Targeting the Gut: A Systematic Review of Specific Drug Nanocarriers
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Gut Structure
1.2. Highly Impactful Gut Pathologies
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Nano- and Micro-Carriers
2.2. Literature Search Strategy and Study Selection Process
3. Results
3.1. General Overview of the Selected Papers
3.2. pH Responsiveness Properties
3.3. Nanocarrier Mucophilic Properties
3.4. Release by Degradation Due to Colonic Flora or Intestinal Enzymes
3.5. External Stimuli-Driven Release
3.6. Molecular Targeting
3.7. Uptake-Enhancing Strategies
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Patra, J.K.; Das, G.; Fraceto, L.F.; Campos, E.V.R.; del Pilar Rodriguez-Torres, M.; Acosta-Torres, L.S.; Diaz-Torres, L.A.; Grillo, R.; Swamy, M.K.; Sharma, S.; et al. Nano based drug delivery systems: Recent developments and future prospects. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Wu, W.; Zhang, X. The feasibility of oral targeted drug delivery: Gut immune to particulates? Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2023, 13, 2544–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashique, S.; Sandhu, N.K.; Chawla, V.; Chawla, P.A. Targeted Drug Delivery: Trends and Perspectives. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2021, 18, 1435–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamath, S.; Stringer, A.M.; Prestidge, C.A.; Joyce, P. Targeting the gut microbiome to control drug pharmacomicrobiomics: The next frontier in oral drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2023, 20, 1315–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Okagu, O.D.; Udenigwe, C.C. Encapsulation technology for protection and delivery of bioactive peptides. In Biologically Active Peptides: From Basic Science to Applications for Human Health; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronin, C.G.; Delappe, E.; Lohan, D.G.; Roche, C.; Murphy, J.M.; Fehrmann, A.; Treutlein, M.; Rudolph, T.; Rudolph, V.; Weiss, K.; et al. Normal small bowel wall characteristics on MR enterography. Eur. J. Radiol. 2010, 75, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, J.T.; Nguyen, A.; Badireddy, M. Anatomy, abdomen and pelvis, small intestine. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Azzouz, L.L.; Sharma, S. Physiology, Large Intestine. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Satsu, H. Molecular and cellular studies on the absorption, function, and safety of food components in intestinal epithelial cells. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2017, 81, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallingborg, J. Intraluminal pH of the human gastrointestinal tract. Dan. Med. Bull. 1999, 46, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fikree, A.; Byrne, P. Management of functional gastrointestinal disorders. Clin. Med. J. R. Coll. Physicians 2021, 21, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharucha, A.E.; Chakraborty, S.; Sletten, C.D. Common Functional Gastroenterological Disorders Associated with Abdominal Pain. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2016, 91, 1118–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgart, D.C.; Sandborn, W.J. Inflammatory bowel disease: Clinical aspects and established and evolving therapies. Lancet 2007, 369, 1641–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alatab, S.; Sepanlou, S.G.; Ikuta, K.; Vahedi, H.; Bisignano, C.; Safiri, S.; Sadeghi, A.; Nixon, M.R.; Abdoli, A.; Abolhassani, H.; et al. The global, regional, and national burden of inflammatory bowel disease in 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghazadeh, R.; Zali, M.R.; Bahari, A.; Amin, K.; Ghahghaie, F.; Firouzi, F. Inflammatory bowel disease in Iran: A review of 457 cases. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2005, 20, 1691–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbert, A.; Rafiq, M.; Pham, T.M.; Renzi, C.; Abel, G.A.; Price, S.; Hamilton, W.; Petersen, I.; Lyratzopoulos, G. Predictive values for different cancers and inflammatory bowel disease of 6 common abdominal symptoms among more than 1.9 million primary care patients in the UK: A cohort study. PLoS Med. 2021, 18, e1003708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumgart, D.C.; Le Berre, C. Newer Biologic and Small-Molecule Therapies for Inflammatory Bowel Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1302–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enck, P.; Aziz, Q.; Barbara, G.; Farmer, A.D.; Fukudo, S.; Mayer, E.A.; Niesler, B.; Quigley, E.M.; Rajilić-Stojanović, M.; Schemann, M.; et al. Irritable bowel syndrome. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, S.; Karuniawati, H.; Jairoun, A.A.; Urbi, Z.; Ooi, D.J.; John, A.; Lim, Y.C.; Kibria, K.M.K.; Mohiuddin, A.M.; Ming, L.C.; et al. Colorectal Cancer: A Review of Carcinogenesis, Global Epidemiology, Current Challenges, Risk Factors, Preventive and Treatment Strategies. Cancers 2022, 14, 1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagnoff, M.F. Overview and pathogenesis of celiac disease. Gastroenterology 2005, 128, S10–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebwohl, B.; Rubio-Tapia, A. Epidemiology, Presentation, and Diagnosis of Celiac Disease. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Xu, Z.; Viennois, E.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Han, M.K.; Kang, Y.; Merlin, D. Orally Targeted Delivery of Tripeptide KPV via Hyaluronic Acid-Functionalized Nanoparticles Efficiently Alleviates Ulcerative Colitis. Mol. Ther. 2017, 25, 1628–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, N.; Zhao, Y.; Ge, N.; Qian, L. A pH/ROS cascade-responsive and self-accelerating drug release nanosystem for the targeted treatment of multi-drug-resistant colon cancer. Drug Deliv. 2020, 27, 1073–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Cho, W.J.; Jin, A.T.; Kok, L.Y.; Shi, Y.; Heller, D.E.; Lee, Y.L.; Zhou, Y.; Xie, X.; Korzenik, J.R.; et al. Heparin-Coated Albumin Nanoparticles for Drug Combination in Targeting Inflamed Intestine. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2020, 9, e2000536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Chen, G.; Zhang, J. A Review of Liposomes as a Drug Delivery System: Current Status of Approved Products, Regulatory Environments, and Future Perspectives. Molecules 2022, 27, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grumezescu, A.M. Nanobiomaterials in Cancer Therapy: Applications of Nanobiomaterials; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Wei, M.; Liu, C.; Yang, J. Cetuximab-modified silica nanoparticle loaded with ICG for tumor-targeted combi-national therapy of breast cancer. Drug Deliv. 2019, 26, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Pan, J.; Liu, J.; Ma, Y.; Qiu, F.; Mei, L.; Zeng, X.; Pan, G. Dynamically PEGylated and Borate-Coordination-Polymer-Coated Polydopamine Nanoparticles for Synergetic Tumor-Targeted, Chemo-Photothermal Combination Therapy. Small 2018, 14, 1703968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Yu, H.; Ru, Q. Bioavailability and delivery of nutraceuticals using nanotechnology. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, R50–R57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahara, Y.; Mukai, S.A.; Sawada, S.I.; Sasaki, Y.; Akiyoshi, K. Nanocarrier-Integrated Microspheres: Nanogel Tectonic Engi-neering for Advanced Drug-Delivery Systems. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 5080–5088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ota, S.; Takemura, Y. Characterization of Néel and Brownian Relaxations Isolated from Complex Dynamics Influenced by Dipole Interactions in Magnetic Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 28859–28866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque-Michel, E.; Lemaire, L.; Blanco-Prieto, M.J. SPION and doxorubicin-loaded polymeric nanocarriers for glioblastoma theranostics. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2021, 11, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Li, P.-Z.; Nguyen, K.T.; Wang, X.-J.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, H.; Tan, N.S.; Zhao, Y. Biocompatible, uniform, and redispersible mesoporous silica nanoparticles for cancer-targeted drug delivery in vivo. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 2450–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, P.; Zhao, R.; Zhao, L.; Liu, J.; Peng, S.; Fu, X.; Wang, X.; Luo, R.; Wang, R.; et al. Silica nanoparticles: Biomedical applications and toxicity. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 151, 113053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.N.A.; Shakweer, M.S.; Algharib, S.A.; Abdelaty, A.I.; Kamel, S.; Ismail, T.A.; Daoush, W.M.; Ismail, S.H.; Mahboub, H.H. Silica nanoparticles acute toxicity alters ethology, neuro-stress indices, and physiological status of African catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Aquac. Rep. 2022, 23, 101034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Lillard, J.W., Jr. Nanoparticle-based targeted drug delivery. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2009, 86, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scavo, M.P.; Gentile, E.; Wolfram, J.; Gu, J.; Barone, M.; Evangelopoulos, M.; Martinez, J.O.; Liu, X.; Celia, C.; Tasciotti, E.; et al. Multistage vector delivery of sulindac and silymarin for prevention of colon cancer. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 136, 694–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaza-Oliver, M.; Santander-Ortega, M.J.; Lozano, M.V. Current approaches in lipid-based nanocarriers for oral drug delivery. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2021, 11, 471–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na Jung, H.; Lee, S.-Y.; Lee, S.; Youn, H.; Im, H.-J. Lipid nanoparticles for delivery of RNA therapeutics: Current status and the role of in vivo imaging. Theranostics 2022, 12, 7509–7531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsairat, H.; Khater, D.; Sayed, U.; Odeh, F.; Al Bawab, A.; Alshaer, W. Liposomes: Structure, composition, types, and clinical applications. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathi, S.; Oyelere, A.K.; Caron, G.; Ermondi, G.; Morais, P.A.B.; Daltoé, R.D.; de Paula, H.; Li, T.; Weng, T.; Zuo, M.; et al. Liposomal drug delivery systems for targeted cancer therapy: Is active targeting the best choice? Futur. Med. Chem. 2016, 8, 2091–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimarães, D.; Cavaco-Paulo, A.; Nogueira, E. Design of liposomes as drug delivery system for therapeutic applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 601, 120571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Xu, X.; Pan, Y.; Yang, H.; Han, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, W. Specific surface modification of liposomes for gut targeting of food bioactive agents. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2023, 22, 3685–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, M.K.; Riaz, M.A.; Zhang, X.; Lin, C.; Wong, K.H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, G.; Lu, A.; Yang, Z. Surface functionalization and targeting strategies of liposomes in solid tumor therapy: A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.D.; Liu, X.; Jiang, J.; Liao, Y.-P.; Chang, C.H.; Nel, A.E.; Meng, H. Immune checkpoint inhibition in syngeneic mouse cancer models by a silicasome nanocarrier delivering a GSK3 inhibitor. Biomaterials 2021, 269, 120635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Neupane, Y.R.; Mangla, B.; Shafi, S.; Kohli, K. PEGylated Nanoliposomes Potentiated Oral Combination Therapy for Effective Cancer Treatment. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2020, 17, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalva, N.; Uthaman, S.; Augustine, R.; Jeon, S.H.; Huh, K.M.; Park, I.K.; Kim, I. Photo- and pH-Responsive Polycarbonate Block Copolymer Prodrug Nanomicelles for Controlled Release of Doxorubicin. Macromol. Biosci. 2020, 20, 2000118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechsri, K.; Suwanchawalit, C.; Chitropas, P.; Ngawhirunpat, T.; Rojanarata, T.; Opanasopit, P.; Pengnam, S. Rapid Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of pH-Sensitive Carbon-Based Nanoparticles for the Controlled Release of Doxorubicin to Cancer Cells. AAPS PharmSciTech 2023, 24, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvi, V.R.; Pawar, P. Nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) system: A novel drug targeting carrier. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 51, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, I.; Yasir, M.; Verma, M.; Singh, A.P. Nanostructured lipid carriers: A groundbreaking approach for transdermal drug delivery. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 10, 150–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Driscoll, C.M.; Griffin, B.T. Biopharmaceutical challenges associated with drugs with low aqueous solubility—The potential impact of lipid-based formulations. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Badry, M.; Haq, N.; Fetih, G.; Shakeel, F. Solubility and Dissolution Enhancement of Tadalafil Using Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery System. J. Oleo Sci. 2014, 63, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gursoy, R.N.; Benita, S. Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS) for improved oral delivery of lipophilic drugs. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2004, 58, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scavo, M.P.; Depalo, N.; Rizzi, F.; Ingrosso, C.; Fanizza, E.; Chieti, A.; Messa, C.; Denora, N.; Laquintana, V.; Striccoli, M.; et al. FZD10 carried by exosomes sustains cancer cell proliferation. Cells 2019, 8, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wu, D.; Ma, X.; Wang, J.; Hou, W.; Zhang, W. Exosomes as drug carriers for cancer therapy and challenges regarding exosome uptake. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 128, 110237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Hasan, A.; Babadaei, M.M.N.; Behzadi, E.; Nouri, M.; Sharifi, M.; Falahati, M. Exosomes: Multiple-targeted multifunctional biological nanoparticles in the diagnosis, drug delivery, and imaging of cancer cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 129, 110442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longatti, A.; Schindler, C.; Collinson, A.; Jenkinson, L.; Matthews, C.; Fitzpatrick, L.; Blundy, M.; Minter, R.; Vaughan, T.; Shaw, M.; et al. High affinity single-chain variable fragments are specific and versatile targeting motifs for extracellular vesicles. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 14230–14244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.M.; Banyard, A.; Smith, C.; Mironov, A.; McCabe, M.G. Large extracellular vesicles can be characterised by multiplex labelling using imaging flow cytometry. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Zickler, A.M.; El Andaloussi, S. Dosing extracellular vesicles. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 178, 113961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, I.K.; Wood, M.J.A.; Fuhrmann, G. Extracellular vesicles as a next-generation drug delivery platform. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 748–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, T.; Sumrin, A.; Bilal, M.; Bashir, H.; Khawar, M.B. Tumor-derived extracellular vesicles: Potential tool for cancer diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 2063–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freiberg, S.; Zhu, X.X. Polymer microspheres for controlled drug release. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 282, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, B.; Mady, O.Y.; Tambuwala, M.M.; Haggag, Y.A. PH-sensitive nanoparticles containing 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin as an improved anti-cancer option for colon cancer. Nanomedicine 2022, 17, 367–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amara, S.; Bourlieu, C.; Humbert, L.; Rainteau, D.; Carrière, F. Variations in gastrointestinal lipases, pH and bile acid levels with food intake, age and diseases: Possible impact on oral lipid-based drug delivery systems. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 142, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juang, V.; Chang, C.H.; Wang, C.S.; Wang, H.E.; Lo, Y.L. pH-Responsive PEG-Shedding and Targeting Peptide-Modified Na-noparticles for Dual-Delivery of Irinotecan and microRNA to Enhance Tumor-Specific Therapy. Small 2019, 15, 1903296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, P.-Y.; Lee, G.-Y.; Zheng, J.-H.; Huang, J.-H.; Cho, E.-C.; Lee, K.-C. Intercalating pyrene with polypeptide as a novel self-assembly nano-carrier for colon cancer suppression in vitro and in vivo. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 109, 110593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayan, R.; Gadag, S.; Cheruku, S.P.; Raichur, A.M.; Day, C.M.; Garg, S.; Manandhar, S.; Pai, K.S.R.; Suresh, A.; Mehta, C.H.; et al. Chitosan-glucuronic acid conjugate coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles: A smart pH-responsive and receptor-targeted system for colorectal cancer therapy. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 261, 117893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, W.; Yang, Q.; Wang, G.; Wang, Z.; Huang, P.; Huang, W.; Zhang, R.; Yan, D. Amphiphilic irinotecan–melampomagnolide B conjugate nanoparticles for cancer chemotherapy. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 8958–8966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abid, M.; Naveed, M.; Azeem, I.; Faisal, A.; Nazar, M.F.; Yameen, B. Colon specific enzyme responsive oligoester crosslinked dextran nanoparticles for controlled release of 5-fluorouracil. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 586, 119605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, E.; Zhang, Z. pH-sensitive CuS@Cu2S@Au nanoparticles as a drug delivery system for the chemotherapy against colon cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 525, 204–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraja, K.; Krishna Rao KS, V.; Zo, S.; Han, S.S.; Rao, K.M. Synthesis of novel tamarind gum-co-poly(Acrylamidoglycolic acid)-based ph responsive semi-ipn hydrogels and their ag nanocomposites for controlled release of chemotherapeutics and inactivation of multi-drug-resistant bacteria. Gels 2021, 7, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, P.; Hu, T.-G.; Li, L.; Zong, M.-H.; Wu, H. A colon-specific delivery system for quercetin with enhanced cancer prevention based on co-axial electrospinning. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 5999–6009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Li, F.; Yuan, L.; Bing, Z.; Li, X.; Yang, K. pH-responsive resveratrol-loaded ZIF-8 nanoparticles modified with tannic acid for promoting colon cancer cell apoptosis. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2024, 112, e35320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draget, K.I.; Taylor, C. Chemical, physical and biological properties of alginates and their biomedical implications. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sookkasem, A.; Chatpun, S.; Yuenyongsawad, S.; Wiwattanapatapee, R. Alginate beads for colon specific delivery of self-emulsifying curcumin. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2015, 29, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.-Q.; Zhang, H.-B.; Wang, G.-F.; Xu, D.; Zhang, W.-Y.; Wang, Q.-S.; Cui, Y.-L. Colon-specific microspheres loaded with puerarin reduce tumorigenesis and metastasis in colitis-associated colorectal cancer. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 570, 118644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wezgowiec, J.; Tsirigotis-Maniecka, M.; Saczko, J.; Wieckiewicz, M.; Wilk, K.A. Microparticles vs. Macroparticles as curcumin delivery vehicles: Structural studies and cytotoxic effect in human adenocarcinoma cell line (lovo). Molecules 2021, 26, 6056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Stefano, C.; Gianguzza, A.; Piazzese, D.; Sammartano, S. Modelling of proton and metal exchange in the alginate biopolymer. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2005, 383, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, H.I.; Ayub, A.D.; Yusuf, S.N.A.M.; Yahaya, N.; Kadir, E.A.; Lim, V. Docetaxel-loaded disulfide cross-linked nanoparticles derived from thiolated sodium alginate for colon cancer drug delivery. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, M.; Chi, Z.; Liu, Y.J.; Liu, C.G. Preparation, characterization, and in vitro drug release behavior of thiolated alginate na-noparticles loaded budesonide as a potential drug delivery system toward inflammatory bowel diseases. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2020, 31, 2299–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, D.; Su, W.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Hua, Z.; Miao, S.; Tan, M. Microfluidic Fabrication of pH-Responsive Nanoparticles for Encapsulation and Colon-Target Release of Fu-coxanthin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, L.; Shen, R.; Wei, L.; Xu, S.; Xia, W.; Hou, Y.; Cui, J.; Qu, R.; Luo, J.; Cao, J.; et al. Designing a microbial fermentation-functionalized alginate microsphere for targeted release of 5-ASA using nano dietary fiber carrier for inflammatory bowel disease treatment. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Z.-P.; Cui, Y.-L.; Wang, Q.-S. ROS-responsive thioketal-linked alginate/chitosan carriers for irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea therapy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 209, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, A.K.; Doolaanea, A.A.; Al-Mahmood, S.M.A.; Kennedy, J.F.; Chatterjee, B.; Bera, H. Electro-hydrodynamic assisted synthesis of lecithin-stabilized peppermint oil-loaded alginate microbeads for intestinal drug delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 185, 861–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayub, A.D.; Chiu, H.I.; Yusuf, S.N.A.M.; Kadir, E.A.; Ngalim, S.H.; Lim, V. Biocompatible disulphide cross-linked sodium alginate derivative nanoparticles for oral colon-targeted drug delivery. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 353–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirdamadian, S.Z.; Varshosaz, J.; Minaiyan, M.; Taheri, A. 3D printed tablets containing oxaliplatin loaded alginate nanoparticles for colon cancer targeted delivery. An in vitro/in vivo study. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 205, 90–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, A.; Mahmood, S.; Enezei, H.H.; Hussain, S.A.; Hamad, H.A.; Aldoghachi, A.F.; Hagar, A.; Doolaanea, A.A.; Ibrahim, W.N. Formulation, characterization and biological activity screening of sodium alginate-gum Arabic nanoparticles loaded with curcumin. Molecules 2020, 25, 2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, J.; Yang, T.; Li, K.; Wei, L.; Li, J.; He, W. Hydrogel beads based on carboxymethyl cassava starch/alginate enriched with MgFe2O4 nanoparticles for controlling drug release. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 220, 573–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi-Chaleshtari, M.; Kiaie, S.H.; Irandoust, M.; Karami, H.; Nabi Afjadi, M.; Ghani, S.; Aghaei Vanda, N.; Ghaderi Sede, M.J.; Ahmadi, A.; Masjedi, A.; et al. Concomitant blockade of A2AR and CTLA-4 by siRNA-loaded polyethylene gly-col-chitosan-alginate nanoparticles synergistically enhances antitumor T-cell responses. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 10068–10080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, M.; Sohail, M.; Minhas, M.U.; Mahmood, A.; Shah, S.A.; Munir, A.; Kashif, M.-U. Folic acid-decorated alginate nanoparticles loaded hydrogel for the oral delivery of diferourylmethane in colorectal cancer. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 233, 123585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostami, N.; Nikkhoo, A.; Khazaei-poul, Y.; Farhadi, S.; Sadat Haeri, M.; Moghadaszadeh Ardebili, S.; Aghaei Vanda, N.; Atyabi, F.; Namdar, A.; Baghaei, M.; et al. Coinhibition of S1PR1 and GP130 by siRNA-loaded alginate-conjugated trimethyl chitosan nanoparticles robustly blocks development of cancer cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 9702–9717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ren, H.; Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Qiu, Q.; Zhang, N.; Jiang, N.; Lovell, J.F.; Zhang, Y. Orally-Delivered, Cytokine-Engineered Extracellular Vesicles for Targeted Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Small 2023, 19, 2304023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marotti, V.; Xu, Y.; Michalowski, C.B.; Zhang, W.; Domingues, I.; Ameraoui, H.; Moreels, T.G.; Baatsen, P.; Van Hul, M.; Muccioli, G.G.; et al. A nanoparticle platform for combined mucosal healing and immunomodulation in inflammatory bowel disease treatment. Bioact. Mater. 2024, 32, 206–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vafaei, S.Y.; Abdolghaffari, A.H.; Mahjub, R.; Eslami, S.M.; Esmaeili, M.; Abdollahi, M.; Atyabi, F.; Dinarvand, R. Budesonide-Loaded Hyaluronic Acid Nanoparticles for Targeted Delivery to the Inflamed Intestinal Mucosa in a Rodent Model of Colitis. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 7776092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seoudi, S.S.; Allam, E.A.; El-Kamel, A.H.; Elkafrawy, H.; El-Moslemany, R.M. Targeted delivery of budesonide in acetic acid induced colitis: Impact on miR-21 and E-cadherin expression. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2023, 13, 2930–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phatak, N.; Bhattacharya, S.; Shah, D.; Manthalkar, L.; Sreelaya, P.; Jain, A. CD44 targeted delivery of hyaluronic-acid-coated polymeric nanoparticles against colorectal cancer. Nanomedicine 2023, 18, 1613–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, C.; Zhang, T.; Li, S.; Xu, Z.; Pan, B.; Xu, S.; Jin, S.; Lu, G.; Yang, S.; Xue, Z.; et al. Hybrid nanoparticles modified by hyaluronic acid loading an hsp90 inhibitor as a novel delivery system for subcutaneous and orthotopic colon cancer therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 1743–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, K.Y.; Saravanakumar, G.; Park, J.H.; Park, K. Hyaluronic acid-based nanocarriers for intracellular targeting: Interfacial interactions with proteins in cancer. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 99, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, R.; Cao, Y.; Yan, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, M.; Zhang, M. Oral Delivery of Pterostilbene by L-Arginine-Mediated “Nano-Bomb” Carrier for the Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis. Int. J. Nanomed. 2022, 17, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Kerdsakundee, N.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, F.; Liu, X.; Bauleth-Ramos, T.; Lian, W.; Mäkilä, E.; et al. Hierarchical structured and programmed vehicles deliver drugs locally to inflamed sites of intestine. Biomaterials 2018, 185, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Tan, N. Programmable site-specific delivery of an alkaline phosphatase-activatable prodrug and a mitochondria-targeted cyclopeptide for combination therapy in colon cancer. Biomater. Sci. 2023, 11, 7114–7123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, A.; Xu, Z.; Ingram, N.; Coletta, P.L.; Millner, P.A.; Tyler, A.I.; Hughes, T.A. Hyaluronic-Acid-Tagged Cubosomes Deliver Cytotoxics Specifically to CD44-Positive Cancer Cells. Mol. Pharm. 2022, 19, 4601–4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-J.; Perumalsamy, H.; Castro-Aceituno, V.; Kim, D.; Markus, J.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.; Liu, Y.; Yang, D.C. Photoluminescent and self-assembled hyaluronic acid-zinc oxide-ginsenoside rh2 nanoparticles and their potential caspase-9 apoptotic mechanism towards cancer cell lines. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 8195–8208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostroverkhov, P.; Semkina, A.; Naumenko, V.; Plotnikova, E.; Yakubovskaya, R.; Vodopyanov, S.; Abakumov, A.; Majouga, A.; Grin, M.; Chekhonin, V.; et al. HSA—Coated magnetic nanoparticles for mri-guided photodynamic cancer therapy. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimifard, S.; Kiani, F.K.; Eshaghi, F.S.; Izadi, S.; Shahdadnejad, K.; Masjedi, A.; Heydari, M.; Ahmadi, A.; Hojjat-Farsangi, M.; Hassannia, H.; et al. Codelivery of BV6 and anti-IL6 siRNA by hyaluronate-conjugated PEG-chitosan-lactate nanoparticles inhibits tumor progression. Life Sci. 2020, 260, 118423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmaily, M.; Masjedi, A.; Hallaj, S.; Afjadi, M.N.; Malakotikhah, F.; Ghani, S.; Ahmadi, A.; Sojoodi, M.; Hassannia, H.; Atyabi, F.; et al. Blockade of CTLA-4 increases anti-tumor response inducing potential of dendritic cell vaccine. J. Control. Release 2020, 326, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Shang, E.; Ju, A.; Li, Y.; Wu, Q.; Li, Q.; Yang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Yang, D.; Lv, S. Tumor-targeted hyaluronic acid-mPEG modified nanostructured lipid carriers for cantharidin delivery: An in vivo and in vitro study. Fitoterapia 2021, 155, 105033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Ren, Y.; Tan, L.; Song, X.; Wang, M.; Li, Y.; Cao, Z.; Guo, C. Norcantharidin: Research advances in pharmaceutical activities and derivatives in recent years. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 131, 110755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badhana, S.; Garud, N.; Garud, A. Colon specific drug delivery of mesalamine using eudragit S100-coated chitosan microspheres for the treatment of ulcerative colitis. Int. Curr. Pharm. J. 2013, 2, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhgari, A.; Heshmati, Z.; Makhmalzadeh, B.S. Indomethacin electrospun nanofibers for colonic drug delivery: Preparation and characterization. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2013, 3, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turanlı, Y.; Acartürk, F. Preparation and characterization of colon-targeted pH/Time-dependent nanoparticles using anionic and cationic polymethacrylate polymers. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 171, 106122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.S.; Altayari, A.A.; Khan, L.M.; Alharthi, S.E.; Ahmed, O.A.; El-Shitany, N.A.; Ali, S.S.; Saadah, O.I. Colon-Targeted Therapy of Tacrolimus (FK506) in the Treatment of Experimentally Induced Colitis. Pharmacology 2020, 105, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qelliny, M.R.; Aly, U.F.; Elgarhy, O.H.; Khaled, K.A. Budesonide-Loaded Eudragit S 100 Nanocapsules for the Treatment of Acetic Acid-Induced Colitis in Animal Model. AAPS PharmSciTech 2019, 20, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anwer, M.K.; Ahmed, M.M.; Aldawsari, M.F.; Iqbal, M.; Soliman, G.A.; Aljuffali, I.A. Eluxadoline-Loaded Eudragit Nanoparticles for Irritable Bowel Syndrome with Diarrhea: Formulation, Optimization Using Box–Behnken Design, and Anti-Diarrheal Activity. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassem, A.M.; Almukainzi, M.; Faris, T.M.; Ibrahim, A.H.; Anwar, W.; Elbahwy, I.A.; El-Gamal, F.R.; Zidan, M.F.; Akl, M.A.; Abd-ElGawad, A.M.; et al. A pH-sensitive silica nanoparticles for colon-specific delivery and controlled release of catechin: Optimi-zation of loading efficiency and in vitro release kinetics. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 192, 106652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Maghawry, E.; Tadros, M.I.; Elkheshen, S.A.; Abd-Elbary, A. Eudragit®-s100 coated plga nanoparticles for colon targeting of etoricoxib: Optimization and pharmacokinetic assessments in healthy human volunteers. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 3965–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Sood, A.; Dhiman, A.; Shrimali, N.; Singhmar, R.; Guchhait, P.; Agrawal, G. Redox responsive poly(allylamine)/eudragit S-100 nanoparticles for dual drug delivery in colorectal cancer. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 143, 213184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhakamy, N.A.; Fahmy, U.A.; Ahmed, O.A.A.; Caruso, G.; Caraci, F.; Asfour, H.Z.; Bakhrebah, M.A.; Alomary, M.N.; Abdulaal, W.H.; Okbazghi, S.Z.; et al. Chitosan coated microparticles enhance simvastatin colon targeting and pro-apoptotic activity. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakral, S.; Thakral, N.K.; Majumdar, D.K. Eudragit®: A technology evaluation. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 131–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jablan, J.; Jug, M. Development of Eudragit® S100 based pH-responsive microspheres of zaleplon by spray-drying: Tailoring the drug release properties. Powder Technol. 2015, 283, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hady, S.M.; AbouGhaly MH, H.; El-Ashmoony, M.M.; Helmy, H.S.; El-Gazayerly, O.N. Colon targeting of celecoxib nano-mixed micelles using pulsatile drug delivery systems for the prevention of inflammatory bowel disease. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 576, 118982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Ren, M.; Yao, M.; Zou, J.; Fang, S.; Wang, Y.; Lan, M.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, F. Colon-specific delivery of methotrexate using hyaluronic acid modified pH-responsive nanocarrier for the therapy of colitis in mice. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 635, 122741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abolmaali, S.S.; Tamaddon, A.M.; Dinarvand, R. A review of therapeutic challenges and achievements of methotrexate delivery systems for treatment of cancer and rheumatoid arthritis. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2013, 71, 1115–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Wang, X.; He, M.; Wang, Y.; Lan, M.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, F. Colon-targeted delivery of tacrolimus using pH-responsive polymeric nanoparticles for murine colitis therapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 606, 120836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Wang, Y.; Lv, Y.; Fang, S.; Ren, M.; Yao, M.; Lan, M.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, F. XA pH-Responsive and Colitis-Targeted Nanoparticle Loaded with Shikonin for the Oral Treatment of Inflam-matory Bowel Disease in Mice. Mol. Pharm. 2022, 19, 4157–4170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wells, C.J.; King, A.M.; Bear, J.C.; Davies, G.L.; Williams, G.R. PH-Responsive nanocomposite fibres allowing MRI monitoring of drug release. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 7264–7274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amico, V.; Arduino, I.; Vacca, M.; Iacobazzi, R.M.; Altamura, D.; Lopalco, A.; Rizzi, R.; Cutrignelli, A.; Laquintana, V.; Massimo, F.; et al. Colonic budesonide delivery by multistimuli alginate/Eudragit® FS 30D/inulin-based microspheres as a paediatric formulation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 302, 120422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borderwala, K.; Rathod, S.; Yadav, S.; Vyas, B.; Shah, P. Eudragit S-100 Surface Engineered Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Colon Targeting of 5-Fluorouracil: Optimization and In Vitro and In Vivo Characterization. AAPS PharmSciTech 2021, 22, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ispas-Szabo, P.; De Koninck, P.; Calinescu, C.; Mateescu, M.A. Carboxymethyl Starch Excipients for Drug Chronodelivery. AAPS PharmSciTech 2017, 18, 1673–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranjbar, E.; Namazi, H.; Pooresmaeil, M. Carboxymethyl starch encapsulated 5-FU and DOX co-loaded layered double hy-droxide for evaluation of its in vitro performance as a drug delivery agent. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 201, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pujara, N.; Giri, R.; Wong, K.Y.; Qu, Z.; Rewatkar, P.; Moniruzzaman; Begun, J.; Ross, B.P.; McGuckin, M.; Popat, A. pH—Responsive colloidal carriers assembled from β-lactoglobulin and Epsilon poly-L-lysine for oral drug delivery. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 589, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorzkiewicz, M.; Marcinkowska, M.; Studzian, M.; Karwaciak, I.; Pulaski, L.; Klajnert-Maculewicz, B. Mesalazine–PAMAM Nanoparticles for Transporter-Independent Intracellular Drug Delivery: Cellular Uptake and Anti-Inflammatory Activity. Int. J. Nanomed. 2023, 18, 2109–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinho, J.O.; da Silva, I.V.; Amaral, J.D.; Rodrigues, C.M.P.; Casini, A.; Soveral, G.; Gaspar, M.M. Therapeutic potential of a copper complex loaded in pH-sensitive long circulating liposomes for colon cancer management. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 599, 120463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Warszawik, E.; van Rijn, P. pH-Triggered Release and Degradation Mechanism of Layered Double Hydroxides with High Loading Capacity. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 10, 2202396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, M.; Karanastasis, A.A.; Chatziathanasiadou, M.V.; Oguz, M.; Kougioumtzi, A.; Clemente, N.; Kellici, T.F.; Zafeiropoulos, N.E.; Avgeropoulos, A.; Mavromoustakos, T.; et al. Inclusion of Quercetin in Gold Nanoparticles Decorated with Supramolecular Hosts Amplifies Its Tumor Targeting Properties. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2019, 2, 2715–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ma, X.; Yue, Y.; Zhang, K.; Cheng, K.; Feng, Q.; Ma, N.; Liang, J.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, L.; et al. Rapid Surface Display of mRNA Antigens by Bacteria-Derived Outer Membrane Vesicles for a Personalized Tumor Vaccine. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, e2109984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, S.; Li, X.; Feng, M.; Liu, H.; Huang, L.; Niu, X. A fresh pH-responsive imipenem-loaded nanocarrier against Acinetobacter baumannii with a synergetic effect. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1166790. [Google Scholar]
- Teruel, A.H.; Pérez-Esteve, É.; Gonzalez-Alvarez, I.; Gonzalez-Alvarez, M.; Costero, A.M.; Ferri, D.; Gavina, P.; Merino, V.; Martinez-Manez, R.; Sancenon, F. Double Drug Delivery Using Capped Mesoporous Silica Microparticles for the Effective Treatment of In-flammatory Bowel Disease. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 2418–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijewantha, N.; Sane, S.; Eikanger, M.; Antony, R.M.; Potts, R.A.; Lang, L.; Rezvani, K.; Sereda, G. Enhancing Anti-Tumorigenic Efficacy of Eugenol in Human Colon Cancer Cells Using Enzyme-Responsive Nanoparticles. Cancers 2023, 15, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Jiang, J.; Chan, R.; Ji, Y.; Lu, J.; Liao, Y.-P.; Okene, M.; Lin, J.; Lin, P.; Chang, C.H.; et al. Improved Efficacy and Reduced Toxicity Using a Custom-Designed Irinotecan-Delivering Silicasome for Orthotopic Colon Cancer. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 38–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen-Trinh, Q.N.; Trinh, K.X.T.; Trinh, N.-T.; Vo, V.T.; Li, N.; Nagasaki, Y.; Vong, L.B. A silica-based antioxidant nanoparticle for oral delivery of Camptothecin which reduces intestinal side effects while improving drug efficacy for colon cancer treatment. Acta Biomater. 2022, 143, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asiri, S.M.; Khan, F.A.; Bozkurt, A. Delivery of Conjugated Silicon Dioxide Nanoparticles Show Strong Anti-Proliferative Ac-tivities. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 189, 760–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulski, M.; Malarz, K.; Kuczak, M.; Dudek, K.; Matus, K.; Sułowicz, S.; Mrozek-Wilczkiewicz, A.; Nowak, A. An organic–inorganic hybrid nanocomposite as a potential new biological agent. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Jiang, F.; Xing, Z.; Fan, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Ling, J.; Ouyang, X.-K. Efficient Delivery of Curcumin by Alginate Oligosaccharide Coated Aminated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles and In Vitro Anticancer Activity against Colon Cancer Cells. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chen, D.F.; Li, L.S.; Zhao, X.J.; Zhao, M.X. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles loaded with fluorescent couma-rin-5-fluorouracil conjugates as mitochondrial-targeting theranostic probes for tumor cells. Nanotechnology 2021, 32, 455101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Ding, M.; Zhang, Y. MiRNA-204-5p and oxaliplatin-loaded silica nanoparticles for enhanced tumor suppression effect in CD44-overexpressed colon adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 566, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broesder, A.; Berends, J.M.; Scheepers, S.M.; Nguyen, D.N.; Frijlink, H.W.; Hinrichs, W.L. Ileo-colon targeting of the poorly water-soluble drug celecoxib using a ph-dependent coating in combination with self-emulsifying drug delivery or solid dispersion systems. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, R.; Qian, F.; Wang, X.; Li, H.; Wang, L. Targeted delivery of 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3-based polypeptide nanoparticles to treat colon cancer. Biomed. Microdevices 2019, 21, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Pulido, G.; Medina, D.I. An overview of gastrointestinal mucus rheology under different pH conditions and introduction to pH-dependent rheological interactions with PLGA and chitosan nanoparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2021, 159, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosnik, A.; das Neves, J.; Sarmento, B. Mucoadhesive polymers in the design of nano-drug delivery systems for administration by non-parenteral routes: A review. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 2030–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Hao, H.; Liu, Q.; Li, J.; Yao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Yi, H. Effect of Extracelluar Vesicles Derived from Akkermansia muciniphila on Intestinal Barrier in Colitis Mice. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Zhong, Y.; Xie, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Pi, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, L.; Luo, J.; Xu, W. Bacteroides acidifaciens and its derived extracellular vesicles improve DSS-induced colitis. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1304232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, J.; Qiu, T.; Tang, M.; Zhang, X.; Dong, W. In vitro and in vivo combinatorial anticancer effects of oxaliplatin- and resveratrol-loaded N,O-carboxymethyl chitosan nanoparticles against colorectal cancer. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 163, 105864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Banna, F.S.; Mahfouz, M.E.; Leporatti, S.; El-Kemary, M.; Hanafy, N.A.N. Chitosan as a natural copolymer with unique properties for the development of hydrogels. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Gao, S.; Shui, S.; Liu, S.; Qu, H.; Liu, C.; Zheng, L. Small interfering RNA-loaded chitosan hydrochloride/carboxymethyl chitosan nanoparticles for ultra-sound-triggered release to hamper colorectal cancer growth in vitro. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, M.; Chiellini, F.; Ottenbrite, R.M.; Chiellini, E. Chitosan—A versatile semi-synthetic polymer in biomedical applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 981–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, N.; Galbis, E.; Díaz-Blanco, M.J.; Lucas, R.; Benito, E.; De-Paz, M.-V. Nanostructured Chitosan-based biomaterials for sustained and colon-specific resveratrol release. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yu, M.; Zhu, Z.; Lu, C.; Jin, M.; Rao, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Lu, X.; Yu, C. Oral delivery of infliximab using nano-in-microparticles for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 273, 118556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabana, S.; Hamouda, H.I.; Abdalla, M.; Sharaf, M.; Chi, Z.; Liu, C. Multifunctional nanoparticles based on marine polysaccharides for apremilast delivery to inflammatory macrophages: Preparation, targeting ability, and uptake mechanism. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 222, 1709–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, F.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Pang, J.; Pan, W. Galactosylated chitosan-functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles for efficient colon cancer cell-targeted drug delivery. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 181027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Q.; Jia, J.; Niu, X.; Zheng, C.; Zhao, H.; Sun, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y. An oral drug delivery system with programmed drug release and imaging properties for orthotopic colon cancer therapy. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 15958–15970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, C.S.; Thangam, R.; Mary, S.A.; Kannan, P.R.; Arun, G.; Madhan, B. Targeted delivery and apoptosis induction of trans-resveratrol-ferulic acid loaded chitosan coated folic acid conjugate solid lipid nanoparticles in colon cancer cells. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 231, 115682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashedi, J.; Haghjo, A.G.; Abbasi, M.M.; Tabrizi, A.D.; Yaqoubi, S.; Sanajou, D.; Jigheh, Z.A.; Namvaran, A.; Mohammadi, A.; Khoshraj, J.M.; et al. Anti-tumor effect of quercetin loaded chitosan nanoparticles on induced colon cancer in wistar rats. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 9, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayakumar, S.; Chen, J.; Kalaiselvi, V.; Tungare, K.; Bhori, M.; González-Sánchez, Z.I.; Durán-Lara, E.F. Marine polysaccharide laminarin embedded ZnO nanoparticles and their based chitosan capped ZnO nanocomposites: Synthesis, characterization and in vitro and in vivo toxicity assessment. Environ. Res. 2022, 213, 113655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoshtabiat, L.; Meshkini, A.; Matin, M.M. Fenton-magnetic based therapy by dual-chemodrug-loaded magnetic hydroxyap-atite against colon cancer. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 127, 112238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janardhanam LS, L.; Bandi, S.P.; Venuganti VV, K. Functionalized LbL Film for Localized Delivery of STAT3 siRNA and Oxali-platin Combination to Treat Colon Cancer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 10030–10046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, S.; Nawaz, A.; Farid, A.; Latif, M.S.; Fareed, M.; Ghazanfar, S.; Galanakis, C.M.; Alamri, A.S.; Alhomrani, M.; Asdaq, S.M.B. Folate-Modified Chitosan 5-Flourouraci Nanoparticles-Embedded Calcium Alginate Beads for Colon Targeted Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Madni, A.; Shah, H.; Jan, N.; Shafiq, A.; Basit, A.; Rai, N.; Ali, A.; Khan, M.M. Folate decorated lipid chitosan hybrid nanoparticles of 5-fluorouracil for enhanced anticancer efficacy against colon cancer. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 222, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Su, Y.; Pan, H.; Deng, W.; Wang, J.; Liu, D.; Pan, W. Nanodiamond-based multifunctional platform for oral chemo-photothermal combinational therapy of orthotopic colon cancer. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 176, 106080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Kang, L.; Hu, S.; Hu, J.; Fu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yang, X. Carboxymethyl chitosan microspheres loaded hyaluronic acid/gelatin hydrogels for controlled drug delivery and the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 167, 1598–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, A.B.; Chaud, M.V.; Santana, M.H.A. Hyaluronic acid behavior in oral administration and perspectives for nanotechnology-based formulations: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 222, 115001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Q.; Jiang, H.; Cai, C.; Hao, J.; Li, G.; Yu, G. Gut microbiota fermentation of marine polysaccharides and its effects on intestinal ecology: An overview. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 179, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.-F.; Chang, J.T.; Huang, X.-F.; Lin, Y.-L.; Liao, K.-W.; Huang, C.-W.; Tsai, N.-M. Antitumor effects of n-butylidenephthalide encapsulated in lipopolyplexs in colorectal cancer cells. Molecules 2020, 25, 2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zeng, F.; Fan, Z.; He, Z.; Tai, L.; Peng, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Chao, Z.; Jiang, W.; Jia, L.; et al. An Oral Polyphenol Host-Guest Nanoparticle for Targeted Therapy of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Acta Biomater. 2023, 169, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Xia, X.; Xu, X.; Leung, K.K.C.; Rai, A.; Deng, Y.; Yang, B.; Lai, H.; Peng, X.; Shi, P.; et al. Nanoparticle-assembled bioadhesive coacervate coating with prolonged gastrointestinal retention for inflam-matory bowel disease therapy. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 7162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaezi, Z.; Aghdaei, H.A.; Sedghi, M.; Mahdavian, R.; Molakarimi, M.; Hashemi, N.; Naderi-Manesh, H. Hemoglobin bio-adhesive nanoparticles as a colon-specific delivery system for sustained release of 5-aminosalicylic acid in the effective treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 616, 121531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Yu, X.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, S.; Xue, L.; Xue, Q.; Bao, Y. Hemoglobins Likely Function as Peroxidase in Blood Clam Tegillarca granosa Hemocytes. J. Immunol. Res. 2017, 2017, 7125084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, Y.; Kim, H.H.; Kim, H.; Kong, H.; Choi, B.; Yang, Y.; Kim, Y. Evaluation of 5-aminosalicyltaurine as a colon-specific prodrug of 5-aminosalicylic acid for treatment of experi-mental colitis. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 28, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, D.; Choi, D.; Jeon, H.; Han, J.; Jung, Y.; Kong, H.; Kim, Y.M. Synthesis and properties of N,N′-bis(5-aminosalicyl)-L-cystine as a colon-specific deliverer of 5-aminosalicylic acid and cystine. Drug Deliv. 2008, 15, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Islam, T.; Nurunnabi, M. Mucoadhesive carriers for oral drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2022, 351, 504–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jiang, J.; Meng, H. Transcytosis—An effective targeting strategy that is complementary to “EPR effect” for pancreatic cancer nano drug delivery. Theranostics 2019, 9, 8018–8025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinninella, E.; Raoul, P.; Cintoni, M.; Franceschi, F.; Miggiano, G.A.D.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mele, M.C. What is the healthy gut microbiota composition? A changing ecosystem across age, environment, diet, and diseases. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadji, H.; Bouchemal, K. Advances in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease: Focus on polysaccharide nanoparticulate drug delivery systems. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 181, 114101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Fishman, M.L.; Kost, J.; Hicks, K.B. Pectin-based systems for colon-specific drug delivery via oral route. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 3333–3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Xu, J.; Shi, T.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, F.; Yang, C.; Guo, X.; Liu, G.; Shao, D.; Leong, K.W.; et al. Probiotic-Inspired Nanomedicine Restores Intestinal Homeostasis in Colitis by Regulating Redox Balance, Immune Responses, and the Gut Microbiome. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2207890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerasimidis, K.; Nichols, B.; McGowan, M.; Svolos, V.; Papadopoulou, R.; Kokkorou, M.; Rebull, M.; Bello Gonzalez, T.; Hansen, R.; Russell, R.K.; et al. The Effects of Commonly Consumed Dietary Fibres on the Gut Microbiome and Its Fibre Fermentative Capacity in Adults with Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Remission. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, S.; Chen, H.; Liu, E.; Zhang, M.; Zeng, F.; Shen, H.; Fang, Y.; Muhitdinov, B.; Huang, Y. Oral pectin/oligochitosan microspheres for colon-specific controlled release of quercetin to treat inflammatory bowel disease. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 316, 121025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Sun, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Ye, W.; Jiang, C.; Liu, M.; Ji, Q.; Zhang, B.; Mei, Q.; Liu, D.; et al. MCP mediated active targeting calcium phosphate hybrid nanoparticles for the treatment of orthotopic drug-resistant colon cancer. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabra, R.; Billa, N.; Roberts, C. Cetuximab-conjugated chitosan-pectinate (modified) composite nanoparticles for targeting colon cancer. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 572, 118775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trombino, S.; Serini, S.; Cassano, R.; Calviello, G. Xanthan gum-based materials for omega-3 PUFA delivery: Preparation, characterization and antineoplastic activity evaluation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 208, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asnani, G.P.; Kokare, C.R. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of colon cancer targeted epichlorohydrin crosslinked Portulaca-alginate beads. Biomol. Concepts 2018, 9, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, M.; Adena SK, R.; Vardhan, H.; Yadav, S.K.; Mishra, B. Locust bean gum and sodium alginate based interpenetrating polymeric network microbeads encapsulating Capecitabine: Improved pharmacokinetics, cytotoxicity &in vivo antitumor ac-tivity. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 104, 109958. [Google Scholar]
- Bharaniraja, B.; Kumar, K.J.; Prasad, C.M.; Sen, A.K. Modified katira gum for colon targeted drug delivery. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 119, 2644–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Raorane, C.J.; Alka; Shastri, D.; Raj, V.; Kim, S.-C.; Tuteja, M. Recent Progress on Modified Gum Katira Polysaccharides and Their Various Potential Applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharaniraja, B.; Kumar, K.J.; Prasad, C.; Sen, A. Different approaches of katira gum formulations for colon targeting. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 49, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmorshedy, Y.M.; Teleb, M.; Sallam, M.A.; Elkhodairy, K.A.; Bahey-El-Din, M.; Ghareeb, D.A.; Abdulmalek, S.A.; Monaim, S.A.H.A.; Bekhit, A.A.; Elzoghby, A.O.; et al. Engineered Microencapsulated Lactoferrin Nanoconjugates for Oral Targeted Treatment of Colon Cancer. Biomacromolecules 2023, 24, 2149–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Jin, J.; Duan, H.; Liu, C.; Chen, L.; Huang, W.; Gao, Z.; Jin, M. Targeted therapeutic effects of oral inulin-modified double-layered nanoparticles containing chemotherapeutics on orthotopic colon cancer. Biomaterials 2022, 283, 121440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attarwala, H.Z.; Suri, K.; Amiji, M.M. Pharmacokinetics and Biodistribution Analysis of Small Interference RNA for Silencing Tissue Transglutaminase-2 in Celiac Disease After Oral Administration in Mice Using Gelatin-Based Multicompartmental De-livery Systems. Bioelectricity 2020, 2, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attarwala, H.Z.; Suri, K.; Amiji, M.M. Co-Silencing of Tissue Transglutaminase-2 and Interleukin-15 Genes in a Celiac Disease Mimetic Mouse Model Using a Nanoparticle-in-Microsphere Oral System. Mol. Pharm. 2021, 18, 3099–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhavsar, M.D.; Amiji, M.M. Oral IL-10 gene delivery in a microsphere-based formulation for local transfection and therapeutic efficacy in inflammatory bowel disease. Gene Ther. 2008, 15, 1200–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xie, A.; Li, H.; Zou, X.; Zhang, Q. A self-assembled, ROS-responsive Janus-prodrug for targeted therapy of inflammatory bowel disease. J. Control. Release 2019, 316, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, I.L.; Yu, T.W.; Liu, T.I.; Chen, H.H.; Yang, Y.C.; Lo, C.L.; Wang, C.Y.; Chiu, H.C. Microfluidized Dextran Microgels Loaded with Cisplatin/SPION Lipid Nanotherapeutics for Local Colon Cancer Treatment via Oral Administration. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2022, 11, 2201140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Guo, W.; Han, J.; Li, J.; Zhao, Q.; Mao, Y.; Wang, S. Oral spatial-to-point cascade targeting “sugar-coated bullets” for precise and safe chemotherapy by intervention Warburg effect. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2023, 222, 113108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishna, B.S.; Jayakanthan, P.; Pugazhendhi, S.; Kabeerdoss, J. Alterations of mucosal microbiota in the colon of patients with inflammatory bowel disease revealed by real time polymerase chain reaction amplification of 16S ribosomal ribonucleic acid. Indian J. Med. Res. 2015, 142, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gul, L.; Modos, D.; Fonseca, S.; Madgwick, M.; Thomas, J.P.; Sudhakar, P.; Booth, C.; Stentz, R.; Carding, S.R.; Korcsmaros, T. Extracellular vesicles produced by the human commensal gut bacterium Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron affect host immune pathways in a cell-type specific manner that are altered in inflammatory bowel disease. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2022, 11, e12189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Pinel, B.; Ortega-Rodríguez, A.; Porras-Alcalá, C.; Cabeza, L.; Contreras-Cáceres, R.; Ortiz, R.; Díaz, A.; Moscoso, A.; Sarabia, F.; Prados, J.; et al. Magnetically active pNIPAM nanosystems as temperature-sensitive biocompatible structures for con-trolled drug delivery. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2020, 48, 1022–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Gupta, A.; Ansari, M.; Vyawahare, A.; Jayamurugan, G.; Khan, R. Hyperbranched Polymer-Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticle-Mediated Hyperthermia and Niclosamide Bimodal Therapy of Colorectal Cancer Cells. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 1102–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, K.; Watanabe, M.; Iwasaki, T.; Shudou, M.; Uda, R.M. Endosomal escape by photo-activated fusion of liposomes con-taining a malachite green derivative: A novel class of photoresponsive liposomes for drug delivery vehicles. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2019, 18, 1471–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; He, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhang, M.; Gu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liu, E.; Xu, Q.; Asrorov, A.M.; Huang, Y. Magnetism-mediated targeting hyperthermiaimmunotherapy in ‘cold’ tumor with CSF1R inhibitor. Theranostics 2021, 11, 6860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorente, C.; Cabeza, L.; Clares, B.; Ortiz, R.; Halbaut, L.; Delgado, V.; Perazzoli, G.; Prados, J.; Arias, J.L.; Melguizo, C. Formulation and in vitro evaluation of magnetoliposomes as a potential nanotool in colorectal cancer therapy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 171, 553–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Wu, Y.; Xu, W.; Li, Z.; Wang, L. Synergic fabrication of multifunctional liposomes nanocomposites for improved radiofrequency ablation combination for liver metastasis cancer therapy. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 506–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depalo, N.; Fanizza, E.; Vischio, F.; Denora, N.; Laquintana, V.; Cutrignelli, A.; Striccoli, M.; Giannelli, G.; Agostiano, A.; Curri, M.L.; et al. Imaging modification of colon carcinoma cells exposed to lipid based nanovectors for drug delivery: A scanning electron microscopy investigation. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 21810–21825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Boubbou, K.; Ali, R.; Al-Humaid, S.; Alhallaj, A.; Lemine, O.M.; Boudjelal, M.; AlKushi, A. Iron oxide mesoporous magnetic nanostructures with high surface area for enhanced and selective drug delivery to metastatic cancer cells. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Zhu, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Xu, S.; Zhang, X.; Wu, R.; Yang, G. Superparamagnetic chitosan nanocomplexes for colorectal tumor-targeted delivery of irinotecan. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 584, 119394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Lin, P.Y.; Hsieh, S.L.; Kirankumar, R.; Lin, H.Y.; Li, J.H.; Chen, Y.T.; Wu, H.M.; Hsieh, S. Utilizing edible agar as a carrier for dual functional doxorubicin-fe3o4 nanotherapy drugs. Materials 2021, 14, 1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.T.-W.; Martino, U.; Khan, R.; Bazzar, M.; Southern, P.; Tuncel, D.; Al-Jamal, K.T. Engineering red-emitting multi-functional nanocapsules for magnetic tumour targeting and imaging. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 2590–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledda, M.; Fioretti, D.; Lolli, M.G.; Papi, M.; Di Gioia, C.; Carletti, R.; Ciasca, G.; Foglia, S.; Palmieri, V.; Marchese, R.; et al. Biocompatibility assessment of sub-5 nm silica-coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in human stem cells and in mice for potential application in nanomedicine. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 1759–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Garnes, M.; Morales, V.; Sanz, R.; García-Muñoz, R.A. Cytostatic and cytotoxic effects of hollow-shell mesoporous silica nanoparticles containing magnetic iron oxide. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tombuloglu, H.; Khan, F.A.; Almessiere, M.A.; Aldakheel, S.; Baykal, A. Synthesis of niobium substituted cobalt-nickel nano-ferrite (Co0.5Ni0.5NbxFe2-xO4 (x ≤ 0.1) by hydrothermal approach show strong anti-colon cancer activities. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 39, 2257–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jermy, B.R.; Alomari, M.; Ravinayagam, V.; Almofty, S.A.; Akhtar, S.; Borgio, J.F.; AbdulAzeez, S. SPIONs/3D SiSBA-16 based Multifunctional Nanoformulation for target specific cisplatin release in colon and cervical cancer cell lines. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budi, H.S.; Izadi, S.; Timoshin, A.; Asl, S.H.; Beyzai, B.; Ghaderpour, A.; Alian, F.; Eshaghi, F.S.; Mousavi, S.M.; Rafiee, B.; et al. Blockade of HIF-1α and STAT3 by hyaluronate-conjugated TAT-chitosan-SPION nanoparticles loaded with siRNA molecules prevents tumor growth. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2021, 34, 102373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, M.; Sant, S.; Wang, B.; Laurent, S.; Sen, T. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs): Development, surface modification and applications in chemotherapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 24–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huis in’t Veld, R.V.; Lara, P.; Jager, M.J.; Koning, R.I.; Ossendorp, F.; Cruz, L.J. M1-derived extracellular vesicles enhance photodynamic therapy and promote immunological memory in preclinical models of colon cancer. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, B.; Gao, Y.; Guo, F.; Jiang, D.; Guo, R.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Xie, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, H.; et al. Engineering goat milk-derived extracellular vesicles for multiple bioimaging-guided and photothermal-enhanced therapy of colon cancer. Biomater. Sci. 2023, 11, 1408–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, P.; Veld, R.V.H.I.; Jorquera-Cordero, C.; Chan, A.B.; Ossendorp, F.; Cruz, L.J. Zinc-phthalocyanine-loaded extracellular vesicles increase efficacy and selectivity of photodynamic therapy in co-culture and preclinical models of colon cancer. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosi, A.; Banfi, D.; Bistoletti, M.; Moretto, P.; Moro, E.; Crema, F.; Maggi, F.; Karousou, E.; Viola, M.; Passi, A.; et al. Hyaluronan: A neuroimmune modulator in the microbiota-gut axis. Cells 2021, 11, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baião, A.; Sousa, F.; Oliveira, A.V.; Oliveira, C.; Sarmento, B. Effective intracellular delivery of bevacizumab: Via PEGylated polymeric nanoparticles targeting the CD44v6 receptor in colon cancer cells. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 3720–3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, R.; Chu, X.; Zhang, J.; Fu, R.; Feng, C.; Jia, D.; Wang, R.; Yan, H.; Li, G.; Li, J. Liposome-Based Co-Immunotherapy with TLR Agonist and CD47-SIRPα Checkpoint Blockade for Efficient Treatment of Colon Cancer. Molecules 2023, 28, 3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Sun, Y.; Sun, S.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, D.; Li, W.; Liu, Z.; Shang, H.; Guan, X.; Zhang, W. Leveraging Nanodrug Delivery System for Simultaneously Targeting Tumor Cells and M2 Tumor-Associated Macrophages for Efficient Colon Cancer Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 50475–50484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Qiu, W.; Liang, M.; Ma, X.; Ye, M.; Xue, P.; Kang, Y.; Deng, J.; Xu, Z. Active targeting redox-responsive mannosylated prodrug nanocolloids promote tumor recognition and cell internalization for enhanced colon cancer chemotherapy. Acta Biomater. 2022, 147, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Pen, R.; Zuo, W.; Chen, Y.; Sun, X.; Gou, J.; Guo, Q.; Wen, M.; Li, W.; et al. Targeted delivery of irinotecan to colon cancer cells using epidermal growth factor receptor-conjugated liposomes. Biomed. Eng. Online 2022, 21, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Parihar, V.K.; Singh, N.; Hatware, K.; Page, A.; Sharma, M.; Prajapati, M.K.; Kanugo, A.; Pawde, D.; Maru, S.; et al. Targeted delivery of panitumumab-scaffold bosutinib-encapsulated polycaprolactone nanoparticles for EGFR-overexpressed colorectal cancer. Nanomedicine 2023, 18, 713–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bofinger, R.; Weitsman, G.; Evans, R.; Glaser, M.; Sander, K.; Allan, H.; Hochhauser, D.; Kalber, T.L.; Årstad, E.; Hailes, H.C.; et al. Drug delivery, biodistribution and anti-EGFR activity: Theragnostic nanoparticles for simultaneous in vivo delivery of tyrosine kinase inhibitors and kinase activity biosensors. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 18520–18535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.; Zhou, Q.; Zhu, H.; Zhuang, Y.; Bao, J. Enhanced antitumor efficacy in colon cancer using EGF functionalized PLGA nanoparticles loaded with 5-Fluorouracil and perfluorocarbon. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Xu, Z.; Alrobaian, M.; Afzal, O.; Kazmi, I.; Almalki, W.H.; Altamimi, A.S.A.; Al-Abbasi, F.A.; Alharbi, K.S.; Altowayan, W.M.; et al. EGF-functionalized lipid–polymer hybrid nanoparticles of 5-fluorouracil and sulforaphane with enhanced bioa-vailability and anticancer activity against colon carcinoma. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2022, 69, 2205–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.T.; Lin, H.; Wang, C.S.; Chang, C.H.; Lin, A.M.Y.; Yang, J.C.H.; Lo, Y.L. Improving the anticancer effect of afatinib and microRNA by using lipid polymeric nanoparticles conjugated with dual pH-responsive and targeting peptides. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 17, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liszbinski, R.B.; Romagnoli, G.G.; Gorgulho, C.M.; Basso, C.R.; Pedrosa, V.A.; Kaneno, R. Anti-EGFR-coated gold nanoparticles in vitro carry 5-fluorouracil to colorectal cancer cells. Materials 2020, 13, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, I.; Mattingly, S.; Wuest, M.; Leier, S.; Vakili, M.R.; Weinfeld, M.; Lavasanifar, A.; Wuest, F. Synthesis and Analysis of 64Cu-Labeled GE11-Modified Polymeric Micellar Nanoparticles for EGFR-Targeted Molecular Imaging in a Colorectal Cancer Model. Mol. Pharm. 2020, 17, 1470–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalikong, A.; Li, X.-Q.; Zhou, P.-H.; Qi, Z.-P.; Li, B.; Cai, S.-L.; Zhong, Y.-S. A triptolide loaded her2-targeted nano-drug delivery system significantly suppressed the proliferation of her2-positive and braf mutant colon cancer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 2323–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handali, S.; Moghimipour, E.; Rezaei, M.; Ramezani, Z.; Kouchak, M.; Amini, M.; Angali, K.A.; Saremy, S.; Dorkoosh, F.A. A novel 5-Fluorouracil targeted delivery to colon cancer using folic acid conjugated liposomes. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 108, 1259–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handali, S.; Moghimipour, E.; Kouchak, M.; Ramezani, Z.; Amini, M.; Angali, K.A.; Saremy, S.; Dorkoosh, F.A.; Rezaei, M. New folate receptor targeted nano liposomes for delivery of 5-fluorouracil to cancer cells: Strong implication for enhanced potency and safety. Life Sci. 2019, 227, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thirumalaivasan, N.; Venkatesan, P.; Lai, P.-S.; Wu, S.-P. In Vitro and In Vivo Approach of Hydrogen-Sulfide-Responsive Drug Release Driven by Azide-Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2019, 2, 3886–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AbouAitah, K.; Stefanek, A.; Higazy, I.M.; Janczewska, M.; Swiderska-Sroda, A.; Chodara, A.; Wojnarowicz, J.; Szałaj, U.; Shahein, S.A.; Aboul-Enein, A.M.; et al. Effective targeting of colon cancer cells with piperine natural anticancer prodrug using functionalized clusters of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govindarasu, M.; Abirami, P.; Alharthi, S.S.; Thiruvengadam, M.; Rajakumar, G.; Vaiyapuri, M. Synthesis, physicochemical characterization, and in vitro evaluation of biodegradable PLGA nanoparticles entrapped to folic acid for targeted delivery of kaempferitrin. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2022, 69, 2387–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licciardi, M.; Scialabba, C.; Puleio, R.; Cassata, G.; Cicero, L.; Cavallaro, G.; Giammona, G. Smart copolymer coated SPIONs for colon cancer chemotherapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 556, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Azad, A.K.; Nawaz, A.; Shah, K.U.; Iqbal, M.; Albadrani, G.M.; Al-Joufi, F.A.; Sayed, A.A.; Abdel-Daim, M.M. 5-Fluorouracil-Loaded Folic-Acid-Fabricated Chitosan Nanoparticles for Site-Targeted Drug Delivery Cargo. Polymers 2022, 14, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizi, S.; Soleymani, J.; Shadjou, N. Synthesis of folic acid functionalized terbium-doped dendritic fibrous nano-silica and In-teraction with HEK 293 normal, MDA breast cancer and HT 29 colon cancer cells. J. Mol. Recognit. 2020, 33, e2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soleymani, J.; Hasanzadeh, M.; Somi, M.H.; Shadjou, N.; Jouyban, A. Highly sensitive and specific cytosensing of HT 29 colorectal cancer cells using folic acid functionalized-KCC-1 nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 132, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.G.; Lee, J.Y.; Choi, P.S.; Kim, S.W.; Park, J.H. Tumor targeting effect of triphenylphosphonium cations and folic acid coated with Zr-89-labeled silica nanoparticles. Molecules 2020, 25, 2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardania, H.; Jafari, F.; Baneshi, M.; Mahmoudi, R.; Ardakani, M.T.; Safari, F.; Barmak, M.J. Folic Acid-Functionalized Albumin/Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite to Simultaneously Deliver Curcumin and 5-Fluorouracil into Human Colorectal Cancer Cells: An In Vitro Study. BioMed Res. Int. 2023, 2023, 8334102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, M.-Y.; Liu, T.-I.; Yu, T.-W.; Kv, R.; Chiang, W.-H.; Tsai, Y.-C.; Chen, H.-H.; Lin, S.-C.; Chiu, H.-C. Hierarchically targetable polysaccharide-coated solid lipid nanoparticles as an oral chemo/thermotherapy delivery system for local treatment of colon cancer. Biomaterials 2019, 197, 86–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbouAitah, K.; Hassan, H.A.; Swiderska-Sroda, A.; Gohar, L.; Shaker, O.G.; Wojnarowicz, J.; Opalinska, A.; Smalc-Koziorowska, J.; Gierlotka, S.; Lojkowski, W. Targeted nano-drug delivery of colchicine against colon cancer cells by means of mesoporous silica na-noparticles. Cancers 2020, 12, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Tan, J.; Liu, J.; Shan, X.; Ma, Y. Laser-triggered collaborative chemophotothermal effect of gold nanoparticles for targeted colon cancer therapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 130, 110492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Yuhan, J.; Yu, H.; Zhang, B.; Zhu, L.; He, X.; Huang, K.; Xu, W. Aptamer functionalized nucleic acid nano drug for targeted synergistic therapy for colon cancer. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanati, S.; Taghavi, S.; Abnous, K.; Taghdisi, S.M.; Babaei, M.; Ramezani, M.; Alibolandi, M. Fabrication of anionic dextran-coated micelles for aptamer targeted delivery of camptothecin and sur-vivin-shRNA to colon adenocarcinoma. Gene Ther. 2022, 29, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorat, N.D.; Bauer, J.; Tofail, S.A.; Pérez, V.G.; Bohara, R.A.; Yadav, H.M. Silica nano supra-assembly for the targeted delivery of therapeutic cargo to overcome chemoresistance in cancer. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 185, 110571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babaei, M.; Abnous, K.; Taghdisi, S.M.; Taghavi, S.; Saljooghi, A.S.; Ramezani, M.; Alibolandi, M. Targeted rod-shaped mesoporous silica nanoparticles for the co-delivery of camptothecin and survivin shRNA in to colon adenocarcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020, 156, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Li, X.; Duan, J.; Yang, X.-D. Targeted treatment of colon cancer with aptamer-guided albumin nanoparticles loaded with docetaxel. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 6737–6748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zappavigna, S.; Abate, M.; Cossu, A.M.; Lusa, S.; Campani, V.; Scotti, L.; Luce, A.; Yousif, A.M.; Merlino, F.; Grieco, P.; et al. Urotensin-II-Targeted Liposomes as a New Drug Delivery System towards Prostate and Colon Cancer Cells. J. Oncol. 2019, 2019, 9293560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wang, M.; He, H.; Li, J. Doxorubicin-Loaded Tumor-Targeting Peptide-Decorated Polypeptide Nanoparticles for Treating Primary Orthotopic Colon Cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 744811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinka, S.; Rachamalla, H.K.; Bhattacharyya, T.; Sridharan, K.; Jaggarapu, M.M.C.S.; Yakati, V.; Banerjee, R. Glucocorticoid receptor-targeted liposomal delivery system for delivering small molecule ESC8 and an-ti-miR-Hsp90 gene construct to combat colon cancer. Biomed. Mater. 2021, 16, 024105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahraki, N.; Mehrabian, A.; Amiri-Darban, S.; Moosavian, S.A.; Jaafari, M.R. Preparation and characterization of PEGylated liposomal Doxorubicin targeted with leptin-derived peptide and evaluation of their anti-tumor effects, in vitro and in vivo in mice bearing C26 colon carcinoma. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 200, 111589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biabangard, A.; Asoodeh, A.; Jaafari, M.R.; Mashreghi, M. Study of FA12 peptide-modified PEGylated liposomal doxorubicin (PLD) as an effective ligand to target Muc1 in mice bearing C26 colon carcinoma: In silico, in vitro, and in vivo study. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2022, 19, 1710–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biabangard, A.; Asoodeh, A.; Jaafari, M.R.; Baigi, F.M. AR13 peptide-conjugated liposomes improve the antitumor efficacy of doxorubicin in mice bearing C26 colon carcinoma; in silico, in vitro, and in vivo study. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2023, 466, 116470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, R.; Fu, R.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Feng, C.; Wang, R.; Yan, H.; Li, G.; Chu, X.; Yuan, F.; et al. Codelivery of TRAIL and Mitomycin C via Liposomes Shows Improved Antitumor Effect on TRAIL-Resistant Tumors. Mol. Pharm. 2023, 20, 2864–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scavo, M.P.; Cutrignelli, A.; Depalo, N.; Fanizza, E.; Laquintana, V.; Gasparini, G.; Giannelli, G.; Denora, N. Effectiveness of a controlled 5-fu delivery based on fzd10 antibody-conjugated liposomes in colorectal cancer in vitro models. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashreghi, M.; Zamani, P.; Moosavian, S.A.; Jaafari, M.R. Anti-Epcam Aptamer (Syl3c)-Functionalized Liposome for Targeted Delivery Of Doxorubicin: In Vitro And In Vivo Antitumor Studies in Mice Bearing C26 Colon Carcinoma. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Qin, B.; Luo, L.; Li, X.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, J.; Luo, Z.; Zhu, C.; Guan, G.; Du, Y.; et al. A clinically acceptable strategy for sensitizing anti-PD-1 treatment by hypoxia relief. J. Control. Release 2021, 335, 408–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nik, M.E.; Jaafari, M.R.; Mashreghi, M.; Nikoofal-Sahlabadi, S.; Amin, M.; Sadeghnia, H.R.; Iranshahi, M.; Navashenaq, J.G.; Malaekeh-Nikouei, B. The effect of RGD-targeted and non-targeted liposomal Galbanic acid on the therapeutic efficacy of pegylated liposomal doxorubicin: From liposomal preparation to in-vivo studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 604, 120710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clegg, J.R.; Sun, J.A.; Gu, J.; Venkataraman, A.K.; Peppas, N.A. Peptide conjugation enhances the cellular co-localization, but not endosomal escape, of modular poly(acrylamide-co-methacrylic acid) nanogels. J. Control. Release 2021, 329, 1162–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manturthi, S.; Bhattacharya, D.; Sakhare, K.R.; Narayan, K.P.; Patri, S.V. Cimetidine-Based Cationic Amphiphiles for in Vitro Gene Delivery Targetable to Colon Cancer. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 31388–31402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Huang, J.; Chen, J.; Yang, M.; Wang, H.; Qiao, H.; Chen, Z.; Hu, L.; Di, L.; Li, J. Enhanced anti-colon cancer efficacy of 5-fluorouracil by epigallocatechin-3- gallate co-loaded in wheat germ agglutinin-conjugated nanoparticles. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2019, 21, 102068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, H.I.; Lim, V. Wheat germ agglutinin-conjugated disulfide cross-linked alginate nanoparticles as a docetaxel carrier for colon cancer therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 2995–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.-F.; Zheng, D.; Zeng, S.-M.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, X.-Z. Targeting to Tumor-Harbored Bacteria for Precision Tumor Therapy. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 17402–17413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casillo, A.; Di Guida, R.; Cavasso, D.; Stellavato, A.; Rai, D.; Yokoyama, F.; Kamasaka, K.; Kawamoto, J.; Kurihara, T.; Schiraldi, C.; et al. Polysaccharide corona: The acetyl-rich envelope wraps the extracellular membrane vesicles and the cells of Shewanella vesiculosa providing adhesiveness. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 297, 120036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zuo, B.; Yu, Z.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, Y.; He, K.; Seow, Y.; Yin, H. Complete remission of tumors in mice with neoantigen-painted exosomes and anti-PD-1 therapy. Mol. Ther. 2023, 31, 3579–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahar, R.; Chakraborty, A.; Nainwal, N.; Bahuguna, R.; Sajwan, M.; Jakhmola, V. Application of PLGA as a Biodegradable and Biocompatible Polymer for Pulmonary Delivery of Drugs. AAPS PharmSciTech 2023, 24, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.-Y.; Yan, S.-Z.; Li, Q.; Xu, Q.; Lin, X.; Qi, S.-S.; Yu, S.-Q.; Chen, S.-L. Poly(lactic-: Co -glycolic) acid nanoparticles improve oral bioavailability of hypocrellin A in rat. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 42073–42082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davoudi, Z.; Peroutka-Bigus, N.; Bellaire, B.; Jergens, A.; Wannemuehler, M.; Wang, Q. Gut organoid as a new platform to study alginate and chitosan mediated plga nanoparticles for drug delivery. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonard, F.; Srinivasan, S.; Liu, X.; Collnot, E.-M.; Ferrari, M.; Lehr, C.-M.; Godin, B. Design and in vitro characterization of multistage silicon-PLGA budesonide particles for inflammatory bowel disease. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020, 151, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, W.; Yu, J.; Zheng, T.; Liu, P.; Zhao, F.; Liu, J.; Hong, Z.; Ren, H.; Gu, G.; Wang, G.; et al. CCL4-mediated targeting of spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk) inhibitor using nanoparticles alleviates inflammatory bowel disease. Clin. Transl. Med. 2021, 11, e339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Zhang, F.; Yang, C.; Wang, L.; Sung, J.; Garg, P.; Zhang, M.; Merlin, D. Oral targeted delivery by nanoparticles enhances efficacy of an Hsp90 inhibitor by reducing systemic exposure in murine models of colitis and colitis-associated cancer. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2020, 14, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, W.-L.; Wu, Q.; Hu, B.; Sun, D.; Zhao, S.; Shen, X.; Cheng, H.; Shen, W. Oral nanoparticles of snx10-shrna plasmids ameliorate mouse colitis. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeeshan, M.; Atiq, A.; Ain, Q.U.; Ali, J.; Khan, S.; Ali, H. Evaluating the mucoprotective effects of glycyrrhizic acid-loaded polymeric nanoparticles in a murine model of 5-fluorouracil-induced intestinal mucositis via suppression of inflammatory mediators and oxidative stress. Inflammopharmacology 2021, 29, 1539–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sufi, S.A.; Hoda, M.; Pajaniradje, S.; Mukherjee, V.; Coumar, S.M.; Rajagopalan, R. Enhanced drug retention, sustained release, and anti-cancer potential of curcumin and indole-curcumin ana-log-loaded polysorbate 80-stabilizied PLGA nanoparticles in colon cancer cell line SW480. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 588, 119738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimian, M.; Shahgordi, S.; Yazdian-Robati, R.; Etemad, L.; Hashemi, M.; Salmasi, Z. Targeted delivery of galbanic acid to colon cancer cells by PLGA nanoparticles incorporated into human mesenchymal stem cells. Avicenna J. Phytomed. 2022, 12, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handali, S.; Moghimipour, E.; Rezaei, M.; Ramezani, Z.; Dorkoosh, F.A. PHBV/PLGA nanoparticles for enhanced delivery of 5-fluorouracil as promising treatment of colon cancer. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2020, 25, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Zhu, W.; Yu, L.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, M.; Huang, J.; Shen, G.; Zhou, J.; Yao, H. TPGS2k-PLGA composite nanoparticles by depleting lipid rafts in colon cancer cells for overcoming drug resistance. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2021, 35, 102307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, M.; Liu, G.; Wang, J.; Zhao, X.; Qi, Y.; Shi, J.; Cheng, K.; et al. Reversing tumor stemness via orally targeted nanoparticles achieves efficient colon cancer treatment. Biomaterials 2019, 216, 119247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, M.Y.; Chang, S.H.; Liu, T.I.; Lu, T.Y.; Sabu, A.; Chen, H.H.; Chiu, H.C. Combo-targeted nanoassemblies as a chemotherapy delivery system against peritoneal carcinomatosis col-orectal cancer. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 3885–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, B.; Gaonkar, R.H.; Dutta, D.; Dasi, R.; Mukherjee, B.; Ganguly, S.; Das, S.K. Inhibitory potential of iRGD peptide-conjugated garcinol-loaded biodegradable nanoparticles in rat colorectal carcinoma. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 134, 112714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naserifar, M.; Hosseinzadeh, H.; Abnous, K.; Mohammadi, M.; Taghdisi, S.M.; Ramezani, M.; Alibolandi, M. Oral delivery of folate-targeted resveratrol-loaded nanoparticles for inflammatory bowel disease therapy in rats. Life Sci. 2020, 262, 118555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Xin, H.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, B.; Su, L.; Wang, S.; Zeng, J.; Chen, Q.; Deng, R.; et al. Mitochondria-targeting folic acid-modified nanoplatform based on mesoporous carbon and a bioactive peptide for improved colorectal cancer treatment. Acta Biomater. 2022, 152, 453–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkın, S.; Varan, G.; Aksüt, D.; Malanga, M.; Ercan, A.; Şen, M.; Bilensoy, E. A different approach to immunochemotherapy for colon Cancer: Development of nanoplexes of cyclodextrins and Interleukin-2 loaded with 5-FU. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 623, 121940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafiei, G.; Jafari-Gharabaghlou, D.; Farhoudi-Sefidan-Jadid, M.; Alizadeh, E.; Fathi, M.; Zarghami, N. Targeted delivery of silibinin via magnetic niosomal nanoparticles: Potential application in treatment of colon cancer cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1174120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghezzi, M.; Pescina, S.; Padula, C.; Santi, P.; Del Favero, E.; Cantù, L.; Nicoli, S. Polymeric micelles in drug delivery: An insight of the techniques for their characterization and assessment in biorelevant conditions. J. Control. Release 2021, 332, 312–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Ling, P.; Zhang, T. Polymeric Micelles, a Promising Drug Delivery System to Enhance Bioavailability of Poorly Wa-ter-Soluble Drugs. J. Drug. Deliv. 2013, 2013, 340315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, F.; Ma, J.-C.; Jia, J.; Li, F.-Z.; Wu, J.-L.; Wang, S.; Teng, X.; Cui, Z.-K. Synergistic effect of the anti-PD-1 antibody with blood stable and reduction sensitive curcumin micelles on colon cancer. Drug Deliv. 2021, 28, 930–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Chen, S.; Chen, C.; Ming, Y.; Du, J.; Mu, J.; Luo, F.; Huang, D.; Wang, N.; Lin, Z.; et al. Colon-targeted oral nanoparticles based on ROS-scavenging hydroxyethyl starch-curcumin conjugates for efficient inflammatory bowel disease therapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 623, 121884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banskota, S.; Saha, S.; Bhattacharyya, J.; Kirmani, N.; Yousefpour, P.; Dzuricky, M.; Zakharov, N.; Li, X.; Spasojevic, I.; Young, K.; et al. Genetically Encoded Stealth Nanoparticles of a Zwitterionic Polypeptide-Paclitaxel Conjugate Have a Wider Therapeutic Window than Abraxane in Multiple Tumor Models. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 2396–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajewska, J.B.; Pietruszka, P.; Tomczyk, D.; Chen, C.; Owczarek, A.; Karolewicz, B.; Czapor-Irzabek, H.; Gorniak, A.; Fichna, J. Evaluation of the effect of liposomes loaded with chlorogenic acid in treatment of 2,4,6-trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid-induced murine colitis. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2019, 70, 269–275. [Google Scholar]
- Alaaeldin, E.; Refaat, H.; Saber, E.A.; Aziz, N.M.; Abdel-Maqsoud, N.M.R.; El Aleem, M.M.A.; Kamel, M.Y.; Mady, F.M. Co-administration of Thymoquinone and Propolis in Liposomal Formulations as a Potential Approach for Treatment of Acetic Acid-Induced Ulcerative Colitis: Physiological and Histopathological Analysis. AAPS PharmSciTech 2023, 24, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, Y.; Wang, K.; Chen, J.; Zhuo, Z.; Xiu, Y. LiposomalN-acylethanolamine-hydrolyzing acid amidase (NAAA) inhibitor F96 as a new therapy for colitis. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 34197–34202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yang, C.; Yan, X.; Sung, J.; Garg, P.; Merlin, D. Highly Biocompatible Functionalized Layer-by-Layer Ginger Lipid Nano Vectors Targeting P-Selectin for Delivery of Doxorubicin to Treat Colon Cancer. Adv. Ther. 2019, 2, 1900129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodenak-Kladniew, B.; Castro, M.A.; Gambaro, R.C.; Girotti, J.; Cisneros, J.S.; Viña, S.; Padula, G.; Crespo, R.; Castro, G.R.; Gehring, S.; et al. Cytotoxic Screening and Enhanced Anticancer Activity of Lippia alba and Clinopodium nepeta Essential Oils-Loaded Biocompatible Lipid Nanoparticles against Lung and Colon Cancer Cells. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sesarman, A.; Tefas, L.; Sylvester, B.; Licarete, E.; Rauca, V.; Luput, L.; Patras, L.; Porav, S.; Banciu, M.; Porfire, A. Co-delivery of curcumin and doxorubicin in PEGylated liposomes favored the antineoplastic C26 murine colon carcinoma microenvironment. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2019, 9, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Hong, S.-S.; Lee, M.; Lee, E.-H.; Rhee, I.; Chang, S.-Y.; Lim, S.-J. Krill oil-incorporated liposomes as an effective nanovehicle to ameliorate the inflammatory responses of DSS-induced colitis. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 8305–8320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, J.; Alghoul, Z.; Long, D.; Yang, C.; Merlin, D. Oral delivery of IL-22 mRNA-loaded lipid nanoparticles targeting the injured intestinal mucosa: A novel therapeutic solution to treat ulcerative colitis. Biomaterials 2022, 288, 121707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, P.; Arora, A.; Rana, K.; Mehta, D.; Kar, R.; Verma, V.; Srikanth, C.V.; Patil, V.S.; Bajaj, A. Gemini lipid nanoparticle (GLNP)-mediated oral delivery of TNF-α siRNA mitigates gut inflammation via inhibiting the differentiation of CD4+ T cells. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 14717–14731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xian, S.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, H.; Wang, H. Oral liposomal delivery of an activatable budesonide prodrug reduces colitis in experimental mice. Drug Deliv. 2023, 30, 2183821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, Z.; He, Z.; Liu, H.; Liu, L.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y. Antioxidant Enzymes Sequestered within Lipid-Polymer Hybrid Nanoparticles for the Local Treatment of In-flammatory Bowel Disease. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 55966–55977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uda, R.M.; Yoshida, N.; Iwasaki, T.; Hayashi, K. PH-triggered solubility and cytotoxicity changes of malachite green derivatives incorporated in liposomes for killing cancer cells. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 8242–8248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Cai, T.; Huang, Y.; Xia, X.; Cole, S.P.C.; Cai, Y. A review of the structure, preparation, and application of NLCs, PNPs, and PLNs. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Sharma, S.; Wadhwa, J. Improved uptake and therapeutic intervention of curcumin via designing binary lipid nanoparticulate formulation for oral delivery in inflammatory bowel disorder. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boztepe, T.; Scioli-Montoto, S.; Gambaro, R.C.; Ruiz, M.E.; Cabrera, S.; Alemán, J.; Islan, G.A.; Castro, G.R.; León, I.E. Design, Synthesis, Characterization, and Evaluation of the Anti-HT-29 Colorectal Cell Line Activity of Novel 8-Oxyquinolinate-Platinum(II)-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers Targeted with Riboflavin. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makeen, H.A.; Mohan, S.; Al-Kasim, M.A.; Attafi, I.M.; Ahmed, R.A.; Syed, N.K.; Sultan, M.H.; Al-Bratty, M.; Alhazmi, H.A.; Safhi, M.M.; et al. Gefitinib loaded nanostructured lipid carriers: Characterization, evaluation and anti-human colon cancer activity in vitro. Drug Deliv. 2020, 27, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, Y.; Sym, S.J.; Yoo, B.K.; Baek, J.-H. Long-term Survival, Tolerability, and Safety of First-Line Bevacizumab and FOLFIRI in Combination with Ginsenoside-Modified Nanostructured Lipid Carrier Containing Curcumin in Patients with Unresectable Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2022, 21, 15347354221105498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almoshari, Y.; Iqbal, H.; Razzaq, A.; Ahmad, K.A.; Khan, M.K.; Alqahtani, S.S.; Sultan, M.H.; Khan, B.A. Development of nanocubosomes co-loaded with dual anticancer agents curcumin and temozolomide for effective colon cancer therapy. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 2633–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Huang, C.; Xu, Y. Colon cancer exosome-derived biomimetic nanoplatform for curcumin-mediated sonodynamic therapy and calcium overload. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 1069676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Zhu, Y.; Ali, D.J.; Tian, T.; Xu, H.; Si, K.; Sun, B.; Chen, B.; Xiao, Z. Engineered exosomes for targeted co-delivery of miR-21 inhibitor and chemotherapeutics to reverse drug resistance in colon cancer. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 18, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Chengalvala, V.; Hu, H.; Sun, D. Tumor-derived exosomes: Nanovesicles made by cancer cells to promote cancer metastasis. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 2136–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, B.; Lu, C.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Ji, H.; Li, X.; Xu, L.; Wang, J.; Tang, W.; et al. Engineered exosomes for co-delivery of PGM5-AS1 and oxaliplatin to reverse drug resistance in colon cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2022, 237, 911–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Shan, R.; Qi, T.; Yang, P. Berberine Reverses the Tumorigenic Function of Colon Cancer Cell-Derived Exosomes. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2023, 260, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, B.; Guo, F.; An, R.; Gao, Y.; Li, Y.; Xie, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Gao, T.; et al. Apoptotic tumor cell-derived microparticles loading Napabucasin inhibit CSCs and synergistic immune therapy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Han, M.; Chen, C.; Wang, X.; Han, J.; Gao, Y.; Wang, S. A biomimetic nanocomposite made of a ginger-derived exosome and an inorganic framework for high-performance delivery of oral antibodies. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 20157–20169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, M.; Zhang, G.; Gao, C.; Wang, S.; Zhang, T.; Ma, C.; Wang, L.; Zhu, Q. Micro- and Nanoencapsulated Hybrid Delivery System (MNEHDS): A Novel Approach for Colon-Targeted Oral Delivery of Berberine. Mol. Pharm. 2021, 18, 1573–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Ji, Y.; Hu, N.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Wu, F.; Xu, H.; Tang, Q.; Li, X. Ferroptosis-induced anticancer effect of resveratrol with a biomimetic nano-delivery system in colorectal cancer treatment. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 17, 751–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, R.H.; Kroll, A.V.; Gao, W.W.; Zhang, L.F. Cell Membrane Coating Nanotechnology. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1706759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Yan, J.; Li, Y.; Yan, S.; Wang, S.; Hou, P.; Lu, W. Resurrecting a p53 peptide activator—An enabling nanoengineering strategy for peptide therapeutics. J. Control. Release 2020, 325, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Yan, J.; Wang, L.; Lei, B.; Hou, P.; Lu, W.; Ma, P.X. A lanthanide-peptide-derived bacterium-like nanotheranostic with high tumor-targeting, -imaging and -killing properties. Biomaterials 2019, 206, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, Y.X.; Zhou, J.T.; Wang, T.T.; Huang, Y.F.; Chen, V.P.; Xie, Y.L.; Lin, Z.X.; Gao, J.S.; Su, Z.R.; Zeng, H.F. Self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system of bruceine D: A new approach for anti-ulcerative colitis. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 5887–5907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, S.; Pu, Y.; Li, S.; Xu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B. Beneficial anti-inflammatory effect of paeonol self-microemulsion-loaded colon-specific capsules on experimental ulcerative colitis rats. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 324–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, H.-F.; Yin, C.-M.; Ouyang, T.; Sun, S.-D.; Chen, W.-G.; Yang, X.-L.; He, X.; Zhang, C.-F. Self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system of genkwanin: A novel approach for anti-colitis-associated colorectal cancer. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2021, 15, 557–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khursheed, R.; Singh, S.K.; Wadhwa, S.; Gulati, M.; Awasthi, A.; Kumar, R.; Ramanunny, A.K.; Kapoor, B.; Kumar, P.; Corrie, L. Exploring role of probiotics and Ganoderma lucidum extract powder as solid carriers to solidify liquid self-nanoemulsifying delivery systems loaded with curcumin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 250, 116996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshahrani, S.M.; Alshetaili, A.S.; Alalaiwe, A.; Alsulays, B.B.; Anwer, M.K.; Al-Shdefat, R.; Imam, F.; Shakeel, F. Anticancer Efficacy of Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery System of Sunitinib Malate. AAPS PharmSciTech 2018, 19, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komesli, Y.; Ozkaya, A.B.; Ergur, B.U.; Kirilmaz, L.; Karasulu, E. Design and development of a self-microemulsifying drug delivery system of olmesartan medoxomil for enhanced bioavailability. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2019, 45, 1292–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, T.; Dou, Y.; Huang, Y.; Qu, C.; Gao, J.; Huang, Z.; Xie, Y.; Huang, P.; Lin, Z.; et al. Brusatol ameliorates 2, 4, 6-trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid-induced experimental colitis in rats: Involvement of NF-κB pathway and NLRP3 inflammasome. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 64, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, S. Advances in Oral Drug Delivery for Regional Targeting in the Gastrointestinal Tract—Influence of Physiological, Pathophysiological and Pharmaceutical Factors. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijewantha, N.; Eikanger, M.M.; Antony, R.M.; Potts, R.A.; Rezvani, K.; Sereda, G. Targeting Colon Cancer Cells with Enzyme-Triggered Casein-Gated Release of Cargo from Mesoporous Silica-Based Nanoparticles. Bioconjug. Chem. 2021, 32, 2353–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linskens, R.K.; Huijsdens, X.W.; Savelkoul, P.H.M.; Vandenbroucke-Grauls, C.M.J.E.; Meuwissen, S.G.M. The bacterial flora in inflammatory bowel disease: Current insights in pathogenesis and the influence of antibiotics and probiotics. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2001, 36, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maas, S.L.N.; Breakefield, X.O.; Weaver, A.M. Extracellular Vesicles: Unique Intercellular Delivery Vehicles. Trends Cell Biol. 2017, 27, 172–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini-Giv, N.; Basas, A.; Hicks, C.; El-Omar, E.; El-Assaad, F.; Hosseini-Beheshti, E. Bacterial extracellular vesicles and their novel therapeutic applications in health and cancer. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 962216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrina, C.D.; Perbellini, O.; Scupoli, M.T.; Tomelleri, C.; Zanetti, C.; Zoccatelli, G.; Fusi, M.; Peruffo, A.; Rizzi, C.; Chignola, R. Effects of wheat germ agglutinin on human gastrointestinal epithelium: Insights from an experimental model of immune/epithelial cell interaction. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 237, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brady, P.G.; Vannier, A.M.; Banwell, J.G. Identification of the dietary lectin, wheat germ agglutinin, in human intestinal contents. Gastroenterology 1978, 75, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balčiūnaitė-Murzienė, G.; Dzikaras, M. Wheat germ agglutinin—From toxicity to biomedical applications. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapar, N.; Saliakellis, E.; Benninga, M.A.; Borrelli, O.; Curry, J.; Faure, C.; De Giorgio, R.; Gupte, G.; Knowles, C.H.; Staiano, A.; et al. Paediatric Intestinal Pseudo-obstruction: Evidence and Consensus-based Recommendations from an ES-PGHAN-Led Expert Group. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2018, 66, 991–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viti, F.; De Giorgio, R.; Ceccherini, I.; Ahluwalia, A.; Alves, M.M.; Baldo, C.; Baldussi, G.; Bonora, E.; Borrelli, O.; Dall’oglio, L.; et al. Multi-disciplinary Insights from the First European Forum on Visceral Myopathy 2022 Meeting. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2023, 68, 3857–3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.; Almonti, V.; Cacopardo, L.; Poli, D.; Rapposelli, S.; Ahluwalia, A. Investigating curcumin/intestinal epithelium interaction in a millifluidic bioreactor. Bioengineering 2020, 7, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Parveen, R.; Chatterji, B.P. Toxicology of Nanoparticles in Drug Delivery. Curr. Pathobiol. Rep. 2021, 9, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniam, S.; Elz, A.; Wignall, A.; Kamath, S.; Ariaee, A.; Hunter, A.; Newblack, T.; Wardill, H.R.; Prestidge, C.A.; Joyce, P. Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS) disrupt the gut microbiota and trigger an intestinal inflammatory response in rats. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 648, 123614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naimi, S.; Viennois, E.; Gewirtz, A.T.; Chassaing, B. Direct impact of commonly used dietary emulsifiers on human gut micro-biota. Microbiome 2021, 9, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniam, S.; Kamath, S.; Ariaee, A.; Prestidge, C.; Joyce, P. The impact of common pharmaceutical excipients on the gut microbiota. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2023, 20, 1297–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
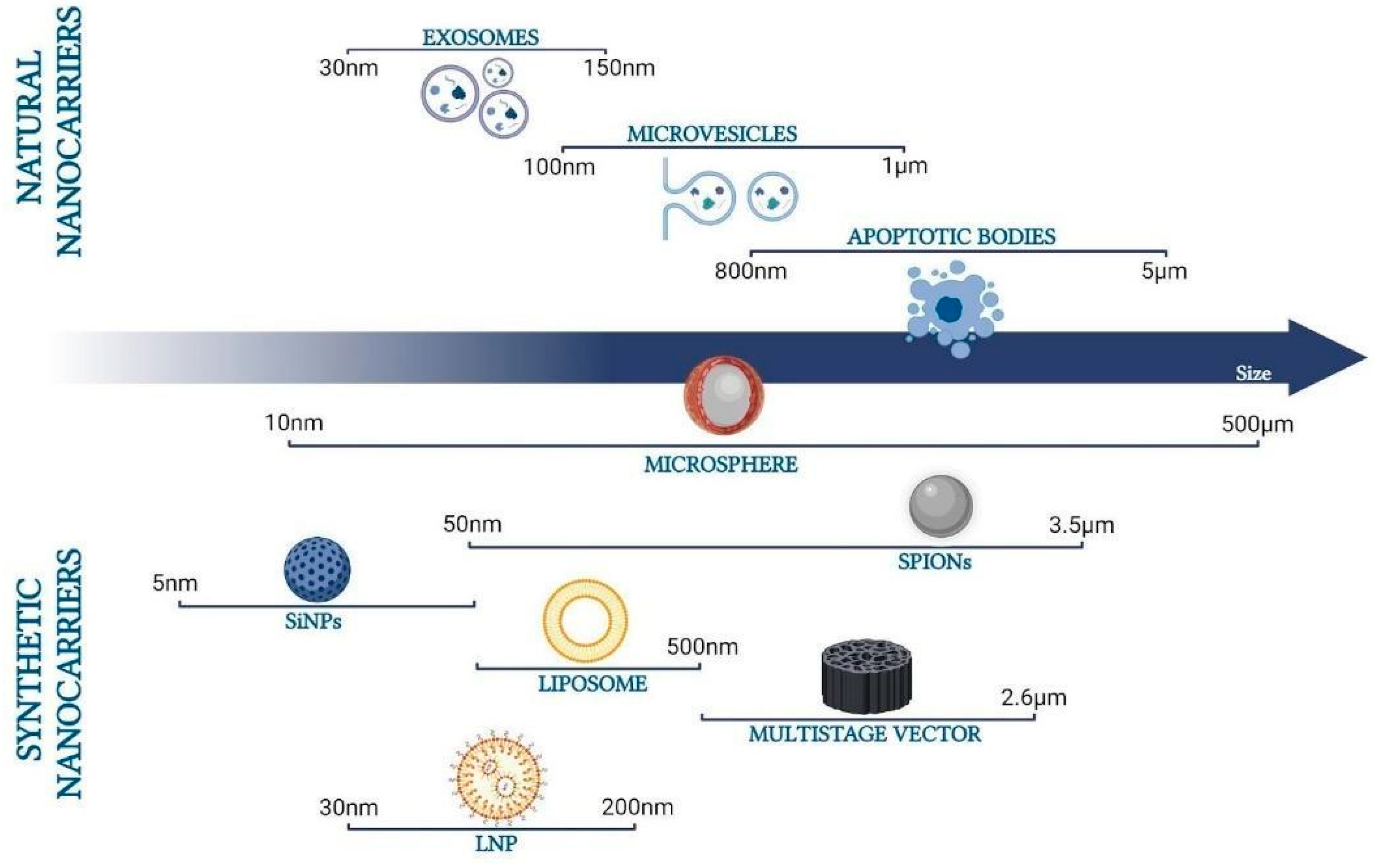

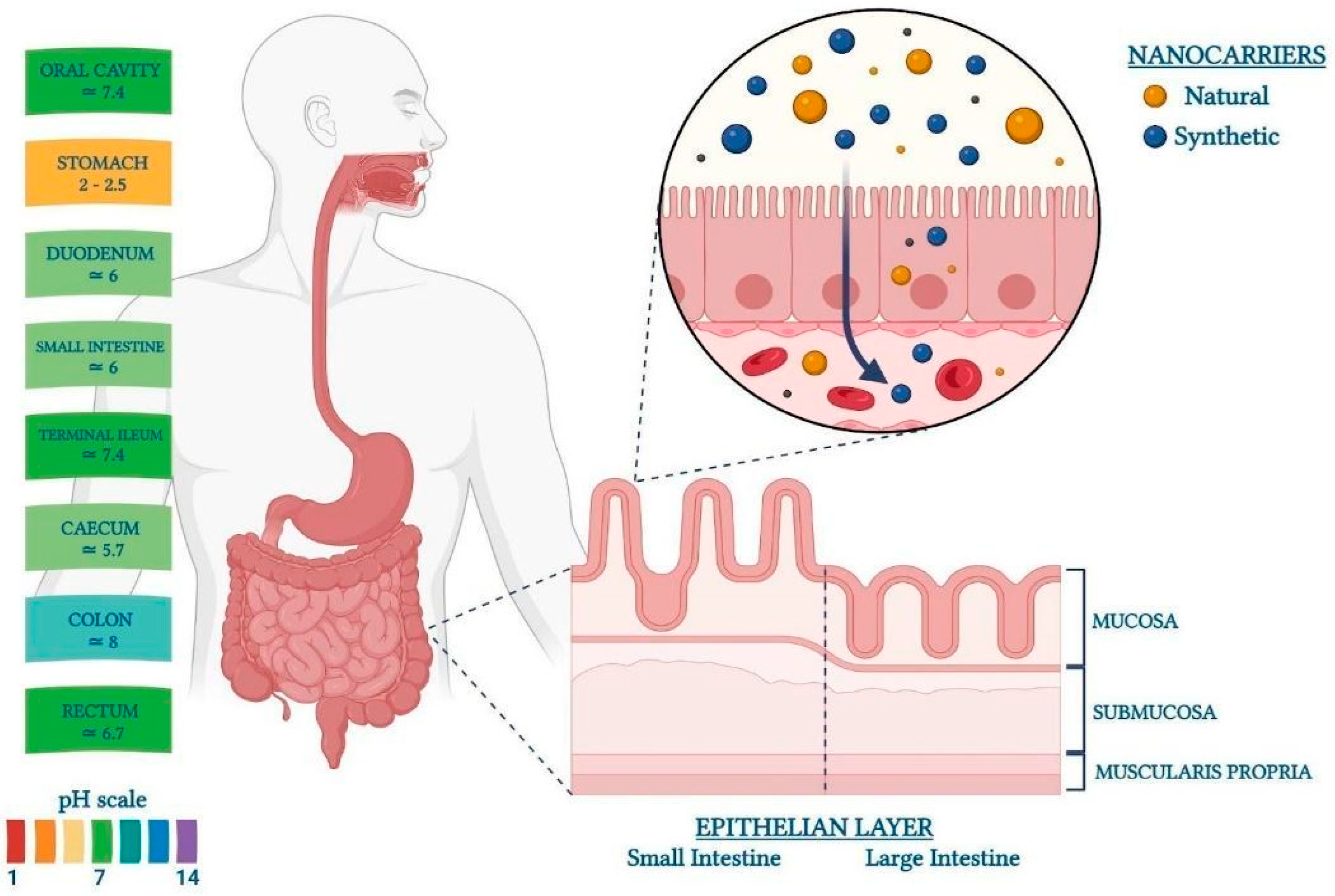
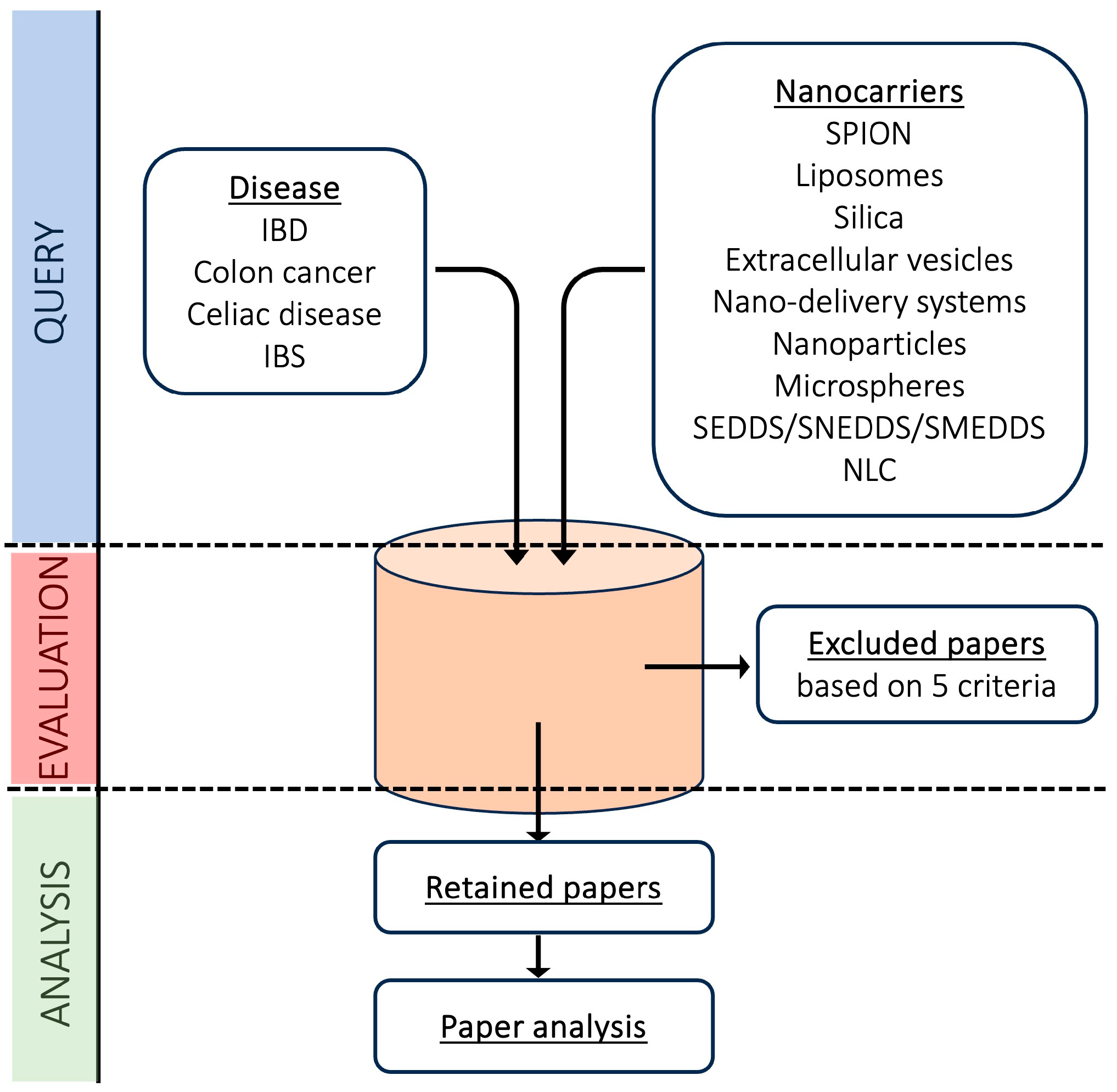


| SPIONs | Liposomes | Silica | “Extracellular Vesicles” and “Therapy” | Nano-Delivery Systems | Nanoparticles and “Drug Delivery” | Microspheres | NLCs | SEDDS/SNEEDS/SMEEDS | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exclusion process | pre | post | pre | post | pre | post | pre | post | Pre | post | pre | post | pre | post | pre | post | pre | post |
| IBD | 0 | 0 | 32 | 9 | 16 | 1 | 45 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 105 | 29 | 17 | 5 | 14 | 1 | 6 | 3 |
| Colon cancer | 4 | 3 | 85 | 35 | 60 | 36 | 45 | 7 | 5 | 1 | 227 | 140 | 16 | 8 | 41 | 7 | 4 | 3 |
| Celiac disease | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 18 * | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 |
| IBS | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 20 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9 * | 3 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Overexpressed Receptors | Specific Ligands |
|---|---|
| CD44 | HA |
| CD44v6 | AbD15179 (antibody fragment) |
| CD206 (mannose receptor) | Mannose |
| Nucleolin | AS1411 |
| EGFR (or HER1) | EGF and GE11 |
| Urotensin receptor | Urotensin |
| Folate receptor | FA |
| Vimentin | VATANST peptide |
| Muc1 | FA12 peptide and AR13 peptide |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garbati, P.; Picco, C.; Magrassi, R.; Signorello, P.; Cacopardo, L.; Dalla Serra, M.; Faticato, M.G.; De Luca, M.; Balestra, F.; Scavo, M.P.; et al. Targeting the Gut: A Systematic Review of Specific Drug Nanocarriers. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16030431
Garbati P, Picco C, Magrassi R, Signorello P, Cacopardo L, Dalla Serra M, Faticato MG, De Luca M, Balestra F, Scavo MP, et al. Targeting the Gut: A Systematic Review of Specific Drug Nanocarriers. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(3):431. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16030431
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarbati, Patrizia, Cristiana Picco, Raffaella Magrassi, Paolo Signorello, Ludovica Cacopardo, Mauro Dalla Serra, Maria Grazia Faticato, Maria De Luca, Francesco Balestra, Maria Principia Scavo, and et al. 2024. "Targeting the Gut: A Systematic Review of Specific Drug Nanocarriers" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 3: 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16030431
APA StyleGarbati, P., Picco, C., Magrassi, R., Signorello, P., Cacopardo, L., Dalla Serra, M., Faticato, M. G., De Luca, M., Balestra, F., Scavo, M. P., & Viti, F. (2024). Targeting the Gut: A Systematic Review of Specific Drug Nanocarriers. Pharmaceutics, 16(3), 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16030431








