A Rational Approach to Predicting Immediate Release Formulation Behavior in Multiple Gastric Motility Patterns: A Combination of a Biorelevant Apparatus, Design of Experiments, and Machine Learning †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Dissolution in PhysioCell
2.2.1. Apparatus
2.2.2. Dissolution Test Conditions
2.3. Software
2.4. Matrix of Dissolution Tests
2.5. Modeling and Evaluation of Dissolution Profiles
2.5.1. DoE Model of Drug Dissolution
2.5.2. Classification Model: Logistic Regression Algorithm
2.5.3. Regression Model: Random Forest Algorithm
2.5.4. Evaluation of the Predicted Dissolution Profiles
2.5.5. Simulating Dissolution Profiles for Customizable IS Parameters
3. Results
3.1. Dissolution Results
3.2. The Predictions of the Verification Test Set
3.3. Simulation of Dissolution under Customizable IS Parameters
3.3.1. Impact of the IS Stress Magnitude
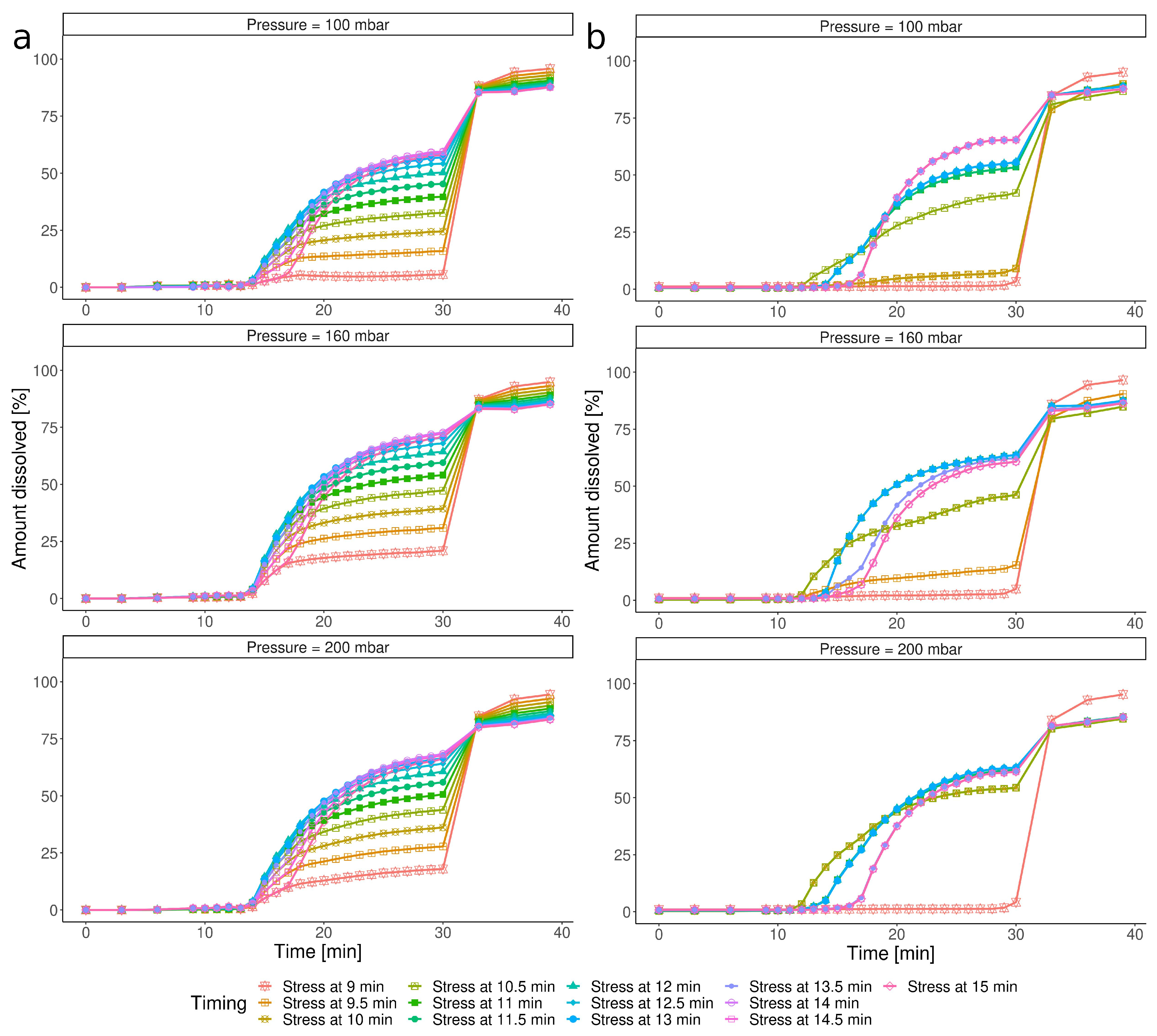
3.3.2. Impact of the Timing of the IS Stress
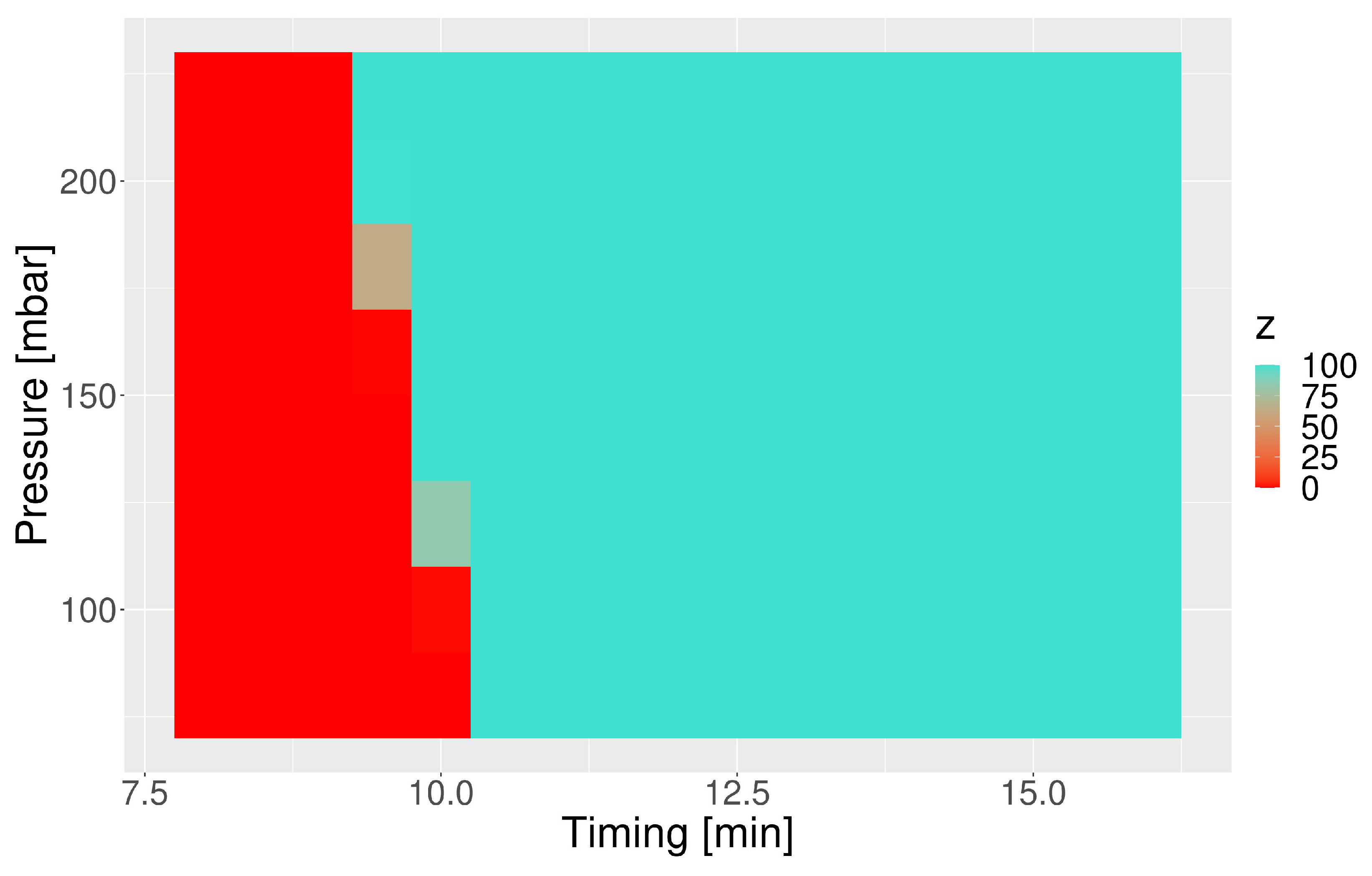
3.4. Susceptibility of the Capsule towards the IS Timing and Pressure
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CCD | central composite design |
| DoE | design of experiments |
| ER | extended-release |
| GE | gastric emptying |
| GI | gastrointestinal |
| IR | immediate-release |
| IS | intragastric stress |
| IVIVP | in vitro–in vivo predictions |
| MAE | mean absolute error |
| MDPI | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| ML | machine learning |
| PK | pharmacokinetic |
| RMSE | root mean square error |
| RSM | response surface methodology |
| SD | standard deviation |
| SGF | simulated gastric fluid |
| SIF | simulated intestinal fluid |
| VBE | virtual bioequivalence |
References
- Shrivas, M.; Khunt, D.; Shrivas, M.; Choudhari, M.; Rathod, R.; Misra, M. Advances in In Vivo Predictive Dissolution Testing of Solid Oral Formulations: How Closer to In Vivo Performance? J. Pharm. Innov. 2020, 15, 296–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lex, T.R.; Rodriguez, J.D.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, W.; Gao, Z. Development of In Vitro Dissolution Testing Methods to Simulate Fed Conditions for Immediate Release Solid Oral Dosage Forms. AAPS J. 2022, 24, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, S. Advancements in Dissolution Testing of Oral and Non-oral Formulations. AAPS PharmSciTech 2019, 20, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, J.; Hens, B.; Vertzoni, M.; Brouwers, J.; Berben, P.; Dressman, J.; Andreas, C.J.; Schaefer, K.J.; Mann, J.; McAllister, M.; et al. In vitro models for the prediction of in vivo performance of oral dosage forms: Recent progress from partnership through the IMI OrBiTo collaboration. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 136, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, F.; Grimm, M.; Koziolek, M.; Modeß, C.; Dokter, A.; Roustom, T.; Siegmund, W.; Weitschies, W. Resolving the physiological conditions in bioavailability and bioequivalence studies: Comparison of fasted and fed state. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 108, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kong, F. Simulating human gastrointestinal motility in dynamic in vitro models. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 3804–3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohylyuk, V.; Goldoozian, S.; Andrews, G.P.; Dashevskiy, A. IVIVC for Extended Release Hydrophilic Matrix Tablets in Consideration of Biorelevant Mechanical Stress. Pharm. Res. 2020, 37, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takieddin, M.; Fassihi, R. A Novel Approach in Distinguishing Between Role of Hydrodynamics and Mechanical Stresses Similar to Contraction Forces of GI Tract on Drug Release from Modified Release Dosage Forms. AAPS PharmSciTech 2015, 16, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schick, P.; Sager, M.; Voelker, M.; Weitschies, W.; Koziolek, M. Application of the GastroDuo to study the interplay of drug release and gastric emptying in case of immediate release Aspirin formulations. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020, 151, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Ngo, C.; Ye, W.; Rodriguez, J.D.; Keire, D.; Sun, D.; Wen, H.; Jiang, W. Effects of Dissolution Medium pH and Simulated Gastrointestinal Contraction on Drug Release From Nifedipine Extended-Release Tablets*. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 1189–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiya, P.; Rojviriya, C.; Pichayakorn, W.; Phaechamud, T. New Insight into the Impact of Effervescence on Gel Layer Microstructure and Drug Release of Effervescent Matrices Using Combined Mechanical and Imaging Characterisation Techniques. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbacz, G.; Wedemeyer, R.S.; Nagel, S.; Giessmann, T.; Mönnikes, H.; Wilson, C.G.; Siegmund, W.; Weitschies, W. Irregular absorption profiles observed from diclofenac extended release tablets can be predicted using a dissolution test apparatus that mimics in vivo physical stresses. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 70, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbacz, G.; Klein, S.; Weitschies, W. A biorelevant dissolution stress test device – background and experiences. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2010, 7, 1251–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sager, M.; Schick, P.; Mischek, M.; Schulze, C.; Hasan, M.; Kromrey, M.L.; Benameur, H.; Wendler, M.; Tzvetkov, M.V.; Weitschies, W.; et al. Comparison of In Vitro and In Vivo Results Using the GastroDuo and the Salivary Tracer Technique: Immediate Release Dosage Forms under Fasting Conditions. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrbanac, H.; Trontelj, J.; Berglez, S.; Petek, B.; Opara, J.; Jereb, R.; Krajcar, D.; Legen, I. The biorelevant simulation of gastric emptying and its impact on model drug dissolution and absorption kinetics. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020, 149, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schick, P.; Sager, M.; Wegner, F.; Wiedmann, M.; Schapperer, E.; Weitschies, W.; Koziolek, M. Application of the GastroDuo as an in Vitro Dissolution Tool To Simulate the Gastric Emptying of the Postprandial Stomach. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 4651–4660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, M.; Koziolek, M.; Kühn, J.P.; Weitschies, W. Interindividual and intraindividual variability of fasted state gastric fluid volume and gastric emptying of water. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 127, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, F.; Beeck, R.; Hoppe, M.; Koziolek, M.; Weitschies, W. In vitro simulation of realistic gastric pressure profiles. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 107, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minekus, M. The TNO Gastro-Intestinal Model (TIM); Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, M.; Faulks, R.; Mann, J.; Mandalari, G. The design, operation, and application of a dynamic gastric model. Dissolution Technol. 2012, 19, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, D.C. Design and Analysis of Experiments, 9th ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ilzarbe, L.; Álvarez, M.J.; Viles, E.; Tanco, M. Practical applications of design of experiments in the field of engineering: A bibliographical review. Qual. Reliab. Eng. Int. 2008, 24, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politis, S.N.; Colombo, P.; Colombo, G.; Rekkas, D.M. Design of experiments (DoE) in pharmaceutical development. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2017, 43, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, M.A.; Santelli, R.E.; Oliveira, E.P.; Villar, L.S.; Escaleira, L.A. Response surface methodology (RSM) as a tool for optimization in analytical chemistry. Talanta 2008, 76, 965–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujtaba, A.; Ali, M.; Kohli, K. Statistical optimization and characterization of pH-independent extended-release drug delivery of cefpodoxime proxetil using Box–Behnken design. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2014, 92, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malladi, M.; Jukanti, R. Formulation development and evaluation of a novel bi-dependent clarithromycin gastroretentive drug delivery system using Box-Behnken design. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2016, 35, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, P.; Rastogi, V.; Verma, A. Application of Box–Behnken design and desirability function in the development and optimization of self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system for enhanced dissolution of ezetimibe. Future J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Shi, S.; He, J.; Deng, J.; Ji, J. Development of In Vivo Predictive pH-Gradient Biphasic Dissolution Test for Weakly Basic Drugs: Optimization by Orthogonal Design. Dissolution Technol. 2021, 28, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z. In Vitro Dissolution Testing of Gelatin Capsules with Applied Mechanical Compression—A Technical Note. AAPS PharmSciTech 2017, 18, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkart, N.; Huber, M.F. A Survey on the Explainability of Supervised Machine Learning. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2020, 70, 245–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, L.; Shukla, T.; Huang, X.; Ussery, D.W.; Wang, S. Machine Learning Methods in Drug Discovery. Molecules 2020, 25, 5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannigan, P.; Aldeghi, M.; Bao, Z.; Häse, F.; Aspuru-Guzik, A.; Allen, C. Machine learning directed drug formulation development. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 175, 113806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendyk, A.; Tuszyński, P.; Polak, S.; Jachowicz, R. Generalized in vitro-in vivo relationship (IVIVR) model based on artificial neural networks. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2013, 7, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staniszewska, M.; Romański, M.; Dobosz, J.; Kołodziej, B.; Lipski, U.; Garbacz, G.; Danielak, D. PhysioCell®;—A Novel, Bio-relevant Dissolution Apparatus: Hydrodynamic Conditions and Factors Influencing the Dissolution Dynamics. AAPS PharmSciTech 2023, 24, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbacz, G.; Rappen, G.M.; Koziolek, M.; Weitschies, W. Dissolution of mesalazine modified release tablets under standard and bio-relevant test conditions. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2015, 67, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbacz, G.; Cadé, D.; Benameur, H.; Weitschies, W. Bio-relevant dissolution testing of hard capsules prepared from different shell materials using the dynamic open flow through test apparatus. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 57, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haznar-Garbacz, D.; Hoc, D.; Garbacz, G.; Lachman, M.; Słomińska, D.; Romański, M. Dissolution of a Biopharmaceutics Classification System Class II Free Acid from Immediate Release Tablets Containing a Microenvironmental pH Modulator: Comparison of a Biorelevant Bicarbonate Buffering System with Phosphate Buffers. AAPS PharmSciTech 2022, 23, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, J.; Dressman, J.; Rosenblatt, K.; Ashworth, L.; Muenster, U.; Frank, K.; Hutchins, P.; Williams, J.; Klumpp, L.; Wielockx, K.; et al. Validation of Dissolution Testing with Biorelevant Media: An OrBiTo Study. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 4192–4201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyota, T.; Kambayashi, A.; Takagi, T.; Yamashita, S. Importance of Gastric Secretion and the Rapid Gastric Emptying of Ingested Water along the Lesser Curvature (“Magenstraße”) in Predicting the In Vivo Performance of Liquid Oral Dosage Forms in the Fed State Using a Modeling and Simulation. Mol. Pharm. 2022, 19, 642–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romański, M.; Staniszewska, M.; Paszkowska, J.; Dobosz, J.; Romanova, S.; Pieczuro, J.; Kątny, M.; Roznerska, D.; Szczepański, J.; Schraube, M.; et al. Application of a novel PhysioCell apparatus for biopredictive dissolution tests of oral immediate release formulations—A case study workflow for in vitro-in vivo predictions. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 641, 123061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nestorowicz, M.; Staniszewska, M.; Paszkowska, J.; Garbacz, G.; Banach, G.; Dobosz, J. A Device for Placing a Pharmaceutical Dosage form. Poland P.444367, 14 February 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Develve Software. [Homepage on the Internet]. Available online: https://develve.net/ (accessed on 7 June 2023).
- Frank, E.; Hall, M.A.; Witten, I.H. The WEKA Workbench. Online Appendix for “Data Mining: Practical Machine Learning Tools and Techniques”, 4th ed.; Morgan Kaufmann: Burlington, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Waikato Environment for Knowledge Analysis. [Homepage on the Internet]. Available online: Https://www.cs.waikato.ac.nz/ml/index.html (accessed on 7 June 2023).
- Shohin, I.E.; Kulinich, J.I.; Ramenskaya, G.V.; Abrahamsson, B.; Kopp, S.; Langguth, P.; Polli, J.E.; Shah, V.P.; Groot, D.; Barends, D.M.; et al. Biowaiver Monographs for Immediate-Release Solid Oral Dosage Forms: Ketoprofen. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 101, 3593–3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercuri, A.; Pagliari, M.; Baxevanis, F.; Fares, R.; Fotaki, N. Understanding and predicting the impact of critical dissolution variables for nifedipine immediate release capsules by multivariate data analysis. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 518, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carapeto, G.V.; Duque, M.D.; Issa, M.G.; Ferraz, H.G. Development of Biopredictive Dissolution Method for Extended-Release Desvenlafaxine Tablets. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Peng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Shukla, A.J. Application of artificial neural networks in the design of controlled release drug delivery systems. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2003, 55, 1201–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freiesleben, J.; Keim, J.; Grutsch, M. Machine learning and Design of Experiments: Alternative approaches or complementary methodologies for quality improvement? Qual. Reliab. Eng. Int. 2020, 36, 1837–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilde, L.; Bock, M.; Glöckl, G.; Garbacz, G.; Weitschies, W. Development of a pressure-sensitive glyceryl tristearate capsule filled with a drug-containing hydrogel. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 461, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, J.; Bogdahn, M.; Schneider, F.; Koziolek, M.; Weitschies, W. Design and characterization of a novel 3D printed pressure-controlled drug delivery system. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 140, 105060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbacz, G.; Golke, B.; Wedemeyer, R.S.; Axell, M.; Söderlind, E.; Abrahamsson, B.; Weitschies, W. Comparison of dissolution profiles obtained from nifedipine extended release once a day products using different dissolution test apparatuses. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 38, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klančar, U.; Horvat, M.; Baumgartner, S. Correlating cellulose derivative intrinsic viscosity with mechanical susceptibility of swollen hydrophilic matrix tablets. Aaps Pharmscitech 2012, 13, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juszczyk, E.; Kisło, K.; Żero, P.; Tratkiewicz, E.; Wieczorek, M.; Paszkowska, J.; Banach, G.; Wiater, M.; Hoc, D.; Garbacz, G.; et al. Development and Bio-Predictive Evaluation of Biopharmaceutical Properties of Sustained-Release Tablets with a Novel GPR40 Agonist for a First-in-Human Clinical Trial. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bego, M.; Patel, N.; Cristofoletti, R.; Rostami-Hodjegan, A. Proof of Concept in Assignment of Within-Subject Variability During Virtual Bioequivalence Studies: Propagation of Intra-Subject Variation in Gastrointestinal Physiology Using Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling. AAPS J. 2022, 24, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loisios-Konstantinidis, I.; Cristofoletti, R.; Fotaki, N.; Turner, D.B.; Dressman, J. Establishing virtual bioequivalence and clinically relevant specifications using in vitro biorelevant dissolution testing and physiologically-based population pharmacokinetic modeling. case example: Naproxen. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 143, 105170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
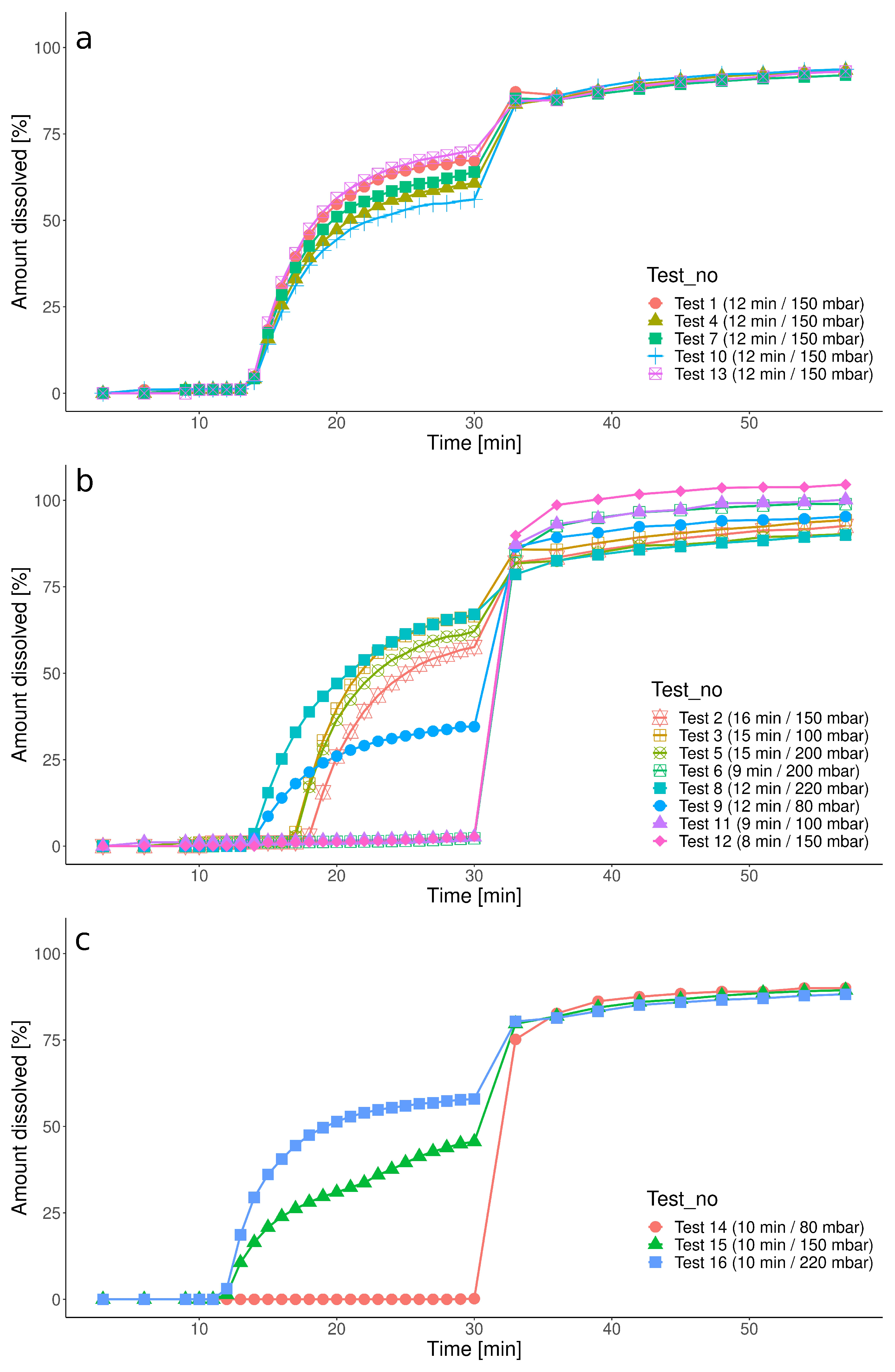
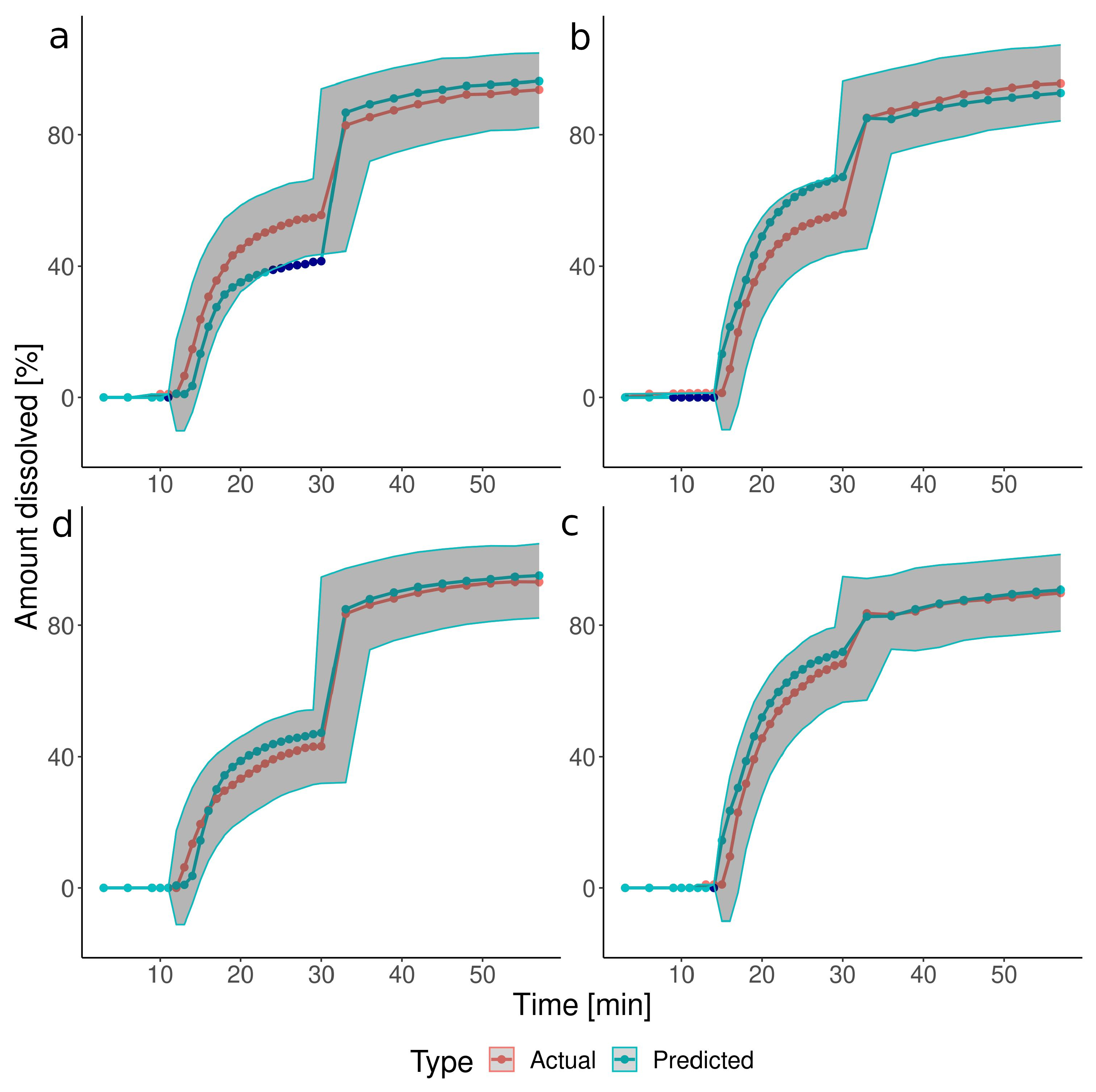
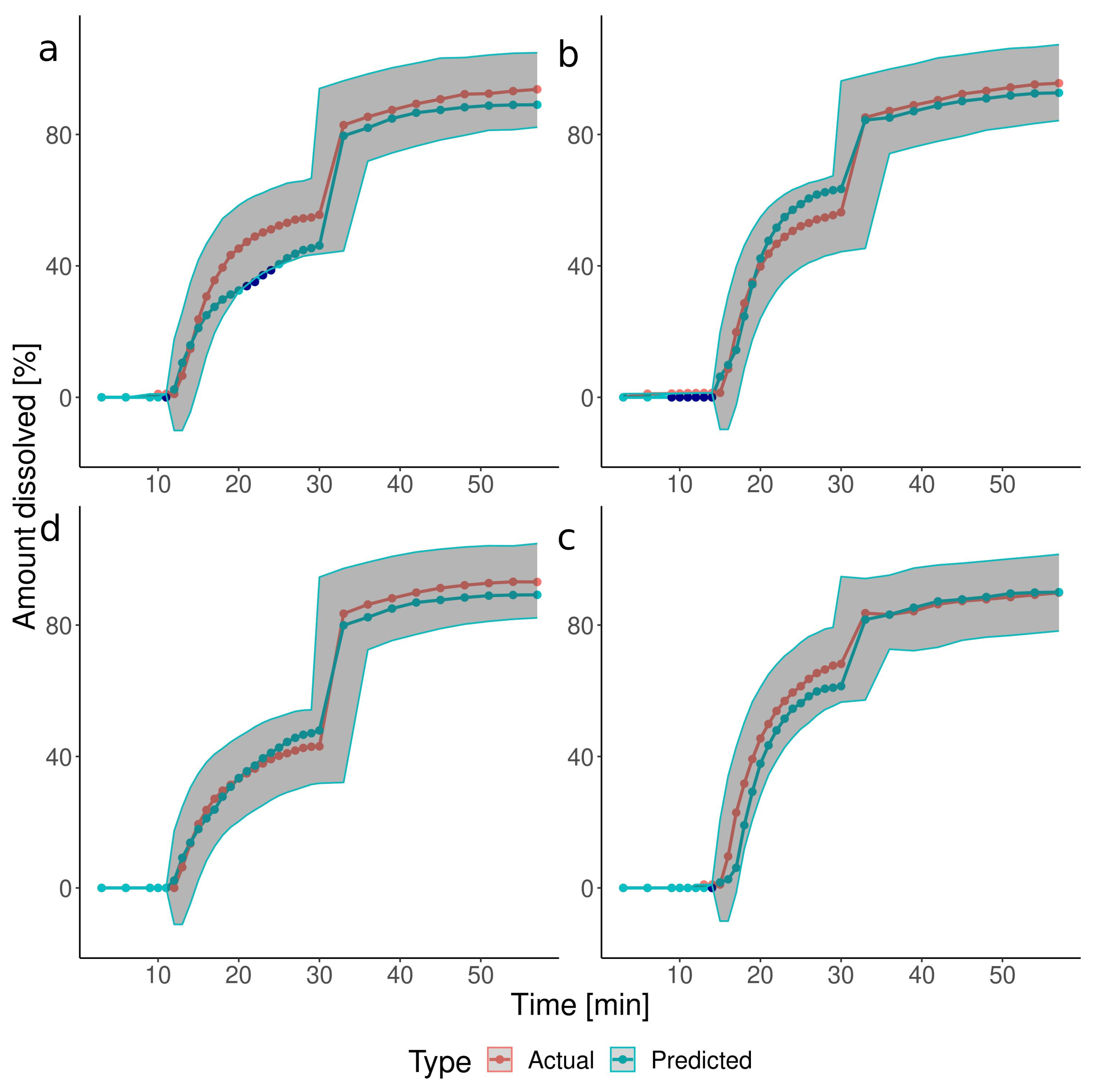
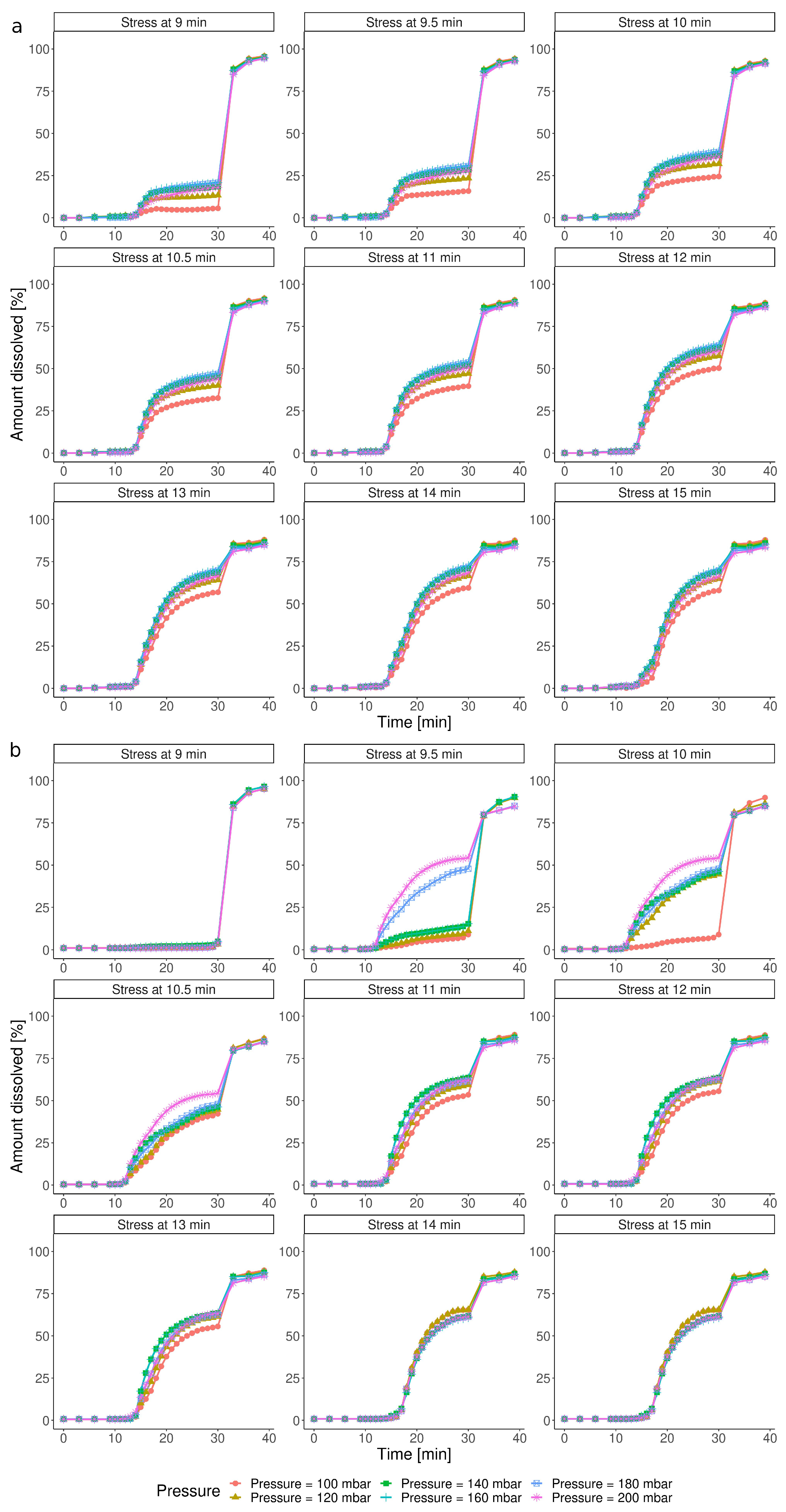
| Group | Test | Pressure [mbar] | Timing [min] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic tests | Test 1 * | 150 | 12 |
| Test 2 | 150 | 16 | |
| Test 3 | 100 | 15 | |
| Test 4 * | 150 | 12 | |
| Test 5 | 200 | 15 | |
| Test 6 | 200 | 9 | |
| Test 7 * | 150 | 12 | |
| Test 8 | 220 | 12 | |
| Test 9 | 80 | 12 | |
| Test 10 * | 150 | 12 | |
| Test 11 | 100 | 9 | |
| Test 12 | 150 | 8 | |
| Test 13 * | 150 | 12 | |
| Additional tests | Test 14 | 80 | 10 |
| Test 15 | 150 | 10 | |
| Test 16 | 220 | 10 | |
| Verification tests | Test V1 | 175 | 10.5 |
| Test V2 | 175 | 13.5 | |
| Test V3 | 125 | 13.5 | |
| Test V4 | 125 | 10.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Staniszewska, M.; Romański, M.; Polak, S.; Garbacz, G.; Dobosz, J.; Myslitska, D.; Romanova, S.; Paszkowska, J.; Danielak, D. A Rational Approach to Predicting Immediate Release Formulation Behavior in Multiple Gastric Motility Patterns: A Combination of a Biorelevant Apparatus, Design of Experiments, and Machine Learning. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2056. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15082056
Staniszewska M, Romański M, Polak S, Garbacz G, Dobosz J, Myslitska D, Romanova S, Paszkowska J, Danielak D. A Rational Approach to Predicting Immediate Release Formulation Behavior in Multiple Gastric Motility Patterns: A Combination of a Biorelevant Apparatus, Design of Experiments, and Machine Learning. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(8):2056. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15082056
Chicago/Turabian StyleStaniszewska, Marcela, Michał Romański, Sebastian Polak, Grzegorz Garbacz, Justyna Dobosz, Daria Myslitska, Svitlana Romanova, Jadwiga Paszkowska, and Dorota Danielak. 2023. "A Rational Approach to Predicting Immediate Release Formulation Behavior in Multiple Gastric Motility Patterns: A Combination of a Biorelevant Apparatus, Design of Experiments, and Machine Learning" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 8: 2056. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15082056
APA StyleStaniszewska, M., Romański, M., Polak, S., Garbacz, G., Dobosz, J., Myslitska, D., Romanova, S., Paszkowska, J., & Danielak, D. (2023). A Rational Approach to Predicting Immediate Release Formulation Behavior in Multiple Gastric Motility Patterns: A Combination of a Biorelevant Apparatus, Design of Experiments, and Machine Learning. Pharmaceutics, 15(8), 2056. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15082056







