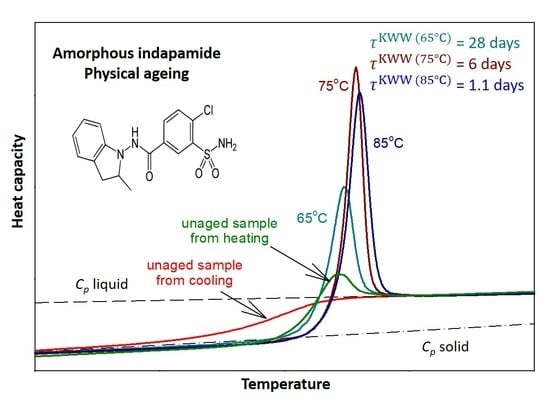
Physical Ageing of Amorphous Indapamide Characterised by Differential Scanning Calorimetry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
2.2. Standard DSC Measurements and Isothermal Physical Ageing
2.3. Temperature-Modulated Differential Scanning Calorimetry (TMDSC) Measurement
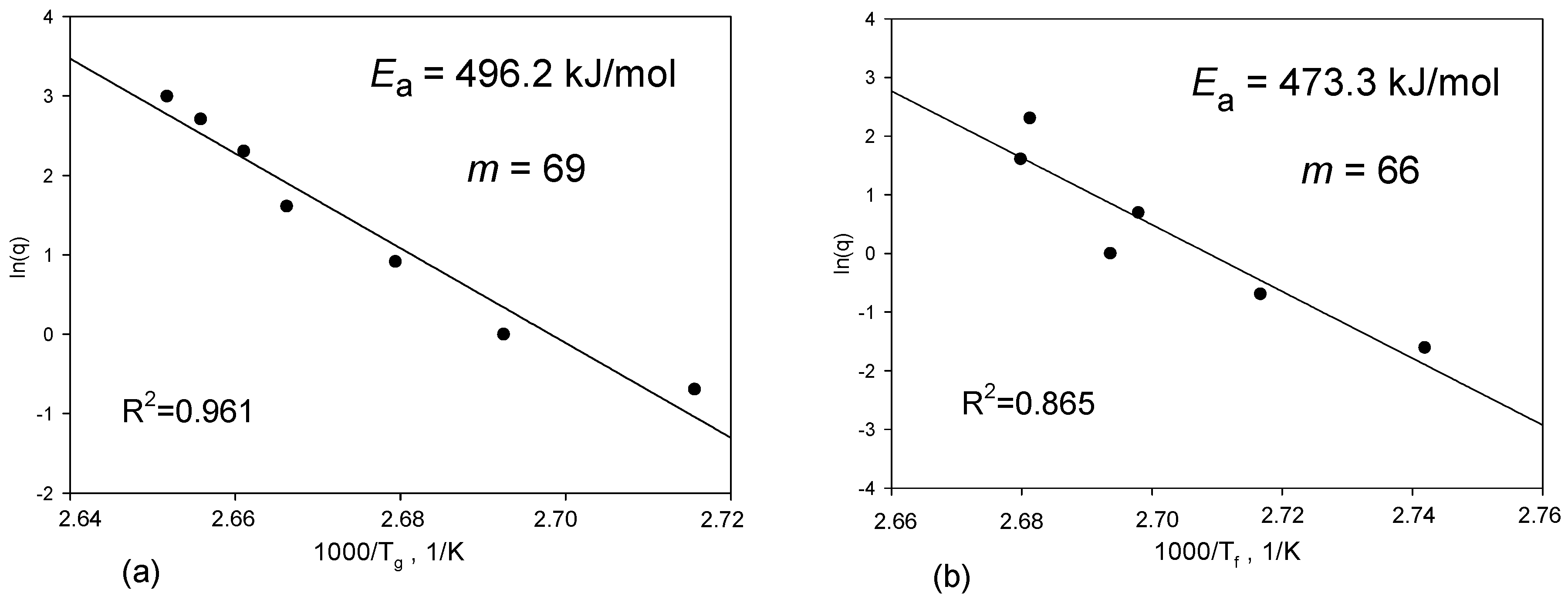
2.4. Determination of Fragility Parameter
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hancock, B.C.; Zografi, G. Characteristics and Significance of the Amorphous State in Pharmaceutical Systems. J. Pharm. Sci. 1997, 86, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kissi, E.O.; Grohganz, H.; Löbmann, K.; Ruggiero, M.T.; Zeitler, J.A.; Rades, T. Glass-Transition Temperature of the β-Relaxation as the Major Predictive Parameter for Recrystallization of Neat Amorphous Drugs. J. Phys. Chem. B 2018, 122, 2803–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, B.C.; Parks, M. What is the true solubility advantage for amorphous pharmaceuticals? Pharm. Res. 2000, 17, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokharkar, V.B.; Mandpe, L.P.; Padamwar, M.N.; Ambike, A.A.; Mahadik, K.R.; Paradkar, A. Development, characterization and stabilization of amorphous form of a low Tg drug. Powder Technol. 2006, 167, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graeser, K.A.; Patterson, J.E.; Zeitler, J.A.; Gordon, K.C.; Rades, T. Correlating thermodynamic and kinetic parameters with amorphous stability. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 37, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rams-Baron, M.; Jachowicz, R.; Boldyreva, E.; Zhou, D.; Jamróz, W.; Paluch, M. Amorphous Drugs: Benefits and Challenges, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mooter, G.V.D.; Augustijns, P.; Kinget, R. Stability prediction of amorphous benzodiazepines by calculation of the mean relaxation time constant using the Williams-Watts decay function. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 1999, 48, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brough, C.; Williams, R. Amorphous solid dispersions and nano-crystal technologies for poorly water-soluble drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 453, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiNunzio, J.C.; Miller, D.A.; Yang, W.; McGinity, J.W.; Williams, R.O. Amorphous Compositions Using Concentration Enhancing Polymers for Improved Bioavailability of Itraconazole. Mol. Pharm. 2008, 5, 968–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L. Amorphous pharmaceutical solids: Preparation, characterization and stabilization. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 48, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunderlich, B. Thermal Analysis of Polymeric Materials; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka, M.; Hancock, B.C.; Zografi, G. Inhibition of indomethacin crystallization in poly(vinylpyrrolidone) coprecipitates. J. Pharm. Sci. 1995, 84, 983–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammann, G. Der Glaszustand; Leopold Voss: Leipzig, Germany, 1933. [Google Scholar]
- Hoare, M. Stability and local order in simple amorphous packings. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1976, 279, 186–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, J.M. Physical aging of polymers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1995, 20, 703–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, E.L.G.E. Struik: Physical Aging in Amorphous Polymers and Other Materials; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, I. Enthalpy relaxation and recovery in amorphous materials. J. Non-Crystalline Solids 1994, 169, 211–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Rigsbee, D.R.; Stotz, C.; Pikal, M.J. Dynamics of Pharmaceutical Amorphous Solids: The Study of Enthalpy Relaxation by Isothermal Microcalorimetry. J. Pharm. Sci. 2002, 91, 1853–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenna, G.B. Glass Formation and Glassy Behavior. In Comprehensive Polymer Science; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1989; pp. 11–62. [Google Scholar]
- McKenna, G.B.; Simon, S.L. The glass transition: Its measurement and underlying physics. In Handbook of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry; Cheng, S.Z.D., Ed.; Elsevier Science, B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; Volume 3, pp. 49–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surana, R.; Pyne, A.; Suryanarayanan, R. Effect of aging on the physical properties of amorphous trehalose. Pharm. Res. 2004, 21, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyne, A.; Surana, R.; Suryanarayanan, R. Crystallization of mannitol below Tg’ during freeze-drying in binary and ternary aqueous systems. Pharm. Res. 2002, 19, 901–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andronis, V.; Zografi, G. Crystal nucleation and growth of indomethacin polymorphs from the amorphous state. J. Non-Crystalline Solids 2000, 271, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Han, J.; Zhang, G.G.Z.; Grant, D.J.W.; Suryanarayanan, R. In Situ Dehydration of Carbamazepine Dihydrate: A Novel Technique to Prepare Amorphous Anhydrous Carbamazepine. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2000, 5, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hay, J.N. The physical ageing of amorphous and crystalline polymers. Pure Appl. Chem. 1995, 67, 1855–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, Y.P.; Simon, S.L. Enthalpy Recovery of Polystyrene: Does a Long-Term Aging Plateau Exist? Macromolecules 2013, 46, 5815–5821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaev, E.; Zografi, G. The concept of ‘structure’ in amorphous solids from the perspective of the pharmaceutical sciences. In Amorphous Food and Pharmaceutical Systems; Levine, H., Ed.; The Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2002; pp. 11–30. [Google Scholar]
- Skotnicki, M.; Apperley, D.C.; Aguilar, J.A.; Milanowski, B.; Pyda, M.; Hodgkinson, P. Characterization of Two Distinct Amorphous Forms of Valsartan by Solid-State NMR. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 13, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, B.B.K.; Karunakar, A. Biopharmaceutics Classification System: A Regulatory Approach. Dissolution Technol. 2011, 18, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojnarowska, Z.; Grzybowska, K.; Hawelek, L.; Dulski, M.; Wrzalik, R.; Gruszka, I.; Paluch, M.; Mojsiewicz-Pieńkowska, K.; Sawicki, W.; Bujak, P.; et al. Molecular Dynamics, Physical Stability and Solubility Advantage from Amorphous Indapamide Drug. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 3612–3627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghugare, P.; Dongre, V.; Karmuse, P.; Rana, R.; Singh, D.; Kumar, A.; Filmwala, Z. Solid state investigation and characterization of the polymorphic and pseudopolymorphic forms of indapamide. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2010, 51, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edueng, K.; Mahlin, D.; Larsson, P.; Bergström, C.A.S. Mechanism-based selection of stabilization strategy for amorphous formulations: Insights into crystallization pathways. J. Control. Release 2017, 256, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, B.; Zhang, L.; Pan, Z.; Gou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, X. A comparison of the effect of temperature and moisture on the solid dispersions: Aging and crystallization. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 475, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tool, A.Q. Relation between inelastic deformability and thermal expansion of glass in its annealing range*. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1946, 29, 240–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, A.J. Glass transition in amorphous polymer: A phenomenological study. In Advanced Polymer Science; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1963; Volume 3, pp. 394–508. [Google Scholar]
- Kohlrausch, R. Nachtrag uber die elastiche Nachwirkung beim Cocon und Glasladen. Ann. Phys. (Leipzig) 1847, 72, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, G.; Watts, D.C. Non-symmetrical dielectric relaxation behaviour arising from a simple empirical decay function. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1970, 66, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angell, C.A.; Ngai, K. Relaxations in Complex Systems; Ngai, K., Wright, G.B., Eds.; National Technical Information Service: Springfield, VA, USA; US Department of Commerce: Washington, DC, USA, 1985; p. 1.
- Angell, C.A.; Monnerie, L.; Torell, L.M. Strong and Fragile Behavior in Liquid Polymers. Symp. Mat. Res. Sot. 1991, 215, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angell, C.; Bressel, R.; Green, J.; Kanno, H.; Oguni, M.; Sare, E. Liquid fragility and the glass transition in water and aqueous solutions. J. Food Eng. 1994, 22, 115–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O. Correlation between fragility and glass-forming ability of metallic alloys. Phys. Rev. B 2007, 76, 104202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bataillard, A.; Schiavi, P.; Sassard, J. Pharmacological Properties of Indapamide. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1999, 37, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Pharmacopoeia, 7th ed.; Council of Europe: Strasbourg, France, 2012.
- Das, U.; Halder, S.; Kabir, A.K.L.; Rashid, H.O.; Rouf, A.S.S. Development and in vitro Evaluation of Sustained Release Matrix Tablets of Indapamide from Methocel® K15 MCR and K100 LVCR. Dhaka Univ. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 10, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzybowska, K.; Capaccioli, S.; Paluch, M. Recent developments in the experimental investigations of relaxations in pharmaceuticals by dielectric techniques at ambient and elevated pressure. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 100, 158–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapik-Kowalczuk, J.; Wojnarowska, Z.; Grzybowska, K.; Jurkiewicz, K.; Tajber, L.; Paluch, M. Molecular Dynamics and Physical Stability of Coamorphous Ezetimib and Indapamide Mixtures. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 3610–3619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skotnicki, M.; Drogoń, A.; Calvin, J.J.; Rosen, P.; Woodfield, B.; Pyda, M. Heat capacity and enthalpy of indapamide. Thermochim. Acta 2019, 674, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serajuddin, A.T.M.; Rosoff, M.; Mufson, D. Effect of thermal history on the glassy state of indapamide. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1986, 38, 219–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simatos, D.; Blond, G.; Roudaut, G.; Champion, D.; Perez, J.; Faivre, A. Influence of heating and cooling rates on the glass transition temperature and the fragility parameter of sorbitol and fructose as measured by DSC. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 1996, 47, 1419–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, K.; Harada, T.; Yoshihashi, Y.; Yonemochi, E.; Terada, K.; Moriyama, H. Correlation between Glass-Forming Ability and Fragility of Pharmaceutical Compounds. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 4873–4880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyda, M.; Wunderlich, B. Reversing and Nonreversing Heat Capacity of Poly (lactic acid) in the Glass Transition Region by TMDSC. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 10472–10479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skotnicki, M.; Aguilar, J.A.; Pyda, M.; Hodgkinson, P. Bisoprolol and bisoprolol-valsartan compatibility studied by differential scanning calorimetry, nuclear magnetic resonance and X-ray powder diffractometry. Pharm. Res. 2014, 32, 414–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodge, I.M. Strong and fragile liquids—A brief critique. J. Non-Crystalline Solids 1996, 202, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Chamarthy, S.P.; Pinal, R. Time-Dependence of Molecular Mobility during Structural Relaxation and its Impact on Organic Amorphous Solids: An Investigation Based on a Calorimetric Approach. Pharm. Res. 2006, 23, 1906–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H. Relationship among glass-forming ability, fragility, and short-range bond ordering of liquids. J. Non-Crystalline Solids 2005, 351, 678–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Zhang, G.G.; Law, D.; Grant, D.J.; Schmitt, E.A. Physical Stability of Amorphous Pharmaceuticals: Importance of Configurational Thermodynamic Quantities and Molecular Mobility. J. Pharm. Sci. 2002, 91, 1863–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angell, C. Relaxation in liquids, polymers and plastic crystals—Strong/fragile patterns and problems. J. Non-Crystalline Solids 1991, 131, 13–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhmer, R.; Ngai, K.L.; Angell, C.A.; Plazek, D.J. Nonexponential relaxations in strong and fragile glass formers. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 99, 4201–4209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angell, C.A. Formation of Glasses from Liquids and Biopolymers. Science 1995, 267, 1924–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikal, M.J.; Lukes, A.L.; Lang, J.E.; Gaines, K. Quantitative Crystallinity Determinations for β-Lactam Antibiotics by Solution Calorimetry: Correlations with Stability. J. Pharm. Sci. 1978, 67, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukushi, I.; Yamamuro, O.; Suga, H. Heat capacities and glass transitions of ground amorphous solid and liquid-quenched glass of tri-O-methyl-ß-cyclodextrin. J. Non-Crystalline Solids 1994, 175, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcgonigle, E.-A.; Daly, J.H.; Jenkins, S.D.; Liggat, J.; Pethrick, R.A. Influence of Physical Aging on the Molecular Motion and Structural Relaxation in Poly(ethylene terephthalate) and Related Polyesters. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, R.; Shen, D.; Sun, F.; Wu, L. The effects of physical ageing on conformational changes of poly(ethylene terephthalate) in the glass transition region. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 1996, 197, 1485–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, S.L.; Bernazzani, P. Structural relaxation in the glass: Evidence for a path dependence of the relaxation time. J. Non-Crystalline Solids 2006, 352, 4763–4768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moynihan, C.T.; Macedo, P.B.; Montrose, C.J.; Gupta, P.K.; DeBolt, M.A.; Dill, J.F.; Dom, B.E.; Drake, P.W.; Easteal, A.J.; Elterman, P.B.; et al. Structural relaxation in vitreous materials. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1976, 279, 15–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, C.; Taylor, A.J.; Farhat, I.A.; Macnaughtan, W. Modelling of physical ageing in starch using the TNM equation. Carbohydr. Res. 2011, 346, 1122–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Guo, J.; Robertson, R.E.; Amidon, G.L. Influence of Physical Aging on Mechanical Properties of Polymer Free Films: The Prediction of Long-Term Aging Effects on the Water Permeability and Dissolution Rate of Polymer Film-Coated Tablets. Pharm. Res. 1991, 8, 1500–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, T.M.; Langhe, D.; Ponting, M.; Baer, E.; Freeman, B.D.; Paul, D. Enthalpy recovery and structural relaxation in layered glassy polymer films. Polymer 2012, 53, 4002–4009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, K.; Sugawara, A.; Kazama, S.; Freeman, B.D. Effects of physical aging on solubility, diffusivity, and permeability of propane andn-butane in poly(4-methyl-2-pentyne). J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2004, 42, 2407–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, G. Molecular Mobility and Physical Stability of Amorphous Irbesartan. Sci. Pharm. 2009, 77, 695–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, K.; Pikal, M.J. Calorimetric Investigation of the Structural Relaxation of Amorphous Materials: Evaluating Validity of the Methodologies. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 94, 948–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chieng, N.; Teo, X.; Cheah, M.H.; Choo, M.L.; Chung, J.; Hew, T.K.; Keng, P.S. Molecular Dynamics and Physical Stability of Pharmaceutical Co-amorphous Systems: Correlation Between Structural Relaxation Times Measured by Kohlrausch-Williams-Watts with the Width of the Glass Transition Temperature (ΔTg) and the Onset of Crystallization. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 3848–3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claudy, P.; Jabrane, S.; Létoffé, J. Annealing of a glycerol glass: Enthalpy, fictive temperature and glass transition temperature change with annealing parameters. Thermochim. Acta 1997, 293, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


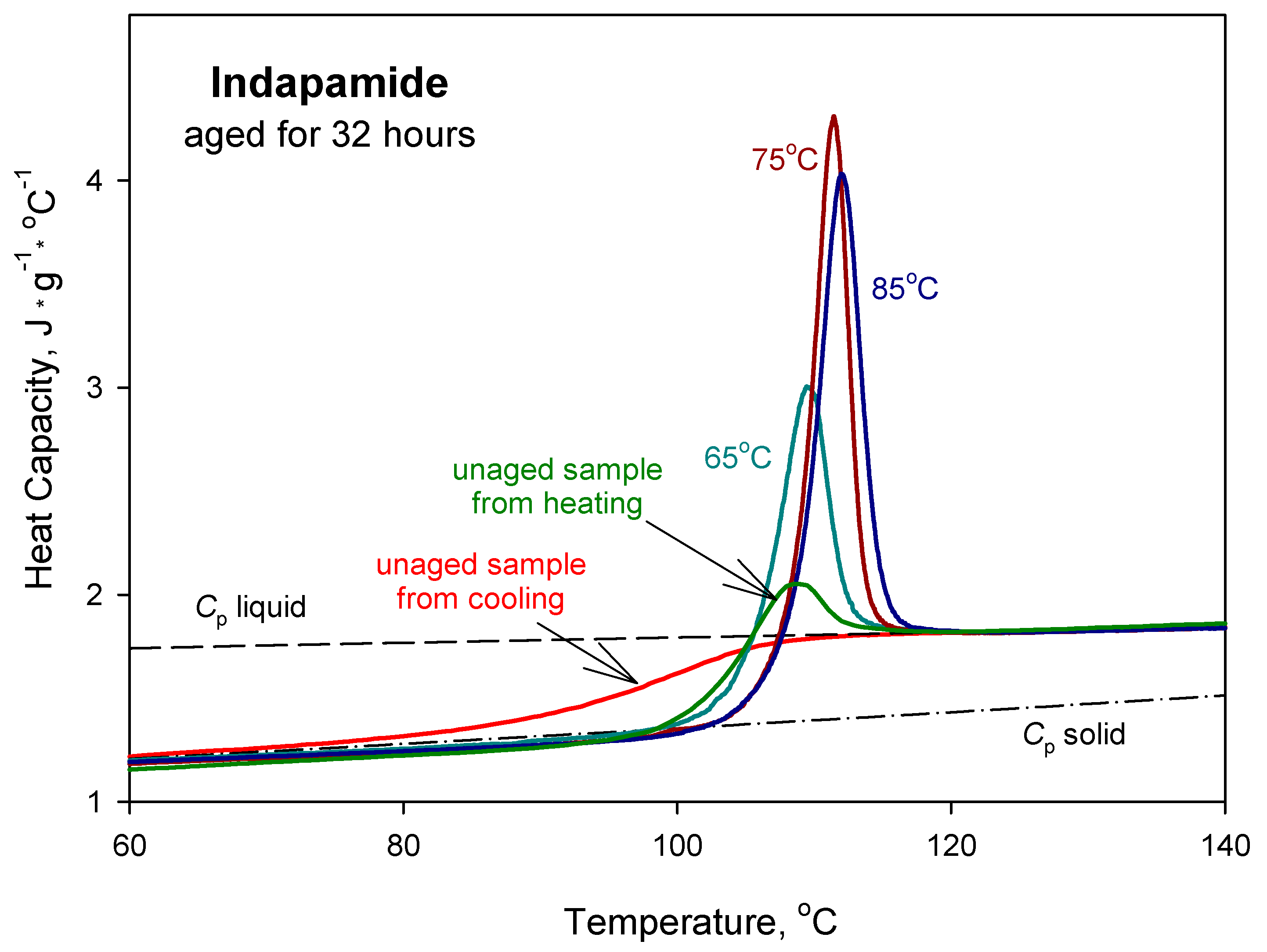
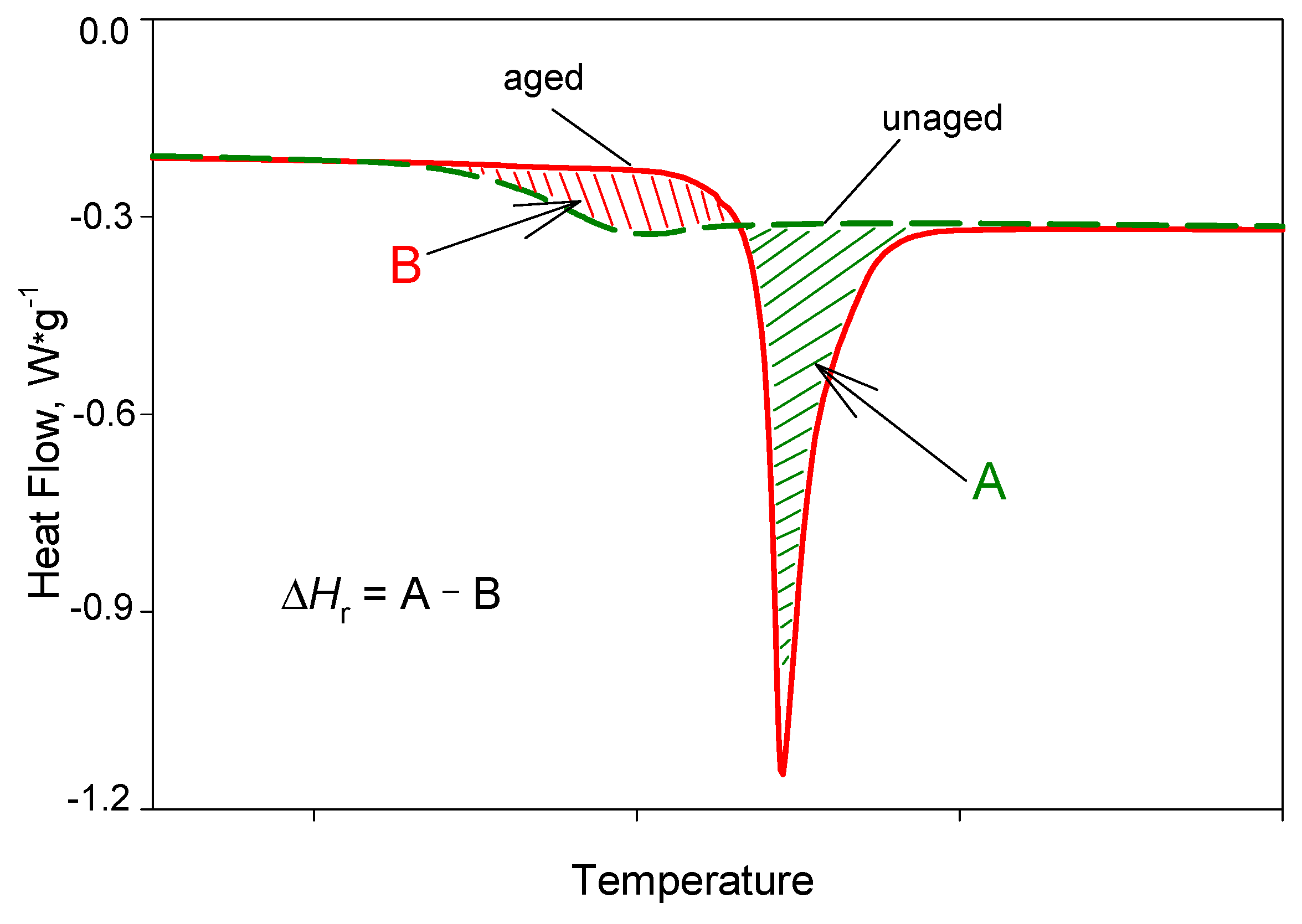
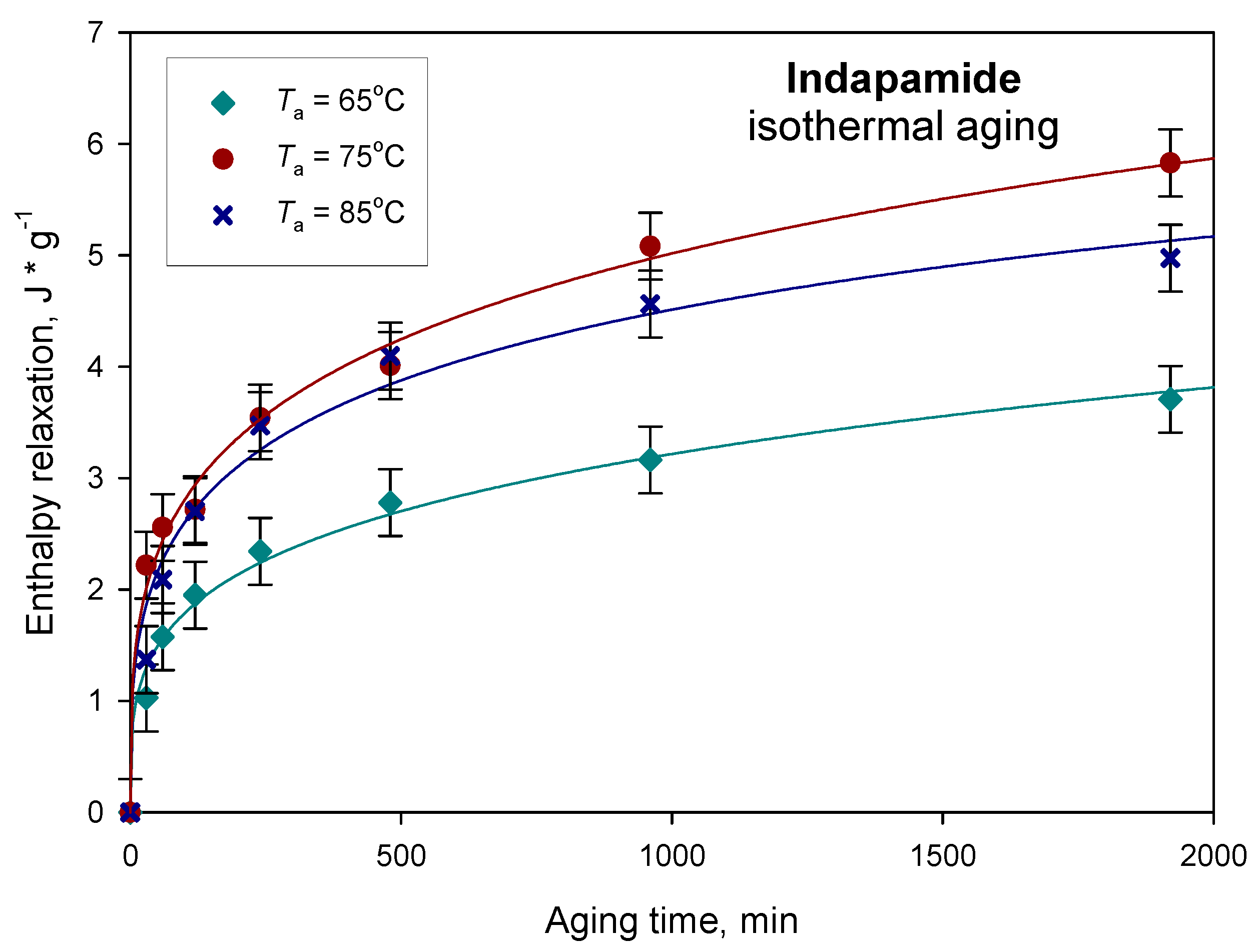
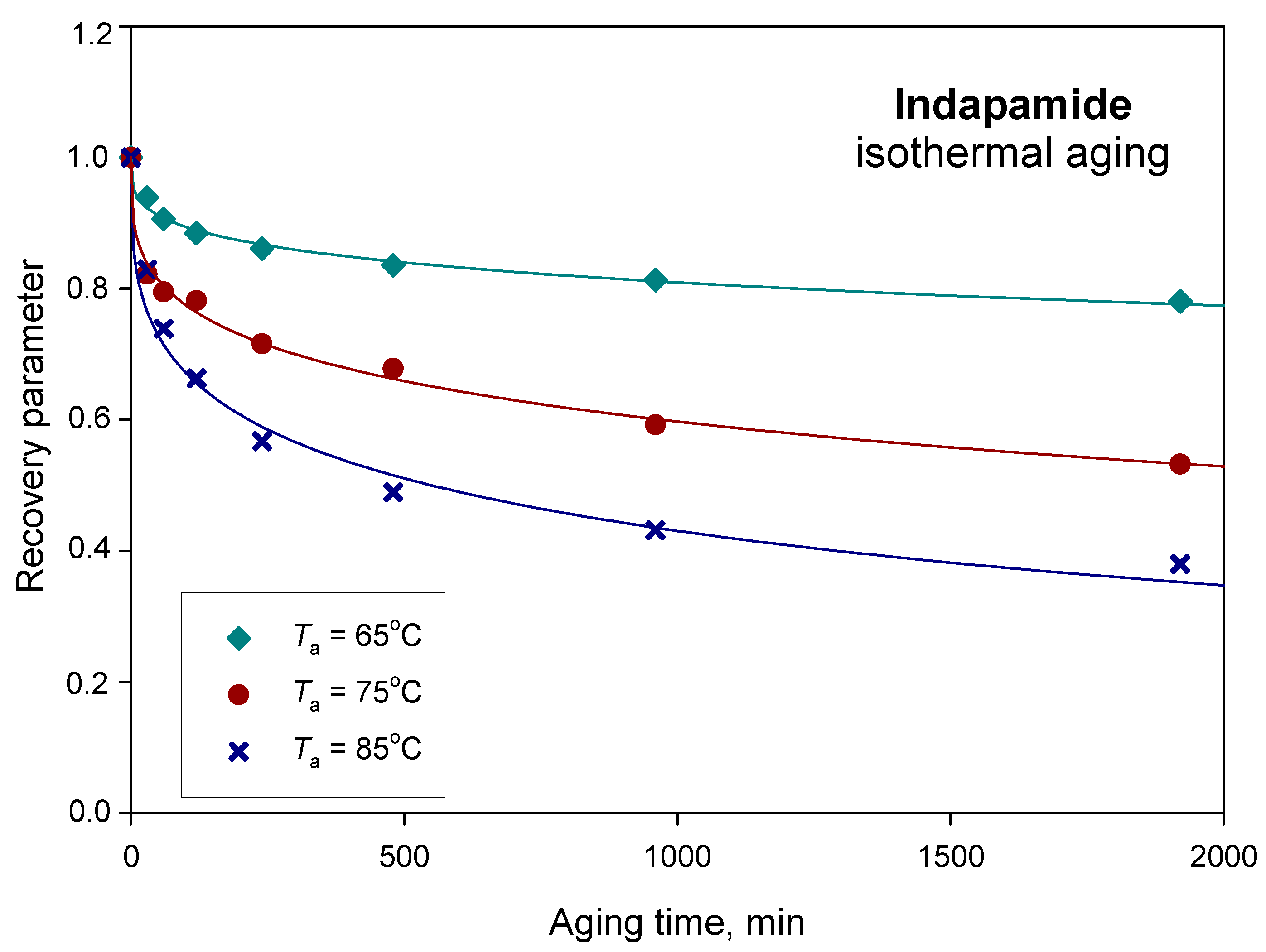

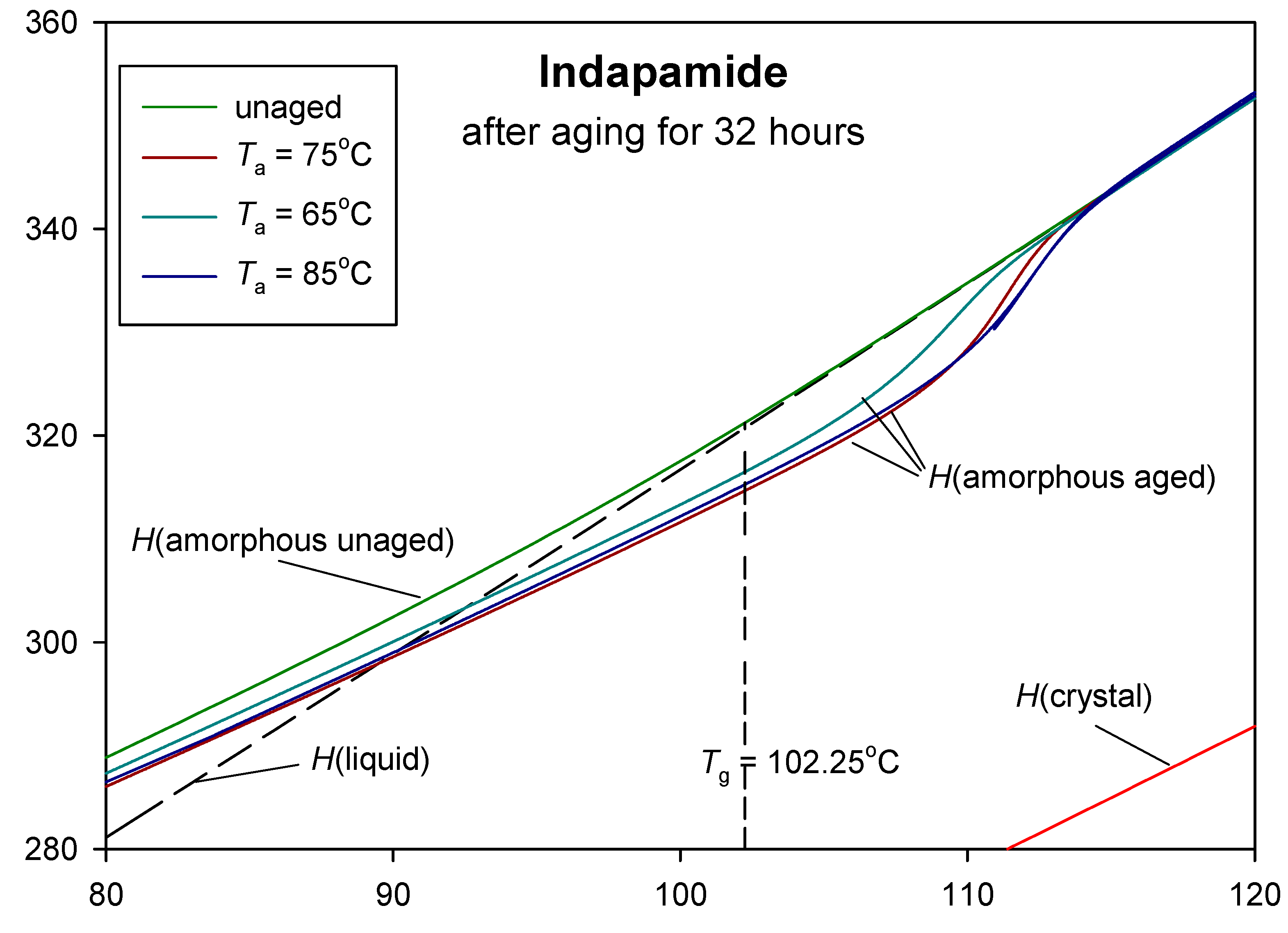
| Parameters | Ta = 65 °C | Ta = 75 °C | Ta = 85 °C |
|---|---|---|---|
| (J·g−1) | 16.88 | 12.45 | 7.92 |
| 0.277 | 0.306 | 0.327 | |
| ~189 days | 6 days | 28 h |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Drogoń, A.; Skotnicki, M.; Skotnicka, A.; Pyda, M. Physical Ageing of Amorphous Indapamide Characterised by Differential Scanning Calorimetry. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 800. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12090800
Drogoń A, Skotnicki M, Skotnicka A, Pyda M. Physical Ageing of Amorphous Indapamide Characterised by Differential Scanning Calorimetry. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(9):800. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12090800
Chicago/Turabian StyleDrogoń, Agata, Marcin Skotnicki, Agnieszka Skotnicka, and Marek Pyda. 2020. "Physical Ageing of Amorphous Indapamide Characterised by Differential Scanning Calorimetry" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 9: 800. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12090800
APA StyleDrogoń, A., Skotnicki, M., Skotnicka, A., & Pyda, M. (2020). Physical Ageing of Amorphous Indapamide Characterised by Differential Scanning Calorimetry. Pharmaceutics, 12(9), 800. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12090800