated and 108 electrons were found in a volume of 518 Å3 in 1 void per unit cell. This is consistent with the presence of 0.5[CH2Cl2; 2H2O] per Asymmetric Unit, which account for 120 electrons per unit cell.; Figure S4.5 Ellipsoid representation of [Au(HL2Ph)2]Cl∙CH3OH (Au2∙CH3OH). The hydrogen atoms have been omitted for clarity; Figure S4.6: Hydrogen bonds involved in the crystalline structure of the Au2 complex. Intermolecular hydrogen bonds: [N(1)···Cl(1) = 3.173(4) Å, N(1)-H(1)···Cl(1) = 113.8°], [O(1S)···Cl(1) = 3.135(5) Å, O(1S)-H(1S)···Cl(1) = 152.4°], [N(3A)···O(1) = 2.775(14) Å, N(3A)-H(3A)···O(1) = 146.1°], [N(3B)···O(1) = 3.149(14) Å, N(3B)-H(3B)···O(1) = 136.9°]. Intramolecular hydrogen bonding: [N(2)···O(1S) = 2.905(5) Å, N(2)-H(2)···O(1S)= 135.6°]. Used symmetry operations (′) −x, +y, −z. Blue dotted lines (between donor and acceptor atoms) represent hydrogen bonds; Figure S5.1: Electronic spectra of Ag3 (green line), Ag4 (orange line), Ag5 (red line) and Ag6 (purple line) in the 210 to 350 nm range (10−6 M CH3CN solution); Figure S5.2: Electronic spectra of Au1 (blue line), Au2 (pink line), Au3 (green line), Au4 (orange line), Au5 (red line) and Au6 (purple line) in the 210 to 350 nm range (10−6 M CH3OH solution for Au1, Au2, Au3, Au6 and 10−6 M solution CH3CN for Au4 and Au5); Figure S5.3: Linear regression for Ag3 (green line), Ag4 (orange line), Ag5 (red line) and Ag6 (purple line); Table S2: Electronic spectra data obtained for the Ag3 and Ag4 complexes; Table S3: Electronic spectra data obtained for the Ag5 and Ag6 complexes; Figure S5.4: Linear regression for Au1 (blue line), Au2 (pink line), Au3 (green line), Au4 (orange line), Au5 (red line) and Au6 (purple line); Table S4: Electronic spectra data obtained for the Au1 and Au2 complexes; Table S5: Electronic spectra data obtained for the Au3 and Au4 complexes; Table S6: Electronic spectra data obtained for the Au5 and Au6 complexes; Figure S5.5: (a) Emission spectra of Au1 (blue line) and Au2 (pink line) in CH3OH at 298 K; λexc = 255 nm for Au1 and 270 nm for Au2; (b) Emission spectra of CH3OH at 298 K; λexc = 250 nm; Figure S5.6: Emission spectra of Au1 (blue dashed line) and Au2 (pink dashed line) in MeOH at 77 K; λexc = 255 nm for Au1 and 270 nm for Au2; Table S7. Basis set functions scheme used for the gold complexes. Table S8: Vibrational modes and their theoretical assignments related to the C=S bond; Figure S6.1: Optimized structures of the silver complexes; Table S9: Main theoretical structural data of the silver complexes; Figure S6.2: Optimized structures of the gold complexes; Table S10: Main theoretical structural data of the gold complexes; Figure S6.3: HOMO and LUMO orbitals in the silver complexes; Figure S6.4—HOMO and LUMO orbitals in the gold complexes; Figure S6.5: Optimized structure of [Au(HL3FPh)2]+ (Au3) with the charges obtained for the AIM data; Table S11: Electronic properties of the gold(I) complexes. The values are shown, respectively, for each bond in the order they appear; Figure S7.1: Graph of the viability versus concentrations (μM) of the compounds; Figure S7.2: Leishmanicidal activity against to the Leishmania infantum parasite by concentrations of the compound. Blue curve represents the reference leishmanicidal drug, Glucantime. Black curve represents each compound; Figure S7.3: Leishmanicidal activity against to the Leishmania braziliensis parasite by concentrations of the compound. Blue curve represents the reference leishmanicidal drug, Glucantime. Black curve represents each compound; Figure S7.4: (a) percentage of the number of infected in 200 macrophages by Leishmania infantum; (b) percentage of leishmaniasis that infect 100 cells/macrophages; (c) average percentage of leishmaniasis that infect 200 cells/macrophages; of the selected compounds; Figure S7.5: Image captures under a fluorescence microscope (EVOS) of Raw macrophages infected by Leishmania infantum after treatment with a Glucantime (leishmanicidal drug) (A) and the selected compounds; Figure S7.6:(A) Fluorescence emission spectra (λex = 295 nm) of LbOYE protein in the concentration of 1 µmol L−1 in the presence of increasing concentrations of the HL1Ch compound. (B) Variation of maximum fluorescence intensities (λmax = 333 nm) and non-linear fit to the Hill equation (Equation (1)). (C) Logarithmic relationship to obtain the number of bonding sites according to Equation (2). (D) Relationship of temperatures of 25 ºC and 37 ºC. The spectra were obtained in Tris-HCl buffer, pH 8.0; 100 mmol L−1 of NaCl and 2.5 % of DMSO; Figure S7.7: (A) Fluorescence emission spectra (λex = 295 nm) of LbOYE protein in the concentration of 1 µmol L−1 in the presence of increasing concentrations of the HL3FPh compound. (B) Variation of maximum fluorescence intensities (λmax = 333 nm) and non-linear fit to the Hill equation (Equation (1)). (C) Logarithmic relationship to obtain the number of bonding sites according to Equation (2). (D) Relationship of temperatures of 25 and 37 °C. The spectra were obtained in Tris-HCl buffer, pH 8.0; 100 mmol L−1 of NaCl and 2.5 % of DMSO; Figure S8.1: Representative figure of the HL1Ch ligand at the site of the LbOYE; Figure S8.2: Representative figure of the HL3FPh ligand at the site of the LbOYE; Figure S8.3: Representative figure of the HL4ClPh ligand at the site of the LbOYE; Figure S8.4: Representative figure of the HL5NO2Ph ligand at the site of the LbOYE; Figure S8.5: Representative figure of the HL6Al ligand at the site of the LbOYE; Figure S8.6: Representative figure of the [Ag(HL1Ch)2]NO3 complex at the site of the LbOYE; Figure S8.7: Representative figure of the [Ag(HL2Ph)2]NO3 complex at the site of LbOYE; Figure S8.8: Representative figure of the [Ag(HL3FPh)2]NO3 complex at the site of the LbOYE; Figure S8.9: Representative figure of the [Ag(HL4ClPh)2]NO3 complex at the site of the LbOYE; Figure S8.10: Representative figure of the [Ag(HL5NO2Ph)2]NO3 complex at the site of the LbOYE; Figure S8.11: Representative figure of the [Au(HL1Ch)2]Cl complex at the site of the LbOYE; Figure S8.12: Representative figure of the [Au(HL2Ph)2]Cl complex at the site of the LbOYE; Figure S8.13: Representative figure of the [Au(HL3FPh)2]Cl complex at the site of the LbOYE; Figure S8.14: Representative figure of the [Au(HL4ClPh)2]Cl complex at the site of the LbOYE; Figure S8.15: Representative figure of the [Au(HL5NO2Ph)2]Cl complex at the site of the LbOYE.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.P.B., M.M.S.O., S.H.L. and P.I.S.M.; methodology, L.A.S.C., V.M.D., U.A., A.O.T.P., M.V.d.S., J.C.B. and P.I.S.M.; validation, M.V.d.S., J.C.B. and P.I.S.M.; formal analysis, A.P.B., M.M.S.O., S.H.L., R.O.T., V.M.D., F.B.F., L.A.S.C., A.O.T.P., M.V.d.S., J.C.B. and P.I.S.M.; investigation, A.P.B., M.M.S.O., S.H.L., R.O.T., V.M.D., F.B.F., L.A.S.C., A.O.T.P. and P.I.S.M.; resources, J.C.B., M.V.d.S., U.A. and P.I.S.M.; data curation, A.P.B., M.M.S.O., S.H.L. and P.I.S.M.; writing—original draft preparation, A.P.B. and P.I.S.M.; writing—review and editing, A.P.B., M.M.S.O., S.H.L., L.A.S.C., A.O.T.P., M.V.d.S. and P.I.S.M.; visualization, P.I.S.M.; supervision, M.V.d.S., J.C.B. and P.I.S.M.; project administration, P.I.S.M.; funding acquisition, P.I.S.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the CNPq: (grants: 309145/2020-1, 408926/2021-0, 310927/2021-8, 310365/2021-0 and 311747/2023-0), FAPESP (grants: 2017/07335-9 and 2018/05576-1), FAPEMIG (grant: APQ-03174-18) and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES). The authors are also thankful to the Cancer Theranostics Innovation Center (CancerThera, funded by FAPESP process 2021/10265-8) and to the Rede Mineira de Materiais Inorgânicos (RM2I), a research group supported by FAPEMIG (RED-00116-23).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data can be requested from authors.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the assistance of the Core Facility BioSupraMol supported by the DFG.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Leishmaniasis. Available online: https://www.who.int/westernpacific/health-topics/leishmaniasis (accessed on 10 December 2022).
- Burza, S.; Croft, S.L.; Boelaert, M. Leishmaniasis. Lancet 2018, 392, 951–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oryan, A.; Akbari, M. Worldwide risk factors in leishmaniasis. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2016, 9, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Postigo, J.A.; Jain, S.; Mikhailov, A.; Maia-Elkhoury, A.N.; Valadas, S.; Warusavithana, S.; Osman, M.; Lin, Z.; Beshah, A.; Yajima, A.; et al. Global leishmaniasis surveillance: 2019–2020, a baseline for the 2030 roadmap. Wkly. Epidemiol. Rec. 2021, 96, 401–419. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Urbanization: An increasing risk factor for leishmaniasis. Wkly. Epidemiol. Rec. 2002, 77, 365–370. [Google Scholar]
- Reguera, R.M.; Morána, M.; Pérez-Pertejo, Y.; García-Estrada, C.; Balana-Fouce, R. Current status on prevention and treatment of canine leishmaniasis. Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 227, 98–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limeira, C.H.; Alves, C.J.; Azevedo, S.S.; Santos, C.S.A.B.; Melo, M.A.; Soares, R.R.; Barnabé, N.N.C.; Rodrigues, G.Q. Clinical aspects and diagnosis of leishmaniasis in equids: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2019, 28, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, D. Leishmaniasis. J. Infect. 2014, 69, S10–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roatt, B.M.; Aguiar-Soares, R.D.; Coura-Vital, W.; Ker, H.G.; Moreira, N.; Vitoriano-Souza, J.; Giunchetti, R.C.; Carneiro, C.M.; Reis, A.B. Immunotherapy and immunochemotherapy in visceral leishmaniasis: Promising treatments for this neglected disease. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keogan, D.M.; Oliveira, S.S.C.; Sangenito, L.S.; Branquinha, M.H.; Jagoo, R.D.; Twamley, B.; Santos, A.L.S.; Griffith, D.M. Novel antimony(III) hydroxamic acid complexes as potential anti-leishmanial agents. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 7245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berenguer, D.; Sosa, L.; Alcover, M.; Sessa, M.; Halbaut, L.; Guillén, C.; Fisa, R.; Calpena-Campmany, A.C.; Riera, C. Development and Characterization of a Semi-Solid Dosage Form of Meglumine Antimoniate for Topical Treatment of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, A.C.; Souza, M.V.N. Current leishmaniasis drug discovery. RSC Med. Chem. 2022, 13, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dammak, K.; Porchia, M.; Franco, M.; Zancato, M.; Naïli, H.; Gandin, V.; Marzano, C. Antiproliferative Homoleptic and Heteroleptic Phosphino Silver(I) Complexes: Effect of Ligand Combination on Their Biological Mechanism of Action. Molecules 2020, 25, 5484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soldera, P.F.; Chagas, A.F.S.; Brasil, A.M.V.; Comandolli-Wyrepkowski, C.D.; Porchia, M.; Pereira, A.M.R.F. In vitro and in vivo Anti-leishmanial Potential of [Ag (PTA)4]BF4 and [Ag(HBPz3)(PPh3)] Silver Complexes. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2022, 55, e0478–e2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tunes, L.G.; Morato, R.E.; Garcia, A.; Schmitz, V.; Steindel, M.; Corrêa-Junior, J.D.; Santos, H.F.; Frézard, F.; Almeida, M.V.; Silva, H.; et al. Preclinical Gold Complexes as Oral Drug Candidates to Treat Leishmaniasis Are Potent Trypanothione Reductase Inhibitors. ACS Infect. Dis. 2020, 6, 1121–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley, R. Different roads to discovery; Prontosil (hence sulfa drugs) and penicillin (hence beta-lactams). J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 36, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scozzafava, A.; Owa, T.; Mastrolorenzo, A.; Supuran, C.T. Antincancer and antiviral sulfonamides. Curr. Med. Chem. 2003, 10, 925–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendieta-Wejebe, J.E.; Rosales-Hernández, M.C.; Padilla-Martínez, I.I.; García-Báez, E.V.; Cruz, A. Design, Synthesis and Biological Activities of (Thio)Urea Benzothiazole Derivatives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carneiro, Z.A.; Lima, J.C.; Lopes, C.D.; Gaspari, A.P.S.; Albuquerque, S.; Dinelli, L.R.; Veloso-Silva, L.L.W.; Paganelli, M.O.; Libardi, S.H.; Oliveria, C.G.; et al. Heterobimetallic nickel(II) and palladium(II) complexes derived from S-benzyl-N-(ferrocenyl)methylenedithiocarbazate: Trypanocidal activity and interaction with Trypanosoma cruzi Old Yellow Enzyme (TcOYE). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 180, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, P.I.S.; Carneiro, Z.A.; Lopes, C.D.; Silva, J.S.; Albuquerque, S.; Hagenbach, A.; Gust, R.; Deflon, V.M.; Abram, U. Organometallic gold(iii) complexes with hybrid SNS-donating thiosemicarbazone ligands: Cytotoxicity and anti-Trypanosoma cruzi activity. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 2559–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.C.R.; Carneiro, Z.A.; Oliveira, C.G.; Danuello, A.; Guerra, W.; Oliveira, R.J.; Ferreira, F.B.; Veloso-Silva, L.L.W.; Batista, F.A.H.; Borges, J.C.; et al. PtII, PdII and AuIII complexes with a thiosemicarbazone derived from diacethylmonooxime: Structural analysis, trypanocidal activity, cytotoxicity and first insight into the antiparasitic mechanism of action. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 141, 615–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, A.P.; Gaspari, A.P.S.; Oliveira, C.G.; Sousa, S.F.; Silva, R.S.; Deflon, V.M.; Machado, A.E.H.; Patrocínio, A.O.T.; Maia, P.I.S. Photophysical and DFT Studies of Cationic Ag(I) Complexes with Thiosemicarbazides Derived from p-Toluenesulfohydrazide. ChemistrySelect 2018, 3, 2108–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karges, J.; Stokes, R.W.; Cohen, S.M. Metal complexes for therapeutic applications. Trends Chem. 2021, 3, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, A.P.; Carneiro, Z.A.; Prado, F.S.; Souza, J.R.; Silva, L.H.F.; Oliveira, C.G.; Deflon, V.M.; Albuquerque, S.; Leite, N.B.; Machado, A.E.H.; et al. Cu(I) complexes with thiosemicarbazides derived from p-toluenesulfohydrazide: Structural, luminescence and biological studies. Polyhedron 2018, 155, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EI-Asmy, A.A.; Babaqi, A.S.; AI-Hubaishi, A.A. Ligational, corrosion inhibition and antimicrobial properties of 4-phenyl-1-benzenesulphonyl-3-thiosemicarbazide. Transit. Met. Chem. 1987, 12, 428–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doering, M.; Uhlig, E.; Undeutsch, B.; Gloe, K.; Muehl, P. Sulfonamide substituted thiono compounds as ligands in copper(II) chelates and as extractants for the late 3d-element ions. ZAAC 1988, 567, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, P.I.S.; Deflon, V.M.; Abram, U. Gold(III) complexes in medicinal chemistry. Future Med. Chem. 2014, 6, 1515–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, M.; Gabbiani, C.; Messori, L.; Gambino, D. Metal-based drugs for malaria, trypanosomiasis and leishmaniasis: Recent achievements and perspectives. Drug Discov. Today 2010, 15, 1070–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilari, A.; Baiocco, P.; Messori, L.; Fiorillo, A.; Boffi, A.; Gramiccia, M.; Muccio, T.; Colotti, G. A gold-containing drug against parasitic polyamine metabolism: The X-ray structure of trypanothione reductase from Leishmania infantum in complex with auranofin reveals a dual mechanism of enzyme inhibition. Amino Acids 2012, 42, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neto, R.L.M.; Moreira, P.O.L.; Sousa, A.M.; Garcia, M.A.N.; Maran, S.R.; Moretti, N.S. Antileishmanial metallodrugs and the elucidation of new drug targets linked to post-translational modifications machinery: Pitfalls and progress. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2022, 117, e210403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, L.B.; Aires, R.L.; Oliveira, L.S.; Fontes, J.V.; Miguel, D.C.; Abbehausen, C. A “Golden Age” for the discovery of new antileishmanial agents: Current status of leishmanicidal gold complexes and prospective targets beyond the trypanothione system. ChemMedChem 2021, 16, 1682–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schenone, S.; Bruno, O.; Ranise, A.; Bondavalli, F.; Filippelli, W.; Falcone, G.; Giordano, L.; Vitelli, M.R. 3-Arylsulphonyl-5-arylamino-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2(3H)ones as Anti-inflammatory and Analgesic Agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2001, 9, 2149–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalavde, Y.M.; Joshi, V. Synthesis of new substituted sulfonylhydrazinecarboxamides and sulfonylhydrazinecarbothioamides having antifungal and antibacterial activities. Indian J. Chem. Sect. B Org. Chem. Incl. Med. Chem. 2000, 39, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peretyazhko, M.Z.; Pel’kis, P.S. Synthesis of 2-arylsulfonylhydrazones. 3-Aryl-1,3-thiazolidine-2,4-diones. Ukr. Chem. J. (Russ. Ed.) 1969, 35, 532–535. [Google Scholar]
- Bruker. SADABS; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Stoe & Cie. X-RED32; Stoe & Cie GmbH: Darmstadt, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick, G.M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A 2008, 64, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXT—Integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. A Found Adv. 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolomanov, O.V.; Bourbis, L.J.; Gildea, R.J.; Howard, J.A.K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macrae, C.F.; Sovago, I.; Cottrell, S.J.; Galek, P.T.A.; McCabe, P.; Pidcock, E.; Platings, M.; Shields, G.P.; Stevens, J.S.; Towler, M.; et al. Mercury 4.0: From visualization to analysis, design and prediction. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2020, 53, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandenburg, K. Diamond Crystal and Molecular Structure Visualization (Version 4.0.2); Crystal Impact GbR: Bonn, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hohenberg, P.; Kohn, W. Inhomogeneous Electron Gas. Phys. Rev. 1964, 136, B864–B871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becke, A.D. Density-functional thermochemistry. III. The role of exact exchange. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 5648–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimme, S.; Ehrlich, S.; Goerigk, L. Effect of the damping function in dispersion corrected density functional theory. J. Comput. Chem. 2011, 32, 1456–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, T.; Hirao, K. The Douglas–Kroll–Hess Approach. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 385–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammi, R.; Mennucci, B.; Tomasi, J. Fast Evaluation of Geometries and Properties of Excited Molecules in Solution: A Tamm-Dancoff Model with Application to 4-Dimethylaminobenzonitrile. J. Phys. Chem. A 2000, 104, 5631–5637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neese, F. The ORCA Program System. WIREs Comput. Mol. Sci. 2012, 2, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigend, F.; Häser, M.; Patzelt, H.; Ahlrichs, R. RI-MP2: Optimized auxiliary basis sets and demonstration of efficiency. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1998, 294, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neese, F.; Wennmohs, F.; Becker, U.; Riplinger, C. The ORCA quantum chemistry program package. J. Chem. Phys. 2020, 152, 224108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdonk, M.L.; Cole, J.C.; Hartshorn, M.J.; Murray, C.W.; Taylor, R.D. Improved protein-ligand docking using GOLD. Proteins 2003, 52, 609–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, M.T.; Rodrigues, N.C.; Gava, L.M.; Canduri, F.; Oliva, G.; Barbosa, L.R.S.; Borges, J.C. 4E2D: Structure of the old yellow enzyme from Trypanosoma cruzi. Protein Data Bank 2013, 184, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, K.A.F.; Dias, C.N.S.; Néris, P.L.N.; Rocha, J.C.; Scotti, M.T.; Scotti, L.; Mascarenhas, S.R.; Veras, R.C.; Medeiros, I.A.; Keesen, T.S.L.; et al. 2-Amino-thiophene derivatives present antileishmanial activity mediated by apoptosis and immunomodulation in vitro. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 106, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, J.; Wilson, I.; Orton, T.; Pognan, F. Investigation of the Alamar Blue (resazurin) fluorescent dye for the assessment of mammalian cell cytotoxicity. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 5421–5426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, J.C.; Heinhuis, B.; Gomes, R.S.; Damen, M.S.M.A.; Real, F.; Mortara, R.A.; Keating, S.T.; Dinarello, C.A.; Joosten, L.A.B.; Ribeiro-Dias, F. Cytokines and microbicidal molecules regulated by IL-32 in THP-1-derived human macrophages infected with New World Leishmania species. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veloso-Silva, L.L.W.; Dores-Silva, P.R.; Bertolino-Reis, D.E.; Moreno-Oliveira, L.F.; Libardi, S.H.; Borges, J.C. Structural studies of Old Yellow Enzyme of Leishmania braziliensis in solution. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2019, 661, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, S.; Ding, L.; Tian, Y.; Song, D.; Zhoy, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H. Investigation of the interaction between flavonoids and human serum albumin. J. Mol. Struct. 2004, 703, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakowicz, J.R. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy, 2nd ed.; Kluwer Academic/Plenum: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epps, D.E.; Raub, T.J.; Caiolfa, V.; Chiari, A.; Zamai, M. Determination of the Affinity of Drugs toward Serum Albumin by Measurement of the Quenching of the Intrinsic Tryptophan Fluorescence of the Protein. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1999, 51, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawel, H.M.; Frey, S.K.; Meidtner, K.; Kroll, J.; Schweigert, F.J. Determining the binding affinities of phenolic compounds to proteins by quenching of the intrinsic tryptophan fluorescence. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2006, 50, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libardi, S.H.; Ahmad, A.; Ferreira, F.B.; Oliveira, R.J.; Caruso, Í.P.; Melo, F.A.; Albuquerque, S.; Cardoso, D.R.; Burtoloso, A.C.B.; Borges, J.C. Interaction between diterpene icetexanes and old yellow enzymes of Leishmania braziliensis and Trypanosoma cruzi. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 259, 129192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geary, W.J. The Use of Conductivity Measurements in Organic Solvents for the Characterization of Coordination Compounds. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1971, 7, 81–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sucena, S.F.; Demirer, T.I.; Baitullina, A.; Hagenbach, A.; Grewe, J.; Spreckelmeyer, S.; März, J.; Barkleit, A.; Maia, P.I.S.; Nguyen, H.H.; et al. Gold-Based Coronands as Hosts for M3+ Metal Ions: Ring Size Matters. Molecules 2023, 28, 5421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidbaur, H.; Schier, A. Aurophilic interactions as a subject of current research: An up-date. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 370–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itokazu, M.K.; Polo, A.S.; Ilha, N.Y.M. Luminescent rigidochromism of fac-[Re(CO)3(phen)(cis-bpe)]+ and its binuclear complex as photosensors. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2003, 160, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lees, A.J. Luminescence Properties of Organometallic complexes. Chem. Rev. 1987, 87, 711–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyykkö, P. Theoretical chemistry of gold. II. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2005, 358, 4113–4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyykkö, P. Theoretical chemistry of gold. III. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 1967–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyykkö, P. Theoretical chemistry of gold. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 4412–4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez Delgado, G.Y.; Ferreira, F.H.D.C.; Paschoal, D.F.S.; Dos Santos, H.F. The role of tridentate ligands on the redox stability of anticancer gold(III) complexes. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2022, 236, 111970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paschoal, D.F.S.; Gomes, M.S.; Machado, L.P.N.; Dos Santos, H.F. Basis Sets for Heavy Atoms. In Basis Sets in Computational Chemistry; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 107, pp. 183–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vale-Costa, S.; Vale, N.; Matos, J.; Tomás, A.; Moreira, R.; Gomes, P.; Gomes, M.S. Peptidomimetic and Organometallic Derivatives of Primaquine Active against Leishmania infantum. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 5774–5781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minori, K.; Rosa, L.B.; Bonsignore, R.; Casini, A.; Miguel, D.C. Comparing the Antileishmanial Activity of Gold(I) and Gold(III) Compounds in L. amazonensis and L. braziliensis in Vitro. ChemMedChem 2020, 15, 2146–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostafavi, M.; Sharifi, I.; Farajzadeh, S.; Khazaeli, P.; Sharifi, H.; Pourseyedi, E.; Kakooei, S.; Bamorovat, M.; Keyhani, A.; Parizi, M.H.; et al. Niosomal formulation of amphotericin B alone and in combination with glucantime: In vitro and in vivo leishmanicidal effects. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 116, 108942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarra, F.; Busto, N.; Guerri, A.; Marchetti, L.; Marzo, T.; García, B.; Biver, T.; Gabbiani, C. Cytotoxic Ag(I) and Au(I) NHC-carbenes bind DNA and show TrxRInhibition. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2020, 205, 110998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana, M.; Rodriguez-Rius, A.; Vellé, A.; Vives, S.; Miguel, P.J.S.; Triola, G. Dinuclear silver and gold bisNHC complexes as drug candidates for cancer therapy. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2022, 67, 116814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraiji, L.K.; Hayes, D.M.; Werner, T.C. Static and dynamic fluorescence quenching experiments for the physical chemistry laboratory. J. Chem. Educ. 1992, 69, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, H.; Bliznyuk, A.A.; Gready, E.J. Combining Docking and Molecular Dynamic Simulations in Drug Design. Med. Res. Rev. 2006, 26, 531–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, T.; Li, Q.; Zhou, Z. Structure-Based Virtual Screening for Drug Discovery: A Problem-Centric Review. AAPS J. 2012, 14, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, D.L.; Cox, M.M. Princípios de Bioquímica de Lehninger, 6th ed.; Artmed: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Angelotti, W.F.D.; Batista, V.H.S.; Granato, A.C. Comparação entre Funcionais de Densidade no Estudo de Propriedades Eletrônicas de derivados da Artemisinina. Quim. Nova 2016, 39, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).