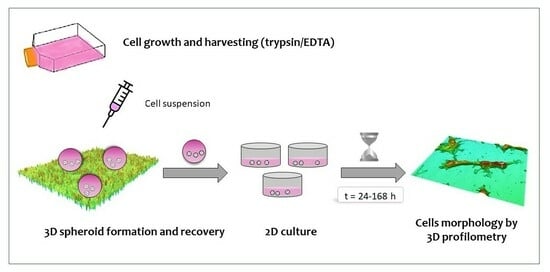
Spheroid Formation and Recovery Using Superhydrophobic Coating for Regenerative Purposes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Surface Preparation and Characterization
2.2.2. Cell Cultures
2.2.3. Cell Culture in Superhydrophobic Substrates
2.2.4. Spheroid Recovery and Growth under Standard 2D Conditions
2.2.5. Profilometry Studies
2.2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Surface Characterization
3.2. Spheroid Preparation
3.3. Spheroid Recovery
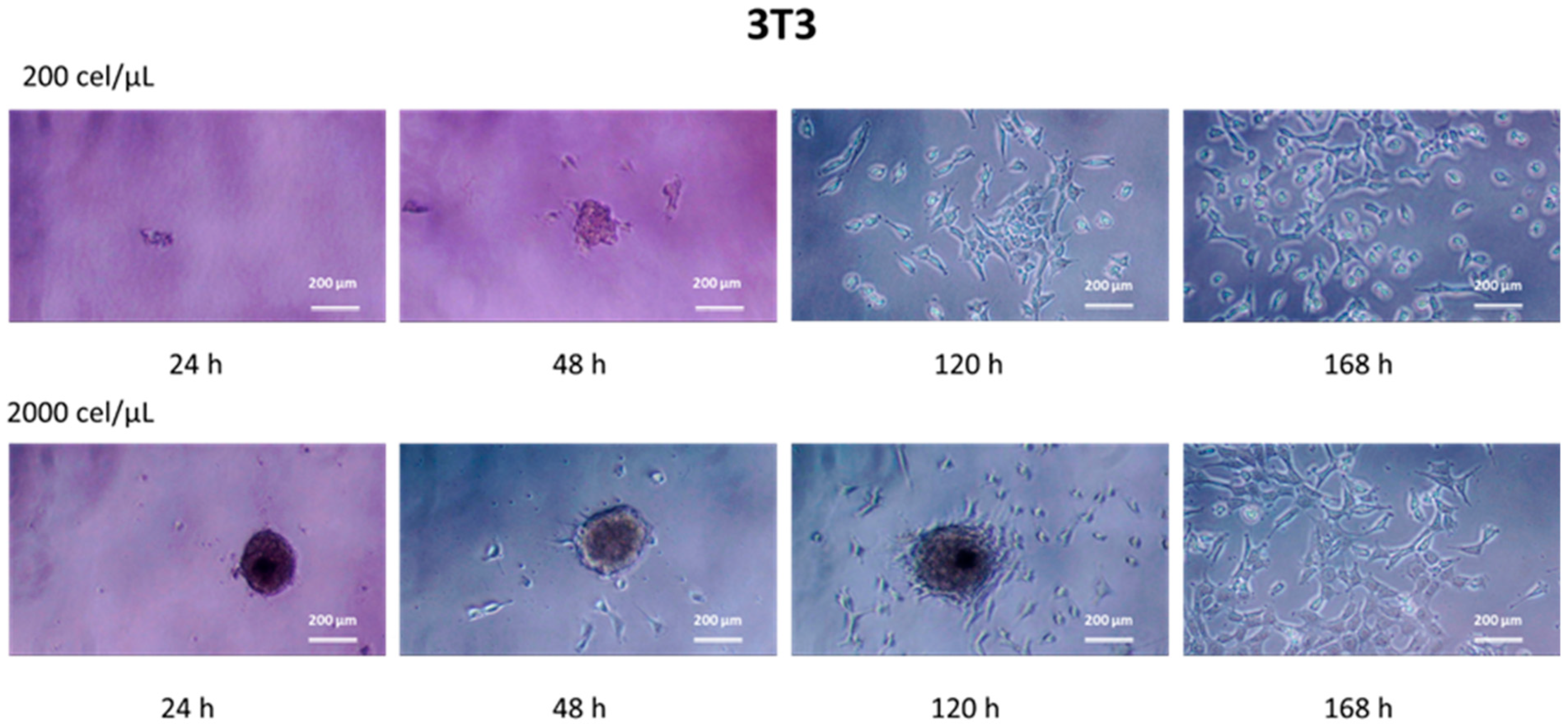
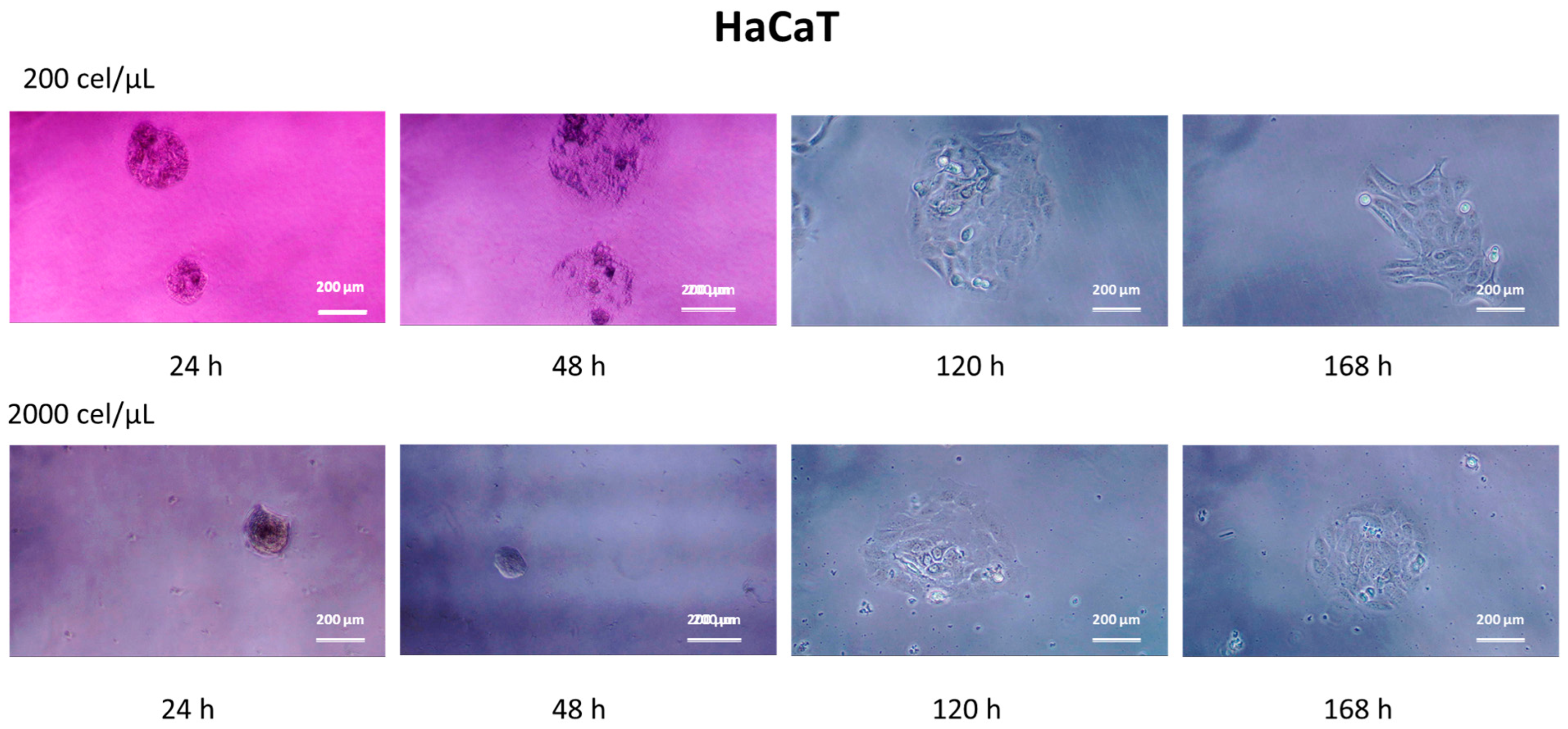
3.4. Cell Migration and Growth under 2D Conditions
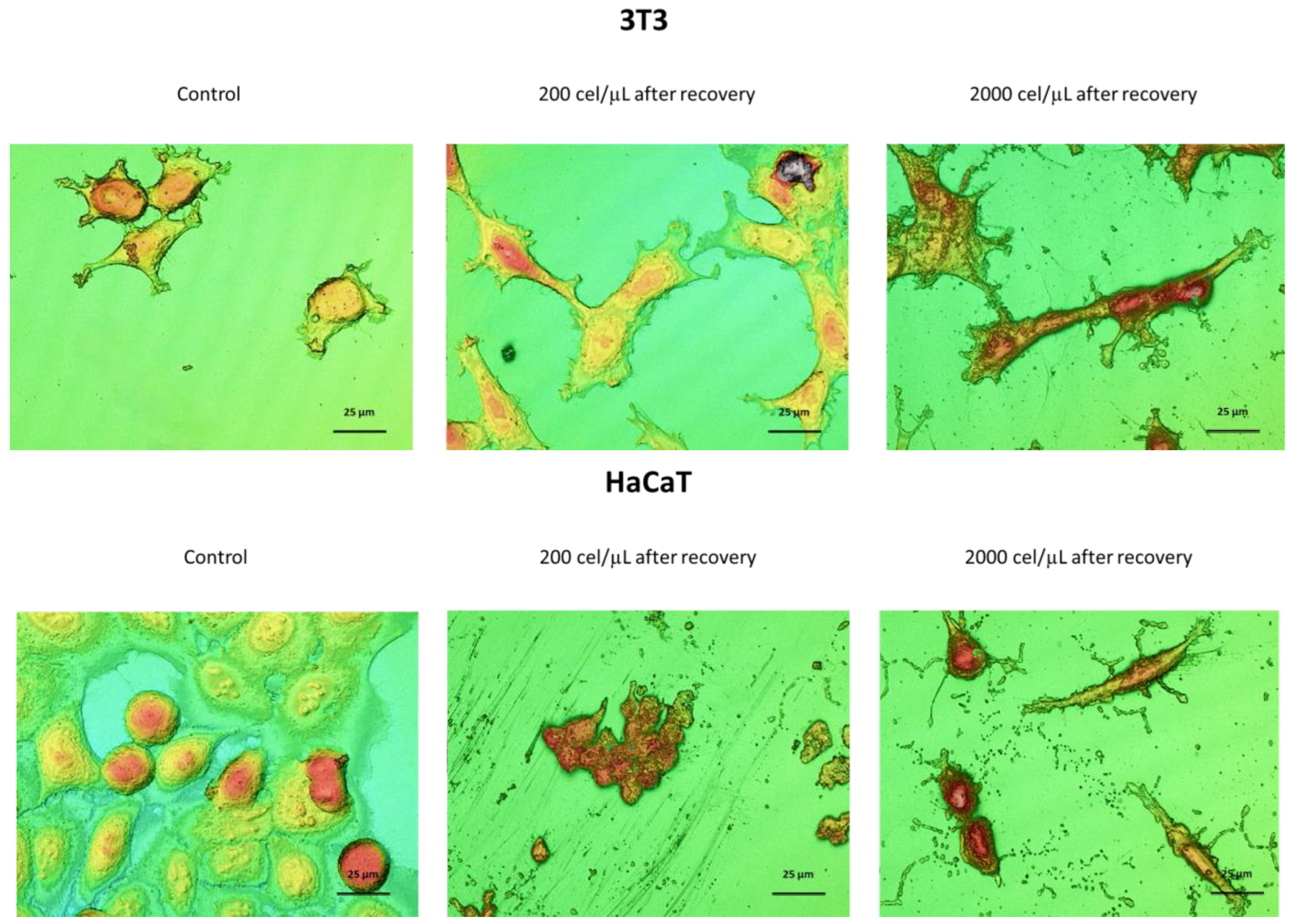
3.5. Morphological Characterization of Migrated Cells from the SHS-Derived Spheroids
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nosonovsky, M.; Bhushan, B. Energy transitions in superhydrophobicity: Low adhesion, easy flow and bouncing. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2008, 20, 395005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyal, S. Culture and assay systems used for 3D cell culture. Corning 2014, 9, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Liumbruno, G.; Bennardello, F.; Lattanzio, A.; Piccoli, P.; Rossetti, G. Recommendations for the transfusion of red blood cells. Blood Transfus. 2009, 7, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majhail, N.S.; Farnia, S.H.; Carpenter, P.A.; Champlin, R.E.; Crawford, S.; Marks, D.I.; Omel, J.L.; Orchard, P.J.; Palmer, J.; Saber, B.N.; et al. Indications for autologous and allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation: Guidelines from the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015, 21, 1863–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, H.; Connock, M.; Pink, J.; Shyangdan, D.; Clar, C.; Royle, P.; Court, R.; Biant, L.C.; Metcalfe, A.; Waugh, N. Autologous chondrocyte implantation in the knee: Systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol. Assess. 2017, 21, 1–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldari, S.; Di Rocco, G.; Piccoli, M.; Pozzobon, M.; Muraca, M.; Toietta, G. Challenges and strategies for improving the regenerative effects of mesenchymal stromal cell-based therapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moya, A.; Paquet, J.; Deschepper, M.; Larochette, N.; Oudina, K.; Denoeud, C.; Bensidhoum, M.; Logeart-Avramoglou, D.; Petite, H. Human mesenchymal stem cell failure to adapt to glucose shortage and rapidly use intracellular energy reserves through glycolysis explains poor cell survival after implantation. Stem Cells 2018, 36, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manassero, M.; Paquet, J.; Deschepper, M.; Viateau, V.; Retortillo, J.; Bensidhoum, M.; Logeart-Avramoglou, D.; Petite, H. Comparison of survival and osteogenic ability of human mesenchymal stem cells in orthotopic and ectopic sites in mice. Tissue Eng. Part A 2016, 22, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Methot, D.; Poppa, V.; Fujio, Y.; Walsh, K.; Murry, C.E. Cardiomyocyte grafting for cardiac repair: Graft cell death and anti-death strategies. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2001, 33, 907–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breslin, S.; O’Driscoll, L. Three-dimensional cell culture: The missing link in drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today 2013, 18, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.; Chi, J.; Zhang, H.; Fan, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Ye, F. Development of Cell Spheroids by Advanced Technologies. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2020, 5, 2000183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, M.; Cirisano, F.; Morán, M.C. Mammalian Cell Behavior on Hydrophobic Substrates: Influence of Surface Properties. Colloids Interfaces 2019, 3, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morán, M.C.; Ruano, G.; Cirisano, F.; Ferrari, M. Mammalian cell viability on hydrophobic and superhydrophobic fabrics. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 99, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, M.; Cirisano, F.; Morán, M.C. Regenerable Superhydrophobic Coatings for Biomedical Fabrics. Coatings 2020, 10, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, M.; Cirisano, F.; Morán, M.C. Super Liquid-repellent Surfaces and 3D Spheroids Growth. Front. Biosci. 2022, 27, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, M.; Cirisano, F.; Morán, M.C. Mammalian Cell Spheroids on Mixed Organic–Inorganic Superhydrophobic Coating. Molecules 2022, 27, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Shi, T.; Xu, A.; Zhang, L. 3D spheroid culture enhances survival and therapeutic capacities of MSCs injected into ischemic kidney. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2016, 20, 1203–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, K.; Grover, H.; Han, L.H.; Mou, Y.; Pegoraro, A.F.; Fredberg, J.; Chen, Z. Modeling Physiological Events in 2D vs. 3D Cell Culture. Physiology 2017, 32, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Follin, B.; Juhl, M.; Cohen, S.; Pedersen, A.E.; Kastrup, J.; Ekblond, A. Increased Paracrine Immunomodulatory Potential of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in Three-Dimensional Culture. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2016, 22, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicer, M.; Cottrell, G.S.; Widera, D. Impact of 3D cell culture on bone regeneration potential of mesenchymal stromal cells. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellaquila, A.; Le Bao, C.; Letourneur, D.; Simon-Yarza, T. In Vitro Strategies to Vascularize 3D Physiologically Relevant Models. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2100798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pampaloni, F.; Reynaud, E.G.; Stelzer, E.H.K. The third dimension bridges the gap between cell culture and live tissue. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urzì, O.; Gasparro, R.; Costanzo, E.; De Luca, A.; Giavaresi, G.; Fontana, S.; Alessandro, R. Three-Dimensional Cell Cultures: The Bridge between In Vitro and In Vivo Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.; Gwon, Y.; Park, S.; Kim, H.; Kim, J. Therapeutic strategies of three-dimensional stem cell spheroids and organoids for tissue repair and regeneration. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 19, 50–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Li, G. A Sessile Drop Method for Facile and Robust Spheroid Cultures. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 8, 2100972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Madden, L.A.; Paunov, V.N. Advanced biomedical applications based on emerging 3D cell culturing platforms. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 10487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, M.; Piccardo, P.; Vernet, J.; Cirisano, F. High transmittance superhydrophobic coatings with durable self-cleaning properties. Coatings 2021, 11, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liggieri, L.; Passerone, A. An automatic technique for measuring the surface tension of liquid metals. High Temp. Technol. 1989, 7, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plikus, M.V.; Wang, X.; Sinha, S.; Forte, E.; Thompson, S.M.; Herzog, E.L.; Driskell, R.R.; Rosenthal, N.; Biernaskie, J.; Horsley, V. Fibroblasts: Origins, definitions, and functions in health and disease. Cell 2021, 184, 3852–3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehman, T.A.; Modali, R.; Boukamp, P.; Stanek, J.; Bennett, W.P.; Welsh, J.A.; Metcalf, R.A.; Stampfer, M.R.; Fusenig, N.; Rogan, E.M.; et al. p53 mutations in human immortalized epithelial cell lines. Carcinogenesis 1993, 14, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinn, J.L.; Bondre, C.; Gladstone, H.B.; Brown, P.O.; Chang, H.Y. Anatomic demarcation by positional varia-tion in fibroblast gene expression programs. PLoS Genet. 2006, 2, e119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carson, S.; Miller, H.B.; Srougi, M.C.; Witherow, D.S. Molecular Biology Techniques: A Classroom Laboratory Manual; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Morán, M.C.; Cirisano, F.; Ferrari, M. 3D profilometry and cell viability studies for drug response screening. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 115, 111142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, J.; Chun, J.; Zangle, T.A.; Kalim, S.; Hong, J.S.; Pefley, S.E.; Zheng, X.; Gimzewski, J.K.; Teitell, M.A. Rapid, massively parallel single-cell drug response measurements via live cell interferometry. Biophys. J. 2011, 101, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermeulen, S.; Honig, F.; Vasilevich, A.; Roumans, N.; Romero, M.; Eren, A.D. Expanding Biomaterial Surface Topographical Design Space through Natural Surface Reproduction. Adv. Mat. 2021, 33, 2102084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, E.K.; Lambert, I.H.; Pedersen, S.F. Physiology of Cell Volume Regulation in Vertebrates. Physiol. Rev. 2009, 89, 193–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.Z.; Chang, H.Y. Recent advances in three-dimensional multicellular spheroid culture for biomedical research. Biotechnol. J. 2008, 3, 1172–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.Z.; Chou, L.F.; Chien, C.C.M.; Chang, H.Y. Dynamic analysis of hepatoma spheroid formation: Roles of E-cadherin and 1-integrin. Cell Tissue Res. 2006, 324, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, D.; Hu, Z.; Lu, L.; Lu, H.; Xu, X. Three-dimensional cell culture: A powerful tool in tumor research and drug discovery (Review). Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 6999–7010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, K.; Joensson, H.N. Rapid Production and Recovery of Cell Spheroids by Automated Droplet Microfluids. SLAS Technol. 2020, 25, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Białkowska, K.; Komorowski, P.; Bryszewska, M.; Miłowska, K. Spheroids as a Type of Three-Dimensional Cell Cultures-Examples of Methods of Preparation and the Most Important Application. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, A.; Lin, C.C. Generation and recovery of β-cell spheroids from step-growth PEG-peptide hydrogels. J. Vis. Exp. 2012, 70, e50081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sart, S.; Tomasi, R.F.X.; Amselem, G.; Baroud, C.N. Multiscale Cytometry and Regulation of 3D Cell Cultures on a Chip. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Kumacheva, E. Hydrogel Microenvironments for Cancer Spheroid Growth and Drug Screening. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaas8998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otsuji, T.G.; Bin, J.; Yoshimura, A.; Tomura, M.; Tateyama, D.; Minami, I.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Aiba, K.; Heuser, J.E.; Nishino, T.; et al. A 3D Sphere Culture System Containing Functional Polymers for Large-Scale Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Production. Stem Cell Rep. 2014, 2, 734–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Yu, Y.; Hu, Y.; He, X.; Berk Usta, O.; Yarmush, M.L. Generation and Manipulation of Hydrogel Microcapsules by Droplet-Based Microfluidics for Mammalian Cell Culture. Lab. Chip. 2017, 17, 1913–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Xiu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Pan, W.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, X. A 3D Printed Hanging Drop Dripper for Tumor Spheroids Analysis without Recovery. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case Study. Morphological Surface Analysis to Study Cell Viability Induced by Proliferative and Toxic Treatments. Available online: https://www.sensofar.com/cs28-morphological-analysis-cell-viability/ (accessed on 6 March 2023).
- Ishizaki, T.; Saito, N.; Takai, O. Correlation of Cell Adhesive Behaviors on Superhydrophobic, Superhydrophilic, and Micropatterned Superhydrophobic/Superhydrophilic Surfaces to Their Surface Chemistry. Langmuir 2010, 26, 8147–8154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
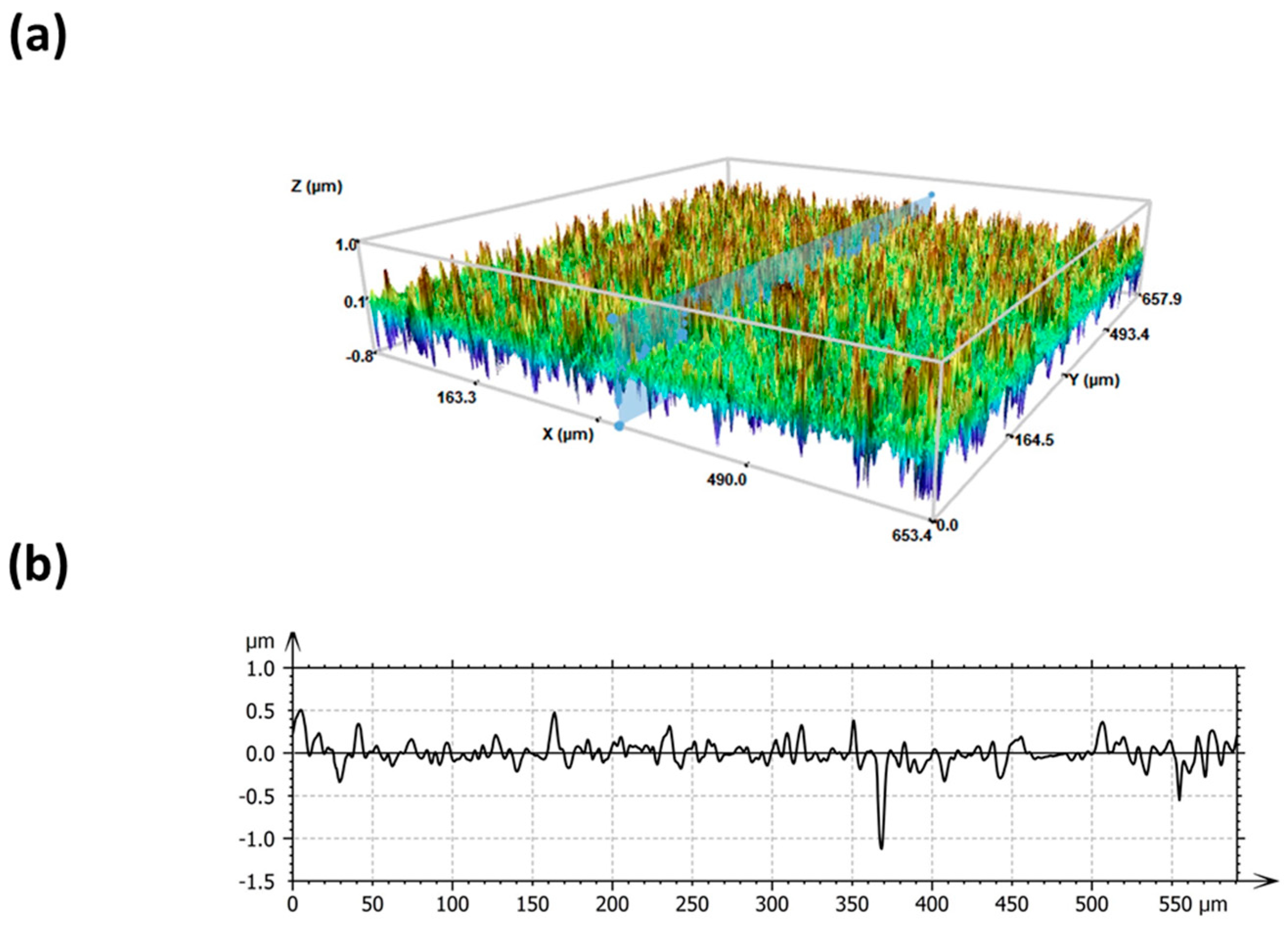


| Sample | Surface Factor | Height (µm) | Volume (µm3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 1.72 ± 0.50 | 1.59 ± 0.11 | 446.25 ± 68.25 |
| 3T3 200 cel/µL | 2.61 ± 0.64 ** | 0.93 ± 0.26 ** | 300 ± 49.44 ** |
| 2000 cel/µL | 3.24 ± 0.18 **●● | 4.1 ± 0.63 **●● | 1245.70 ± 163.68 **●● |
| Control | 1.05 ± 0.04 | 1.91± 0.08 | 392.40 ± 86.26 |
| HaCaT 200 cel/µL | 1.31 ± 0.14 * | 3.39 ± 1.37 ** | 315.40 ± 112.85 ** |
| 2000 cel/µL | 6.98 ± 0.06 **●● | 4.29 ± 0.64 **●● | 956.70 ± 257.81 **●● |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morán, M.d.C.; Cirisano, F.; Ferrari, M. Spheroid Formation and Recovery Using Superhydrophobic Coating for Regenerative Purposes. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2226. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15092226
Morán MdC, Cirisano F, Ferrari M. Spheroid Formation and Recovery Using Superhydrophobic Coating for Regenerative Purposes. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(9):2226. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15092226
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorán, María del Carmen, Francesca Cirisano, and Michele Ferrari. 2023. "Spheroid Formation and Recovery Using Superhydrophobic Coating for Regenerative Purposes" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 9: 2226. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15092226
APA StyleMorán, M. d. C., Cirisano, F., & Ferrari, M. (2023). Spheroid Formation and Recovery Using Superhydrophobic Coating for Regenerative Purposes. Pharmaceutics, 15(9), 2226. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15092226