Abstract
Physicochemical characterization is a crucial step for the successful development of solid dispersions, including the determination of drug crystallinity and molecular interactions. Typically, the detection of molecular interactions will assist in the explanation of different drug performances (e.g., dissolution, solubility, stability) in solid dispersions. Various prominent reviews on solid dispersions have been reported recently. However, there is still no overview of recent techniques for evaluating the molecular interactions that occur within solid dispersions of poorly water-soluble drugs. In this review, we aim to overview common methods that have been used for solid dispersions to identify different bond formations and forces via the determination of interaction energy. In addition, a brief background on the important role of molecular interactions will also be described. The summary and discussion of methods used in the determination of molecular interactions will contribute to further developments in solid dispersions, especially for quick and potent drug delivery applications.
1. Introduction
Poorly soluble or insoluble drugs result in low absorption, which certainly affects drug bioavailability, especially in oral drug delivery [1,2,3,4,5]. Therefore, many formulation strategies have been developed to overcome the limitations of these drugs [6,7,8,9,10]. Both traditional approaches (e.g., polymorphs, prodrugs, salt formation, and solid dispersions (SDs)) and current nanotechnologies (e.g., solid lipid nanoparticles, nanoprecipitations, and nanoemulsions) have contributed useful techniques and strategies for the development of formulations of poorly water-soluble drugs [8,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23]. Among them, the development of SDs (even in combination with nanotechnology) is still being heavily investigated to improve the drug solubility, dissolution rate and stability of poorly water-soluble drugs [24,25,26,27,28].
Physicochemical analysis is necessary to characterize SDs during their preparation. Many pieces of information can be obtained, such as how the polymer affects drug crystallinity, how the molecular interactions between the drug and the components in the formulation occur and how the binding force is generated. The data from these studies will be useful in the explanation of different drug performances and will contribute to the selection of the best formulation in drug development. Therefore, the scrutinization of the molecular interactions in SDs is critical information that needs extensive investigation. This review will provide insights into common methods for the detection of the molecular interactions in SDs used in recent studies. Moreover, the strategies used in the determination of binding forces will also be discussed as they are helpful in differentiating the different binding interactions between formulations. Figure 1 illustrates common techniques used in the detection of molecular interactions in SDs.
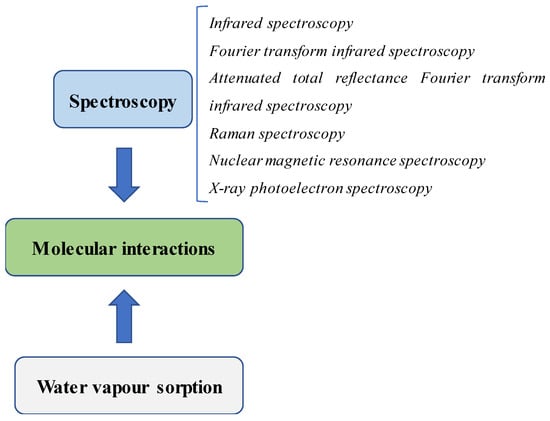
Figure 1.
Common techniques used in the detection of molecular interactions in SDs.
2. How Molecular Interactions Are Important in SDs
In SD systems, typically a poorly water-soluble drug is dispersed in a carrier or a mixture of carrier and additives [29,30]. Details of several generations of SDs were well described in previous reviews [31,32]. While in the first generation of SD carriers are commonly in crystalline state, amorphous polymers are utilized in the second generation of SD to transform a drug crystal to an amorphous form [31,32]. For the third and fourth generations of SDs, researchers take into account adding additives (e.g., surfactants, pH-modifiers) in formulations for further improving drug bioavailability. Particularly, insoluble carriers or swellable polymers have been suggested in the fourth generation of SDs for a constant drug release rate [31,32,33].
Once a poorly water-soluble drug is dispersed in a polymer for SD formation, a weak physical bond may be formed between these components to modulate drug release (Figure 2). Weak physical bonds (formed by non-covalent interactions) such as hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, van der Waals, dipole-dipole interactions and acid-base interactions are common interactions occurred between components in SDs [26,34,35,36,37,38]. Among them, hydrogen bonding formation is typically observed in SDs [39,40,41,42]. The formation of these bonds between a drug and one of the SD components may prevent self-association between drug molecules, leading to changes in the crystallization kinetics [43].
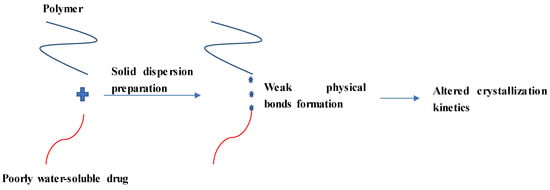
Figure 2.
Illustrations of typical molecular interactions in solid dispersions and their effects on drug crystallinity.
The interaction at the molecular level between a drug and a polymer is crucial to explain the mechanism of drug release and stability in SD systems. Generally, these interactions may maintain a drug in an amorphous form during the dissolution process as well as during storage [44,45]. In particular, hydrogen bonding has been demonstrated to be an important factor in improving amorphous stability [46,47].
The molecular interaction (for example, between griseofulvin and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose acetate succinate) is even maintained in the liquid state, as demonstrated in the study of Al-Obaidi et al. [44]. In summary, the interaction between a drug and a polymer affects the solubility, dissolution and physical stability of a drug in its SD. Although different types of molecular interactions may occur within SDs, a selection of common methods to clarify the interactions, which will be described below, depends on the physicochemical properties of SDs rather than their generations.
3. Spectroscopic Techniques Used in the Investigation of Molecular Interactions
3.1. Infrared Spectroscopy (IR)
IR has been widely used as one of the most effective techniques to identify a chemical or detect impurities because it can obtain the structural information of a wide range of compounds [48,49,50,51]. Figure 3 illustrates different IR methods and their detection of molecular interactions in SDs. In SD studies, IR is a common technique for the determination of molecular interactions between components, particularly those between a drug and an SD component [17,26,52,53,54,55,56]. Indeed, the use of IR was recommended in early studies on SD to identify the interaction between a model drug and a polymer. For example, Tachibana et al. used IR in 1965 to evaluate the molecular dispersion of β-carotene in polyvinyl pyrrolidone [57].
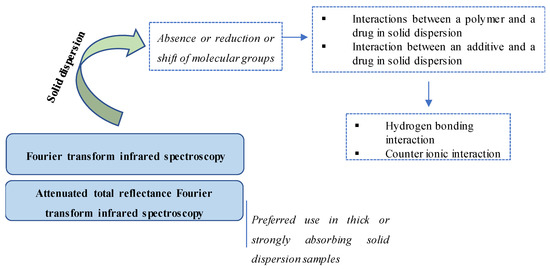
Figure 3.
Illustration of IR methods and their detection in molecular interactions in SDs.
The most common type of IR is Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, which transforms the recorded data into a spectrum [58,59]. In principle, FTIR is used to investigate and compare the spectra of individual components in mixtures of samples (including SD samples) [60,61]. The absence, reduction or shift in the spectra of molecular groups would suggest the occurrence of molecular interactions in SDs [57,62,63].
For example, in a study of SDs containing esomeprazole, the hydrogen bonding interactions were determined by FTIR [34]. Specifically, the binary SD of esomeprazole and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) showed a shift in the spectra of the sulfonyl group (S=O) and amino group (C=N), which was demonstrated to be the result of hydrogen bonding interactions [34]. However, ternary SDs with added pH modifiers, showed strong hydrogen bonding, which was demonstrated by the reduction of the stretching vibration frequency of those peaks [34,64]. Similarly, in a study of SDs containing zein and isradipine, the disappearance of C=O and NH groups in the FTIR spectrum indicated hydrogen bond formation between the model drug and the polymer in the SD [65].
The peak height ratio can be used to quantify the level of hydrogen bonding. Indeed, Ozeki et al. utilized this information in the evaluation of an increase in the ratio of hydrogen bonding between flurbiprofen and poly(ethylene oxide) [66]. Specifically, while the carbonyl stretching band of flurbiprofen was shown at 1703 cm−1 in the FTIR spectrum, the new peak at 1736 cm−1 confirmed hydrogen bonding formation [66]. The authors showed that the increase in the peak height ratio was correlated with the release rate of flurbiprofen and the increase in the ratio of hydrogen bonding [66].
FTIR can also detect counterionic interactions. In a study of SDs using ionic and non-ionic polymers, Sarode et al. found that the carbonyl groups (with peaks between 1670 cm−1 and 1800 cm−1) of the drugs (indomethacin and itraconazole) were stretched when the drugs were included in SD formulations [35]. In particular, significant stretching was observed with SDs using ionic polymers [35]. Therefore, counterionic interactions occurred in SDs, particularly a stronger interaction between the weakly acidic drug and the cationic polymer [35].
In the case of thick or strongly absorbing SD samples, attenuated total reflectance FTIR (ATR-FTIR) spectroscopy, which has been utilized widely as a powerful technique in recent SD studies and the analysis of biopharmaceuticals, is recommended to overcome the intense peaks that are produced by these samples [67,68,69,70]. This system consists of an FTIR spectroscope and an ATR accessory to create an evanescent wave that is then directed into the sample [71]. Contact between an ATR crystal surface and a sample will affect the quality of measurement [72]. The investigation of any shifted peaks or changes in intensity is similar to FTIR. For instance, in a study of intermolecular interactions in SDs using copovidone carriers, ATR-FTIR was used to examine the hydrogen bonding between the mixture of polymers ((poly(vinylpyrrolidone-vinyl acetate) copolymer and Plasdone S-630)) and indomethacin [73]. Indeed, a shift in the amide carbonyl peak (1672 cm−1 to 1680 cm−1) demonstrated a hydrogen bond formation in SDs [73].
In addition to the detection of the interaction with polymers, ATR-FTIR can also detect the interactions between a model drug and an additive in an SD [74]. In a study of ternary SDs containing naftopidil/fumaric acid/d-α-tocopherol polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate (TPGS), the interaction between naftopidil and fumaric acid was discovered by comparing binary SDs and ternary SDs [74]. Specifically, C=O stretching (1737.3 cm−1) did not change in the binary SDs, while C=O stretching was observed at 1737.3/1697.7 cm−1, which was attributed to the C=O peaks of TPGS and fumaric acid, respectively [74]. In short, the shift in the C=O peak of fumaric acid in SDs demonstrated hydrogen bond formation between naftopidil and fumaric acid [74].
3.2. Raman Spectroscopy
It should be noted that the presence of functional groups in polymers (e.g., carbonyl groups), which are similar to those in a model drug, could interfere with methods to distinguish the spectra of a drug and a polymer [73]. Therefore, combination methods are often used to identify molecular interactions [73]. Raman spectroscopy is an example of these techniques. Indeed, the use of Raman spectroscopy can distinguish differences in short-range ordering [75]. Moreover, aqueous samples can be studied with Raman spectroscopy [75,76]. Table 1 summarizes key characters complementary to each other of Raman spectroscopy, FTIR and ATR-FTIR.

Table 1.
Key characters complementary to each other of Raman spectroscopy, FTIR (Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy) and ATR-FTIR (attenuated total reflectance FTIR).
One of the remarkable advantages of Raman spectroscopy is the estimation of drug crystallinity in SDs [77]. Generally, a drug crystal is represented by the defined peaks in the Raman spectrum because of the phonon region pattern of the crystalline form [78,79,80,81]. In contrast, a broad spectrum is observed when the drug is in an amorphous state [78,79,80,81]. In 1998, Taylor et al. used Raman spectroscopy to quantitate the degree of indomethacin crystallinity in mixtures of its crystal and amorphous states [82]. In detail, the authors utilized the peak intensity ratio of the crystal and amorphous spectra to establish a correlation curve [82]. In a later study, Okumura et al. developed a calibration model using chemometric FT-Raman spectroscopy that could evaluate the small differences in microcrystallinity in an indomethacin tablet (both on the surface and in cross-section) [83].
The determination of drug crystallinity could also be made during the preparation of an SD, which was shown in the study of Saerens et al. [84]. In this study, the hot-melt extrusion process was used to produce SDs [84]. During this process, a Raman spectrometer probe, which was built into the extrusion die, monitored the samples before they were forced through the die [84]. Similar to IR spectroscopy, the peak shifts in the spectra of the SDs indicate the interaction between a drug and a polymer [84]. The existence hydrogen bonding forces, formed between the drug and a polymer, are typically inferred from the blueshift and redshift in Raman spectra [85,86].
3.3. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy
NMR is another powerful technique that can be used to perform high sensitivity detection and obtain quantitative information at the molecular level [87]. In general, NMR monitors possible changes of electron density around specific interacting atoms to detect molecular interactions at the atomic level [88,89]. For instance, the observation of chemical shifts in 1H NMR spectra can reveal hydrogen bond formation in SDs [90,91,92,93]. Typically, the chemical shift is attributed to the change in electron density around the proton caused by hydrogen bond formation [91,94]. Potential disadvantages of NMR involve the requirement of a high-field NMR spectrometer with a combination of multi-channel probe and multiple magnetic fields in certain circumstances [95].
The level of hydrogen bonding can also be detected by NMR spectroscopy. For example, in the study of Karavas et al., the authors used 1H-NMR to compare the interaction between felodipine-polyethylene glycol and felodipine-polyvinyl pyrrolidone in SDs [96]. Although FTIR could indicate the hydrogen bonds between felodipine and the two polymers, 1H-NMR was used to evaluate the intensity of the felodipine-polymer interactions [96]. Specifically, they observed the secondary amino group of felodipine at 5.75 ppm [96]. This peak was shifted to 6.39 ppm, 6.57 ppm and 6.62 ppm when SDs with polyvinyl pyrrolidone were manufactured with 10%, 20% and 50% felodipine, respectively [96]. In contrast, this peak was almost stable as the amount of felodipine in the SDs increased further [96]. Therefore, 1H-NMR could indicate a stronger hydrogen bonding interaction when using polyvinyl pyrrolidone in SDs than when using polyethylene glycol [96].
Solid-state NMR (ssNMR) spectroscopy can also detect hydrogen bond formation in SDs. In a study of SDs containing nifedipine, 13C ssNMR was used to observe the difference in the C=O peaks of nifedipine in SDs [97]. While the C=O peaks in SDs with Eudragit® were observed at 170 ppm, the SDs with HPMC showed the C=O peak at 168 ppm, which indicated a hydrogen bonding formation as a lower magnetic field was observed compared to the non-hydrogen bond [97,98,99].
3.4. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)
In terms of characterizing polymer surfaces, XPS is more sensitive than NMR and FTIR [100]. XPS can provide valuable information such as layer structure, elemental distribution, and chemical bonding within material surfaces (even in nanostructure materials) [100,101]. In the study of Maniruzzaman et al., the authors found that although molecular modelling was able to predict two types of hydrogen bonds, XPS could indicate the exact interaction between a cationic drug and an anionic polymer via intermolecular ionic interactions to form a hydrogen bond [100].
In particular, XPS is considered a powerful technique in the evaluation of acid-base interactions because it can detect the binding energy shifts of the selected atoms resulting from protonation [102,103]. For instance, Song et al. utilized XPS to identify the interactions in SDs containing polystyrene sulfonic acid/apatinib or polystyrene sulfonic acid/gefitinib [36]. By detecting the increase in binding energy of the basic nitrogen atoms of the drugs, XPS provided information about the protonation of these nitrogen atoms [36]. This study also noted that XPS is unable to distinguish different NH groups (e.g., aliphatic secondary amine NH vs. aniline NH), although XPS can detect local protonation [36]. Therefore, a combination of XPS and NMR spectroscopy was suggested for detecting acid-base interactions in SDs [36]. However, XPS alone has been used to detect acid-base interactions. For example, in another study by the same research group above, the tertiary amine of lumefantrine was used to evaluate the extent of protonation through interactions with acidic polymers (hydroxypropyl methylcellulose phthalate, hydroxypropyl methylcellulose acetate succinate, poly(methacrylic acid-co-ethyl acrylate), polystyrene sulfonic acid and polyacrylic acid) using XPS [102].
4. Water Vapour Sorption (WPS)
WPS is a method used to examine the water sorption behaviour of a powder to investigate its affinity towards water [104]. By measuring the deviation in water sorption, interactions in the mixture arising from the masking of monolayer water-binding sites can be deduced [105]. In other words, the interactions in SDs affect the water sorption of polymers and active pharmaceutical ingredients. For example, Costantino et al. utilized gravimetric sorption analysis to calculate the water monolayer in lyophilized protein-sugar systems [105]. Specifically, the water monolayer was lower in the entire system than in component in the system (protein and sugar) [105]. These data indicated that the interaction between sugar and protein occurred in the solid-state, leading to a decrease in the availability of water-binding sites [105]. In a study of SDs containing hydrophobic drugs (indomethacin, ursodeoxycholic acid or indapamide) and poly(vinylpyrrolidone), a similar result was observed with water vapour sorption [106].
However, it should be noted that the hydrogen bonding interactions in SDs are not sufficient to affect the water sorption of individual components [107]. Zhang et al. demonstrated that two amorphous SD systems (sucrose-poly(vinylpyrrolidone) and trehalose-poly(vinylpyrrolidone)) showed a similar water vapour sorption as the pure components, although there were hydrogen bonding interactions present in the SDs [107]. Because of this limitation, water vapour sorption only has predictive potential [104].
5. Conclusions
In the preparation of SDs, it is important to choose a method to evaluate the interactions between a drug and a polymer (or other components). Spectroscopic methods including IR, Raman, NMR and XPS are the most common methods used to identify the intermolecular interactions in SDs. Although these methods can indicate the types of bonding formations or even quantify the interactions themselves, the methods used in the determination of interaction energy such as molecular modelling and quantum chemical calculation would be useful tools in determining the level of bonding formation as well as the prediction of bonding type [108,109]. With regard to future perspectives in the characterization of SDs, the development of advanced analytical equipment/methods that can distinguish and quantify molecular interactions will play a key role in the development of SDs.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft preparation and editing, T.T.D.T.; writing—review and editing, P.H.L.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Phuong Ha Lien Tran is the recipient of Australian Research Council’s Discovery Early Career Researcher Award (project number DE160100900).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Li, T.; Geng, T.; Md, A.; Banerjee, P.; Wang, B. Novel scheme for rapid synthesis of hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles (HMSNs) and their application as an efficient delivery carrier for oral bioavailability improvement of poorly water-soluble BCS type II drugs. Colloids Surf. B 2019, 176, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abuzar, S.M.; Hyun, S.-M.; Kim, J.-H.; Park, H.J.; Kim, M.-S.; Park, J.-S.; Hwang, S.-J. Enhancing the solubility and bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs using supercritical antisolvent (SAS) process. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 538, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogienko, A.G.; Markov, A.V.; Sen’kova, A.V.; Logashenko, E.B.; Salomatina, O.V.; Myz, S.A.; Ogienko, A.A.; Nefedov, A.A.; Losev, E.A.; Drebushchak, T.N.; et al. Increasing bioavailability of very poorly water-soluble compounds. A case study of an anti-tumor drug, soloxolon methyl. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janská, P.; Rychecký, O.; Zadražil, A.; Štěpánek, F.; Čejková, J. Liquid Oil Marbles: Increasing the Bioavailability of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 2136–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, P.H.L.; Tran, T.T.D. Dosage form designs for the controlled drug release of solid dispersions. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 581, 119274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vithani, K.; Jannin, V.; Pouton, C.W.; Boyd, B.J. Colloidal aspects of dispersion and digestion of self-dispersing lipid-based formulations for poorly water-soluble drugs. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 142, 16–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, H.; Holm, R.; Müllertz, A. Lipid-based formulations for oral administration of poorly water-soluble drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 453, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Chow, S.F.; Zheng, Y. Application of flash nanoprecipitation to fabricate poorly water-soluble drug nanoparticles. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 9, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.; Walker, G. Recent strategies in spray drying for the enhanced bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs. J. Control. Release 2018, 269, 110–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridgeirsdottir, G.A.; Harris, R.; Fischer, P.M.; Roberts, C.J. Support Tools in Formulation Development for Poorly Soluble Drugs. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 2260–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korn, C.; Balbach, S. Compound selection for development—Is salt formation the ultimate answer? Experiences with an extended concept of the “100 mg approach”. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 57, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serajuddin, A.T.M. Salt formation to improve drug solubility. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stella, V.J.; Nti-Addae, K.W. Prodrug strategies to overcome poor water solubility. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 677–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.; Meghani, N.; Loebenberg, R.; Cui, J.-H.; Cao, Q.-R.; Lee, B.-J. Fatty acid chain length impacts nanonizing capacity of albumin-fatty acid nanomicelles: Enhanced physicochemical property and cellular delivery of poorly water-soluble drug. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020, 152, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hibino, M.; Yamada, Y.; Fujishita, N.; Sato, Y.; Maeki, M.; Tokeshi, M.; Harashima, H. The Use of a Microfluidic Device to Encapsulate a Poorly Water-Soluble Drug CoQ10 in Lipid Nanoparticles and an Attempt to Regulate Intracellular Trafficking to Reach Mitochondria. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 2668–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Singh, A.; Garg, N. Acoustic cavitation assisted hot melt mixing technique for solid lipid nanoparticles formulation, characterization, and controlled delivery of poorly water soluble drugs. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 101277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, D.T.T.; Tran, P.H.L.; Tran, T.T.D. Development of solid dispersion lipid nanoparticles for improving skin delivery. Saudi Pharm. J. 2019, 27, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, P.H.L.; Wang, T.; Yin, W.; Tran, T.T.D.; Nguyen, T.N.G.; Lee, B.J.; Duan, W. Aspirin-loaded nanoexosomes as cancer therapeutics. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 572, 118786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrn, S.R.; Henck, J.-O. Optimizing the physical form–opportunities and limitations. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2012, 9, e73–e78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.T.D.; Tran, P.H.L. Nanoconjugation and Encapsulation Strategies for Improving Drug Delivery and Therapeutic Efficacy of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göke, K.; Lorenz, T.; Repanas, A.; Schneider, F.; Steiner, D.; Baumann, K.; Bunjes, H.; Dietzel, A.; Finke, J.H.; Glasmacher, B.; et al. Novel strategies for the formulation and processing of poorly water-soluble drugs. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 126, 40–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umemoto, Y.; Uchida, S.; Yoshida, T.; Shimada, K.; Kojima, H.; Takagi, A.; Tanaka, S.; Kashiwagura, Y.; Namiki, N. An effective polyvinyl alcohol for the solubilization of poorly water-soluble drugs in solid dispersion formulations. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 101401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, N.; Zhang, H. Poorly water-soluble drug nanoparticles via an emulsion-freeze-drying approach. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 356, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Mohac, L.M.; Raimi-Abraham, B.; Caruana, R.; Gaetano, G.; Licciardi, M. Multicomponent solid dispersion a new generation of solid dispersion produced by spray-drying. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 101750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taokaew, S.; Ofuchi, M.; Kobayashi, T. Chitin biomass-nifedipine amorphous solid dispersion for enhancement of hydrophobic drug dissolution in aqueous media. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2020, 17, 100284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krstić, M.; Manić, L.; Martić, N.; Vasiljević, D.; Mračević, S.Đ.; Vukmirović, S.; Rašković, A. Binary polymeric amorphous carvedilol solid dispersions: In vitro and in vivo characterization. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 150, 105343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, W.; Di, L. The Preparation of Curcumin Sustained-Release Solid Dispersion by Hot-Melt Extrusion—II. Optimization of Preparation Process and Evaluation in Vitro and in Vivo. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 109, 1253–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.-Y.; Lei, X.-P.; Fu, J.-J.; Chen, M.-Y.; Li, J.-X.; Yu, X.-Y.; Lin, Y.-L.; Liu, J.-P.; Du, L.-R.; Li, X.; et al. The use of amphiphilic copolymer in the solid dispersion formulation of nimodipine to inhibit drug crystallization in the release media: Combining nano-drug delivery system with solid preparations. Mat. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 111, 110836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.T.-D.; Tran, P.H.-L.; Lim, J.; Park, J.B.; Choi, S.-K.; Lee, B.-J. Physicochemical principles of controlled release solid dispersion containing a poorly water-soluble drug. Ther. Deliv. 2010, 1, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuong, H.L.T.; Wei, D.; Lee, B.-J.; Tran, T.T.D. Modulation of Drug Crystallization and Molecular Interactions by Additives in Solid Dispersions for Improving Drug Bioavailability. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 2099–2107. [Google Scholar]
- Vasconcelos, T.; Sarmento, B.; Costa, P. Solid dispersions as strategy to improve oral bioavailability of poor water soluble drugs. Drug Discov. Today 2007, 12, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vo, C.L.-N.; Park, C.; Lee, B.-J. Current trends and future perspectives of solid dispersions containing poorly water-soluble drugs. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 85, 799–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.T.D.; Tran, P.H.L. Perspectives on Strategies Using Swellable Polymers in Solid Dispersions for Controlled Drug Release. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 1639–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Nguyen, H.; Baek, N.; Lee, B.-J. Enhanced gastric stability of esomeprazole by molecular interaction and modulation of microenvironmental pH with alkalizers in solid dispersion. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 523, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarode, A.L.; Sandhu, H.; Shah, N.; Malick, W.; Zia, H. Hot melt extrusion (HME) for amorphous solid dispersions: Predictive tools for processing and impact of drug-polymer interactions on supersaturation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 48, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zemlyanov, D.; Chen, X.; Nie, H.; Su, Z.; Fang, K.; Yang, X.; Smith, D.; Byrn, S.; Lubach, J.W. Acid-Base Interactions of Polystyrene Sulfonic Acid in Amorphous Solid Dispersions Using a Combined UV/FTIR/XPS/ssNMR Study. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Gala, U.; Chauhan, H. Classification of solid dispersions: Correlation to (i) stability and solubility (ii) preparation and characterization techniques. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2015, 41, 1401–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Osman, Y.; Liavitskaya, T.; Vyazovkin, S. Polyvinylpyrrolidone affects thermal stability of drugs in solid dispersions. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 551, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarabu, S.; Kallakunta, V.R.; Bandari, S.; Batra, A.; Bi, V.; Durig, T.; Zhang, F.; Repka, M.A. Hypromellose acetate succinate based amorphous solid dispersions via hot melt extrusion: Effect of drug physicochemical properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 233, 115828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Ju, X.; Yang, D.; Kong, Y.; Tang, X. Effect of the third component on the aging and crystallization of cinnarizine-soluplus® binary solid dispersion. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 580, 119240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Jin, L.; Liu, Q.; Xu, H.; Wu, H.; Zhang, X.; Mao, S. Exploration of supersaturable lacidipine ternary amorphous solid dispersion for enhanced dissolution and in vivo absorption. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 139, 105043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Jacobs, E.; Jones, D.S.; McCoy, C.P.; Wu, H.; Andrews, G.P. The design and development of high drug loading amorphous solid dispersion for hot-melt extrusion platform. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 586, 119545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, L.S.; Zografi, G. Spectroscopic Characterization of Interactions Between PVP and Indomethacin in Amorphous Molecular Dispersions. Pharm. Res. 1997, 14, 1691–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Obaidi, H.; Lawrence, M.J.; Shah, S.; Moghul, H.; Al-Saden, N.; Bari, F. Effect of drug-polymer interactions on the aqueous solubility of milled solid dispersions. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 446, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Obaidi, H.; Buckton, G. Evaluation of griseofulvin binary and ternary solid dispersions with HPMCAS. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2009, 10, 1172–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, J.E.; James, M.B.; Forster, A.H.; Lancaster, R.W.; Butler, J.M.; Rades, T. Preparation of glass solutions of three poorly water soluble drugs by spray drying, melt extrusion and ball milling. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 336, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, T.; Zografi, G. Physical properties of solid molecular dispersions of indomethacin with poly (vinylpyrrolidone) and poly (vinylpyrrolidone-co-vinyl-acetate) in relation to indomethacin crystallization. Pharm. Res. 1999, 16, 1722–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.A.; Jaafar, J.; Ismail, A.F.; Othman, M.H.D.; Rahman, M.A. Chapter 1—Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy. In Membrane Characterization, 1st ed.; Hilal, N., Ismail, A.F., Matsuura, T., Oatley-Radcliffe, D., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 3–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, R.; Nieuwoudt, H.; Bauer, F.F.; Kossmann, J.; Koch, K.R.; Esbensen, K.H. FTIR spectroscopy for grape and wine analysis. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 1371–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthomieu, C.; Hienerwadel, R. Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy. Photosynth. Res. 2009, 101, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamancheva, I.; Staneva, T. Determination of possible impurities in piracetam using FTIR spectroscopy. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2000, 21, 1161–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reginald-Opara, J.N.; Attama, A.; Ofokansi, K.; Umeyor, C.; Kenechukwu, F. Molecular interaction between glimepiride and Soluplus®-PEG 4000 hybrid based solid dispersions: Characterisation and anti-diabetic studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 496, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, W.; Williams, A.C.; Rawlinson, C.F. Stochiometrically governed molecular interactions in drug: Poloxamer solid dispersions. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 391, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, D.K.; Shah, D.S.; Amin, P.D. Thermodynamic aspects of the preparation of amorphous solid dispersions of Naringenin with enhanced dissolution rate. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 583, 119363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Xiao, X.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Yi, X. Solubilization of phloretin via steviol glycoside-based solid dispersion and micelles. Food Chem. 2020, 308, 125569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakshman, D.; Chegireddy, M.; Hanegave, G.K.; Sree, K.N.; Kumar, N.; Lewis, S.A.; Dengale, S.J. Investigation of drug-polymer miscibility, biorelevant dissolution, and bioavailability improvement of Dolutegravir-polyvinyl caprolactam-polyvinyl acetate-polyethylene glycol graft copolymer solid dispersions. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 142, 105137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tachibana, T.; Nakamura, A. A methode for preparing an aqueous colloidal dispersion of organic materials by using water-soluble polymers: Dispersion of β-carotene by polyvinylpyrrolidone. Kolloid Z. Z. Polym. 1965, 203, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baravkar, A.A.; Kale, R.N.; Sawant, S.D. FTIR Spectroscopy: Principle, technique and mathematics. Int. J. Pharma Bio Sci. 2011, 2, 513–519. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, E. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR): Methods, Analysis, and Research Insights; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, T.T.-D.; Tran, P.H.-L.; Choi, H.-G.; Han, H.K.; Lee, B.-J. The roles of acidifiers in solid dispersions and physical mixtures. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 384, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.T.-D.; Tran, P.H.-L.; Lee, B.-J. Dissolution-modulating mechanism of alkalizers and polymers in a nanoemulsifying solid dispersion containing ionizable and poorly water-soluble drug. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009, 72, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, W.L.; Riegelman, S. Pharmaceutical applications of solid dispersion systems. J. Pharm. Sci. 1971, 60, 1281–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiranidchapong, C.; Tucker, I.G.; Rades, T.; Kulvanich, P. Miscibility and interactions between 17β-estradiol and Eudragit® RS in solid dispersion. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 4879–4888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, T. The hydrogen bond in the solid state. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2002, 41, 48–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, H.V.; Nguyen, P.K.; Van Vo, T.N.; Duan, W.; Tran, V.-T.; Tran, P.H.-L.; Tran, T.T.-D. Hydrophilic-hydrophobic polymer blend for modulation of crystalline changes and molecular interactions in solid dispersion. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 513, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ozeki, T.; Yuasa, H.; Kanaya, Y. Application of the solid dispersion method to the controlled release of medicine. IX. Difference in the release of flurbiprofen from solid dispersions with poly(ethylene oxide) and hydroxypropylcellulose and the interaction between medicine and polymers. Int. J. Pharm. 1997, 155, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slámová, M.; Školáková, T.; Školáková, A.; Patera, J.; Zámostný, P. Preparation of solid dispersions with respect to the dissolution rate of active substance. J. Drug Deliv. Sci.Technol. 2020, 56, 101518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djuris, J.; Milovanovic, S.; Medarevic, D.; Dobricic, V.; Dapčević, A.; Ibric, S. Selection of the suitable polymer for supercritical fluid assisted preparation of carvedilol solid dispersions. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 554, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medarević, D.; Cvijić, S.; Dobričić, V.; Mitrić, M.; Djuriš, J.; Ibrić, S. Assessing the potential of solid dispersions to improve dissolution rate and bioavailability of valsartan: In vitro-in silico approach. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 124, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiernan, H.; Byrne, B.; Kazarian, S.G. ATR-FTIR spectroscopy and spectroscopic imaging for the analysis of biopharmaceuticals. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2020, 241, 118636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakmak-Arslan, G.; Haksoy, H.; Goc-Rasgele, P.; Kekecoglu, M. Determination of the dose-dependent toxic effects of mad honey on mouse liver using ATR-FTIR spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2020, 228, 117719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durak, T.; Depciuch, J. Effect of plant sample preparation and measuring methods on ATR-FTIR spectra results. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2020, 169, 103915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, D.; Carter, D.; Foong Ng, L.Y.; Davis, M.; Walker, G.M.; Lyons, J.G.; Higginbotham, C.L. An investigation of the inter-molecular interaction, solid-state properties and dissolution properties of mixed copovidone hot-melt extruded solid dispersions. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 101132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-S.; Byeon, J.C.; Park, J.-S. Naftopidil-fumaric acid interaction in a solid dispersion system: Improving the dissolution rate and oral absorption of naftopidil in rats. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 95, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talik, P.; Moskal, P.; Proniewicz, L.M.; Wesełucha-Birczyńska, A. The Raman spectroscopy approach to the study of Water–Polymer interactions in hydrated hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC). J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1210, 128062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, A.; Raijada, D.; Rantanen, J. Raman spectroscopy in pharmaceutical product design. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 89, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, H.; Ida, Y.; Kadota, K.; Tozuka, Y. Raman mapping for kinetic analysis of crystallization of amorphous drug based on distributional images. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 462, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuzzucoli Crucitti, V.; Migneco, L.M.; Piozzi, A.; Taresco, V.; Garnett, M.; Argent, R.H.; Francolini, I. Intermolecular interaction and solid state characterization of abietic acid/chitosan solid dispersions possessing antimicrobial and antioxidant properties. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 125, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhalil, A.; Nanubolu, J.B.; Burley, J.C. Analysis of phase transitions in molecular solids: Quantitative assessment of phonon-mode vs intra-molecular spectral data. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dulaimi, S.; Aina, A.; Burley, J. Rapid polymorph screening on milligram quantities of pharmaceutical material using phonon-mode Raman spectroscopy. CrystEngComm 2010, 12, 1038–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukeck, R.; Sieger, P.; Karmwar, P. Investigation and correlation of physical stability, dissolution behaviour and interaction parameter of amorphous solid dispersions of telmisartan: A drug development perspective. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 49, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, L.S.; Zografi, G. The quantitative analysis of crystallinity using FT-Raman spectroscopy. Pharm. Res. 1998, 15, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, T.; Otsuka, M. Evaluation of the microcrystallinity of a drug substance, indomethacin, in a pharmaceutical model tablet by chemometric FT-Raman spectroscopy. Pharm. Res. 2005, 22, 1350–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saerens, L.; Dierickx, L.; Lenain, B.; Vervaet, C.; Remon, J.P.; Beer, T.D. Raman spectroscopy for the in-line polymer–drug quantification and solid state characterization during a pharmaceutical hot-melt extrusion process. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2011, 77, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Fan, N.; Wang, X.; Li, C.; Sun, M.; Wang, J.; Fu, Q.; He, Z. Interfacial interaction track of amorphous solid dispersions established by water-soluble polymer and indometacin. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Fan, N.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; Li, S.; He, Z. The tracking of interfacial interaction of amorphous solid dispersions formed by water-soluble polymer and nitrendipine. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 420, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.T.-D.; Tran, P.H.-L.; Khanh, T.N.; Van, T.V.; Lee, B.-J. Solubilization of poorly water-soluble drugs using solid dispersions. Recent Pat. Drug Deliv. Formul. 2013, 7, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, G.P.; AbuDiak, O.A.; Jones, D.S. Physicochemical characterization of hot melt extruded bicalutamide–polyvinylpyrrolidone solid dispersions. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 1322–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghel, S.; Cathcart, H.; O’Reilly, N.J. Understanding the generation and maintenance of supersaturation during the dissolution of amorphous solid dispersions using modulated DSC and 1H NMR. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 536, 414–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Ren, W.; Dushkin, A.V.; Su, W. Preparation, characterization, in vitro and in vivo studies of olmesartan medoxomil in a ternary solid dispersion with N-methyl-D-glucamine and hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin. J. Drug Delivery Sci. Technol. 2020, 56, 101546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Mintoo, M.J.; Mondhe, D.M.; Bharate, S.B.; Vishwakarma, R.A.; Bharate, S.S. Binary and ternary solid dispersions of an anticancer preclinical lead, IIIM-290: In vitro and in vivo studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 570, 118683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Ohno, Y.; Okura, R.; Ishida, M.; Higashi, T.; Motoyama, K.; Arima, H. Identification of molecular-interaction sites between lowly hydrolyzed polyvinyl alcohols and indomethacin by NMR spectroscopy. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 549, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, D.; Chauhan, H.; Atef, E. Role of molecular interactions for synergistic precipitation inhibition of poorly soluble drug in supersaturated drug–polymer–polymer ternary solution. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 756–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Mooter, G.; Wuyts, M.; Blaton, N.; Busson, R.; Grobet, P.; Augustijns, P.; Kinget, R. Physical stabilisation of amorphous ketoconazole in solid dispersions with polyvinylpyrrolidone K25. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 12, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwahara, J.; Zandarashvili, L.; Kemme, C.A.; Esadze, A. NMR-based investigations into target DNA search processes of proteins. Methods 2018, 148, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karavas, E.; Georgarakis, E.; Sigalas, M.P.; Avgoustakis, K.; Bikiaris, D. Investigation of the release mechanism of a sparingly water-soluble drug from solid dispersions in hydrophilic carriers based on physical state of drug, particle size distribution and drug-polymer interactions. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2007, 66, 334–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, H.; Ueda, K.; Yasuda, Y.; Higashi, K.; Inoue, M.; Ito, M.; Noguchi, S.; Kawakami, K.; Moribe, K. Correlation between drug dissolution and resistance to water-induced phase separation in solid dispersion formulations revealed by solid-state NMR spectroscopy. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 577, 119086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aso, Y.; Yoshioka, S. Molecular mobility of nifedipine-PVP and phenobarbital-PVP solid dispersions as measured by 13C-NMR spin-lattice relaxation time. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 95, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S.W.; Chang, F.C. Studies of miscibility behavior and hydrogen bonding in blends of poly (vinylphenol) and poly (vinylpyrrolidone). Macromolecules 2001, 34, 5224–5228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniruzzaman, M.; Morgan, D.J.; Mendham, A.P.; Pang, J.; Snowden, M.J.; Douroumis, D. Drug-polymer intermolecular interactions in hot-melt extruded solid dispersions. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 443, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baer, D.R.; Engelhard, M.H. XPS analysis of nanostructured materials and biological surfaces. J. Electron. Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 2010, 178–179, 415–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zemlyanov, D.; Chen, X.; Su, Z.; Nie, H.; Lubach, J.W.; Smith, D.; Byrn, S.; Pinal, R. Acid-base interactions in amorphous solid dispersions of lumefantrine prepared by spray-drying and hot-melt extrusion using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 514, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, J.S.; Byard, S.J.; Seaton, C.C.; Sadiq, G.; Davey, R.J.; Schroeder, S.L.M. Proton transfer and hydrogen bonding in the organic solid state: A combined XRD/XPS/ssNMR study of 17 organic acid-base complexes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 1150–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punčochová, K.; Heng, J.Y.Y.; Beránek, J.; Štěpánek, F. Investigation of drug-polymer interaction in solid dispersions by vapour sorption methods. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 469, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costantino, H.R.; Curley, J.G.; Wu, S.; Hsu, C.C. Water sorption behavior of lyophilized protein-sugar systems and implications for solid-state interactions. Int. J. Pharm. 1998, 166, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, K.J.; Zografi, G. Water vapor absorption into amorphous hydrophobic drug/poly (vinylpyrrolidone) dispersions. J. Pharm. Sci. 2002, 91, 2150–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zografi, G. Water vapor absorption into amorphous sucrose-poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) and trehalose-poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) mixtures. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 90, 1375–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, Á.A.N.; Soares-Sobrinho, J.L.; Silva, J.L.; Corrêa-Júnior, R.A.C.; Lyra, M.A.M.; Santos, F.L.A.; Oliveira, B.G.; Hernandes, M.Z.; Rolim, L.A.; Rolim-Neto, P.J. The Use of Solid Dispersion Systems in Hydrophilic Carriers to Increase Benznidazole Solubility. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 2443–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pahovnik, D.; Reven, S.; Grdadolnik, J.; Borštnar, R.; Mavri, J.; Žagar, E. Determination of the interaction between glimepiride and hyperbranched polymers in solid dispersions. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 4700–4709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).